Broadband microwave absorption and mechanical properties of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composites
-
摘要:
本工作以拓宽结构型吸波复合材料的吸收频带为目的,在玻璃纤维增强尼龙复合材料中同时引入磁损耗型吸波剂羰基铁粉(carbonyl iron powder, CIP)和电阻损耗型吸波剂炭黑(Carbon black, CB),采用热压成型工艺制备了CB-CIP@SiO2/玻璃纤维/尼龙6(CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6)吸波复合材料。重点研究了CIP表面包覆SiO2薄膜及其加入量对复合材料微波吸收和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明:SiO2薄膜包覆不仅解决了CIP氧化问题,同时改善了复合材料的阻抗匹配特性,使得CIP与CB协同提升了复合材料的吸波性能。在保障复合材料具有良好吸波性能前提下,CIP的负载量从70 wt.%降低至30 wt.%左右,大大减轻了复合材料的质量。其中,掺量为1 wt.%CB和30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽在材料厚度为1.91-1.95 mm时超过了5.6 GHz,且覆盖了整个Ku波段。这种方法一方面拓宽了吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽,实现了宽带吸波。另一方面,CIP@SiO2颗粒与GF的纤维实现共同增强,提升了复合材料的整体力学性能。当CIP@SiO2的含量为40 wt.%时,复合材料的力学性能最佳,弯曲强度为212.8±9.8 MPa,剪切强度为21.0±1.4 MPa,摆锤冲击强度为64.4±6.2 kJ/m2。
Abstract:With the aim of broadening the absorption band of structural microwave absorbing composites, a magnetic loss absorber carbonyl iron powder (CIP) and the resistive loss absorber carbon black (CB) were simultaneously introduced into glass fiber reinforced polyamide 6 composites, and CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composites were prepared by the hot press molding process. Focusing on the effect of CIP surface coated SiO2 film and its incorporation on the microwave absorption and mechanical properties of composites. The results show that SiO2 coating not only prevents the oxidation of CIP, but also improves the impedance matching of the composites, so that CIP and CB synergistically enhance the microwave absorbing properties of the composites. Under the premise of guaranteeing good microwave absorbing properties, the loading of CIP is reduced from 70 wt.% to about 30 wt.%, which greatly lightens the mass of the composites. The effective absorption bandwidth of the composites with 1 wt.% CB and 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2 exceeds 5.6 GHz at a thickness of 1.91-1.95 mm and covers the entire Ku-band. On the one hand, this method broadens the effective absorption bandwidth of the composites and realizes broadband absorption. On the other hand, the particle reinforcement of CIP@SiO2 has a co-enhancing effect with GF. When the content of CIP@SiO2 was 40 wt.%, the mechanical properties of the composites were optimal, with a flexural strength of 212.8±9.8 MPa, a shearing strength of 21.0±1.4 MPa, and a pendulum impact strength of 64.4±6.2 kJ/m2.
-
随着电子信息技术的飞速发展,民用领域对吸波材料的需求量正逐渐增大,不同的使用环境所对应的吸收波段不同,因此使得吸波材料的宽带吸收特性变得越来越重要[1-4]。结构型吸波材料相比于涂层材料的性价比更高,更适用于民用领域。典型的结构型吸波材料一般由聚合物基体和吸波剂组成[5-7]。电阻损耗型吸波剂炭黑(CB)的价格低廉,具有良好的吸波性能,是碳材料中常用的吸波材料[8, 9],其优异的吸波性能通常表现在较高频段(8-18 GHz)[10, 11]。羰基铁粉(CIP)作为一种磁损耗型金属微粉,具有较高的饱和磁化强度和磁导率,依靠磁损耗可以实现优异的吸波效果[12, 13],其优异的吸波特性通常表现在低频(2-6 GHz)[14, 15]。然而,由于CIP的电阻率较低,使复合材料的复介电常数通常较高,这给吸波复合材料的阻抗匹配设计带来了不少困难[16]。另外,CIP在温度超过200℃时容易被氧化,从而对其磁性能和吸波性能产生较大的影响[17, 18]。以往的研究通常使用表面涂覆的方式对CIP进行改性处理来解决此问题,如使用聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)[19, 20]、聚苯胺(PANI)[21, 22]和二氧化硅(SiO2)[23, 24]等材料作包覆层。其中,SiO2的沉积工艺易于控制且成本较低,因此包覆SiO2薄膜是制备高抗氧化性CIP的理想方法,同时还能在很大程度上保持CIP的物理和电磁特性[25, 26]。此外,SiO2材料还是理想的透波材料,通过合理的结构设计可以改善CIP的阻抗匹配[27]。
在复合材料中使用单一的CIP作为吸波剂时,通常需要较大的负载量才能发挥出较好的吸波性能[28, 29],但会导致复合材料的重量大大增加并使材料的力学性能降低。因此,使用CIP作为吸波剂时与其他吸波剂复合使用,可以更好地调整和设计材料的吸波性能和力学性能。磁性损耗型吸波剂CIP在低频具有较好的吸波性能,而电阻损耗型吸波剂CB在高频具有较好的吸波性能,二者的协同吸收有利于对材料吸收频带的拓宽[30]。本文以正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)作为硅源,采用Stöber法[31]在CIP表面包覆了一层SiO2薄膜,使其与氧气隔离从而达到抗氧化的效果[32],同时希望改善材料的阻抗匹配。将制备好的CIP@SiO2与CB和PA6混合,选用GF作为增强体保证复合材料的力学性能且不影响微波吸收,通过热压成型工艺制备了CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料,研究了不同类型的吸波剂CIP@SiO2和CB对复合材料微波吸收性能和力学性能的影响。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
以市售羰基铁粉(中国河北莱伯金属材料科技有限公司生产)为磁损耗型吸波剂原料,其粒径为3-5 μm,α-铁含量大于99.8 wt.%。正硅酸乙酯试剂(中国天津大茂化学试剂厂生产)用于制备SiO2涂层。乙炔炭黑(中国天津易华昌新材料科技有限公司生产)作为电阻损耗型吸波剂,其颗粒直径为30-40 nm。尼龙6粉末(中国南京宏瑞塑料制品有限公司生产)作为基体材料,其熔化温度为220℃。二维平纹E型玻璃纤维作为复合材料的增强体(中国巨石股份有限公司生产),其密度为400 g/m2。TEOS、氨水和无水乙醇均为分析纯。
1.2 CIP@SiO2的制备
采用Stöber法在CIP表面制备SiO2薄膜:首先,将CIP超声分散在17.5 ml TEOS、700 ml无水乙醇和140 ml去离子水的混合溶液中(CIP与TEOS摩尔比为6∶1),然后在水浴加热温度为35℃的条件下加入氨水将混合溶液的pH值调至8-9,机械搅拌3 h。反应结束后,用无水乙醇和去离子水分别洗涤三次,最后在真空烘箱中80℃干燥6 h。
1.3 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的制备
复合材料采用热压成型工艺制备:首先,通过高速机械搅拌将CB、CIP@SiO2和PA6粉末按配比混合均匀。然后,将玻璃纤维和混合好的粉末以逐层堆叠的方式铺在模具中,在240℃的温度和8 MPa的压力下压制并保压5分钟,自然冷却后CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合层压板制备完成。CIP-GF/PA6和CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的制备方法相同,除了不使用CB。其中,所有复合材料的GF含量均为30 wt.%。
1.4 表征方法
通过场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM,ZEISS,Gemini 500)和能量色散光谱(Energy Dispersive Spectrum, EDS)观察了复合材料的微观结构和元素的确定。采用X射线衍射仪(Rigaku SmartLab SE)对材料的物相组成进行分析,使用Cu靶的Kα射线,扫描速度为10 °/min,扫描范围为10-90°。热处理样品是在烘箱中240℃加热处理10 min。使用矢量网络分析仪(Ceyear
3672 B-S)采用波导法测试了吸波复合材料在Ku波段(12.4-18 GHz)的电磁参数,其中试样尺寸为15.89×7.9 mm。利用传输线理论可以对材料的吸波特性进行评估,反射损耗(Reflection loss, RL)计算如下[33]:Zin=Z0√μrεrtanh[j(2πftc√μrεr)] (1) RL(dB)=20log10|Zin−Z0Zin+Z0| (2) 其中,Zin是吸波材料的输入阻抗,Z0是自由空间阻抗。μr和εr分别是复磁导率和复介电常数。f为微波频率,c为光速,t为复合材料厚度。衰减常数可以评估吸波材料对微波的衰减程度,α计算如下:
α=√2πfc×√(μ′′ε′′−μ′ε′)+√(μ′′ε′′−μ′ε′)2+(μ′ε′′−μ′′ε′)2 (3) 根据ASTM D790标准,使用万能试验机(UTM,WDW-5)以2.0 mm/min的十字头速度进行了三点弯曲试验,弯曲试验的试样尺寸为80×10×4 mm,跨深比为16。复合材料的层间剪切强度(ILSS)是根据ASTM D2344标准进行短梁剪切试验,十字头速度为1.0 mm/min,跨深比为4,试样尺寸为26×9×4 mm。摆锤冲击试验由冲击试验机(XJUD-22)根据ASTM D-256标准进行测试,冲击能量为22 J,冲击方向与试样长径垂直,试样尺寸为65×12×7 mm。其中,弯曲强度、ILSS和摆锤冲击强度分别取自四个平行样品测试的平均值。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 CIP的抗氧化处理
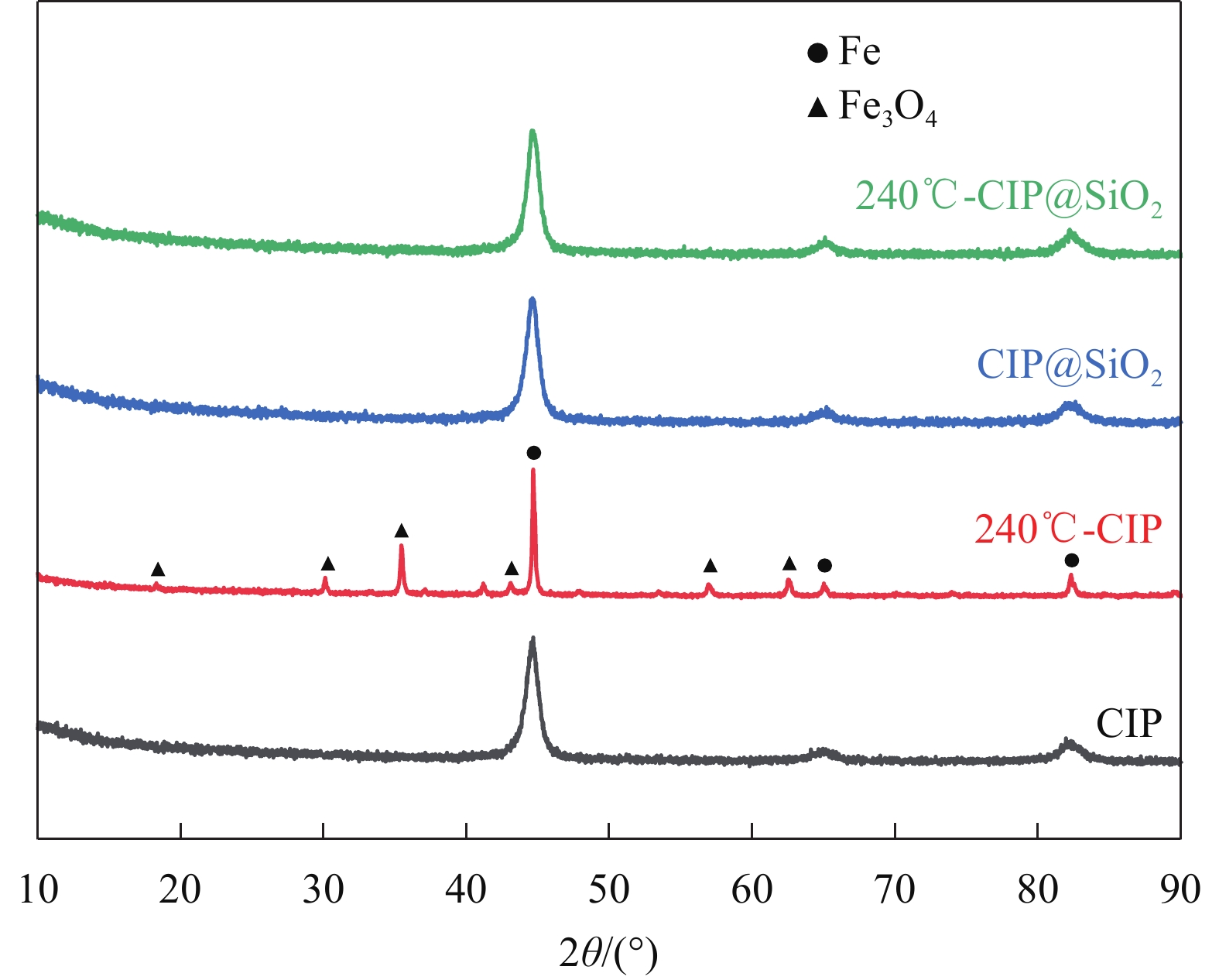
包覆前后的样品在热处理后表现出不同的物相组成。图1是CIP和CIP@SiO2热处理前后的XRD图谱。从结果中可以看出,CIP、CIP@SiO2及热处理的CIP@SiO2具有相同的三个衍射峰,分别位于44.68°、64.9°和82.32处,对应立方相α-Fe的(110)、(200)和(211)面。这三个立方相α-Fe的宽衍射峰也表明了SiO2外壳为非结晶态,且在热处理过程中未发生铁的氧化现象。而未包覆的CIP则在热处理过程中氧化生成了Fe3O4,这个结果说明SiO2对CIP的包覆可以达到抗氧化的效果。
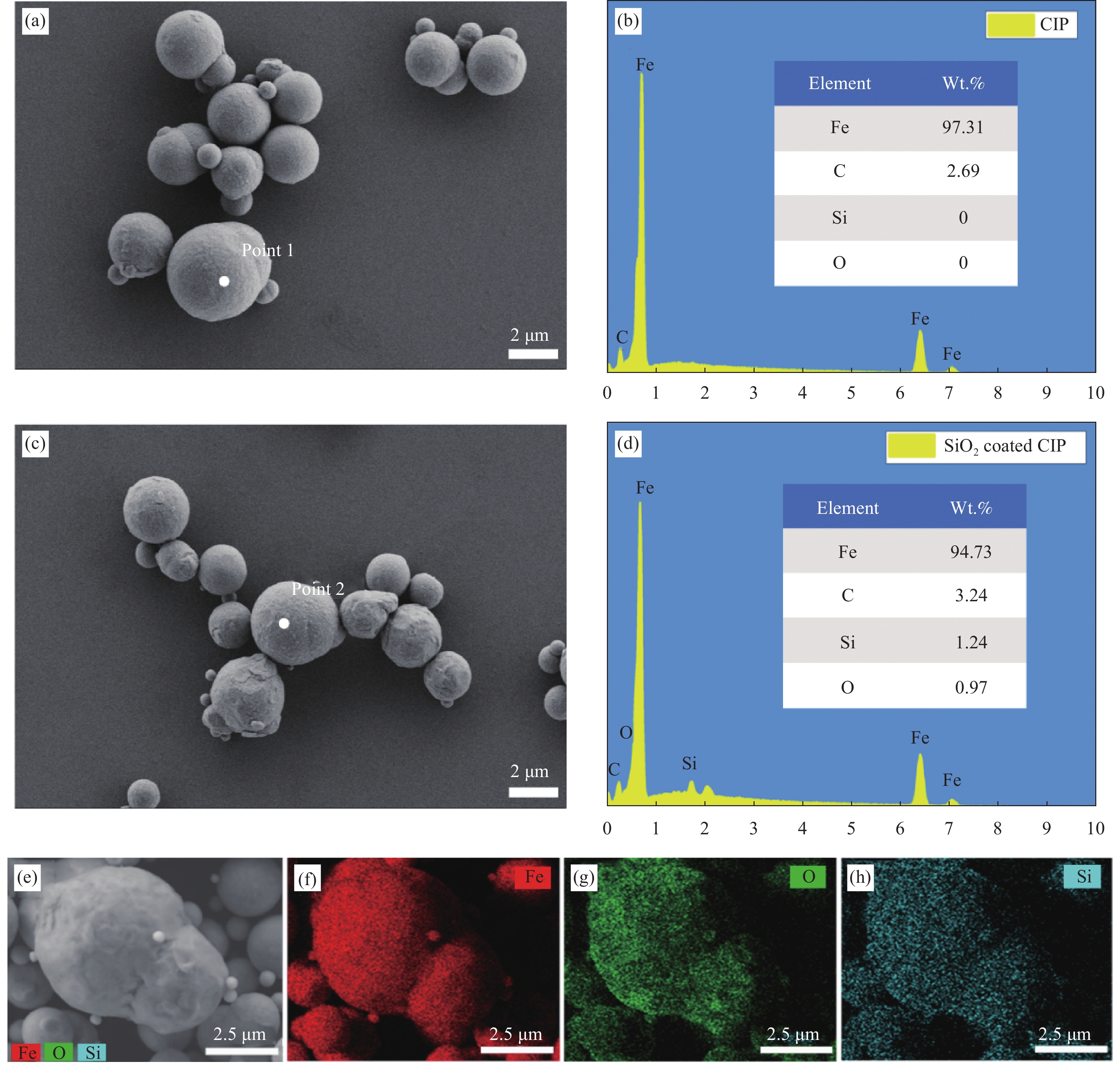
通过Stöber工艺可以将SiO2薄膜有效地包覆在CIP表面。图2显示了包覆SiO2前后CIP的微观形貌。从图2(a)中可以看出,CIP的微观结构呈现出典型的洋葱头状形貌,且颗粒表面较为光滑,粒径大约为3-5 μm。而从图2(c)中可以清楚地看到,CIP@SiO2的颗粒表面变得更粗糙,这可以初步判断CIP表面覆有涂层。结合EDS检测对图中点1和点2的位置进行了分析,进一步确定了表面涂层的成分为SiO2。如图2(d)所示,在CIP表面检测到了硅元素和氧元素的存在,而在图2(b)中却未检测到,这证明了TEOS的水解产物SiO2在CIP表面形成了一层薄膜。通过面扫描分布图2(e-h)可以清晰地看出,在CIP表面均匀分布有硅元素和氧元素,说明其形成了以CIP为核心,SiO2为外壳的核壳结构,从而达到抗氧化效果。
![]() 图 2 SiO2包覆CIP前后的SEM图像:(a)包覆前;(b)包覆后。EDS点扫描谱图:(c)点1;(d)点2。面扫描元素分布图像:(e) CIP@SiO2电子图像;(f) Fe元素分布图像;(g) O元素分布图像;(h) Si元素分布图像。Figure 2. SEM images before and after SiO2 coated CIP: (a) before coating; (b) after coating. EDS spectrum: (c) point 1; (d) point 2. Element distribution maps: (e) CIP@SiO2 image; (f) Fe distribution map; (g) O distribution map; (h) Si distribution map.
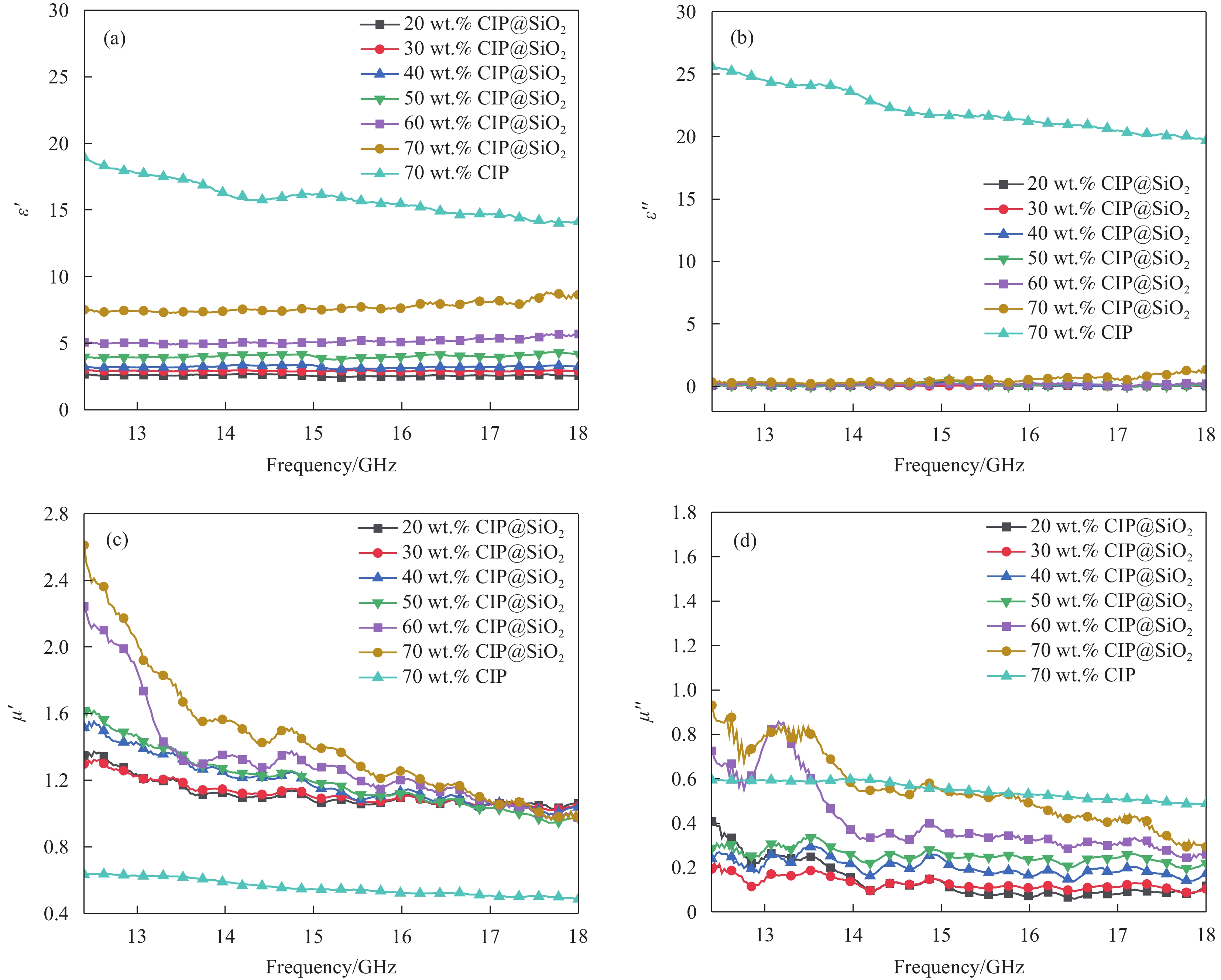
图 2 SiO2包覆CIP前后的SEM图像:(a)包覆前;(b)包覆后。EDS点扫描谱图:(c)点1;(d)点2。面扫描元素分布图像:(e) CIP@SiO2电子图像;(f) Fe元素分布图像;(g) O元素分布图像;(h) Si元素分布图像。Figure 2. SEM images before and after SiO2 coated CIP: (a) before coating; (b) after coating. EDS spectrum: (c) point 1; (d) point 2. Element distribution maps: (e) CIP@SiO2 image; (f) Fe distribution map; (g) O distribution map; (h) Si distribution map.通过复介电常数(εr=ε'−jε'')和复磁导率(μr=μ'-jμ'')可以确定吸波复合材料的吸波特性[33]。CIP-GF/PA6和CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料(其中,由于GF为良好的透波材料,不影响材料的吸波性能,因此随CIP含量的增加,60 wt.%和70 wt.%的复合材料中GF含量降低为10 wt.%,其余均为30 wt.%)的电磁参数和反射损耗(reflection loss,RL)如图3所示。未抗氧化处理的CIP吸波复合材料的介电常数实部和虚部均超过了CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料,说明氧化行为会造成复合材料介电常数的骤增。并且其虚部ε''值超过了实部ε'值,这将会导致复合材料的阻抗失配。在CIP表面包覆SiO2薄膜后,吸波复合材料的ε'和ε''值均有所降低,并且材料介电常数较为稳定,与未包覆的CIP相比,曲线不随频率的增大而呈下降趋势,在测试频率范围内趋于水平,表明SiO2的包覆有利于CIP介电常数的稳定。而未包覆处理的CIP由于在复合材料热压成型的过程中发生了严重的氧化,使复合材料的介电常数增大,将导致阻抗匹配变差,通过SiO2对CIP进行抗氧化处理后,复合材料的介电常数显著降低,有助于改善复合材料的阻抗匹配。通过磁导率实部和虚部的对比可以发现,包覆前复合材料的磁导率实部μ'较低,说明氧化行为对CIP的磁性能也产生了负面影响。磁导率虚部μ''则与包覆后数值相近,约在0.6附近,但明显不同的是,未包覆的曲线变得平滑,波动减少,而包覆材料的曲线均存在多处波动。这是因为曲线的波动是由于材料发生了磁共振现象,而未包覆的CIP发生氧化后对其磁性能产生了较大的影响,使其磁共振能力减弱。由此可见,严重的氧化会导致CIP的μ'值变小,并衰减磁共振能力。
![]() 图 3 复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ''。Figure 3. Electromagnetic parameters of composites: (a) the real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) the imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) the real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) the imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability.
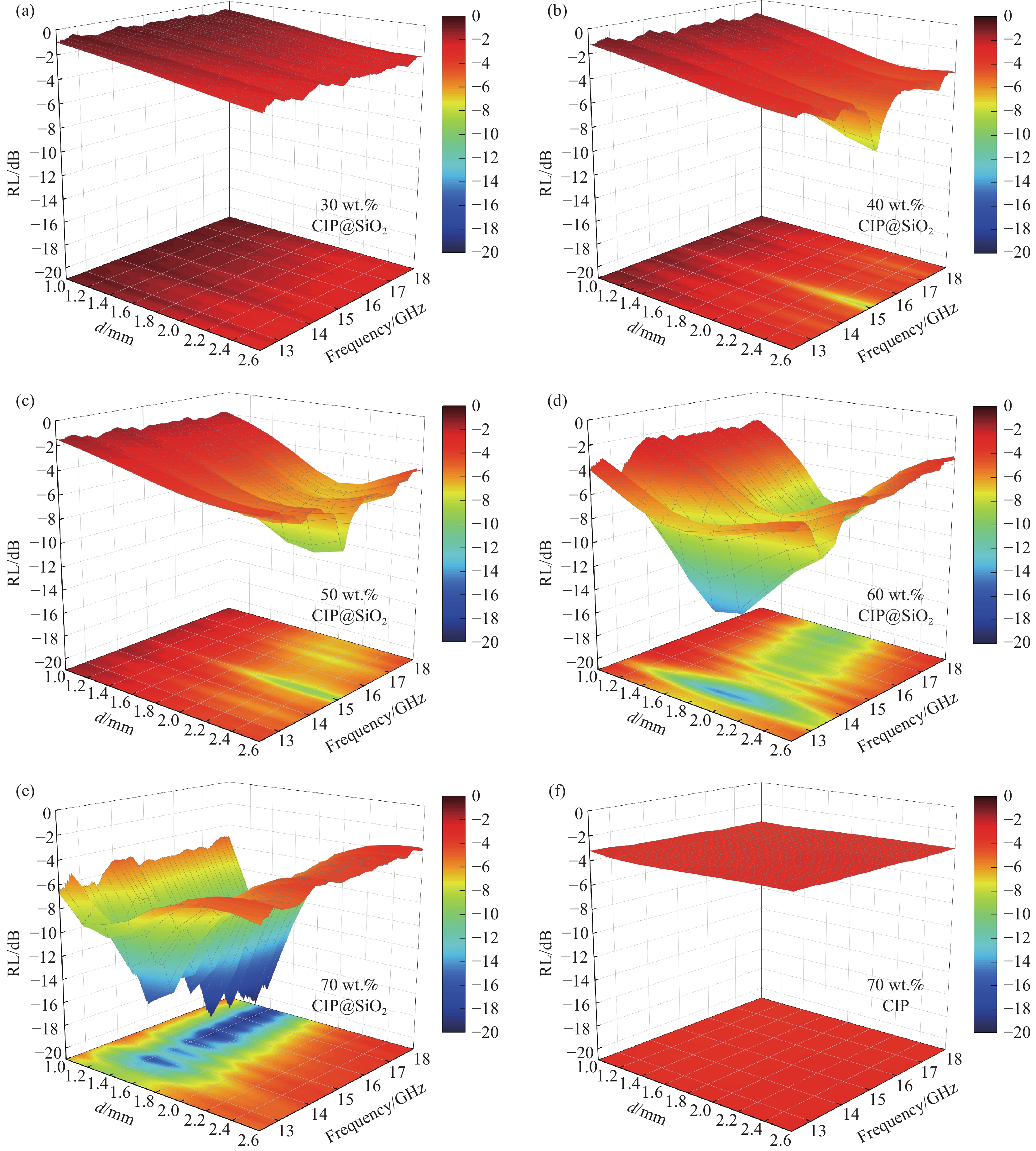
图 3 复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ''。Figure 3. Electromagnetic parameters of composites: (a) the real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) the imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) the real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) the imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability.CIP作为单一吸波剂使用时的负载量较大,如图4所示,当CIP@SiO2的添加量达到70 wt.%时,才显现出复合材料较好的吸波性能。因此,使用单一CIP作为吸波剂不利于复合材料的轻量化处理。另外,通过图4(e)和(f)对比可知,CIP-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的吸波性能较差,其RL基本保持在−3 dB左右,说明在制备复合材料的过程中,CIP的严重氧化导致复合材料吸波性能的严重受损。而包覆SiO2薄膜后制备的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的吸波性能则大大提升,70 wt%CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料在厚度为1.4 mm,频率为17.38 GHz下的最小反射损耗(RLmin)为−19.87 dB,有效吸收带宽(RL≤−10 dB)为4.98 GHz。说明在CIP表面包覆SiO2薄膜,对复合材料的吸波性能提升十分有利。
![]() 图 4 吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a) 30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(b) 40 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(c) 50 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(d) 60 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(e) 70 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(f)70 wt.%CIP的CIP-GF/PA6。Figure 4. RL 3 D plots of composites: (a) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (b) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (c) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (d) 60 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (e) 70 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (f) 70 wt.%CIP of CIP-GF/PA6.
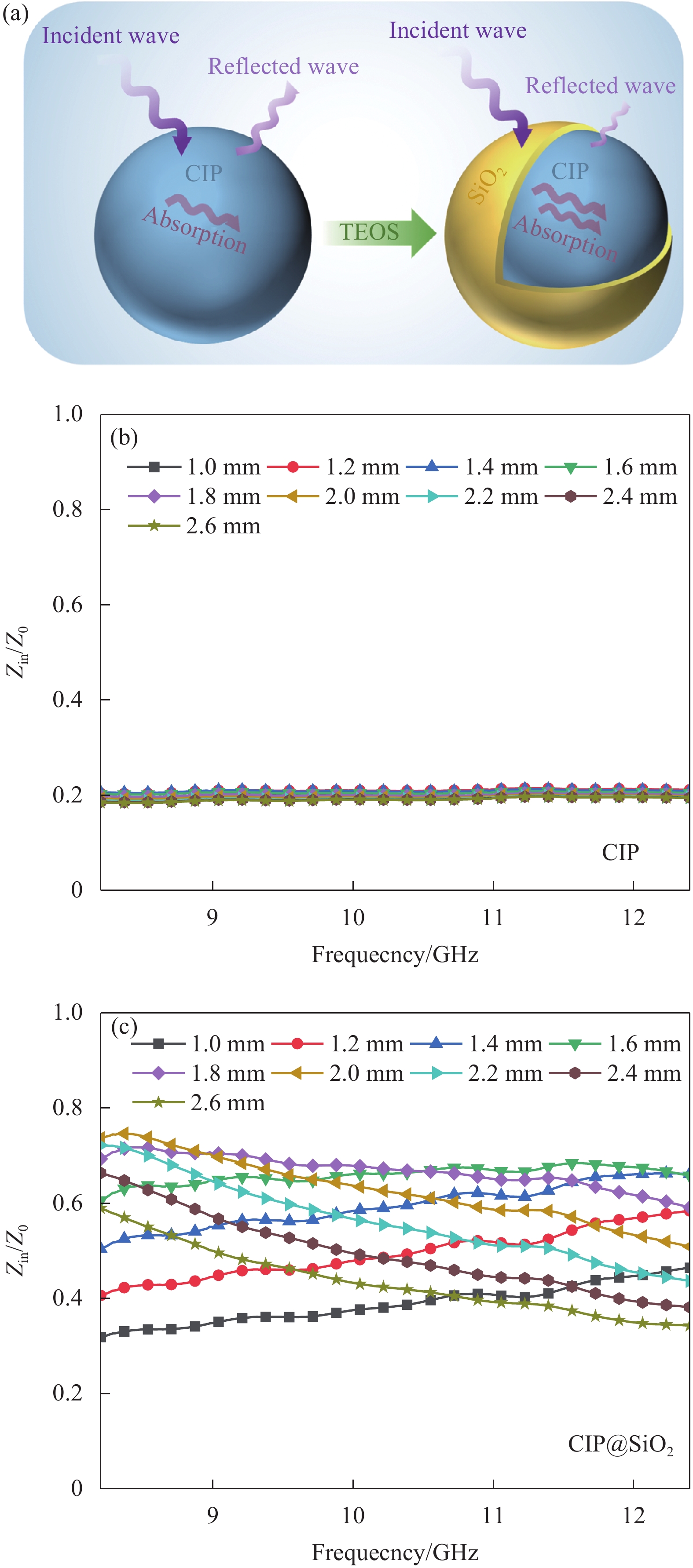
图 4 吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a) 30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(b) 40 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(c) 50 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(d) 60 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(e) 70 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(f)70 wt.%CIP的CIP-GF/PA6。Figure 4. RL 3 D plots of composites: (a) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (b) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (c) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (d) 60 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (e) 70 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (f) 70 wt.%CIP of CIP-GF/PA6.磁性金属微粉CIP相比于非金属吸波剂的阻抗匹配性较差,从而不利于复合材料对微波的吸收。当CIP表面包覆SiO2薄膜后,可以有效降低材料的介电常数,这有利于复合材料的阻抗匹配。如示意图5(a)所示,阻抗匹配较差会使入射波在材料表面发生反射,从而影响微波吸收性能。SiO2薄膜包覆在CIP外可以减少微波在表面发生反射,更多的入射波可以进入材料内部发生微波损耗。通常使用Zin/Z0来表示材料的阻抗匹配特性,其值越接近1.0,则表示阻抗匹配越好,意味着有更多微波可以进入复合材料内。从图5(b)中可知,未处理的CIP使吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值与理论值1.0相差甚远,其值约为0.2。这表明CIP-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的阻抗匹配较差,也预示着复合材料的吸波性能较差。而图5(c)可知,包覆有SiO2薄膜的CIP吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值有了明显的改善,当吸波复合材料厚度为2.0 mm时,在8.36 GHz频率下的Zin/Z0值达到了0.74,最接近于理想值。CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的阻抗匹配优于CIP-GF/PA6吸波复合材料,这表明复合材料的阻抗匹配通过SiO2包覆层得到了改善,从而对复合材料的吸波性能有较大的帮助。
2.2 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的吸波性能
根据以往的研究[8]可知,仅CB作为单一吸波剂时,需加入至少5 wt.%的CB时,复合材料表现出较好的吸波性能,但过量添加纳米材料CB会导致复合材料的力学性能下降。图6所示为1 wt.%CB的CB-GF/PA6复合材料的RL图,在厚度为2.6 mm,频率为14.3 GHz下的RLmin为−8.51 dB,此时复合材料拥有较弱的吸波能力。因此,固定CB的含量为1 wt.%以保证其在高频段的吸波性能,并配合CIP@SiO2以达到拓宽吸收频带的目的。
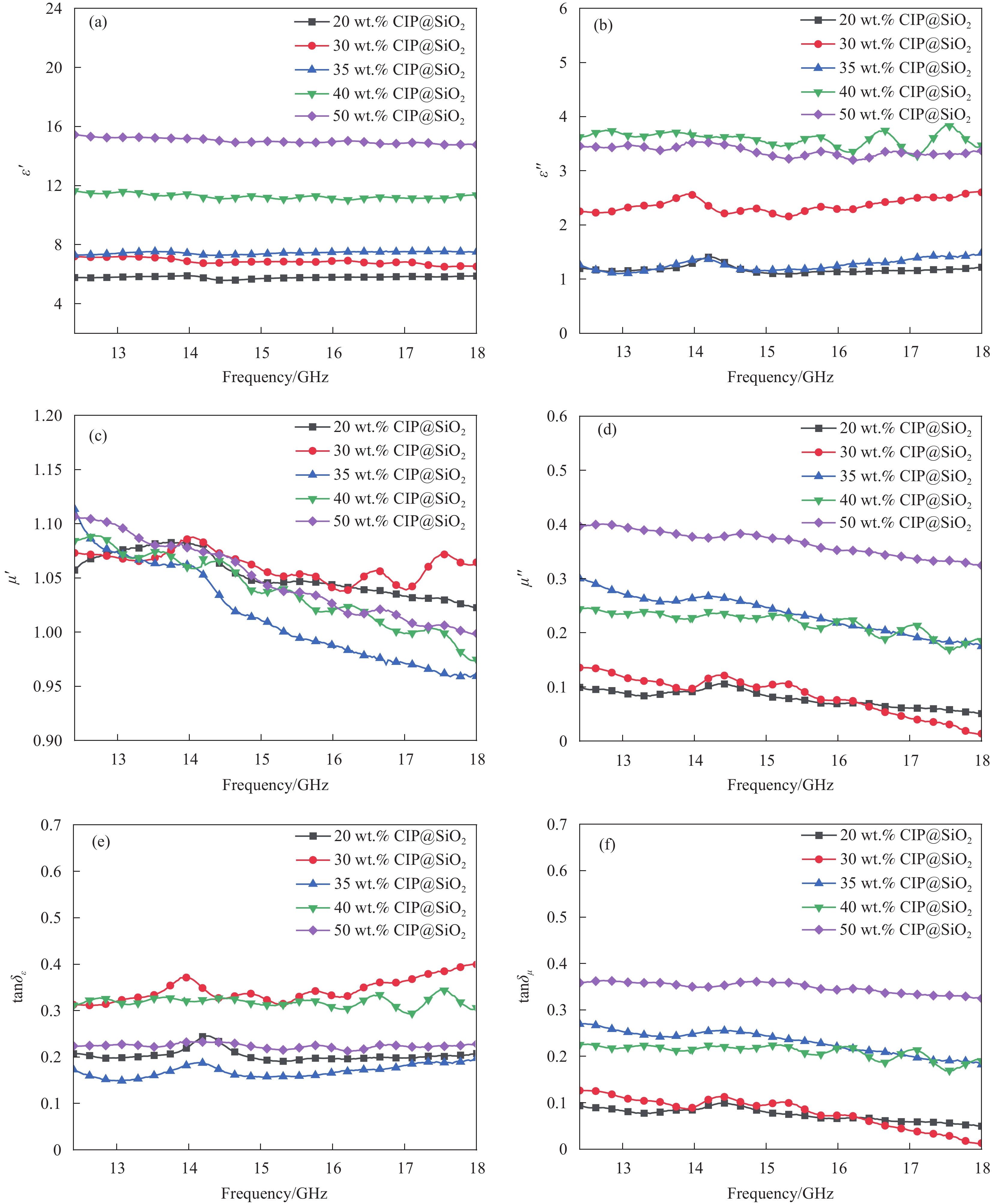
图7分别展示了CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的电磁参数和损耗角正切(CIP@SiO2含量分别为20 wt.%、30 wt.%、35 wt.%、40 wt.%和50 wt.%)。ε'代表材料对电能的存储能力,随着CIP@SiO2含量的逐渐增加,CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的ε'逐渐增大。当CIP@SiO2的含量从20 wt.%增加到50 wt.%时,在12.4 GHz处的ε'值从5.77增加到15.44。ε''代表材料对电能的消耗能力,从图7(b)中可以看出,不同含量CIP@SiO2对电能的消耗能力不同,其中40 wt.%CIP@SiO2含量的吸波复合材料的ε''值最大,大约为3.6。曲线的波动可能是由于在高频电场作用下,电偶极子的定向极化滞后于电场的周期性变化,这是电损耗材料的主要特征。μ'和μ''分别代表材料对磁能的存储和消耗能力,如图7(c,d)所示,五种复合材料的μ'值相似,均维持在0.95-1.05之间,且都随频率的增加呈现出下降趋势。μ''则展现出了不同的变化趋势,其中,50 wt.%CIP@SiO2含量的吸波复合材料的μ''值最大,这表明复合材料的磁能消耗最强。而评价吸波材料对电能和磁能的损耗则需要综合考虑实部和虚部,介电损耗角正切(tanδε=ε′′ε′)和磁损耗角正切(tanδμ=μ′′μ′)可分别表示吸波复合材料对电能的损耗强度和对磁能损耗强度。如图7(e,f)所示,CIP@SiO2含量为20 wt.%、30 wt.%和40 wt.%的吸波复合材料的tanδε值比tanδμ值大,这表明吸波复合材料对微波的损耗方式由介电损耗主导。其中,CIP@SiO2含量为30 wt.%的吸波复合材料的tanδε值最大,表明其介电损耗能力最强。而35 wt.%和50 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的tanδε值小于tanδμ值,表明吸波复合材料对微波的损耗机制主要是磁损耗。在CB和CIP不同损耗机制的协同增强下,复合材料的吸波性能将得到较大的提升。另外,由于CB的加入,使复合材料中的界面增多,从而使界面极化也得到了提升,有利于复合材料吸波性能的提升。
![]() 图 7 不同CIP@SiO2含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ'';(e)介电损耗角正切tanδε;(f)磁损耗角正切tanδμ。Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of different contents of CIP@SiO2 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composites: (a) real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability; (e) dielectric loss angle tangent tanδε; (f) magnetic loss angle tangent tanδμ.
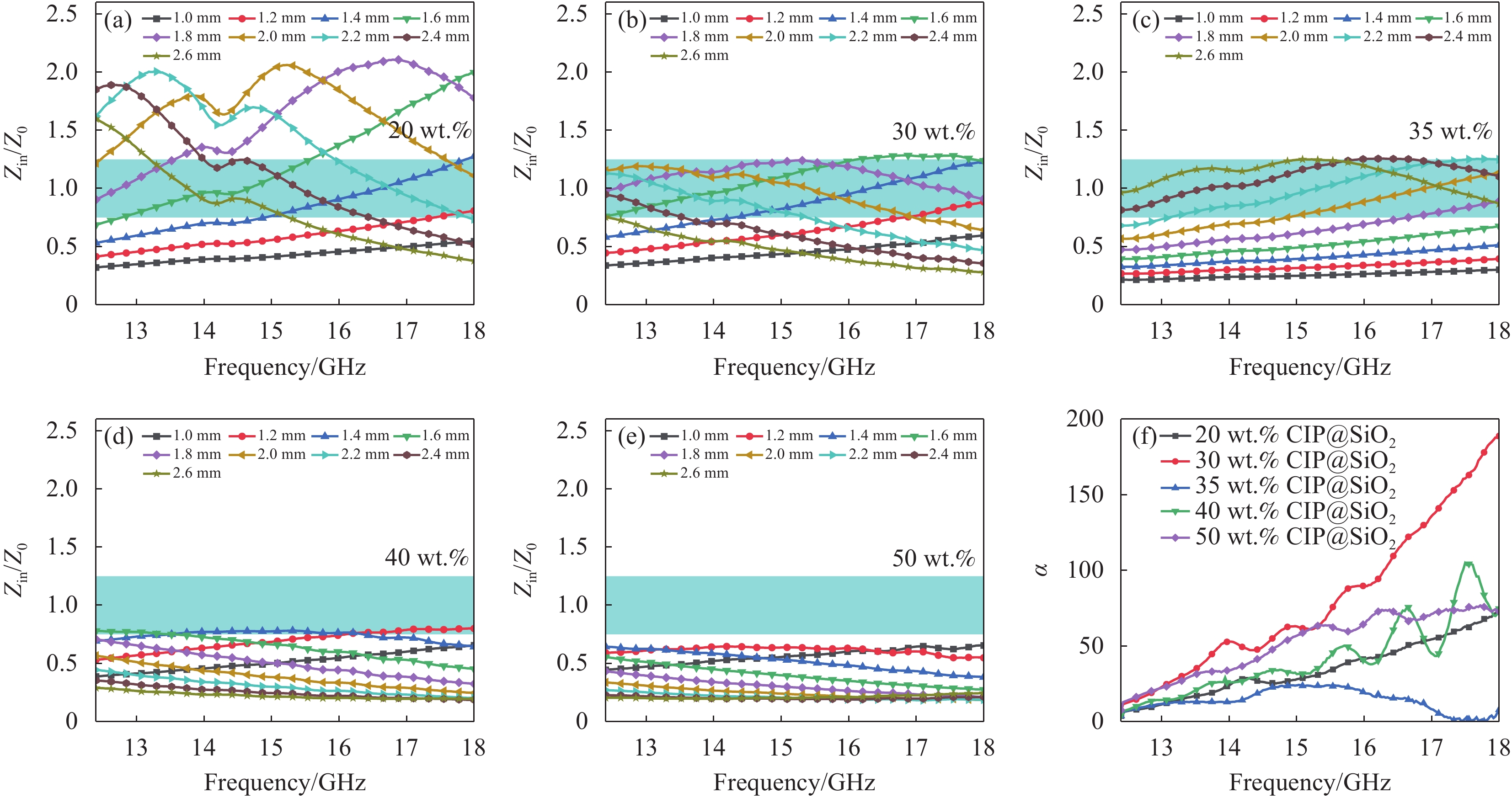
图 7 不同CIP@SiO2含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ'';(e)介电损耗角正切tanδε;(f)磁损耗角正切tanδμ。Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of different contents of CIP@SiO2 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composites: (a) real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability; (e) dielectric loss angle tangent tanδε; (f) magnetic loss angle tangent tanδμ.图8为CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料在不同厚度下的Zin/Z0曲线。如图8(a)所示,CIP@SiO2含量为20 wt.%的吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值远超过1.0,最高值达到2.1,表明其复合材料的阻抗匹配较差。如图8(b,c)所示,30 wt.%和35 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值最接近于理想值1.0,说明复合材料具有较好的阻抗匹配,这有利于复合材料对微波的吸收。随着CIP@SiO2含量的增加,如图8(d,e)所示,40 wt.%和50 wt.% CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值逐渐远离理想值1.0,其中40 wt.%CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值均小于0.8,50 wt.% CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0值均小于0.7,并可以预测当CIP@SiO2含量继续增大后,复合材料的阻抗匹配会逐渐变差。这主要是由于CIP@SiO2含量的增大,导致复合材料产生趋肤效应,从而使微波的入射深度减小,最终影响材料的微波吸收效果。另外,衰减常数ɑ是评估吸波材料微波损耗能力的另一重要依据。如图8(f)所示,30 wt.% CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的ɑ值最高,表明此时CB和CIP的协同增强效果最好,复合材料的微波损耗能力达到最强。
![]() 图 8 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0:(a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(d) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(f)不同含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的衰减常数ɑ。Figure 8. Zin/Z0 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (f) Attenuation constant ɑ of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite with different content.
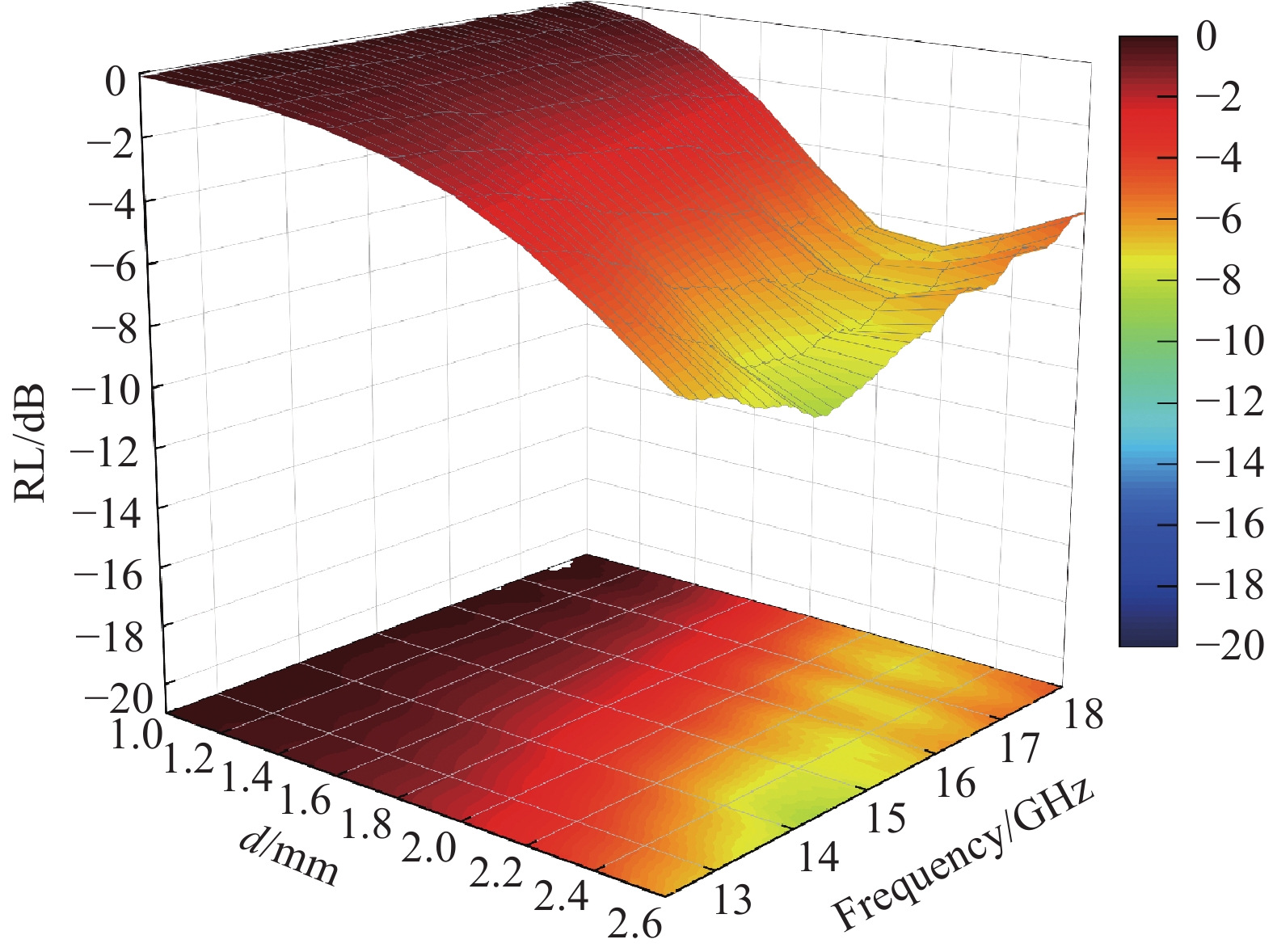
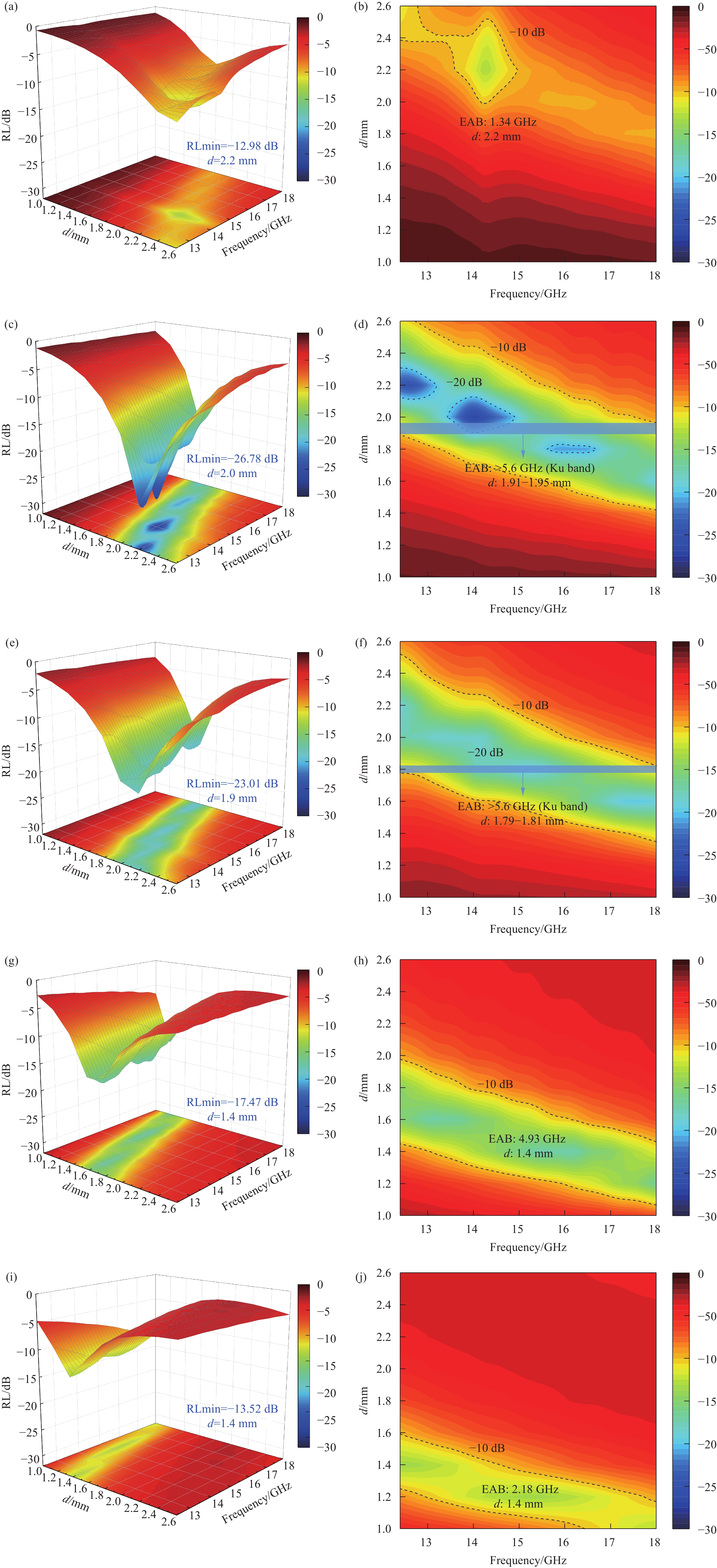
图 8 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0:(a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(d) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(f)不同含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的衰减常数ɑ。Figure 8. Zin/Z0 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (f) Attenuation constant ɑ of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite with different content.为了进一步评估CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的吸波特性,图9给出复合材料的RL三维图和吸收带宽示意图。CIP@SiO2含量为20 wt.%的吸波复合材料在厚度为2.2 mm,频率为14.27 GHz下的RLmin为−12.98 dB,有效吸收带宽为1.34 GHz。当CIP@SiO2含量增加到30 wt.%时,如图9(c,d)所示,吸波复合材料在厚度为2.0 mm,频率为13.99 GHz下的RLmin为−26.79 dB,有效吸收带宽拓宽到5.09 GHz;在厚度为1.91-1.95 mm时,有效吸收带宽超过了5.6 GHz,涵盖了整个Ku波段。35 wt.% CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料在厚度为1.9 mm,频率为14.19 GHz下的RLmin为-23.01 dB,有效吸收带为4.59 GHz;在厚度为1.79-1.81 mm时的有效吸收带宽也超过了5.6 GHz,涵盖整个Ku波段。当CIP@SiO2的含量继续增加后,吸波复合材料的微波吸收性能开始下降。40 wt.% CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的RLmin在厚度为1.4 mm,频率为16.12 GHz下为−17.47 dB,有效吸带宽为4.93 GHz。50 wt.%时,RLmin为−13.52 dB,有效吸收带宽为2.18 GHz。这是由于过多的CIP@SiO2导致趋肤效应的产生,从而吸波性能逐渐变差。从以上结果可以看出,随着CIP@SiO2含量的逐渐增加,吸波复合材料的吸波性能呈现出先提升后下降的趋势。含有30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料具有最强的微波损耗能力,且其阻抗匹配性能最好,因而具有最佳的吸波性能。由结果可知,添加两种吸波剂复合材料的有效吸收带宽比使用单一的CB或CIP的吸波复合材料更宽,这表明可以通过不同类型吸波剂的复合来调节和设计材料的吸波性能。
![]() 图 9 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a, b)20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c, d)30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e, f)35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(g, h)40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(i, j)50 wt.% CIP@SiO2。Figure 9. RL of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a, b) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c, d) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e, f) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (g, h) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (i, j) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2.
图 9 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a, b)20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c, d)30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e, f)35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(g, h)40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(i, j)50 wt.% CIP@SiO2。Figure 9. RL of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a, b) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c, d) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e, f) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (g, h) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (i, j) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2.吸波材料的磁损耗形式主要有磁滞损耗、畴壁共振、自然共振和涡流损耗等。在2-18 GHz的频率范围内,磁滞损耗和畴壁共振可以忽略不计[34]。因此,吸波复合材料在Ku波段的磁损耗主要由自然共振和涡流损耗决定,具体的损耗形式可由C0来确定,公式如下[35]:
C0=μ′′(μ′)2f (4) 通常,如果C0值随频率改变而发生变化,为磁共振现象,低频范围的振动属于自然共振,而高频范围的振动为交换共振。如果C0值不随频率的改变而改变,则为涡流损耗。CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的C0值随频率变化的曲线如图10所示。五条曲线都随着频率的增加而逐渐减小,因此CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的磁损耗方式为磁共振,且振动峰均位于高频段,属于交换共振。其中,20 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的C0曲线在频率14.4 GHz附近出现波动;30 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的曲线在14-16 GHz频率范围内出现多处波动;40 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的曲线在15-18 GHz内出现多处波动,这些都是由于交换共振较强所产生的。而35 wt.%和50 wt.% CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的C0曲线却相对较为平滑,波动较小,这说明其交换共振损耗较弱。
综上所述,CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料吸波性能的提升机理主要有以下四方面:
(1)阻抗匹配:二氧化硅的包覆降低了CIP的介电常数,改善了复合材料的阻抗匹配性能,从而使更多的微波进入材料内部发生损耗。
(2)界面极化:多组分材料的复合增加了异相界面的数量,从而增强了界面极化,提高了复合材料的吸波性能。
(3)偶极极化:CB与CIP在高频电场的作用下,电偶极子的定向极化滞后于电场的周期性变化,从而产生极化弛豫现象消耗掉微波的能量。
(4)磁共振损耗:复合材料以交换共振损耗的方式实现了对微波能量的衰减,从而提升了材料的吸波性能。
2.3 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的力学性能
图11为CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料(CB含量为1 wt.%,CIP@SiO2含量分别为20 wt.%、25 wt.%、30 wt.%、35 wt.%和40 wt.%)的断口微观形貌以及弯曲强度、剪切强度和摆锤冲击强度。综合对比发现,当CIP@SiO2含量为40 wt.%时,吸波复合材料的力学性能最好,其抗弯强度为212.8±9.8 MPa,抗剪强度为21.0±1.4 MPa,冲击强度为64.4±6.2 kJ/m2。由于CB为纳米颗粒,会导致基体结构变得疏松,将PA6原本的塑性变形行为改变成脆性断裂,从而大幅度降低了复合材料的力学性能[8]。CIP@SiO2颗粒的引入,强化了复合材料的颗粒增强效果(裂纹钉扎、桥联和绕过机制),并与玻璃纤维共同增强,保证了复合材料的力学性能[36]。从图11(a)中可以看出,拔出的GF上粘连有PA6基体,说明GF与基体的结合情况较好,GF的存在保证了复合材料的力学性能。另外,基体中CIP@SiO2颗粒的分散较为均匀。从图11(b)的局部放大图中可以看出,CIP@SiO2颗粒与PA6基体的结合紧密,这有利于提升复合材料的颗粒增强效果,与GF实现了协同增强。然而,随着CIP@SiO2含量的逐渐增加,复合材料的力学性能在提高的同时,材料的重量和密度也在增加,因此有必要综合考虑复合材料的各项性能来选择最佳的配比方案。
3. 结 论
本工作重点研究了磁损耗型吸波剂羰基铁粉(CIP)表面包覆SiO2薄膜处理及其加入量对于炭黑(CB)-CIP@SiO2-玻璃纤维/尼龙6(CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6)复合材料吸波性能和力学性能的影响,得到了如下结论:
(1) SiO2薄膜包覆CIP所形成的核壳结构解决了CIP的易氧化问题,保证了CIP的电磁性能,并改善了阻抗匹配。
(2) CB和CIP@SiO2对复合材料吸波性能的协同增强,使吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽得到拓展。其中,含量为30 wt.%和35 wt.%CIP@SiO2吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽超过了5.6 GHz,涵盖整个Ku波段。
(3)随着CIP@SiO2含量的逐渐增加,在颗粒增强与纤维增强的共同作用下使复合材料的力学性能也逐渐提高,含40 wt.% CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料的弯曲强度为212.8±9.8 MPa,剪切强度为21.0±1.4 MPa,摆锤冲击强度为64.4±6.2 kJ/m2。
综合择出结构与吸波一体化的最佳CIP@SiO2含量为35 wt.%。这种方法有效地提升了材料的吸波性能,拓宽了吸收频带,并为吸波性能的调节和设计提供了思路。另外,改善了复合材料的力学性能的同时减少了CIP在复合材料中的负载量,有利于复合材料的轻量化。
-
图 2 SiO2包覆CIP前后的SEM图像:(a)包覆前;(b)包覆后。EDS点扫描谱图:(c)点1;(d)点2。面扫描元素分布图像:(e) CIP@SiO2电子图像;(f) Fe元素分布图像;(g) O元素分布图像;(h) Si元素分布图像。
Figure 2. SEM images before and after SiO2 coated CIP: (a) before coating; (b) after coating. EDS spectrum: (c) point 1; (d) point 2. Element distribution maps: (e) CIP@SiO2 image; (f) Fe distribution map; (g) O distribution map; (h) Si distribution map.
图 3 复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ''。
Figure 3. Electromagnetic parameters of composites: (a) the real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) the imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) the real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) the imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability.
图 4 吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a) 30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(b) 40 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(c) 50 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(d) 60 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(e) 70 wt.%CIP@SiO2的CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6;(f)70 wt.%CIP的CIP-GF/PA6。
Figure 4. RL 3 D plots of composites: (a) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (b) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (c) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (d) 60 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (e) 70 wt.% CIP@SiO2 of CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6; (f) 70 wt.%CIP of CIP-GF/PA6.
图 7 不同CIP@SiO2含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数的实部ε';(b)介电常数的虚部ε'';(c)磁导率的实部μ';(d)磁导率的虚部μ'';(e)介电损耗角正切tanδε;(f)磁损耗角正切tanδμ。
Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of different contents of CIP@SiO2 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composites: (a) real part ε' of dielectric constant; (b) imaginary part ε'' of dielectric constant; (c) real part μ' of magnetic permeability; (d) imaginary part μ'' of magnetic permeability; (e) dielectric loss angle tangent tanδε; (f) magnetic loss angle tangent tanδμ.
图 8 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的Zin/Z0:(a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(d) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(f)不同含量的CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的衰减常数ɑ。
Figure 8. Zin/Z0 of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (b) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (f) Attenuation constant ɑ of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite with different content.
图 9 CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6吸波复合材料的RL三维图:(a, b)20 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(c, d)30 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(e, f)35 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(g, h)40 wt.% CIP@SiO2;(i, j)50 wt.% CIP@SiO2。
Figure 9. RL of CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6 composite: (a, b) 20 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (c, d) 30 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (e, f) 35 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (g, h) 40 wt.% CIP@SiO2; (i, j) 50 wt.% CIP@SiO2.
-
[1] CHOI W H, KIM C G. Broadband microwave-absorbing honeycomb structure with novel design concept[J]. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2015, 83: 14-20. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.08.027
[2] HUANG H M, WANG W, CAO T S, et al. Broadband radar absorbing performance of corrugated structure[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 253: 112809. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112809
[3] MARRA F, LECINI J, TAMBURRANO A, et al. Broadband Electromagnetic Absorbing Structures Made of Graphene/Glass-Fiber/Epoxy Composite[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2020, 68(2): 590-601. DOI: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2950223
[4] 张明伟, 曲冠达, 庞梦瑶, et al. 电磁屏蔽机理及涂敷/结构型吸波复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(Z1): 62-70. ZHANG Mingwei, QU Guanda, PANG Mengyao, et al. Research Progress of Electromagnetic Shielding Mechanism and Coated /Structural Absorbing Composite Materials[J]. Mterials reports, 2021, 35(Z1): 62-70 (in Chinese).
[5] CHOI W H, JANG H K, SHIN J H, et al. Wideband radar absorbing structure with low density material and load-bearing MWCNT added composite material[J]. Electronics Letters, 2013, 49(9): 620-621. DOI: 10.1049/el.2013.0645
[6] LIANG C B, GU Z J, ZHANG Y L, et al. Structural Design Strategies of Polymer Matrix Composites for Electromagnetic Interference Shielding: A Review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2021, 13(1): 181. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-021-00707-2
[7] 熊健, 李志彬, 刘惠彬. 航空航天轻质复合材料壳体结构研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6): 1628-1650. XIONG Jian, LI Zhibin, LIU Huibin, et al. Advances in aerospace lightweight composite shell structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(6): 1628-1650 (in Chinese).
[8] HU W X, YIN H F, YUAN H D, et al. Microwave absorption and mechanical properties of glass fiber/polyamide 6 composites containing carbon black by microstructural design[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2023, 233: 109927. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2023.109927
[9] DONG J, ZHOU W C, QING Y C, et al. Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of CB doped SiO2f/PI double-layer composites[J]. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12): 14007-14012. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.04.252
[10] DONG J, ZHOU W C, DUAN S C, et al. Mechanical, dielectric and microwave absorption properties of carbon black (CB) incorporated SiO2f/PI composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(20): 17100-17107. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-018-9860-z
[11] 胡婉欣, 尹洪峰, 袁蝴蝶, et al. 纤维增强树脂基吸波复合材料的研究进展[J]. 中国塑料, 2022, 36(10): 178-189. HU Wanxin, YIN Hongfeng, YUAN Hudie, et al. Research status of fiber reinforced resin matrix microwave absorbing composite[J]. China Plastics, 2022, 36(10): 178-189 (in Chinese).
[12] HUANG Y X, WU D, CHEN M J, et al. Evolutionary optimization design of honeycomb metastructure with effective mechanical resistance and broadband microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2021, 177: 79-89. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.02.066
[13] ZHOU D, HUANG X Z, DU Z J. Analysis and Design of Multilayered Broadband Radar Absorbing Metamaterial Using the 3-D Printing Technology-Based Method[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2017, 16: 133-136. DOI: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2560904
[14] YUCHANG Q, WANCHENG Z, SHU J, et al. Microwave electromagnetic property of SiO2-coated carbonyl iron particles with higher oxidation resistance[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2011, 406(4): 777-780. DOI: 10.1016/j.physb.2010.11.079
[15] ZHANG J X, FENG Y B, QIU T, et al. Preparation and characterization of carbonyl iron powder/millable polyurethane elastomer microwave absorbing patch[J]. Polymer Composites, 2014, 35(7): 1318-1324. DOI: 10.1002/pc.22782
[16] GAO Y, GAO X Y, LI J, et al. Improved microwave absorbing property provided by the filler's alternating lamellar distribution of carbon nanotube/carbonyl iron/poly (vinyl chloride) composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2018, 158: 175-185. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.11.029
[17] HUANG L X, DUAN Y P, YANG X, et al. Ultra-flexible composite metamaterials with enhanced and tunable microwave absorption performance[J]. Composite Structures, 2019, 229: 111469. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111469
[18] LI W P, ZHU L Q, GU J, et al. Microwave absorption properties of fabric coated absorbing material using modified carbonyl iron power[J]. Composites Part B-Engineering, 2011, 42(4): 626-630. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.02.019
[19] TANG J, MA L, HUO Q, et al. The influence of PVP on the synthesis and electromagnetic properties of PANI/PVP/CIP composites[J]. Polymer Composites, 2014, 36(10): 1799-1806.
[20] TANG J H, MA L, TIAN N, et al. Synthesis and electromagnetic properties of PANI/PVP/CIP core-shell composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B-Advanced Functional Solid-State Materials, 2014, 186: 26-32.
[21] CHEN X T, ZHANG D, CHEN H Y, et al. Preparation and characterization of CIP@Fe3O4@PANI composites[J]. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2021, 628: 127410.
[22] HE Z F, FANG Y, WANG X J, et al. Microwave absorption properties of PANI/CIP/Fe3O4 composites[J]. Synthetic Metals, 2011, 161(5-6): 420-425. DOI: 10.1016/j.synthmet.2010.12.020
[23] WANG H Y, ZHU D M, ZHOU W C, et al. Electromagnetic property of SiO2-coated carbonyl iron/polyimide composites as heat resistant microwave absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2015, 375: 111-116. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.09.061
[24] LI J, FENG W J, WANG J S, et al. Impact of silica-coating on the microwave absorption properties of carbonyl iron powder[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2015, 393: 82-87. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.05.049
[25] AMIRMAHANI N, MAHDIZADEH H, MALAKOOTIAN M, et al. Evaluating Nanoparticles Decorated on Fe3O4@SiO2-Schiff Base (Fe3O4@SiO2-APTMS-HBA) in Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Environments[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2020, 30(9): 3540-3551. DOI: 10.1007/s10904-020-01499-5
[26] ZHANG N, WANG Y, CHEN P Z, et al. A rational route towards dual wave-transparent type of carbonyl iron@SiO2@heterogeneous state polypyrrole@paraffin composites for electromagnetic wave absorption application[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 581: 84-95. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.07.087
[27] 穆锐, 刘元雪, 刘晓英. SiO2气凝胶复合材料及其在航空航天领域的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(7): 3359-3375. MU Rui, LIU Yuanxue, LIU Xiaoying, et al. Advances in silica aerogel composites and their research in aerospace[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(7): 3359-3375 (in Chinese).
[28] LAI W W, WANG Y, HE J K. Effects of Carbonyl Iron Powder (CIP) Content on the Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Mechanical Properties of CIP/ABS Composites[J]. Polymers, 2020, 12(8): 1694. DOI: 10.3390/polym12081694
[29] ZHENG Y S, WANG Y. Electromagnetic-Wave Absorption Properties of 3D-Printed Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Carbonyl Iron Powder Composites[J]. Polymers, 2022, 14(22): 4960. DOI: 10.3390/polym14224960
[30] LYU L H, LIU W D, SUN B Z. Electromagnetic Wave-Absorbing and Bending Properties of Three-Dimensional Honeycomb Woven Composites[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(9): 1485. DOI: 10.3390/polym13091485
[31] WANG H Q, WANG M, ZHANG X C, et al. A new type of catalyst allows carbonyl iron powder to be coated with SiO2 for tuned microwave absorption[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces, 2020, 21: 100755. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100755
[32] CHEN Q L, LI L Y, WANG Z L, et al. Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption performance of CIP@ SiO2@Mn0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrite composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 779: 720-727. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.112
[33] YAN J, HUANG Y, WEI C, et al. Covalently bonded polyaniline/graphene composites as high-performance electromagnetic (EM) wave absorption materials[J]. Composites Part a-Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 99: 121-128. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.04.016
[34] WEI C H, HE M K, LI M Q, et al. Hollow Co/NC@MnO2 polyhedrons with enhanced synergistic effect for high-efficiency microwave absorption[J]. Materials Today Physics, 2023, 36: 101142. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2023.101142
[35] WU N N, XU D M, WANG Z, et al. Achieving superior electromagnetic wave absorbers through the novel metal-organic frameworks derived magnetic porous carbon nanorods[J]. Carbon, 2019, 145: 433-444. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.028
[36] 王子健, 周晓东. 连续纤维增强热塑性复合材料成型工艺研究进展[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2021, 10: 120-128. WANG Zijian, ZHOU Xiaodong. Research progress on forming process of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2021, 10: 120-128 (in Chinese).
-
其他相关附件
-
本文图文摘要
点击下载
-
-
目的
随着民用吸波材料需求的增加,宽带吸收性能变得越来越重要。羰基铁粉作为一种磁损耗型金属微粉,具有较高的饱和磁化强度和磁导率,依靠磁损耗可以实现优异的吸波效果,其优异的吸波特性通常表现在较低频段。然而,由于CIP的电阻率较低,复介电常数通常较高,致使阻抗匹配性能较差,并且CIP容易被氧化,从而对其磁性能和吸波性能产生较大的影响。因此本文采用二氧化硅对CIP表面进行包覆,解决其氧化问题,并提升了阻抗匹配。另外,电阻损耗型吸波剂CB通常在较高频段显示出优异的吸波性能,与CIP复合后可拓宽有效微波吸收频带,从而提升复合材料的微波吸收性能。
方法采用了Stber法以正硅酸乙酯为硅源,在CIP表面制备了SiO薄膜。又将CB、CIP@SiO和PA6粉末按不同配比混合均匀,将玻璃纤维和混合好的粉末以逐层堆叠的方式铺在模具中进行压制成型,制备出了CB-CIP@SiO-GF/PA6吸波复合材料。通过场发射扫描电子显微镜和能量色散光谱观察了复合材料的微观结构和元素的确定。采用X射线衍射对材料的物相组成进行分析。使用矢量网络分析仪测试了吸波复合材料在Ku波段的电磁参数。最后,使用万能试验机对材料的弯曲强度和剪切强度进行了测试,使用摆锤冲击试验机对材料的冲击性能进行了测试。
结果(1)SiO薄膜包覆CIP所形成的核壳结构解决了CIP的易氧化问题,保证了CIP的电磁性能,并改善了复合材料的阻抗匹配。(2)CB和CIP@SiO对复合材料吸波性能的协同增强,使吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽得到拓展。其中,含量为30 wt.%和35 wt.%CIP@SiO吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽超过了5.6 GHz,涵盖整个Ku波段。(3)随着CIP@SiO含量的逐渐增加,在颗粒增强与纤维增强的共同作用下使复合材料的力学性能也逐渐提高,含40 wt.% CIP@SiO的吸波复合材料的弯曲强度为212.8±9.8 MPa,剪切强度为21.0±1.4 MPa,摆锤冲击强度为64.4±6.2 kJ/m。
结论这种方法有效地提升了材料的吸波性能,拓宽了吸收频带,并为吸波性能的调节和设计提供了思路。另外,改善了复合材料的力学性能的同时减少了CIP在复合材料中的负载量,有利于复合材料的轻量化。
-
磁性金属微粉羰基铁粉(CIP)拥有良好的电磁性能,且强度高,在吸波复合材料领域的研究越来越多。但其在复合过程中容易被氧化,从而对其电磁性能和吸波性能产生较大的影响。并且在复合材料中的负载量通常较大,导致材料质量的增加,不利于轻量化处理。因此,与其他类型的吸波剂复合是调整CIP吸波复合材料的有效途径。
本文通过二氧化硅(SiO2)薄膜的包覆解决了CIP的易氧化问题,保证了其电磁性能的同时又通过核壳结构提升了CIP的阻抗匹配。并以拓宽微波吸收频带为目的,采用热压成型工艺与吸波剂炭黑(CB)制备了CB-CIP@SiO2-玻璃纤维/尼龙6(CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6)吸波复合材料。研究了磁损耗型吸波剂CIP@SiO2和电阻损耗型吸波剂CB对复合材料微波吸收和力学性能的影响。研究结果表明,在SiO2薄膜的包覆下,CIP充分发挥了其微波吸收特性,并与CB协同提升了复合材料的吸波性能。另外,CIP的负载量从70 wt.%降低至30 wt.%左右,大大减轻了复合材料的质量。其中,掺量为1 wt.%CB和30 wt.%CIP@SiO2的吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽在材料的厚度为1.91-1.95 mm时超过了5.6 GHz且覆盖了整个Ku波段。这种方法一方面拓宽了吸波复合材料的有效吸收带宽,实现了宽带吸波。另一方面,CIP@SiO2的颗粒增强与GF的纤维增强实现共同增强,提升了复合材料的整体力学性能。当CIP@SiO2的含量为40 wt.%时,复合材料的力学性能最佳,弯曲强度为212.8±9.8 MPa,剪切强度为21.0±1.4 MPa,摆锤冲击强度为64.4±6.2 kJ/m2。
(a)CIP@SiO2的微波损耗示意图;(b)CB-CIP@SiO2-GF/PA6宽带吸收性能。





 下载:
下载: