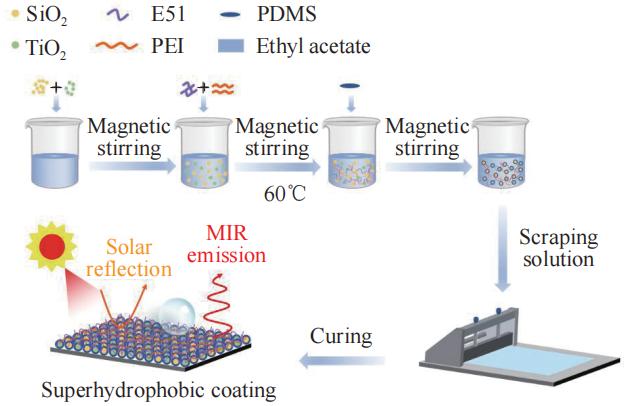
A multifunctional composite coating based on E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 with self-cleaing, anti-icing and radiative cooling properties
-
摘要: 户外电力设施运作时不仅需要降温,在冬季还受冰雪困扰,因此制备具有自清洁、防冰和辐射制冷的多功能复合涂层具有重要的现实意义。本文采用一步刮涂法,制备了由环氧树脂(E51)、聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)、聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)和纳米SiO2、TiO2颗粒组成的多功能复合涂层。通过调节SiO2与TiO2的用量比,涂层能同时实现优异的超疏水性(WCA = 157.25°),良好的防冰性能(延迟结冰时间t ≈
1223 s),以及辐射降温效果(在阳光直射下最高冷却至环境温度下13.6 ℃)。涂层制备未使用含氟试剂,对环境友好,其自清洁特性可使其表面避免被外界污染从而保持稳定的防冰和辐射制冷性能。此外,该复合涂层在磨损试验、化学稳定性试验和户外耐候试验中表现出良好的耐久性,有利于涂层在室外的实际应用。Abstract: Outdoor power facilities were required to have heat dissipation for the hot summer and to adopt anti-icing measures for the winter. The development of radiative cooling coating materials with both self-cleaning and anti-icing functions was of practical importance. A novel multifunctional composite coating, which exhibited self-cleaning, anti-icing, and radiative cooling properties, was developed using a one-step blade coating method. The multifunctional composite coating is composed of epoxy resin (E51), polyethyleneimine (PEI), polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), and SiO2 and TiO2 nanoparticles. By optimizing the SiO2 to TiO2 ratio, the coating achieves remarkable superhydrophobicity (water contact angle WCA = 157.25°), notable anti-icing performance (delayed icing time t ≈1223 s), and significant radiative cooling effects (cooling up to 13.6℃ below ambient temperature under direct sunlight). The preparation process excludes the use of fluorinated reagents, enhancing its environmental friendliness. The self-cleaning capability of the coating prevents surface contamination, thereby maintaining consistent anti-icing and radiative cooling performance. Additionally, the composite coating demonstrates excellent durability in wear tests, chemical stability assessments, and outdoor weather resistance evaluations, underscoring its suitability for practical outdoor applications.-
Key words:
- Superhydrophobic /
- Anti-icing /
- Radiative cooling /
- Self-cleaning /
- Composite coating
-
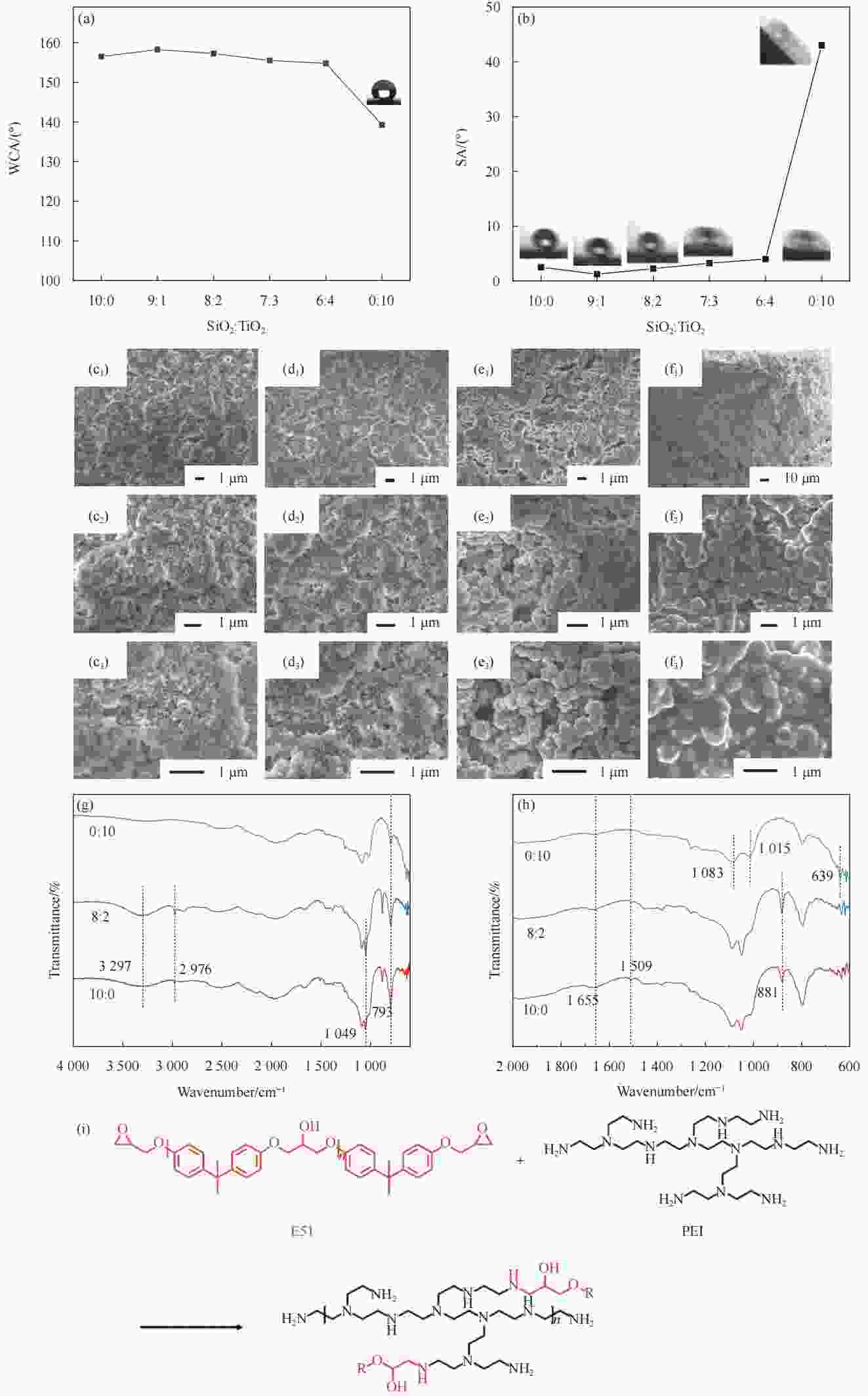
图 2 不同纳米SiO2和TiO2含量下E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层(a) WCA、(b) SA变化和SEM图像:(c1-c3) 10∶0,(d1-d3) 9∶1,(e1-e3) 6∶4,(f1-f3) 0∶10;(g) SiO2∶TiO2为10∶0、8∶2和0∶10的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层FTIR光谱图;(h)在600-2000 cm−1范围内的红外光谱图;(i)环氧树脂E51和聚乙烯亚胺PEI的交联反应
Figure 2. (a) WCA and (b) SA of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coatings with different ratio of SiO2 and TiO2 contents. (c-f) SEM images of composite coatings: (c1-c3) 10∶0, (d1-d3) 9∶1, (e1-e3) 6∶4, (f1-f3) 0∶10. (g) FTIR spectra of E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coatings with SiO2:TiO2 ratios of 10∶0, 8∶2 and 0∶10. (h) FTIR spectra in the 600-2000 cm−1 range. (i) Crosslinking reaction between Epoxy E51 and PEI
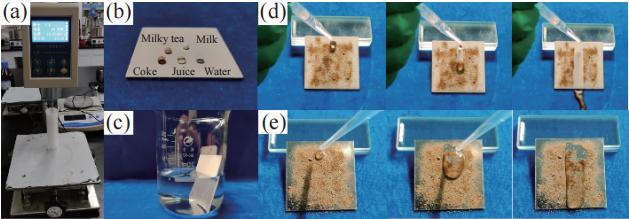
图 3 (a) E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂料黏度测试装置;(b)涂层表面和对水、果汁、可乐、奶茶和牛奶的拒液性和(c)银镜现象;(d) E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层与(e)无涂层的铝基底自清洁效果
Figure 3. (a) Viscosity testing device and (b) Liquid repellency of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating surface against water, juice, cola, milk tea, and milk and (c) Silver mirror phenomenon. (d) Self-cleaning effect of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating and (e) bare aluminum substrate without coating.
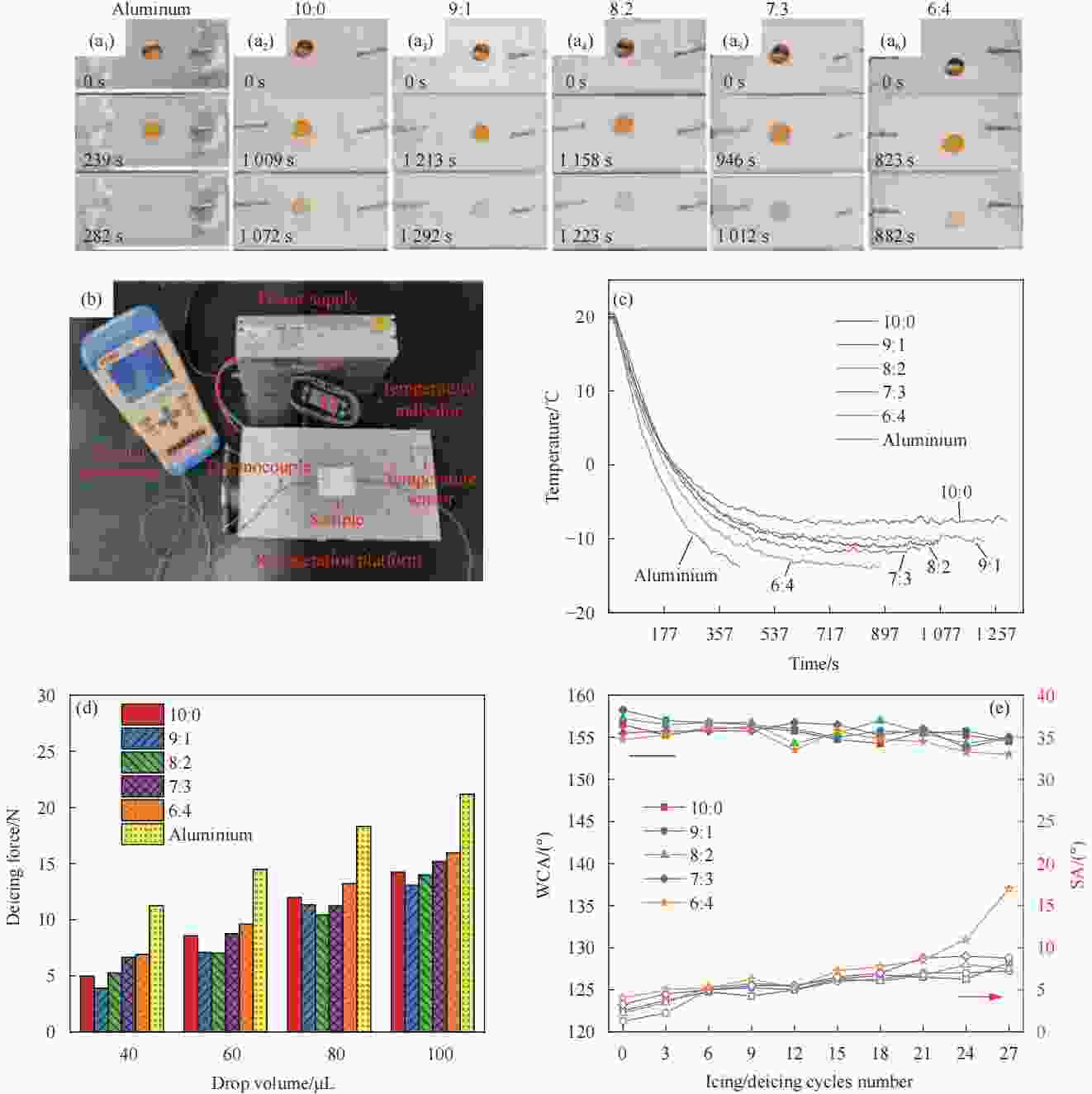
图 4 水滴在纳米SiO2和TiO2不同质量比的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层表面的(a)冻结过程;(b)测试装置;(c)冻结时温度变化曲线;(d)除冰力测试和(e)结冰/除冰过程中WCA和SA的变化
Figure 4. The changes in WCA and SA during (a) Freezing process, (b) Testing device, (c) Temperature variation curve of the coating during water droplet freezing, (d) De-icing force test and (e) Ice formation/removal process of water droplets on the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating with different ratio of SiO2 and TiO2 contents.
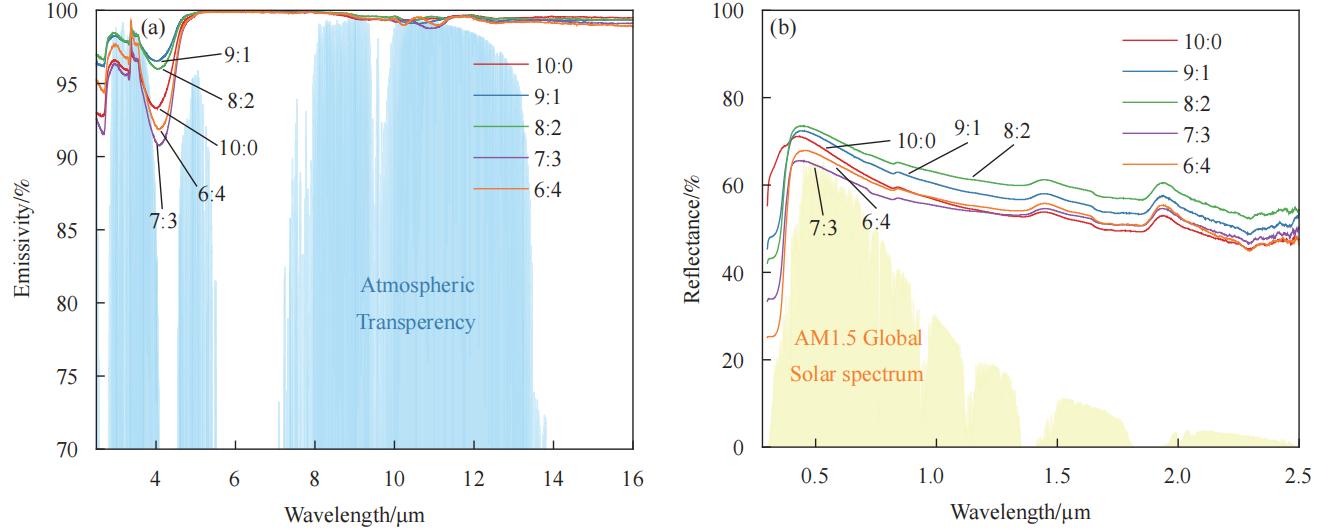
图 5 纳米SiO2和TiO2不同质量比的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层在(a) 2 ~ 16 μm波长范围内的发射率和(b) 0.2 ~ 2.5 μm波长范围内的反射率
Figure 5. (a) Spectral emissivity in the wavelength range of 2 to 16 μm. (b) Reflectance in the wavelength range of 0.2 to 2.5 μm of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating with different ratio of SiO2 and TiO2 contents
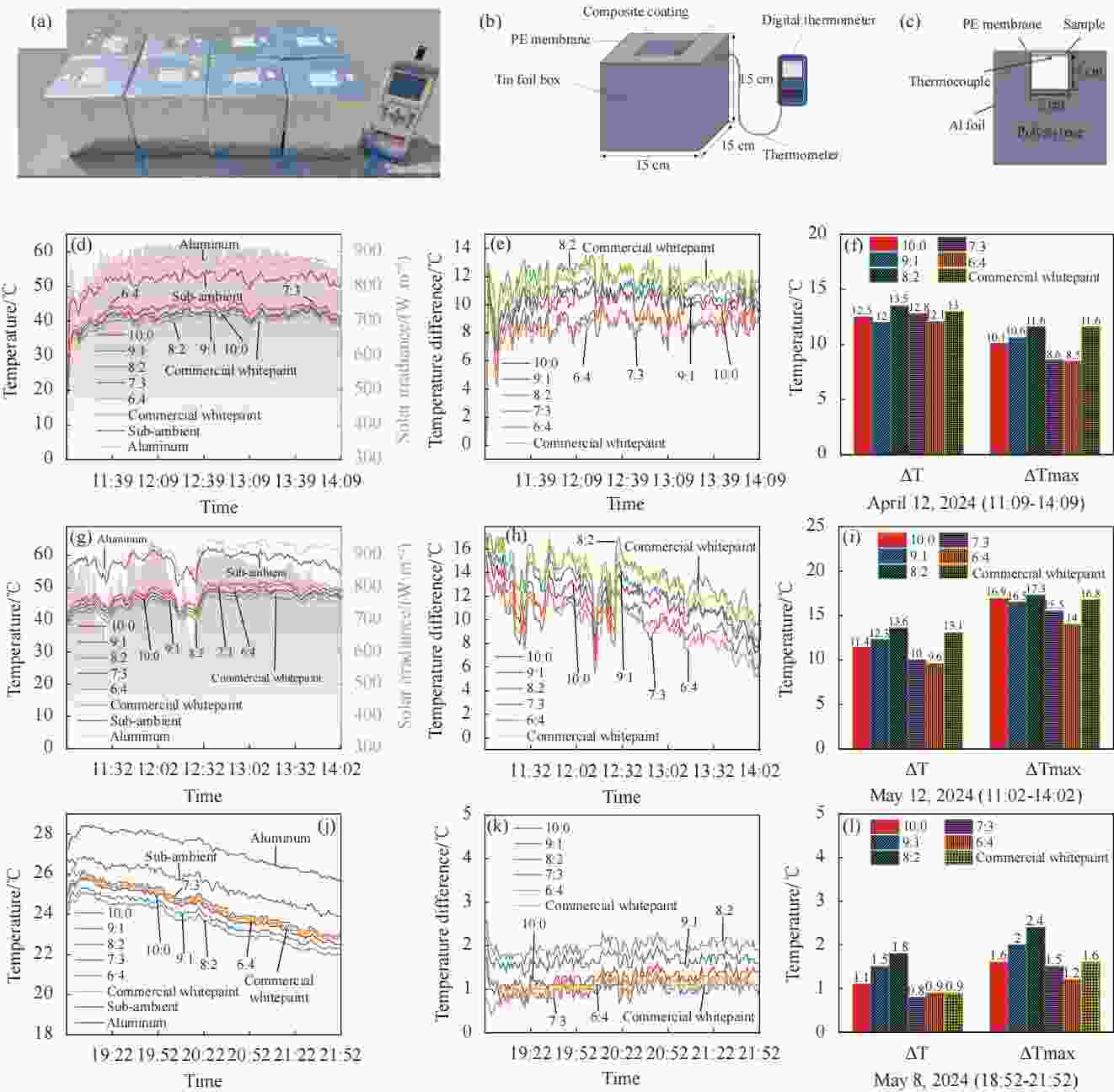
图 6 SiO2∶TiO2为10∶0、9∶1、8∶2、7∶3和6∶4的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层(a)测试装置照片;(b-c)试验装置示意图;(d) 2024年4月12日白天(11:09-14:09)温度变化和辐照度;(e-f)ΔT和ΔTmax。(g) 2024年5月12日白天(11:02-14:02)温度变化和辐照度;(h-i)ΔT和ΔTmax。(j) 2024年5月8日夜间(18:52-21:52)温度变化;(k-l)ΔT和ΔTmax。
Figure 6. (a) Photo of the test devices, (b-c) Schematic diagram of the test device, (d) Temperature variation and during the daytime on April 12, 2024 (11:09-14:09) and (e-f) ΔT (average temperature difference) and ΔTmax (maximum temperature difference), (g) Temperature variation and irradiance during the daytime on May 12, 2024 (11:02-14:02) and (h-i) ΔT and ΔTmax, (j) Temperature variation at night on May 8, 2024 (18:52-21:52) and (k-l) ΔT and ΔTmax of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating with different ratio of SiO2 and TiO2 contents.
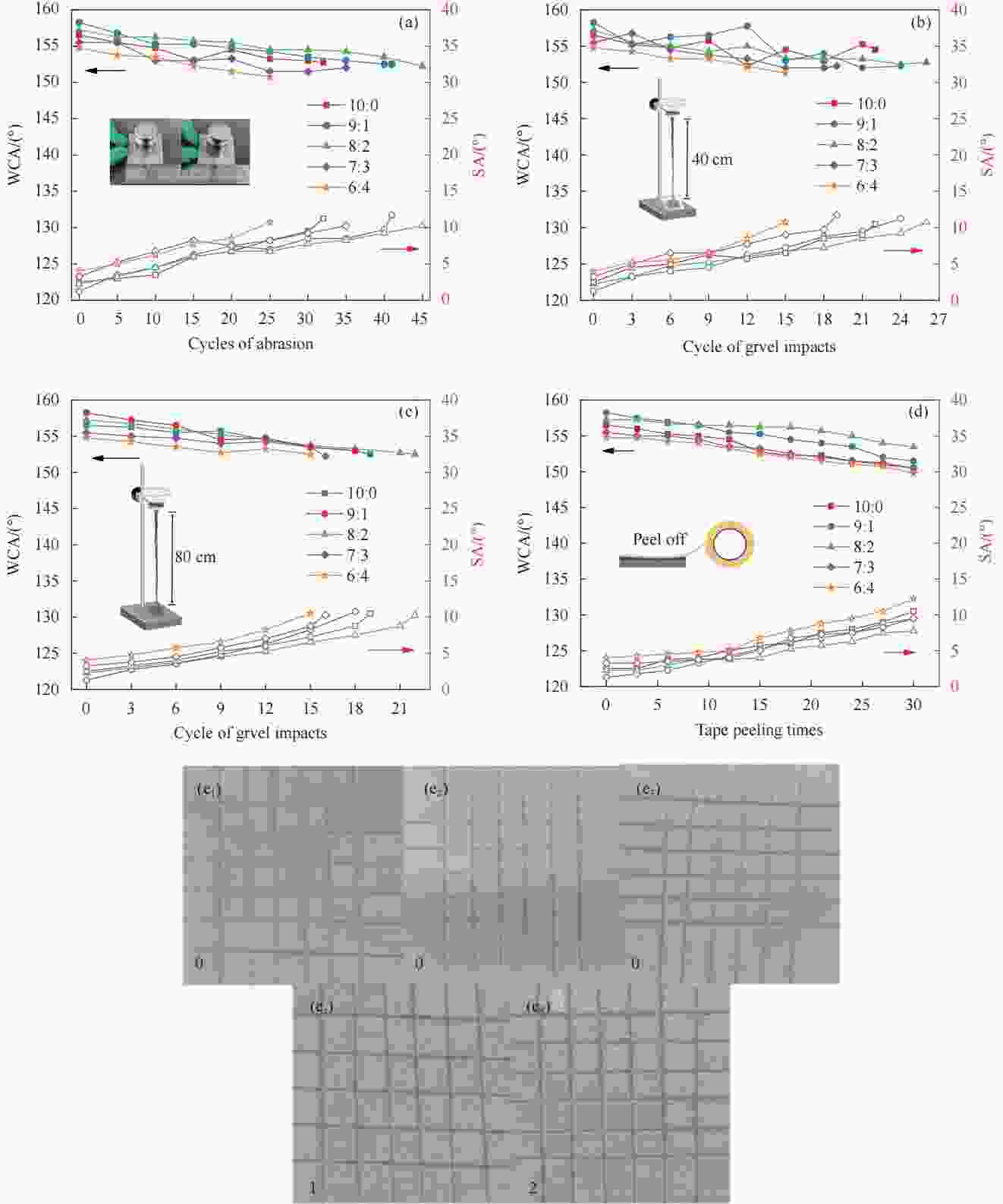
图 7 SiO2:TiO2为10:0、9:1、8:2、7:3和6:4的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层在(a)砂纸磨擦试验;(b-c)40 cm和80 cm高度沙砾冲击试验;(d)胶带剥离试验过程中WCA和SA的变化;(e)附着力等级
Figure 7. The changes of WCA and SA during (a) Sandpaper abrasion test. (b-c) Gravel impact test at heights of 40 cm and 80 cm. (d) Tape stripping test of E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coatings with SiO2:TiO2 ratios of 10:0, 9:1, 8:2, 7:3 and 6:4. (e) Adhesion rating
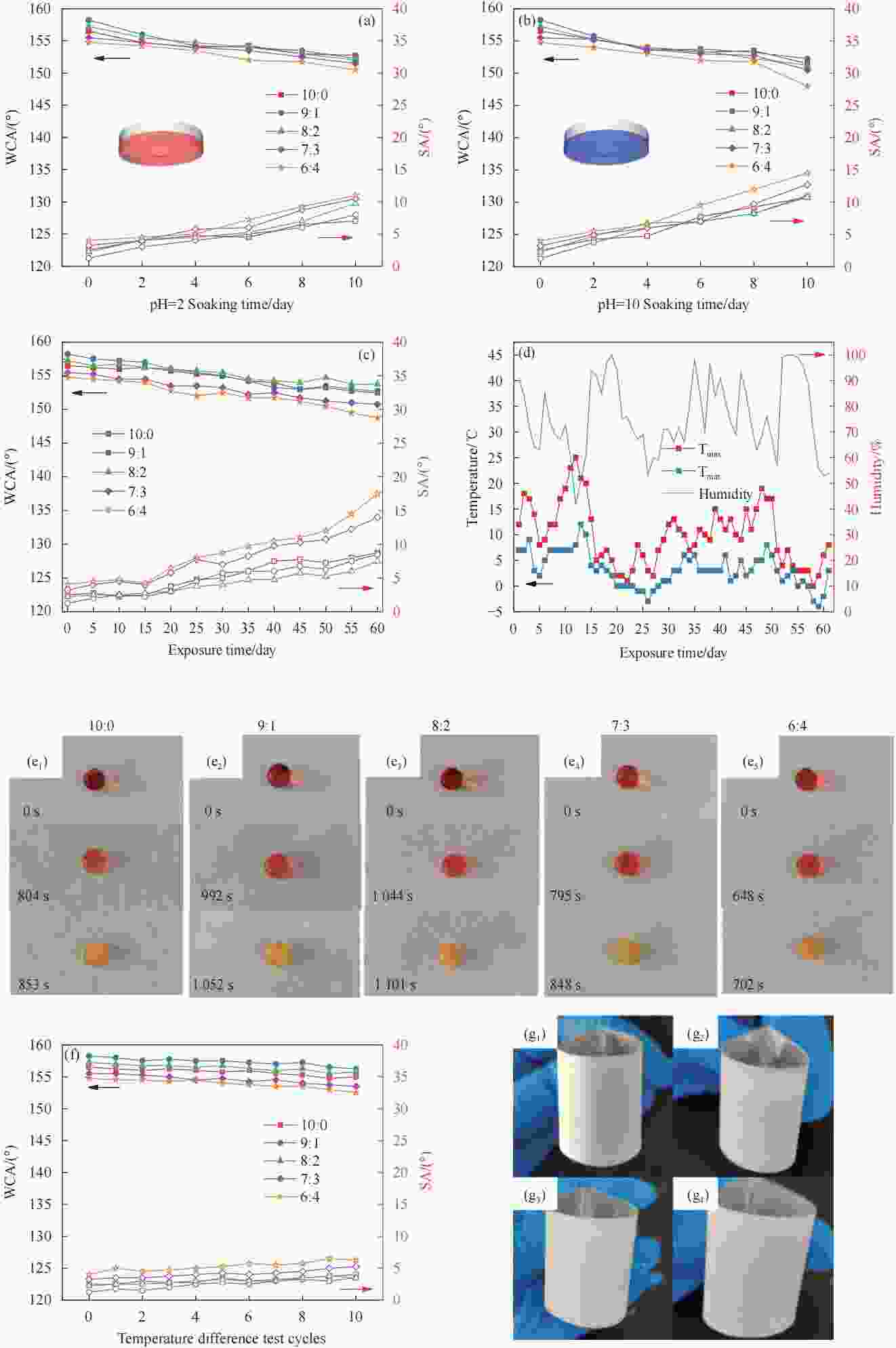
图 8 SiO2:TiO2为10:0、9:1、8:2、7:3和6:4的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层在(a-b)耐酸碱试验;(c)室外暴露试验过程中WCA和SA的变化;(d)室外暴露试验过程中温度和湿度的变化;(e)经耐候性测试后的防冰测试结果;(f)温差循环试验;(g1-g4)分别为高温、冷冻和酸碱处理后的E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂层的弯折测试
Figure 8. The changes of WCA and SA during (a-b) Acid and alkali resistance test. (c) Outdoor exposure test of E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coatings with SiO2:TiO2 ratios of 10:0, 9:1, 8:2, 7:3 and 6:4. (d) Changes in temperature and humidity during the outdoor exposure test. (e) Results of anti-icing test after weathering test. (f) Temperature cycling test. (g1-g4) The bending tests of E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating after high temperature, freezing and acid-base treatment was conducted, respectively
表 1 E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2多功能复合涂料黏度测试结果
Table 1. Viscosity testing results of the E51-PEI-PDMS-SiO2-TiO2 multifunctional composite coating
sample 10∶0 9∶1 8∶2 7∶3 6∶4 Viscosity/(mPaŸs) 17.8 18.1 18.6 18.2 17.5 -
[1] 武壮壮, 马国佳, 崔向中, 等. 微纳结构超疏水表面的浸润性及防冰性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11): 2769-2775.WU Zhuangzhuang, MA Guojia, CUI Xiangzhong, et al. Wettability and anti-icing performance of micro-nano structure superhydrophobic surface[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(11): 2769-2775(in Chinese). [2] 赵美蓉, 周惠言, 康文倩, 等. 超疏水表面制备方法的比较[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2): 361-379.ZHAO Meirong, ZHOU Huiyan, KANG Wenqian, et al. Comparison of methods for fabricating superhydrophobic surface[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(2): 361-379(in Chinese). [3] XU M H, GUO Y, ZHANG D W, et al. Research on anti-icing technology of high voltage line insulator based on advanced sensor[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 769: 042026. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/769/4/042026 [4] JIANG B C, LEI Y H, SUN K, et al. Superhydrophobic F-SiO2/tea polyphenol coating with high efficiency photothermal anti-icing and de-icing properties[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2024, 683: 132846. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2023.132846 [5] ZHAO Z H, CHEN H W, LIU X L, et al. Development of high-efficient synthetic electric heating coating for anti-icing/de-icing[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2018, 349: 340-346. [6] WANG Y B, XU Y M, HUANG Q. Progress on ultrasonic guided waves de-icing techniques in improving aviation energy efficiency[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2017, 79: 638-645. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.129 [7] KE G J, ZHANG J, TIAN B. Evaluation and selection of de-icing salt based on multi-factor[J]. Materials, 2019, 12: 912. doi: 10.3390/ma12060912 [8] ZHANG Z S, LIU X Y. Control of ice nucleation: Freezing and antifreeze strategies[J]. chemical society reviews, 2018, 47(18): 7116-7139. doi: 10.1039/C8CS00626A [9] ZHU Z W, LI J B, LUO Y M, et al. The criterion of supercooled bionic lotus surfaces repelling impacting droplets for anti-icing engineering[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2023, 10(16): 2300115. doi: 10.1002/admi.202300115 [10] LEI Y H, JIANG B C, LIU H, et al. Mechanically robust superhydrophobic polyurethane coating for anti-icing application[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2023, 183: 107795. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2023.107795 [11] Guo Y, Zhao H B, Zhang C S, et al. Super photothermal/electrothermal response and anti-icing/deicing capability of superhydrophobic multi-walled carbon nanotubes/epoxy coating[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 497: 154383. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2024.154383 [12] GAO Y F, SONG X H, FAROOQ A S, et al. Cooling performance of porous polymer radiative coating under different environmental conditions throughout all-year[J]. Solar Energy, 2021, 228: 474-485. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2021.09.062 [13] SUN Y Q, HE H, HUANG X L, et al. Superhydrophobic SiO2-glass bubbles composite coating for stable and highly efficient daytime radiative cooling[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2023, 15(3): 4799-4813. [14] ZHAO D L, AILI A, ZHAI Y, et al. Radiative sky cooling: Fundamental principles, materials, and applications[J]. Applied Physics Reviews, 2019, 6(2): 021306. doi: 10.1063/1.5087281 [15] ZHAO B, HU M K, AO X Z, et al. Radiative cooling: A review of fundamentals, materials, applications, and prospects[J]. Applied Energy, 2019, 236: 489-513. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.12.018 [16] JOSE S, JOSHY D, NARENDRANATH S B, et al. Recent advances in infrared reflective inorganic pigments[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 194: 7-27. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.01.037 [17] JUNG J, YOON S, KIM B, et al. Development of high-performance flexible radiative cooling film using PDMS/TiO2 microparticles[J]. Micromachines, 2023, 14(12): 2223. doi: 10.3390/mi14122223 [18] ZHANG H Y, YU M, DU Y, et al. High-efficiency oil-water separation and passive radiant cooling performance of nano-ZnO-embedded dust-free paper[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 285: 126069. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126069 [19] SUN L D, LIU Z X, HUANG H, et al. Flexible Al2O3/polymethyl methacrylate composite nanofibers for high-performance sun shading and radiative cooling[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2023, 37: 106903. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106903 [20] QI Y L, ZHANG J. Chemically modified Sb2O3, a new member of high solar-reflective material family, incorporating with ASA (acrylonitrile-styrene-acrylate copolymer) for fabrication of cooling composite with lower wetting behavior[J]. Composites Part B, 2019, 162: 112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.014 [21] SUN H X, QI Y L, ZHANG J. Surface organic modified magnesium titanate particles with three coupling agents: Characterizations, properties and potential application areas[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 520: 146322. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146322 [22] MAO Z P, YANG Z B, ZHANG J. SrTiO3 as a new solar reflective pigment on the cooling property of PMMA-ceramic composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(13): 16078-16087. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.124 [23] MA S Q, WANG Z Y, YANG L, et al. Effect of Sr doping and temperature on the optical properties of BaTiO3[J]. Ceramics International, 2023, 49(15): 26102-26109. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2023.05.166 [24] QI Y L, YANG Z B, HUANG W X, et al. Robust superhydrophobic surface for anti-icing and cooling performance: Application of fluorine-modified TiO2 and fumed SiO2[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 538: 148131. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148131 [25] MALLICK S, AHMAD Z, TOUATI F, et al. PLA-TiO2 nanocomposites: Thermal, morphological, structural, and humidity sensing properties[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44: 16507-16513. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.06.068 [26] WANG H X, LOU C H, YU J J, et al. Modification mechanism of modified diatomite with flexible amine-based structure as a filler of epoxy resin and mechanical properties and curing kinetic of composites[J]. Polymer composites, 2024, 45(2): 1153-1164. doi: 10.1002/pc.27842 [27] KIM G, LEE S, KIM C. Assessment of the physical, mechanical, and tribological properties of PDMS thin films based on different curing conditions[J]. Materials, 2021, 14(16): 4489. doi: 10.3390/ma14164489 [28] ZHUANG J W, LIN Y F, AN G P, et al. Steady superlubricity achieved by epoxy resin composite coatings containing polydimethylsiloxane[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings, 2023, 175: 107361. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2022.107361 [29] 中国国家标准化管理委员会(标准制定单位). 色漆和清漆 划格试验: GB/T 9286—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021.Standardization Administration of the People’s Republic of China. Paints and varnishes—Cross-cut test: GB/T 9286—2021[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2021(in Chinese). [30] SHANG B, WANG Y B, PENG B, et al. Bioinspired polydopamine particles-assisted construction of superhydrophobic surfaces for oil/water separation[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2016, 482(15): 240-251. [31] LI B, BAI J, HE J H, et al. A review on superhydrophobic surface with anti-icing properties in overhead transmission lines[J]. Coatings, 2023, 13(2): 301. doi: 10.3390/coatings13020301 [32] HE Q, XU Y, ZHANG F Y, et al. Preparation methods and research progress of super-hydrophobic anti-icing surface[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2024, 323: 103069. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2023.103069 [33] XIAO T, WEI K, WANG Y D, et al. Transparent and durable PDMS(O)/HDTMS anti-icing surfaces derived from candle soot[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 445: 128717. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128717 [34] QI Y L, YANG Z B, CHEN T T, et al. Fabrication of superhydrophobic surface with desirable anti-icing performance based on micro/nano-structures and organosilane groups[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2020, 501: 144165. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144165 [35] 陈星晖. 纳米TiO2的粒径和形貌对吸附和光催化的影响[D]. 山西: 太原理工大学, 2018.CHEN Xinghui. Effect of particle size and morphology on the adsorption and photocatalytic activity of nanometer TiO2[D]. Shanxi: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [36] XI Y L, YANG Z B, ZHANG J. Fabrication of superhydrophobic bilayer composite coating for roof cooling and cleaning[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 291: 123283. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123283 [37] KANG H X, ZHAO B W, LI L X, et al. Durable superhydrophobic glass wool@polydopamine@PDMS for highly efficient oil/water separation[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2019, 544: 257-265. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.02.096 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 35
- HTML全文浏览量: 15
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: