Preparation and microwave absorption properties of ferrite/ reed charcoal composites
-
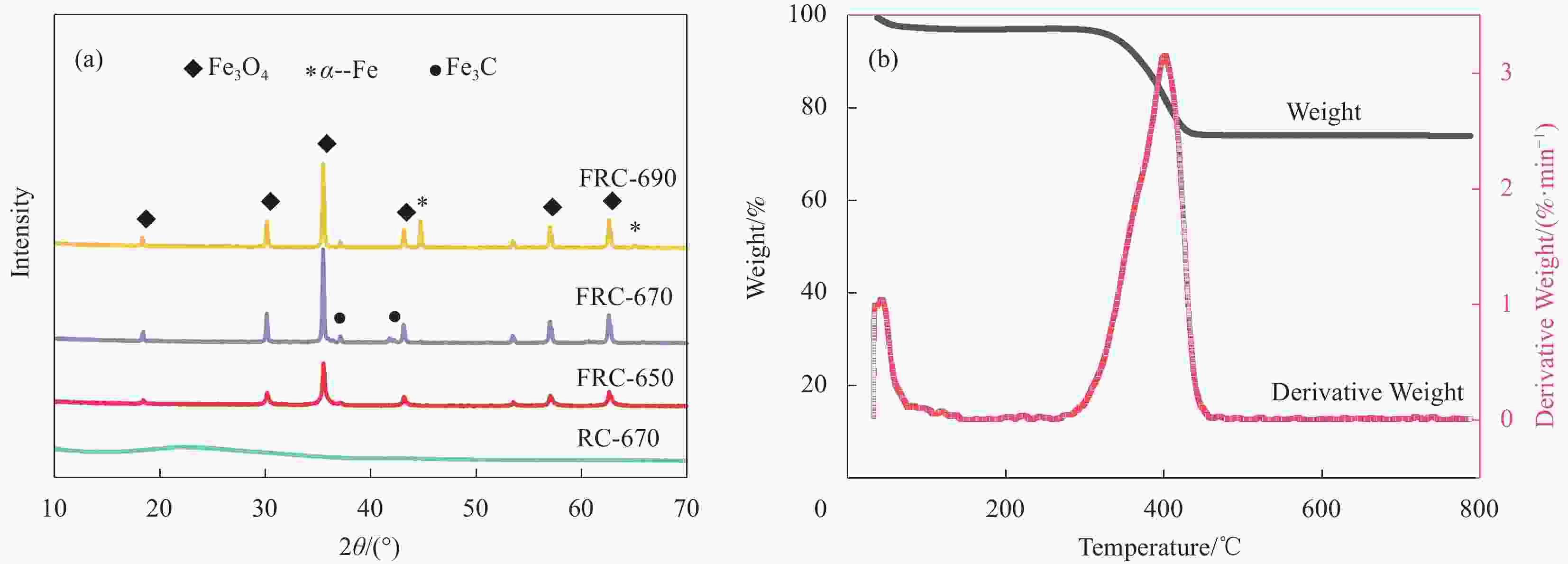
摘要: 为了解决铁氧体吸波材料密度大、吸收带宽窄等问题,以芦苇茎秆为原料,采用常温浸渍及高温原位生长法制备了铁氧体/芦苇秆炭(Ferrite/RC)复合材料,通过调节碳化温度调控复合材料的电磁特性和电磁波吸收性能。SEM、TEM、XRD及VNA等结果表明:Ferrite/RC复合材料保留了芦苇杆天然的三维蜂窝状网络结构,Fe3O4及铁纳米颗粒均匀分布在芦苇秆炭壁与孔道中;提升碳化温度(650~690℃)可增大复合材料的电导率与介电损耗能力,但温度过高会导致材料阻抗失配从而降低电磁衰减能力。碳化温度为670℃时制备的复合材料(FRC-670)吸波性能最佳,它在匹配厚度仅为1.7 mm时反射损耗达到−45.7 dB,对应有效吸收带宽为3.4 GHz;在厚度为2 mm时有效吸收带宽为5.7 GHz (12.1-17.8 GHz)。其主要的电磁波衰减机制源于复合材料良好的电导损耗、极化弛豫损耗以及电损耗与磁损耗的协同作用。铁氧体/芦苇秆炭复合材料优异的吸波性能在电磁波吸收领域具有良好前景,可促进芦苇资源的高值化与功能化应用。Abstract: In order to solve the problems of high density and narrow absorption bandwidth of ferrite absorbing materials, the ferrite/reed charcoal (Ferrite/RC) composites were prepared from reed stalks by impregnation and high temperature in-situ growth methods. The electromagnetic characteristics and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of the composites were controlled by tailoring the carbonization temperature. The results of SEM, TEM, XRD, and VNA showed that the Ferrite/RC composites retained the natural three-dimensional honeycomb network structures of the reed stalks, and Fe3O4 and iron nanoparticles were uniformly distributed in the charcoal wall and pores of the reed stem; Raising the carbonization temperature (650~690℃) can increase the conductivity and dielectric loss ability of composites, but excessive temperature can lead to impedance mismatch of the material and reduce its electromagnetic attenuation ability. The composites prepared at a carbonization temperature of 670℃ exhibit the best absorption performance, with a reflection loss of -45.7 dB at a thickness of only 1.7 mm and an effective absorption bandwidth of 5.7 GHz (12.1-17.8 GHz) at a thickness of 2 mm, which is attributed to the good conductivity loss, polarization relaxation, and the synergistic effect of electrical and magnetic losses of composite materials. The excellent absorption performance of Ferrite/RC composites has good prospects in the field of electromagnetic wave absorption, which can promote the high-value and functional application of reed resources.
-
Key words:
- reed /
- Fe3O4 /
- carbonization /
- absorbing performance /
- magnetic loss /
- electromagnetic characteristics
-
表 1 碳基吸波材料的性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of microwave absorption properties of carbon-based materials
Absorber RLmin/dB EAB/GHz Thickness/mm Filler loading/wt% Ref. FRC-670 −45.7 3.4 1.7 35 This work FRC-670 −32.1 5.7 2.0 35 This work Walnut shell-based porous carbon −42.4 1.8 2.0 70 [35] Functionalized loofah sponge −43.8 5.3 3.0 50 [36] Rice husk-based porous C/Co −21.8 5.6 1.4 25 [37] Fe3O4@lignin −29.5 2.0 4.0 20 [38] NiO/porous carbon −33.8 6.7 8.0 30 [39] Wheat straw-derived carbon foam −37.0 8.8 2.5 10 [40] Shaddock peel-based CA −29.5 5.8 1.7 20 [31] BHPC −47.46 3.40 2.8 10 [41] Fe3C/biochar −45.6 5.5 4.24 30 [30] Cotton-derived porous Fe3O4/C composite −22.1 4.4 2.0 50 [42] NC@Fe3O4 −40.3 4.0 2.0 70 [43] Notes: RLmin is the minimum reflection loss value; EAB is the effective absorption bandwidth; CA―Carbon aerogel; BHPC―Biomass hierarchical porous carbon; NC―Nanoporous carbon. -
[1] LV H, YAO Y, LI S, et al. Staggered circular nanoporous graphene conerts electromagentic wave into electricity[J]. Nature Communications, 2023, 14: 1982. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37436-6 [2] YANG B, FANG J, XU C, et al. One-dimensional magnetic FeCoNi alloy toward low-frequency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano-micro letters, 2022, 14(1): 170. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00920-7 [3] ZHAO X, YAN J, HUANG Y, et al. Magnetic porous CoNi@ C derived from bamboo fiber combined with metal-organic-framework for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 595: 78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.03.109 [4] 禹刚, 杨嗣星. 移动电话射频电磁辐射对精子质量影响的研究进展[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2022, 29(05): 22-28+45.YU Gang, YANG Sixing. Research progress on the effects of radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation from mobile phone on sperm quality[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2022, 29(05): 22-28+45(in Chinese). [5] 叶好, 胡平, 王策, 等. 磁性纤维电磁波吸收剂研究进展[J/OL]. 化工进展: 1-142023-09-25]. YE Hao, HU Ping, WANG Ce, et al. Advances in research on magnetic fibrous electromagnetic wave absorbers [J/OL]. Chemical progress: 1-14[2023-09-25](in Chinese). [6] ZHOU X, ZHAO B, LV H. Low-dimensional cobalt doped carbon composite toward electromagnetic dissipation[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16: 70-79. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4950-x [7] HUANG X, WANG Y, LOU Z, et al. Porous, magnetic carbon derived from bamboo for microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2023, 209: 118005. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118005 [8] 杨喜, 曹敏, 简煜, 等. 多孔木炭/Fe3O4复合吸波材料的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10): 4590-4601.YANG Xi, CAO Min, JIAN Yu, et al. Preparation and microwave absorption properties of porous charcoal/ Fe3O4 composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2022, 39(10): 4590-4601(in Chinese). [9] GAO X, WU X, QIU J. High electromagnetic waves absorbing performance of a multilayer-like structure absorber containing activated carbon hollow porous fibers–carbon nanotubes and Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Electronic Materials, 2018, 4(5): 1700565. doi: 10.1002/aelm.201700565 [10] LIU Y, FU Y, LIU L, et al. Low-cost carbothermal reduction preparation of monodisperse Fe3O4/C core-shell nanosheets for improved microwave absorption[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2018, 10(19): 16511-16520. [11] 赵佳, 姚艳青, 杨煊赫, 等. 铁氧体及其复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11): 2684-2699.ZHAO Jia, YAO Yanqing, YANG Xuanhe et al. Research progress of ferrite and its composite absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2020, 37(11): 2684-2699(in Chinese). [12] SHAO Y Q, LU W B, CHEN H, et al. Flexible ultra-thinFe3O4/MnO2 coreshell decorated CNT composite with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2018, 144: 111-117. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.015 [13] LIU J, LIANG H, WU H. Hierarchical flower-likeFe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2020, 130: 105760. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760 [14] XU H, YIN X, ZHU M, et al. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2017, 9(7): 6332-6341. [15] LI G, XIE T, YANG S, et al. Microwave absorption enhancement of porous carbon fibers compared with carbon nanofibers[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(16): 9196-9201. doi: 10.1021/jp300050u [16] ZHAO S, GAO Z, CHEN C, et al. Alternate nonmagnetic and magnetic multilayer nanofilms deposited on carbon nanocoils by atomic layer deposition to tune microwave absorption property[J]. Carbon, 2016, 98: 196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.10.101 [17] LI J, DUAN Y, LU W, et al. Polyaniline-stabilized electromagnetic wave absorption composites of reduced graphene oxide on magnetic carbon nanotube film[J]. Nanotechnology, 2018, 29(15): 155201. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aaac72 [18] SHI B, LIU K, CHEN J, et al. Microwave absorption properties of ZnFe2O4/graphite composites prepared by high-temperature ball milling[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 905: 164210. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164210 [19] LV H, GUO Y, YANG Z, et al. A brief introduction to the fabrication and synthesis of graphene based composites for the realization of electromagnetic absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(3): 491-512. doi: 10.1039/C6TC03026B [20] LI B, ZENG Z, QIAO J, et al. Hollow ZnO/Fe3O4@ C Nanofibers for Efficient Electromagnetic Wave Absorption[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(8): 11617-11626. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c02616 [21] WANG X, HUANG X, CHEN Z, et al. Ferromagnetic hierarchical carbon nanofiber bundles derived from natural collagen fibers: truly lightweight and high-performance microwave absorption materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(39): 10146-10153. doi: 10.1039/C5TC02689J [22] ZHANG Z, ZHAO Y, LI Z, et al. Synthesis of carbon/SiO2 core-sheath nanofibers with Co-Fe nanoparticles embedded in via electrospinning for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022: 1-12. [23] DAI B, DONG F, WANG H, et al. Fabrication of CuS/Fe3O4@ polypyrrole flower-like composites for excellent electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 634: 481-494. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.12.029 [24] 程显彬. Fe3O4/介电复合材料的制备与吸波性能研究[D]. 沈阳工业大学, 2019.CHENG Xianbin. Preparation and microwave absorption performance of Fe3O4/Dielectric Composites [D]. Shenyang University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [25] WANG L, SU S, WANG Y. Fe3O4-Graphite Composites as a Microwave Absorber with Bimodal Microwave Absorption[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5(12): 17565-17575. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.2c02977 [26] ZHANG R, WANG L, XU C, et al. Vortex tuning magnetization configurations in porous Fe3O4 nanotube with wide microwave absorption frequency[J]. Nano Research, 2022, 15(7): 6743-6750. doi: 10.1007/s12274-022-4401-8 [27] 白良平. 芦苇多孔材料的水蒸发及水输运机理研究[D]. 南京林业大学, 2023.BAI Liang ping. Study on water evaporation and transport mechanism of reed porous materials [D]. Nanjing Forestry University, 2023(in Chinese). [28] 赵双双, 田中建, 陈嘉川, 等. 碱浸渍对芦苇茎秆微观结构及其机械浆性能的影响[J]. 中国造纸, 2021, 40(03): 20-26. doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2021.03.004ZHAO Shuangshuang, TIAN Zhongjian, CHEN Jiachuan, et al. Effect of alkali impregnation on microstructure and mechanical pulp properties of reed stems[J]. China Paper, 2021, 40(03): 20-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2021.03.004 [29] YANG X, PANG X, CAO M, et al. Efficient microwave absorption induced by hierarchical pores of reed-derived ultralight carbon materials[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2021, 171: 113814. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113814 [30] LOU Z, WANG Q, SUN W, et al. Regulating lignin content to obtain excellent bamboo-derived electromagnetic wave absorber with thermal stability[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 430: 133178. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.133178 [31] GU W, SHENG J, HUANG Q, et al. Environmentally friendly and multifunctional shaddock peel-based carbon aerogel for thermal-insulation and microwave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13: 1-14. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-00525-y [32] HAN M, YANG Y, LIU W, et al. Recent advance in three-dimensional porous carbon materials for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Science China Materials, 2022, 65(11): 2911-2935. doi: 10.1007/s40843-022-2153-7 [33] LIU X, CUI X, CHEN Y, et al. Modulation of electromagnetic wave absorption by carbon shell thickness in carbon encapsulated magnetite nanospindles-poly (vinylidene fluoride) composites[J]. Carbon, 2015, 95: 870-878. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.09.036 [34] ZHANG X J, LV G C, WANG G S, et al. High-performance microwave absorption of flexible nanocomposites based on flower-like Co superstructures and polyvinylidene fluoride[J]. RSC Advances, 2015, 5: 55468-55473. doi: 10.1039/C5RA06597F [35] QIU X, WANG L, ZHU H, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nano-porous carbon[J]. Nanoscale, 2017, 9(22): 7408-7418. doi: 10.1039/C7NR02628E [36] LIU L, YANG S, HU H, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave-absorbing materials based on loofah-sponge-derived hierarchically porous carbons[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2018, 7(1): 1228-1238. [37] FANG J, SHANG Y, CHEN Z, et al. Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(19): 4695-4705. doi: 10.1039/C7TC00987A [38] PEI W, SHANG W, LIANG C, et al. Using lignin as the precursor to synthesize Fe3O4@ lignin composite for preparing electromagnetic wave absorbing lignin-phenol-formaldehyde adhesive[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2020, 154: 112638. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112638 [39] WANG H, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Biomass carbon derived from pine nut shells decorated with NiO nanoflakes for enhanced microwave absorption properties[J]. RSC advances, 2019, 9(16): 9126-9135. doi: 10.1039/C9RA00466A [40] ASLAM MA, DING W, UR REHMAN S, et al. Low cost 3D bio-carbon foams obtained from wheat straw with broadened bandwidth electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2021, 543: 148785. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148785 [41] WU Z, MENG Z, YAO C, et al. Rice husk derived hierarchical porous carbon with lightweight and efficient microwave absorption[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2022, 275: 125246. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125246 [42] FANG Y, XUE W, ZHAO R, et al. Effect of nanoporosity on the electromagnetic wave absorption performance in a biomass-templated Fe3O4/C composite: A small-angle neutron scattering study[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8: 319-327. doi: 10.1039/C9TC04569D [43] ZHOU P , WANG X, WANG L, et al. Walnut shell-derived nanoporous carbon@Fe3O4 composites for outstanding microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 805: 1071-1080. -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 128
- HTML全文浏览量: 86
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载:






