Configuration design and thermal properties of diamond reinforced graphite film/aluminum composite
-
摘要: 针对石墨膜/铝复合材料纵向导热能力不足的缺点,本研究利用高导热金刚石穿透铝层,连接上下两层石墨膜,成功在石墨膜/铝复合材料内部构建了导热通道,为复合材料提供纵向导热路径,从而有效提高复合材料纵向热传导效率。为了改善金刚石与铝基的界面结合,使用物理气相沉积(PVD)技术对金刚石表面进行镀钨处理,随后采用快速热压烧结法(FHP)制备金刚石增强石墨膜/铝复合材料。研究了界面结合质量和金刚石体积分数对复合材料热导率性能的影响,研究表明:当镀钨金刚石体积分数为10%,复合材料面内热导率达到峰值658 W/(m·K),相较于未镀金刚石增强复合材料提升了7%。当镀钨金刚石体积分数超过10%时,复合材料面内热导率呈现下降趋势。对于镀钨金刚石高体积分数(30 vol%)的复合材料而言,其面内热导率降低至535 W/(m·K)。然而,随着金刚石体积分数的增加,复合材料内部导热通道数量增加,纵向热导率达到最高值177 W/(m·K),相较于未镀金刚石增强复合材料提升了34%。本研究表明通过在石墨膜/铝之间引入金刚石导热通道,可有效提高复合材料的纵向导热能力。Abstract: To improve the low longitudinal thermal conductivity of graphite film/aluminum composites, this study employed high-thermal diamond to penetrate the aluminum layer and establish a thermal conduction channel within the composites to effectively enhance their longitudinal thermal conductivity. To enhance the interface bonding between diamond and aluminum matrix. Tungsten coating was applied on the diamond surface using physical vapor deposition (PVD) technology. Subsequently, diamond-reinforced graphite film/aluminum composites were fabricated through fast hot pressing sintering (FHP) method. The influence of interfacial bonding and diamond volume fraction on the thermal conductivity of the composite were investigated. The results demonstrate that at a 10% volume fraction of W-coated diamond, the in-plane thermal conductivity reaches its peak value at 658 W/(m·K), which is 7% higher than that of an uncoated corundum reinforced composite. However, when the volume fraction of tungsten diamond plating exceeds 10%, the in-plane thermal conductivity shows a decreasing trend. The in-plane thermal conductivity is reduced to 535 W/(m·K) for composites with a high volume fraction of tungsten diamond coated (30 vol%). Nevertheless, as the diamond volume fraction increases, more thermal conduction channels are formed within the composite leading to an increase in longitudinal thermal conductivity up to its highest value at 177 W/(m·K), which is 34% higher than that of uncoated diamond reinforced composites. The present study demonstrates that the incorporation of diamond thermal conduction channels between graphite film and aluminum effectively enhances the longitudinal thermal conductivity of composites.
-
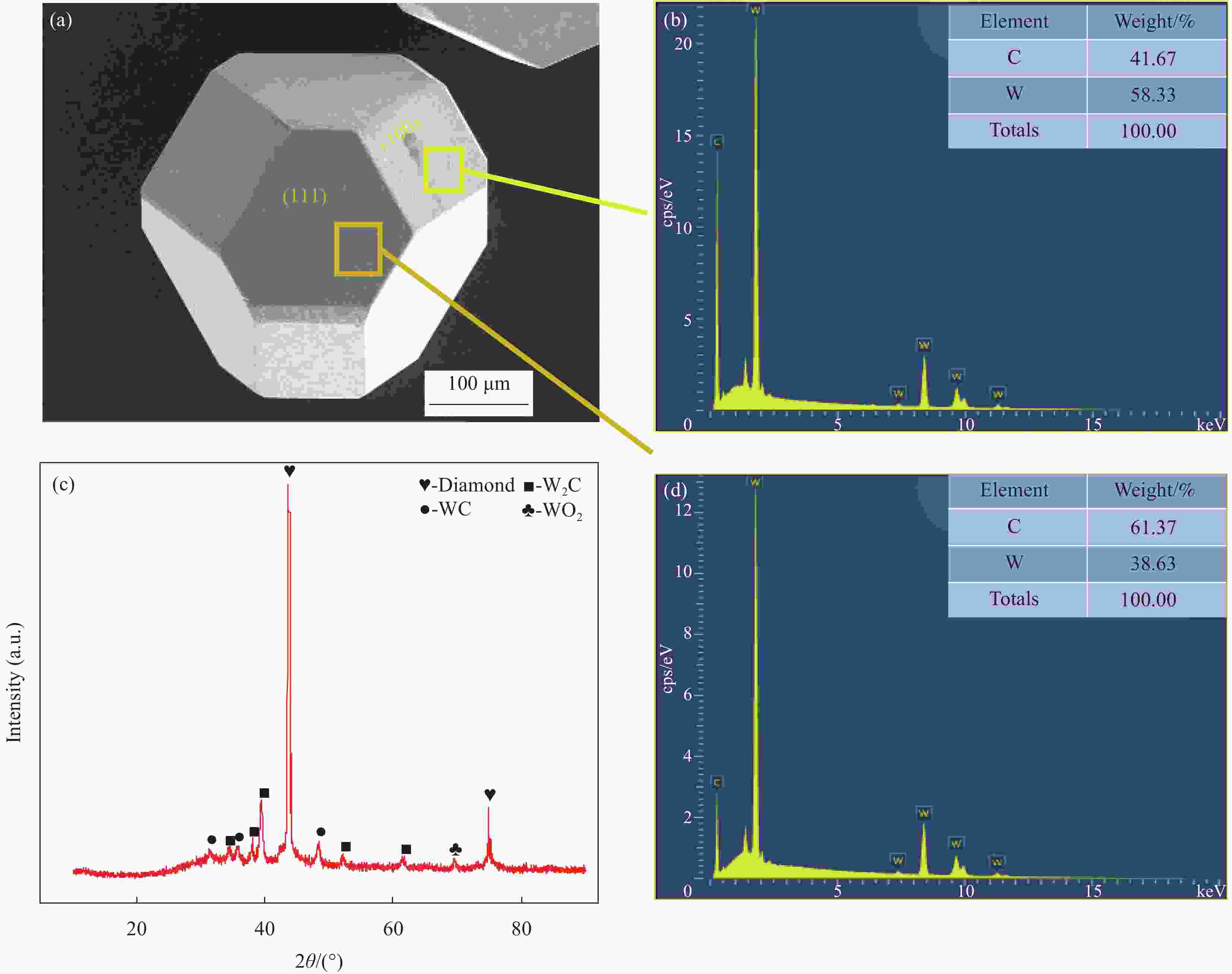
图 1 (a) 镀钨金刚石颗粒的SEM图像;(b) 镀钨金刚石(100)晶面EDS分析;(c) 镀钨金刚石XRD图谱;(d) 镀钨金刚石(111)晶面EDS分析
Figure 1. (a) SEM image of W-coated diamond particle; (b) EDS analysis of W-coated diamond particles on (100) facet; (c) XRD pattern of W-coated diamond particle; (d) EDS analysis of W-coated diamond particles on (100) facet
图 3 (a) 金刚石穿透铝基宏观图(已去除上下表面石墨膜); (b) 金刚石颗粒的SEM图; (c) 石墨膜上压痕宏观图;(d) 石墨膜上压痕的SEM图
Figure 3. (a) Macroscopic morphology of diamond penetration of aluminum base(with upper and lower surface graphite film removed); (b) SEM image of diamond particle; (c) Macroscopic morphology of graphite film indentations; (d) SEM image of indentation on graphite film
图 6 (a) 镀钨复合材料断口的SEM图像; (b) 撕开石墨膜后镀钨复合材料芯层表面的SEM图像; (c) 图6 (b)的EDS分析; (d) 图6 (a) 中放大的镀钨金刚石颗粒SEM图像; (e)图6 (d)的EDS分析; (f) 镀钨金刚石(111) 晶面EDS分析
Figure 6. (a) SEM image of W-coated composites fracture; (b) SEM images of the composite core surface after tearing the graphite film; (c) EDS analysis of figure 6 (b); (d) Enlarged SEM images of W-coated diamond particles in figure 6 (a); (e) EDS analysis of figure 6 (d); (f) EDS analysis of W-coated diamond (111) facet
图 7 镀钨金刚石增强石墨膜/铝复合材料热导率与未镀对比:(a) 面内方向; (b) 厚度方向; (c) 未镀金刚石所在复合材料热成像图; (d) 镀钨金刚石所在复合材料热成像图; (e) 石墨膜/铝复合材料模拟热流图; (f) 金刚石增强石墨膜/铝复合材料模拟热流图
Figure 7. Comparison of thermal conductivity of W-coated diamond reinforced graphite film/aluminum composite with original: (a) In-plane direction; (b) Thickness direction; (c) Diamond in the composite material by infrared thermal imagery; (d) W-coated diamond in the composite by infrared thermal imagery; (e) Simulated heat flow diagram of graphite film/aluminum composite; (f) Diamond reinforced graphite film/aluminum composite simulation heat flow diagram
-
[1] 王菁. 电子设备的散热技术分析[J]. 电子技术, 2022, 51(07): 184-185.WANG J. Analysis of Heat DissipationTechnology of Electronic Equipment[J]. Electronic Technology, 2022, 51(07): 184-185(in Chinese) [2] MALLIK S, EKERE N, BEST C, et al. Investigation of thermal management materials for automotive electronic control units[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 31(2-3): 355-362. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2010.09.023 [3] 陈贞睿, 刘超, 谢炎崇, 等. 高导热金属基复合材料的制备与研究进展[J]. 粉末冶金技术, 2022, 40(1): 40-52.CHEN Z R, LIU C, XIE Y C, et al. Preparation and research process of high thermal conductivity metal matrix composites[J]. Powder Metallurgy Technology, 2022, 40(1): 40-52(in Chinese) [4] FENG C P, SUN K Y, JI J C, et al. 3D Printable, form stable, flexible phase-change-based electronic packaging materials for thermal management[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2023, 71: 103586. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2023.103586 [5] HUANG Y, OUYANG Q, GUO Q, et al. Graphite film/aluminum laminate conductivity for thermal management applications[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 90: 508-515. [6] 黄宇. 高导热石墨膜/铝复合材料的设计、制备与性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017.HUANG Y. Design, Fabrication and thermal properties of high thermal conductive Graphite film/Aluminum Composites[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017(in Chinese) [7] 孙铭. 石墨膜/Al-Mg-Si层状复合材料界面性质及组织性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2022.SUN M. Research on interfacial properties, microstructure and properties of graphite film/Al-Mg-Si laminated composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2022(in Chinese) [8] CHANG J, ZHANG Q, LIN Y, et al. Layer by layer graphite film reinforced aluminum composites with an enhanced performance of thermal conduction in the thermal management applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 742: 601-609. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.332 [9] 田聪. 石墨膜/铝导热复合基板的制备与散热应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.TIAN C. Preparation and application of heat dissipation of graphite film/aluminum thermal conductive substrates [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020(in Chinese) [10] 宁越洋. 表面改性石墨铜/铝力学性能及导热率研究[D]. 武汉: 江汉大学, 2020.NING Y Y. Study on mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of surface-modified graphite copper aluminum[D] Wuhan: Jianghan University, 2020 (in Chinese) [11] 佟兴宇. 微波改性石墨膜/铝层状复合材料的显微组织与热性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.Tong X Y. Microstruture and thermal properties of microwave modified graphite film/aluminum composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese) [12] PENG X, HUANG Y, HAN X, et al. High volume fraction of copper coated graphite flake\Nitrogen doped carbon fiber reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 822: 153584. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.153584 [13] INAGAKI M, KABURAGI Y, HISHIYAMA Y. Thermal Management Material: Graphite:[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2014, 16(5): 494-506. doi: 10.1002/adem.201300418 [14] LIU Q, HE X B, REN S B, et al. Thermophysical properties and microstructure of graphite flake/copper composites processed by electroless copper coating[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 587: 255-259. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.09.207 [15] DOO J H, HA M Y, MIN J K, et al. Theoretical prediction of longitudinal heat conduction effect in cross-corrugated heat exchanger[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(15-16): 4129-4138. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.03.054 [16] LIN Q H, HE S, LIU Q Q, et al. Construction of a 3D interconnected boron nitride nanosheets in a PDMS matrix for high thermal conductivity and high deformability[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2022, 226: 109528. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109528 [17] YANG J, QI G Q, LIU Y, et al. Hybrid graphene aerogels/phase change material composites: Thermal conductivity, shape-stabilization and light-to-thermal energy storage[J]. Carbon, 2016, 100: 693-702. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.01.063 [18] PINES M L, BRUCK H A. Pressureless sintering of particle-reinforced metal–ceramic composites for functionally graded materials: Part I. Porosity reduction models[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(6): 1457-1465. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.10.060 [19] GU Q, PENG J, XU L, et al. Preparation of Ti-coated diamond particles by microwave heating[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 909-916. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.08.168 [20] YANG W, PENG K, ZHOU L, et al. Finite element simulation and experimental investigation on thermal conductivity of diamond/aluminium composites with imperfect interface[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2014, 83: 375-380. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.11.059 [21] 代晨. W涂层对金刚石增强铝基复合材料组织与性能的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2016.DAI C. Microstructure and properties of tungsten coated diamond/aluminum composites [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2016 (in Chinese) [22] ZHOU H, RAN M, LI Y, et al. Improvement of thermal conductivity of diamond/Al composites by optimization of liquid-solid separation process[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2021, 297: 117267. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2021.117267 [23] ZHANG C, CAI Z, WANG R, et al. Microstructure and thermal properties of Al/W-coated diamond composites prepared by powder metallurgy[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 95: 39-47. [24] XIN L, TIAN X, YANG W, et al. Enhanced stability of the Diamond/Al composites by W coatings prepared by the magnetron sputtering method[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 763: 305-313. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.310 [25] BERGSTROM D B, PETROV I, GREENE J E. Al/TixW1−x metal/diffusion-barrier bilayers: Interfacial reaction pathways and kinetics during annealing[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1997, 82(5): 2312-2322. doi: 10.1063/1.366039 [26] WEBER L, TAVANGAR R. On the influence of active element content on the thermal conductivity and thermal expansion of Cu–X (X=Cr, B) diamond composites[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2007, 57(11): 988-991. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.08.007 [27] CHE Z, ZHANG Y, LI J, et al. Nucleation and growth mechanisms of interfacial Al4C3 in Al/diamond composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 657: 81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.075 [28] ZHU P, ZHANG Q, QU S, et al. Effect of interface structure on thermal conductivity and stability of diamond/aluminum composites[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 162: 107161. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107161 [29] ZHANG C, WANG R, CAI Z, et al. Effects of dual-layer coatings on microstructure and thermal conductivity of diamond/Cu composites prepared by vacuum hot pressing[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2015, 277: 299-307. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.07.059 [30] LEE M T, FU M H, WU J L, et al. Thermal properties of diamond/Ag composites fabricated by eletroless silver plating[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2011, 20(2): 130-133. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2010.11.017 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 75
- HTML全文浏览量: 56
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载:







