Janus moisture induced hydrovoltaic electricity GO-rGO composite material via reduction and tabletting method
-
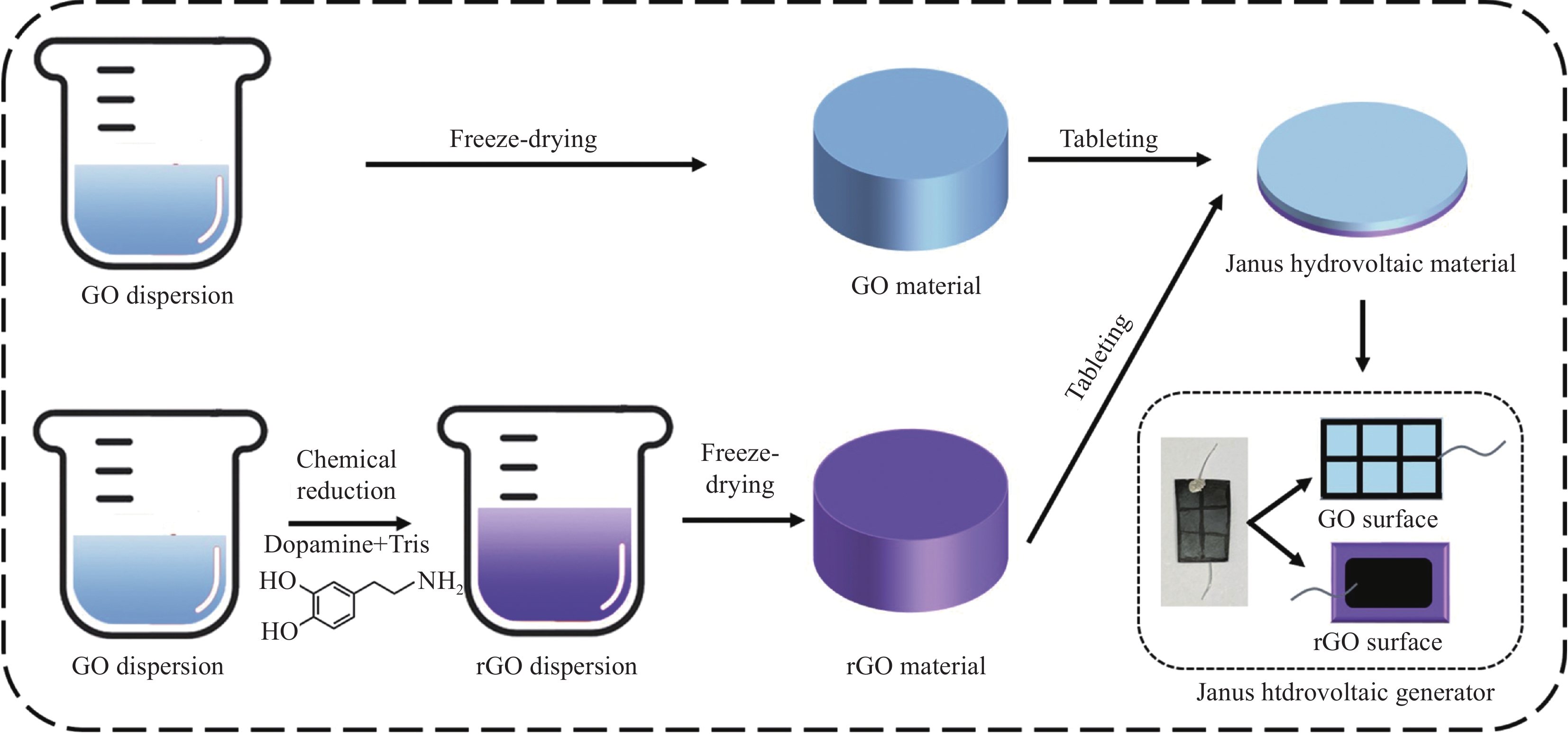
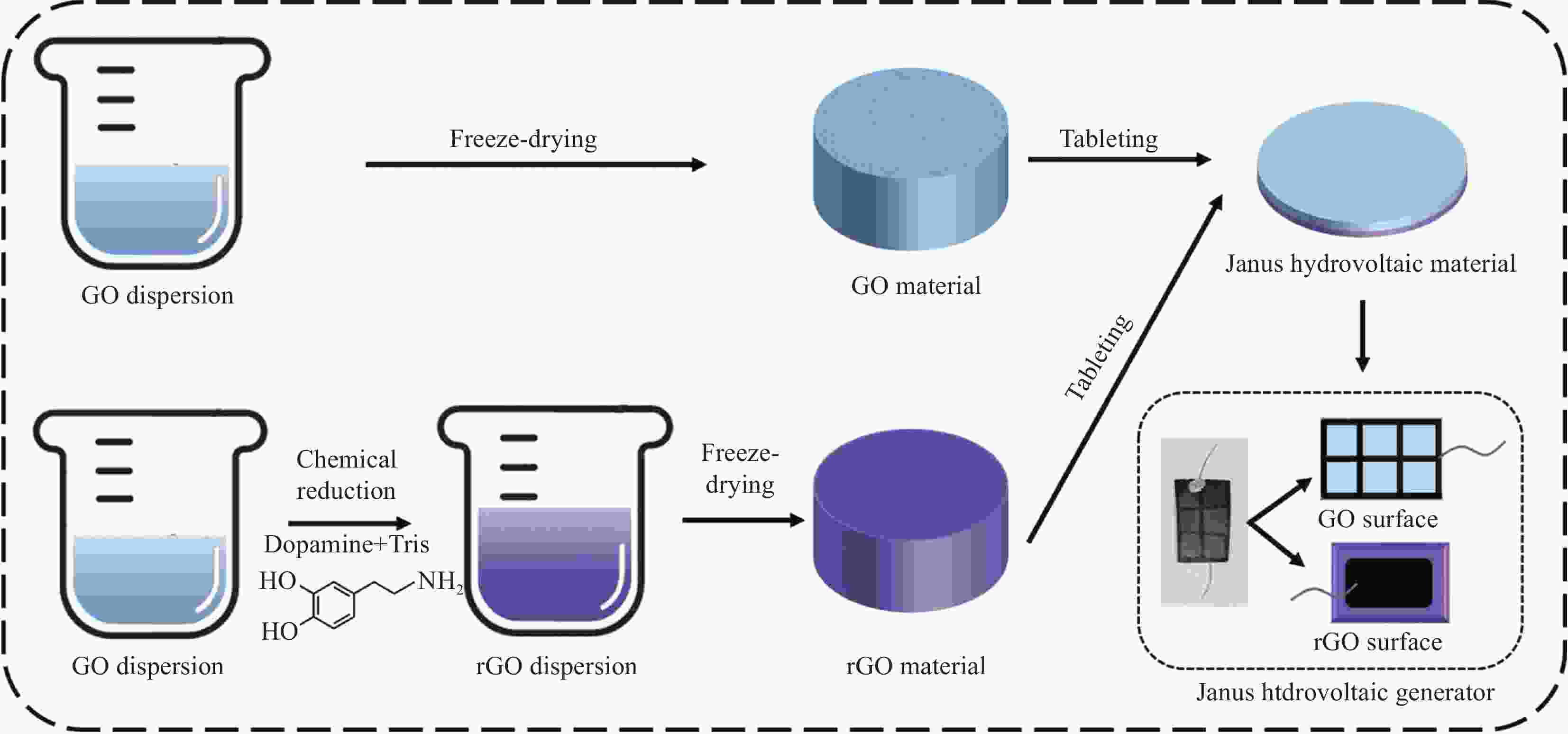
摘要: 随着万物互联、信息时代下新型传感器自供电需求的增加与传统化石能源使用所造成的全球变暖和环境问题的加剧,亟需开发新的能源利用与发电方式。水伏发电作为一种无源、零碳、负热的电能转化方式,能够充分利用自然界中的水循环,具有重要的研究价值。本文以湿气诱导水伏发电为能源利用形式,以氧化石墨烯(GO)为原材料,通过多巴胺自聚合反应将部分原材料反应为还原氧化石墨烯(rGO),结合冻干与压片的方法制备出具有两面特性的Janus水伏发电GO-rGO复合材料。该材料具有明显的含氧官能团梯度分布性质,在高湿度条件下可以进行长时发电,集成后的单个器件的开路电压接近400 mV,功率密度可达25 μW/cm3,同时具有良好的稳定性,在使用1年后仍然具有较好的输出性能。更重要的是,此发电机通过串联可实现阵列化,从而进一步提升发电性能,8个器件串联输出电压便可轻易达到3 V以上,可用于小功率器件的驱动与呼气-吸气行为的响应。本湿气发电材料及器件制备方法简单,输出性能优异,在自供电与传感领域展现出良好的应用前景。Abstract: With the increasing demand of sensor self-power supply device under the information age and the aggravation of global warming and environmental problems caused by the use of traditional fossil energy, it is urgent to come up with new energy utilization and power generation ways. As a passive, zero-carbon and negative heat energy conversion method, hydrovoltaic power generation can make full use of the water cycle in nature and has significant research value. In this paper, moisture induced hydrovoltaic technology is chosen as the energy utilization form and graphene oxide (GO) was used as the raw material. Through the self-polymerization reaction of dopamine, part of the raw material could be reacted to reduced grapheme oxide (rGO), and the freeze-drying and tableting were combined to fabricate the Janus hydrovoltaic GO-rGO composite material. The as-prepared material has obvious characteristics of gradient distribution of oxygen-containing functional groups and can generate electricity for a long time under high humidity conditions, the output voltage of a single hydrovoltaic device is nearly 400 mV and the peak power density is up to 25 μW/cm3. Besides, it exhibits excellent stability which still maintain good output performance after 1 year. More importantly, this generator can be arrays in series to further improve the generation property for driving low-power devices and responding the expiration-inspiration behavior, the output voltage of 8 devices in series can easily reach to 3 V. The as-prepared moisture hydrovoltaic material and generator have the advantage of simple preparation method and excellent output performance, thus showing good application prospect in the field of self-power supply and sensing.
-
Key words:
- hydrovoltaic power /
- chemical reduction /
- Janus material /
- moisture induction /
- self-power mode /
- sensing
-
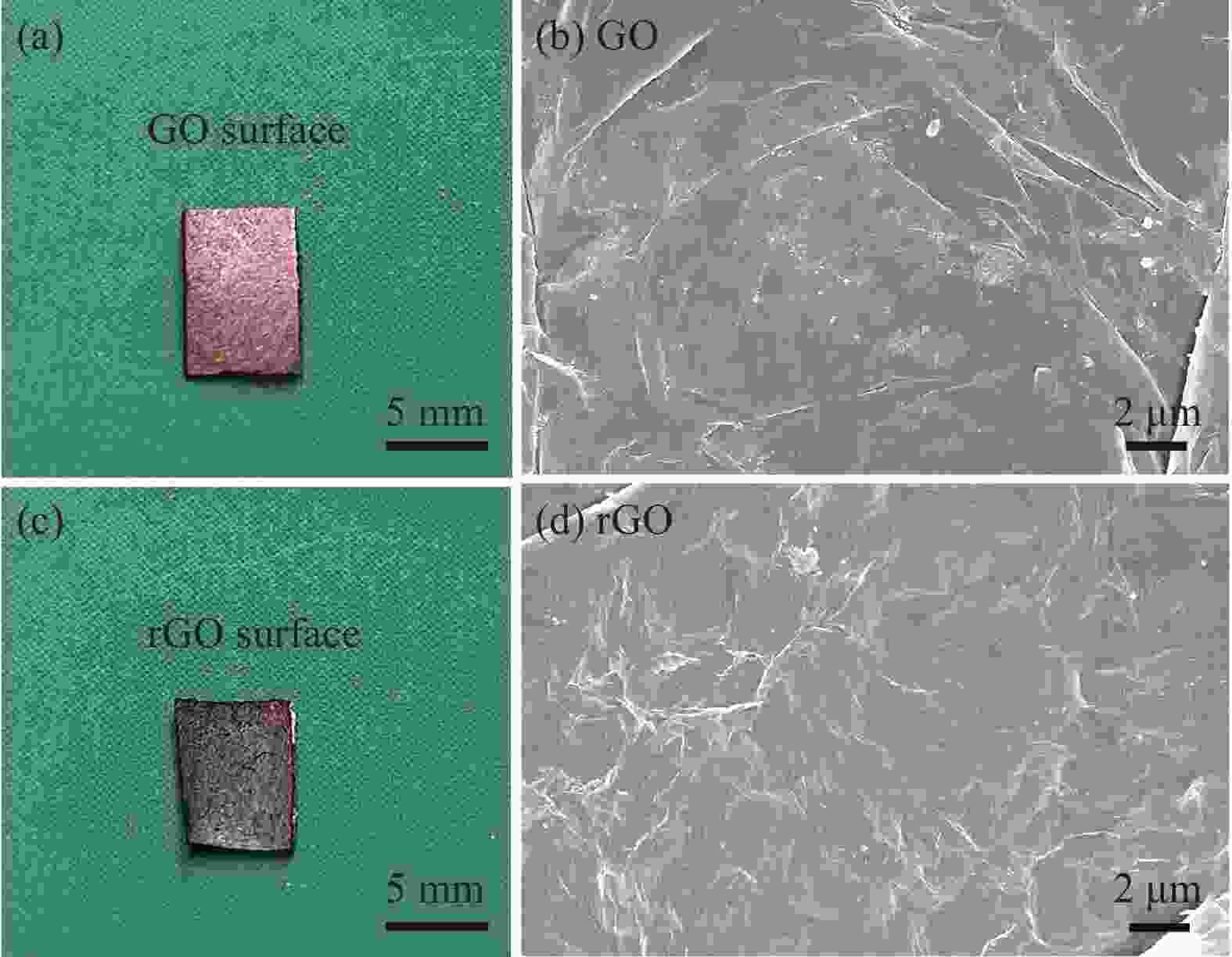
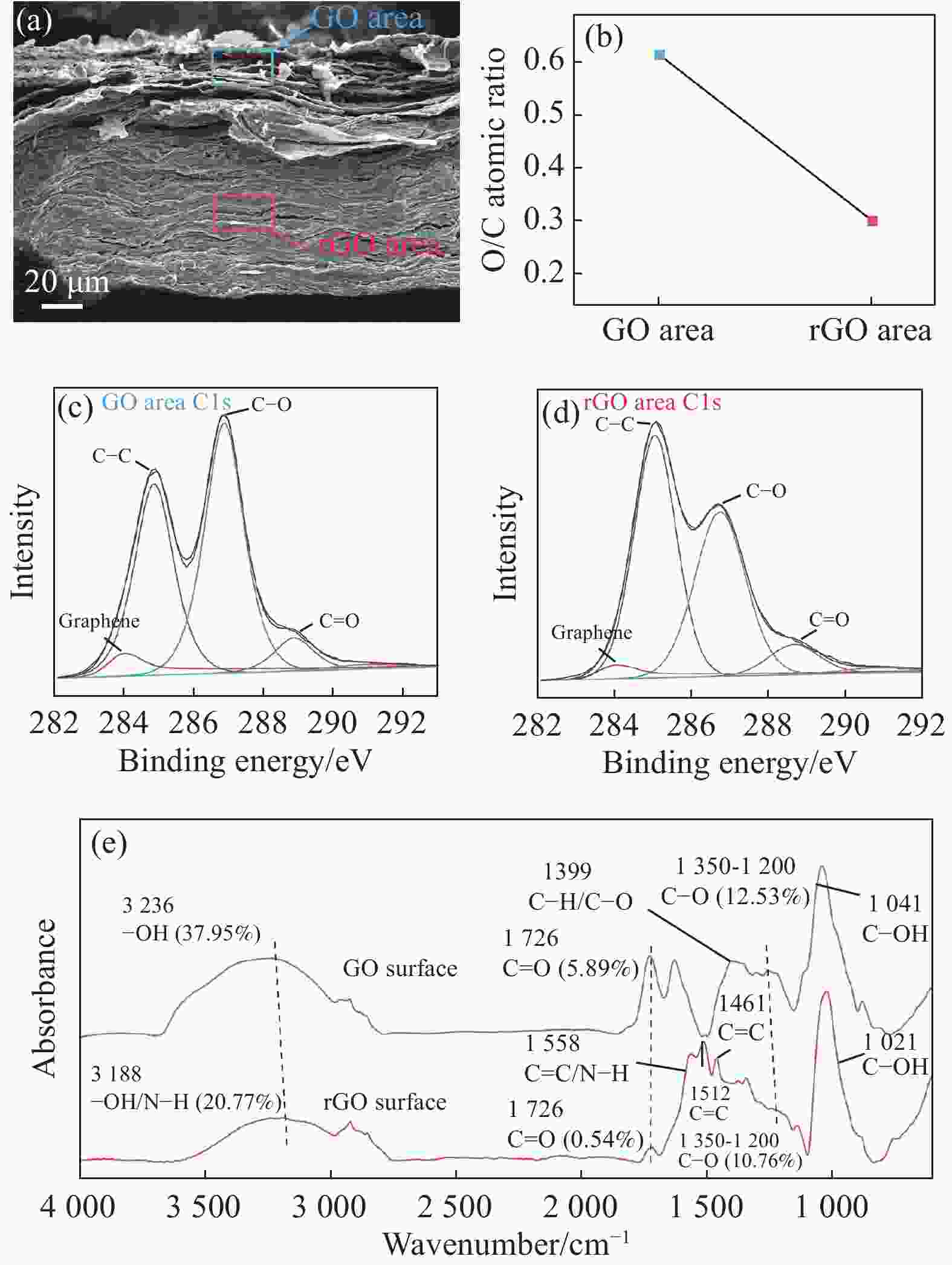
图 3 Janus湿气诱导水伏发电GO-rGO复合材料的 官能团浓度梯度表征:(a) Janus水伏发电材料(MEGM)的SEM截面照片;(b) GO区域与rGO区域的O/C原子含量比;((c), (d)) GO区域与rGO区域的C元素XPS C1s谱图;(e) GO面与rGO面的FTIR图谱
Figure 3. Characterization of functional group concentration gradient in Janus moisture induced electricity generation GO-rGO composite material: (a) Cross section SEM image of the Janus moisture induced electricity generation material (MEGM); (b) O/C atomic ratio of the GO surface and rGO surface; ((c), (d)) High-resolution XPS C as narrow scans of the GO surface and rGO surface, respectively; (e) FTIR spectra of GO surface and rGO surface
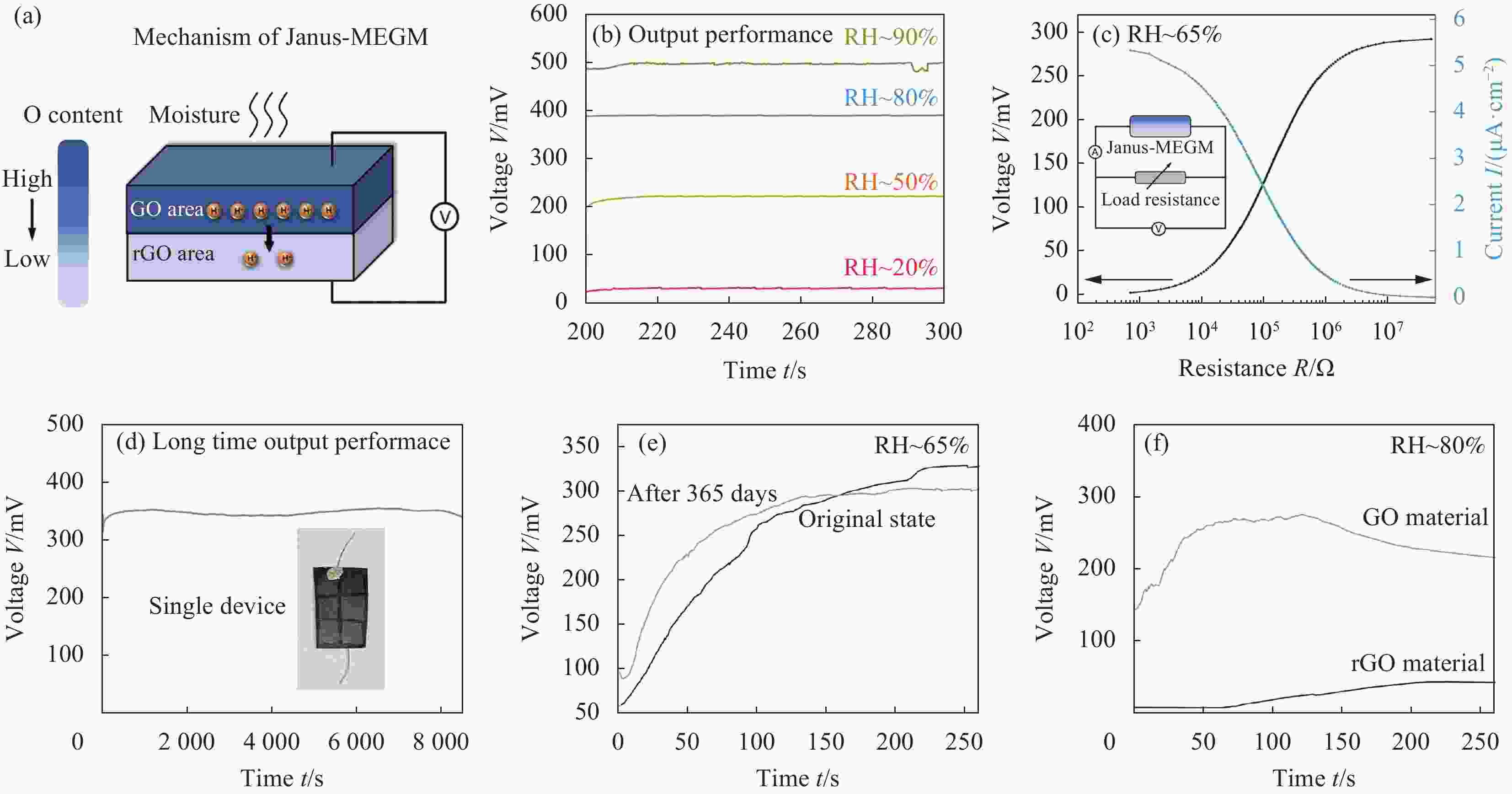
图 4 Janus湿气诱导水伏发电GO-rGO复合材料与发电机的发电性能: (a) Janus湿气诱导水伏发电复合材料的发电机制;(b) 材料在不同湿度下的输出电压; (c) 水伏器件的输出电压/输出电流随外接负载的变化;(d) 水伏器件长时间工作时的输出电压;(e) 材料在0天与放置365天后的输出电压;(f) 纯rGO与GO膜材料的湿气发电性能
Figure 4. Performance of the Janus moisture induced electricity generation GO-rGO composite material and generator: (a) Electricity generation scheme of the Janus GO-rGO composite material; (b) Output voltage of the as-prepared material at different moisture condition; (c) Output voltage and current density of the Janus MEGM with different electric resistors; (d) Output voltage of the hydrovoltaic device working for a long time; (e) Output performance of the material at the original state and after 365 days, respectively; (f) Output voltage of the pure rGO and GO material, respectively
RH—Relative humidity
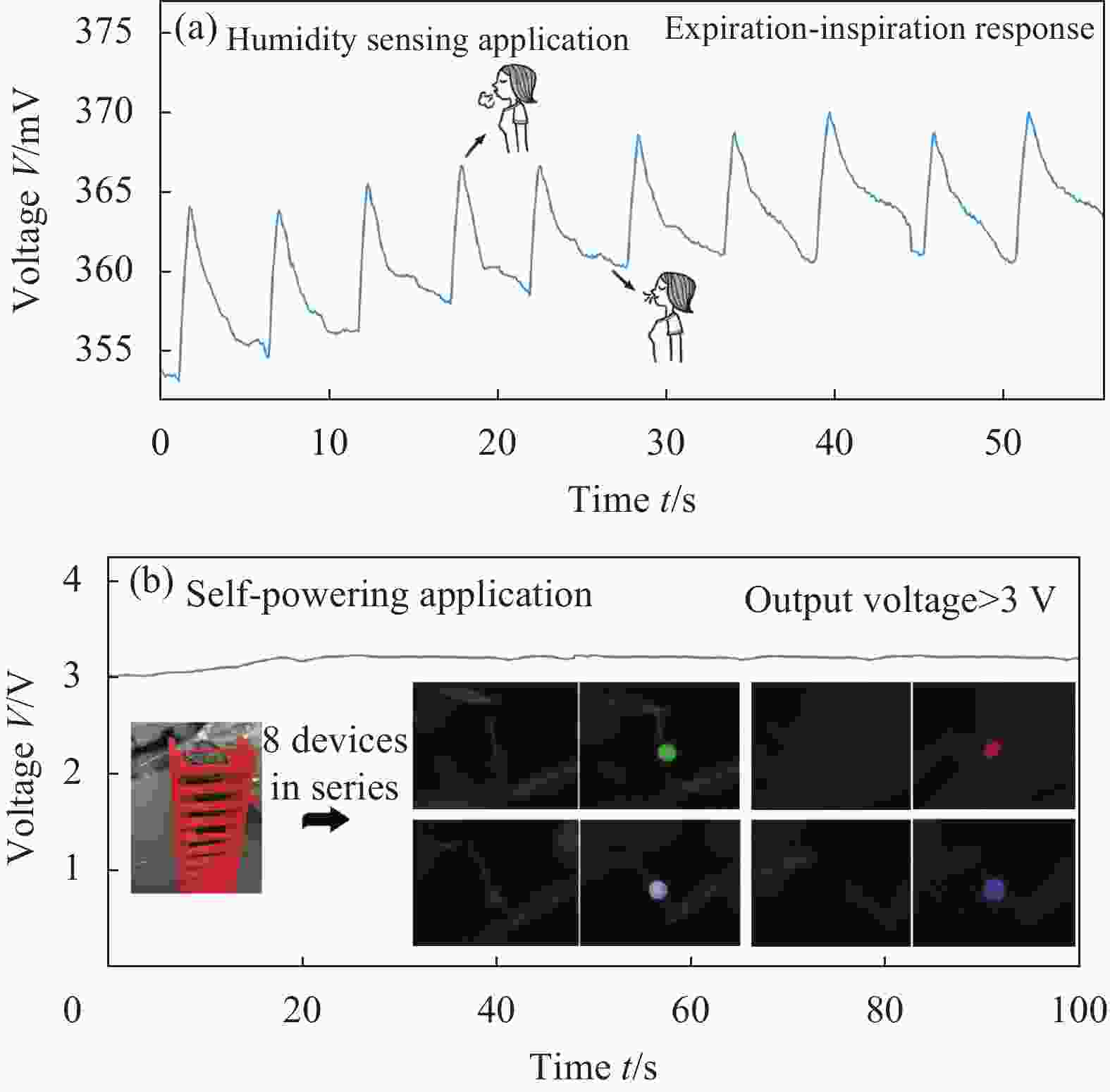
图 5 湿气诱导水伏发电机的应用展示:(a) Janus湿气诱导水伏发电机输出电压随呼气-吸气的变化;(b) 8器件串联水伏器件阵列的输出电压,附图是阵列外观数码照片
Figure 5. Application illustration of the moisture induced hydro-voltaic generator: (a) Responsive performance of the Janus hydrovoltaic device between expiration and inspiration; (b) Output voltage of the hydrovoltaic array with 8 individual devices connected in series, insets are the digital photo of the device array and the illustration of LED self-powered application
-
[1] ZHANG Z H, LI X M, YIN J, et al. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2018,13(12):1109-1119. doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0228-6 [2] YIN J, ZHOU J X, FANG S M, et al. Hydrovoltaic energy on the way[J]. Joule,2020,4(9):1852-1855. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.07.015 [3] TARELHOJ P G, SOARESDOS SANTOS M P, FERREIRA J A F, et al. Graphene-based materials and structures for energy harvesting with fluids–A review[J]. Materials Today,2018,21(10):1019-1041. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2018.06.004 [4] TANG Q W, YANG P Z. The era of water-enabled electricity generation from graphene[J]. Journal of Materials Che-mistry A,2016,4(25):9730-9738. doi: 10.1039/C6TA03107B [5] FANG S M, LI J D, XU Y, et al. Evaporating potential[J]. Joule,2022,6(3):690-701. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2022.02.002 [6] 刘刚, 欧宝立, 赵欣欣, 等. 共价功能化石墨烯超疏水防腐复合涂层材料的制备[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3236-3246. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210208.002LIU Gang, OU Baoli, ZHAO Xinxin, et al. Preparation of covalently functionalized graphene superhydrophobic anticorrosive composite coating materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3236-3246(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210208.002 [7] 刘洋洋, 易敏, 陈涛, 等. 石墨烯-有机物复合光催化材料及其应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4):1937-1950.LIU Yangyang, YI Min, CHEN Tao, et al. Applications of graphene-organic compound photocatalytic materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(4):1937-1950(in Chinese). [8] 李正, 尚军军, 刘夏, 等. 可穿戴石墨烯复合材料压阻传感性能计算方法及其参数分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1066-1075. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201229.002LI Zheng, SHANG Junjun, LIU Xia, et al. Computational method and parameters analysis of piezoresistive sensing properties of wearable graphene composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1066-1075(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201229.002 [9] SHEN D Z, DULEY W W, PENG P, et al. Moisture-enabled electricity generation: From physics and materials to self-powered applications[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(52):2003722. doi: 10.1002/adma.202003722 [10] BAI J X, HUANG Y X, CHENG H H, et al. Moist-electric generation[J]. Nanoscale,2019,11(48):23083-23091. doi: 10.1039/C9NR06113D [11] XU T, DING X T, SHAO C X, et al. Electric power generation through thedirect interaction of pristine graphene-oxide with water molecules[J]. Small,2018,14:1704473. doi: 10.1002/smll.201704473 [12] LIANG Y, ZHAO F, CHENG Z H, et al. Electric power generation via asymmetric moisturizing of graphene oxide for flexible, printable and portable electronics[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2018,11(7):1730-1735. [13] WANG H Y, HE T C, HAO X Z, et al. Moisture adsorption-desorption full cycle power generation[J]. Nature Communications,2022,13:2524. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30156-3 [14] LIU X M, GAO H Y, WARD J E, et al. Power generation from ambient humidity using protein nanowires[J]. Nature,2020,578(7796):550-554. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2010-9 [15] ZHAO F, LIANG Y, CHENG H H, et al. Highly efficient moisture-enabled electricity generation from graphene oxide frameworks[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2016,9(3):912-916. [16] HUANG Y X, CHENG H H, YANG C, et al. Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts[J]. Nature Communications,2018,9:4166. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06633-z [17] ZHAO F, WANG L X, ZHAO Y, et al. Graphene oxide nanoribbon assembly toward moisture-powered information storage[J]. Advanced Materials,2017,29(3):1604972. doi: 10.1002/adma.201604972 [18] CHENG H H, HUANG Y X, ZHAO F, et al. Spontaneous power source in ambient air of a well-directionally reduced graphene oxide bulk[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2018,11(10):2839-2845. [19] ZHAO F, CHENG H H, ZHANG Z P, et al. Direct power generation from a graphene oxide film under moisture[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27(29):4351-4357. doi: 10.1002/adma.201501867 [20] LIANG Y, ZHAO F, CHENG Z H, et al. Self-powered wearable graphene fiber for information expression[J]. Nano Energy,2017,32:329-335. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.12.062 [21] SHAO C X, GAO J, XU T, et al. Wearable fiberform hygroelectric generator[J]. Nano Energy,2018,53:698-705. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.09.043 [22] CHENG H H, HUANG Y X, QU L T, et al. Flexible in-plane graphene oxide moisture-electric converter for touchless interactive panel[J]. Nano Energy,2018,45:37-43. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.12.033 [23] LIU K, YANG P H, LI S, et al. Induced potential in porous carbon films through water vapor absorption[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2016,55(28):8003-8007. doi: 10.1002/anie.201602708 [24] ZHANG Y X, GUO S A, YU Z G, et al. An asymmetric hygroscopic structure for moisture-driven hygro-ionic electricity generation and storage[J]. Advanced Materials,2022,34:2201228. doi: 10.1002/adma.202201228 [25] XUE J L, ZHAO F, HU C G, et al. Vapor-activated power generation on conductive polymer[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2016,26(47):8784-8792. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201604188 [26] NIE X W, JI B X, CHEN N, et al. Gradient doped polymer nanowire for moistelectric nanogenerator[J]. Nano Energy,2018,46:297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.02.012 [27] GAO X E, XU T, SHAO C X, et al. Electric power generation using paper materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7(36):20574-20578. doi: 10.1039/C9TA08264F [28] LI M J, ZONG L, YANG W Q, et al. Biological nanofibrous generator for electricity harvest from moist air flow[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29:1901798. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201901798 [29] WANG H Y, CHENG H H, HUANG Y X, et al. Transparent, self-healing, arbitrary tailorable moist-electric film generator[J]. Nano Energy,2020,67:104238. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.104238 [30] MANDAL S, ROY S, MANDAL A, et al. Protein-based flexible moisture-induced energy-harvesting devices as self-biased electronic sensors[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials,2020,2(3):780-789. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.9b00842 [31] WANG H Y, SUN Y L, HE T C, et al. Bilayer of polyelectrolyte films for spontaneous power generation in air up to an integrated 1000 V output[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2021,16(7):811-819. doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00903-6 [32] LI H N, YANG J, XU Z K. Asymmetric surface engineering for Janus membranes[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces,2020,7(7):1902064. doi: 10.1002/admi.201902064 [33] YANG H C, XIE Y S, HOU J W, et al. Janus membranes: Creating asymmetry for energy efficiency[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(43):1801495. doi: 10.1002/adma.201801495 [34] YANG H C, HOU J W, CHEN V, et al. Janus membranes: Exploring duality for advanced separation[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2016,55(43):13398-13407. doi: 10.1002/anie.201601589 [35] LEE H, DELLATORE S M, MILLER W M, et al. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings[J]. Science,2007,318(5849):426-430. doi: 10.1126/science.1147241 [36] CUI W, LI M Z, LIU J Y, et al. A strong integrated strength and toughness artificial nacre based on dopamine cross-linked graphene oxide[J]. ACS Nano,2014,8(9):9511-9517. doi: 10.1021/nn503755c [37] CHENG C, LI S, ZHAO J, et al. Biomimetic assembly of polydopamine-layer on grapheme: Mechanisms, versatile 2D and 3D architectures and pollutant disposal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,228:468-481. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.05.019 [38] LEE W, LEE J U, JUNG B M, et al. Simultaneous enhancement of mechanical, electrical and thermal properties of graphene oxide paper by embedding dopamine[J]. Carbon,2013,65:296-304. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.08.029 [39] KANG S M, PARK S, KIM D, et al. Simultaneous reduction and surface functionalization of graphene oxide by mussel-inspired chemistry[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2011,21(1):108-112. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201001692 [40] SHEN D Z, XIAO M, ZOU G S, et al. Self-powered wearable electronics based on moisture enabled electricity generation[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(18):1705925. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705925 [41] SHEN D Z, XIAO M, XIAO Y, et al. Self-powered, rapid-response, and highly flexible humidity sensors based on moisture-dependent voltage generation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(15):14249-14255. -





 下载:
下载: