Performance of the protective gear inspired by fish scale structure against armor-piercing incendiary bullets
-
摘要: 借鉴硬骨鱼鳞片的多级结构,采用软硬复合防护理念,本文提出了一种新型双层式柔性防护装具。该仿生防护装具的上层采用周期性叠加的复合鳞片构建鳞片层,下层采用多层超高分子量聚乙烯(UHMWPE)无纺布作为垫层。根据GJB 4300A—2012标准 III 级要求,对防护装具进行弹道测试和有限元仿真,验证了防护装具的抗穿甲燃烧弹性能和有限元模型的可靠性。结果表明:复合鳞片的陶瓷层厚度是影响防护装具抗侵彻性能的主要因素之一,在总厚度不变的情况下,复合鳞片的层厚比为2∶1时满足防护要求,倾斜复合鳞片对子弹的钝化作用及子弹的横向偏转,叠加鳞片的整体协同能量耗散及UHMWPE垫层的能量分散作用都是决定仿生装具防护能力的重要作用机制。Abstract: In this study, a novel double-layer flexible protective gear was proposed based on the multi-level structure of the bony fish scale and the concept of soft and hard composite protection. The upper layer of this protective gear is a scale-like layer which consists of periodically overlapping composite scales, the lower layer consists of multiple layers of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) sheets as the backing layer. In accordance with the Level III requirements of the standard GJB 4300A—2012, the protection performance of the protective gear has been tested and simulated with finite element models, and the results verified the good protection performance of the gear against the armor-piercing incendiary bullet, and also confirmed the reliability of the numerical simulations. The results indicate that the thickness of the ceramic layer of the composite scale is one of the key factors that affect the anti-penetration performance of the protective gear. When the total thickness is unchanged, the layer thickness ratio of the composite scale is 2∶1 to meet the protection requirements. Some key mechanisms take effect to determine the anti-penetration performance of the protective gear, including the blunting and lateral deflection of bullets by composite scales, the overall synergistic energy dissipation of the overlapping scales, and the energy dispersion of the UHMWPE backing layer.
-
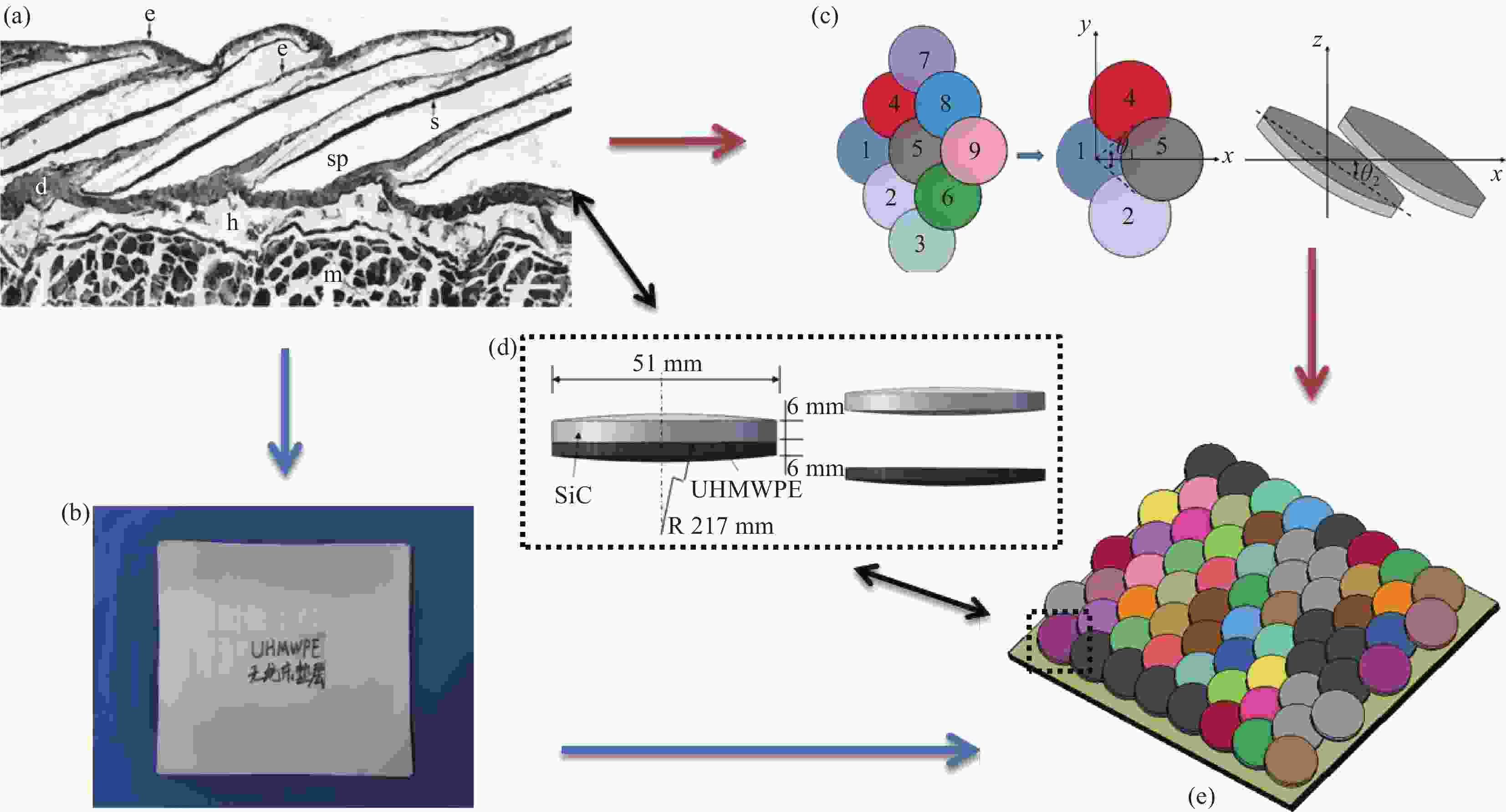
图 1 仿生防护装具设计示意图:(a) 真实鱼鳞片排列模式[15];(b) 超高分子量聚乙烯(UHMWPE)垫层;(c) 仿生鳞片排列;(d) 单个复合鳞片设计;(e) 仿生防护装具
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the design of bio-inspired protection device: (a) Real fish scale arrangement pattern[15]; (b) Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) backing layers; (c) Bionic scale arrangement; (d) Single composite scale design; (e) Bio-inspired protection devices
e—Epidermis; s—Scale; sp—Scale pouch; h—Hypoderm; d—Dermis; m—Muscle; θ1—Overlapping angle; θ2—Incline angle; R—Radius
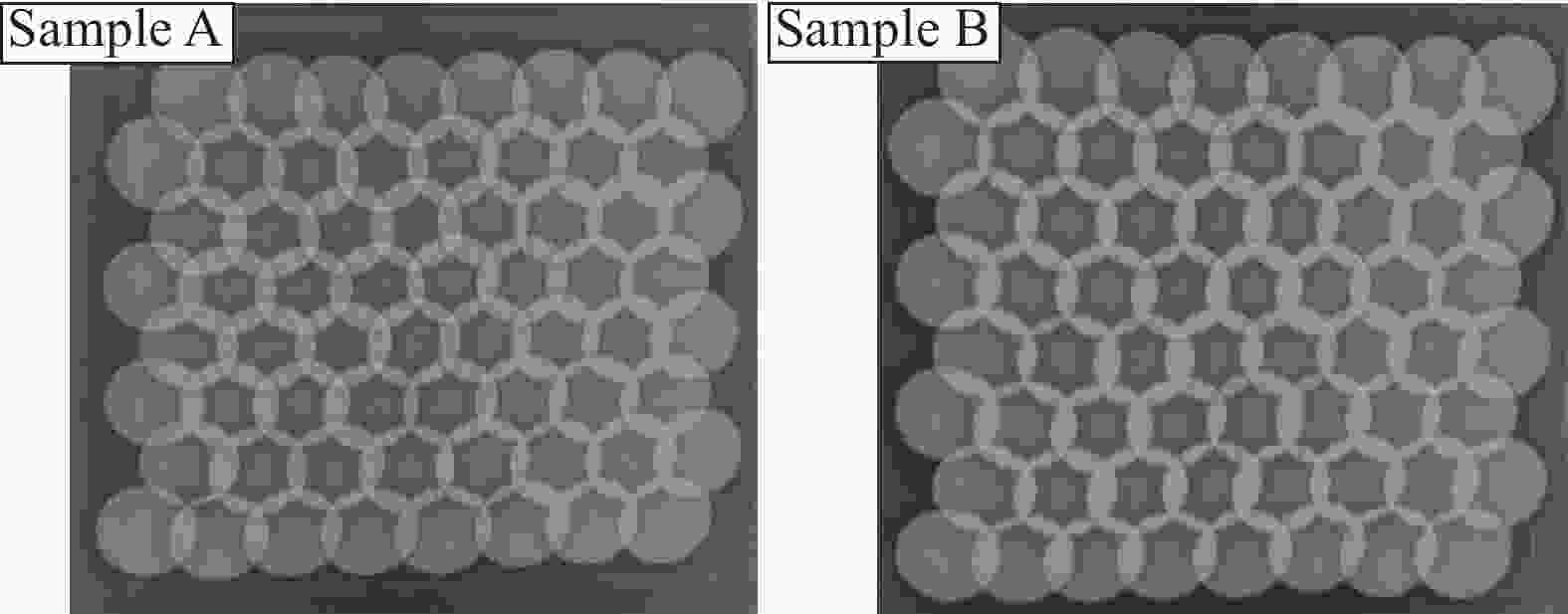
表 1 防护装具的仿生鳞片尺寸及垫层数量
Table 1. Bionic scale size and number of backing layers in protection gears
Sample t/mm t1/mm t2/mm Ratio of t1/t2 Number of backing layers Sample A 12 6 6 1∶1 50 Sample B 12 8 4 2∶1 50 Notes: t—Thickness of composite scale; t1—Thickness of SiC layer; t2—Thickness of UHMWPE layer. 表 2 穿甲燃烧弹的弹壳与弹芯材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of the shell and the core of the armor-piercing incendiary bullet
Material parameter ρ/(kg·m−3) E/GPa ν SIGY/GPa ETAN/GPa BETA FS Bullet jacket 8858 117 0.4 0.345 0.0 0.0 1.0 Bullet core 7850 207 0.33 0.355 0.0 0.2 3.0 Notes: ρ—Density; E—Young's modulus; ν—Poisson's ratio; SIGY—Yield stress; ETAN—Tangent modulus; BETA—Hardening parameter; FS—Failure strain. 表 3 两套防护装具弹道测试结果
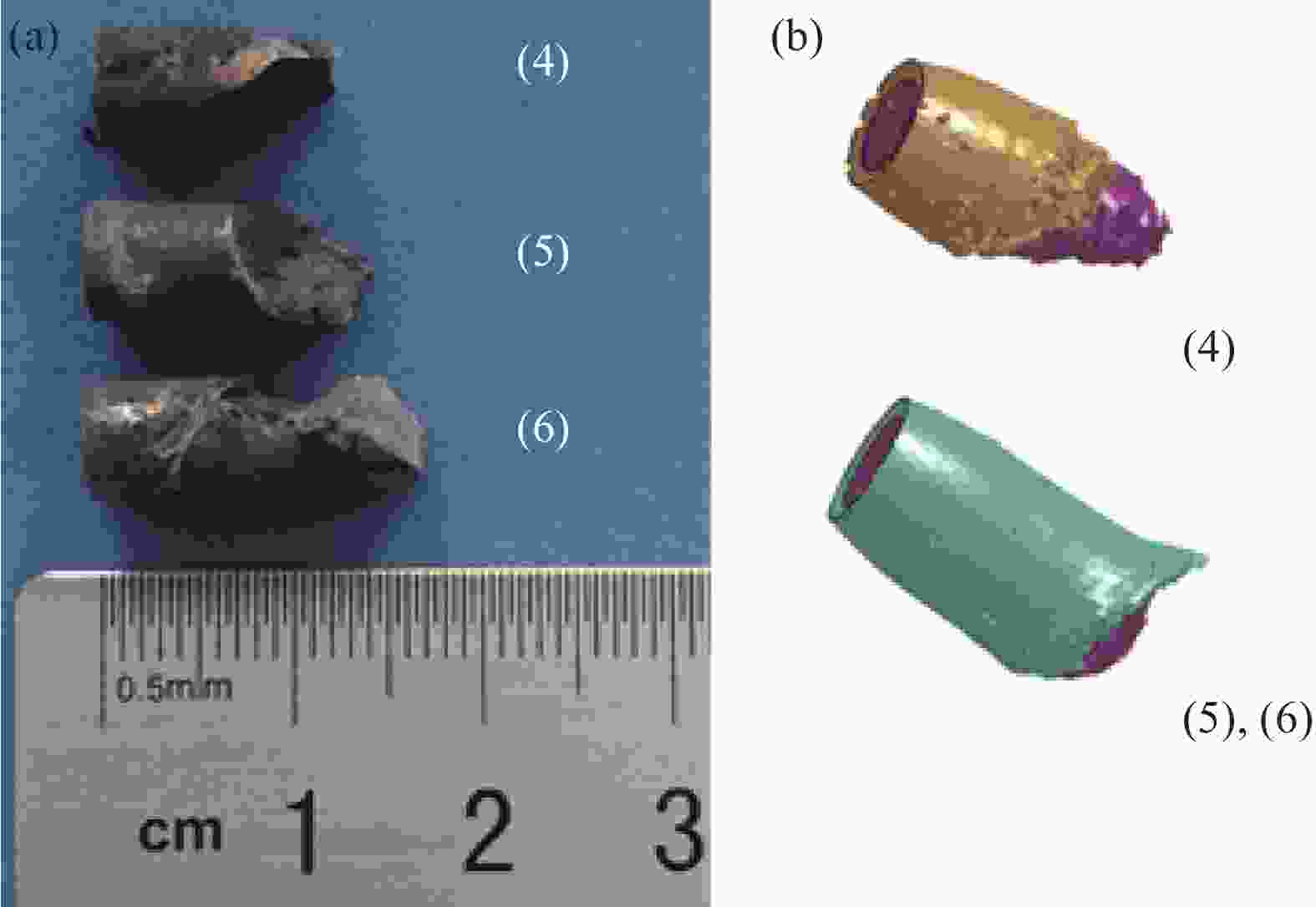
Table 3. Experimental result of ballistic tests of two protection gears
Sample
nameReference
pointBullet
velocity/
(m·s−1)Backface
signature/
mmNumber of
penetrated
backing
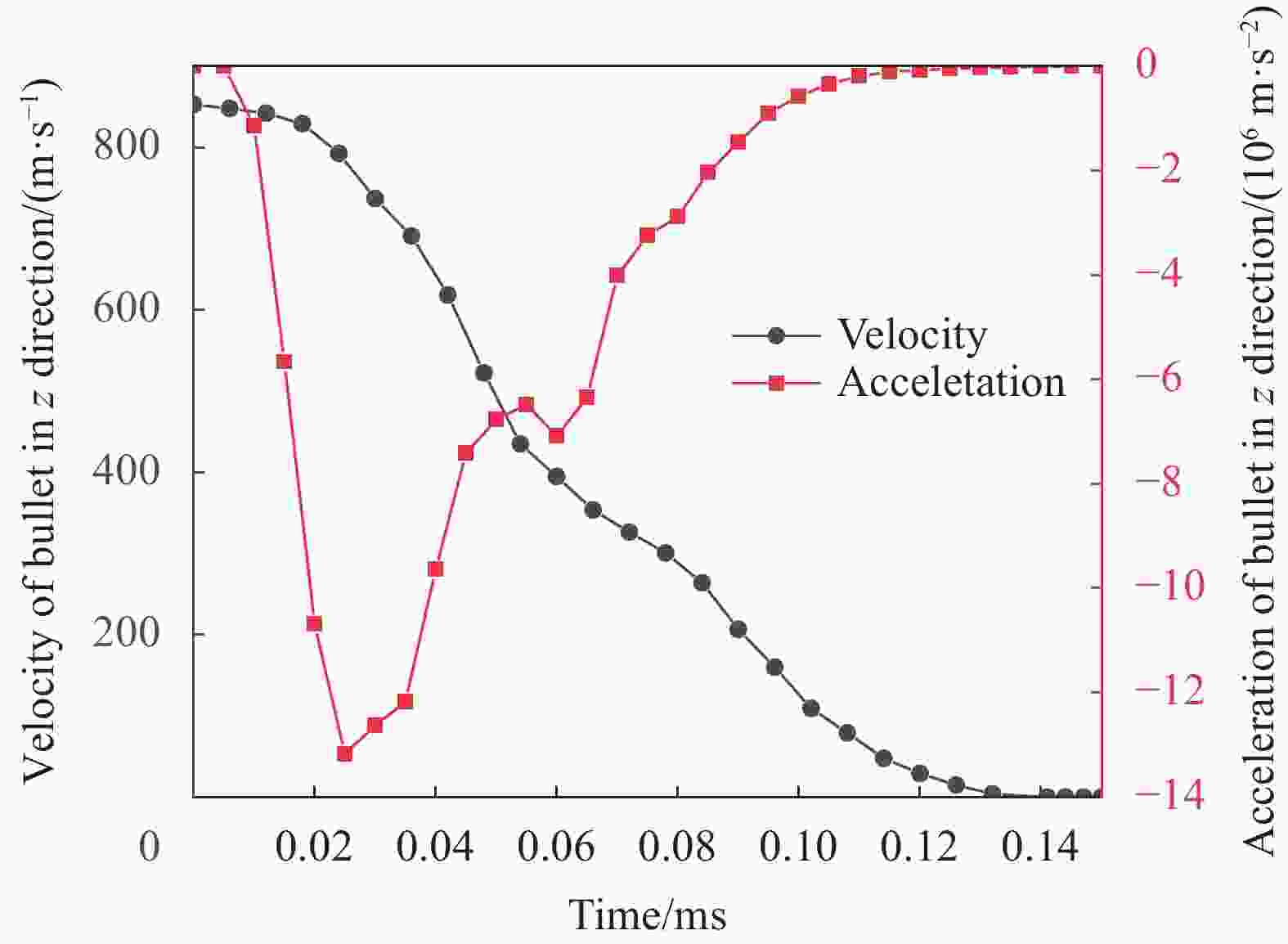
layersSample A (1) 843 — — (2) 840 — — (3) 840 — — Sample B (4) 846 20.8 5 (5) 840 23.4 6 (6) 849 26.6 9 表 4 样件B试验结果与数值模拟结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of experimental and numerical results of sample B
Parameters Reference
pointExperi-
mentsSimula-
tionsDiffer-
ence/%Remaining length
of bullet/mm(4) 12.8 13.4 4.5 (5) 14.4 15.5 7.1 (6) 16.3 15.5 5.2 Number of
penetrated
backing layers(4) 5 6 16.7 (5) 6 8 25.0 (6) 9 8 −12.5 Backface
signature/mm(4) 20.8 19.7 5.6 (5) 23.4 24.2 3.3 (6) 26.6 24.2 9.9 Notes: (4)—Located in the center of the target scale; (5), (6)—Located at the junction of two target scales. -
[1] ABTEW M A, BOUSSU F, BRUNIAUX P, et al. Ballistic impact mechanisms-A review on textiles and fibre-reinforced composites impact responses[J]. Composite Structures,2019,223:110966. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.110966 [2] WEI Z, XU X. FEM simulation on impact resistance of surface gradient and periodic layered bionic composites[J]. Composite Structures,2020,247:112428. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112428 [3] FELI S, ASGARI M R. Finite element simulation of ceramic/composite armor under ballistic impact[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2011,42(4):771-780. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.01.024 [4] CHEN J, HAO C, ZHANG J. Fabrication of 3D-SiC network reinforced aluminum–matrix composites by pressureless infiltration[J]. Materials Letters,2006,60(20):2489-2492. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.01.027 [5] JIANG H, REN Y, LIU Z, et al. Low-velocity impact resis-tance behaviors of bio-inspired helicoidal composite laminates with non-linear rotation angle based layups[J]. Composite Structures,2019,214:463-475. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.02.034 [6] LIU P, ZHU D, YAO Y, et al. Numerical simulation of ballistic impact behavior of bio-inspired scale-like protection system[J]. Materials & Design,2016,99:201-210. [7] MARTINI R, BARTHELAT F. Stability of hard plates on soft substrates and application to the design of bioinspired segmented armor[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,2016,92:195-209. doi: 10.1016/j.jmps.2016.04.009 [8] RUDKH S, BOYCE M C. Analysis of elasmoid fish imbricated layered scale-tissue systems and their bio-inspired analogues at finite strains and bending[J]. IMA Journal of Applied Mathematics,2014,79(5):830-847. doi: 10.1093/imamat/hxu005 [9] REZAEE JAVAN A, SEIFI H, LIN X, et al. Mechanical behaviour of composite structures made of topologically interlocking concrete bricks with soft interfaces[J]. Materials & Design,2020,186:108347. [10] 刘鹏, 汪俊文, 朱德举. 草鱼鳞片的多级结构及力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(3):657-665.LIU Peng, WANG Junwen, ZHU Deju. Hierarchical structure and mechenical properties of scales from grass carp[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(3):657-665(in Chinese). [11] DALAQ A S, BARTHELAT F. Strength and stability in architectured spine-like segmented structures[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2019,171:146-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2019.04.012 [12] CHANDLER M Q, ALLISON P G, RODRIGUEZ R I, et al. Finite element modeling of multilayered structures of fish scales[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2014,40:375-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.09.013 [13] 朱德举, 汤兴. 基于犰狳外壳仿生的SiC-超高分子量聚乙烯柔性防护板的试验测试和有限元模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(10):2561-2571.ZHU Deju, TANG Xing. Experimental testing and finite element simulation of SiC-ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene flexible protective plate inspired by armadillo shell[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(10):2561-2571(in Chinese). [14] 朱德举, 赵波. 仿生柔性防护装具的设计及防弹性能测试[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1411-1417.ZHU Deju, ZHAO Bo. Design and ballistic performance testing of bio-inspired flexible protection devices[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1411-1417(in Chinese). [15] ZHANG C, RAWAT P, LIU P, et al. A new design and performance optimization of bio-inspired flexible protective equipment[J]. Bioinspir Biomim. 2020, 15(6): 066003. [16] 中国人民解放军总后勤部. 军用防弹衣安全技术性能要求: GJB 4300A—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012.The General Logistics Department of PLA. Requirements of safety technical performance for military body armor: GJB 4300A—2012[S]. Beijing: Standars Press of China, 2012(in Chinese). [17] 朱德举, 彭恋. SiC-超高分子量聚乙烯仿生柔性叠层结构防弹性能关键影响因素的仿真与试验[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2928-2940.ZHU Deju, PENG Lian. Simulation and experiment of key influencing factors on the ballistic performance of SiC-ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene biomimetic flexible laminated structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(11):2928-2940(in Chinese). [18] ZHANG T G, SATAPATHY S S, VARGAS-GONZALEZ L R, et al. Ballistic impact response of ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE)[J]. Composite Structures,2015,133:191-201. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.06.081 [19] PARK E H, LEE S H. Scale growth and squamation chronology for the laboratory-reared hermaphroditic fish rivulus marmoratus (cyprinodontidae)[J]. Ichthyological Research, 34(4): 476-482. [20] FLORES-JOHNSON E A, SHEN L, GUIAMATSIA I, et al. Numerical investigation of the impact behaviour of bioinspired nacre-like aluminium composite plates[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2014,96:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.03.001 [21] DHANDAPANI K. Experimental investigation and development of a constitutive model for ultra high molecular weight polyethylene materials[D]. Phoenix: Arizona State University, 2009. [22] KRISHNAN K, SOCKALINGAM S, BANSAL S, et al. Numerical simulation of ceramic composite armor subjected to ballistic impact[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2010,41(8):583-593. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2010.10.001 [23] 崔凤单, 马天, 李伟萍, 等. SiC和B4C防弹插板抗多发弹打击损伤特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(9):967-972. doi: 10.15541/jim20160667CUI Fengdan, MA Tian, LI Weiping, et al. Damage characteristics of SiC and B4C ballistic insert plates subjected to multi-hit[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2017,32(9):967-972(in Chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20160667 -





 下载:
下载: