Preparation and Electromagnetic Absorbing Performance of EPS-Graphene-Cement-based Composites
-
摘要:
为了应对城市建筑空间的电磁辐射威胁,本文研究了多层石墨烯(Multilayer graphene,MG)与发泡聚苯乙烯(Expanded polystyrene,EPS)球形颗粒对水泥基复合材料电磁吸波性能的影响规律,探究了双层平板结构EPS-MG-水泥基复合吸波材料的最优组合,阐述了该复合材料的吸波作用机制。实验结果表明:复合材料中的EPS颗粒在基体内形成了独特的多孔阵列结构,显著增强了材料与自由空间的电磁匹配性能;并且EPS球形颗粒既是透波剂也是谐振腔,在合理的掺量下能与MG搭配形成良好的多孔导电网络,可通过界面极化、电阻损耗以及极化弛豫等方式吸收入射电磁波的能量。在此基础上,通过双层平板组合结构,充分利用密度梯度及层间效应,进一步提高了电磁波能量在传输过程中的耗散作用,实现了结构与材料组分之间良好的协同增强效果,在2~18 GHz的有效吸收带宽达到了7.93 GHz,并获得−18.80 dB的最强吸收峰,具备良好的电磁吸波性能,为低成本建筑吸波材料的发展提供了新思路。
Abstract:In order to cope with the threat of electromagnetic radiation in urban building spaces, the influence law of multi-layer graphene (MG) and expanded polystyrene (EPS) spherical particles on the electromagnetic absorption properties of cementitious composites was investigated. The optimal combination of EPS-MG-cement-based composite wave-absorbing materials with double-layer flat plate structure was explored, and the mechanism of wave-absorbing action of the composites was elaborated. The experimental results showed that the EPS particles in the composites form a unique porous array structure in the matrix, which significantly enhances the electromagnetic matching performance between the material and the free space. Moreover, the EPS spherical particles are both wave-transparent agents and resonance cavities, which can form a good porous conductive network with MG under reasonable doping, and can absorb the energy of the incident electromagnetic wave through interfacial polarization, resistive loss and polarization relaxation. On this basis, this paper makes full use of the density gradient and interlayer effect through the double-layer flat plate combination structure, which further improves the dissipation of electromagnetic wave energy in the transmission process, realizes a good synergistic enhancement effect between the structure and the material components, and the effective absorption bandwidth of 2~18 GHz reaches 7.93 GHz. The maximum absorption peak of −18.80 dB is obtained, which has a good electromagnetic wave absorbing performance, and provides a new idea for the development of wave-absorbing materials for low-cost buildings.
-
聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)是全球用量最大的高分子材料之一,其纤维制品俗称涤纶,是全球第一大化纤品种[1]。但PET属于易燃材料,且其燃烧时还伴有严重的熔滴现象,极易导致火灾蔓延和二次伤害,这为PET的应用带来了极大的安全隐患,也使其在军事、工业等诸多领域的应用受到限制[2]。目前PET阻燃改性的主流方法是引入含磷阻燃剂,但含磷聚酯的阻燃性主要是通过熔体滴落带走燃烧区域的热量和火焰来实现的[3-4],未能解决PET的熔滴问题。因此,同时赋予PET阻燃和抗熔滴特性是目前PET阻燃改性面临的一大难点。
相关研究表明,提高聚合物高温下的熔体黏度和炭化能力是实现阻燃和抗滴落的关键[5-6]。但由于PET分子链的线性结构,其在高温下具有较低的熔融黏度,这一特性在赋予其可纺性的同时,也导致其在燃烧过程中表现出严重的熔滴行为,并难以形成连续的炭层[7]。在PET中引入可交联结构单元是提高熔体黏度的一个有效途径[6, 8]。例如,Wu等[9]合成了一种芳香族席夫碱5-(亚苄基-氨基)-间苯二甲酸二甲酯,并将其用作PET的共聚单体;研究结果显示,芳族席夫碱可以在PET的熔融温度和分解温度之间形成稳定的交联网络,并在燃烧中进一步转变为致密的炭层,因而使得PET共聚酯显示出优异的自熄和抗滴落行为。但尽管上述共聚酯表现出较为理想的阻燃性和抗滴落性能,问题仍然存在。除了工艺复杂、成本高、工业化困难之外,共聚法往往会破坏分子链的规整性,从而损害PET的力学性能和可纺性。
近年来,碳基阻燃剂作为一种新型阻燃剂表现出巨大的发展潜力。研究表明,碳纳米管[10]、富勒烯[11]、纳米炭黑[12]、石墨烯[13]、碳微球[14]等碳基阻燃剂在改善聚合物的成炭质量、降低热释放速率、提高热稳定性等方面表现突出。与传统阻燃剂相比,往往少量碳基阻燃剂的引入即可显著提高聚合物的阻燃性,除此之外,引入碳基阻燃剂还能不同程度地改善聚合物的力学、热学以及电学等性能[15]。其中,碳纳米球(Carbon nanospheres,CNSs)具有无卤环保、粒径小、热稳定性高等优势,能满足PET高温加工和熔融纺丝的理论要求,但迄今为止,将碳基阻燃剂应用于PET的研究较少。
基于此,本文以CNSs为基体,在其表面接枝芳香席夫碱4-苯亚甲基氨基苯酚(4-phenyl-methyleneamino-phenol,BA)制备了一种新型碳纳米球基复合阻燃剂(CNSs-BA),旨在将CNSs和BA的优势有机结合,使阻燃剂同时具备“智能自交联”特性,从而在燃烧时在PET基体中形成三维交联网络,进而改善熔滴。重点研究了CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的阻燃性及其阻燃机制。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
蒸馏水,使用XY-ZL-20型蒸馏水器自制。碳纳米球(CNSs),纯度99.99%,宁波金雷纳米材料科技有限公司;30%过氧化氢,优级纯,上海沃凯生物技术有限公司;硫酸,分析纯,华东医药股份有限公司;二氯甲烷(DCM),分析纯,华东医药股份有限公司;4-苯亚甲基氨基苯酚(BA),纯度98%,东京化成工业株式会社;4-二甲氨基吡啶(DMAP),纯度99%,阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;无水乙醇,分析纯,嘉兴市甬宏化工有限公司;PET切片,半消光型SD500,中国石化仪征化纤股份有限公司。
1.2 CNSs-BA阻燃剂的制备
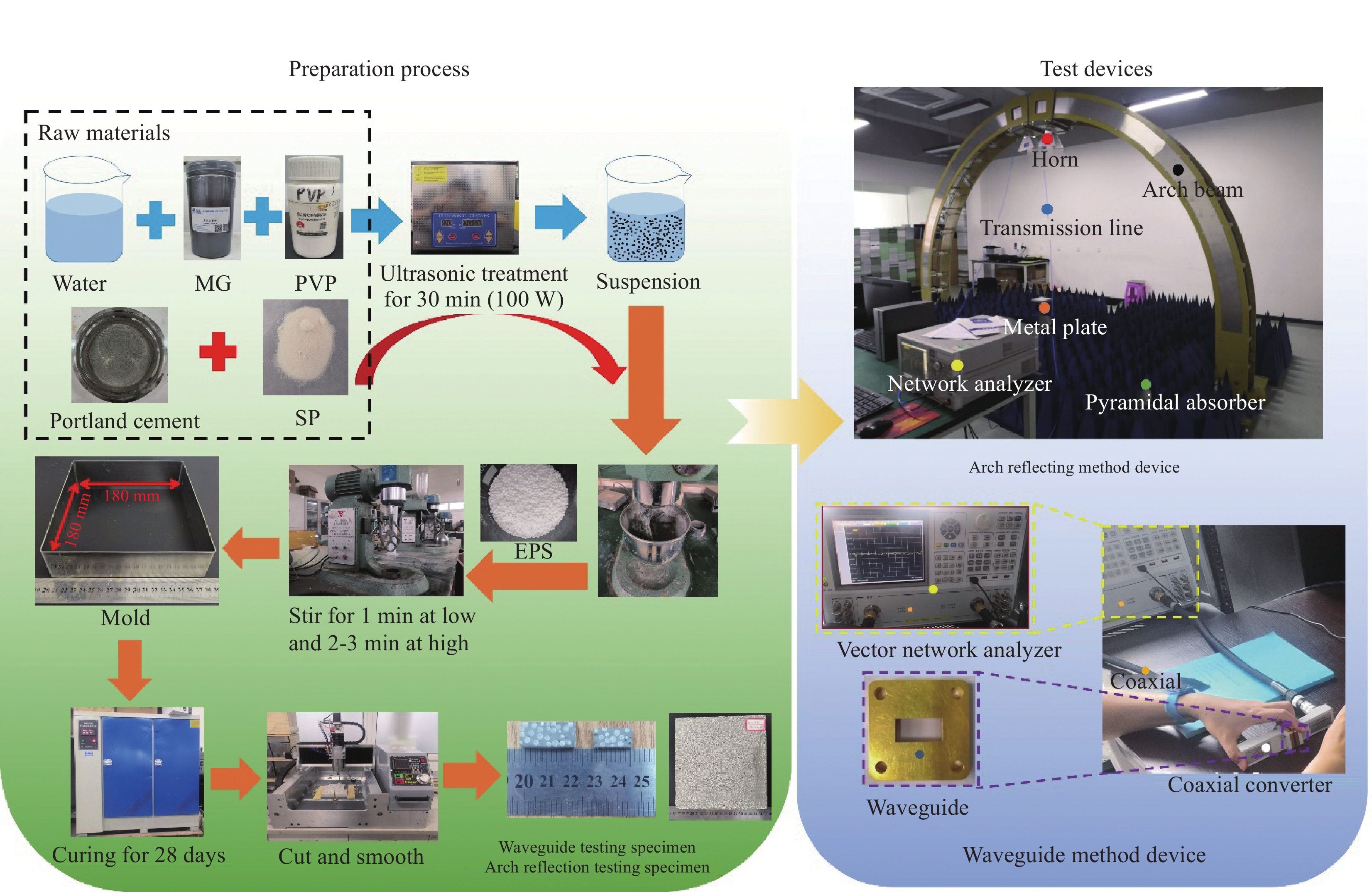
首先采用酸化法[16]制备羧基化碳纳米球(CNSs-COOH);在DCM中加入适量氯化钙,常温振荡12 h以去除其中的水分,使用时用吸管吸取上层液体用。在三口烧瓶中加入一定量的无水DCM (50~100 mL)作为反应溶剂。搅拌状态下加入3 g CNSs-COOH,再加入1 g BA和DMAP (作为碱性催化剂,DMAP的用量为BA用量的1/10),升温至30℃,之后在搅拌状态下反应2 h,反应完成后抽滤除去液体。将反应所得固体依次用乙醇和蒸馏水洗涤,100℃下干燥6 h后研磨均匀,即得CNSs-BA阻燃剂,CNSs-BA的制备示意图见图1。
1.3 CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的制备
首先将纯PET切片和制备的CNSs-BA阻燃剂分别在120℃下真空干燥12 h后冷却至室温备用,然后分别按CNSs-BA占PET的质量分数为0.5wt%、1.0wt%、2.0wt%、3.0wt% 的比例将CNSs-BA与PET切片混合均匀后喂入BP-8188型转矩流变仪(东莞市宝品精密仪器有限公司)中,转矩流变仪各区的温度依次为150、255、273、275℃,转速为35~60 r/min,熔体依次经过熔融共混、挤出、切粒工序得到CNSs-BA/PET复合材料。
1.4 测试与表征
CNSs-BA阻燃剂的测试与表征:用JSM-6510LA型场发射扫描电镜(SEM,日本电子株式会社)和EM420型透射电子显微镜(赛默飞世尔科技)观察阻燃剂的微观形貌,加速电压3 kV 和20 kV。用Perkin Elmer Frontier型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪(FTIR),溴化钾压片法分析测定阻燃剂表面性质和化学结构,光谱记录范围
4000 ~400 cm−1。用Perkin Elmer TG4000型热重分析仪(TG),在N2气氛下测试阻燃剂的热稳定性,气体流速20 mL/min,程序设定为:30℃恒温1 min后以20℃/min的升温速率升温至800℃。CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的测试与表征:用TM606 数显氧指数测试仪(青岛睿新杰仪器有限公司),按照GB/T 2406.2—2009[17]测试PET及其阻燃复合材料的极限氧指数(LOI),样条尺寸为120 mm×6.5 mm×3 mm。用CZF-5水平垂直燃烧仪(沧州冀路试验仪器有限公司),按照 GB/T 2408—2008[18]判定PET及其阻燃复合材料的UL-94垂直燃烧等级,样品尺寸为130 mm×13 mm×3 mm。用C-1087型锥形量热仪(英国FTT),按照ISO 5660-1: 2015[19]测试PET及其阻燃复合材料的燃烧热释放(HRR)等参数,样品尺寸:100 mm×100 mm×3 mm,辐射照度50 kW/m2。用Perkin Elmer TG4000型热重分析仪(TG),在N2气氛下测试PET及其阻燃复合材料(阻燃剂含量2wt%)的热稳定性,气体流速20 mL/min,程序设定为:30℃恒温1 min后以20℃/min的升温速率升温至800℃。用Netzsch STA449F5型同步热分析仪(TG-DSC)研究PET及其阻燃复合材料(阻燃剂含量2.0wt%)的交联行为,氩气做保护气,空气气氛,气体流速20 mL/min,升温速率为10℃/min,测试温度范围为30~800℃。用气相Agilent 6980N色谱仪,Agilent 5975质谱仪,采用HP-5MS色谱柱对PET及其阻燃复合材料(阻燃剂含量2.0wt%)进行裂解-气相色谱-质谱联用(Py-GC-MS)测试。裂解条件:裂解温度750℃,时间20 s,升温速率200℃/s。色谱条件:柱温在50℃保持5 min,然后以10℃/min升温至260℃,在260℃保持10 min;进样温度220℃,传输温度280℃,He做载气,流量1.0 mL/min;裂解产物经色谱柱分离后进入质谱仪,电子能量为70 eV。
残炭的测试与表征:采用SEM观察PET及其阻燃复合材料(阻燃剂含量2.0wt%)燃烧后残炭的形貌,并用其配套的EDS能谱设备对残炭进行元素分析。采用TG在N2气氛下测试残炭的热稳定性,气体流速20 mL/min,程序设定为:30℃恒温1 min后以20℃/min的升温速率升温至800℃。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 CNSs-BA的形貌结构和热稳定性
图2为原CNSs (图2(a))和CNSs-BA (图2(b))的SEM、TEM和EDS能谱图。可知:CNSs和CNSs-BA二者均呈规则的球形颗粒状。不同的是,原始CNSs表面光滑,平均粒径约45 nm。而经BA接枝后,CNSs-BA的表面变得粗糙,平均粒径增大到50 nm左右,由EDS谱图可知:纯CNSs中的主要成分为C元素,与CNSs相比,CNSs-BA的表面增加了N元素,源自其表面接枝的BA中的氨基。
图3是CNSs和CNSs-BA的红外图谱。对比CNSs和CNSs-BA的FTIR曲线可知,在CNSs-BA的红外曲线中,
3330 cm−1和3380 cm−1处对应N—H的伸缩振动峰,2925 cm−1和2850 cm−1处为亚甲基的伸缩振动峰,1450 cm−1处的特征峰是芳环骨架的伸缩振动峰,1269 cm−1处的特征峰是酯基C(O)—O的伸缩振动峰,1045 cm−1处的特征峰是芳环上1, 4位取代的振动峰,以上特征峰源自CMSs表面接枝的BA。图4为CNSs和CNSs-BA的TG曲线。可知:纯CNSs的初始分解温度(Tonset,定义为热失重5wt%时的温度)大于800℃,经BA接枝后Tonset降低到483.1℃,该温度远高于PET的加工温度和热分解温度。纯CNSs和CNSs-BA的最高热分解速率的温度(Tmax)分别为158.4℃和177.4℃,说明CNSs经BA接枝后热分解速率减慢。CNSs在30~800℃之间表现出3个较为明显的失重阶段,338.7℃之前对应CNSs中的少量结晶水和无定形碳的分解,338.7~544.1℃之间对应CNSs主体的热分解,544.1℃之后对应热分解产物的再分解。而CNSs-BA可划分为4个失重阶段:前两个阶段分别对应结晶水、无定形碳、小分子产物的分解以及CNSs-BA主体的分解,值得注意的是,544.1℃之后,CNSs-BA出现一个较为明显的失重峰,而CNSs的DTG曲线上并无该峰,该失重峰的出现证明CNSs表面接枝的BA在第二阶段(PET的熔融温度和分解温度之间)形成了一个较为稳定的交联网络结构,这将十分有助于燃烧时保护炭层的形成。
2.2 复合材料的阻燃性能
表1是CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的LOI和UL-94垂直燃烧测试结果。可知,与CNSs/PET相比,CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的LOI进一步提高,二者LOI规律变化一致,即随着阻燃剂含量的增大,LOI先提高后降低,当CNSs-BA含量为2.0wt%时,CNSs-BA/PET的LOI指数达到最大值28.1%,此时与纯PET相比,CNSs-BA/PET的LOI提高了33.8%。UL-94垂直燃烧测试结果表明,CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的抗熔滴性能较CNSs/PET也有明显提高,两次施加火焰后的余焰时间明显缩短,当CNSs-BA的添加量超过2.0wt%时,CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的阻燃等级可达到V-0级。
表 1 复合材料的极限氧指数(LOI)和UL-94垂直燃烧测试结果Table 1. Limiting oxygen index (LOI) and UL-94 vertical burning test results of compositesSample Flame retardant content/wt% LOI/% UL-94 vertical combustion test results t1/s t2/s t3/s Ignite cotton? Rate PET — 21.0 Burn out — — Yes NR CNSs/PET 0.5 23.2 2.6 2.5 0 Yes V-2 1.0 25.0 2.4 2.4 0 Yes V-2 2.0 26.2 2.4 2.8 0 Yes V-2 3.0 24.6 3.1 2.2 0 Yes V-2 CNSs-BA/PET 0.5 24.0 1.5 2.3 0 Yes V-2 1.0 26.9 1.2 2.1 0 Yes V-2 2.0 28.1 0.5 2.2 0 No V-0 3.0 27.5 0.6 1.9 0 No V-0 Notes: PET—Polyethylene terephthalate; t1—Afterglow time after the first application of flame; t2—Afterglow time after the second application of flame; t2—Afterglow time; NR—No rate. 锥形量热仪测试结果见图5和表2。热释放速率(HRR)是表征材料火灾危险性的主要依据。结合图5和表2可知,纯PET被点燃后热释放速率急剧增大,其峰值热释放速率(pk-HRR)为810.45 kW/m2,总热释放(THR)为150.27 MJ/m2。与之相比,CNSs-BA/PET的THR与之接近,但HRR曲线却明显变平缓。值得注意的是,CNSs-BA/PET的HRR曲线表现出两个明显的热释放阶段,即在热释放速率达到峰值之后又出现了一个较为平缓的放热平台(当CNSs-BA含量为0.5wt%时表现为放热峰),这意味着CNSs-BA/PET在燃烧过程中的热释放受到抑制,这是由燃烧时炭层的形成或可燃气体减少导致的[20]。此外,表2表明,与CNSs/PET相比,CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的pk-HRR进一步降低。当CNSs-BA 含量为2.0wt%时,CNSs-BA/PET的pk-HRR最小,为435 kW/m2,该值与相同阻燃剂含量的CNSs/PET相比降低了7.6%,较纯PET降低了46.3%,说明CNSs经BA接枝后对PET的燃烧抑制作用进一步增强,阻燃效果进一步提高。
表 2 复合材料的锥形量热仪测试数据Table 2. Data of cone calorimeter test of compositesSample FR content/wt% TTI/s Time to pk-HRR/s pk-HRR/(kW·m−2) THR/(MJ·m−2) PET 0 47 104 810.45 150.27 CNSs/PET 0.5 44 34 528.96 151.64 1 34 34 503.44 148.03 2 40 41 470.72 146.06 3 30 29 501.49 143.19 CNSs-BA/PET 0.5 35 39 485.54 146.54 1 31 55 469.98 156.04 2 34 39 435.00 146.54 3 30 39 466.05 156.69 Notes: TTI—Time to ignition; pk-HRR—Peak heat release rate; FR—Flame retardant. 2.3 复合材料的阻燃机制研究
2.3.1 阻燃复合材料的热重分析
为了研究阻燃剂的引入对PET的热降解行为的影响,对PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET在氮气气氛下的TG-DTG曲线作了对比分析,并计算了CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET在500℃时残炭量的理论值,如图6和表3所示。由图6可知:在氮气气氛下,PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET三者的TG曲线和DTG曲线基本重合,说明加入少量(2.0wt%)的CNSs和CNSs-BA均不会对PET的无氧降解行为造成明显影响。由表4可知,PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET三者的Tonset和Tmax均较为接近,但三者在高温(500℃)下的残余质量有所不同。经计算发现CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET二者在高温下残炭量的实际值(CR500℃,exp)均大于理论值(CR500℃,cal),这说明阻燃剂CNSs和CNSs-BA对PET均有促进成炭作用。其中,CNSs-BA/PET在500℃下残炭量的实际值与理论值的差值(∆CR500℃)大于CNSs/PET,这说明CNSs经BA接枝后对PET的促进成炭作用加强。聚合物在高温下形成的残炭越多,燃烧时发生热分解的部分就越少[21],这便是阻燃复合材料热释放速率降低的主要原因之一。
表 3 CNSs、CNSs-BA以及PET、CNSs/PET、CNSs-BA/PET在氮气气氛下的TG-DTG数据Table 3. TG-DTG data of CNSs, CNSs-BA, PET, CNSs/PET and CNSs-BA/PET under nitrogen atmosphereSample Tonset/℃ Tmax/℃ CR500℃/% ∆CR500℃/%c exp.a/cal.b CNSs >800 — 96.88/— — CNSs-BA 476.4 — 94.92/— — PET 379.1 419.1 10.09/— — CNSs/PET 380.1 421.4 13.97/11.52 2.45 CNSs-BA/PET 382.0 420.1 15.68/11.79 3.89 Notes: a CR500℃,exp. is the experimental value of char residue; b CR500℃,cal. is the calculated value of char residue; c ∆CR500℃=CR500℃,exp.−CR500℃,cal.. 表 4 PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET在空气气氛下的TG-DTG数据Table 4. TG-DTG data of PET, CNSs/PET and CNSs-BA/PET under air atmosphereSample Tonset/℃ Tmax-1/℃ Tmax-2/℃ PET 397.3 433.4 585.1 CNSs/PET 359.1 438.4 567.5 CNSs-BA/PET 391.0 439.7 563.3 Notes: Tmax-1—Maximum weightlessness temperature in the first stage; Tmax-2—Maximum weightlessness temperature of the second stage. 2.3.2 残炭分析
对纯PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET锥形量热仪测试后的残炭做了SEM和TG分析以进一步研究阻燃机制。
炭层的形貌结构和稳定性对于提高聚合物的阻燃性能至关重要,有效的炭层可通过阻止聚合物内部与可燃气体、氧气的接触来实现阻燃目的。图7为纯PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET炭层的SEM图像。可见,纯PET燃烧生成的炭层稀薄空且松散,表面存在大量气体逸出形成的气孔,显然这种形貌的炭层无法形成有效的屏障作用。与纯PET相比,CNSs/PET的炭层的致密性明显提高,气孔明显变小,意味着炭层有效性的提高。值得注意的是,与CNSs/PET相比,CNSs-BA/PET炭层的致密性和连续性得到了进一步改善,表面气孔也明显变少和变小,另外还存在大量鼓起的未破裂气泡,这种形貌的炭层在燃烧时一方面能有效地阻隔热量的传递,另一方面还能有效地阻隔PET燃烧降解生成的气态可燃物的逸出,起到隔热和隔氧的作用[22-23]。除此之外,CNSs-BA受热分解生成的CO2、氨气、氮气等难燃性气体能够稀释燃烧区域可燃气体的浓度,抑制燃烧的发展,这便是CNSs-BA/PET阻燃性提高的重要原因。
图8是PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET炭层的TG曲线。可知,纯PET炭层的Tonset较低,为215.08℃,其中100℃前失重为4.36wt%,这主要是由于纯PET的炭层结构松散、孔洞较多,容易吸收水分和储存小分子气体所致,其800℃时的残余质量为87.2wt%。在整个升温过程中,纯PET的炭层表现出3个失重阶段,第一个失重阶段发生在100℃之前,主要对应炭层中贮存的水分以及气态小分子的降解;第二个失重阶段发生在100~530℃之间,对应炭层主体部分的降解;第三个失重阶段发生在530℃之后,对应炭层热降解产物的再降解。与之相比,CNSs/PET炭层的Tonset提高到615.37℃,800℃时的残余质量提高到89.1wt%,这主要是由于CNSs/PET的炭层的致密性提高所致,其TG曲线基本保持了纯PET炭层的3个失重阶段。与PET和CNSs/PET的炭层相比,CNSs-BA/PET炭层的Tonset提高到800℃以上,意味着炭层在燃烧时能耐受更高的温度,从而更持久有效地起到凝聚相阻燃作用。值得注意的是,其炭层在热分解过程中只有一个较为明显的失重平台,并未像PET和的CNSs/PET的炭层一样经历3个失重阶段,说明阻燃剂CNSs-BA能使PET燃烧生成结构稳定的炭层,该炭层在燃烧过程中能耐受较高的火焰温度,从而对内部的基体起到持久有效的保护作用。
2.3.3 交联行为分析
聚合物的交联直接影响其热性能、流变性、成炭性、熔滴和自熄行为,并有助于聚合物的芳香化或炭化[24]。图9是PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET在热氧降解过程中的TG-DSC曲线,相关数据见表4。由图9可以看出,PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET在空气中均有两个失重阶段,说明PET及其复合材料发生的是两步降解反应[25]。第一个失重阶段是PET的主要失重阶段,发生在360~470℃之间。第二个失重阶段发生在470~590℃之间,该阶段对应第一个降解阶段生成的降解产物的进一步降解。值得注意的是,纯PET的Tonset为397.3℃,而PET的燃点通常在420℃左右,这说明PET在燃烧之前,首先会发生一定程度的降解并生成一些可燃性的气体或挥发性产物,以此来维持燃烧的进行。与纯PET相比,在第一个失重阶段,CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET的热失重曲线稍向低温方向移动,但二者在第一个降解阶段结束时的剩余质量却大于PET,且该阶段的最大失重率所对应温度(Tmax-1)大于PET,说明阻燃剂的存在使PET的主体降解提前,但在该阶段却重组生成了热稳定性较高的物质。DSC曲线表明,CNSs-BA/PET在熔融峰和分解峰之间出现了明显的放热峰,该峰是PET的交联峰[26],而在PET和CNSs/PET的DSC曲线上交联峰却不明显,这说明CNSs经BA接枝改性后促进了PET的交联,这是由于阻燃剂表面接枝的芳香族席夫碱(BA)可以在PET的熔融温度和分解温度之间形成稳定的交联网络。
2.3.4 高温裂解产物分析
裂解-气相色谱-质谱联用(Py-GC-MS)是目前研究聚合物高温裂解产物的常用方法[27]。为了研究阻燃剂的引入对PET的热裂解行为及其高温裂解产物的影响,对PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET做了Py-GC-MS分析,三者的高温裂解产物对比见表5。可知,与纯PET的裂解产物相比,CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET的裂解产物中都包含更多的杂环、稠环、共轭芳环类化合物,这些裂解产物具有较高的热稳定性,是难燃性的保护炭层形成的物质基础[28]。而CNSs-BA/PET的裂解产物中出现了诸如二甲基胺、偶氮苯等含氮产物,这是由于阻燃剂CNSs-BA表面接枝的苯亚甲基氨基苯酚所致。另外,与PET和CNSs/PET相比,CNSs-BA/PET的裂解产物中菲、萘、苊、芴等稠环芳烃类以及联苯类产物明显增多,佐证了CNSs-BA促进了PET降解过程中的交联,该交联一方面通过增大熔体黏度改善了熔滴现象,另一方面提高了炭层的致密性和热稳定性,这就是CNSs-BA/PET阻燃性和抗熔滴性提高的主要原因。
表 5 PET、CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET裂解产物Table 5. Pyrolysis products of PET, CNSs/PET and CNSs-BA/PETPyrolysis products which found only in PET Tetrahydropyran; 2,2-dimethylpropanal; 4,8,12-trimethyl-tridecanoic acid methyl ester; 2,2-dimethoxybutane; 2-methyl-1,5-hexadien-3-yne; 1,6-heptadiyne; p-xylene; Decane; Methyl benzoate; Dodecylethyl ketone; 1-(3-methylphenyl)benzyl(2-methyl-1-methylenepropylidene); 4-methylphenyl-1-pentyn-3-ol phenol; Dimethyl 1,3-benzenedicarboxylate; Vinylmethyl terephthalate; Diphenylacetylene; Biphenyl-4-ylacetophenone; 1-(5,5-dimethyl-1,3-dioxocyclohexan-2-ylidene)-2-(N-ethylbenzothiazol-2-ylidene)-ethanes; Phthalic acid 4-formylphenyl ester; o-tertiaryl tricyclic [8.2.2.2(4,7)]hexadeca-2,4,6,8,10,12,13,15-octene; 4-(diethylaminomethyl)-2,5-dimethylphenol Pyrolysis products which found only in CNSs/PET Phenol; 1,2-dihydro-indene; 1-(4-methylphenyl)-ethanone; Stilbene; 1H-cyclopropyl[l]phenanthrene; Dihydro-p-terphenyl; 1-naphthol; Fluorene-9-methanol; 2-ethyl-1,1'-biphenyl; 1,1-diphenylethene; 4-(2-benzoyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl)-1,2-dihydrophenanthrene; 2-phenylnaphthalenyl benzoate; 1,1-dihydro-2-phenylnaphthalenyl benzoate; 3-chlorobenzylnonyl; 1-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)ethanone; 1-(2,5-dimethylphenethyl) ethanone; Dimethyl-1H-indene; Diethylmalonic acid; 3-chlorobenzylnonyl ester Pyrolysis products which found only in CNSs-BA/PET 1,5-hexadiyne; Dimethylamine; Nitrous oxide; 1,1'-(1,4-phenylene)bis-acetophenone; 2-methylindene; Azobenzene; Benzene; (1-methyl-2-cyclopropen-1-yl)-2-methylindene; Stilbene; Ethylketone; 1-(3,4-dimethylphenyl); 1-(4-methylphenyl); 1-ethenyl-4-methylbenzene; Dibenzofuran; 2-naphthol; 4-hydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthrene; 9,10-dihydrophenanthrene; Benzopropiophenone; Fluorene; 4-vinylbiphenyl; 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrofil; 9,10-dihydrofil; 4-vinylbiphenyl; 1,4-vinylbiphenyl; Phenylacetone; 1,3,5-cycloheptatriene; 2-phenylnaphthalene; 1-acrylbenzene; 2-methylnaphthalene; 4-(2-benzoyl-5-phenyl-3-thienyl)-methylbenzoic acid; 1,3-dimethyl-1H-indene; Tricyclohexen-8-ol; Hexaethylcyclohexane; 9-phenyl-9-fluorenol; Ethylene oxide; Methoxyphenyltricyclohexadecen-5-ylmethanol; 4-benzylbiphenyl; Tritylbenzene; 9-phenylanthracene; 3-(1-phenylethoxy)-3H-isobenzofuran-1-one; 4-phenyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinoline; Oxetane; 2-phenyl; 3-phenylethynyl; Tetraphenyl; 1-[4-(2-phenylethenyl)phenyl]-ethanone; Acenaphthene; 1,2,3,5-tetraisopropyl-cyclohexane; 6,9-dimethoxy-phenazine-1-carboxylic acid; [1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl-phenylmethanone; 1,1':4',1''-3'-methyltriphenylene Pyrolysis products which found both in PET and CNSs/PET Acetophenone; Benzoic acid; Biphenyl; 2-methyl-1,1'-biphenyl; 1,1'-(1,4-phenylene)bisacetophenone; p-terphenyl Pyrolysis products which found both in PET and CNSs-BA/PET Styrene; Acetophenone; Benzoic acid; Biphenyl; 2-ethyl-1,1'-biphenyl; Benzophenone; 9H-fluoren-9-one; p-terphenyl Pyrolysis products which found both in CNSs/PET and CNSs-BA/PET Benzene; Biphenyl; Acetophenone; Naphthalene; Toluene; Phenanthrene; Indene; 6,6-diphenylfulvene; p-terphenyl; Methylstyrene; Biphenylacetophenone; 4-ethylbiphenyl; Diphenylmethane Pyrolysis products found in PET, CNS/PET and CNSs-BA/PET Acetophenone; Benzoic acid; Biphenyl; p-terphenyl 2.4 复合材料的力学性能
图10为PET阻燃复合材料的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率图。可知,随着阻燃剂含量的增加,CNSs/PET和CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率均呈下降趋势。尤其是当阻燃剂含量超过2.0wt%时,PET复合材料的抗拉强度和断裂伸长率大幅度下降。这是由于高含量的阻燃剂在PET基体中形成了较大的团聚体,破坏了基体的连续性,阻碍了应力的传递所致,后续研究中应重点关注材料力学性能的改善。
3. 结 论
(1)为同时改善聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯(PET)的阻燃性和抗熔滴性,在碳纳米球表面接枝4-苯亚甲基氨基苯酚制备了一种新型碳基复合阻燃剂(CNSs-BA)。CNSs-BA为粒径约50 nm的球形颗粒,热稳定性良好。
(2) CNSs-BA的引入可显著提高PET的阻燃性和抗熔滴性。当CNSs-BA添加量为2.0wt%时,CNSs-BA/PET复合材料的极限氧指数(LOI)从PET的21.0%提高至28.1%,阻燃等级达到V-0级,热释放速率峰值降低了46.3%。
(3) CNSs-BA/PET表现出典型的凝聚相阻燃机制。CNSs-BA的引入能促进PET成炭,CNSs-BA/PET的高温残炭量(CR500℃)比PET提高了55.4%,且成炭量的实际值大于理论值。与纯PET的炭层相比,CNSs-BA/PET燃烧生成的炭层的致密性、连续性以及热稳定性都显著提高。这是由于CNSs-BA的引入促进了PET的高温交联,使其高温降解生成了更多的难燃性焦炭物质。
(4)本文为碳基阻燃剂的发展提供了重要理论补充,对开发无卤、阻燃、抗熔滴的PET材料具有一定的指导意义。
-
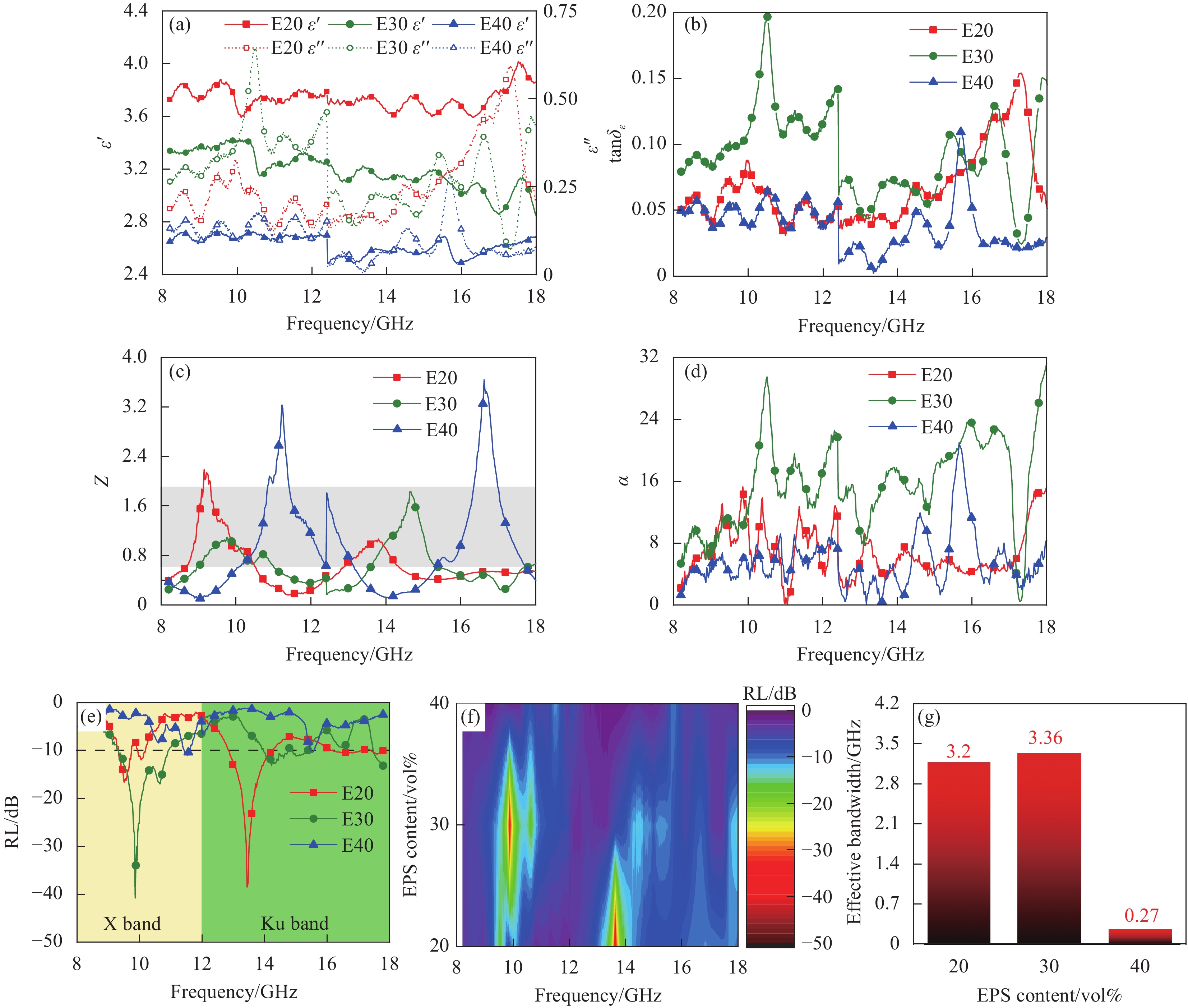
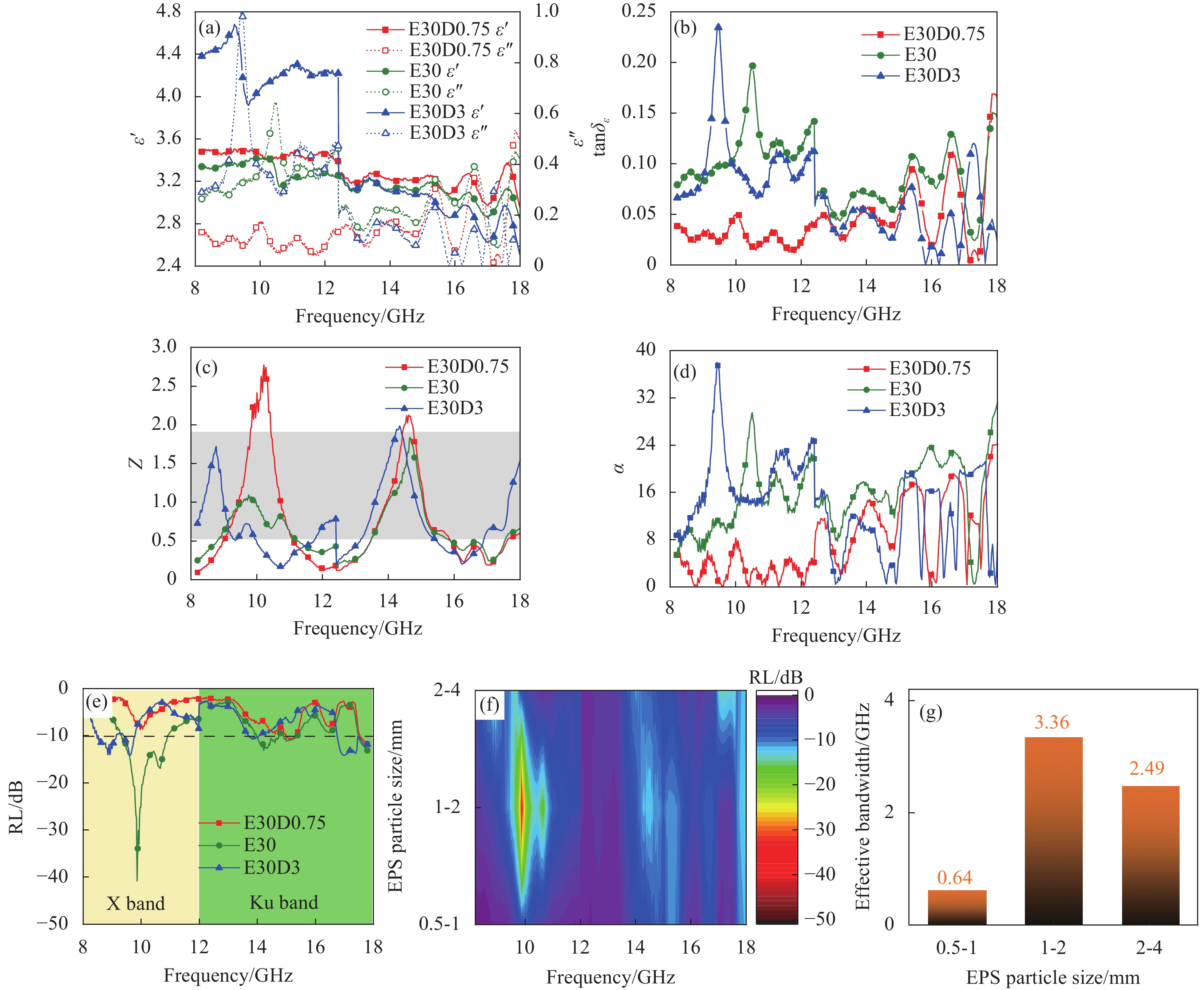
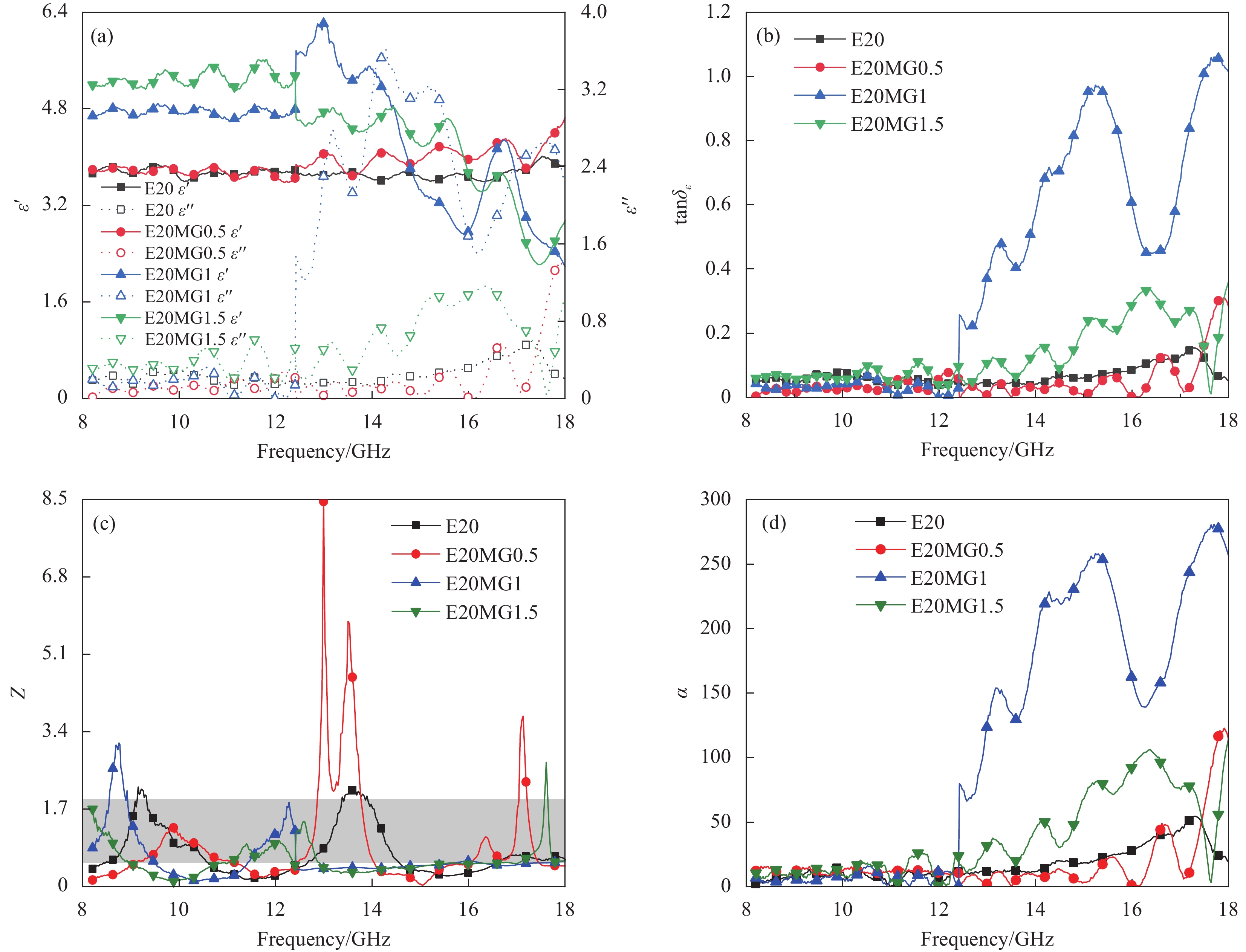
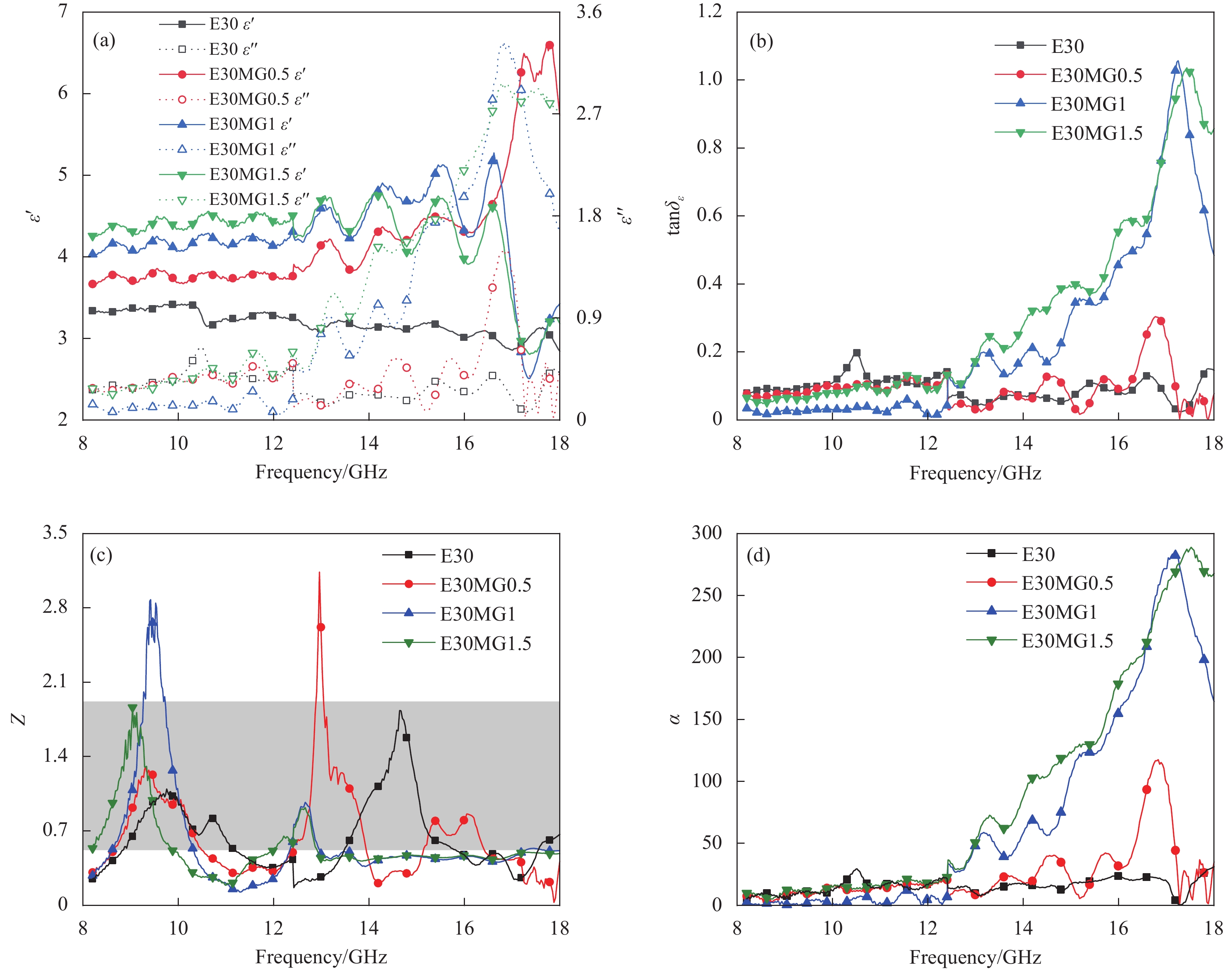
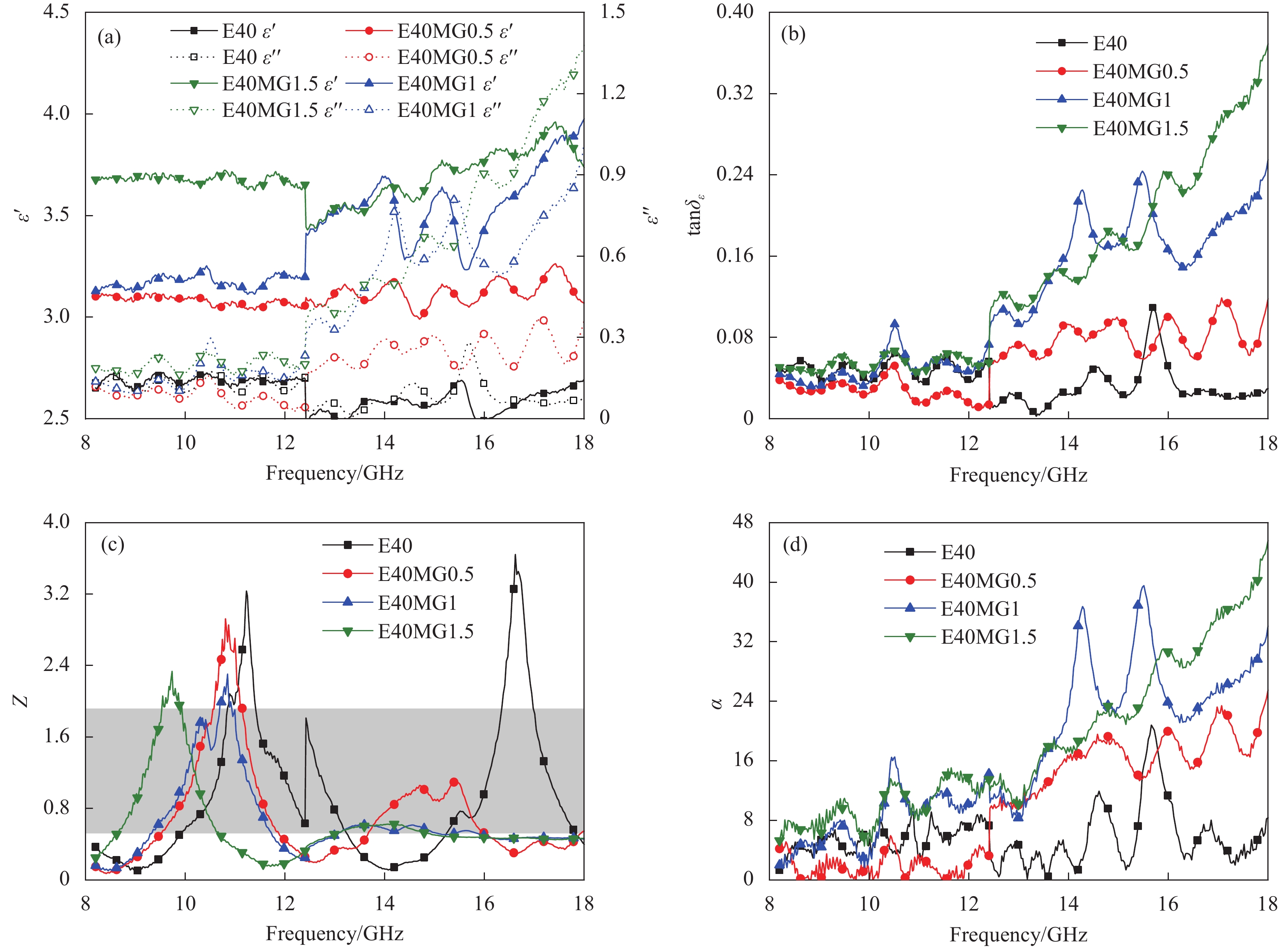
图 4 不同EPS粒径复合材料的(a)介电常数;(b)介电损耗角正切;(c)归一化阻抗;(d)衰减系数;(e) RL曲线图;(f) RL等高线图;(g)有效带宽
Figure 4. (a) Permittivity; (b) Dielectric loss tangent; (c) Normalized impedance; (d) Loss coefficient; (e) RL curve diagram; (f) RL contour map; (g) Effective bandwidth of absorbing composites with different EPS particle size
图 9 双层结构EPS-MG-水泥基复合吸波材料的(a)结构示意图和(b)不同EPS掺量及厚度组合试件的吸波性能;(c) E30+E30 MG1.5试件的理论计算与实测RL对比图
Figure 9. (a) Structure diagram of the double-layer EPS-MG-cement-based composite absorbing material and (b) the absorbing properties of the combined specimens with different EPS content and thickness; (c) Comparison of calculated and experimental RL values of E30+E30 MG1.5
表 1 多层石墨烯(MG)的主要性能参数
Table 1 Main properties of Multilayer graphene (MG)
Size Layer Purity Thickness Carbon content 5~50 μm 5~10 >95% 3.4~8 nm <97% 表 2 发泡聚苯乙烯(EPS)-MG-水泥基复合吸波材料试样配比
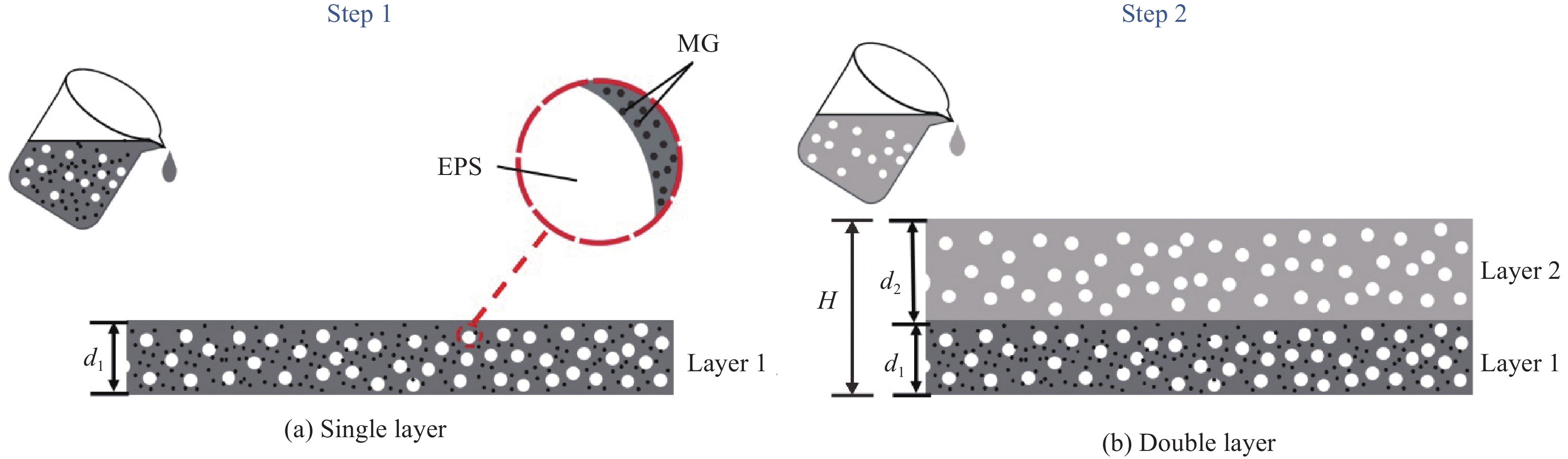
Table 2 Expanded polystyrene (EPS)-MG-cement-based composite wave-absorbing material specimen proportioning
Sample Cement/g W: C EPS/vol.% MG/wt.% EPS particle size range/mm SP/g E20 276.80 0.40 20 / 1~2 0.14 E30 242.20 0.40 30 / 1~2 0.12 E40 207.60 0.40 40 / 1~2 0.10 E30D0.75 242.20 0.40 30 / 0.5~1 0.12 E30D3 242.20 0.40 30 / 2~4 0.12 E20MG0.5 276.80 0.40 20 0.50 1~2 0.14 E20MG1 276.80 0.40 20 1.0 1~2 0.14 E20MG1.5 276.80 0.40 20 1.5 1~2 0.14 E30MG0.5 242.20 0.40 30 0.50 1~2 0.12 E30MG1 242.20 0.40 30 1.0 1~2 0.12 E30MG1.5 242.20 0.40 30 1.50 1~2 0.12 E40MG0.5 207.60 0.40 40 0.50 1~2 0.10 E40MG1 207.60 0.40 40 1.0 1~2 0.10 E40MG1.5 207.60 0.40 40 1.50 1~2 0.10 Notes: E—EPS; D—particle size of EPS; W: C represents the mass ratio of water to the cementitious material. The particle size of the unlabeled D value is unified as 1~2 mm. 表 3 不同EPS粒径下复合吸波材料的波速、RL及输入阻抗
Table 3 vm, nr and Zin of absorbing composites with different EPS particle size
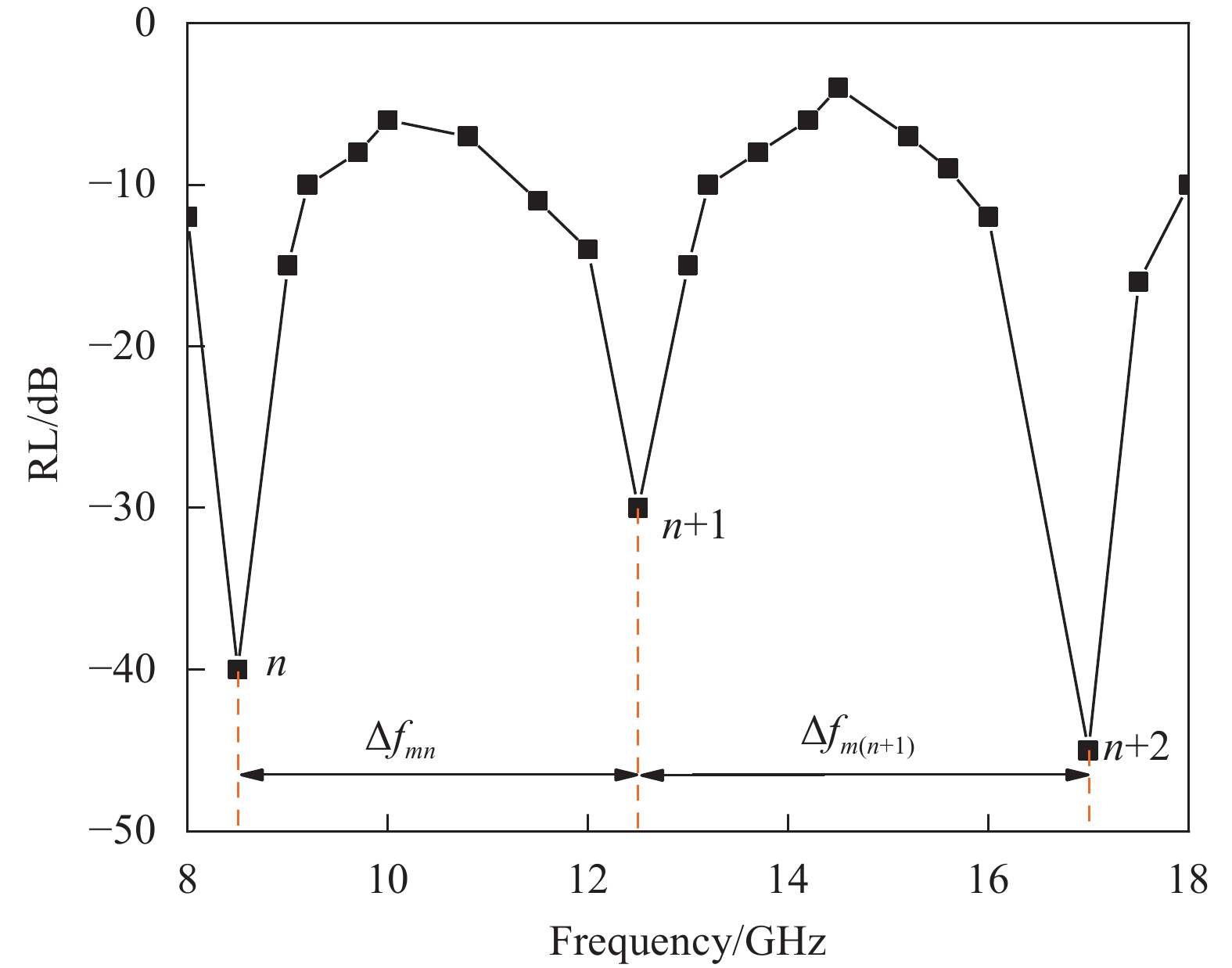
EPS particle size fm1~fm5 Δfm1~Δfm4 0.5~1 mm 9.96 14.79 15.33 16.65 / 4.83 0.54 1.32 / 1~2 mm 9.86 10.64 14.40 16.65 / 0.78 3.76 2.25 / 2~4 mm 8.91 9.61 14.04 17.16 17.58 0.70 4.43 3.12 0.42 EPS particle size vm1~vm4 Average vm SD* nr Zin 0.5~1 mm 1.93 0.22 0.53 / 0.89 0.74 3.37 111.87 1~2 mm 0.31 1.50 0.90 / 0.90 0.49 3.33 113.21 2~4 mm 0.28 1.77 1.25 0.17 0.87 0.67 3.45 109.28 Notes: fmn denotes frequency corresponding to the nth coherent peak in the range of 8~18 GHz; Δfmn and vmn denotes the bandwidth and wave velocity between fm and fm(n+1), respectively; SD* are the standard deviation of the wave velocity. -
[1] XIA Y X, GAO W W, GAO C. A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(42): 2204591. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202204591
[2] LI Y, LIU J L, JIN C Y, et al. Experimental study and mechanism analysis of functional nanocrystalline cellulose to improve the electromagnetic transmission performance of ordinary Portland cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2023, 143: 105272. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2023.105272
[3] LU Y H, ZHANG S L, HE M Y, et al. 3D cross-linked graphene or/and MXene based nanomaterials for electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding[J]. Carbon, 2021, 178: 413-435. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.01.161
[4] LI X L, YIN X W, SONG C Q, et al. Self-assembly core-shell graphene-bridged hollow MXenes spheres 3D foam with ultrahigh specific EM absorption performance[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(41): 1803938. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201803938
[5] WANG Z Y, WANG Z, NING M. Optimization of electromagnetic wave absorption bandwidth of cement-based composites with doped expanded perlite[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 259: 119863. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119863
[6] LI C F, ZHOU C X, LV J B, et al. Bio-molecule adenine building block effectively enhances electromagnetic interference shielding performance of polyimide-derived carbon foam[J]. Carbon, 2019, 149: 190-202. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.04.012
[7] MA G W, SUN J B, WANG L, et al. Electromagnetic and microwave absorbing properties of cementitious composite for 3D printing containing waste copper solids[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 94: 215-225. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.09.005
[8] DENG S, WANG B M, AI H M, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties and mechanism of graphene/Ni0.4Zn0.6Fe2O4 cement composites[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2022, 34(7): 04022142. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004264
[9] HE Y J, LU L N, SUN K K, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorbing cement-based composite using Nano-Fe3O4 magnetic fluid as absorber[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2018, 92: 1-6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2018.05.004
[10] 李宝毅, 段玉平, 刘顺华. 多孔集料砂浆的吸波特性[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2011, 39(10): 1682-1686. LI B Y, DUAN Y P, LIU S H. Absorbing properties of cement mortar filled with porous aggregates[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cement Society, 2011, 39(10): 1682-1686(in Chinese).
[11] 岑思谨. 碳微球/铁-钴合金/钴铁氧体@空心微珠吸波材料的制备与性能, 华南理工大学, 2021. CEN S J. Preparation and properties of carbon microspheres/ iron-cobalt alloy/cobalt ferrite @ hollow microspheres microwave absorbing materials[D]. South China University of Technology, 2021(in Chinese).
[12] XIE S, JI Z J, ZHU L C, et al. Recent progress in electromagnetic wave absorption building materials[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2020, 27: 100963. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100963
[13] 刘思遥, 王旱雨, 刘兵兵, 等. 损耗型吸波材料与水泥基复合吸波材料的制备及性能调控研究现状[J]. 化工新型材料, 2024, 52(2): 288-293. LIU S Y, WANG H Y, LIU B B, et al. Research status of preparation and performance regulation of loss-typewave-absorbing materials and cement-based composite wave-absorbing materials[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2024, 52(2): 288-293(in Chinese).
[14] 王晓冉. 基于碳纳米管纤维水泥基材料的吸波超结构[D], 浙江大学, 2023. WANG X R. Electromagnetic wave absorbing metastructure based on carbon nanotube fiber reinforced cementitious composites[D]. Zhejiang University, 2023(in Chinese).
[15] DENG G, YANG Y Y, ZHOU Q, et al. Lightweight and broadband electromagnetic wave absorbing foamed cement-based composites incorporated with hybrid dielectric fibers[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2022, 327: 126931. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126931
[16] Ren M M, Li F X, Gao P, et al. Design and preparation of double-layer structured cement-based composite with inspiring microwave absorbing property[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 263: 120670. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120670
[17] 解帅, 冀志江, 水中和, 等. 网格表面结构石膏基材料的电磁波吸收性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(1): 156-162. XIE S, JI Z J, SHUI Z H, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of gypsum-based materials with grid structure[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 46(1): 156-162(in Chinese).
[18] HU J H, LIU Y Y, JIANG J L, et al. Development of electromagnetic microwave absorbers in cementitious materials[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 312.
[19] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 固体材料微波频段使用波导装置的电磁参数测量方法: GBT356792017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Measuring method for electromagnetic parameters of solid materials at microwave frequencies using waveguide[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017(in Chinese).
[20] 国防科学技术工业委员会. 雷达吸波材料反射率测试方法[S]. 1994. Commission of Sicience, Technology and Industry for National Defense. Methods for measurement of reflectivity of radar absorbing material[S]. 1994(in Chinese).
[21] 张秀芝, 郑沛祺, 陶文宏, 闫孝伟, 黄京立, 王嘉伟, 翟云芳. 纳米吸波剂改性水泥基材料研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2023, 51(5): 1363-1372. ZHANG X Z, ZHENG P Q, TAO W H, et al. Research progress on ano-absorber modified cement-based wave absorbing material[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 51(5): 1363-1372(in Chinese).
[22] BAI Y H, XIE B, LI H W, et al. Mechanical properties and electromagnetic absorption characteristics of foam cement-based absorbing materials[J]. Construction and Building. Materials, 2022, 330: 127221. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127221
[23] ZHANG W, ZHENG Q F, WANG D N, et al. Electromagnetic properties and mechanisms of multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified cementitious composites[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 208: 427-443. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.029
[24] ZHANG L Q, LI L W, WANG Y L, et al. Multifunctional cement-based materials modified with electrostatic self-assembled CNT/TiO2 composite filler[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 238: 11787.
[25] 张月芳, 郝万军, 刘顺华. 频率选择表面对PET水泥基材料吸波性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(1): 118-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.019 ZHANG Y F, HAO W J, LIU S H. Effect of frequency selective surface on microwave absorbing properties of PET cement-based materials[J]. Journal of Buiding Materials, 2018, 21(1): 118-123(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2018.01.019
[26] 赵彦波, 刘顺华, 管洪涛. 水泥基多孔复合材料吸波性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2006, 34(2): 225-228. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2006.02.019 ZHAO Y B, LIU S H, GUAN H T. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of cement-based composite filled with expanded polystyrene[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2006, 34(2): 225-228(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2006.02.019
[27] MA C, XIE S, WU Z H, et al. Research and simulation of three-layered lightweight cement-based electromagnetic wave absorbing composite containing expanded polystyrene and carbon black[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 393: 132047. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132047
[28] LIU X, WANG Z, WANG N, et al. Effects of EPS, Mn-Zn ferrite, and layers on the electromagnetic absorption performance of magnesium phosphate cement[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 2023, 35(2): 04022430. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004593
[29] LV X J, DUAN Y P, CHEN G Q. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of cement-based composites filled with graphene nano-platelets and hollow glass microspheres[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 162: 280-285. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.12.047
[30] BARBER P W. Absorption and scattering of light by small particles[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 1984, 98(1): 290-291.
[31] 杨喜, 曹敏, 简煜, 等. 多孔木炭Fe3O4复合吸波材料的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10): 4591-4601. YANG X, CAO M, JIAN Y, et al. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of porous charcoal/ Fe3O4 composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(10): 4591-4601(in Chinese).
[32] 刘佳良, 徐东卫, 陈平. 磁性多孔rGO@Co/CoO复合材料的制备和吸波性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2022, 36(5): 333-342. LIU J L, XU D W, CHEN P. Preperation and microwave absorption properties of magnetic porous rGO@Co/CoO composites[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Resarch, 36(5): 333-342(in Chinese).
[33] MA C, XIE S, JI Z J, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorbing properties of pyramidal engineered cement mortar containing carbon black[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2024, 84: 108618. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2024.108618
[34] LI B, JI Z J, XIE S, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon black/cement-based composites filled with porous glass pellets[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(13): 12416-12425. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-019-01600-w
[35] XU H L, YIN X W, LI M H, et al. Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with red blood cell like morphology for efficient microwave absorption at elevated temperature[J]. Carbon, 2018, 132: 343-351. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.02.040
[36] QIAO J, ZHANG X, XU D M, et al. Design and synthesis of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 380: 122591. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122591
[37] FENG L, LI W C, WANG Y. Broadband electromagnetic wave absorbing metamaterial based on FeSiAl alloy[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2022, 541: 168510. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168510
[38] LI W C, LI C S, LIN L H, et al. All-dielectric radar absorbing array metamaterial based on silicon carbide/carbon foam material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 781: 883-891. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.010
[39] ZHOU D F, YUAN H, YU Z R, et al. Broadband electromagnetic absorbing performance by constructing alternate gradient structure (AGS) for PMMA-based foams[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2021, 149: 106557. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106557
[40] LI M H, FAN X M, XU H L, et al. Controllable synthesis of mesoporous carbon hollow microsphere twined by CNT for enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2020, 59: 164-172.
[41] ZHAO B, DENG J S, ZHAO C X, et al. Achieving wideband microwave absorption properties in PVDF nanocomposite foams with an ultra-low MWCNT content by introducing a microcellular structure[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(1): 58-70. DOI: 10.1039/C9TC04575A
[42] SUN X X, LI Y B, HUANG Y X, et al. Achieving super broadband electromagnetic absorption by optimizing impedance match of rGO sponge metamaterials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 32(5): 2107508.
[43] CAO M S, WANG X X, ZHANG M, et al. Electromagnetic response and energy conversion for functions and devices in low-dimensional materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(25): 1807398. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201807398
-
其他相关附件
-
本文图文摘要
点击下载
-
-
目的
为了应对城市建筑空间的电磁辐射威胁,研发具有良好性能的建筑电磁吸波材料。本文研究了多层石墨烯(Multilayer graphene,MG)与发泡聚苯乙烯(Expanded polystyrene,EPS)球形颗粒对水泥基复合材料电磁吸波性能的影响规律,探究了双层平板结构EPS-MG-水泥基复合吸波材料的最优组合,阐述了该复合材料的吸波作用机制。
方法本文以普通硅酸盐水泥为基体,MG作为吸波剂,EPS球形颗粒作为透波和谐振组分,以提高电磁波吸收性能。利用波导法和拱形反射率法测试样品电磁参数及反射损耗(),并通过模拟计算得到相应的阻抗匹配、衰减系数和有效带宽值。分别研究了MG掺量、EPS体积掺量及粒径大小,以及双层平板组合结构对复合材料吸波性能的影响规律。并结合Cole-Cole半圆曲线图和Smith圆图分析并讨论双层EPS-MG-水泥基复合材料吸波作用机制。
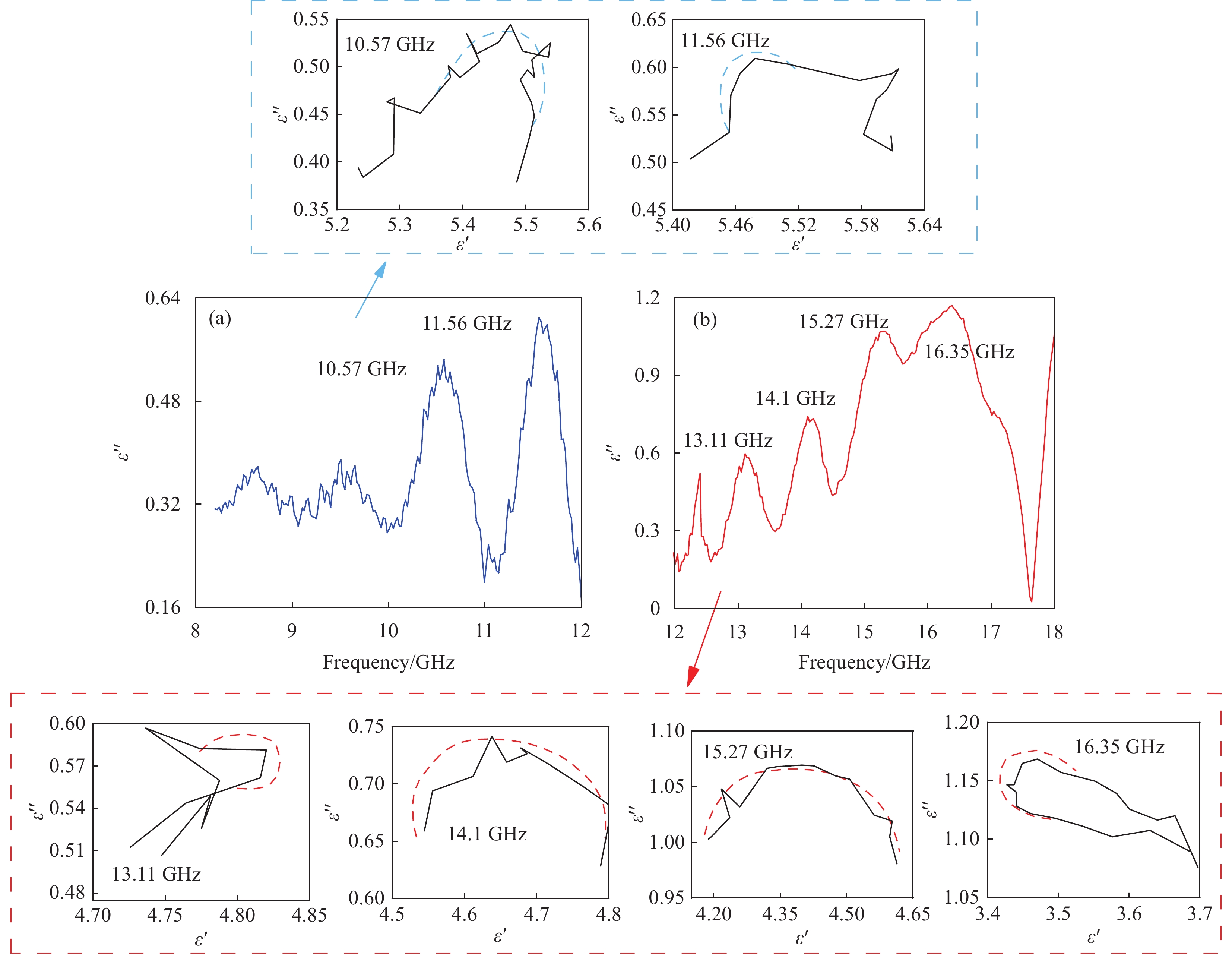
结果对各项吸波性能评价参数的综合对比分析发现:①EPS的加入,使水泥基体通过电磁谐振作用改善了材料与自由空间的阻抗匹配性能,有助于材料对电磁能量的耗散。然而,EPS的复介电常数较低,几乎不具备电磁损耗能力。因此,随着PES掺量的增加,材料的吸波性能先增加后降低。②除了掺量以外,EPS的粒径对复合材料吸波性能也有着显著的影响。通过调控EPS粒径大小,可以得到良好的空腔谐振效果,从而改善复合材料对电磁波的吸收作用。当EPS粒径在1~2 mm时,获得了最佳吸波效果。③MG作为介电损耗型电磁吸波剂,大幅提高了复合材料的介电特性,使其具备优异的电磁损耗能力。但复合材料的吸波性能由阻抗匹配和电磁损耗能力综合决定,且二者互为矛盾。因此过量的MG会导致材料与自由空间之间的匹配失衡,从而使水泥基复合材料的吸波性能下降。④双层结构吸波材料通过梯度渐变阻抗设计,使更多的电磁波进入到材料内部进行损耗。且材料各层界面处的反射波发生了干涉相消现象,从而产生了强吸收峰。当匹配层与吸收层厚度分别为12 mm和8 mm时,双层结构复合材料在2~18 GHz有效吸收带宽达到7.93 GHz,并获得-18.80 dB的最强吸收峰,具备良好的电磁吸波性能。⑤从Cole-Cole半圆曲线图和Smith圆图可以看出,材料发生了多个稳定的极化过程,且双层结构复合材料的阻抗匹配明显优于单层结构材料。此外,复合材料还通过多重反射与散射效应、电导损耗、界面极化和偶极子极化等作用促进了电磁波能力的耗散。
结论EPS颗粒在复合材料基体内形成了独特的多孔阵列结构,增强了材料与自由空间的阻抗匹配性能;并且EPS球形颗粒既是透波剂也是谐振腔,在合理的掺量下与MG搭配形成良好的多孔导电网络,可通过界面极化、电阻损耗以及极化弛豫等方式吸收入射电磁波的能量。在此基础上,通过双层平板组合结构,充分利用密度梯度及层间效应,进一步提高了电磁波能量在传输过程中的耗散作用,实现了结构与材料组分之间良好的协同增强效果,获得了良好的电磁吸波性能。
-
现代电子技术的高速发展,为人类工作和生活带来极大便利的同时,也产生了大量的电磁辐射威胁,各类建筑物作为保护人类生产生活最重要的屏障,却往往忽略了对电磁辐射防护性的需求。针对这一问题,研究人员发现,通过对水泥基复合材料结构或组分展开合理设计,能有效增强吸波材料电磁匹配特性及对电磁波的谐振、干涉和散射等损耗作用,既不改变建筑主体结构,还能有效地降低电磁辐射的危害,成为了建筑吸波材料发展的有力方向。基于此,本文以普通硅酸盐水泥为基体,采用多层石墨烯(Multilayer graphene,MG)作为吸波剂,并以发泡聚苯乙烯(Expanded polystyrene,EPS)球形颗粒作为透波和谐振组分,分别研究了MG掺量、EPS体积掺量及粒径大小,以及双层平板组合结构对复合材料吸波性能的影响规律,并成功制备出了2~18 GHz范围内有效吸收带宽为7.93 GHz,最强吸收峰值达到-18.80 dB的EPS-MG-水泥基复合吸波材料。该材料通过特殊的“双层多孔复合结构”对电磁波产生散射、干涉和谐振行为,有效提升了水泥基体的电磁匹配和损耗作用,同时赋予水泥基复合材料轻质保温隔热的功能,为低成本建筑吸波复合材料的发展提供了新思路。
EPS-MG-水泥基复合材料吸波机制图:(a)宏观尺度;(b-d)微观尺度






 下载:
下载: