Damage-acoustic emission characterization of basalt fiber foam concrete under freeze-thaw environment
-
摘要: 对600和1000密度下4种不同玄武岩纤维掺量(0%、0.15%、0.30%和0.45%)泡沫混凝土(BFRFC)试样进行不同冻融环境下(0、20、40、60和80次冻融循环)单轴压缩联合声发射试验,探究了密度、纤维掺量、冻融循环次数对BFRFC单轴压缩性能的影响,并依据声发射与单轴压缩试验参数建立冻融环境下BFRFC受压损伤本构模型,定量分析不同冻融循环下BFRFC的损伤。结果表明:BFRFC在受压过程有明显的阶段性,分为密实、弹性、屈服和平台四个阶段,声发射特征呈现出接触期、陡增期和缓增期三个阶段;不同冻融循环次数下各试样的强度损失率范围为3.4%~63.6%;冻融环境会降低声发射的活跃度,严重影响BFRFC力学性能;玄武岩纤维掺入使试样累计振铃数先增加后减小,能在一定程度上减缓峰值强度的损失;冻融循环加速裂纹开展,玄武岩纤维可有效抑制裂纹发展,但高掺量时纤维团聚现象凸显,内部损伤加剧;BFRFC在受压前期损伤较低,在相对峰值应力大于0.7时损伤发展加速,直至破坏。
-
关键词:
- 玄武岩纤维增强泡沫混凝土 /
- 冻融循环 /
- 声发射 /
- 单轴压缩 /
- 本构模型
Abstract: The uniaxial compression-acoustic emission tests were carried out on four different basalt fiber admixture (0%, 0.15%, 0.30%, and 0.45%) foam concrete (BFRFC) specimens at 600 and 1000 densities in different freeze-thaw environments (0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 freeze-thaw cycles) to investigate the effects of density, fiber admixture, and number of freeze-thaw cycles on the uniaxial compression performance of BFRFC. The compression damage model was established based on the acoustic emission and uniaxial compression parameters to quantitatively analyze the damage of BFRFC under different freezing and thawing cycles. The results show that: BFRFC has obvious stages in the compression process, which are divided into four stages of dense, elastic, yield and platform, and the acoustic emission characteristics show three stages of contact, steep increase and slow increase; the strength loss rate of each specimen under different numbers of freezing and thawing cycles ranges from 3.4% to 63.6%; the freezing and thawing environment would reduce the activity of acoustic emission, which would seriously affect the mechanical properties of BFRFC; basalt fiber doping causes the cumulative ringing number of the specimen to increase and then decrease, which could slow down the loss of peak strength to a certain extent; Freeze-thaw cycle accelerates the crack development, basalt fibers could effectively inhibit the development of cracks, but the fiber agglomeration phenomenon is highlighted at high doping, and the internal damage is aggravated; The damage of the BFRFC in the pre-pressure stage is low, and the damage development is accelerated at the relative peak stress of more than 0.7, until the damage is damaged. -
表 1 玄武岩纤维增强泡沫混凝土的配合比及密度
Table 1. Mix ratio and density of basalt fiber reinforced foam concrete
Density level Cement/(kg·m−3) Water/(kg·m−3) Foam/(kg·m−3) Basalt fiber volume fraction/vol% Mass of basalt fiber/(kg·m−3) A06 416.67 208.33 35.49 0/0.15/0.3/0.45 0/4.2/8.4/12.6 A10 743.05 371.53 21.83 0/0.15/0.3/0.45 0/4.2/8.4/12.6 Notes: A06 and A10 represent BFRFC with the density level of 600 and 1000 kg/m3, respectively. 表 2 不同纤维含量下BFRFC峰值差异(MPa)
Table 2. Differences in peak values of basalt fiber foam concrete with different fiber contents (MPa)
Density grade 0 0.15% 0.30% 0.45% A06 3.164 4.012 5.500 6.587 A10 6.431 7.042 8.336 11.176 表 3 不同冻融循环次数下A10-0.30%试件的拟合参数值
Table 3. Fitted parameter values of A10-0.30% specimens under different freeze-thaw cycles
Freeze-thaw
cyclesc m n 0 1.8347 3.7982 −0.0363 20 2019.3510 0.4204 0.0490 40 681.7456 1.2910 0.0227 60 203.2789 0.3836 0.1033 80 172.9196 −0.6244 0.1847 -
[1] 吴中如, 陈波. 大坝变形监控模型发展回眸[J]. 现代测绘, 2016, 39(5): 1-3+8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2016.05.001WU Zhongru, CHEN Bo. A retrospective look at the development of dam deformation monitoring model[J]. Modern Surveying and Mapping, 2016, 39(5): 1-3+8(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4097.2016.05.001 [2] 郑茂盛. 寒区水利水电工程设计与施工技术[J]. 中国水利, 2010, (20): 72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2010.20.020Zheng Maosheng. Design and construction technology of water conservancy and hydropower projects in cold regions[J]. China Water Resources, 2010, (20): 72-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2010.20.020 [3] Lin Jiankang, Chen Zhongfan, Ding Xiaomeng, et al. BIM-based construction technologies forprecast foamed lightweight concrete wallboards[J]. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition), 2022, 38(3): 270-277. [4] 高志涵, 陈波, 陈家林, 等. 冻融环境下泡沫混凝土的孔结构与力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(2): 827-838.GAO Zhihan, CHEN Bo, CHEN Jialin, et al. Pore structure and mechanical properties of foam concrete under freeze-thaw environment[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 827-838(in Chinese). [5] 叶林杰, 夏新华, 吴迪高, 等. 基于冻融循环和疲劳荷载共同作用下泡沫混凝土的微观力学性能研究[J]. 混凝土, 2022, (9): 56-61.YE Linjie, XIA Xinhua, WU Di Gao, et al. Study on the micromechanical properties of foam concrete based on the combined effect of freeze-thaw cycle and fatigue loading[J]. Concrete, 2022, (9): 56-61(in Chinese). [6] M. Amran, R. Fediuk, N. Vatin, et al. Fibre-Reinforced Foamed Concretes: A Review[J]. Materials, 2020, 13, 4323. Li T, Huang F, Zhu J, et al. Effect of foaming gas and cement type on the thermal conductivity of foamed concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 231. [7] 董进秋, 杜艳廷, 闻宝联, 等. 玄武岩纤维混凝土力学性能与增韧机理研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2011, 41(S1): 638-641.DONG Jinqiu, DU Yanting, WEN Baolian, et al. Mechanical properties and toughening mechanism of basalt fiber concrete[J]. Industrial Building, 2011, 41(S1): 638-641(in Chinese). [8] 李为民, 许金余, 沈刘军, 等. 玄武岩纤维混凝土的动态力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008, (2): 135-142. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.023Li Weimin, Xu Jinyu, Shen Liujun, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties of basalt fiber concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2008, (2): 135-142(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.02.023 [9] 王起台, 任根立. 冻融循环作用下玄武岩纤维混凝土抗压和抗折性能分析[J]. 湖南城市学院学报(自然科学版), 2023, 32(4): 6-12.Wang Q T, Ren G L. Analysis of compressive and flexural properties of basalt fiber reinforced concrete under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of hunan city university (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 32(4): 6-12(in Chinese). [10] 王小娟, 崔浩儒, 周宏元, 等. 玄武岩纤维增强泡沫混凝土的单轴拉伸及准静态压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(3): 1569-1585.Wang X J, Cui H R, Zhou H Y, et al. Uniaxial tensile and quasi-static compressive properties of basalt fiber reinforced foam concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(3): 1569-1585(in Chinese). [11] Gencel O, Nodehi M, Bayraktar O Y, et al. Basalt fiber-reinforced foam concrete containing silica fume: An experimental study[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 326. [12] 周程涛, 陈波, 张娟, 等. 玄武岩纤维泡沫混凝土的细观结构及损伤特性[J/OL]. 复合材料学报: 1-11.Zhou C T, Chen B, Zhang J, et al. Microstructure and damage characteristics of basalt fiber foamed concrete [J/OL]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica: 1-11. (in Chinese). [13] 段力群, 董璐, 马林建, 等. 泡沫混凝土单轴压缩下声发射特征试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2018, 47(4): 742-747.Duan Liqun, Dong Lu, Ma Linjian, et al. Experimental study on acoustic emission characteristics of foam concrete under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2018, 47(4): 742-747(in Chinese). [14] 李升涛, 陈徐东, 张锦华, 等. 不同密度等级泡沫混凝土的单轴压缩破坏特征[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2021, 24(6): 1146-1153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.06.004Li Shengtao, Chen Xudong, Zhang Jinhua, et al. Uniaxial compression damage characteristics of foam concrete with different density grades[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2021, 24(6): 1146-1153(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2021.06.004 [15] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 泡沫混凝土: JG/T266−2011[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2011.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, People's Republic of China. Foam concrete [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2011(in Chinese). [16] 王丹薇. 常用纤维对水工泡沫混凝土物理力学性能的影响研究[J]. 吉林水利, 2022, (3): 10-13+18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2022.03.004WANG Danwei. Study on the influence of common fibers on the physical and mechanical properties of hydraulic foam concrete[J]. Jilin Water Resources, 2022, (3): 10-13+18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2846.2022.03.004 [17] 中华人民共和国水利部. 水工混凝土试验规程: SL/T 352-2020[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020.Ministry of Water Resources, People's Republic of China. Test procedure for hydraulic concrete: SL/T 352-2020 [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2020(in Chinese). [18] 周宏元, 王业斌, 王小娟, 等. 泡沫混凝土压缩性能尺寸效应研究[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(18): 18076-18082+18095. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20090009Zhou Hongyuan, Wang Yebin, Wang Xiaojuan, et al. Study on the size effect of compression properties of foam concrete[J]. Materials Herald, 2021, 35(18): 18076-18082+18095(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.20090009 [19] 朱兴一, 张启帆, 于越, 等. 基于离散元的EMAS泡沫混凝土贯入力学性能研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(2): 122-128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.02.002ZHU Xingyi, ZHANG Qifan, YU Yue, et al. Study on penetration mechanical properties of EMAS foam concrete based on discrete elements[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(2): 122-128(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.02.002 [20] 周程涛, 陈波, 高志涵. 冻融环境下泡沫混凝土的单轴压缩特性[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42(4): 1233-1241. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2023.4.gsytb202304011ZHOU Chengtao, CHEN Bo, GAO Zhihan. Uniaxial compression characteristics of foam concrete under freeze-thaw environment[J]. Silicate Bulletin, 2023, 42(4): 1233-1241(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2023.4.gsytb202304011 [21] 黄海健, 宫能平, 穆朝民, 等. 泡沫混凝土动态力学性能及本构关系[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(2): 466-472. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.02.033Huang Haijian, Gong Nengping, Mu Zhaomin, et al. Dynamic mechanical properties and constitutive relationship of foam concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(2): 466-472(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.02.033 [22] 高志涵, 陈波, 陈家林, 等. 基于X-CT的泡沫混凝土孔隙结构与导热性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(7): 723-730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.07.004Gao Zhihan, Chen Bo, Chen Jialin, et al. Pore structure and thermal conductivity of foam concrete based on X-CT[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(7): 723-730(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.07.004 [23] 张亚梅, 孙超, 王申, 等. 不同密度等级泡沫混凝土的性能和孔结构[J]. 重庆大学学报, 2020, 43(8): 54-63.Zhang Y M, Sun C, Wang S, et al. Performance and pore structure of foam concrete with different density grades[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2020, 43(8): 54-63(in Chinese). [24] 王静文, 王伟. 玄武岩纤维增强泡沫混凝土响应面多目标优化[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(24): 4092-4097. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19010130WANG Jingwen, WANG Wei. Multi-objective optimization of response surface of basalt fiber reinforced foam concrete[J]. Materials Herald, 2019, 33(24): 4092-4097(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.19010130 [25] Benaboud S, Takarli M, Pouteau B, et al. Fatigue process analysis of aged asphalt concrete from two-point bending test using acoustic emission and curve fitting techniques[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 301: 124109. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124109 [26] De Smedt M, Vrijdaghs R, Van Steen C, et al. Damage analysis in steel fibre reinforced concrete under monotonic and cyclic bending by means of acoustic emission monitoring[J]. Cement & Concrete Composites, 2020, 114. [27] Li S, Chen X, Zhang J. Acoustic emission characteristics in deterioration behavior of dam concrete under post-peak cyclic test[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 292: 123324. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123324 [28] OHTSU M. Acoustic emission characteristics in concrete and diagnostic application[J]. Journal of Acoustic Emission, 1987, 6(2): 99-108. [29] 陈波, 袁志颖, 陈家林, 等. 冻融循环后蒸汽养护混凝土的损伤—声发射特性[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(2): 143-149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.02.005CHEN Bo, YUAN Zhiying, CHEN Jialin, et al. Damage-acoustic emission characteristics of steam-cured concrete after freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(2): 143-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.02.005 [30] 张明, 李仲奎, 杨强, 等. 准脆性材料声发射的损伤模型及统计分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(12): 2493. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.12.015Zhang M, Li Zhongkui, Yang Q, et al. Damage modeling and statistical analysis of acoustic emission from quasi-brittle materials[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(12): 2493(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.12.015 [31] 纪洪广, 蔡美峰. 混凝土材料声发射与应力-应变参量耦合关系及应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2003, 22(2): 227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.02.012Ji Hongguang, Cai Meifeng. Coupling relationship between acoustic emission and stress-strain parameters in concrete materials and applications[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003, 22(2): 227(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2003.02.012 [32] LEMAITRE J. How to use damage mechanics[J]. NuclearEngineering and Design, 1984, 80(1): 233-245. [33] 龙广成, 杨振雄, 白朝能, 等. 荷载-冻融耦合作用下充填层自密实混凝土的耐久性及损伤模型[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2019, 47(7): 855-864.LONG Guangcheng, YANG Zhenxiong, BAI Chaoneng, et al. Durability and damage model of self-compacting concrete filled layer under load-freeze-thaw coupling[J]. Journal of the ChineseCeramic Society, 2019, 47(7): 855-864(in Chinese). -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 52
- HTML全文浏览量: 22
- 被引次数: 0




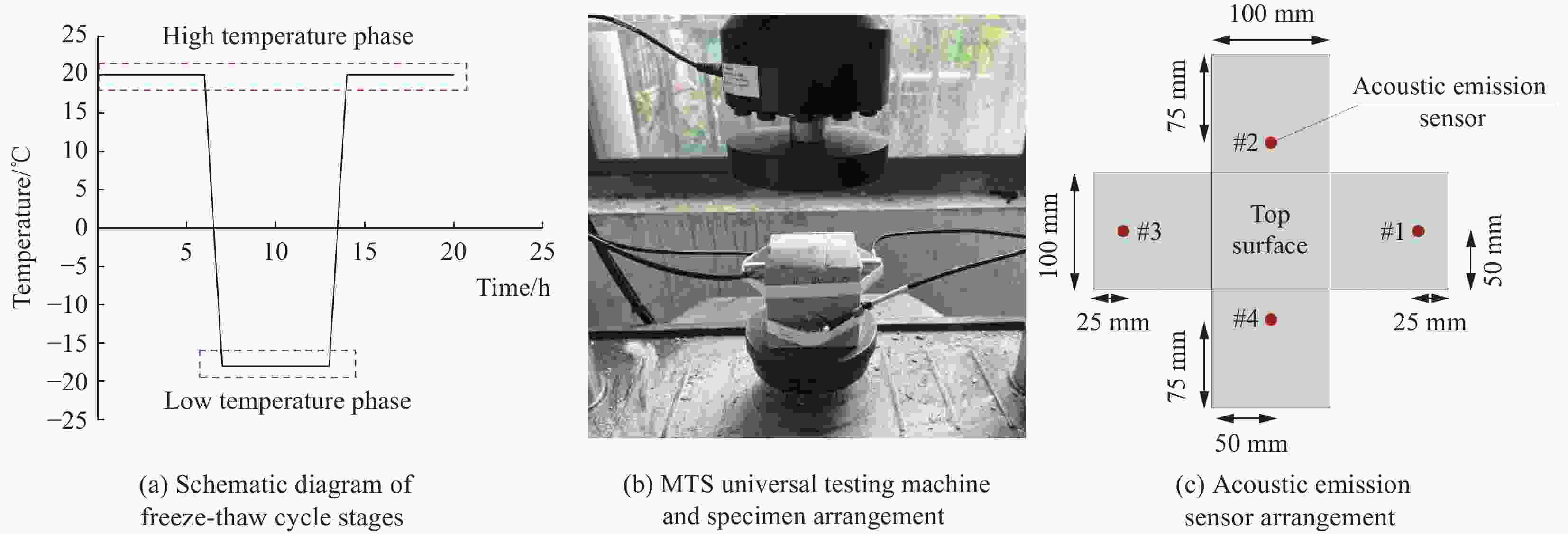
 下载:
下载:









