Influence of poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix properties on interfacial properties and interlayer properties of composites
-
摘要: 针对不同特性的国产高性能聚芳醚酮(PAEK-L、PAEK-H)树脂,采用微球脱黏的方法研究了PAEK树脂基体与国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35)碳纤维间的界面强度;采用国产碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)热塑性预浸料制备复合材料,研究了树脂基体对复合材料的90°拉伸性能、短梁剪切性能、I型断裂韧性、II型断裂韧性的影响。结果表明:SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能受树脂基体的流动性影响,流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂能够与纤维之间形成较好的界面结合及较高的界面强度,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中,树脂与纤维的接触角约为34.4°,界面剪切强度约为79 MPa,复合材料90°拉伸强度约为76 MPa,模量约为9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为92 MPa;而流动性较低的PAEK-L树脂与SCF35碳纤维复合材料中,树脂与纤维的接触角约为35.8°,界面剪切强度约为64 MPa,复合材料90°拉伸强度约为55 MPa,模量约为8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为86 MPa。SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能受到树脂基体塑性变形能力的影响,基体塑性变形能力较强的PAEK-L较PAEK-H而言,其复合材料具有较高的断裂韧性,SCF35/PAEK-L的I型断裂韧性约为938 J/m2,II型断裂韧性约为2232 J/m2,SCF35/PAEK-H的I型断裂韧性约为638 J/m2,II型断裂韧性约为1702 J/m2。Abstract: The interfacial strength between PAEK resin matrix and domestic T300 grade carbon fiber (SCF35) carbon fiber was studied by microsphere debonding method for domestic high performance poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK-L, PAEK-H) resins with different characteristics. The composites were prepared by using domestic carbon fiber reinforced poly aryl ether ketone (SCF35/PAEK) thermoplastic prepreg, and the effects of resin matrix on 90° tensile properties, short beam shear properties, type I fracture toughness and type II fracture toughness of the composites were studied. The results show that the interfacial properties of SCF35/PAEK composites are influenced by the fluidity of the resin matrix, and PAEK-H resin with higher fluidity can form a better interfacial bond with the fibers and higher interfacial strength. In the SCF35/PAEK-H composite, the resin-fiber contact angle is ~34.4°, the interfacial shear strength is ~79 MPa, the 90° tensile strength of the composite is ~76 MPa, the modulus is ~9.7 GPa, and the short-beam shear strength is ~92 MPa. While in the lower-fluidity PAEK-L resin and SCF35 carbon fiber composite, the resin-fiber contact angle of ~35.8°, interfacial shear strength of ~64 MPa, composite 90° tensile strength of ~55 MPa, modulus of ~8.6 GPa, and short-beam shear strength of ~86 MPa. The interlaminar properties of SCF35/PAEK composites are influenced by the plastic deformation ability of the resin matrix. PAEK-L, which has a stronger plastic deformation ability of the matrix, has a higher fracture toughness than PAEK-H. The type I fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK-L is ~938 J/m2 and the type II fracture toughness is ~2232 J/m2, and the type I fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK-H is ~638 J/m2 and the type II fracture toughness is ~1702 J/m2.
-
蜂窝材料具有轻质、抗弯、耐冲击等优异的力学性能,被广泛应用于汽车、航天、军事、医疗等工业领域[1]。相较于传统蜂窝材料,具有负泊松比效应的蜂窝结构有着更为优越的吸能效果[2]。自1982年Gibson等[3]设计出最早的内凹六边形负泊松比胞元并推导了其弹性模量及泊松比表达式后,各种各样的胞元结构开始涌现,常见的有重入凹角结构、手性/反手性结构、旋转刚体结构等[4-7]。魏路路等[8]设计了一种结合六边形内凹结构和手性结构的内凹-反手性结构。Jin等[9]将星型内凹结构嵌入六边形内凹结构中,提出了一种负泊松比嵌套结构。常见的负泊松比胞元大多由内凹直杆构成,蒋伟等[10]将曲杆引入到内凹六边形胞元中,构建了一种新型的半圆形内凹结构,这种方法也提供了一种新的设计思路,避免了直杆中出现的应力集中现象。沿着此思路,沈建邦和肖俊华[11]在此基础上提出了一种可变弧角的曲边内凹负泊松比结构,并研究了不同胞元参数对其力学性能的影响。作为最典型的负泊松比结构,内凹型胞元常用于构建蜂窝材料。张新春等[12]采用有限元方法探讨了内凹六边形胞元凹角度数以及冲击速度大小对结构能量吸收性能的影响。Shen等[13]利用有限元软件研究了可变弧角曲边负泊松比结构的面内冲击性能。尤泽华和肖俊华[14]对完全对称的弧边内凹蜂窝负泊松比结构的面内冲击性能进行了详细的数值研究。郭之熙和肖俊华[15]提出了一种全新的多弧段曲边内凹可调泊松比胞元,并基于能量法导出了结构的等效泊松比与等效弹性模量的解析表达式。他们利用仿真软件深入分析了不同冲击速度下结构的冲击变形失效行为和单位质量能量吸收率。
随着负泊松比胞元设计研究的不断深入,人们逐渐认识到单一材料胞元结构设计的局限性。为了克服这些限制,借鉴复合材料设计理念,提出了将不同种材料组合起来以获得优异力学性能的全新胞元设计方案。Li等[16]设计了一种由双材料构成的二维四边形蜂窝结构,并通过实验和数值模拟系统地研究了其热变形行为。研究结果显示,可以通过自由调节结构的胞形来调整其泊松比。He等[17]以双材料三角形网格单元为基础设计了一种新型结构,推导出了通用热弹性方程,建立了有界节点平面网格结构的外力、温度载荷和变形之间的关系,计算了有效泊松比、杨氏模量和热膨胀系数。马芳武等[18]提出了一种双材料双箭头负泊松比结构,在保持胞元几何参数不变的情况下,深入研究了不同速度和参数对面内抗冲击能力和能量吸收能力的影响。此外,不同的排布方式也会显著影响结构的性能,因此梯度设计方法对提升材料的抗冲击性能至关重要。Shao等[19]数值研究了具有厚度梯度排布的内凹负泊松比结构的能量耗散特性,结果表明负梯度排布的结构表现出优异的吸能效果。Li等[20]结合模拟和实验研究了沿横向呈逐层梯度变化的多层蜂窝结构的抗冲击性能。Wu等[21]借助调整内凹蜂窝结构的内凹角度,设计了一系列不同角度梯度排布的模式,系统研究了冲击速度、梯度排布等因素对结构性能的影响,并与均匀排布结构进行了全面对比。研究结果显示,角度梯度内凹蜂窝结构相对于均匀排布结构在吸能效果上表现更为突出。朱冬梅等[22]结合甲虫鞘翅结构提出一种新型负泊松比蜂窝结构,以胞元角度作为梯度变换参数来构造不同梯度排列的新型负泊松比结构,数值分析了其抗冲击性能。张晓楠等[23]提出了一种变截面内凹蜂窝结构,并结合实验与模拟讨论了在不同冲击速度下梯度变截面内凹蜂窝结构的能量吸收性能。
典型的夹芯结构由两个薄面板和一个轻质芯层组成,选择合适的芯层对夹芯结构的性能有显著影响。鉴于负泊松比蜂窝材料优越的力学性能,其逐渐取代了夹芯板的传统芯层,研究人员发现将负泊松比蜂窝结构应用于夹芯板可以显著提高抗冲击能力。王堃等[24]模拟了铝蜂窝夹芯板被刚体低俗冲击的过程,研究了夹芯板各结构参数对夹芯板冲击动态响应的影响。罗伟铭等[25]采用落锤冲击试验研究了铝质夹芯结构在局部冲击载荷作用下的变形模式和吸能特性。Luo等[26]研究了不同泊松比的蜂窝夹芯板的抗弹丸冲击性能。邓云飞等[27]制备并研究了泡沫填充褶皱夹芯结构低速冲击下的响应特性与损伤机制,通过落锤试验机对夹芯板节点与基座两个位置进行了冲击试验。陈鹏宇[28]结合实验与有限元仿真研究了不同冲击速度对内凹弧形蜂窝夹芯板的影响。辛亚军等[29]通过试验和数值模拟对铝蜂窝夹芯板的面外剪切行为和力学性能进行了研究,讨论了其失效模式,并分析了面板厚度、蜂窝胞元尺寸和芯层厚度对夹芯板的影响。Bohara等[30]研究对比了内凹蜂窝夹芯板与传统六边形蜂窝夹芯板的防护性能,证明了内凹蜂窝夹芯板具有更好的防护能力。杨姝等[31]设计制备了两种铝合金材质的夹芯板,结合钢柱冲击试验与有限元数值仿真,研究对比了两类蜂窝夹芯板抗冲击性能。蒋舟顺等[32]提出了一种双向相同力学性能的正弦曲边三维负泊松比夹芯板,并将其应用于防爆保护,数值研究了夹芯板在空爆载荷下的力学性能。郭之熙[33]将梯度蜂窝材料作为芯层构建厚度梯度和角度梯度两种夹芯板结构,讨论了局部冲击时梯度蜂窝夹芯板的失效行为及吸能效果。
目前关于负泊松比芯层夹芯板的研究大多使用单一材料且直杆负泊松比多胞蜂窝结构,本文基于作者提出的双材料曲边内凹负泊松比胞元[34],基于纵横向材料模量比梯度设计的思想,将梯度双材料曲边内凹负泊松比蜂窝构建为夹芯层,通过改变芯层纵横向材料的模量比构建了正梯度、负梯度、对称正梯度和对称负梯度四种夹芯板结构,研究了夹芯板受局部冲击时的失效行为,讨论了梯度排布和冲击速度对夹芯板抗冲击性能的影响。
1. 梯度双材料负泊松比蜂窝夹芯板
1.1 计算模型
图1为基于提出的双材料曲边内凹胞元(图2(a))构建的夹芯板及其边界条件的模型示意图,其中h1为纵向曲边投影半长,h2为横向曲边投影半长,m1和m1为连接杆伸出长度。纵向曲杆模量E1,圆弧角θ1,半径r1=h1/sin(θ1/2),横向曲杆模量E2,圆弧角θ2,半径r2=h2/sin(θ2/2),面内厚度为t,面外厚度为b(垂直纸面)。夹芯板由上下两层板及中间负泊松比夹芯层构成,夹芯层与上下两层板之间设置为绑定约束。夹芯层由6×75个双材料单胞在纵向拉伸后阵列而成。单胞中几何参数为:θ1=30°,θ2=60°,h1=0.5 mm,h2=1 mm,m1=m2=0.5 mm,t=0.1 mm和b=150 mm。
图1中冲头为半球形冲头,直径为18 mm,长度30 mm,质量18 kg。冲头在上端板上部2 mm中心位置处。固定上下板的四条边,约束冲头x、z方向的位移及旋转,对其施加一个y方向的初速度,全局设置为通用接触,切向无摩擦,法向为硬接触。采用ABAQUS显式动力学对夹芯板进行冲击模拟,冲头设置为离散刚体,面板与夹层为S4R壳单元,考虑控制沙漏现象,将伪应变能控制在3%左右,为兼顾计算准确性与时效,对模型中心70 mm×70 mm部分网格进行细化,计算模型如图3。冲头设置为离散刚体,上下板均为铝板,厚度1 mm。
1.2 梯度双材料设计
夹芯板芯层由单胞阵列组成(图2(b)),面板为铝合金,定义胞元纵横向材料模量比E1/E2=k,数值仿真中采用J-C本构及损伤模型[35],材料与组合方式见表1和表2,k值取为1.38、1和0.48。
表 1 材料性能Table 1. Material propertiesMaterial Density/
(g·cm−3)Young's
modulus/GPaPoisson's
ratioA/
MPaB/
MPan C m D1 D2 D3 D4 D5 2024 Aluminum 2.7 73 0.33 369 684 0.73 0.0083 1 0.112 0.123 −1.5 0.007 0 Cast-iron 7.2 150 0.3 525 650 0.6 0.0205 1 0.029 0.44 −1.5 0 0 4340 Steel 7.85 207 0.29 910 586 0.26 0.014 1.03 −0.8 2.1 −0.5 0.002 0.61 Notes: A—Initial yield stress at reference strain rate and reference temperature; B, n—Strain hardening modulus and hardening index of the material; C—Material strain rate strengthening parameter; m—Thermal softening index of material; D1, D2, D3, D4, D5—Failure parameters in the damage formula. 表 2 纵横向材料组合方式Table 2. Vertical and horizontal material combinationModulus ratio E1/E2 Vertical/transverse materials 1.38 4340 Steel/Cast-iron 1 Cast-iron/Cast-iron 0.48 2024 Aluminum/Cast-iron 2. 实验与仿真结果
2.1 试件与仿真模型
为了验证本文数值方法的可行性与准确性,作者制备了单层夹芯板进行实验,并将实验结果与仿真结果进行比较。由于条件限制,作者目前无法制备双材料夹芯板,仅利用3D打印技术制备均质曲边内凹负泊松比蜂窝夹芯板,材料为316L不锈钢。夹芯层为1×8胞元阵列结构,单胞几何参数为θ1=θ2=45°,h1=h2=4 mm,m1=m2=1 mm,面内厚度t为0.5 mm,上下板厚度为0.75 mm,图4为制备的试件与相应的仿真计算模型。
2.2 实验平台
图5为实验装置,采用万能试验机(CEAST9350,英斯特朗公司)为加载设备,配备传感器输出载荷位移曲线。为了研究夹芯板的力学性能和失效机制,对夹芯板进行压缩穿透实验,加载速率为2 mm/min,试件位于平台和压板之间,试件下放置空心垫圈,将冲头垂直放置于板上,冲头下压直至穿透夹芯板,通过摄像机(vivo X90)记录压缩过程获取试件穿透过程。
2.3 实验与模拟结果比较
采用ABAQUS显式动力学研究结构的面内冲击性能,边界条件见图1,材料选取与前文一致,冲头为圆柱钉形,设置为离散刚体,长20 mm。冲头初始在上端板上部2 mm中心位置。冲击速度1 m/s,该过程动能小于内能的5%,可近似认为是准静态加载。图6为夹芯板在准静态局部压缩时的穿透破坏模式与应力云图。可以看出压头穿透夹芯板时,实验与模拟的破坏模式非常相似,下端板均呈现出被直接冲破的方式,开裂面较大。原因在于内部夹层的层数较少,使得冲头与底板接触面积较大,且冲头底部为圆形,使得底板被大面积冲破。不同的是,实验中底板未被完全破坏冲出,而仿真中底板则被冲头直接冲破顶出,原因在于实验中冲头的压缩速度较小,使得底板破坏处未被顶出;同时仿真中未考虑冲头与夹层板之间的摩擦,忽略了夹层对冲头阻碍的影响。
图7给出了夹层板局部压缩穿透时实验和模拟的冲头接触力-位移曲线。可以看出二者显示出相似的曲线变化:在冲击前期,冲头接触力迅速增大直到冲破上端板,随后呈现下降趋势。两条曲线经过第一峰值之后,再次上升,不同的是仿真结果先上升而后再下降趋势。原因是冲头穿破上层板后接触芯层时,仿真中忽略了冲头与夹芯板之间摩擦的影响,使得冲头所受阻力小于实验结果。随着冲头位移增加,实验和模拟的接触力再次增大,达到峰值后表示冲头穿破下板,最后接触力逐渐下降。
3. 梯度双材料夹芯板及其局部冲击性能数值研究
3.1 梯度排列模式
夹芯板的芯层选取6层(图8),保持横向材料模量不变,改变纵向材料的模量获得不同模量比k的层阵列胞元(表2材料组合方式),从而构建出不同梯度排布的夹芯板。4种蜂窝结构具有相同的相对密度与质量。
3.2 夹芯板冲击破坏模式
冲头的初速度分别取低速(10 m/s)与高速(30 m/s)对夹芯板进行冲击穿透,4种排布模式夹芯板在不同速度时的穿透破坏如图9和图10。可知,低速(10 m/s)冲击下正梯度与对称正梯度下端板均出现Z方向开裂,而负梯度与对称负梯度则呈现出直接被冲破的方式,开裂面较大。原因为芯层底部胞元纵横向模量比k较高时胞元不易变形,从而使得胞元下端外伸杆向下挤压造成下端板沿Z方向开裂,而当底部胞元k较小时,胞元形变较大,内部胞元受挤压后与底板接触面积增大,使得底板出现被大面积冲破的现象。冲头高速(30 m/s)冲击时,不同排布模式时的底板穿透方式与低速时类似,但由于冲击速度增大,破开处面积明显增大,破坏方式与低速冲击时一致。可知,底板的穿透模式与芯层的排布方式有关,冲击速度显著影响穿透时造成破坏的面积。
3.3 冲头接触力
图11和图12给出了不同芯层排布时两种速度冲击下冲头的接触力-时间曲线。可以看出,4种排布模式的夹芯板在承受低、高两种冲击速度时,冲头接触力随时间变化曲线有相同之处也有不同之处。相同之处为:4种模式的变化趋势一致,都会出现两个峰值;第一个峰值出现在上端板被冲破时,可以发现负梯度与对称正梯度的第一个峰值明显大于其他两种,其中负梯度的峰值最大,对称负梯度最小,即上端板遭到破坏时负梯度模式承受冲击力最大。不同之处在于:第二个峰值发生在下端板被冲破时,负梯度的第二个峰值明显小于第一个峰值,而其他3种模式的第二个峰值则明显大于第一个峰值,原因在于前期负梯度模式吸能较多,当下端板被冲破时冲头动能最小,则此时接触力较小。速度高低仅对接触力的峰值大小有影响,而对变化趋势影响不大。
3.4 夹芯板能量吸收特性
图13和图14给出了低、高冲头速度下不同芯层排布时夹芯板的能量吸收-时间曲线。从图13可以看出,低速冲击时,夹芯板在穿透前期(3 ms之前)负梯度相比于其他排布模式表现出较好的吸能效果,夹芯板被彻底穿透之前负梯度夹芯板的能量吸收最高;随着冲击穿透的持续,夹芯板被彻底穿透破坏,此时对称正梯度夹芯板的能量吸收值明显高于其他3种,其他3种在后期几乎相等。图10显示,高速冲击时,负梯度夹芯板的前期能量吸收同样具有优势,且后期与对称正梯度夹芯板之间的能量吸收差异很小。可知,合理的芯层梯度双材料设计可以使夹芯板结构有效抵抗冲击穿透。
图15和图16给出了低、高速冲击下当接触力为0 (完全穿透)时夹芯板各部分的能量值。由图可知,无论何种芯层排布方式,承受冲击时内部芯层均吸收了最多的能量,下端板吸收的能量略低于上端板。图15表明低速冲击下对称正梯度不仅芯层吸收的能量最多,整体吸收能量也最多。负梯度和对称正梯度的上端板吸收能量效果最好。图16显示高速冲击下4种排列时夹芯板的吸能效果差异减小。
4. 结 论
基于提出的双材料曲边内凹负泊松比胞元,通过改变胞元内杆件的纵横向模量比值,构造了不同排布模式的4种梯度双材料负泊松比蜂窝夹芯板,研究了局部冲击时夹芯板的失效力学性能,分别讨论了冲击速度和芯层排布模式对夹芯板抗冲击力学性能的影响。主要结论为:
(1)夹芯结构下端板的开裂方式与芯层的排布方式有关,底部芯层胞元变形越大,底板开裂面积越大;冲击速度显著影响穿透时造成破坏的面积;
(2)不同排布模式的夹芯板在被穿透时,接触力曲线会出现两个峰值,对应着上下板穿透破裂的时间点,芯层排布方式对第二个峰值的影响较大;
(3)夹芯板的能量吸收曲线先增大随后趋于定值,梯度双材料的结构设计可以显著增强夹芯板的吸能效果,负梯度夹芯板的前期吸能效果最好,穿透时对称正梯度夹芯板的芯层吸能最多。合理的芯层梯度双材料设计可以使夹芯板结构有效抵抗冲击穿透。
-
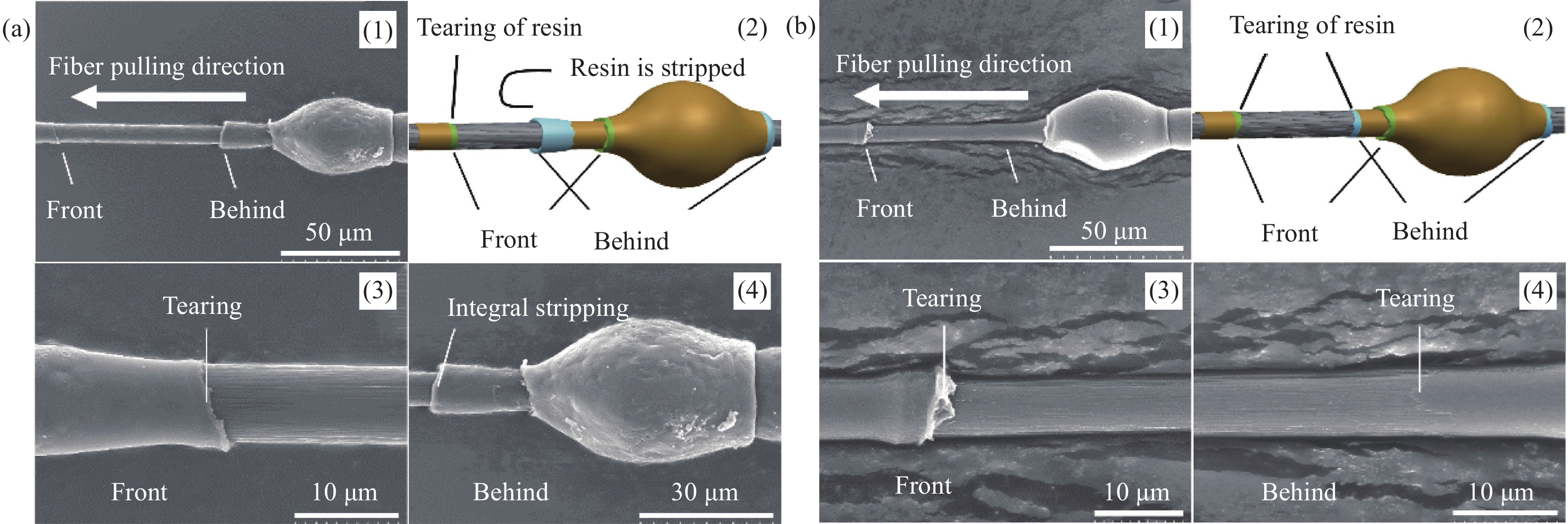
图 5 SCF35/PAEK微球脱粘的表面形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-H:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌
Figure 5. Surface morphologies of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding: (a) SCF35/PAEK-L: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding; (b) SCF35/PAEK-H: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding
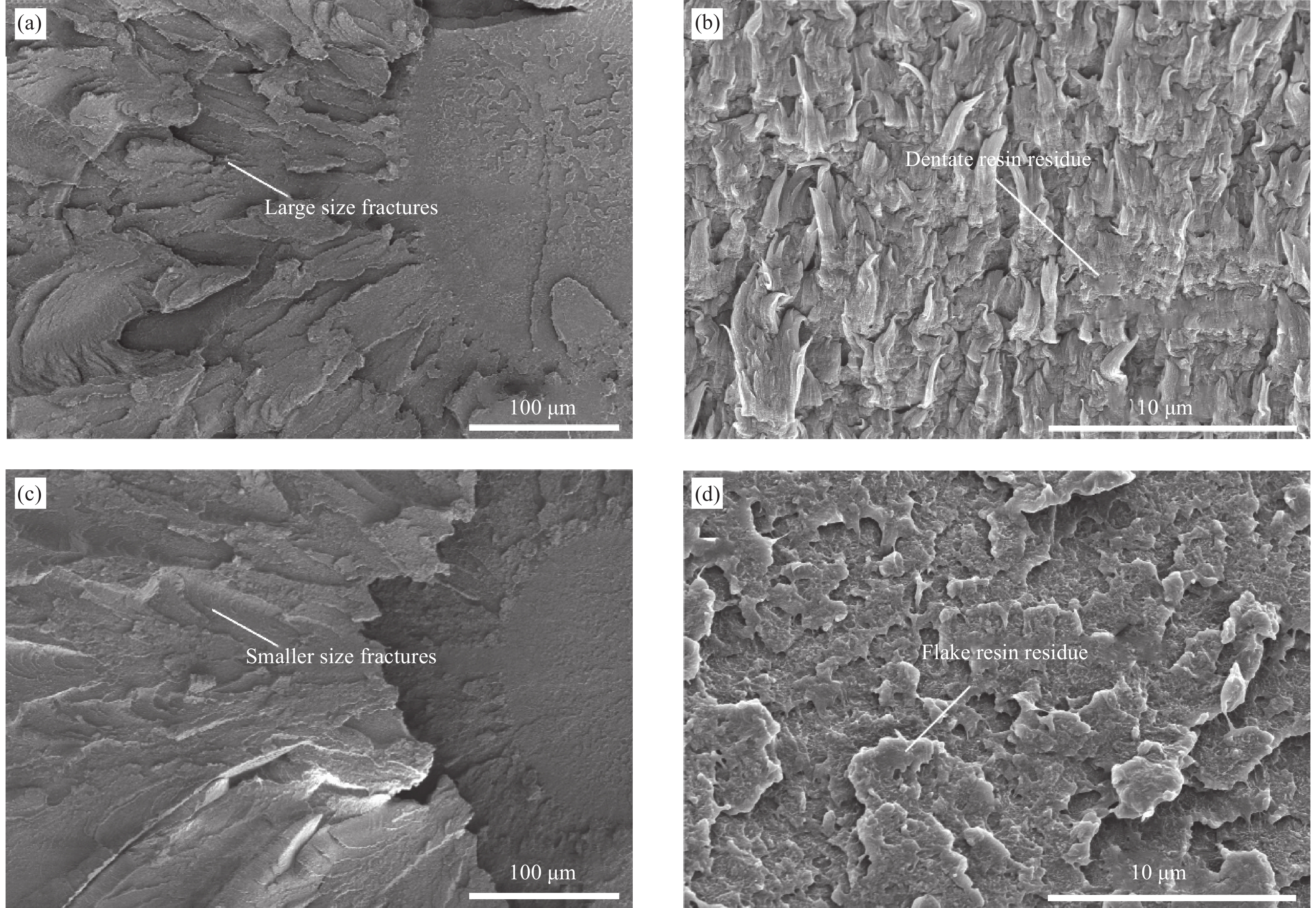
图 13 SCF35/PAEK断裂形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅱ型断裂形貌;(c) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(d) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅱ型断裂形貌
Figure 13. Fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK: (a) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (b) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (c) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H; (d) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H
图 14 PAEK树脂试样断裂形貌:(a) PAEK-L冲击断面形貌;(b) PAEK-L拉伸断面形貌;(c) PAEK-H冲击断面形貌;(d) PAEK-H拉伸断面形貌
Figure 14. Fracture morphology of PAEK resin specimens: (a) Impact section morphology of PAEK-L; (b) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-L; (c) Impact section morphology of PAEK-H; (d) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-H
表 1 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂基体的性能
Table 1 Properties of poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK) resin matrix
Property Tensile
strength/MPaTensile
modulus/GPaElongation/% Notched impact
strength/(kJ∙m–2)Apparent viscosity
(360℃)/(Pa·s)PAEK-L 96±0.5 4.0±0.2 109±7.2 5.7±0.2 1139 PAEK-H 95±0.5 3.9±0.2 101±4.4 5.7±0.2 399 Notes: PAEK-L—Low flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix; PAEK-H—High flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix. 表 2 国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35)的性能
Table 2 Properties of domestic T300 grade carbon fiber (SCF35)
Fibre Specification Tensile strength
/MPaTensile modulus
/GPaElongation
/%Bulk density
/(g∙cm−3)Linear density
/(g∙m−1)SCF35 12 K 4300 230 1.85 1.8 0.8 表 3 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能
Table 3 Interfacial properties of SCF35/PAEK composites
System Interfacial shear
strength/MPaContact angle/
(°)90° tensile
strength/MPa90° tensile
modulus/GPaShort beam shear
strength/MPaSCF35/PAEK-L 64±3.4 35.8±1.0 55±2.9 8.6±0.1 86±1.9 SCF35/PAEK-H 79±6.0 34.4±3.0 76±5.4 9.7±0.4 92±1.4 表 4 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的断裂韧性
Table 4 Fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites
System GIC/(J∙m−2) GIIC/(J∙m−2) SCF35/PAEK-L 938±38 2232±208 SCF35/PAEK-H 638±38 1702±46 Notes: GIC—Type I fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites; GIIC—Type Ⅱ fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites. -
[1] NISHIDA H, CARVELLI V, FUJII T, et al. Thermoplastic vs. thermoset epoxy carbon textile composites[C]//IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. England: IOP Publishing, 2018, 406(1): 012043.
[2] YAO S S, JIN F L, RHEE K Y, et al. Recent advances in carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites: A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,142:241-250. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.12.007
[3] GABRION X, PLACET V, TRIVAUDEY F, et al. About the thermomechanical behaviour of a carbon fibre reinforced high-temperature thermoplastic composite[J]. Compo-sites Part B: Engineering,2016,95:386-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.03.068
[4] MATHIJSEN D. Leading the way in thermoplastic compo-sites[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2016,60(6):405-407. DOI: 10.1016/j.repl.2015.08.067
[5] MANTELL S C, SPRINGER G S. Manufacturing process models for thermoplastic composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1992,26(16):2348-2377. DOI: 10.1177/002199839202601602
[6] 叶鼎铨. 国外纤维增强热塑性塑料发展概况[J]. 国外塑料, 2012, 30(5):34-40. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5219.2012.05.010 YE Dingquan. Developments of fiber reinforced thermoplastics outside China[J]. World Plastics,2012,30(5):34-40(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5219.2012.05.010
[7] 郭云竹. 热塑性复合材料研究及其在航空领域中的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2016, 33(3):20-23. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2016.03.005 GUO Yunzhu. Research on thermoplastic composites and its application in the field of aviation[J]. Fiber Composites,2016,33(3):20-23(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2016.03.005
[8] 王兴刚, 于洋, 李树茂, 等. 先进热塑性树脂基复合材料在航天航空上的应用[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2011, 28(2):44-47. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011 WANG Xinggang, YU Yang, LI Shumao, et al. The research on fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite[J]. Fiber Composites,2011,28(2):44-47(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2011.02.011
[9] ZAHLAN N. Mechanical properties of the carbon fiber/PEEK composite APC-2/AS-4 for structural applications[J]. Advances in Thermoplastic Matrix Composite Materials,1989,1044:199-212.
[10] JOGUR G, NAWAZ KHAN A, DAS A, et al. Impact properties of thermoplastic composites[J]. Textile Progress,2018,50(3):109-183. DOI: 10.1080/00405167.2018.1563369
[11] TAN W, NAYA F, YANG L, et al. The role of interfacial pro-perties on the intralaminar and interlaminar damage behaviour of unidirectional composite laminates: Experimental characterization and multiscale modelling[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,138:206-221. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.043
[12] LU C, WANG J, LU X, et al. Wettability and interfacial pro-perties of carbon fiber and poly(ether ether ketone) fiber hybrid composite[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(34):31520-31531.
[13] SU Y, ZHANG S, ZHANG X, et al. Preparation and properties of carbon nanotubes/carbon fiber/poly(ether ether ketone) multiscale composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,108:89-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.02.030
[14] YAN T, YAN F, LI S, et al. Interfacial enhancement of CF/PEEK composites by modifying water-based PEEK-NH2 sizing agent[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,199:108258. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108258
[15] WU D, MIAO Q, DAI Z, et al. Effect of voids and crystallinity on the interlaminar shear strength of in-situ manufactured CF/PEEK laminates using repass treatment[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2022,224:109448.
[16] 史如静, 吴举, 周剑锋, 等. 模压成型工艺参数对CF/PEEK复合材料Ⅰ型层间断裂韧性的影响[J]. 高科技纤维与应用, 2020, 45(1):26-32. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9815.2020.01.004 SHI Rujing, WU Ju, ZHOU Jianfeng, et al. Influence of hot-press molding parameters for processing CF/PEEK composites on type Ⅰ interlaminar fracture toughness[J]. Hi-Tech Fiber and Application,2020,45(1):26-32(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9815.2020.01.004
[17] CHEN J, WANG K, DONG A, et al. A comprehensive study on controlling the porosity of CCF 300/PEEK composites by optimizing the impregnation parameters[J]. Polymer Composites,2018,39(10):3765-3779. DOI: 10.1002/pc.24407
[18] ASTM. Standard test method for tensile properties of polymer matrix composite materials: D3039/D3039 M-14[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2014.
[19] ASTM. Standard test method for short-beam strength of polymer matrix composite materials and their laminates: D2344/D2344 M-16[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2016.
[20] ASTM. Standard test method for mode I interlaminar fracture toughness of unidirectional fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites: D5528/D5528 M-21[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2021.
[21] ASTM. Standard test method for determination of the mode Ⅱ interlaminar fracture toughness of unidirectional fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites: D7905/D7905 M-19[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2019.
[22] YEAGER M, SIMACEK P, ADVANI S G. Role of fiber distribution and air evacuation time on capillary driven flow into fiber tows[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,93:144-152. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.11.016
[23] BAI T, WANG D, YAN J, et al. Wetting mechanism and interfacial bonding performance of bamboo fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2021,213:108951. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108951
[24] XU P, YU Y, GUO Z, et al. Evaluation of composite interfacial properties based on carbon fiber surface chemistry and topography: Nanometer-scale wetting analysis using molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,171:252-260. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.12.028
[25] CASSIE A B D, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1944,40:546-551. DOI: 10.1039/tf9444000546
[26] WENZEL R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry,1936,28(8):988-994.
[27] GAO S L, KIM J K. Cooling rate influences in carbon fibre/PEEK composites. Part II: Interlaminar fracture toughness[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2001,32(6):763-774. DOI: 10.1016/S1359-835X(00)00188-3
[28] DAVALLO M. Factors affecting fracture behaviour of composite materials[J]. International Journal of ChemTech Research,2010,2(4):2125-2130.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 田楠,卢政斌,李闻达,吕秀雷,韦宁. 聚酯无纺布增强复合材料夹层结构的抗低速冲击性能. 纤维复合材料. 2025(01): 57-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕航宇,陈秉智,周鑫,石姗姗. 碳纤维/格栅增强蜂窝夹芯结构抗冲击性能试验与车体顶棚仿真. 工程力学. 2023(12): 234-244 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)
-
目的
高性能热塑性复合材料具有优异的韧性、耐老化性能及耐疲劳性能,但是其在使用的过程中仍然面临层间损伤、界面失效的风险,针对树脂基体特性对复合材料界面性能和层间性能的影响研究较少。为了研究树脂基体特性对复合材料界面性能及层间性能的影响,本文采用了具有不同特性的同一种聚芳醚酮(PAEK)基体研究树脂基体特性对碳纤维增强PAEK复合材料界面性能及层间性能的影响。
方法采用微球脱黏的方法研究了具有较低流动性能及稍强塑性变形能力的PAEK-L树脂基体及具有较高流动性能及稍弱塑性变形能力的PAEK-H树脂基体分别与国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35)的界面强度,同时使用场发射电子扫描显微镜及光学显微镜观察了树脂微球与碳纤维脱黏后的表面形貌、截面形貌及树脂微球与碳纤维的接触角。采用国产碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)热塑性预浸料制备复合材料,按照美国材料与试验协会(ASTM)标准制备试样并测试了复合材料的90°拉伸性能、短梁剪切性能、Ⅰ型断裂韧性、Ⅱ型断裂韧性,同时采用场发射电子扫描显微镜表征了复合材料的破坏形貌,研究了树脂基体特性对复合材料界面性能及层间性能的影响。
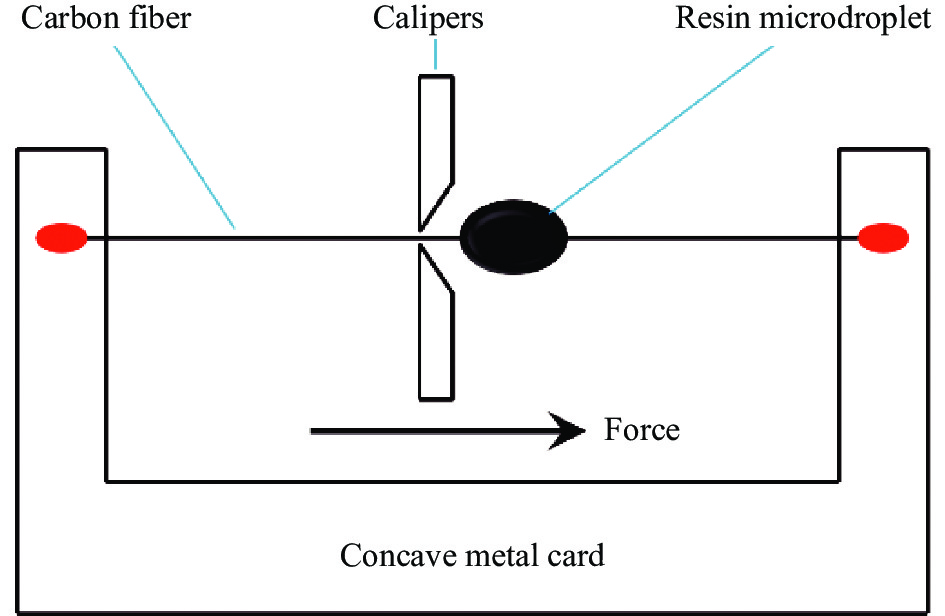
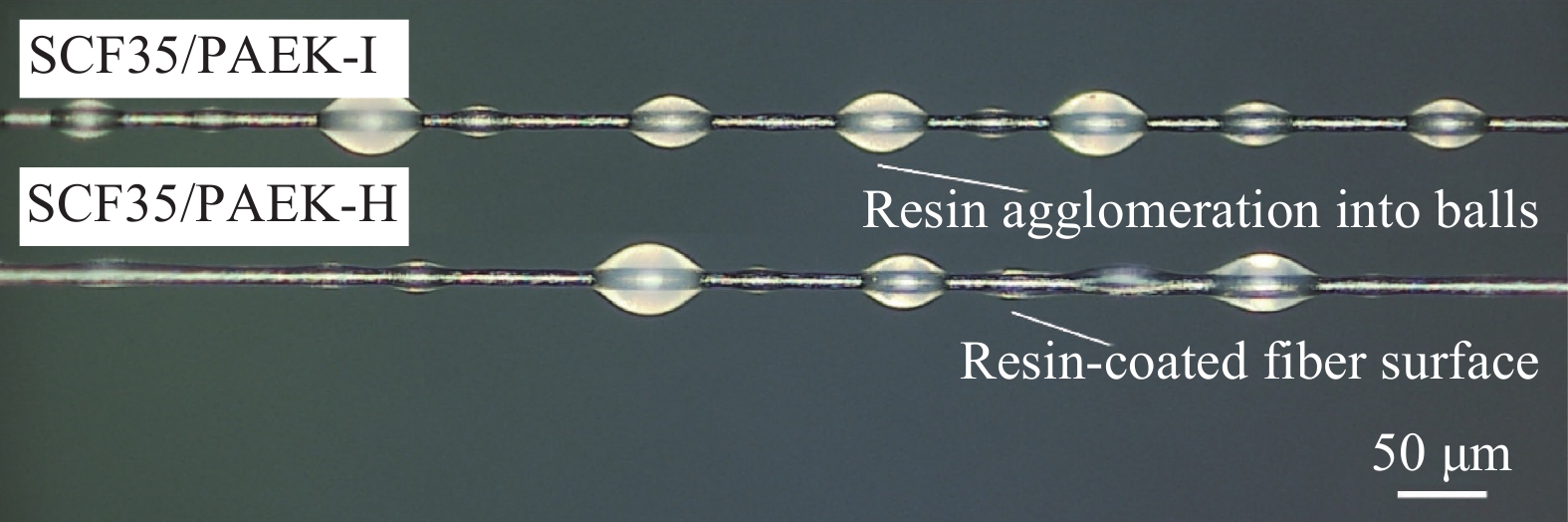
结果SCF35碳纤维与低流动性树脂PAEK-L的界面剪切强度为~64 MPa,接触角为~35.8 °,90°拉伸强度为~55 MPa,90°拉伸模量为~8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度为~86 MPa;SCF35碳纤维与高流动性树脂PAEK-H的界面剪切强度为~79 MPa,接触角为~34.4 °,90°拉伸强度为~76 MPa,90°拉伸模量为~9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度为~92 MPa,从文中微球脱黏的表面形貌、截面形貌及90°拉伸断面形貌可以看出,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中碳纤维表面存在较多的PAEK-H树脂,具有较高流动性的PAEK-H树脂基体能够与SCF35碳纤维形成Wenzel接触状态,因此表现出较高的界面性能,而SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料中碳纤维表面存在不均匀的PAEK-L树脂,具有较低流动性的PAEK-L树脂基体与SCF35碳纤维形成Cassie接触状态,因此表现出稍低的界面性能。SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的Ⅰ型断裂韧性为~938 J/m,Ⅱ型断裂韧性为~2232 J/m;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的Ⅰ型断裂韧性为~638 J/m,Ⅱ型断裂韧性为~1702 J/m,从文中断裂韧性试样的破坏形貌及PAEK树脂试样的断裂形貌可以看出,PAEK-L树脂试样的断面形貌相对于PAEK-H树脂试样具有更大尺寸的断裂变形,即PAEK-L树脂基体相对于PAEK-H树脂基体具有较强的塑性变形能力,因此其复合材料表现出较高的断裂韧性。
结论通过对具有不同基体特性的复合材料界面性能及层间性能的研究,结果表明SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能受到树脂基体流动性的影响,流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂能够与纤维之间形成较好的界面结合及较高的界面强度;SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能受到树脂基体塑性变形能力的影响,基体塑性变形能力较强的PAEK-L相较于PAEK-H,其复合材料具有较高的断裂韧性。
-
碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(CF/PAEK)高性能热塑性复合材料,因其优异的韧性、耐老化性能及耐疲劳性能,使CF/PAEK热塑性复合材料得以替代部分传统热固性复合材料,在航空、航天等领域取得成功应用。相比于国外的成熟应用,受限于国内连续碳纤维增强PAEK热塑性复合材料预浸料的生产技术水平,针对CF/PAEK热塑性复合材料研究和应用依然较少,多数研究集中于采用纳米粒子填充、纤维表面修饰、上浆剂改性等手段优化复合材料的界面性能,采用优化成型工艺条件、树脂基体改性等手段优化复合材料的层间性能,而针对树脂基体特性对复合材料界面性能和层间性能的影响研究较少。
本文采用了两种不同特性的国产高性能聚芳醚酮树脂(PAEK-L、PAEK-H)及国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35),制备了碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)热塑性复合材料,研究了树脂基体对复合材料的界面剪切性能、90°拉伸性能、短梁剪切性能、Ⅰ型断裂韧性、Ⅱ型断裂韧性的影响。结果显示SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能受到树脂基体流动性的影响,流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂能够与纤维之间形成较好的界面结合及较高的界面强度,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中,树脂与纤维的接触角为~34.4 °,界面剪切强度为~79 MPa,复合材料90°拉伸强度为~76 MPa,模量为~9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度为~92 MPa;而流动性较低的PAEK-L树脂与SCF35碳纤维复合材料中,树脂与纤维的接触角为~35.8 °,界面剪切强度为~64 MPa,复合材料90°拉伸强度为~55 MPa,模量约为~8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度为~86 MPa。SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能受到树脂基体塑性变形能力的影响,基体塑性变形能力较强的PAEK-L较PAEK-H,其复合材料具有较高的断裂韧性,SCF35/PAEK-L的Ⅰ型断裂韧性为~938 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性为~2232 J/m2,SCF35/PAEK-H的Ⅰ型断裂韧性为~638 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性为~1702 J/m2。
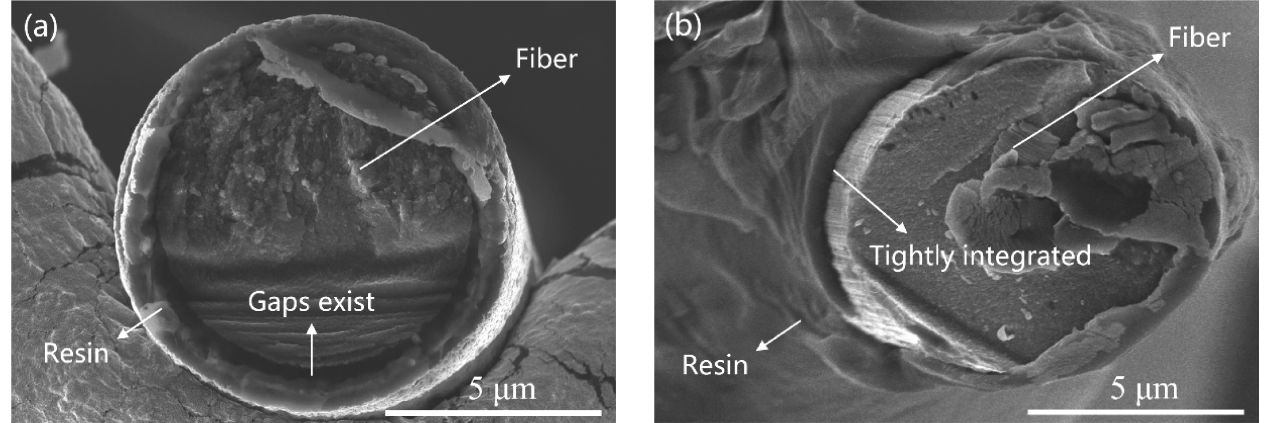
Cross-sectional morphology of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding:(a)SCF35/PAEK-L:(b)SCF35/PAEK-H





 下载:
下载: