Effect of flux agents on properties of ceramifiable flame retardant room temperature vulcanized silicone rubber foam
-
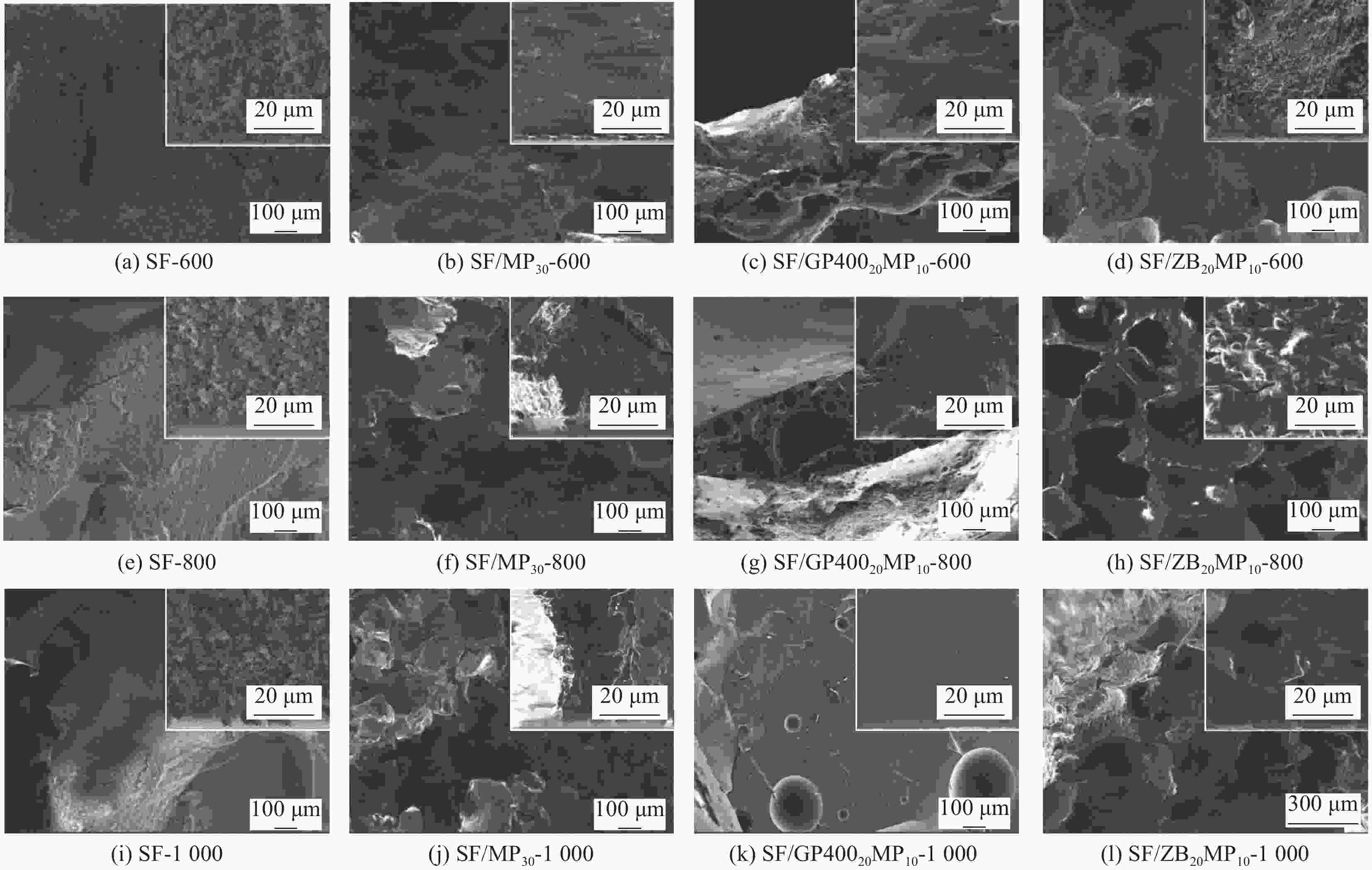
摘要: 为提升室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫的阻燃性能和耐火性能,本文以不同熔点玻璃粉和硼酸锌为助熔剂,云母粉为耐火填料,制备可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫,并研究了不同无机填料种类和配比对硅橡胶泡沫微观形貌、热稳定性、阻燃性能和燃烧行为的影响及不同温度烧蚀下硅橡胶泡沫的陶瓷化行为。结果表明,玻璃粉的引入影响了硅橡胶泡沫的发泡过程,形成了孔径较大的泡沫结构,不利于硅橡胶泡沫阻燃性能、热稳定性、火安全性的提升,但在烧蚀实验中,其能够显著降低硅橡胶泡沫的陶瓷化温度;硼酸锌的引入能够显著提升硅橡胶泡沫的阻燃性能、高温区热稳定性和火安全性,并且硼酸锌与云母粉展现出较好的协同阻燃作用,硅橡胶泡沫的极限氧指数(LOI)最高达到33.2%,并通过垂直燃烧FV-0级,N2气氛下热重分析测试中900℃时的残炭含量最高可达75.9%,硅橡胶泡沫的热释放和烟释放及烧蚀实验后的质量损失率均得到明显降低,同时,硼酸锌还有助于形成陶瓷状残炭。Abstract: In order to improve the flame retardancy and fire resistance of room temperature vulcanized (RTV) silicone rubber foam, glass powder and zinc borate as flux agent, and mica powder as refractory filler were used to prepare ceramifiable flame retardant RTV silicone rubber foam. The effects of different types and proportions of inorganic fillers on the micromorphology, thermal stability, flame retardancy and combustion behavior of the silicone rubber foam, as well as the ceramifiable behavior of the silicone rubber foam after ablation at different temperatures were studied. The results show that the introduction of glass powder affects the foaming process of the silicone rubber foam, forming a foam structure with large pore size, which is not conducive to the improvement of the flame retardancy, thermal stability and fire safety performances of the silicone rubber foam. But, glass power can remarkably decrease ceramization temperature of the silicone rubber foam. The introduction of zinc borate greatly improves the flame retardancy, thermal stability in high temperature zone and fire safety performances of the silicone rubber foam. Meanwhile, zinc borate and mica powder show good synergistic flame retardant effect. limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of the silicone rubber foam can reach to 33.2, and it can pass the vertical combustion FV-0 level. Carbon residue of the silicone rubber foam at 900℃ can reach up to 75.9% in thermogravimetric analysis in N2 atmosphere. The heat release, smoke release of the silicone rubber foam and the mass loss after the ablation experiment are significantly reduced. In addition, zinc borate also contributes to the formation of ceramic carbon residue.
-
Key words:
- RTV silicone rubber foam /
- flux agent /
- flame retardancy /
- combustion behavior /
- ceramifiable property
-
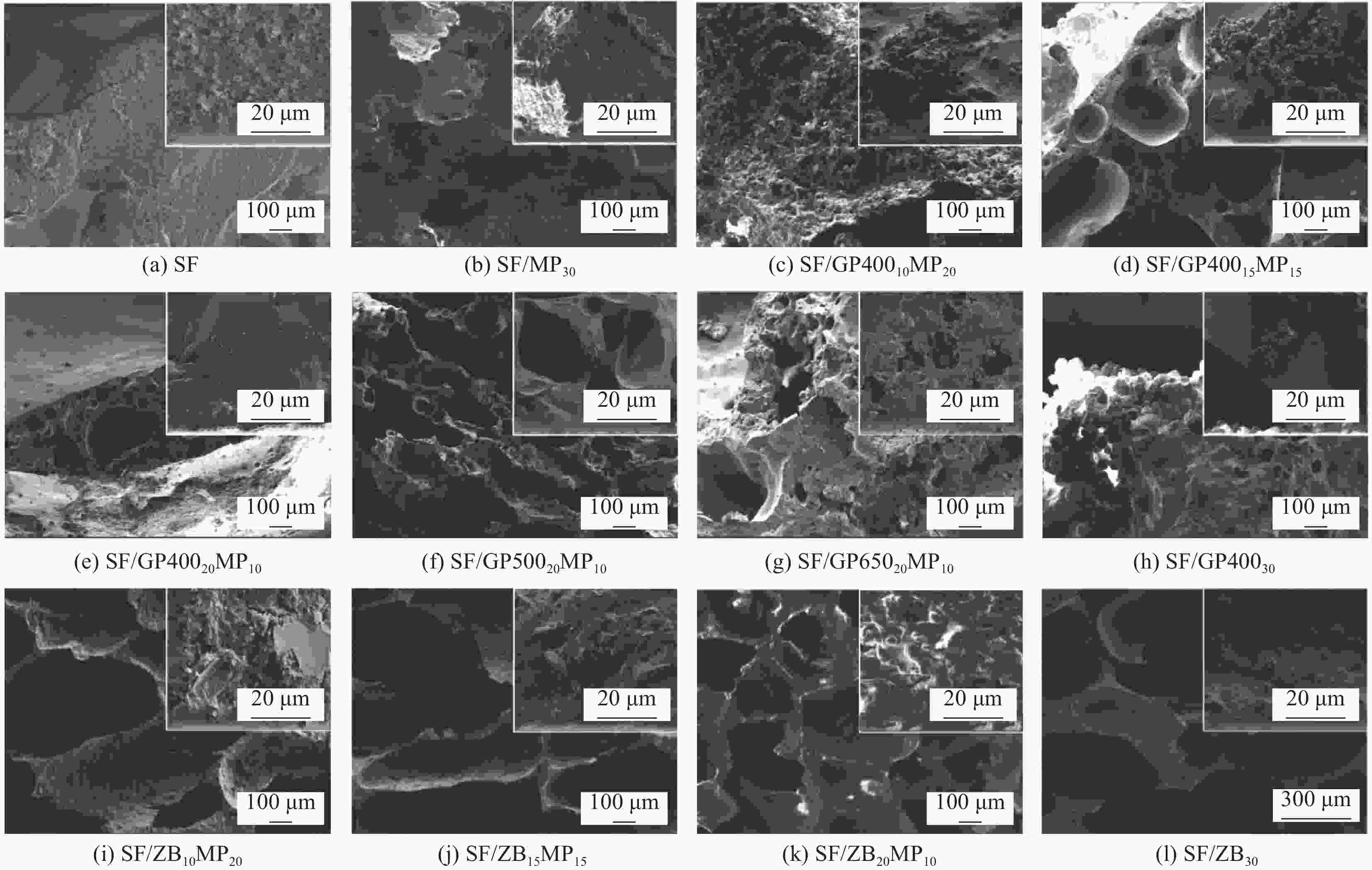
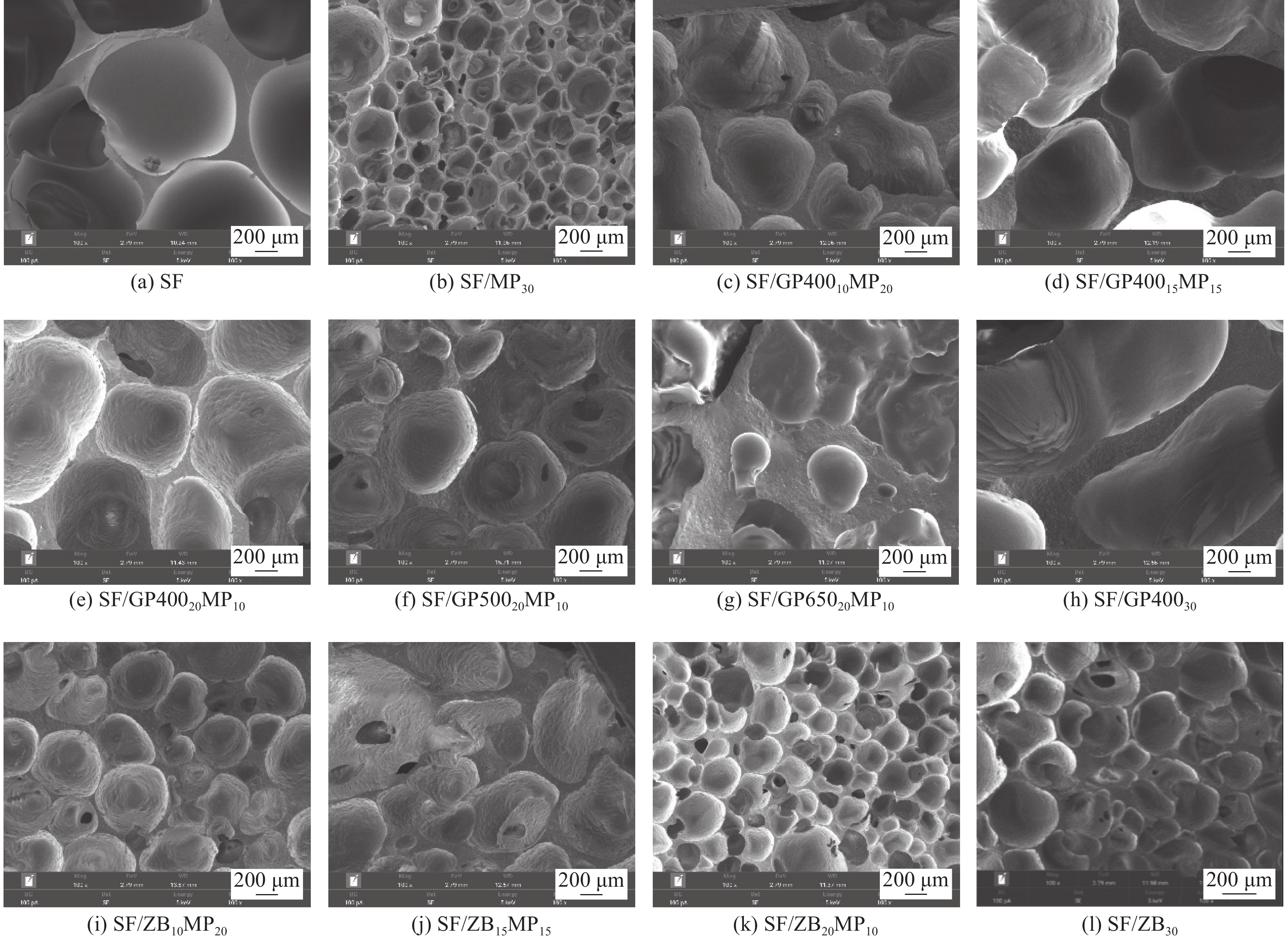
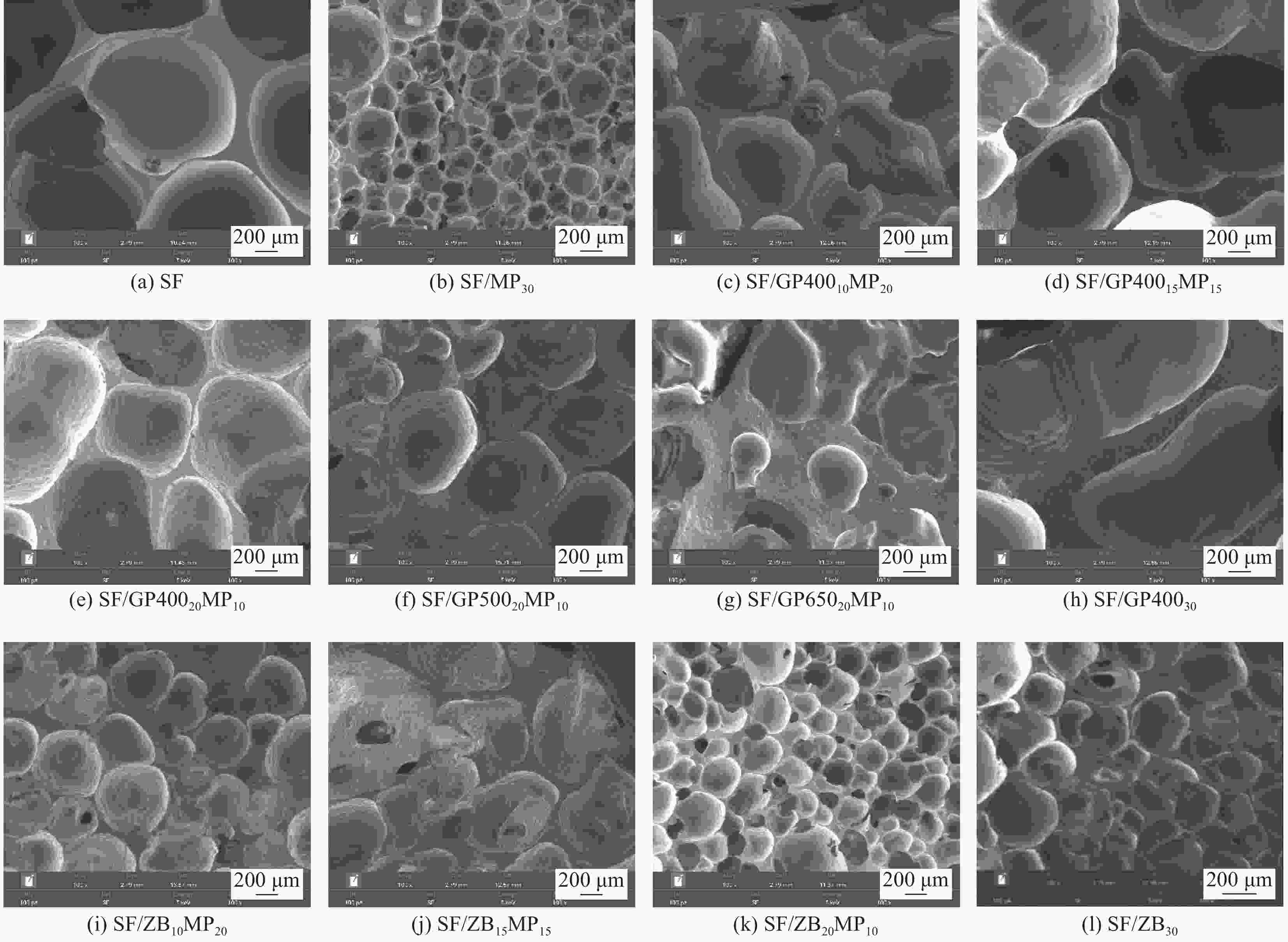
表 1 可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化(RTV)硅橡胶泡沫的配方及极限氧指数(LOI)、垂直燃烧(UL-94)测试结果
Table 1. Formulation, limit oxygen index (LOI) and vertical combustion (UL-94) test results of the ceramifiable flame retardant room temperature vulcanized (RTV) silicone rubber foam
Sample SRF/wt% GP/wt% ZB/wt% MP/wt% Melting point of GP/℃ LOI/% UL-94 SF 100 0 0 0 — 23.4 NR SF/MP30 70 0 0 30 — 31.8 FV-0 SF/GP40010MP20 70 10 0 20 400 23.4 NR SF/GP40015MP15 70 15 0 15 400 24.6 NR SF/GP40020MP10 70 20 0 10 400 23.4 NR SF/GP50020MP10 70 20 0 10 500 24.0 NR SF/GP65020MP10 70 20 0 10 650 22.8 NR SF/GP40030 70 30 0 0 400 26.4 NR SF/ZB10MP20 70 0 10 20 — 33.2 FV-0 SF/ZB15MP15 70 0 15 15 — 31.8 FV-0 SF/ZB20MP10 70 0 20 10 — 31.0 FV-0 SF/ZB30 70 0 30 0 — 31.6 FV-0 Notes: SRF—Silicone rubber foam; GP—Glass powder; ZB—Zinc borate; MP—Mica powder; SF—Silicone foam; NR—No rating. 表 2 可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫N2气氛下的热重测试具体数据
Table 2. TGA parameters of the ceramifiable flame retardant RTV silicone rubber foam under N2 atmosphere
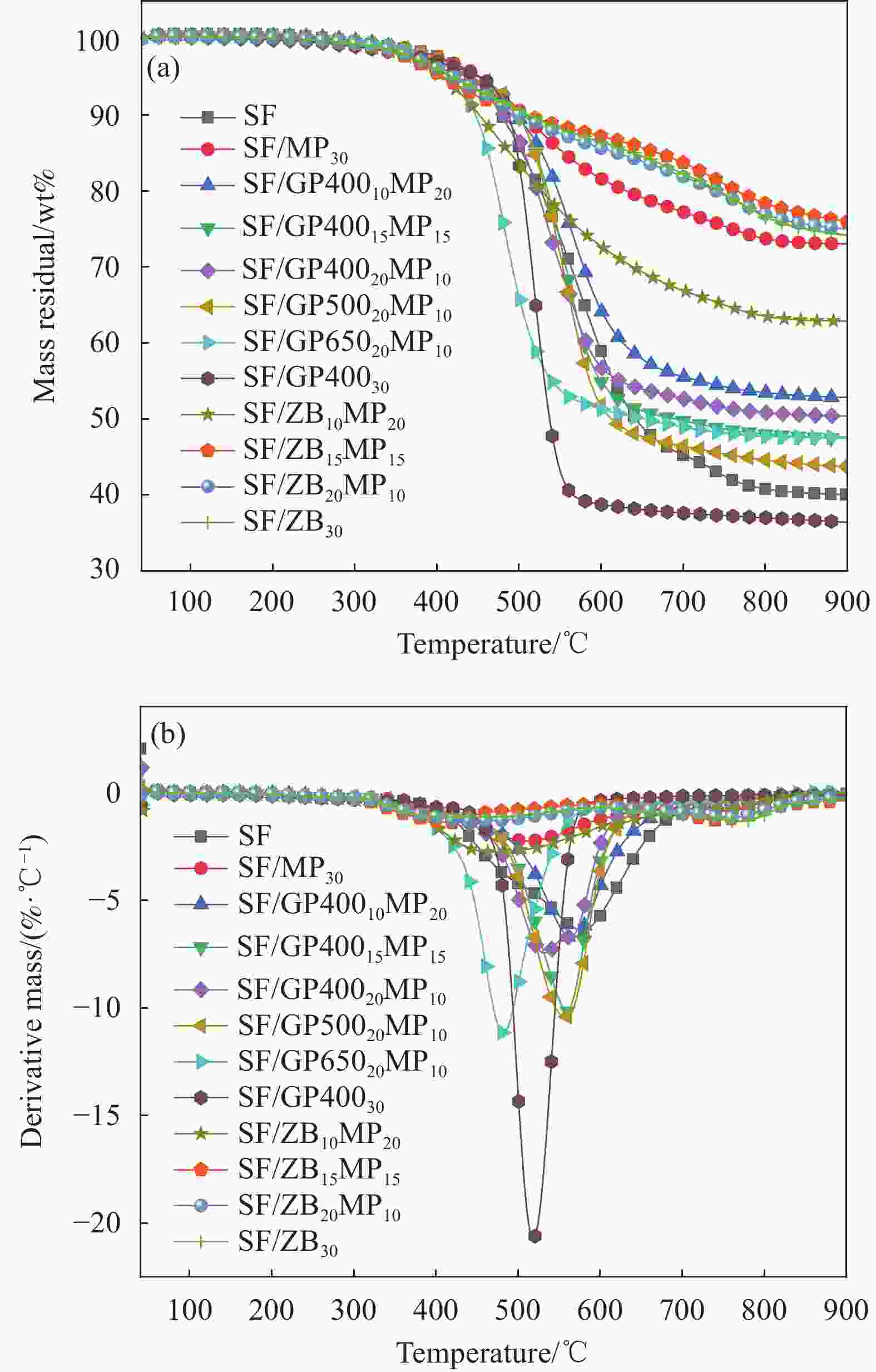
Sample Tonset/℃ Tmax/℃ dW/dT/
(%·min−1)Residue/% SF 442.0 576.0 6.36 40.1 SF/MP30 451.7 510.8 2.24 73.0 SF/GP40010MP20 434.9 566.2 6.75 52.8 SF/GP40015MP15 441.4 559.4 10.20 47.5 SF/GP40020MP10 425.2 532.8 7.44 50.4 SF/GP50020MP10 449.7 557.3 10.41 43.7 SF/GP65020MP10 415.8 482.2 11.14 47.7 SF/GP40030 451.6 518.5 20.71 36.4 SF/ZB10MP20 406.2 467.9 2.74 62.9 SF/ZB15MP15 407.7 422.1 1.39 75.9 SF/ZB20MP10 419.1 463.6 1.28 75.0 SF/ZB30 418.4 421.8 1.14 74.1 Note: Tonset, Tmax and dW/dT are the onset thermal decomposition temperature, the maximum thermal decomposition temperature and the thermal decomposition rate at the Tmax. 表 3 可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫空气气氛下的热重测试具体数据
Table 3. TGA parameters of the ceramifiable flame retardant RTV silicone rubber foam under air atmosphere
Sample Tonset/℃ Tmax/℃ dW/dT/
(%·min−1)Residue/% SF 354.4 362.0 9.81 56.9 SF/MP30 378.5 380.7 5.65 76.0 SF/GP40010MP20 377.0 509.3 11.91 52.2 SF/GP40015MP15 375.3 507.5 14.39 46.0 SF/GP40020MP10 373.7 498.9 15.64 42.1 SF/GP50020MP10 363.3 367.2 6.65 64.1 SF/GP65020MP10 376.5 452.8 17.03 42.4 SF/GP40030 369.6 495.8 16.60 40.6 SF/ZB10MP20 374.4 372.3 4.91 80.2 SF/ZB15MP15 379.8 551.9 3.91 73.0 SF/ZB20MP10 376.4 370.5 3.69 79.5 SF/ZB30 367.7 362.1 3.82 81.2 表 4 可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫的锥形量热测试主要数据
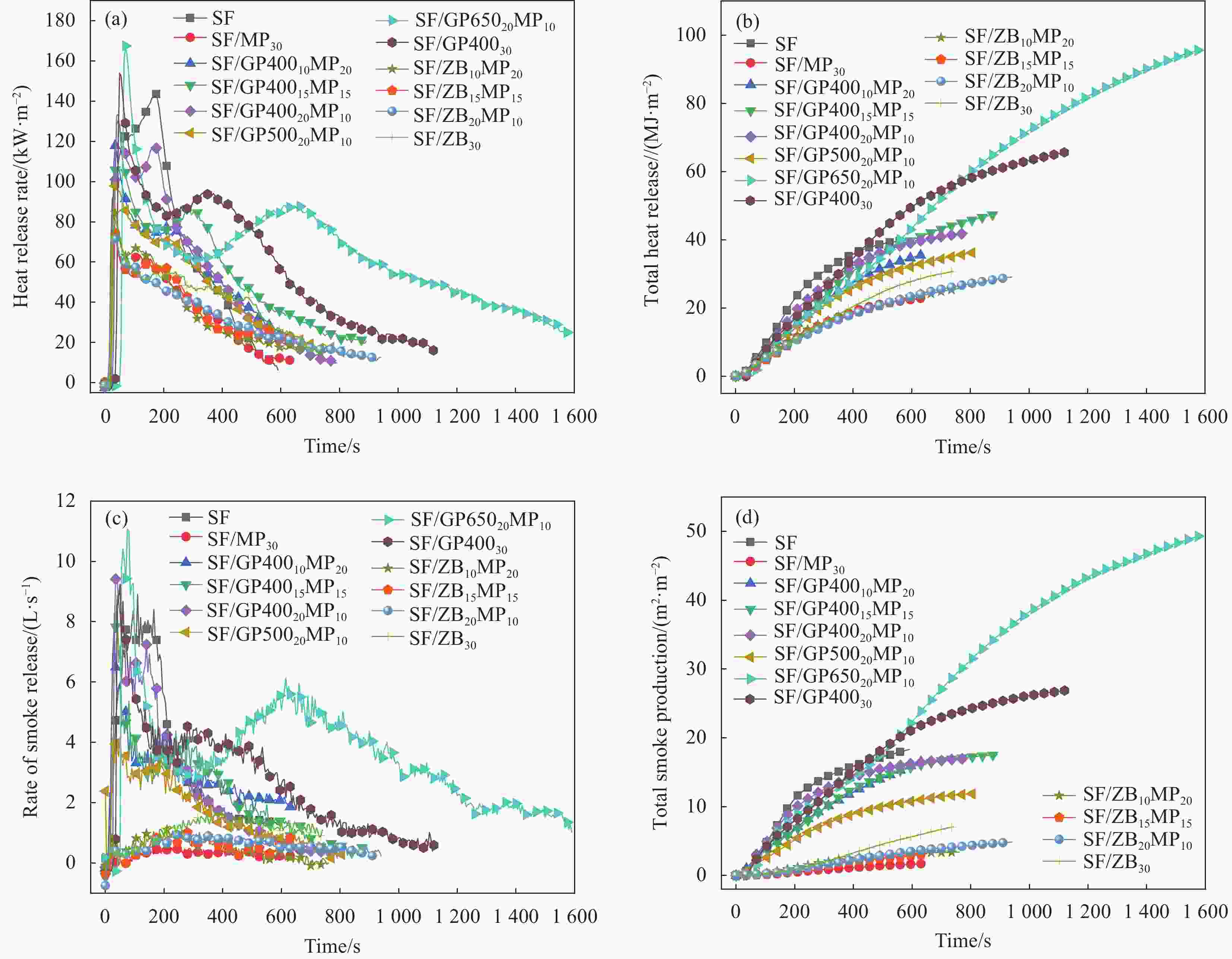
Table 4. Burning parameters of the ceramifiable flame retardant RTV silicone rubber foam in cone calorimeter test
Sample TTI
/sPHRR
/(kW·m−2)THR
/(MJ·m−2)TTPHRR
/sTSP/(m2·m−2) Residue
/%SF 7 145.0 40.0 170 18.3 52.6 SF/MP30 13 76.6 23.0 30 1.7 79.6 SF/GP40010MP20 15 117.9 35.7 35 16.7 68.3 SF/GP40015MP15 23 133.5 47.7 45 17.6 65.4 SF/GP40020MP10 24 130.7 42.0 45 17.0 60.2 SF/GP50020MP10 14 98.6 36.3 40 11.8 69.2 SF/GP65020MP10 50 167.6 96.0 70 49.5 71.4 SF/GP40030 33 154.0 65.6 50 26.9 66.2 SF/ZB10MP20 16 84.5 25.8 35 3.4 81.8 SF/ZB15MP15 16 73.4 24.5 35 3.2 75.7 SF/ZB20MP10 10 72.2 29.1 30 4.8 81.6 SF/ZB30 14 80.1 30.7 35 7.1 80.5 Notes: TTI—Time to ignition; PHRR—Peak of heat release rate; TTPHRR—Time to PHRR. 表 5 可陶瓷化阻燃室温硫化硅橡胶泡沫烧蚀后质量损失率
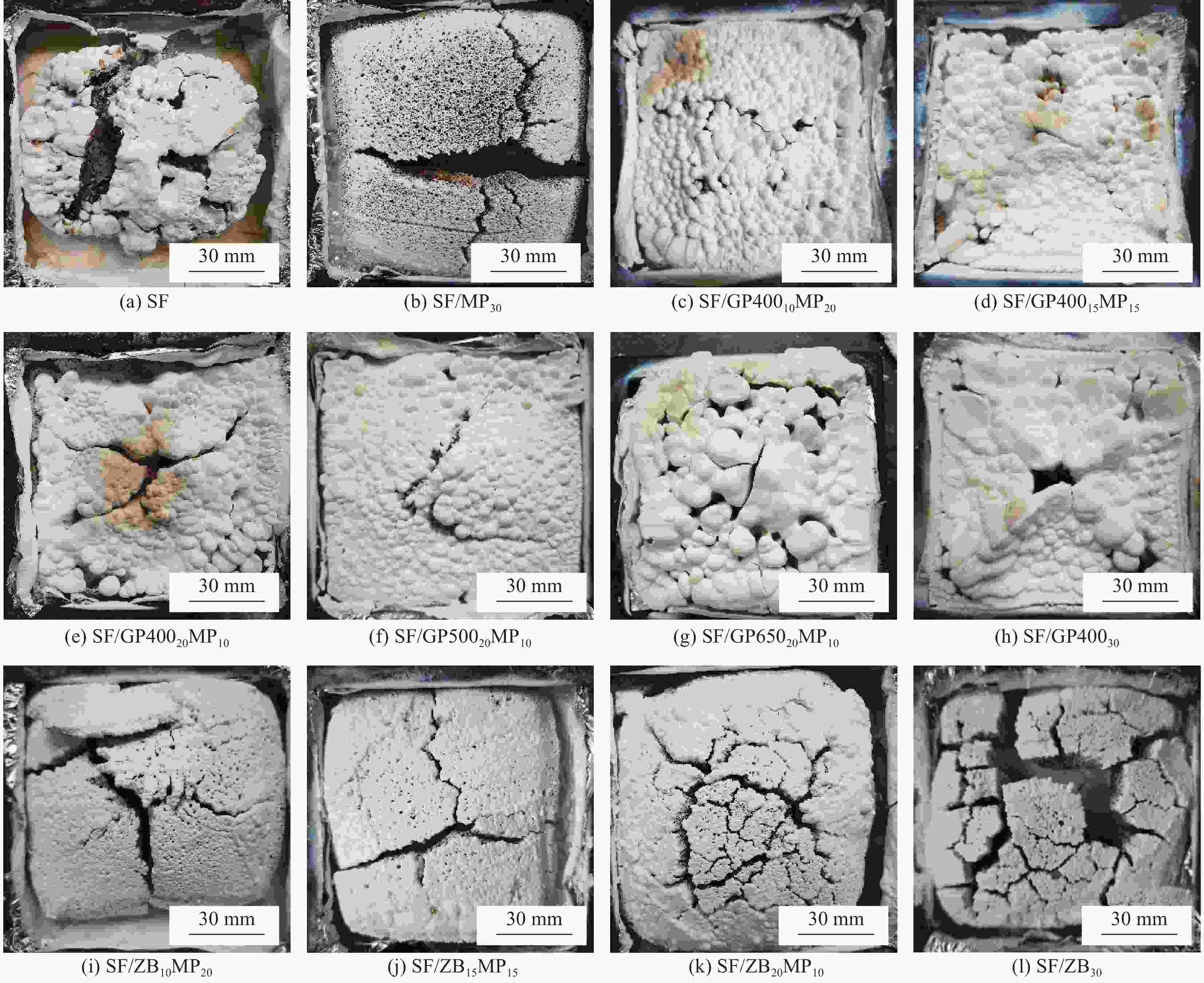
Table 5. Mass loss rate of the ceramifiable flame retardant RTV silicone rubber foam after ablation
Sample Mass loss/% 600℃ 800℃ 1000℃ SF 89.16 75.71 80.33 SF/MP30 45.56 20.45 17.65 SF/GP40010MP20 66.73 67.18 67.52 SF/GP40015MP15 66.02 65.72 64.43 SF/GP40020MP10 62.60 69.52 62.12 SF/GP50020MP10 67.49 66.32 61.66 SF/GP65020MP10 59.73 47.85 51.40 SF/GP40030 64.30 54.52 50.00 SF/ZB10MP20 53.45 32.78 25.61 SF/ZB15MP15 52.07 48.19 26.45 SF/ZB20MP10 35.56 31.63 30.00 SF/ZB30 59.39 35.48 43.35 -
[1] DENG S B, LIAO W, YANG J C, et al. Flame-retardant and smoke-suppressed silicone foams with chitosan-based nanocoatings[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2016,55(27):7239-7248. [2] ABBAD A, JABOVISTE K, OUISSE M, et al. Acoustic performances of silicone foams for sound absorption[J]. Journal of Cellular Plastics,2018,54(3):651-670. doi: 10.1177/0021955X17732305 [3] ROSTAMI-TAPEH-ESMAEIL E, VAHIDIFAR A, ESMIZADEH E, et al. Chemistry, processing, properties, and applications of rubber foams[J]. Polymers,2021,13(10):1565. doi: 10.3390/polym13101565 [4] LUO W Q, LI Z M, LUO H H, et al. Preparation of room temperature vulcanized silicone rubber foam with excellent flame retardancy[J]. Scanning,2021,2021:9976005. doi: 10.1155/2021/9976005 [5] DENG J, KANG F R, XIAO Y, et al. Effects of platinum compounds/superfine aluminum hydroxide/ultrafine calcium carbonate on the flame retardation and smoke suppression of silicone foams[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2020,137(1):47679. doi: 10.1002/app.47679 [6] KANG F R, WANG C P, DENG J, et al. Effects of talc/hollow glass beads on the flame retardancy of silicone foams[J]. Materials Research Express,2019,6(9):095318. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab3084 [7] PANG Q T, KANG F R, DENG J, et al. Flame retardancy effects between expandable graphite and halloysite nanotubes in silicone rubber foam[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(23):13821-13831. doi: 10.1039/D1RA01409A [8] CHEN X L, SONG W K, LIU J B, et al. Synergistic flame-retardant effects between aluminum hypophosphite and expandable graphite in silicone rubber composites[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2015,120(3):1819-1826. doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-4428-0 [9] KANG F R, WANG C P, DENG J, et al. Flame retardancy and smoke suppression of silicone foams with microcapsulated aluminum hypophosphite and zinc borate[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2020,31(4):654-664. doi: 10.1002/pat.4799 [10] CAO C F, WANG P H, ZHANG J W, et al. One-step and green synthesis of lightweight, mechanically flexible and flame-retardant polydimethylsiloxane foam nanocomposites via surface-assembling ultralow content of graphene derivative[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,393:124724. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124724 [11] PANG Q T, DENG J, KANG F R, et al. Effect of expandable graphite/hexaphenoxycyclotriphosphazene beads on the flame retardancy of silicone rubber foam[J]. Materials Research Express,2020,7(5):055308. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab9250 [12] KANG F R, DENG J, JIAO D S, et al. Microfluidic fabrication of polysiloxane/dimethyl methylphosphonate flame-retardant microcapsule and its application in silicone foams[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies,2019,30(5):1269-1278. doi: 10.1002/pat.4560 [13] CHRUSCIEL J J, LESNIAK E. Preparation of flexible, self-extinguishing silicone foams[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2011,119(3):1696-1703. doi: 10.1002/app.32852 [14] HANU L G, SIMON G P, MANSOURI J, et al. Development of polymer-ceramic composites for improved fire resistance[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology,2004,153(1):401-407. [15] CAMINO G, LOMAKIN S M, LAZZARI M. Polydimethylsiloxane thermal degradation Part 1. Kinetic aspects[J]. Polymer,2001,42(6):2395-2402. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00652-2 [16] CAMINO G, LOMAKIN S M, LAZZARI M. Thermal polydimethylsiloxane degradation. Part 2. The degradation mechanisms[J]. Polymer,2002,43(7):2011-2015. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(01)00785-6 [17] MANSOURI J, BURFORD R P, CHENG Y B. Formation of strong ceramified ash from silicone-based compositions[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2005,40(21):5741-5749. doi: 10.1007/s10853-005-1427-8 [18] 孟盼, 王雁冰, 魏冲, 等. 硅藻土/硅橡胶可陶瓷化复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(1):53-59. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160411.003MENG Pan, WANG Yanbing, WEI Chong, et al. Preparation and properties of ceramifiable diatomite/silicone rubber composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(1):53-59(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160411.003 [19] 刘良点, 秦岩宋, 九强, 等. 短切聚酰亚胺纤维增强可瓷化三元乙丙橡胶复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(12):2800-2809. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170310.003LIU Liangdian, QIN Yansong, JIU Qiang, et al. Preparation and properties of ceramifiable ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber composites reinforced with chopped polyimide fibers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(12):2800-2809(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170310.003 [20] LI Y M, DENG C, WANG Y Z. A novel high-temperature-resistant polymeric material for cables and insulated wires via the ceramization of mica-based ceramifiable EVA composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2016,132:116-122. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.07.007 [21] TANG K H, YU Y, XU G Q, et al. Preparation of a ceramifiable phenolic foam and its ceramization behavior[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(8): 1591. [22] 欧芸, 石敏先, 姚亚琳, 等. 可瓷化PDMS改性聚氨酯泡沫复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2020(4):96-100, 111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.04.015OU Yun, SHI Minxian, YAO Yalin, et al. Preparation and properties of ceramicizable PDMS modified polyurethane foam composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering,2020(4):96-100, 111(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.04.015 [23] SONG J Q, HUANG Z X, QIN Y, et al. Ceramifiable and mechanical properties of silicone rubber foam composite with frit and high silica glass fiber[J]. IOP Conference Series-Materials Science and Engineering,2018,423:012168. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/423/1/012168 [24] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 橡胶 燃烧性能的测定: GB/T 10707—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Rubber—Determination of the burning: GB/T 10707—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). [25] International Organization for Standardization. Reaction-to-fire tests—Heat release, smoke production and mass loss rate—Part 1: Heat release rate (cone calorimeter method) and somke production rate (dynamic measurement): ISO 5660-1[S]. Geneva: ISO, 2015. -





 下载:
下载: