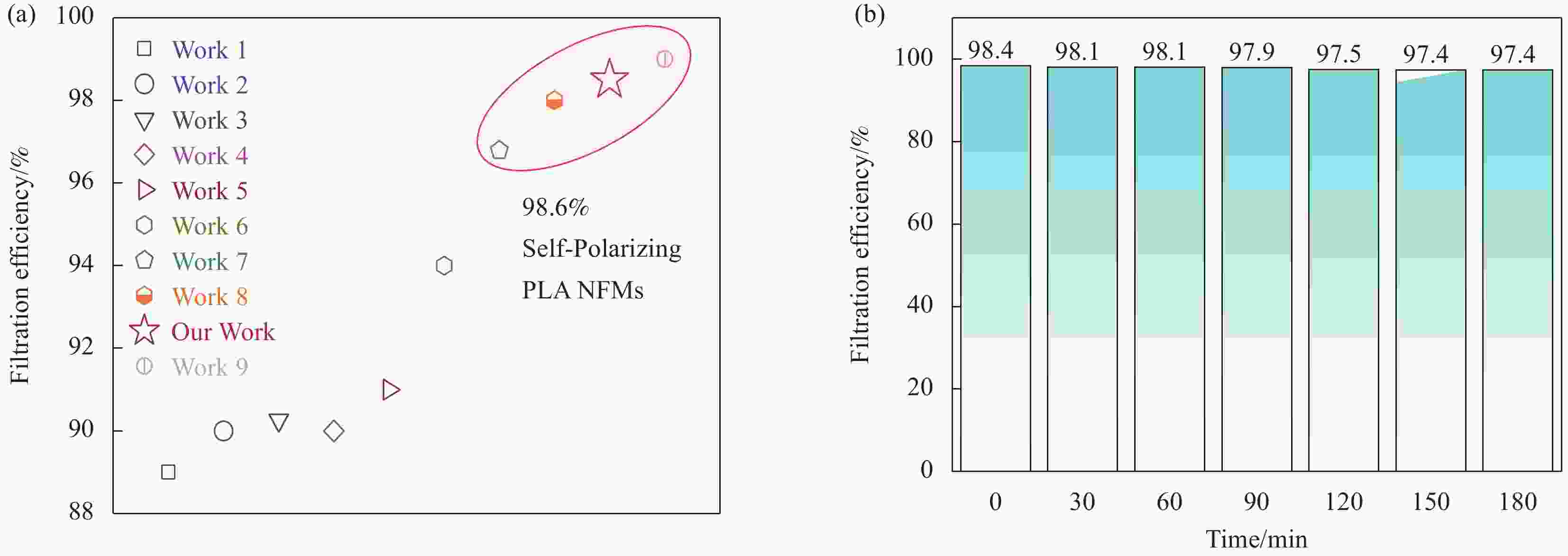
| [1] |
CONTESTABILE M. Air pollution regulation[J]. Nature Sustainability, 2019, 2(1): 10. doi: 10.1038/s41893-018-0214-x
|
| [2] |
SÁNCHEZ-PIÑERO J, NOVO-QUIZA N, PERNAS-CASTAÑO C, et al. Inhalation bioaccessibility of multi-class organic pollutants associated to atmospheric pm2.5: correlation with pm2.5 properties and health risk assessment[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 307: 119577. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119577
|
| [3] |
HUO X, CHEN W, GU H. Electrospun coarse modified polystyrene/carbon aerogel nanofibrous composite membrane for effective pm2.5 air filtration[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 354: 128793. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2024.128793
|
| [4] |
WANG N, FENG Y, ZHENG Y, et al. New hydrogen bonding enhanced polyvinyl alcohol based self-charged medical mask with superior charge retention and moisture resistance performances[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 31(14): 2009172. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202009172
|
| [5] |
CHEN M, JIANG J, FENG S, et al. Graphene oxide functionalized polyvinylidene fluoride nanofibrous membranes for efficient particulate matter removal[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 635: 119463. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119463
|
| [6] |
WANG L, YU L E, CHUNG T. Effects of relative humidity, particle hygroscopicity, and filter hydrophilicity on filtration performance of hollow fiber air filters[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 595: 117561. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2019.117561
|
| [7] |
TANG K H D, LI R, LI Z, et al. Health risk of human exposure to microplastics: a review[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2024, 22(3): 1155-1183. doi: 10.1007/s10311-024-01727-1
|
| [8] |
ZHAO B, REHATI P, YANG Z, et al. The potential toxicity of microplastics on human health[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2024, 912: 168946. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168946
|
| [9] |
沈峥, 徐超, 张一帆, 等. 高抗湿mof化聚乳酸纳纤膜制备及其高效滤除PM0.3性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 42: 1-11.SHEN Z, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. MOF-functionalized poly(lactic acid) nanofiberous membranes for efficient removal of PM0.3 and increased humidity resistance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 42: 1-11 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
宋欣译, 唐梦珂, 王存民, 等. 立构复合化聚乳酸纳纤膜的制备及高效滤除PM2.5性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(2): 9-16.SONG X, TANG M, WANG C, et al. Preparation of stereocomplexed PLA nanofibrous membranes with high PM2.5 filtration efficiency[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(2): 9-16 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
SHANG H, XU K, LI T, et al. Bioelectret poly(lactic acid) membranes with simultaneously enhanced physical interception and electrostatic adsorption of airborne pm0.3[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 458: 132010. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132010
|
| [12] |
ZHU G, WANG C, YANG T, et al. Bio-inspired gradient poly(lactic acid) nanofibers for active capturing of pm0.3 and real-time respiratory monitoring[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2024, 474: 134781. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134781
|
| [13] |
LI L, GAO Y, NIE G, et al. Biodegradable poly (l-lactic acid) fibrous membrane with ribbon-structured fibers and ultrafine nanofibers enhances air filtration performance[J]. Small. 2024.
|
| [14] |
SHAO W, LIU S, WANG K, et al. Using modified raw materials to fabricate electrospun, superhydrophobic poly(lactic acid) multiscale nanofibrous membranes for air-filtration applications[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2024, 333: 125872. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125872
|
| [15] |
LI X, ZHU G, TANG M, et al. Biodegradable mofilters for effective air filtration and sterilization by coupling mof functionalization and mechanical polarization of fibrous poly(lactic acid)[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(22): 26812-26823.
|
| [16] |
SONG X, TANG M, WANG C, et al. Stereocomplexation-enhanced electroactivity of poly(lactic acid) nanofibrous membranes for long-term pm capturing and remote respiratory monitoring[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(9): 3554-3564.
|
| [17] |
ZHANG X, LV S, LU X, et al. Synergistic enhancement of coaxial nanofiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator through dielectric and dispersity modulation[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 75: 104894. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104894
|
| [18] |
ATHIRA B S, GEORGE A, VAISHNA PRIYA K, et al. High-performance flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator based on electrospun pvdf-batio3 nanofibers for self-powered vibration sensing applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(39): 44239-44250.
|
| [19] |
KIM B, JANG Y, KIM J, et al. High-performance electrospun particulate matter (PM) filters embedded with self-polarizable tetragonal BaTiO3 nanoparticles[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138340. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138340
|
| [20] |
ZHANG X, LV S, LU X, et al. Synergistic enhancement of coaxial nanofiber-based triboelectric nanogenerator through dielectric and dispersity modulation[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 75: 104894. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104894
|
| [21] |
LIU C, TAN Y, LIU Y, et al. Microporous carbon nanofibers prepared by combining electrospinning and phase separation methods for supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2016, 25(4): 587-593. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2016.03.017
|
| [22] |
ZHAN N, LI Y, ZHANG C, et al. A novel multinozzle electrospinning process for preparing superhydrophobic PS films with controllable bead-on-string/microfiber morphology[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 345(2): 491-495. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2010.01.051
|
| [23] |
HAN W, RAO D, GAO H, et al. Green-solvent-processable biodegradable poly(lactic acid) nanofibrous membranes with bead-on-string structure for effective air filtration: “kill two birds with one stone”[J]. Nano Energy, 2022, 97: 107237. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107237
|
| [24] |
SONG X, TANG M, WANG C, et al. Stereocomplexation-enhanced electroactivity of poly(lactic acid) nanofibrous membranes for long-term pm capturing and remote respiratory monitoring[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024, 12(9): 3554-3564.
|
| [25] |
TSUJI H. Poly(lactic acid) stereocomplexes: a decade of progress[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 107: 97-135. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.017
|
| [26] |
TANG M, JIANG L, WANG C, et al. Bioelectrets in electrospun bimodal poly(lactic acid) fibers: realization of multiple mechanisms for efficient and long-term filtration of fine pms[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(21): 25919-25931.
|
| [27] |
陈耶福. 立构复合聚乳酸纤维的制备与结构性能研究[D]. 东华大学, 2022(in Chinese).CHEN Y. Study on preparation, structure and properties of stereo composite polylactic acid fiber[D]. Donghua University, 2022.
|
| [28] |
TSUJI H. Poly(lactide) stereocomplexes: formation, structure, properties, degradation, and applications[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience, 2005, 5(7): 569-597. doi: 10.1002/mabi.200500062
|
| [29] |
RAHAMAN H, HOSEN S, GAFUR A, et al. Small amounts of poly( -lactic acid) on the properties of poly( -lactic acid)/microcrystalline cellulose/ poly(-lactic acid) blends[J]. Results in Materials, 2020, 8: 100125. doi: 10.1016/j.rinma.2020.100125
|
| [30] |
QUAN Z, ZU Y, WANG Y, et al. Slip effect based bimodal nanofibrous membrane for high-efficiency and low-resistance air purification[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021, 275: 119258. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119258
|
| [31] |
HUANG J, LIN S, LIANG Y, et al. Preparation of PVA /PEI /CNC /ZnO composite membrane with good mechanical properties and water resistance by electrostatic spinning using for efficient filtration of PM2.5[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, 2023, 61(20): 2451-2461. doi: 10.1002/pol.20230346
|
| [32] |
SHANG H, XU K, LI T, et al. Bioelectret poly(lactic acid) membranes with simultaneously enhanced physical interception and electrostatic adsorption of airborne PM0.3[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2023, 458: 132010. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132010
|
| [33] |
ZHANG J, CHEN G, BHAT G S, et al. Electret characteristics of melt-blown polylactic acid fabrics for air filtration application[J]. Journal of applied polymer science. 2020, 137(4).
|
| [34] |
LI X, ZHU G, TANG M, et al. Biodegradable mofilters for effective air filtration and sterilization by coupling MOF functionalization and mechanical polarization of fibrous poly(lactic acid)[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2023, 15(22): 26812-26823.
|
| [35] |
LIU G, WANG X, YU J, et al. Earthworm-inspired mechanical toughened biodegradable polylactic acid microfiber for sustainable air filtration[J]. Separation and purification technology, 2024, 338: 126575. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126575
|
| [36] |
ZHU Y, GU X, DONG Z, et al. Regulation of polylactic acid using irradiation and preparation of PLA–SiO2–ZnO melt-blown nonwovens for antibacterial and air filtration[J]. RSC advances, 2023, 13(12): 7857-7866. doi: 10.1039/D2RA08274H
|
| [37] |
ZHU G, LI X, LI X P, et al. Nanopatterned electroactive polylactic acid nanofibrous mofilters for efficient PM0.3 filtration and bacterial inhibition[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces Interfaces, 2023, 15(40): 47145-47157.
|
| [38] |
LIU C, DU G, GUO Q, et al. Synergistic antibacterial performance of rosemarinic acid - graphene oxide in electrospun polylactic acid membranes for air filtration[J]. Journal of Polymer Research. 2023, 30(12).
|
| [39] |
DENG Q, HUANG Z, ZHU M, et al. Improving the particulate matter filtration, antibacterial, and degradation properties of electrospinning poly(lactic acid) membranes with ZIF-8@chitosan[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2024, 342: 122427. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.122427
|

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图




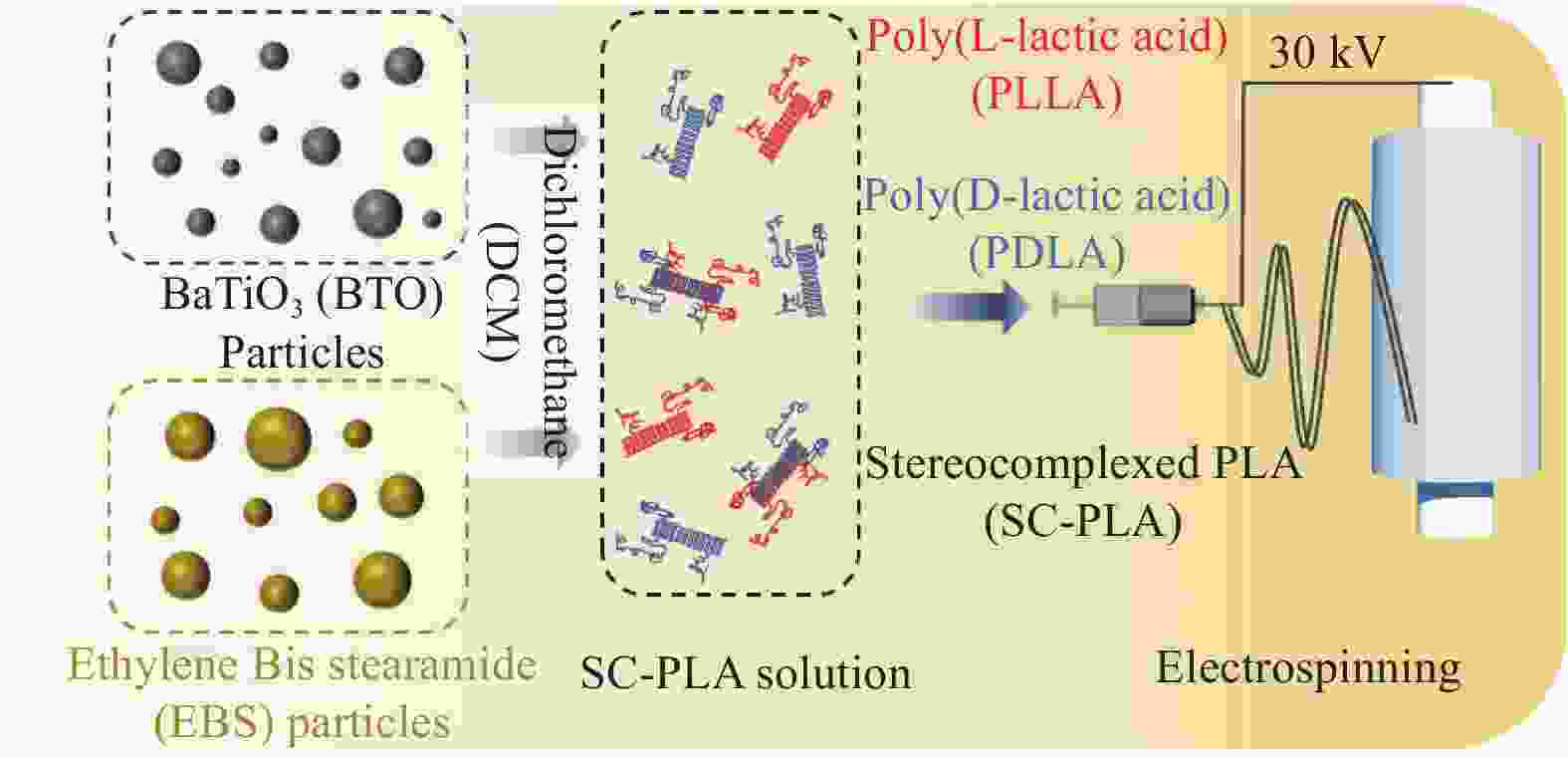
 下载:
下载: