Synthesis of smart dual-response oil-water separation material
-
摘要:
智能材料是一种具有感知、响应和适应环境能力的材料。随着科技的不断发展,智能材料在各个领域的应用越来越广泛,具有十分广阔的发展前景。本文合成了一种含有羧基及可聚合基团的偶氮苯化合物,以该偶氮苯化合物作为光响应单元,甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯作为pH响应单元,采用可逆加成-断裂链转移(RAFT)聚合与甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯进行一步共聚,得到了光和pH智能双响应三元共聚物。聚合物涂层在不同条件的刺激下接触角最大变化可达120.3°,经过亲水-疏水的多次转换,接触角仍可以恢复到初始状态,具有优异的可逆刺激响应能力。将聚合物涂敷在无纺布上制成光/pH双响应油水分离膜,该膜在亲油疏水与亲水疏油之间发生可逆转变,实现选择性油水分离,单次分离效率分别达96.3%和95.8%。这种对光和pH的刺激响应性使其可用于复杂环境的液体传输和油水分离等领域,具有巨大的智能水油分离应用潜力。
Abstract:Smart materials are materials that have abilitys to sense, respond and adapt to their environments. With the continuous development of science and technology, smart materials are more and more widely used in various fields, and have very broad prospects for development in the future. In this paper, one kind of azobenzene compound containing polymerizable groups was synthesized. This azobenzene compound was used as photoresponsive unit and dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate as a pH responsive unit, they can copolymerize with hydroxyethyl methacrylate to form terpolymer by one step reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization (RAFT) method, which has smart dual response to light and pH. When stimulated by different conditions, the maximum contact angle change of the polymer coating can reach 120.3°, and the contact angle can still restore to the initial state after multiple transformations between hydrophilic and hydrophobic. It shows that the material has excellent reversible stimulus responsiveness ability. When the polymer was coated on the non-woven fabric to make light/pH dual-responsive oil-water separation membrane, it can undergo a reversible transition between hydrophilic and hydrophobic, so as to achieve the selective separation of oil and water, the single separation efficiency can reach 96.3% and 95.8%, respectively. This kind of stimulus responsibility to light and pH can be used in areas such as liquid transport and oil-water separation in complex environments, and have great potential for smart water-oil separation application.
-
随着全球经济的发展和化石燃料的消耗剧增,全球石油的需求量在逐年增加,多次采油技术得到了更广泛应用[1],原油采出液的含水率也在逐年增加,正在给中国这一世界最大石油进口国带来严峻的挑战。同时,随着海上油气开发向深海迈进,深海平台的油水分离、采油井井底油水分离等都迫使人们探索新的油水分离技术。
工业生产运输过程中的各类不溶性有机物的泄露和排放导致了各种严重的环境问题[2-5]。例如石油加工和运输过程中的原油和成品泄露导致的水污染。皮革处理、食品加工、冶金、化工等工业生产过程中排放的含油废水。这些含油废水如不经处理直接排放,会对生态系统、农业生产构成严重破坏,危及人类健康,因此需要有效的油水分离技术来解决分离问题。目前主要的油水分离形式包括重力分离、离心、吸附和膜分离等[6-9]。将含油废水进行油水分离后,对废水的后续的处理难度和成本将会大大降低。膜分离技术作为一种先进的水净化技术,由于其经济、节能、易于操作的特点,已经成为一种不可或缺的选择[10-12]。然而,面对愈加复杂的含油污水(轻/重油和水的混合物、水包油乳液和油包水乳液的混合体系)以及不同酸碱环境,单一的除油型、除水型分离材料无法实现按需、高效和可持续的分离。因此,开发先进的智能油水分离材料是解决世界水环境恶化和石油短缺问题的迫切需要。
对某种外界刺激敏感并产生特殊反应的现象称为智能响应。具有可转换润湿行为的人工智能响应界面材料引起了人们越来越多的兴趣[13-15]。研究表明,可转换润湿行为通常可通过调节pH值[16],改变光源[17]、温度[18]、磁场强度[19]等方式实现。pH响应材料可定义为在其结构中包括弱酸性或碱性基团的聚电解质,酸性或碱性基团如羧基、吡啶、磺酸、磷酸盐、叔胺等通常被称为pH响应基团,这些基团响应于pH的变化。基团会随着环境pH变化而接受或释放质子,导致结构和性质的变化,从而实现材料的pH响应。例如,Liu等[20]合成了一种基于分子印迹聚合物的pH响应型纳米药物,该纳米药物在的模拟肿瘤微环境中表现出良好的 pH 响应性,可通过特定的分子印迹位点选择性地从前列腺肿瘤中螯合睾酮。Surapaneni等[21]合成了一种具有温度和 pH 双重刺激响应的聚N-乙烯基己内酰胺和聚赖氨酸的嵌段共聚物,该共聚物可在两种刺激单独或共同作用下增加细胞对聚合物囊泡的渗透性,用于增强细胞内化和溶酶体靶向药物运送。
光作为一种低成本、绿色环保的刺激方法,使含有光响应基团的材料具有非接触式的遥控特性。光响应性能可以通过引入光响应基团来实现,该基团在特定波长的照射下发生结构变化,从而导致材料的性能发生变化[22-24]。目前常用的光响应基团是偶氮苯及其衍生物。偶氮化合物有两种异构体,一种是稳定态的反式结构,另一种是亚稳态的顺式结构。偶氮苯官能团经紫外线照射后,反式的非极性异构体可以转化为顺式的极性异构体,并且这一过程具有可逆性。由于偶氮苯反式构象的极性较弱,顺式构象的极性较强,在顺反异构体转变的过程中会导致材料的极性发生变化,其亲疏水性也随之变化,可以利用这一特性制备光响应智能转换油水分离材料,因为偶氮苯顺反异构体转换的可逆性,所以亲疏水性能的变化过程也是可逆的[25-28]。Yang等[29]利用偶氮苯聚合物作为衬底,制备一种可光切换的超疏水表面,该表面可受紫外和可见光的影响,使聚合物膜发生亲水到疏水的可逆改变。Du等[30]制备了一种功能化的偶氮苯聚合物,制备的偶氮苯溶液在紫外和可见光交替暴露下表现出偶氮苯的光异构化转变以及亲水到亲油的可逆变化。偶氮苯衍生物因其良好的化学稳定性和多功能性在光响应材料的制备和应用中具有广阔的发展前景[31]。
本文采用可逆加成-断裂链转移(RAFT)一步聚合法,制备得到了具有pH/光刺激响应性能的三元无规共聚物,并将其与无纺布相结合,得到了具有智能化可逆响应性能复合织物的油水分离膜。这种油水分离膜在油水分离、工业复杂废水处理等方面具有巨大的应用潜力。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
四氢呋喃(THF)、盐酸(35%)、甲醇,西陇科学公司;二硫代苯甲酸异丙酯(CDB),阿拉丁生物技术有限公司;无纺布,深圳瑞都净化公司;偶氮二异丁腈(AIBN)、甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯(HEMA)、甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯(DMAEMA)、对氨基苯甲酸、苯酚、氢氧化钠、亚硝酸钠、三乙胺、丙烯酰氯,麦克林公司。上述试剂均是分析纯,实验用水为去离子水。
1.2 样品表征
傅里叶红外光谱仪(VERTEX 70 Bruker)、 超导核磁共振波谱仪(BRUKER 500 MHz AVANCE NEO)、紫外可见分光光度计(UV-3600 Plus,日本岛津)、扫描电子显微镜(ZEISS GeminiSEM 500,德国卡尔蔡司) 、视频光学接触角测试仪(OCA25 Eastern-Dataphy)。
1.3 智能响应油水分离材料的合成
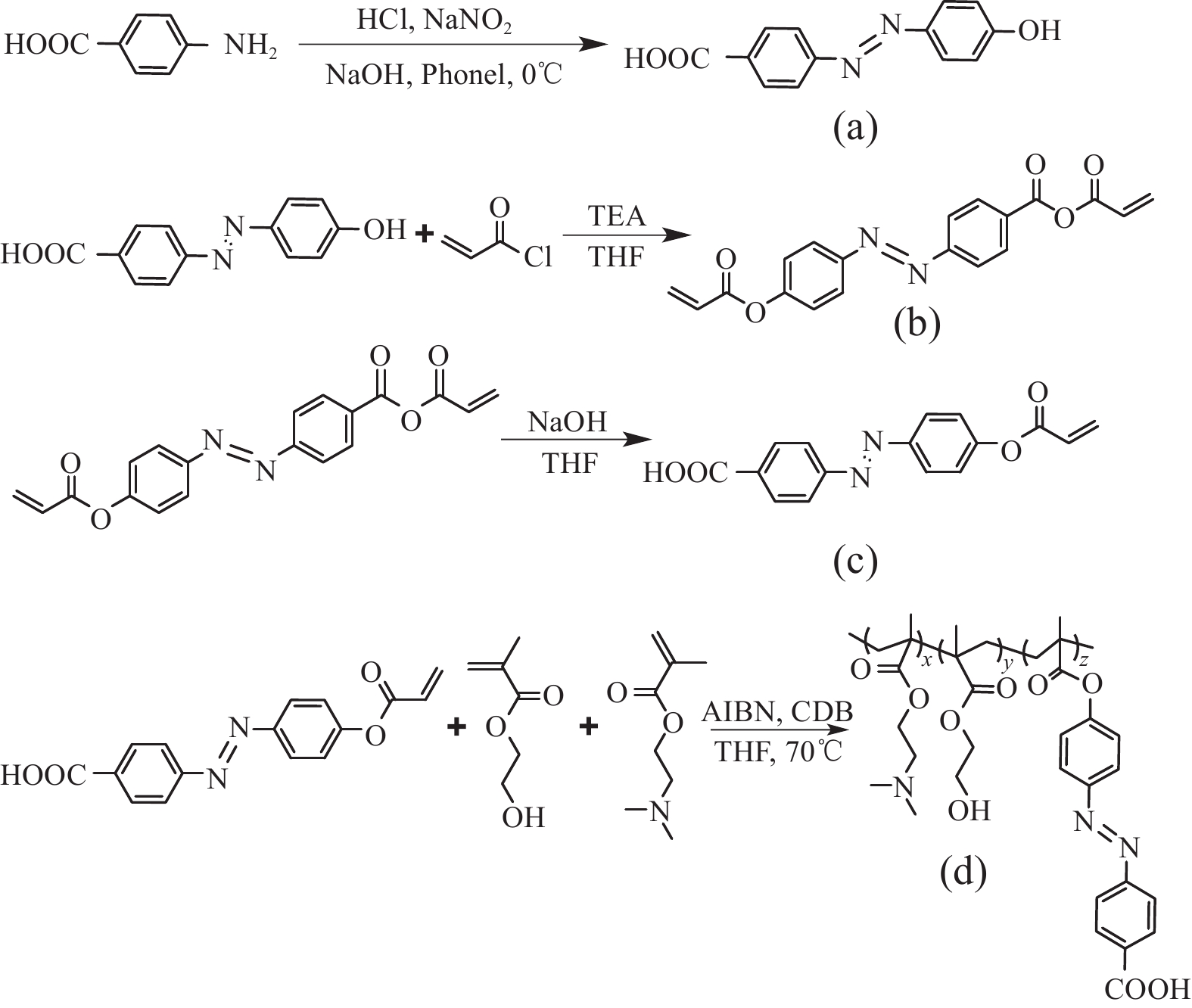
合成主要分为4个步骤:(1)重氮化-偶联反应;(2)酯化反应;(3)酯水解反应;(4)聚合反应。合成路线见图1。
1.3.1 4-(4'-羟基)苯偶氮基苯甲酸的合成
通过重氮化-偶联反应制备4-(4'-羟基)苯偶氮基苯甲酸。将35%的盐酸12 mL与等体积的蒸馏水混合,缓慢滴加到装有对氨基苯甲酸(4.10 g,30 mmol)的烧瓶中搅拌均匀后,将30 mL的NaNO2水溶液(1 mol/L)缓慢滴入烧瓶反应30 min后加300 mL冰水稀释。然后滴加20 mL苯酚(2.94 g,31 mmol)和NaOH (1.72 g,31 mmol)水溶液。0~5℃下反应2 h,用NaOH调节pH至5~6。过滤收集固体,蒸馏水洗涤,得到4-(4'-羟基)苯偶氮基苯甲酸(中间体a)的橘黄色固体6.97 g,产率85%。
1.3.2 丙烯酸-4-((4-(丙烯氧基)苯基)二氮基)苯甲酸酐的合成
将1.3.1制得的偶氮苯(2.42 g,10 mmol)与三乙胺(1.47 mL,10 mmol)溶于25 mL THF并滴加丙烯酰氯(0.8 mL,10 mmol),室温下反应24 h。滤去生成的盐,浓缩滤液并滴入甲醇中沉淀,得到丙烯酸-4-((4-(丙烯氧基)苯基)二氮基)苯甲酸酐黄色固体1.67 g (中间体b),产率57%。
1.3.3 4-((4-(丙烯氧基)苯基)二氮基)苯甲酸的合成
将1.3.2中制备的偶氮苯1.51 g溶解在20 mL THF中,用10%的氢氧化钠水溶液调节pH至7~8,室温反应24 h,后用5%的盐酸水溶液调节pH至2~4,过滤并用蒸馏水洗涤,得到橙色固体1.24 g (单体c),产率83%。
1.3.4 智能双响应聚合物的制备
采用可逆加成-断裂链转移聚合(RAFT),一步反应制得智能响应聚合物。这种聚合也被称为“活性”/可控自由基聚合。由于其反应条件温和、单体选择范围广、分子设计能力强等优点,已发展成为最通用、最强大的聚合技术之一。
将1.3.3中的产物(1.55 g,5 mmol)与 DMAEMA(0.339 g,2.16 mmol)、HEMA (0.280 g,2.16 mmol)溶于THF后通氮排氧,温度升至70℃后加入AIBN (0.08 g,0.5 mmol)、CDB (0.2 g,0.2 mmol)反应48 h,旋蒸去除溶剂,甲醇洗涤后,干燥,得到橘红色聚合物1.84 g (聚合物d),产率85%。
1.4 智能响应涂层的制备
将1.3.4中得到的聚合物均匀地涂膜在载玻片上,60℃下真空干燥,用于测量接触角。
1.5 智能油水分离膜的制备
将直径5 cm的无纺布用无水乙醇浸泡并超声清洁表面灰尘和油脂后,浸入未干燥的聚合物中,使聚合物均匀地涂在无纺布表面,60℃下真空干燥48 h,得到智能双响应油水分离膜。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 表征与形貌
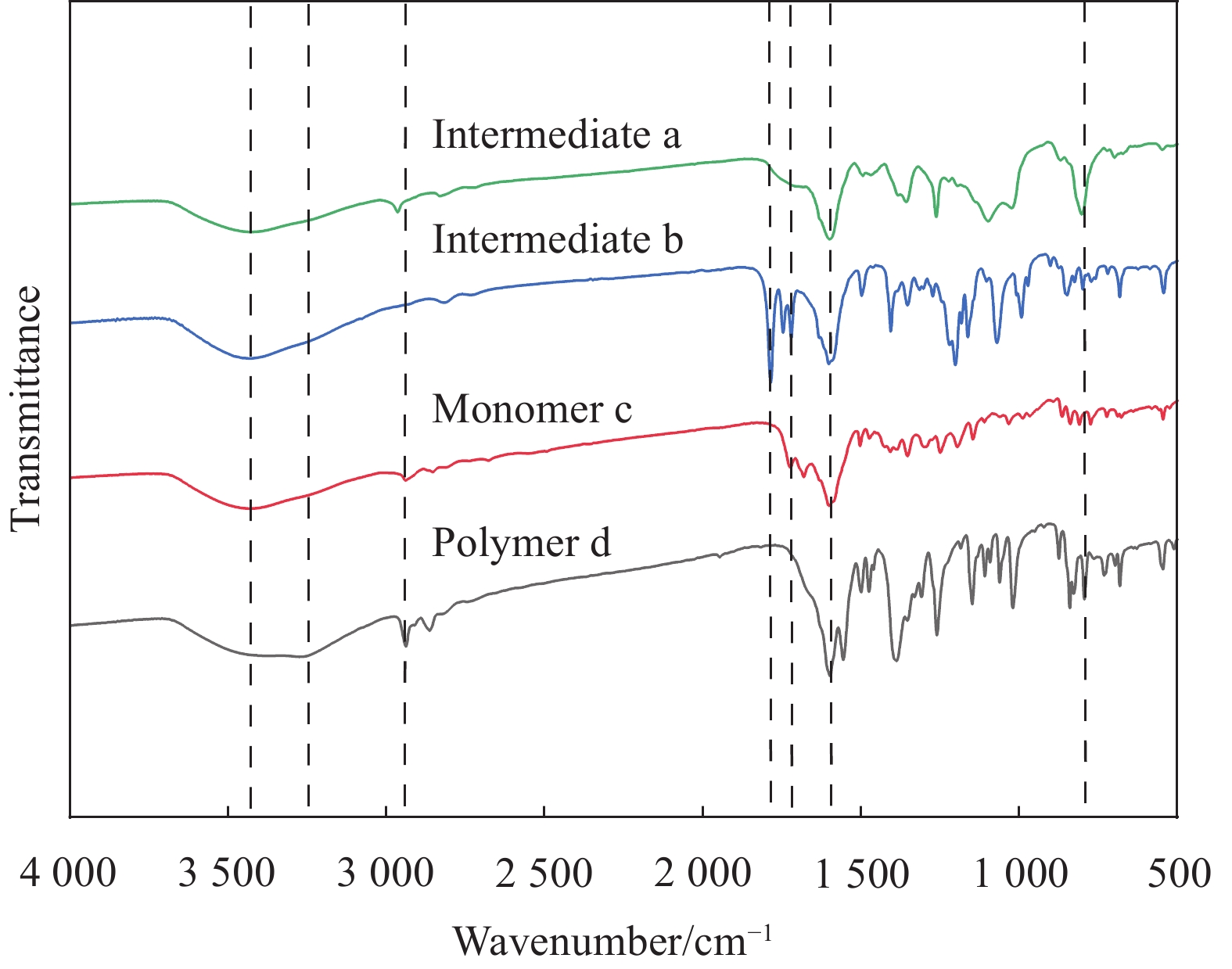
合成的各中间体、单体和聚合物的红外谱图如图2所示。
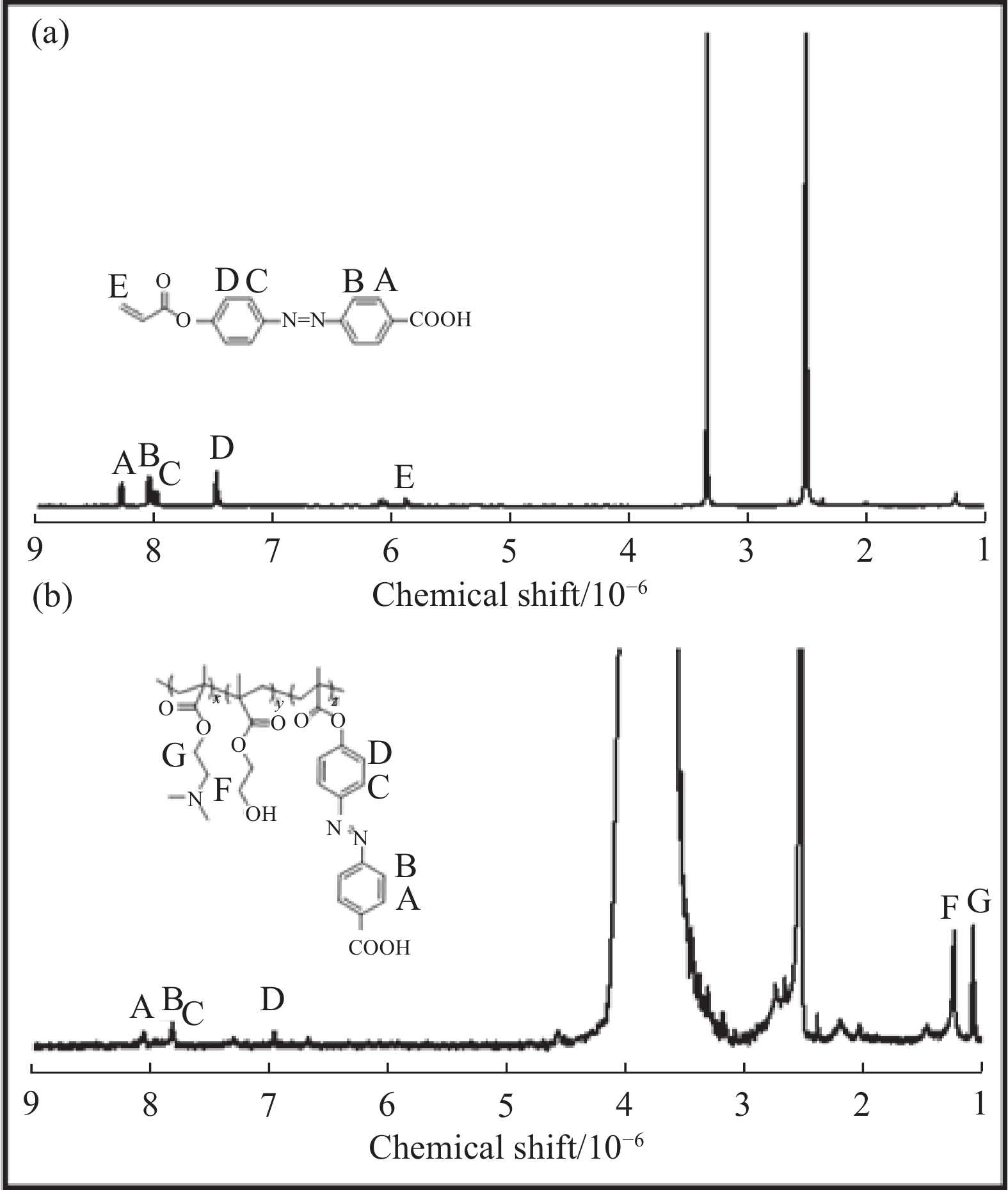
3452 cm−1处的吸收峰为偶氮苯中苯环上不饱和C—H键的伸缩振动,1606 cm−1为苯环骨架的C=C伸缩振动,807 cm−1为苯环上的C—H面外弯曲振动峰。a、c、d 在2942 cm−1处的吸收峰为羧基的O—H伸缩振动峰;b、c在1721 cm−1处存在C=C的伸缩振动;b在1786 cm−1处存在酸酐的C=O伸缩振动;聚合物d在3250 cm−1左右处存在DMAEMA中叔胺甲基上C—H伸缩振动峰和HEMA中的O—H伸缩振动峰。图3为偶氮苯单体及聚合物的1H NMR图,图3(a)中,8.13×10−6、8.01×10−6、7.45×10−6和5.88×10−6处的峰对应单体c结构中为A、B、C和D的氢。图3(b)中,1.13×10−6和1.26×10−6处的氢对应于聚合物d中F和G相应位置的氢,A、B、C和D的氢与单体结构中的峰位置基本一致。
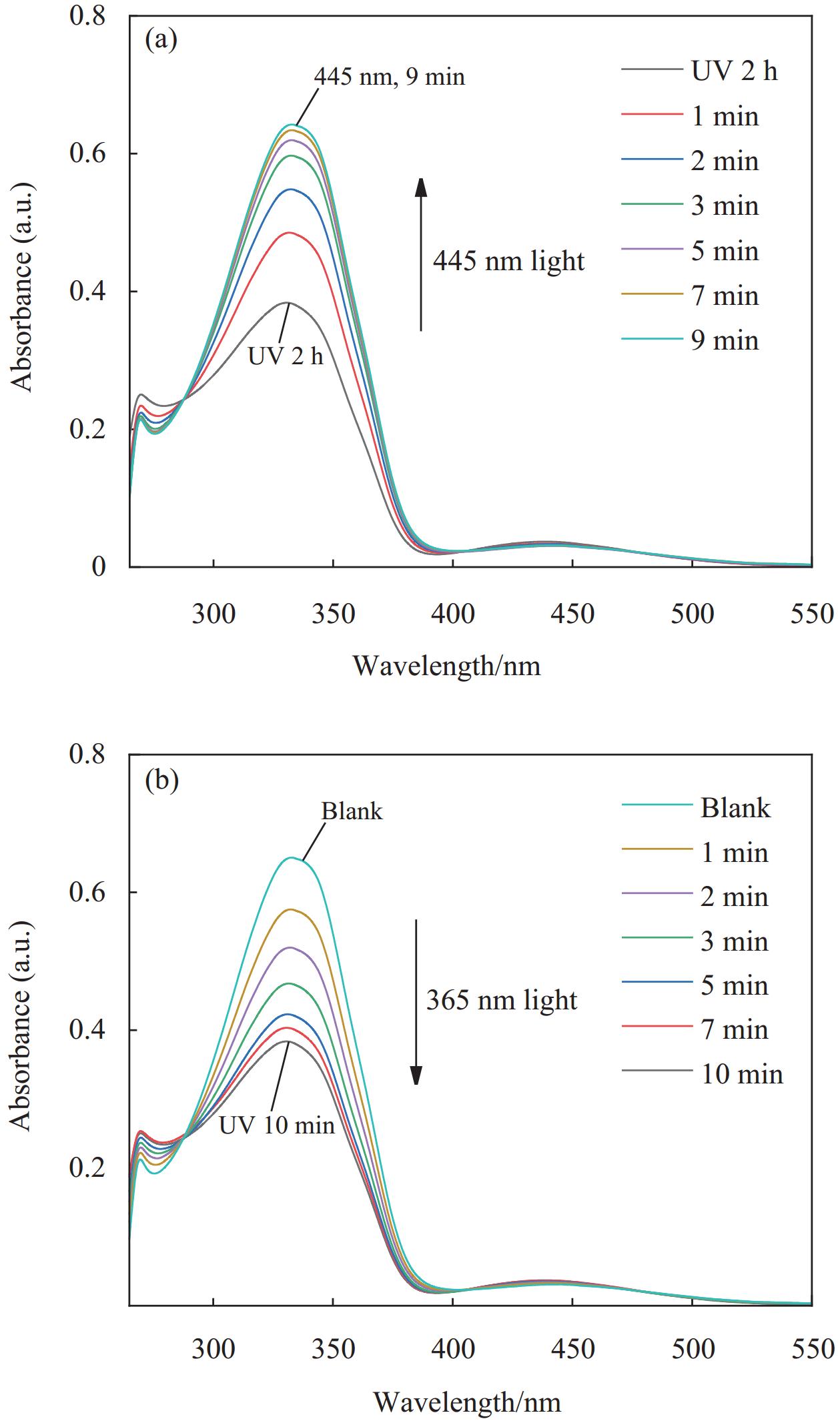
将偶氮苯溶于DMF (0.15 g·L−1)中,用365 nm紫外灯(20 W)照射2 h,使溶液中的单体转化为顺式结构后,分别检测不同照射时间的UV-Vis吸收光谱,吸收光谱随时间变化的关系如图4所示。其中,图4(a)为用LED灯(445 nm,20 W)对溶液进行照射,直至吸光度不再变化的吸收光谱。图4(b)为继续用365 nm紫外灯对溶液进行照射后的吸收光谱。偶氮苯特征吸收峰主要是330~380 nm处的π-π*吸收峰和420~500 nm的n-π*吸收峰。从图4中单体在365 nm和445 nm光照射下吸收光谱的变化情况可以看出,365 nm和445 nm的光照下,随照射时间的增加,单体在溶液中π-π*吸收峰的位置几乎不发生移动,而吸光度会逐渐变化。n-π*特征峰处的吸光度和吸收峰的位置均变化很小。吸光度的变化归因于紫外-可见光照射引起的偶氮苯从顺式到反式的异构化。对比图4(a)与图4(b)中吸收光谱变化,可以看到偶氮苯的顺反异构化是一个可逆的过程。
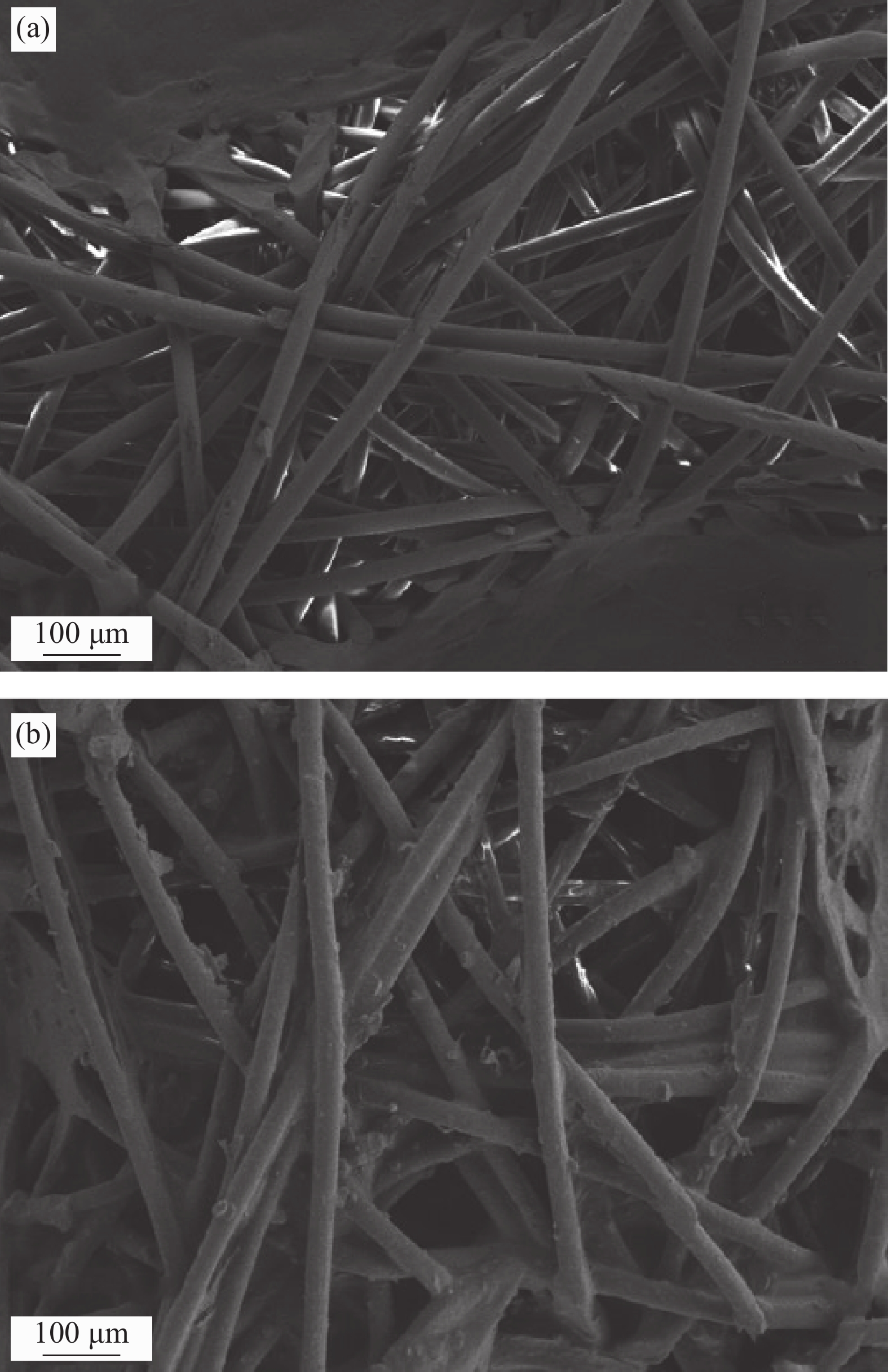
未经处理的无纺布(图5(a))纤维表面相对光滑。经过涂膜的无纺布(油水分离膜,图5(b)),可以观察到纤维表面及相邻纤维间粘附的聚合物,作为基底的无纺布具有多孔结构和交错的纤维,有利于聚合物的粘附并为油水分离提供了必要的空间。无纺布的柔性还使油水分离膜具有良好的柔韧性,可以承受多次折叠而不损坏。
2.2 智能响应及油水分离测试
将聚合物均匀地涂抹在载玻片上烘干后,分别在自然条件、pH=3的缓冲溶液浸泡、紫外-可见光照射、缓冲溶液浸泡后继续用紫外-可见光照射等情况下进行接触角测量实验,每次滴液的量为5 μL,接触角变化如图6所示。
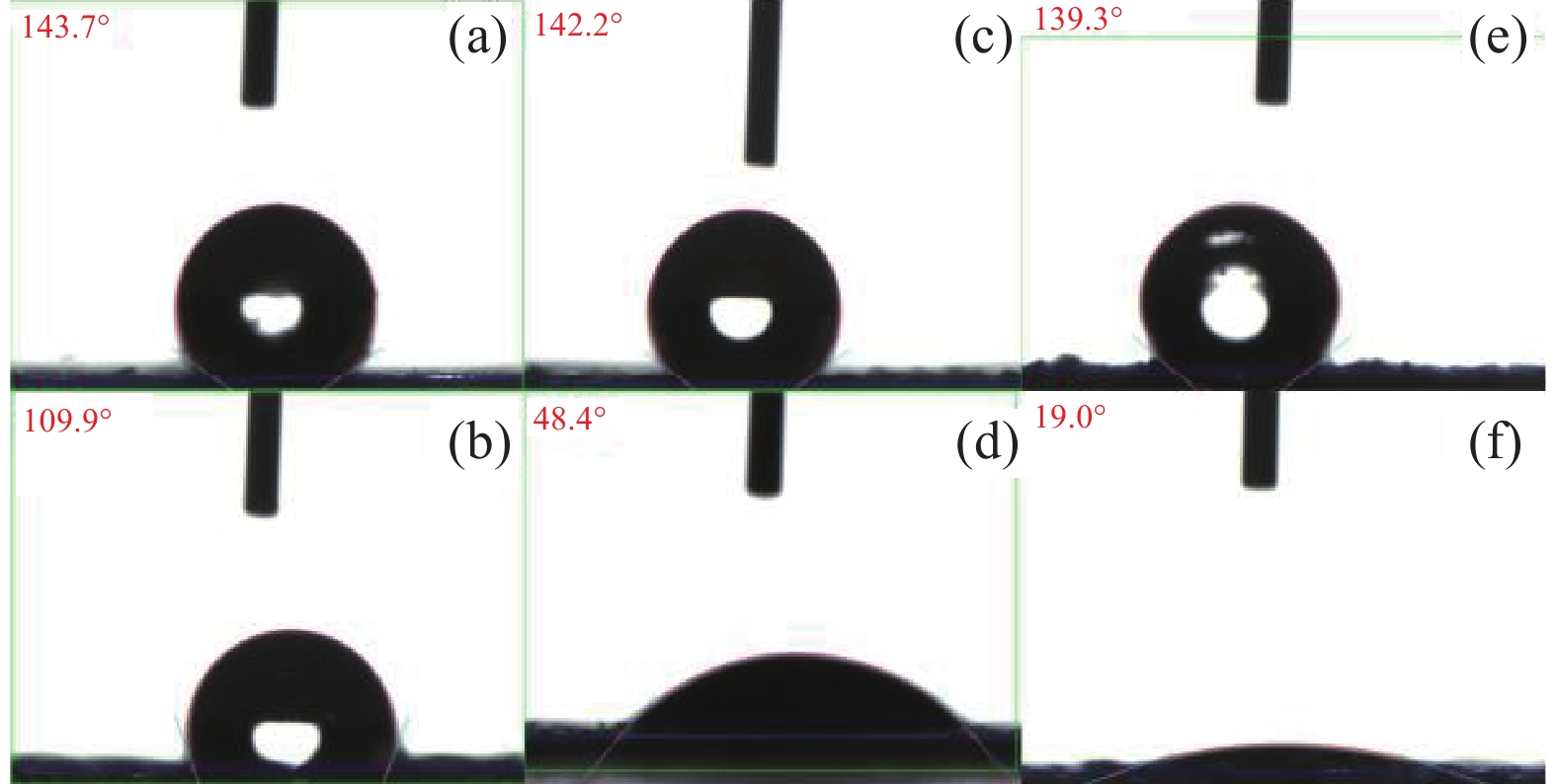
![]() 图 6 聚合物d的载玻片涂层在不同条件下的接触角变化:(a)自然条件下;(b)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡后;(c)经pH=10缓冲溶液浸泡后;(d)经365 nm光照射后;(e)经445 nm光照射后;(f)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡并用365 nm紫外光照射后Figure 6. Contact angle variation of polymer d slide coatings under different conditions: (a) The natural state; (b) After immersion with pH=3 buffer solution; (c) After immersion in pH=10 buffer solution; (d) After exposure to 365 nm light; (e) After exposure to 445 nm light; (f) After immersion in pH=3 buffer solution and irradiation with 365 nm ultraviolet light
图 6 聚合物d的载玻片涂层在不同条件下的接触角变化:(a)自然条件下;(b)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡后;(c)经pH=10缓冲溶液浸泡后;(d)经365 nm光照射后;(e)经445 nm光照射后;(f)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡并用365 nm紫外光照射后Figure 6. Contact angle variation of polymer d slide coatings under different conditions: (a) The natural state; (b) After immersion with pH=3 buffer solution; (c) After immersion in pH=10 buffer solution; (d) After exposure to 365 nm light; (e) After exposure to 445 nm light; (f) After immersion in pH=3 buffer solution and irradiation with 365 nm ultraviolet light图6显示了聚合物涂层在不同条件下的接触角的变化情况,该变化能够反映涂层材料的智能响应特性。在自然条件下的接触角143.7°,见图6(a)。将其在pH=3的缓冲溶液中浸泡1 h后烘干,接触角变化至109.9°,见图6(b)。该过程的接触角是由聚合物中DMAEMA单元和偶氮苯上羧基质子化共同作用导致的。随后将涂层置于pH=10的缓冲溶液中浸泡1 h后烘干,其接触角恢复至142.2°,见图6(c),将烘干后的涂层在365 nm (20 W)紫外灯下照射5 min,接触角变化至48.4°,见图6(d)。用LED灯照射15 min后,其接触角恢复至139.3°,如图6(e)所示。该过程接触角的变化是由于聚合物中偶氮苯单元经过紫外-可见光照射后发生构型转化使涂层的润湿性发生转变。最后将涂层置于pH=3的缓冲溶液中浸泡1 h后烘干,然后将其置于365 nm (20 W)紫外灯下照射15 min,该过程由pH响应单元与光响应单元共同作用,其接触角由139.3°变化至19.0°,见图6(f)。
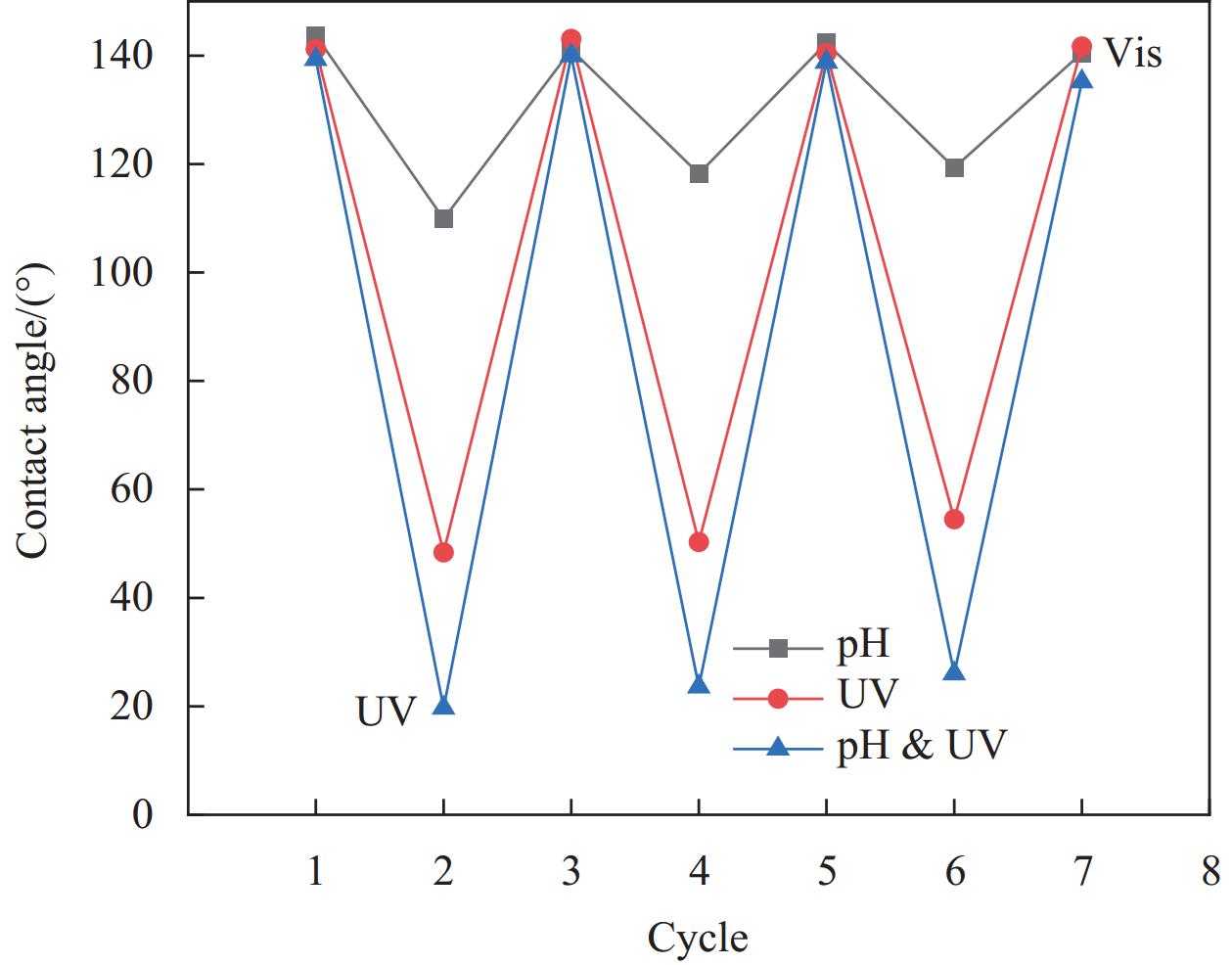
上述过程证明了涂层具有良好的刺激响应能力。以相同的方法重复进行上述实验,接触角的变化如图7所示。实验结果表明,经过多次刺激响应,聚合物涂层发生亲水和疏水的多次转换,且接触角仍可恢复到初始状态,证明了涂层的转换润湿能力具有良好的可逆性。其中,光在转化过程中具有更加显著的效果,这也在随后的油水分离试验中得到证实,切换时间也与偶氮苯单体吸收光谱的转化时间基本对应。由于光照可以在没有物理接触的情况下实现转化,这增强了材料的实际应用的便利性。
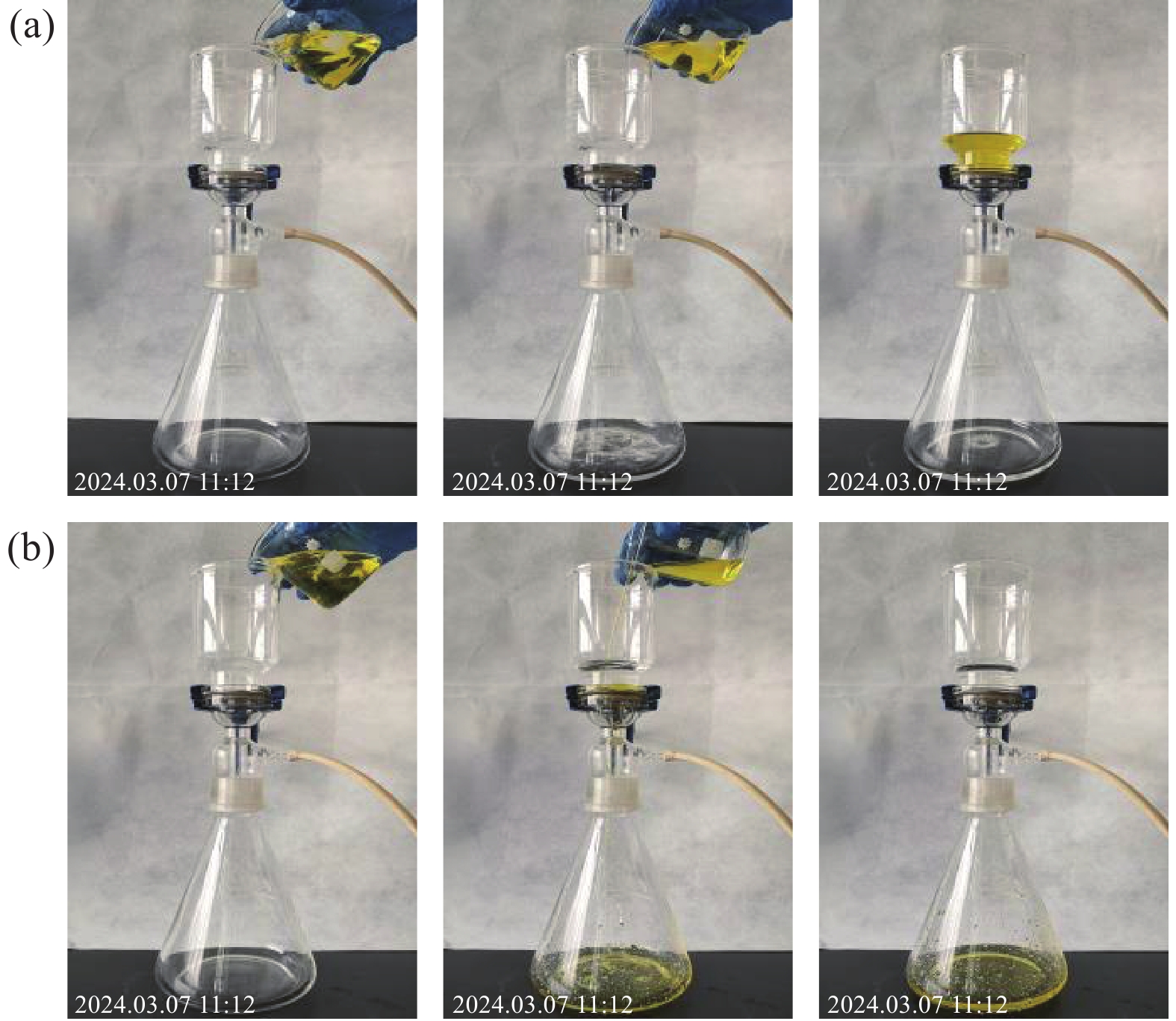
为了测试光/pH双响应油水分离膜的分离效果,将柠檬黄染色的水100 mL与石油醚以2∶1的体积比混合后倒入滤杯中进行油水分离实验。为加快油/水的分离速度,在0.005 MPa的压力下用抽滤的方法模拟油水分离系统 (图8)。图8(a)中,抽滤30 s后,无色的石油醚被抽滤下来,不再有液体从上方流下,染色的水保留在上方滤杯中。在图8(b)中,用365 nm光照射分离膜12 h,以相同的方法进行油水分离,抽滤25 s后,染色的水被抽滤下来,石油醚被保留在上方。
分别测量分离后上方滤杯中的油或水的体积,计算得到分离效率分别为96.3% (图8(a))和95.8%(图8(b))。实验结果证明了分离膜具有良好的智能转换油水分离能力。
3. 结 论
(1)以合成的偶氮苯、甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯(HEMA)和甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯(DMAEMA)为原料,采用可逆加成-断裂链转移(RAFT)法一步聚合,制得光和pH智能双响应三元无规共聚物。该聚合物以偶氮苯作为光响应单元,DMAEMA作为pH响应单元,HEMA使聚合物具有良好的柔性附着性能,FTIR和1HNMR谱图说明了聚合物的成功合成。
(2)通过在不同条件下的润湿性实验,验证了聚合物涂层的可转换润湿性。紫外线的照射导致偶氮苯单元的分子构型发生转变,结构上的变化导致聚合物的润湿性和渗透性的变化。在仅有pH=3的缓冲溶液浸泡后其最大接触角转变达到33.8°,仅有紫外光照射下其最大接触角转变达到93.8°,而在光和pH的共同作用下,其最大接触角变化可达到120.3°。说明了涂层在光照和pH的刺激下具有优异的刺激响应性。经过亲水与疏水的多次转换实验后,接触角仍可恢复到初始状态,证明了涂层对水的润湿能力切换具有可逆性。
(3)偶氮苯的引入使聚合物对光具有良好的响应性,DMAEMA上含有的叔胺基团和偶氮苯上的羧基共同增强了涂层的pH响应性和抗酸性,可以使涂层应对一些复杂情况下的油水分离,油水分离实验证明涂层在光照下的极性转变,单次分离效率分别达96.3%和95.8%。
综上,通过一步RAFT聚合制备得到的光/pH双响应的聚合物材料,可用来制备智能光/pH双响应油水分离膜,该膜具有优异的可逆刺激响应性能。
-
图 6 聚合物d的载玻片涂层在不同条件下的接触角变化:(a)自然条件下;(b)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡后;(c)经pH=10缓冲溶液浸泡后;(d)经365 nm光照射后;(e)经445 nm光照射后;(f)经pH=3缓冲溶液浸泡并用365 nm紫外光照射后
Figure 6. Contact angle variation of polymer d slide coatings under different conditions: (a) The natural state; (b) After immersion with pH=3 buffer solution; (c) After immersion in pH=10 buffer solution; (d) After exposure to 365 nm light; (e) After exposure to 445 nm light; (f) After immersion in pH=3 buffer solution and irradiation with 365 nm ultraviolet light
-
[1] GUO H, QIN Q, HU M, et al. Treatment of refinery wastewater: Current status and prospects[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2024, 12(2): 112508.
[2] LARI K S, DAVIS G B, BASTOW T, et al. On quantifying global carbon emission from oil contaminated lands over centuries[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2024, 907: 168039. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168039
[3] 吴应湘, 许晶禹. 油水分离技术[J]. 力学进展, 2015, 45: 179-216. DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-15-001 WU Yingxiang, XU Jingyu. Oil-water separation technology[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2015, 45: 179-216(in Chinese). DOI: 10.6052/1000-0992-15-001
[4] CHANG L, CAO Y, FAN G, et al. A review of the applications of ion floatation: Wastewater treatment, mineral beneficiation and hydrometallurgy[J]. RSC Advances, 2019, 9: 20226-20239. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA02905B
[5] 陈明功, 周鑫, 赵彬彬, 等. 油水分离技术的研究进展[J]. 现代化工, 2024, 44(1): 63-67. CHEN Minggong, ZHOU Xin, ZHAO Binbin, et al. Research progress of oil-water separation technology[J]. Modern Chemical Industry, 2024, 44(1): 63-67(in Chinese).
[6] MANSOUR M S, ABDEL-SHAFY H I, IBRAHIM A M. Petroleum wastewater: Environmental protection, treatment, and safe reuse: An overview[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2024, 351: 119827. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119827
[7] 胡天佑, 唐瑾, 陈志莉. 石油工业含油废水处理进展[J]. 水处理技术, 2021, 47(6): 12-17. HU Tianyou, TANG Jin, CHEN Zhili. Progress in the treatment of oily wastewater from petroleum industry[J]. Water Treatment Technology, 2019, 47(6): 12-17(in Chinese).
[8] ADETUNJI A I, OLANIRAN A O. Treatment of industrial oily wastewater by advanced technologies: A review[J]. Applied Water Science, 2021, 11: 98.
[9] 徐诗琪, 周洲, 汤睿, 等. 高疏水纳米纤维素-壳聚糖/膨润土气凝胶的构建及其高效油水分离的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(3): 1347-1355. XU Shiqi, ZHOU Zhou, TANG Rui, et al. Construction of highly hydrophobic nanocellulose-chitosan/bentonite aerogel and its application of efficient oil-water separation[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(3): 1347-1355(in Chinese).
[10] YANG H, ZHANG Y, HUANG C, et al. Antifouling multi-functional membrane for oil/dye wastewater treatment: Regeneration while treating mixed pollutants[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 332: 125804. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125804
[11] LI B, QI B, GUO Z, et al. Recent developments in the application of membrane separation technology and its challenges in oil-water separation: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2023, 327: 138528.
[12] ZHANG J, PENG K, XU Z, et al. A comprehensive review on the behavior and evolution of oil droplets during oil/water separation by membranes[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 319: 102971. DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.102971
[13] 穆蒙, 宁学文, 罗新杰, 等. 刺激响应性聚合物微球的制备、性能及应用[J]. 化学进展, 2020, 32(7): 882-894. MU Meng, NING Xuewen, LUO Xinjie, et al. Preparation, properties and application of stimulus-responsive polymer microspheres[J]. Advances in Chemistry, 2019, 32(7): 882-894(in Chinese).
[14] GONG J, XIANG B, SUN Y, et al. Janus smart materials with asymmetrical wettability for on-demand oil/water separation: A comprehensive review[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2023, 11: 25093-25114. DOI: 10.1039/D3TA04160C
[15] QIU L, ZHENG J, YU X, et al. Hydrophobic photore-sponsive azobenzene-containing materials prepared by click reaction[J]. Surface Review and Letters, 2024, 31(7): 2450055.
[16] YU B, HOU K, FAN Z, et al. Design fiber-based membrane with interfacial wettability rapidly regulated behavior by pH for oily wastewater high-efficient treatment[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2024, 189: 108326.
[17] ZHONG Q, LU M, NIEUWENHUIS S, et al. Enhanced stain removal and comfort control achieved by cross-linking light and thermo dual-responsive copolymer onto cotton fabrics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11: 5414-5426.
[18] CHEN W, HE H, ZHU H, et al. Thermo-responsive cellulose-based material with switchable wettability for controllable oil/water separation[J]. Polymers, 2018, 10(6): 592.
[19] SUN R, WU C, HOU B, et al. Magnetically responsive superhydrophobic surface with reversibly switchable wettability: Fabrication, deformation, and switching performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(45): 53146-53158.
[20] LIU X, ZHANG P, SONG H, et al. Unveiling a pH-responsive dual-androgen-blocking magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for enhanced synergistic therapy of prostate cancer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16(4): 4348-4360.
[21] SURAPANENI S G, CHOUDHARI S N, AVHAD S V, et al. Permeable polymersomes from temperature and pH dual stimuli-responsive PVCL-b-PLL block copolymers for enhanced cell internalization and lysosome targeting[J]. Biomaterials Advances, 2023, 151: 213454. DOI: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213454
[22] URBAN D, MARCUCCI N, WÖLFLE C H, et al. Polarization-driven reversible actuation in a photo-responsive polymer composite[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14(1): 6843. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-42590-y
[23] LI Y, XUE B, YANG J, et al, Azobenzene as a photoswitchable mechanophore[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2024, 16: 446-455.
[24] DU Q, ZHAO J, JIANG L, et al. Molecular design on dual stimuli-responsive azobenzene-containing ionic complexes toward self-healing materials under photoirradiation or humid condition at room temperature[J]. Applied Materials Today, 2023, 35: 101945. DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2023.101945
[25] LI B H, JIANG L, WANG Y, et al. Construction and properties of new-type photo-responsive molecular imprinting materials[J]. Polymer Science, Series A, 2023, 64: 673-684.
[26] 陈佳慧, 袁晨瑞, 吴泽宏, 等. 偶氮苯高分子光控可逆黏合剂的制备及性能[J]. 功能高分子学报, 2023, 36(3): 293-301. CHEN Jiahui, YUAN Chenrui, WU Zehong, et al. Preparation and properties of photocontrolled reversible adhesives for azobenzene polymers[J]. Journal of Functional Polymers, 2023, 36(3): 293-301(in Chinese).
[27] YANG Q, GE J, QIN M, et al. Controllable heat release of phase-change azobenzenes by optimizing molecular structures for low-temperature energy utilization[J]. Science China Materials, 2023, 66: 3609-3620.
[28] MERRITT D C I, JACQUEMIN D, VACHER M. cis → trans photoisomerisation of azobenzene: A fresh theoretical look[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2021, 23: 19155-19165. DOI: 10.1039/D1CP01873F
[29] YANG X, JIN H, TAO X, et al. Photo-switchable smart superhydrophobic surface with controllable superwettability[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2021, 12(37): 5303-5309. DOI: 10.1039/D1PY00984B
[30] DU Z, REN B, CHANG X, et al. Aggregation and rheology of an azobenzene-functionalized hydrophobically modified ethoxylated urethane in aqueous solution[J]. Macromolecules, 2016, 49(13): 4978-4988. DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.6b00633
[31] CHENG H B, ZHANG S, QI J, et al. Advances in application of azobenzene as a trigger in biomedicine: Molecular design and spontaneous assembly[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33: e2007290. DOI: 10.1002/adma.202007290
-
其他相关附件
-
目的
智能材料是一种具有感知、响应和适应环境能力的材料。随着科技的不断发展,智能材料在各个领域的应用越来越广泛,未来的发展前景十分广阔。偶氮苯是一种被广泛研究的光响应单元,甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯是pH响应单元,通过光照或pH诱导可使其分子构型或结构发生转变,极性也会随之发生变化。将这些响应单元嵌入到油水分离聚合物材料中可以实现材料的光/pH的可调控性,使材料可以对油水实现选择性的分离。基于此,我们合成了一种智能双响应的聚合物,并将其与无纺布结合制备了智能响应油水分离膜,该膜可受光和pH的刺激而改变极性,达到智能油水分离的目的。
方法首先通过重氮化-偶联反应、醚化反应和酯化反应制备了一种含有羧基及可聚合基团的偶氮苯,将其作为光响应单元。以甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯作为pH响应单元,甲基丙烯酸羟乙作为柔性单元与合成的偶氮苯采用一步RAFT法聚合得到了光/pH双响应的聚合物,将聚合物滴涂到载玻片上,通过紫外-可见光的照射、不同pH缓冲溶液的浸泡测定其接触角的变化。将聚合物浸涂在无纺布上制成油水分离膜,测试其油水分离效率。
结果对合成的偶氮苯单体及聚合物进行红外谱图表征,各位置的峰与其结构对应,核磁共振氢谱中单体和聚合物结构上氢对应的化学位移基本一致。偶氮苯单体在DMF溶剂中的紫外吸收光谱数据表明偶氮苯在445nm光和365nm光的刺激下发生结构转变,并且这一过程是可逆的。通过不同pH和光照条件下接触角测试结果显示:在自然条件下聚合物膜的接触角为143.7°,将其在pH=3的缓冲溶液中浸泡后,接触角变化至109.9°,接触角变化可达33.8°。在pH=10的缓冲溶液中浸泡后,其接触角可恢复至142.1°。在365 nm紫外灯下照射后,接触角变化至48.4°,接触角变化可达93.7°。使用445nm LED灯照射后,其接触角可恢复至139.2°。在pH=3的缓冲溶液中浸泡后并置于365 nm紫外灯下照射,接触角变化至19.0°,接触角变化可达120.2°。柠檬黄染色水与石油醚混合物的油水分离实验发现,油水分离膜可实现抽滤出油或水的智能转换,分离效率分别达到96.3%和95.8%。
结论(1)以合成的偶氮苯、HEMA和DMAEMA为原料,采用RAFT法一步聚合,制得光和pH双响应共聚物。该聚合物以偶氮苯的作为光响应单元,DMAEMA作为pH响应单元,HEMA使聚合物具有良好的柔性附着性能。(2)通过在不同条件下的润湿性实验,验证了聚合物涂层的可转换润湿性。紫外线的照射导致偶氮苯单元的结构上的变化,聚合物的润湿性和渗透性因此发生变化。通过不同的刺激条件验证了涂层在光照和pH的刺激下具有良好的刺激响应性。多次实验后,接触角仍可恢复到初始状态。(3)偶氮苯单元使聚合物对光具有良好的响应性,DMAEMA上含有的叔胺基团和偶氮苯上的羧基增强了涂层的pH响应性和抗酸性,可以应对一些复杂情况下的油水分离,油水分离实验证明单次油水分离效率分别达96.3%和95.8%。
-
智能响应材料可以通过外部刺激改变其结构和性质,在各领域具有广泛的应用,未来具有广阔的发展前景。多刺激响应材料可以对不同的刺激条件实现响应,具有更加多样的方法来应对愈加复杂的使用环境。本文的创新点和亮点如下:
1. 合成了一种含有羧基及可聚合基团的偶氮苯化合物,并以合成的偶氮苯化合物作为光响应单元,甲基丙烯酸二甲氨乙酯作为pH响应单元,甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯作为柔性单元,制备得到光和pH智能双响应聚合物。
2. 采用可逆加成-断裂链转移(RAFT) 一步聚合,制备三元无规共聚物。
3. 聚合物涂层在不同条件的刺激下接触角最大变化可达120.2°,经过亲水-疏水的多次转换,接触角仍可以恢复到初始状态,具有优异的可逆刺激响应能力。将聚合物涂敷在无纺布上制成光/pH双响应油水分离膜,该膜可实现选择性油水分离,单次分离效率分别达96.3%和95.8%。




 下载:
下载: