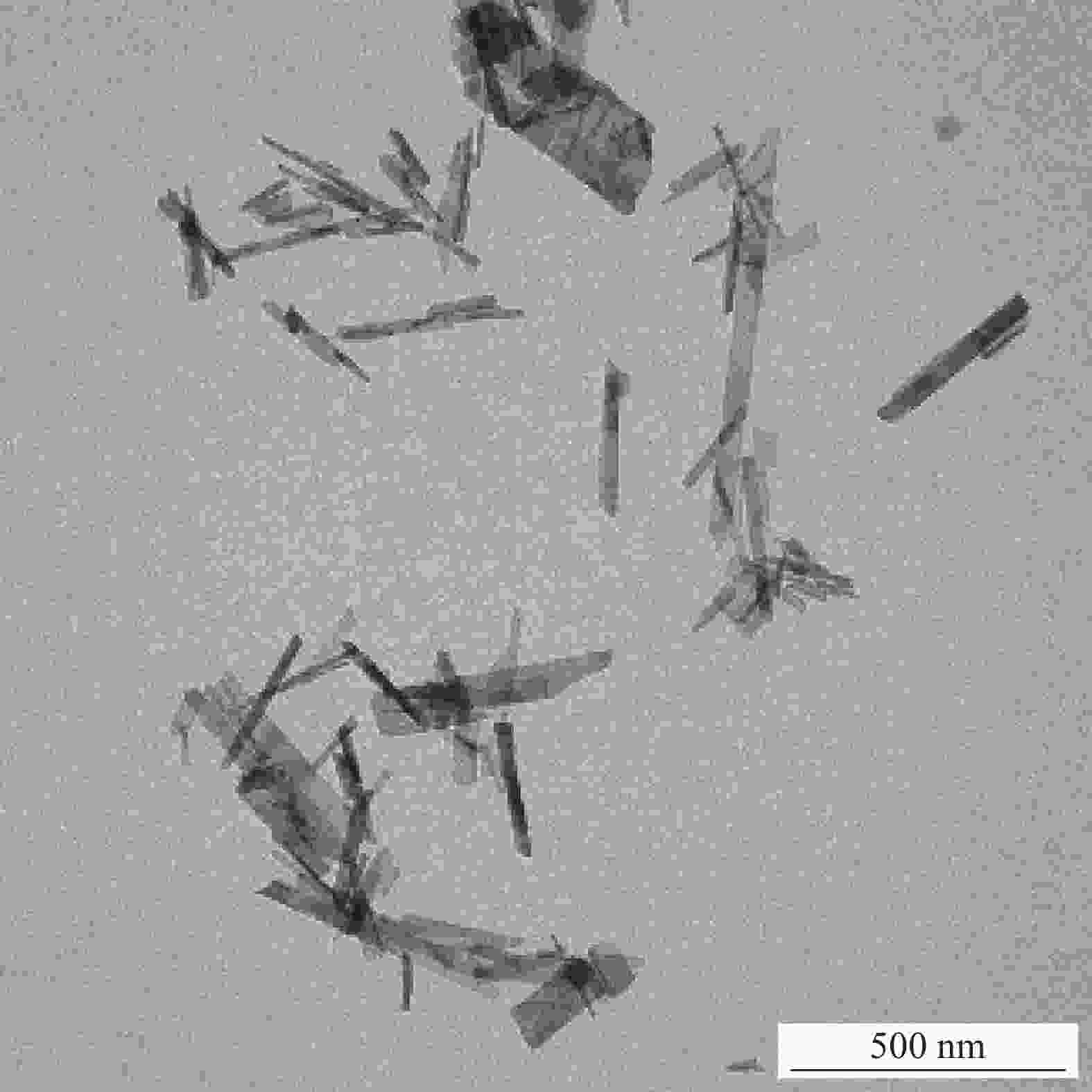
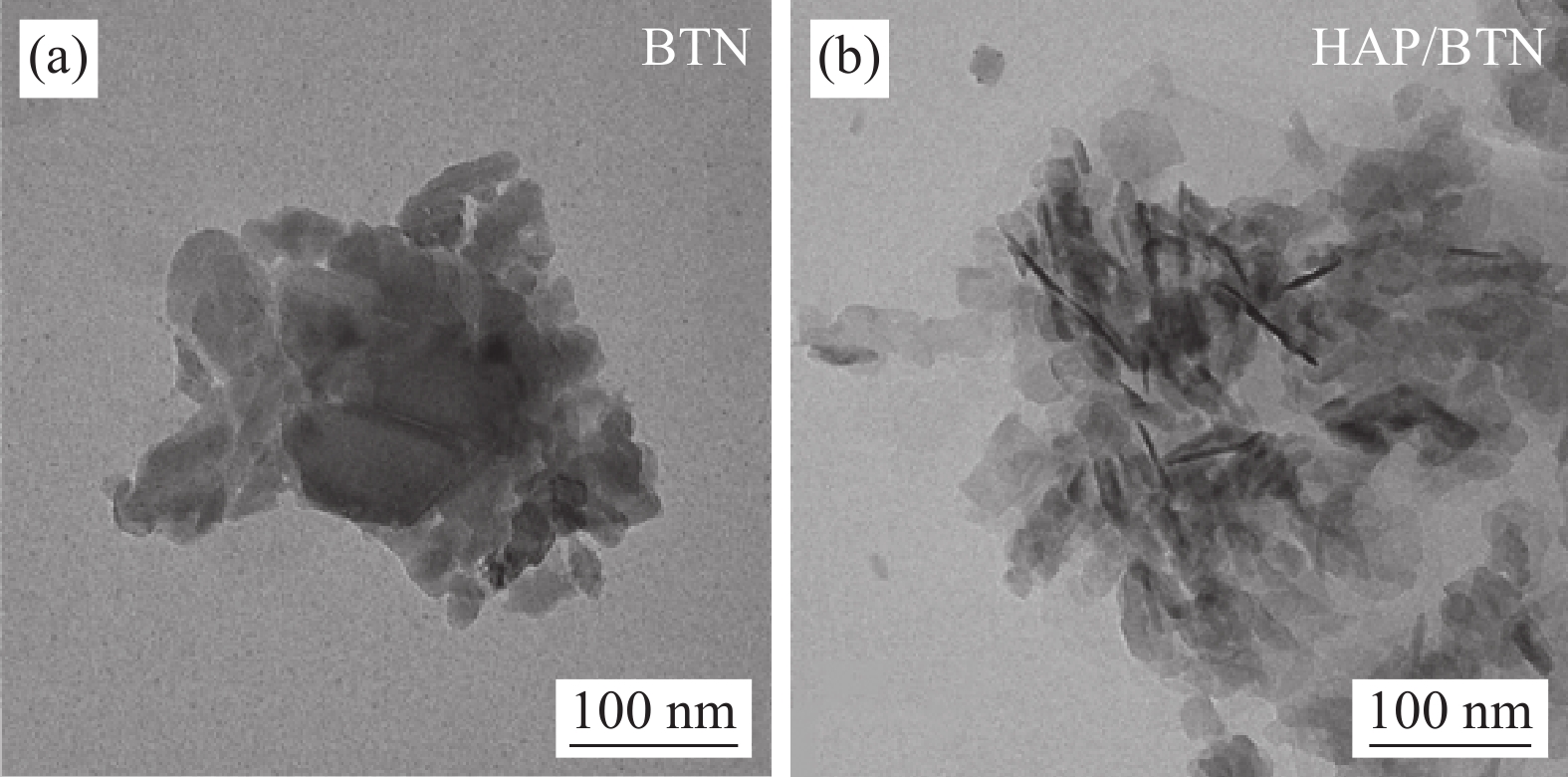
Study on adsorption effect and mechanism of uranium by hydroxyapatite modified bentonite
-
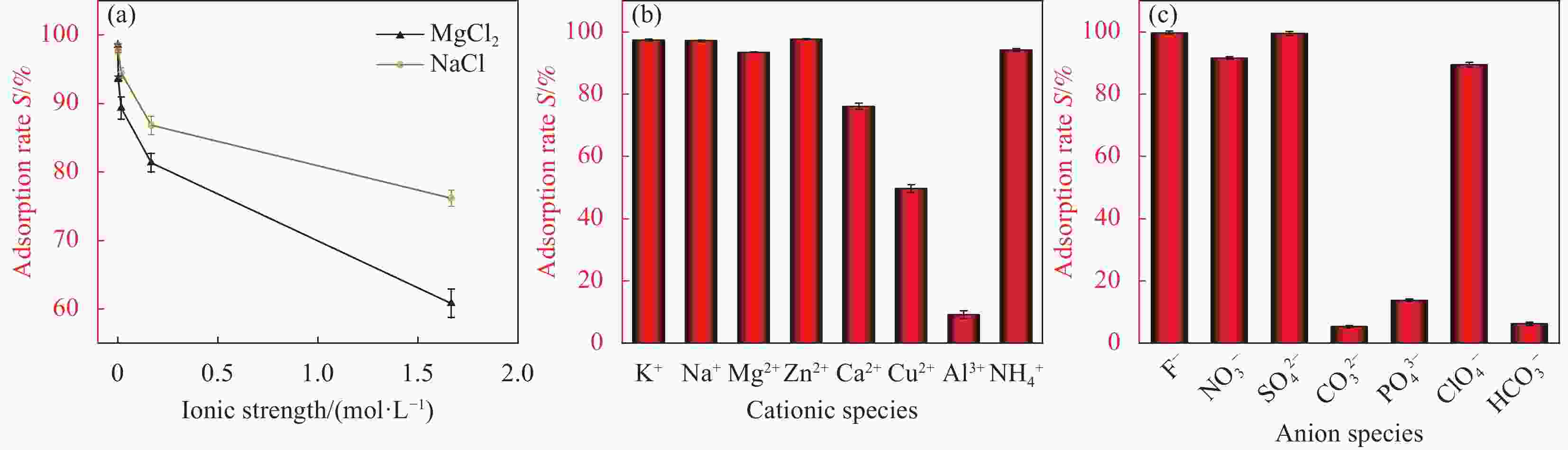
摘要: 伴随我国核能的开发与高效利用,铀已成为我国地表水、地下水和土壤的常见污染物之一,从含铀废水中去除U(VI)已成为亟需解决的环境问题。本工作以膨润土(BTN)、磷酸氢二钠、硝酸钙为原料,采用简单易行的一步水热法成功制备出羟基磷灰石(HAP)改性膨润土复合材料(HAP/BTN)。考察了HAP/BTN对水溶液中铀的吸附性能,利用单因素试验和正交试验探讨了pH、转速、温度、投加量、时间对吸附性能的影响。试验结果表明,在pH=6.0、转速=100 r·min−1、室温(298.15 K)、HAP/BTN投加量1 g·L−1、吸附时间t=30 min时,该吸附材料对10 mg·L−1含铀废水的去除率可达98%,最大吸附量为186.45 mg·g−1。吸附过程更符合Langmuir模型和准二级动力学,热力学参数表明HAP/BTN对铀的吸附是自发吸热的过程,结合XPS及XRD的结果证实了HAP/BTN吸附铀主要归因于络合反应、化学吸附、静电吸附和离子交换作用。Abstract: With the development and efficient utilization of nuclear energy in China, uranium has become one of the common pollutants in surface water, groundwater and soil. The removal of U(VI) from uranium-containing wastewater has become an urgent environmental problem to be solved. Hydroxyapatite modified bentonite composite hydroxyapatite modified bentonite (HAP/BTN) was successfully prepared by a simple one-step hydrothermal method using bentonite, disodium hydrogen phosphate and calcium nitrate as raw materials. The adsorption performance of HAP/BTN on uranium in wastewater was investigated. The effects of pH, rotation speed, temperature, dosage and time on the adsorption performance were discussed by orthogonal test. The results showed that under the conditions of pH=6.0, rotation speed=100 r·min−1, room temperature (298.15 K), HAP/BTN dosage of 1 g·L−1 and adsorption time t=30 min, the removal rate of 10 mg·L−1 uranium-containing wastewater could reach 98%, and the maximum adsorption capacity was 186.45 mg·g−1. The adsorption process was more in line with the Langmuir model and pseudo-second-order kinetics. Thermodynamic parameters show that the adsorption of uranium on HAP/BTN was a spontaneous endothermic process, combined with XPS and XRD results, confirmed that the adsorption of uranium by HAP/BTN was mainly attributed to complexation reaction, chemical adsorption, electrostatic and ion exchange.
-
Key words:
- bentonite /
- hydroxyapatite /
- uranium wastewater /
- adsorption /
- U(VI)
-
图 13 HAP/BTN吸附铀的动力学研究:准一级动力学 (a)、准二级动力学 (b)、Elovich动力学 (c)、Morrist颗粒内扩散模型 (d)
Figure 13. Kinetic study of uranium adsorption on HAP/BTN: Quasi-first-order kinetics (a), Quasi-second-order kinetics (b), Elovich kinetics (c), Morrist intraparticle diffusion model (d)
qt—Adsorption capacity at time t; qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity
图 15 HAP/BTN循环试验 (a)、BTN或HAP/BTN吸附铀前/吸附后的Zeta电位值 (b)、吸附时间对HAP/BTN吸附铀稳定性的影响 (c)、不同水样稀释对HAP/BTN吸附铀的影响(pH=6.0、R=100 r·min−1、T=298.15 K、m=1 g·L−1、V=50 mL、t=30 min) (d)
Figure 15. HAP/BTN cycle test (a), Zeta potential values of BTN or HAP/BTN before and after adsorption (b), effect of time on the stability of HAP/BTN (c), effect of different water samples on H (pH=6.0, R=100 r·min−1, T=298.15 K, m=1 g·L−1, V=50 mL, t=30 min) (d)
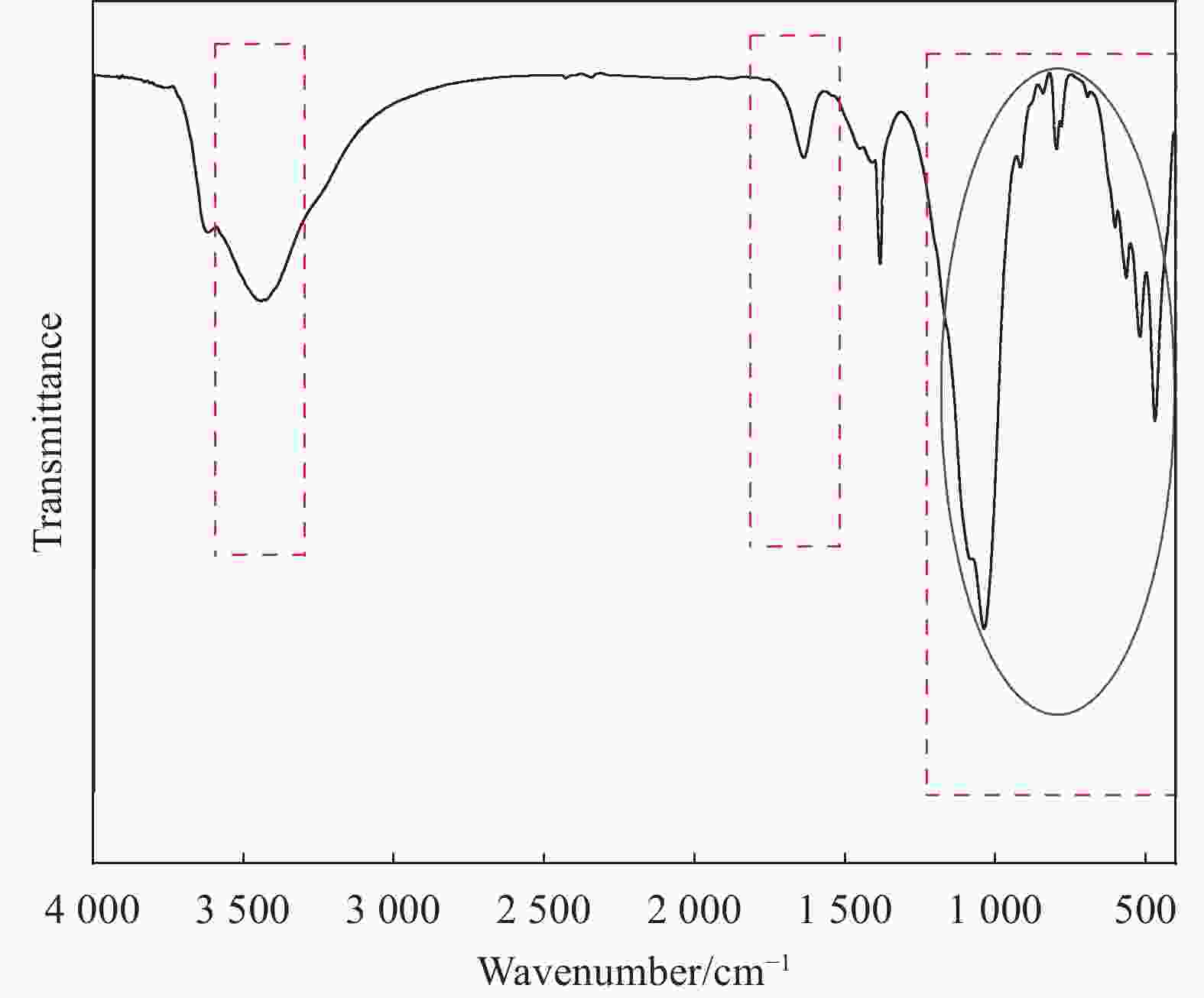
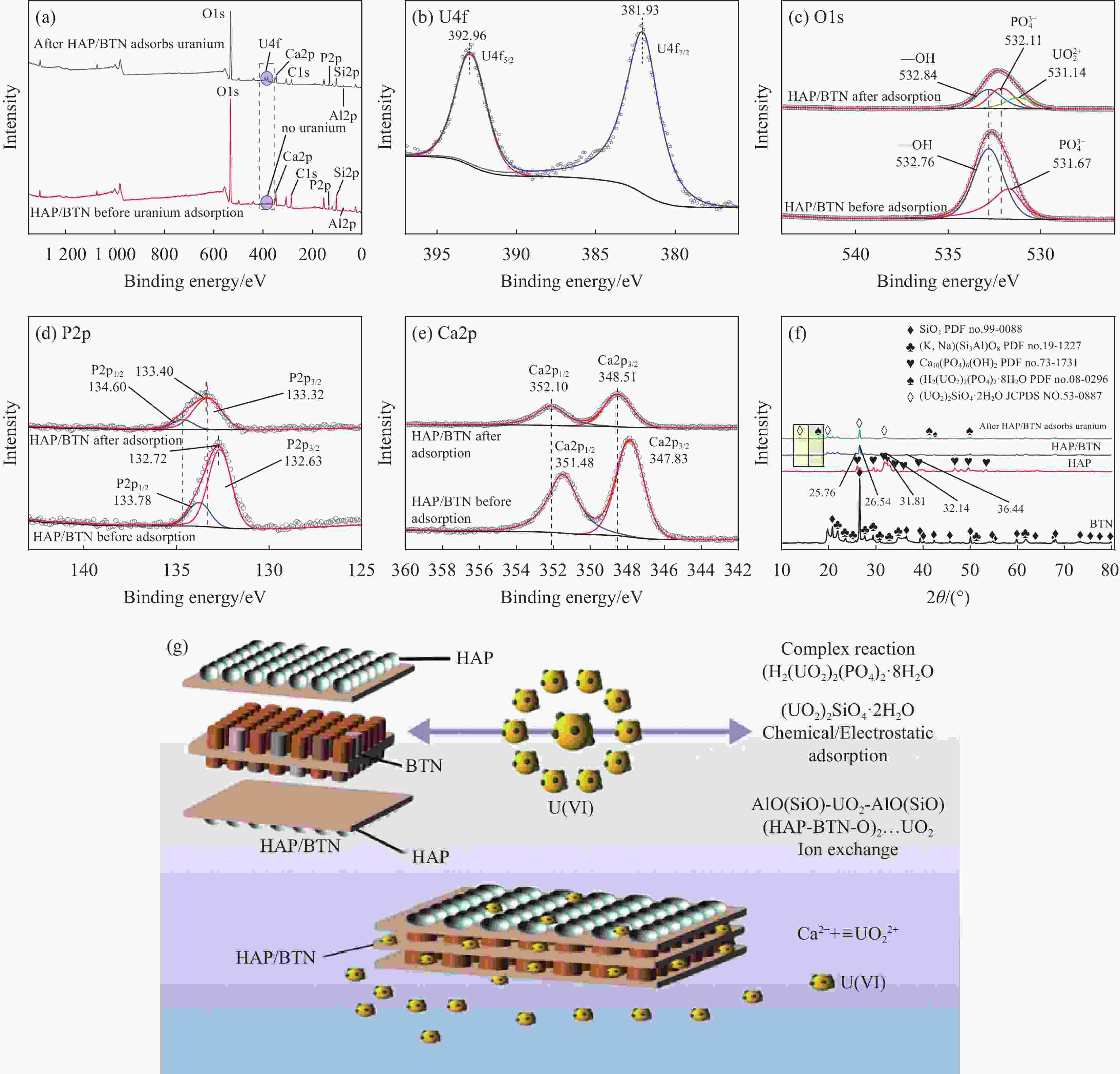
图 17 ((a), (c)~(e)) HAP/BTN吸附铀前后的XPS分析;(b)铀的精细谱;(f) BTN、HAP、HAP/BTN及HAP/BTN吸附铀后的XRD图谱;(g) HAP/BTN吸附铀的机制
Figure 17. ((a), (c)-(e)) XPS analysis before and after adsorption of uranium; (b) Fine spectrum of uranium; (f) XRD patterns of BTN, HAP, HAP/BTN and after HAP/BTN adsorbs uranium; (g) Adsorption mechanism of HAP/BNT
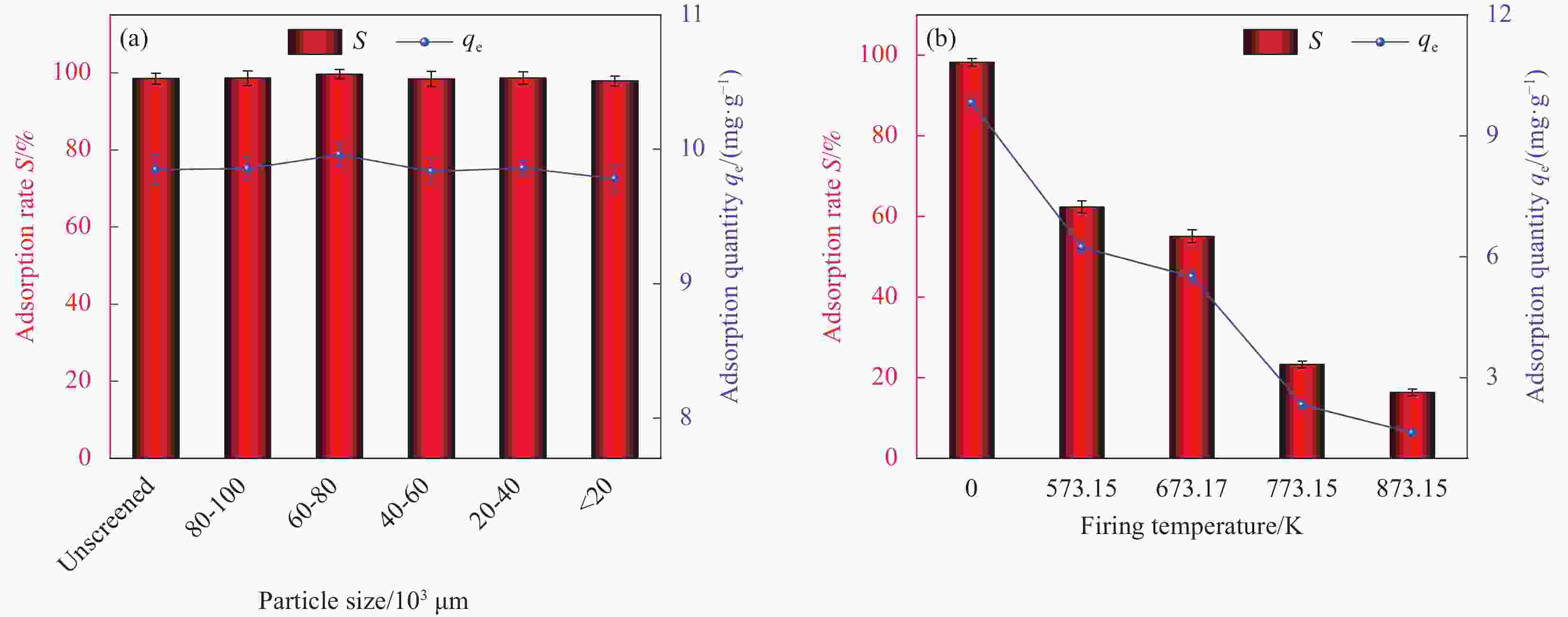
表 1 HAP/BTN吸附铀的正交试验因素及水平设计
Table 1. Orthogonal test factors and level design of HAP/BTN adsorption of uranium
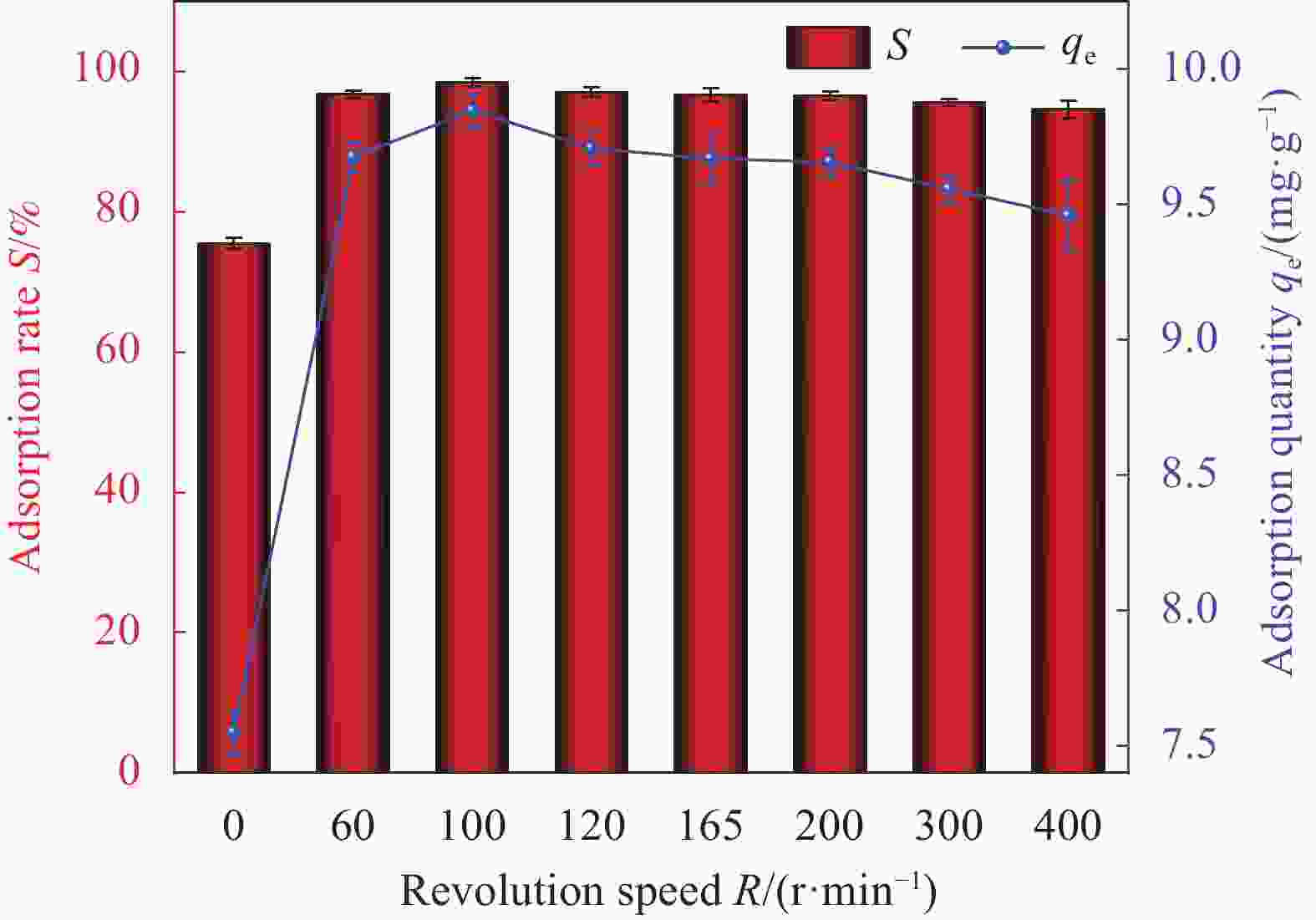
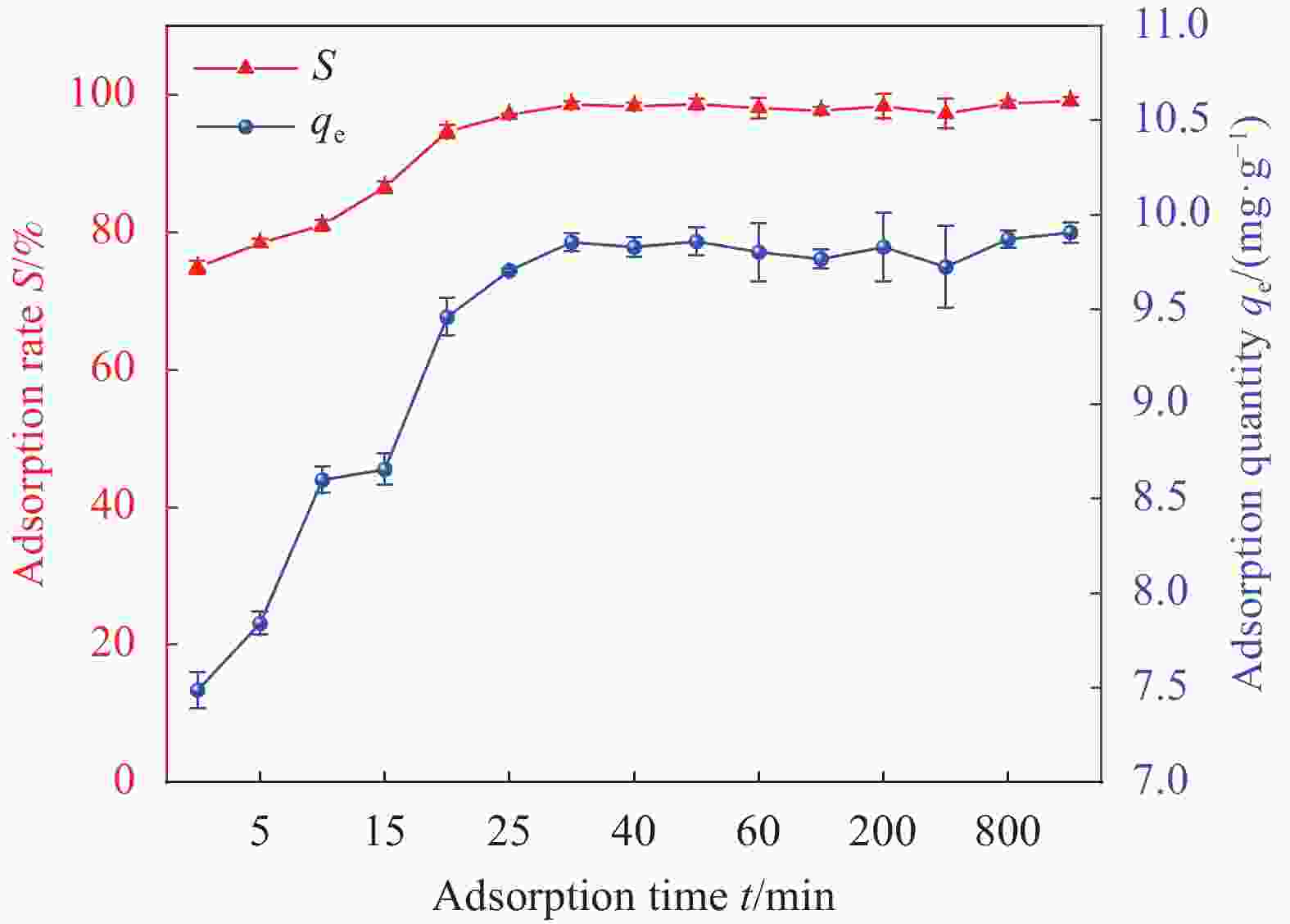
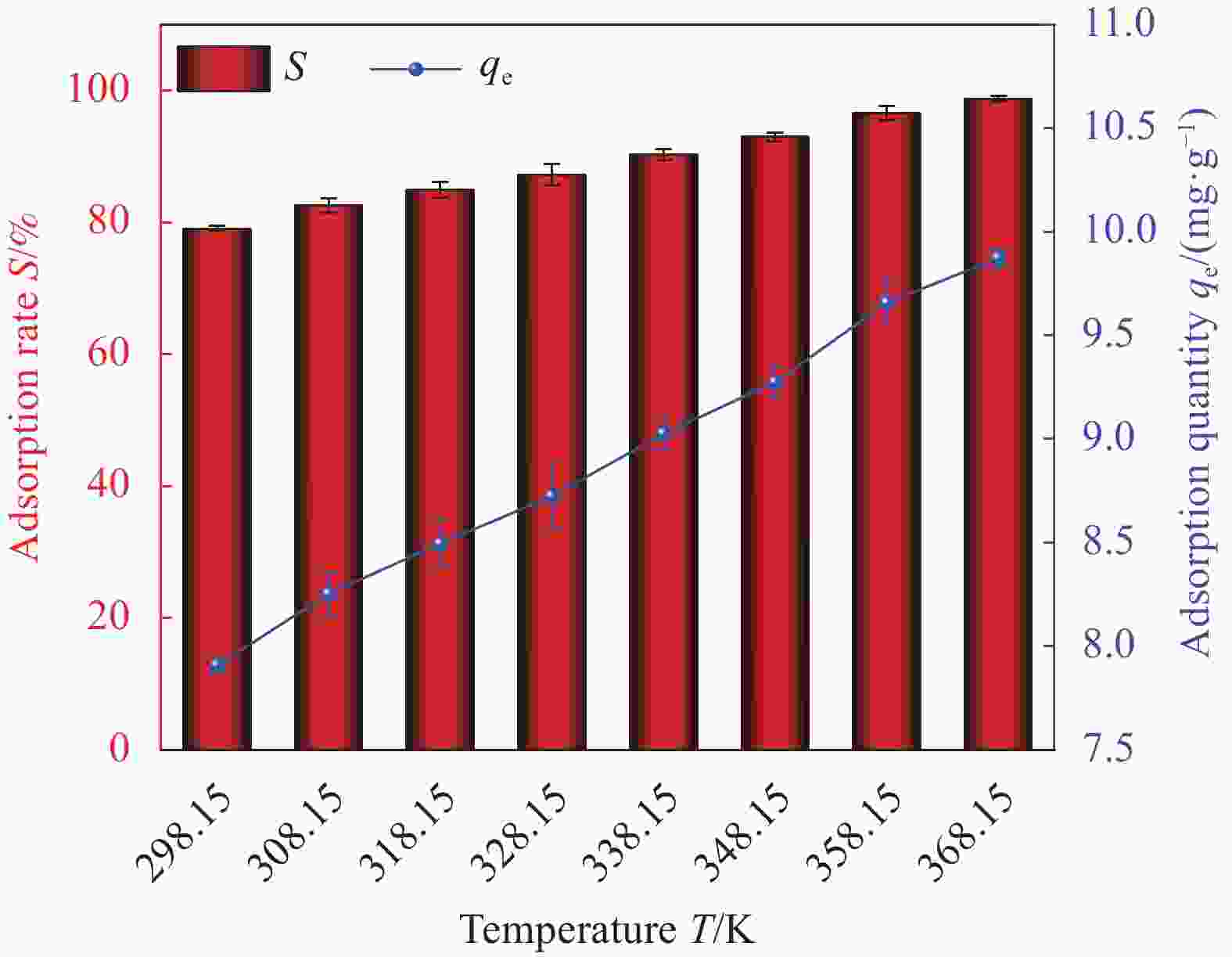
Factor A B C D E 1 2 0 298.15 0.01 1 2 6 60 308.15 0.02 10 3 11 100 318.15 0.05 30 Notes: A—pH of aqueous solution; B—Revolution speed (r·min−1); C—Temperature (K); D—Addition amount (g); E—Adsorption time (min). 表 2 HAP/BTN吸附铀的正交试验设计方案和结果
Table 2. Orthogonal experimental design and results of HAP/BTN adsorption of uranium
Factor A B C D E S/% 1 2 0 298.15 0.01 1 18.55 2 2 60 308.15 0.02 10 22.32 3 2 100 318.15 0.05 30 24.26 4 6 0 298.15 0.02 10 46.30 5 6 60 308.15 0.05 30 92.05 6 6 100 318.15 0.01 1 71.51 7 11 0 308.15 0.01 30 50.05 8 11 60 318.15 0.02 1 40.76 9 11 100 298.15 0.05 10 70.63 10 2 0 318.15 0.05 10 23.56 11 2 60 298.15 0.01 30 26.78 12 2 100 308.15 0.02 1 20.13 13 6 0 308.15 0.05 1 44.25 14 6 60 318.15 0.01 10 86.12 15 6 100 298.15 0.02 30 99.48 16 11 0 318.15 0.02 30 53.26 17 11 60 298.15 0.05 1 42.14 18 11 100 308.15 0.01 10 74.42 K1 135.6 235.97 303.88 327.43 237.34 — K2 439.71 310.17 303.22 282.25 323.35 — K3 331.26 360.43 299.47 296.89 345.88 — k1 45.20 78.66 101.29 109.14 79.11 — k2 146.57 103.39 101.07 94.08 107.78 — k3 110.42 120.14 99.823 98.96 115.29 — R 101.37 41.48 1.47 15.06 36.18 — Primary and secondary order A>B>E>D>C Notes: Ki—The ith (i=1,2,3) level of the factor is the test index.; ki—Average value of Ki; R—Range. 表 4 HAP/BTN吸附铀的动力学模型参数
Table 4. HAP/BTN kinetic fitting data
Model types Equation qe/
(mg·g−1)R2 Pseudo first-order model ln(qe−qt)=−0.10035t+1.26104 3.53 0.911 Pseudo second-order model t/q=0.09797t+0.14599 9.98 0.997 Elovich model qt=0.87196 lnt+6.80159 — 0.981 Morrist intraparticle diffusion model qt=0.67023t1/2+6.52163 — 0.930 qt=0.62663t1/2+6.50141 — 0.961 qt=0.299508t1/2+7.78542 — 0.956 表 3 HAP/BTN吸附铀的吸附等温线参数
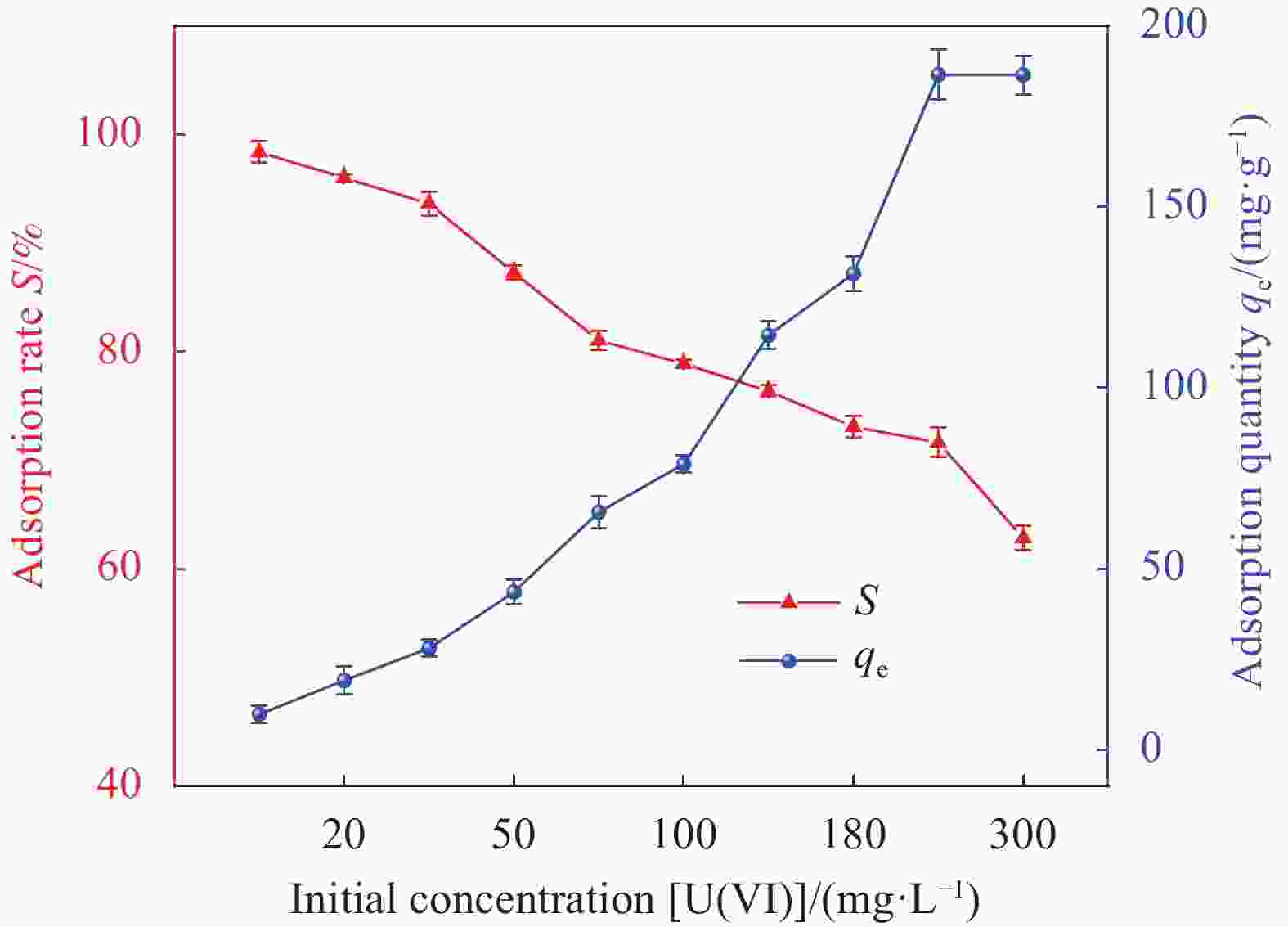
Table 3. Adsorption isotherm parameters of HAP/BTN adsorbing uranium
T Langmuir Freundlich qm/
(mg·g−1)Kc/
(L·mg−1)R2 n−1 Kf
/((mg·g−1)·(mg·L−1)−1/n)R2 273.15 K 186.45 0.04215 0.99992 0.57112 14.29826 0.91888 Notes: qm—Saturated adsorption capacity of monolayer adsorption; Kc—Constant related to adsorption energy; Kf —Constant related to the adsorption capacity; n−1—Measure of the adsorption strength; R2—Correlation coefficient. 表 5 HAP/BTN对铀(VI)的吸附热力学具体参数
Table 5. Thermodynamic parameters of uranium (VI) adsorption on HAP/BTN
T/K ΔHθ/
(KJ·mol−1)ΔSθ/
(J·mol−1·K−1)ΔGθ/
(KJ·mol−1)298.15 45.27 157.58 −1.71 308.15 −3.29 318.15 −4.86 328.15 −6.44 338.15 −8.01 348.15 −9.59 358.15 −11.16 368.15 −12.76 Notes: ΔHθ—Heat of the adsorption; ΔSθ—Standard entropy change; ΔGθ—Gibbs free energy of adsorption. -
[1] 荣丽杉, 夏麟, 周书葵, 等. UiO-66/壳聚糖的制备及其对U(VI)的吸附机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4879-4888. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211025.002RONG Lishan, XIA Lin, ZHOU Shukui, et al. Preparation of UiO-66/chitosan and its adsorption mechanism of U(VI)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4879-4888(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211025.002 [2] SALEH T A, TUZEN M, SARI A. Polyethylenimine modified activated carbon as novel magnetic adsorbent for the removal of uranium from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2017,117:218-227. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2016.10.030 [3] BILAL M, IHSANULLAH I, YOUNAS M, et al. Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: A critical review[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2021,278:119510. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119510 [4] LIU J, SHI S L, LI C, et al. U(VI) adsorption by one-step hydrothermally synthesized cetyltrimethylammonium bromide modified hydroxyapatite-bentonite composites from phosphate-carbonate coexisted solution[J]. Applied Clay Science,2021,203:106027. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2021.106027 [5] 马磊, 黄毅, 邓浩, 等. 氟磷灰石对酸性水溶液中铀(VI)的去除研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4):395-405. doi: 10.15541/jim20210255MA Lei, HUANG Yi, DENG Hao, et al. Removal of uranium(VI) from acidic aqueous solution by fluorapatite[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2022,37(4):395-405(in Chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20210255 [6] 张益硕, 周仲魁, 杨顺景, 等. 重金属污染土壤修复原理与技术[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2022(10):124-134.ZHANG Yishuo, ZHOU Zhongkui, YANG Shunjing, et al. Principles and technologies for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy),2022(10):124-134(in Chinese). [7] ORTABOY S, ACAR E T, ATUN G, et al. Performance of acrylic monomer based terpolymer/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogels for U(VI) removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design,2013,91(4):670-680. doi: 10.1016/j.cherd.2012.12.007 [8] 于静, 王建龙. 无机吸附材料处理放射性废水中铀的研究进展[J]. 核化学与放射化学, 2018, 40(2):81-88. doi: 10.7538/hhx.2018.40.02.0081YU Jing, WANG Jianlong. Research advances in inorganic adsorption materials processing for uranium from radioactive wastewater[J]. Journal of Nuclear and Radioche-mistry,2018,40(2):81-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.7538/hhx.2018.40.02.0081 [9] 熊小红, 林周梁, 王魏, 等. 铁钛柱撑膨润土吸附水中U(Ⅵ)的性能研究[J]. 铀矿冶, 2018, 37(4): 296-303.XIONG Xiaohong, LIN Zhouliang, WANG Wei, et al. Charateristics study on removal of U(Ⅵ) from aqueous solution by iron and titanium pillared bentonite adsorption[J]. Uranium Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 37(4): 296-303(in Chinese). [10] CHEN X, LI P, ZENG X, et al. Efficient adsorption of methylene blue by xanthan gum derivative modified hydroxyapatite[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,151:1040-1048. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.145 [11] 刘国, 徐丽莎, 李知可, 等. 羟基磷灰石/膨润土复合材料对水中Cd2+吸附研究[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(10):1414-1425.LIU Guo, XU Lisha, LI Zhike, et al. Adsorption of cadmium on hydroxyapatite/bentonite composites in aqueous solution[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2018,46(10):1414-1425(in Chinese). [12] 王丝雨, 周仲魁, 张益硕, 等. 十二烷基三甲基溴化铵膨润土处理低浓度U(Ⅵ)废水试验研究[J]. 中国有色冶金, 2022, 51(5):128-136. doi: 10.19612/j.cnki.cn11-5066/tf.2022.05.018WANG Siyu, ZHOU Zhongkui, ZHANG Yishuo, et al. Removal of low concentration U(VI) in wastewater by dodecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide-modified bentonite[J]. China Nonferrous Metallurgy,2022,51(5):128-136(in Chinese). doi: 10.19612/j.cnki.cn11-5066/tf.2022.05.018 [13] 张益硕, 周仲魁, 王丝雨, 等. STAC改性有机膨润土去除水体中U(Ⅵ)试验[J]. 有色金属(冶炼部分), 2022(1):127-132.ZHANG Yishuo, ZHOU Zhongkui, WANG Siyu, et al. Study on removal of U(Ⅵ) from water bodies by STAC modified bentonite[J]. Nonferrous Metals (Extractive Metallurgy),2022(1):127-132(in Chinese). [14] 张益硕, 周仲魁, 杨顺景, 等. 用CTAB改性膨润土从低浓度废水中吸附去除U(Ⅵ)[J]. 湿法冶金, 2022, 41(2):145-149. doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.2022.02.011ZHANG Yishuo, ZHOU Zhongkui, YANG Shunjing, et al. Adsorption of low concentration U(Ⅵ) in wastewater with CTAB modified bentonite[J]. Hydrometallurgy of China,2022,41(2):145-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.13355/j.cnki.sfyj.2022.02.011 [15] 张益硕, 周仲魁, 杨顺景, 等. KH550改性膨润土对低浓度U(Ⅵ)的吸附[J]. 有色金属工程, 2022, 12(9):154-164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.09.21ZHANG Yishuo, ZHOU Zhongkui, YANG Shunjing, et al. Adsorption performance of KH550 modified bentoniteat low concentrations of U(Ⅵ)[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engi-neering,2022,12(9):154-164(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1744.2022.09.21 [16] LEI Y, LI K, LIAO J, et al. Design of 3D alumina-doped magnesium oxide aerogels with a high efficiency removal of uranium (Ⅵ) from wastewater[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers,2021,8(10):2561-2574. doi: 10.1039/D1QI00259G [17] LIAO D X, ZHENG W, LI X M, et al. Removal of lead(II) from aqueous solutions using carbonate hydroxyapatite extracted from eggshell waste[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,177(1-3):126-130. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.12.005 [18] KOŁODYŃSKA D, WNĘTRZAK R, LEAHY J J, et al. Kinetic and adsorptive characterization of biochar in metal ions removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2012,197:295-305. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.025 [19] MEI D C, LIU L J, YAN B. Adsorption of uranium (VI) by metal-organic frameworks and covalent-organic frameworks from water[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2023,475:214917. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2022.214917 [20] 李鑫璐, 赵建海, 王康, 等. 氢氧化镁改性活性炭对Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附[J]. 精细化工, 2020, 37(1): 130-134, 146.LI Xinlu, ZHAO Jianhai, WANG Kang, et al. Magnesium hydroxide modified activated carbon for the adsorption of copper (Ⅱ) ions[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2020, 37 (1): 130-134, 146(in Chinese). [21] LIU H J, FU T Y, MAO Y B. Metal-organic framework-based materials for adsorption and detection of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution[J]. ACS Omega,2022,7(17):14430-14456. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c00597 [22] ZHONG Z P, LI J F, MA Y Y, et al. The adsorption mechanism of heavy metals from coal combustion by modified kaolin: Experimental and theoretical studies[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,418:126256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126256 [23] HUANG R, WANG B, YANG B. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous solution onto HACC-bentonite[J]. Desalination: The International Journal on the Science and Technology of Desalting and Water Purification,2011,280(1/3):297-304. [24] 何豪, 朱宗强, 刘杰, 等. 镁-钙羟基磷灰石吸附剂对水中Pb2+的去除[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(9):4081-4090. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901082HE Hao, ZHU Zongqiang, LIU Jie, et al. Removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution by magnesium-calcium hydroxyapatite adsorbent[J]. Environmental Science,2019,40(9):4081-4090(in Chinese). doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.201901082 [25] XIONG T, JIA L, LI Q, et al. Efficient removal of uranium by hydroxyapatite modified kaolin aerogel[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2022,299:121776. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121776 [26] TAN W T, ZHOU H, TANG S F, et al. Enhancing Cd(II) adsorption on rice straw biochar by modification of iron and manganese oxides[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022,300:118899. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118899 [27] LANGMUIR I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1918, 40(9): 1361-1403. [28] WU L, YANG X, CHEN T, et al. Three-dimensional C3 N5/RGO aerogels with enhanced visible-light response and electron-hole separation efficiencyfor photocatalytic uranium reduction[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,427:131773. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131773 [29] CHEN X D, LI W T, ZHANG G X, et al. Highly stable and activated cerium-based MOFs superstructures for ultrahigh selective uranium (VI) capture from simulated seawater[J]. Materials Today Chemistry,2022,23:100705. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2021.100705 [30] NKOH J N, HONG Z, LU H, et al. Alonite and gibbsite: Adsorption isotherms and spectroscopic analysis[J]. Applied Clay Science,2022,219:106437. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2022.106437 [31] YIN Y, XU G Y, XU Y X, et al. Adsorption of inorganic and organic phosphorus onto polypyrrole modified red mud: Evidence from batch and column experiments[J]. Chemosphere,2022,286:131862. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131862 [32] LIAO J, DING L, ZHANG Y, et al. Efficient removal of uranium from wastewater using pig manure biochar: Understanding adsorption and binding mechanisms[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,423:127190. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127190 [33] WU Y H, CHEN D Y, KONG L, et al. Rapid and effective removal of uranium (VI) from aqueous solution by facile synthesized hierarchical hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,371:397-405. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.02.110 [34] CHEN L, WANG Y Q, CAO X H, et al. Effect of doping cation on the adsorption properties of hydroxyapatite to uranium[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry,2023,317:123687. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2022.123687 [35] 王玉罡, 张卫民, 陈家鸿, 等. 钙铁基磷酸盐复合材料(CFP(CC))对U(Ⅵ)的吸附性能[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(14): 116-123.WANG Yugang, ZHANG Weimin, CHEN Jiahong, et al. Adsorption performance of Ca/Fe-phosphate composites (CFP(CC)) on U(Ⅵ) [J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36 (14): 116-123(in Chinese). [36] 王光辉, 胡苏杭, 韩晨. 半胱氨酸盐酸盐改性膨润土对铀的吸附研究[J]. 日用化学工业, 2014, 44(3): 126-130.WANG Guanghui, HU Suhang, HAN Chen. Study on adsorption of uranium onto bentonite modified by cysteine hydrochloride[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2014, 44 (3): 126-130(in Chinese). [37] 尹英杰, 楚龙港, 朱司航, 等. 表面活性剂改性纳米羟基磷灰石对Cd2+吸附研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(8): 1901-1908.YIN Yingjie, CHU Longgang, ZHU Sihang, et al. Adsorption capacity of surfactant-modified nano-hydroxyapatite for Cd2+ [J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38 (8): 1901-1908(in Chinese). -





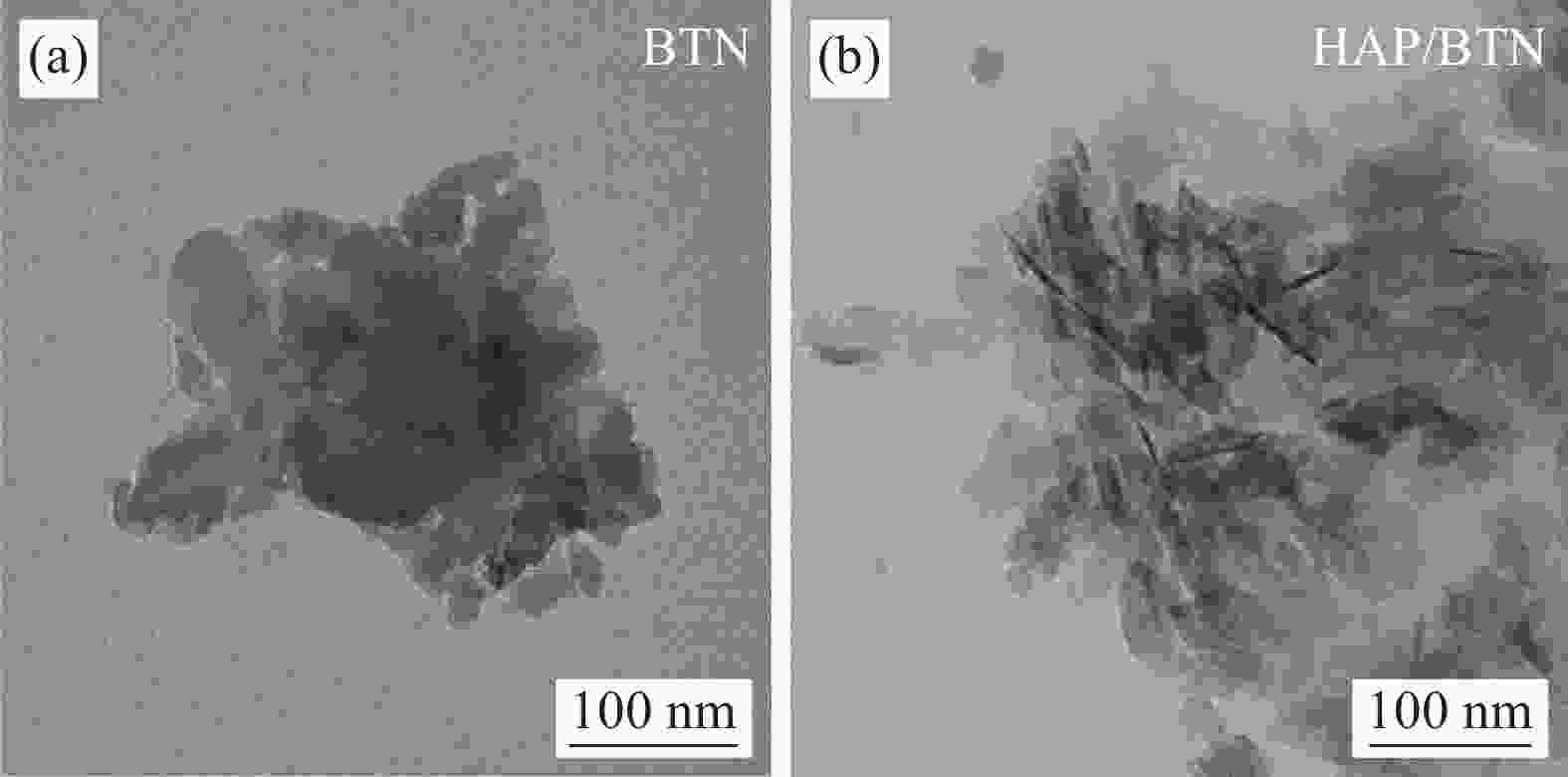
 下载:
下载: