Chemical degradation and recovery of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix composites containing ester bond
-
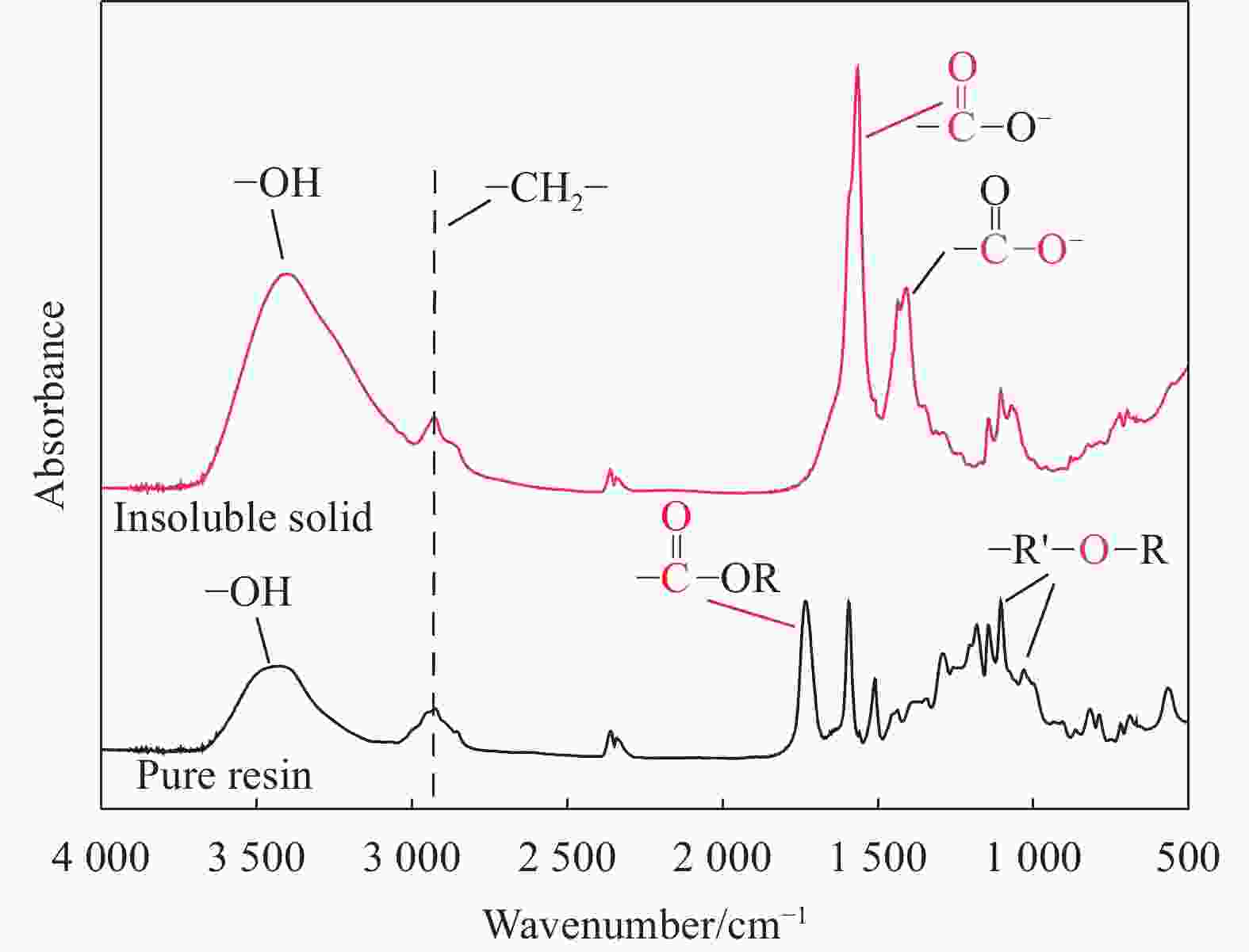
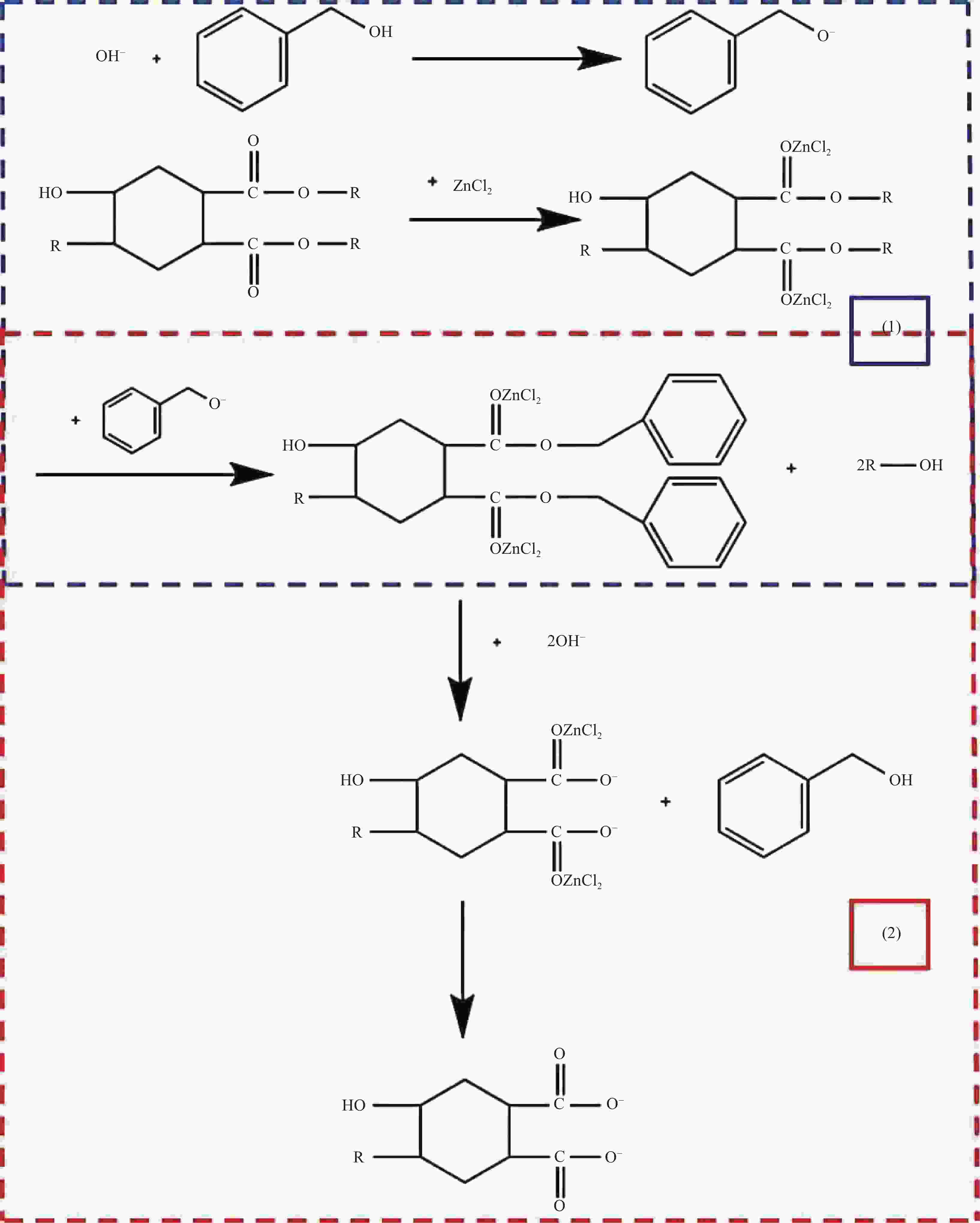
摘要: 随着环氧树脂基碳纤维复合材料的广泛应用,其废旧产品的回收成为低碳发展的重要问题。采用GC-MS、FTIR、XPS、SEM等表征方法研究了含酯键的环氧树脂基碳纤维复合材料的树脂降解机制及降解过程对回收碳纤维结构和性能的影响。研究结果表明:在苯甲醇用量120 mL、质量比W(NaOH)∶W(ZnCl2)=1∶1和降解温度190℃的前提下,最佳降解时间为1 h,较优的降解配方为NaOH和树脂均为1 g。降解得到的产物静置分层,上层清液的苯甲醇含量达99%;环氧树脂的降解机制为苯甲醇在碱性环境下电离生成苄氧基,苄氧基进攻环氧树脂中的酯键,发生酯交换反应,使酯键断裂实现降解,生成苯甲醇酯及醇阴离子,苯甲醇酯在碱性环境下发生皂化反应重新生成苯甲醇,酯交换反应和皂化反应重复进行,直至最终降解完成;回收碳纤维与原始碳纤维的表面O/C、表面光洁程度均在一个水平,回收碳纤维的强度保留率达97%。Abstract: With the wide application of epoxy resin-based carbon fiber composites, the recycling of their waste products had become an important issue for low-carbon development. The resin degradation mechanism of epoxy resin-based carbon fiber composites containing ester bonds and the effect of degradation process on the structure and properties of recycled carbon fibers were studied by GC-MS, FTIR, XPS, SEM and other characterization methods. The results show that the optimal degradation time is 1 h under the conditions of benzyl alcohol dosage of 120 mL, mass ratio W (NaOH)∶W (ZnCl2)=1∶1 and degradation temperature of 190℃, and the optimal dosages of NaOH and resin are both 1 g. The degradation products are separated by standing stratification, and the content of benzyl alcohol in the supernatant is 99%. The degradation mechanism of the resin is as follows: Firstly, benzyl alcohol is ionized to generate benzyloxy group in an alkaline environment, and the benzyloxy groups attack ester bonds in the resin, and transesterification reaction occures to break the ester bond to achieve degradation. Benzyl alcohol ester and alcohol anion are produced by transesterification reaction. Next, the benzyl alcohol ester undergoes saponification reaction in alkaline environment to regenerate benzyl alcohol. The transesterification reaction and the saponification reaction are repeated until the final degradation is completed. The surface O/C and surface smoothness of the recycled carbon fibers and the original carbon fibers are at the same level, and the strength retention rate of the recycled carbon fibers reaches 97%.
-
表 1 碳纤维复合材料环氧树脂降解后所得碳纤维力学性能和表面理化结构与原始碳纤维对比表
Sample Tensile strength of monofilament/GPa Element content surface morphology C/% O/% C/O Initial carbon fibers 3.44±0.08 84.65 13.26 0.157 
Recycled carbon fibers 3.34±0.10 84.51 13.36 0.158 
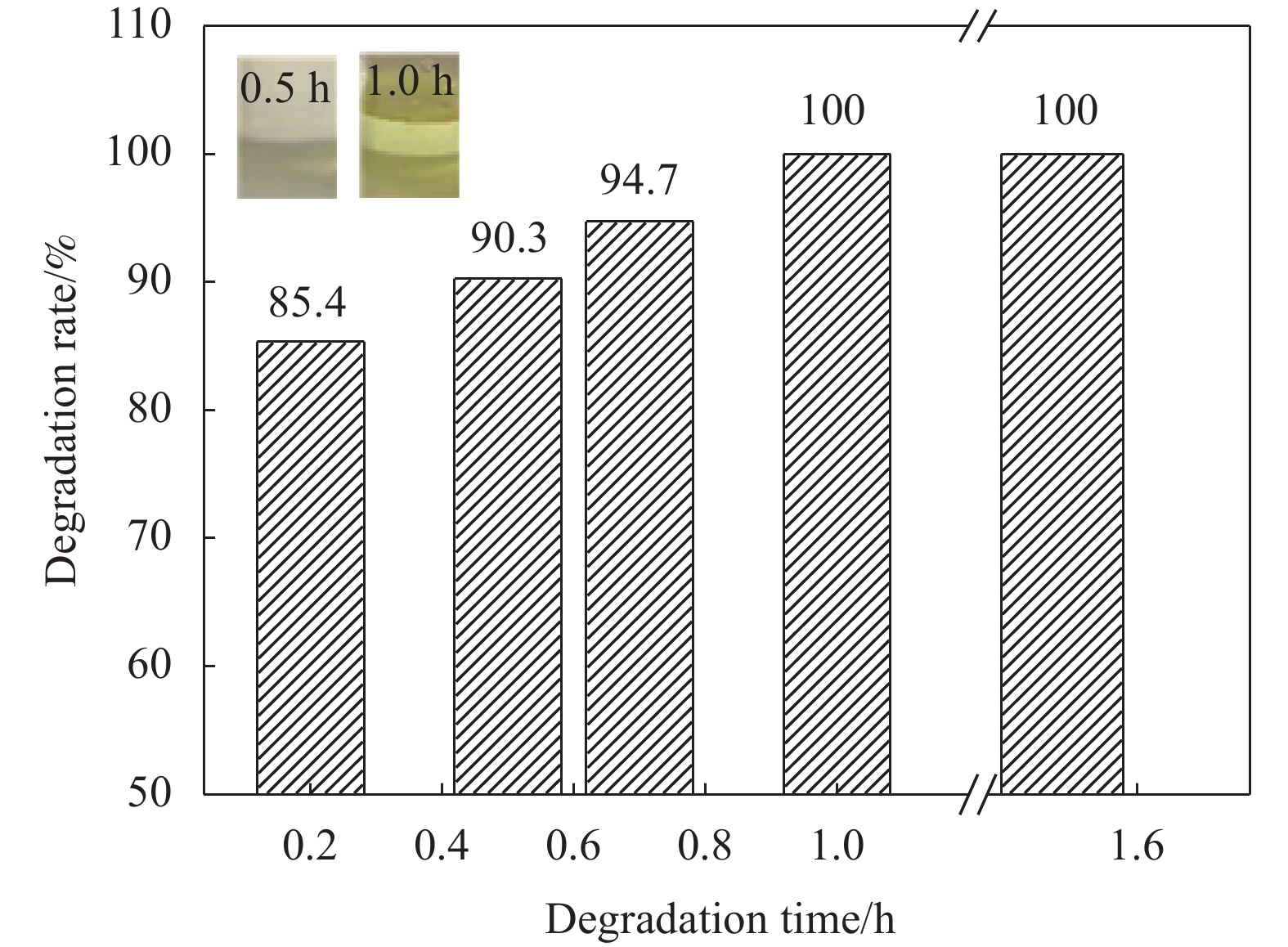
表 1 碳纤维复合材料降解1 h后上清液的GC-MS结果
Table 1. GC-MS results of supernatant after 1 h degradation of carbon fiber composite
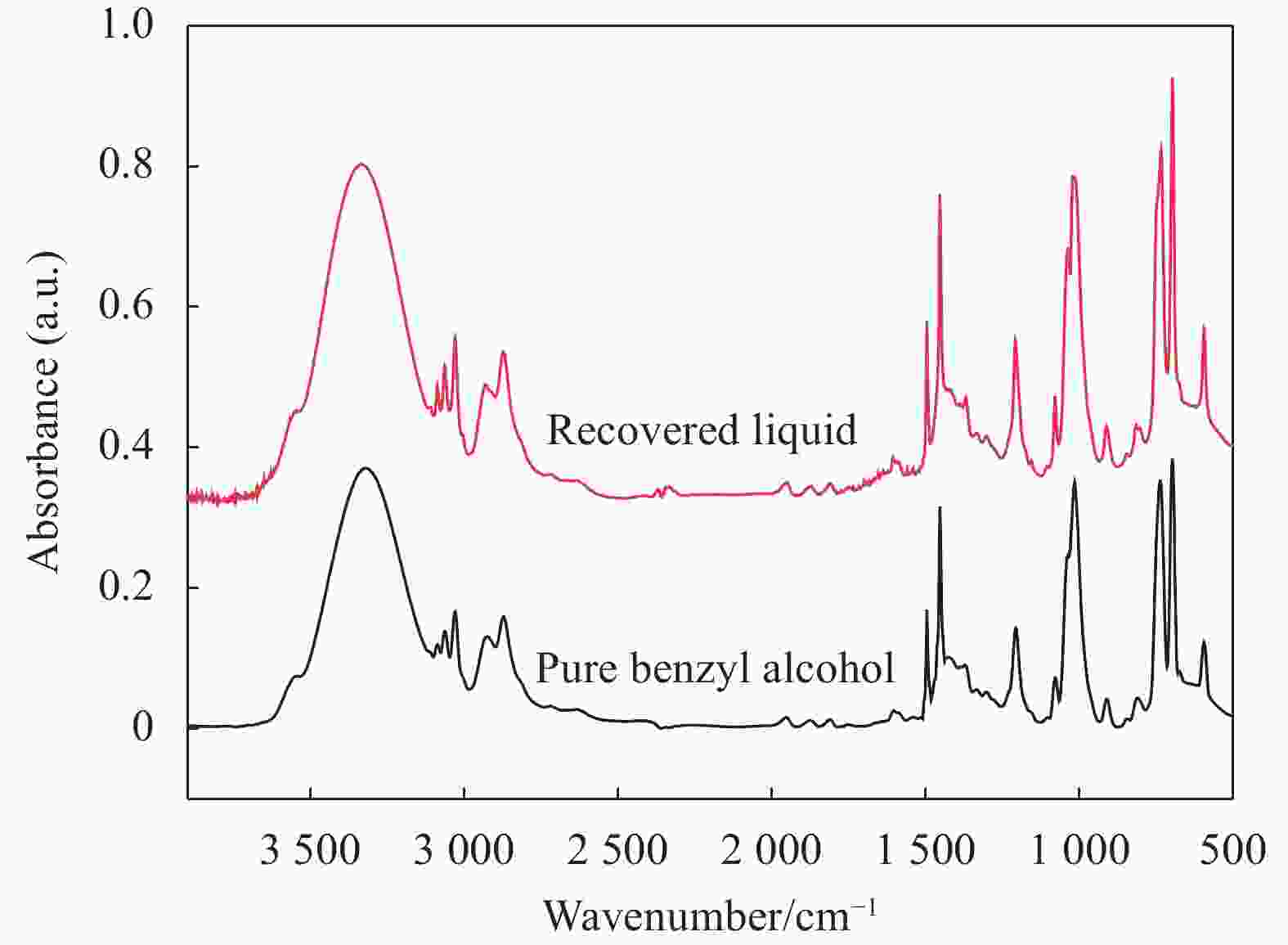
Sequence number Retention time/min Components’ name Molecular structure Content mol/% 1 8.460 Benzaldehyde 
0.101 2 9.842 Benzyl alcohol 
99.878 Others 0.021 表 2 降解前后碳纤维表面的元素含量
Table 2. Element content of carbon fiber surface before and after degradation
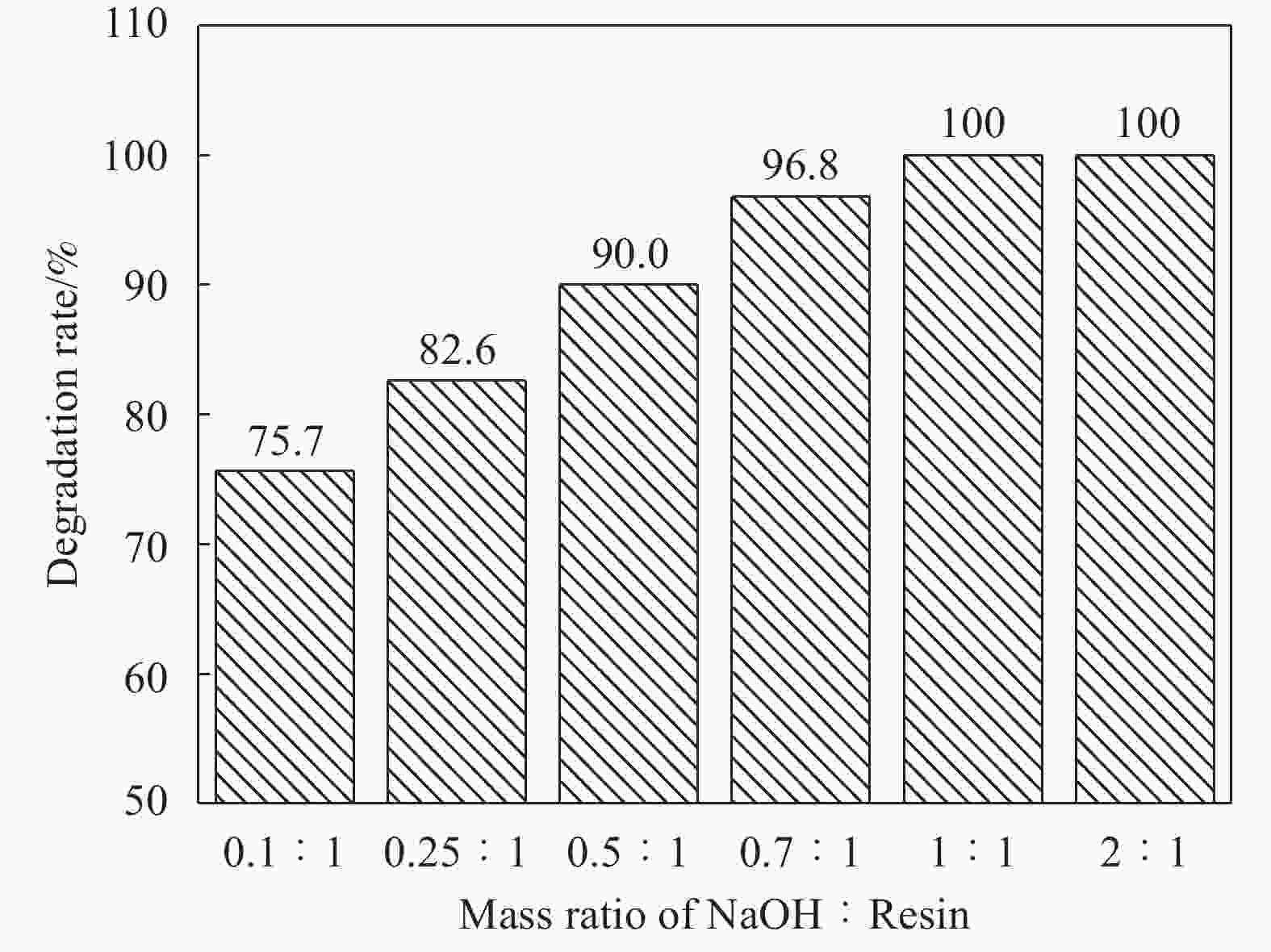
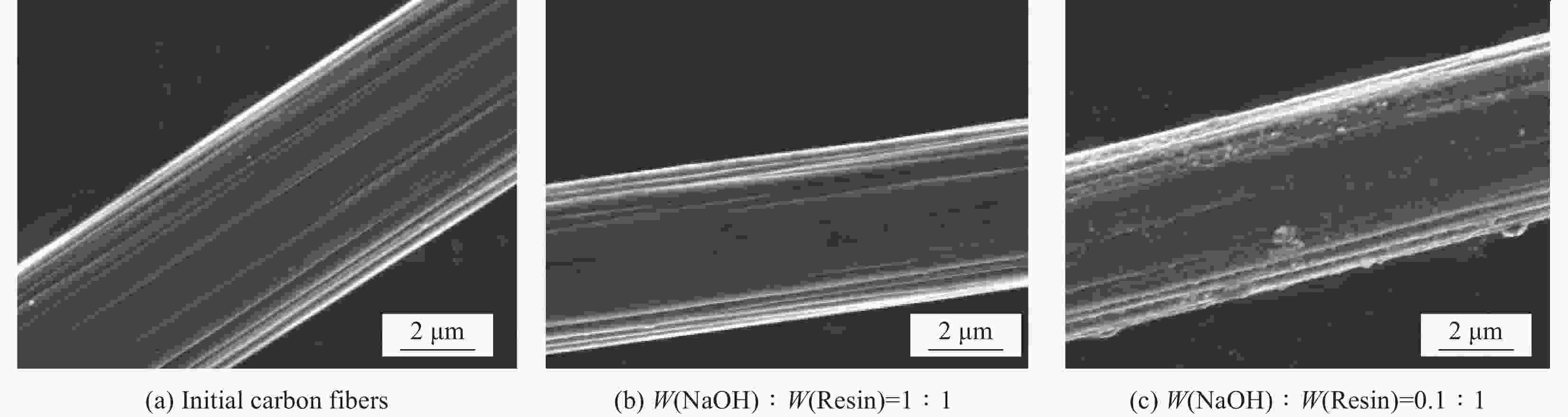
Sample Degradation rate/% C/% O/% C/O Initial carbon fibers – 84.65 13.26 0.157 Recycled carbon fibers (W(NaOH):W(Resin)=1∶1) 100 84.51 13.36 0.158 Recycled carbon fibers (W(NaOH):W(Resin)=0.1∶1) 75.7 80.40 17.34 0.216 表 3 原始碳纤维和降解回收碳纤维的单丝拉伸强度对比
Table 3. Comparison of tensile strength of carbon fiber monofilament before and after degradation
Sample Degradation rate/% Tensile strength of monofilament/GPa Initial carbon fibers – 3.44±0.08 Recycled carbon fibers
(W(NaOH)∶W(Resin)=1∶1)100 3.34±0.10 -
[1] 肖杰, 施涵, 余许多, 等. 碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料轴管的低速冲击失效机制及剩余压缩性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(11):3640-3651.XIAO Jie, SHI Han, YU Xuduo, et al. Failure mechanisms and residual compression performance of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composite shaft tubes subjected to low velocity impact[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(11):3640-3651(in Chinese). [2] YANG Jie, LIU Jie, LIU Wenbin, et al. Recycling of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites under various oxygen concentrations in nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2015,112:253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2015.01.017 [3] 李望南, 卢少娟, 蔡洪能, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料组分疲劳强度表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(2):356-363.LI Wangnan, LU Shaojuan, CAI Hongneng, et al. Characterization of the constituent fatigue strength of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compo-sitae Sinica,2018,35(2):356-363(in Chinese). [4] 陈燕, 葛恩德, 傅玉灿, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料制孔技术研究现状与展望[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(2):301-316.CHEN Yan, GE Ende, FU Yucan, et al. Review and prospect of drilling technologies for carbon fiber reinforced polymer[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(2):301-316(in Chinese). [5] 赵晓青. 碳纤维复合材料回收再利用的现状分析[J]. 化工设计通讯, 2020, 46(10):30-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.10.019ZHAO Xiaoqing. Analysis of the status quo of recycling and reuse of carbon fiber composite materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Design Communications,2020,46(10):30-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6490.2020.10.019 [6] 胡侨乐, 端玉芳, 刘志, 等. 碳纤维增强聚合物基复合材料回收再利用现状[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):64-76. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210615.003HU Qiaole, DUAN Yufang, LIU Zhi, et al. Current status of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites recycling and re-manufacturing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):64-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210615.003 [7] MAY D, GOERGEN C, FRIEDRICH K. Multifunctionality of polymer composites based on recycled carbon fibers: A review[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engineering Polymer Research,2021,4(2):70-81. [8] WANG Yunfeng, WANG Yiwei, XU Lianghua, et al. Radial adjustment of PAN preoxygenated structure and its effect on the properties of carbon fibers[J]. New Carbon Materials,2021,36(4):827-834. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(20)60516-9 [9] RUAN Ruyu, YE Lianwei, FENG Hai, et al. High tempera-ture evolution of the microstructure in the radial direction of PAN-based carbon fibers and its relationship to mecha-nical properties[J]. New Carbon Materials,2020,35(3):295-306. doi: 10.1016/S1872-5805(20)60491-7 [10] LIU Yuyao, HE Jia, LI Yidong, et al. Biobased epoxy vitrimer from epoxidized soybean oil for reprocessable and recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composite[J]. Compo-sites Communications,2020,22:100445. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100445 [11] 叶联葳, 王宇. 超临界流体法降解碳纤维复合材料概述[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(S1):11-15.YE Lianwei, WANG Yu. Degradation of carbon fiber composite by supercritical fluid[J]. New Chemical Materials,2019,47(S1):11-15(in Chinese). [12] LI Wenbin, XIAO Laihui, HANG Jinrui, et al. Bio-based epoxy vitrimer for recyclable and carbon fiber reinforced materials: Synthesis and structure-property relationship[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2022,227:109575. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2022.109575 [13] YAMAGUCHI A, HASHIMOTO T, KAKICHI Y, et al. Recyclable carbon fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP) containing degradable acetal linkages: Synthesis, properties, and chemical recycling[J]. Journal of Polymer Science, Part A: Polymer Chemistry,2015,53(8):1052-1059. doi: 10.1002/pola.27575 [14] LI Pengyun, MA Songqi, WANG Binbo, et al. Degradable benzyl cyclic acetal epoxy monomers with low viscosity: Synthesis, structure-property relationships, application in recyclable carbon fiber composite[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2022,219:109243. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109243 [15] 邢丽英, 冯志海, 包建文, 等. 碳纤维及树脂基复合材料产业发展面临的机遇与挑战[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2700-2706.XING Liying, FENG Zhihai, BAO Jianwen, et al. Facing opportunity and challenge of carbon fiber and polymer matrix composites industry development[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(11):2700-2706(in Chinese). [16] 曹辉, 王勇. 浅谈碳纤维在复合材料行业中应用前景[J]. 信息系统工程, 2017(9):107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2362.2017.09.083CAO Hui, WANG Yong. Application prospect of carbon fiber in composite material industry[J]. China CIO News,2017(9):107(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2362.2017.09.083 [17] HUANG Yongxin, ZHAO Luzi, XIE Man, et al. Electrolytes and electrolyte/electrode interfaces in sodium-ion batteries: From scientific research to practical application[J]. Advanced Materials,2019,31(21):e1808393. doi: 10.1002/adma.201808393 [18] 李大伟. 碳纤维复合材料回收利用现状[J]. 当代化工研究, 2022(12):40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.12.014LI Dawei. Status quo of recycling and utilization of carbon fiber composites[J]. Modern Chemical Research,2022(12):40-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8114.2022.12.014 [19] 张建川. 聚合物基碳纤维复合材料废弃物的几种处理方法分析[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2011, 29(4):577-585.ZHANG Jianchuan. Analysis of treatment methods for carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite wastes[J]. Jour-nal of Materials Science and Engineering,2011,29(4):577-585(in Chinese). [20] KIM K W, JEONG J S, AN K H, et al. A low energy recycling technique of carbon fibers-reinforced epoxy matrix composites[J]. Industrial& Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,58(2):618-624. [21] 李丽英, 尹先鹏, 汪东, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料回收技术研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2021, 49(9):20-22, 27.LI Liying, YIN Xianpeng, WANG Dong, et al. Research progress on recovery technology of carbon fiber reinforced plastic[J]. New Chemical Materials,2021,49(9):20-22, 27(in Chinese). [22] JIANG Jianjun, DENG Guoli, CHEN Xing, et al. On the successful chemical recycling of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites under the mild condition[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,151:243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.08.007 [23] WANG Yuqi, CUI Xiaojing, YANG Qiqi, et al. Chemical recycling of unsaturated polyester resin and its composites via selective cleavage of the ester bond[J]. Green Che-mistry,2015,17(9):4521-4532. [24] DORIGATO A. Recycling of thermosetting composites for wind blade application[J]. Advanced Industrial and Engi-neering Polymer Research,2021,4(2):116-132. [25] 惠林海, 张璐, 李华, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂复合材料废弃物回收技术研究现状[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2020, 18(8):149-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2020.08.028HUI Linhai, ZHANG Lu, LI Hua, et al. Research status of waste recovery technology of carbon fiber reinforced resin composites[J]. Application of Engineering Plastics,2020,18(8):149-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2020.08.028 [26] 张亚东. 碳纤维复合材料的回收与再利用技术研究[J]. 广东化工, 2022, 49(10):26-27, 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.10.009ZHANG Yadong. Study on recycling and reuse technology of carbon fiber reinforced plastic[J]. Guangdong Chemical,2022,49(10):26-27, 52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2022.10.009 [27] MARION P, CYRIL A, ANNE L S, et al. Environmental feasibility of the recycling of carbon fibers from CFRPs by solvolysis using supercritical water[J]. American Chemical Society,2014,2(6):1498-1502. [28] 黄海鸿, 赵志培, 成焕波, 等. 超临界流体对碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料的降解作用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(8):1621-1629.HUANG Haihong, ZHAO Zhipei, CHENG Huanbo, et al. Degradation of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites by supercritical fluid[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(8):1621-1629(in Chinese). [29] 张璐, 王海常, 李华, 等. 超临界流体回收碳纤维树脂复合材料[J]. 应用化学, 2020, 37(12):1357-1363. doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.12.200173ZHANG Lu, WANG Haichang, LI Hua, et al. Progress of recycling of carbon fiber/resin composites via supercritical fluid[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Chemistry,2020,37(12):1357-1363(in Chinese). doi: 10.11944/j.issn.1000-0518.2020.12.200173 [30] YE Lianwei, WANG Ke, FENG Hai, et al. Recycling of carbon fiber-reinforced epoxy resin-based composites using a benzyl alcohol/alkaline system[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2021,22(3):811-818. doi: 10.1007/s12221-021-0266-9 [31] WANG Yu, YAN Tao, WU Shuai, et al. Stretching deformation mechanism of polyacrylonitrile-based carbon fiber structure at high temperatures[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2018,19(4):751-759. doi: 10.1007/s12221-018-7988-3 [32] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 碳纤维增强塑料树脂含量试验方法: GB/T 3855—2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.Standardization Administration of China. Test method for resin content of carbon fiber reinforced plastics: GB/T 3855—2005[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2005(in Chinese). [33] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 碳纤维单丝拉伸性能的测定: GB/T 31290—2014[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.
Standardization Administration of China. Determination of tensile properties of carbon fiber monofilament: GB/T 31290—2014[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2014(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: