In situ compatibilization of the toughening mechanism and properties in PPCU/PLA blends via DCP
-
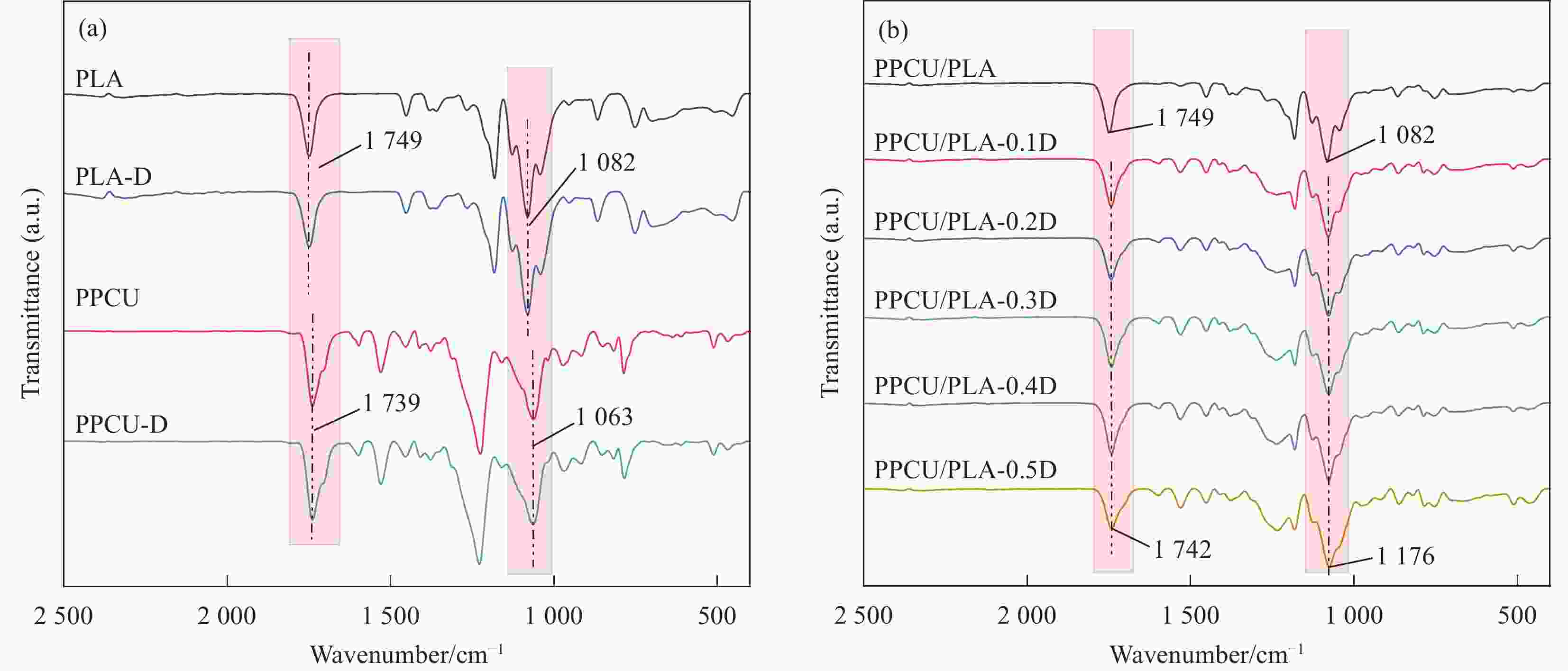
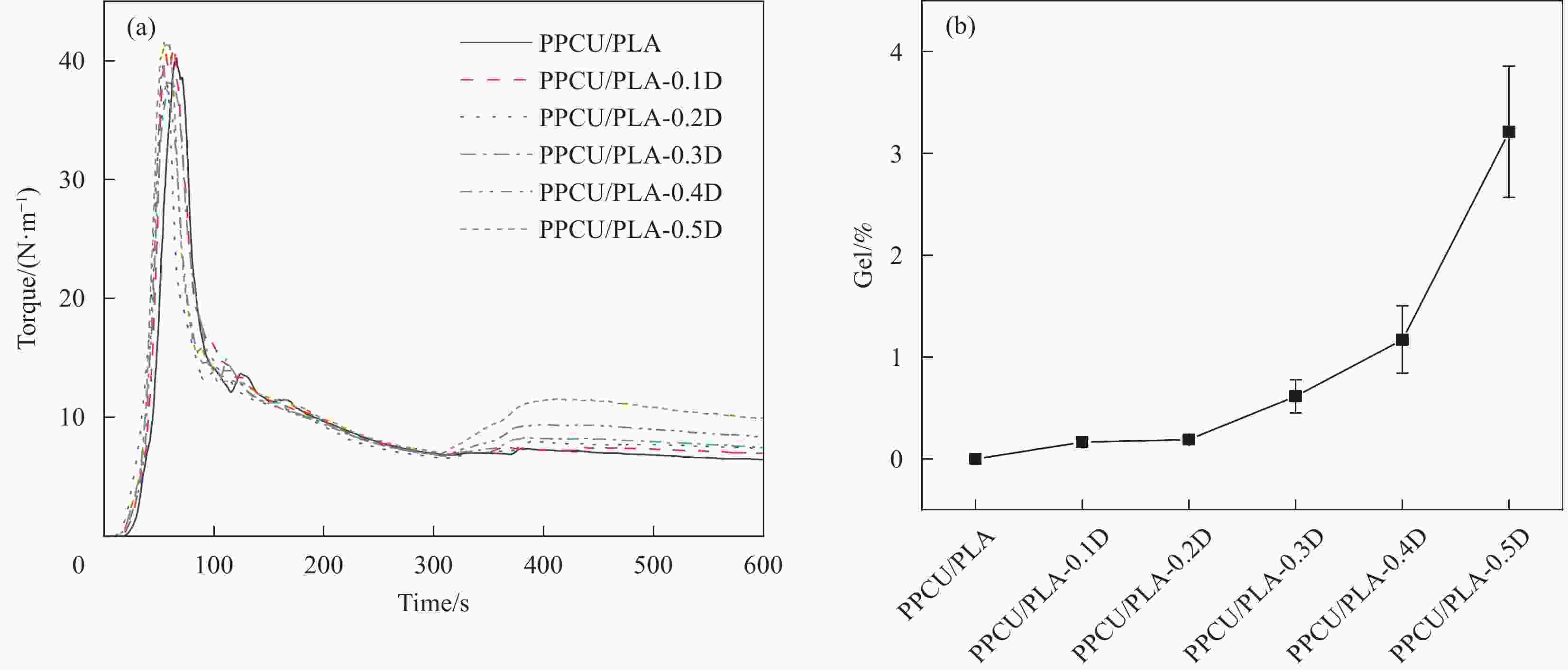
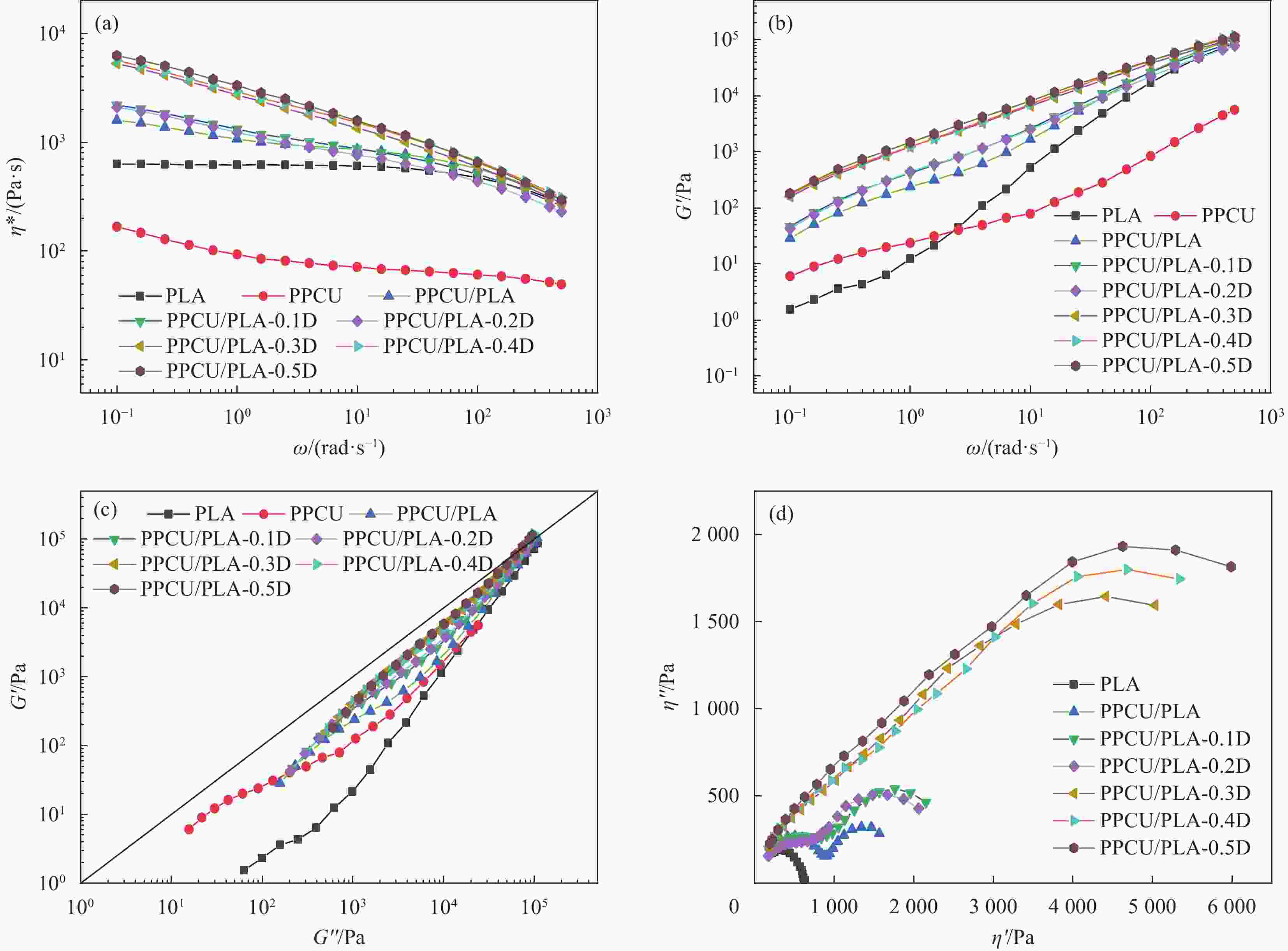
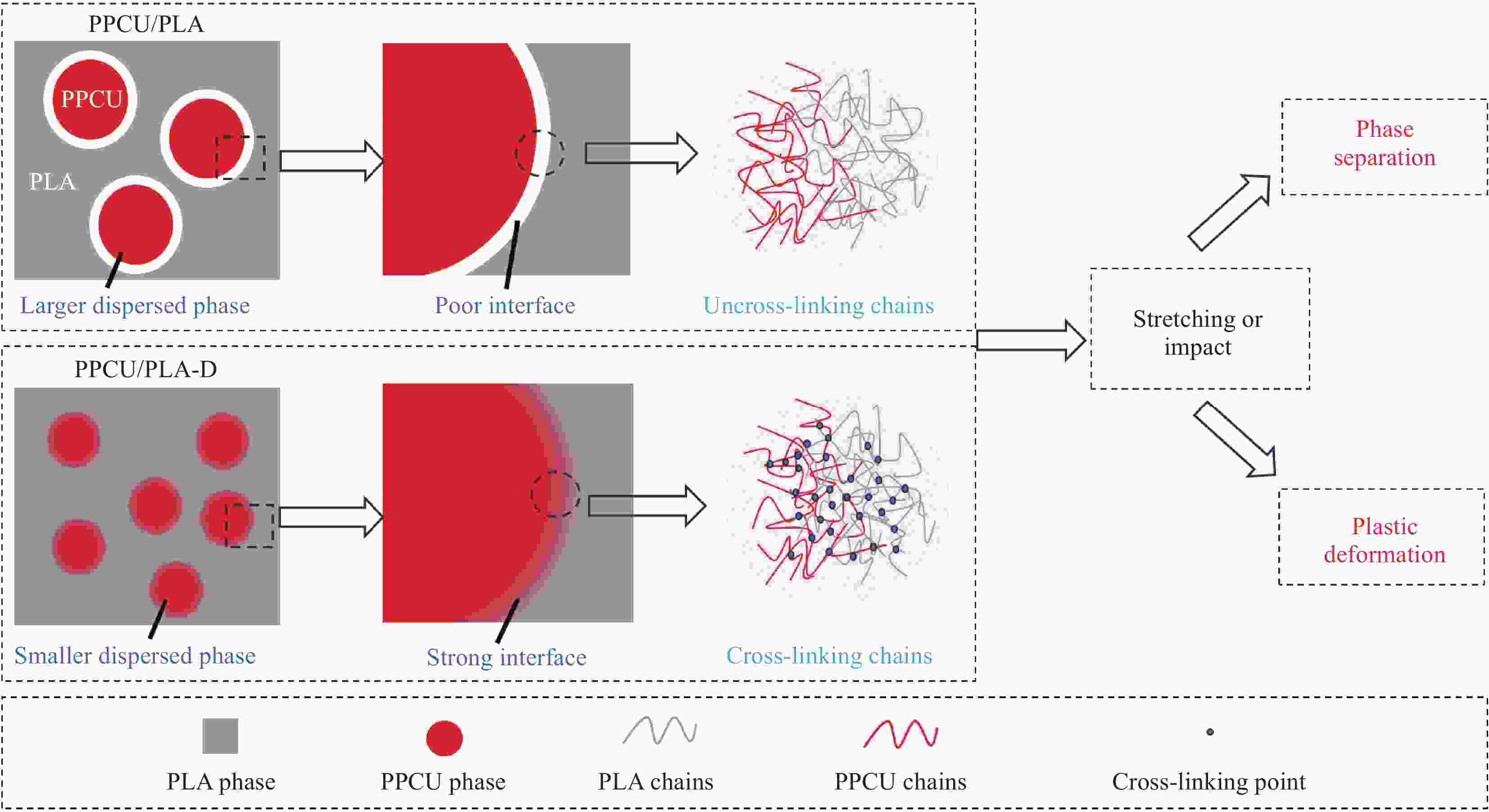
摘要: 聚乳酸(PLA)的脆性严重限制了其应用,使用弹性体共混增韧PLA是一种可行的策略,然而共混物两相相容性较差的问题仍亟待解决。本文采用过氧化二异苯丙(DCP)为反应增容剂与PLA、聚碳酸亚丙酯-热塑性聚氨酯弹性体(PPCU)熔融共混制备了PPCU/PLA共混物,研究了DCP添加量对共混物相形貌、流变性能、力学性能等的影响。结果表明:DCP引发了PLA与PPCU分子链间的支化交联反应,随着DCP添加量增加,PPCU/PLA共混物的复数黏度以及储能模量也随之增大,弹性行为逐渐增强,Cole-Cole图表明当DCP添加量大于0.3wt%后,共混物具有较高的同质性;随着DCP添加量增加,共混物相界面逐渐变得模糊,分散相尺寸明显减小,共混物相形貌得到改善。DCP的加入可显著提高共混物的断裂伸长率,添加量为0.2wt%的共混物断裂伸长率达到最大值224.37%,是未添加DCP共混物断裂伸长率的10.68倍;PPCU/PLA共混物的缺口冲击强度随着DCP添加量的增加而增大,添加量为0.5wt%的共混物其冲击强度达到了7.91 kJ/m2,是未添加DCP的共混物的2.94倍,PPCU/PLA共混物力学性能的提高主要归因于其两相相容性的改善。
-
关键词:
- 聚乳酸 /
- 聚碳酸亚丙酯-热塑性聚氨酯弹性体 /
- 相容性 /
- 流变性能 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: The intrinsic brittleness of polylactic acid (PLA) greatly restricts broader application in multiple fields, while the blending with elastomer is considered a feasible strategy to improve the ductility of PLA materials. Unfortunately, the poor compatibility of two phases needs to be solved. In this work, using diisophenyl peroxide (DCP) as reactive compatibilizer, PLA and poly(propylene carbonate) polyurethane (PPCU) were melt blended to prepare PPCU/PLA blends. The effects of DCP content on the phase morphology, rheological properties and mechanical properties of PPCU/PLA blends were investigated. The results demonstrated that DCP initiated the branched crosslinking reaction between PLA and PPCU molecular chains. With the increase of DCP content, the complex viscosity and storage modulus of PPCU/PLA blends also enhanced, indicating the reinforcement of elastic behavior, and the Cole-Cole plot indicates that when the DCP addition exceeds 0.3wt%, the blend exhibits high homogeneity. As the DCP content increases, the phase interface of the blend gradually becomes blurred, the dispersed phase size significantly decreases, and the phase morphology of the blend is improved. Meanwhile, the addition of DCP significantly enhance the elongation at break of the blends. The elongation at break of 0.2wt% DCP in PPCU/PLA increased to 224.37%, which was 10.68 times as high as that of the blends without adding DCP. Additionally, notched impact strength of PPCU/PLA blends increases with DCP addition. When 0.5wt% DCP was added into the blends, the impact strength of the blends is increased to 7.91 kJ/m², which is more than 2.94 times than the pure PPCU/PLA blends. The proposed modification strategy may be responsible for the enhancement of mechanical properties of PPCU/PLA blends, exhibiting the improvement of compatibility between the two phases. -
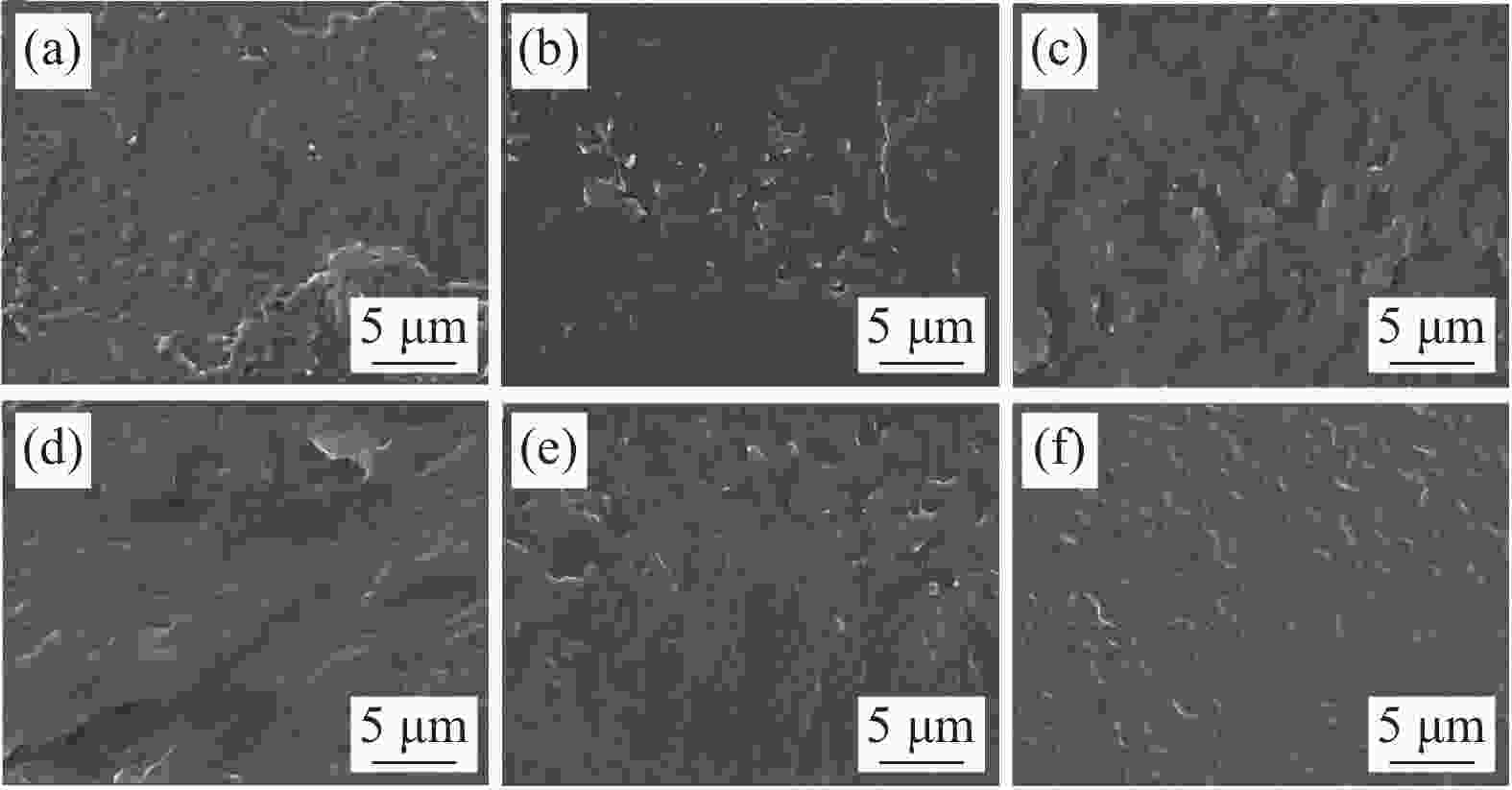
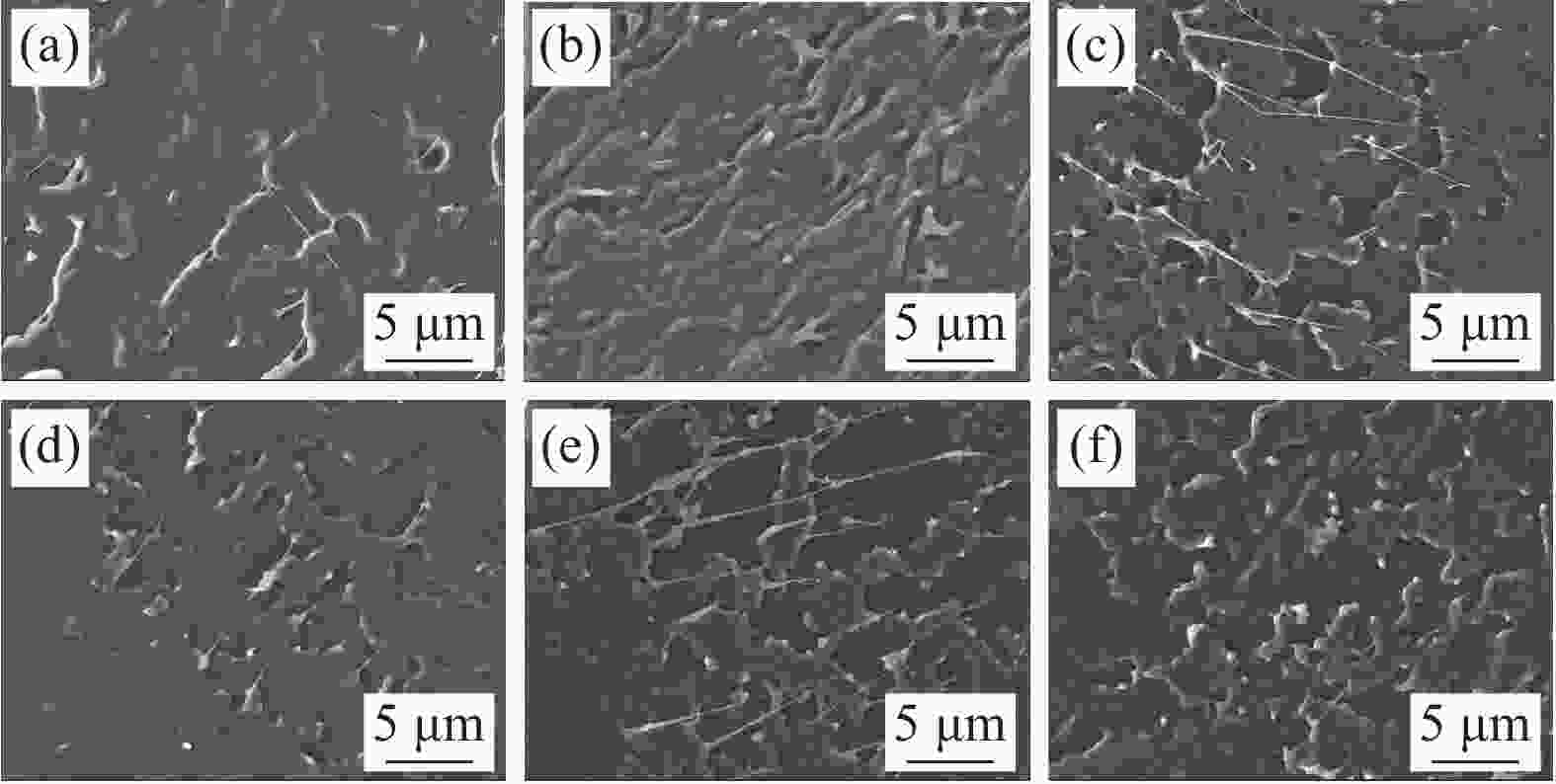
图 5 PPCU/PLA共混物脆断面SEM图:(a) PPCU/PLA; (b) PPCU/PLA-0.1 D; (c) PPCU/PLA-0.2 D; (d) PPCU/PLA-0.3 D; (e) PPCU/PLA-0.4 D;(f) PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
Figure 5. SEM micrographs showing cvro-fractured surface morphology of PPCU/PLA blends: (a) PPCU/PLA; (b) PPCU/PLA-0.1 D; (c) PPCU/PLA-0.2 D; (d) PPCU/PLA-0.4 D; (e) PPCU/PLA-0.4 D; (f) PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
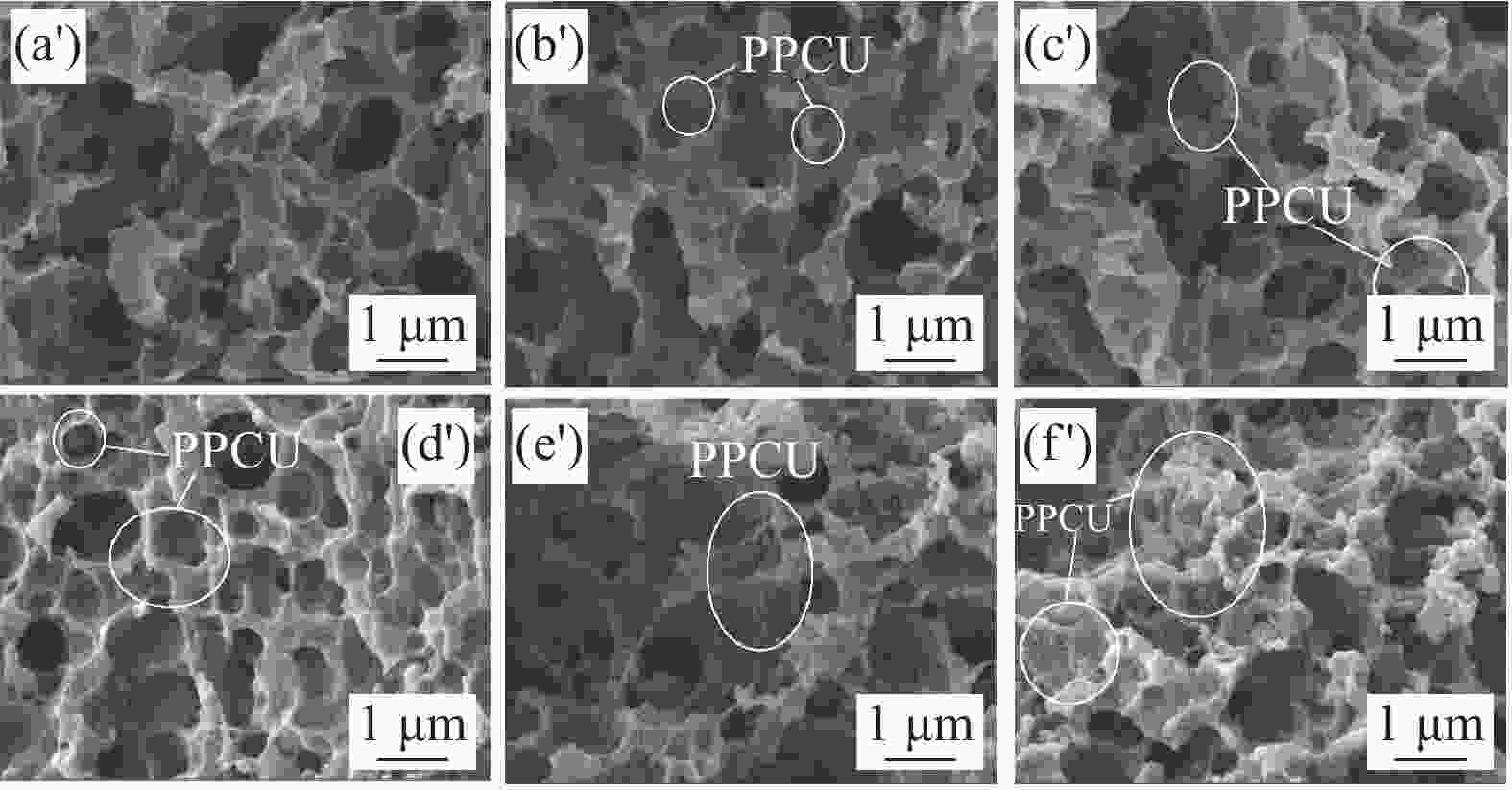
图 6 刻蚀后的PPCU/PLA共混物脆断面SEM图:(a') PPCU/PLA;(b') PPCU/PLA-0.1 D; (c') PPCU/PLA-0.2 D; (d') PPCU/PLA-0.3 D;(e') PPCU/PLA-0.4 D; (f ') PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
Figure 6. SEM micrographs showing cvro-fractured surface morphology of PPCU/PLA blends after etching: (a') PPCU/PLA; (b') PPCU/PLA-0.1 D; (c') PPCU/PLA-0.2 D; (d') PPCU/PLA-0.4 D; (e') PPCU/PLA-0.4 D; (f ') PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
图 11 PPCU/PLA共混物冲击断面SEM图:(a) PPCU/PLA;(b) PPCU/PLA-0.1 D;(c) PPCU/PLA-0.2 D;(d) PPCU/PLA-0.3 D;(e) PPCU/PLA-0.4 D;(f) PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
Figure 11. SEM micrographs of impact-fractured surfaces of PPCU/PLA blends: (a) PPCU/PLA;(b) PPCU/PLA-0.1 D; (c) PPCU/PLA-0.2 D;(d) PPCU/PLA-0.3 D;(e) PPCU/PLA-0.4 D;(f) PPCU/PLA-0.5 D
表 1 PPCU/PLA共混物原料配比
Table 1. Composition of PLA/PPCU blends
Sample PLA/wt% PPCU/wt% DCP/wt% PLA 100 0 0 PPCU/PLA 75 25 0 PPCU/PLA-0.1 D 75 25 0.1 PPCU/PLA-0.2 D 75 25 0.2 PPCU/PLA-0.3 D 75 25 0.3 PPCU/PLA-0.4 D 75 25 0.4 PPCU/PLA-0.5 D 75 25 0.5 Notes:PLA—poly(lactic acid); PPCU—poly(propylene cabonate) polyurethane; The xD in the table represents the amount of diisopropyl peroxide (DCP) added, for example 0.1 D means the amount of DCP added to the blend is 0.1 wt%. 表 2 刻蚀后脆断PPCU/PLA共混物中PPCU相以及空穴尺寸
Table 2. PPCU phase and hole size in cvro-fractured PPCU/PLA blends after etching
Sample PPCU/PLA PPCU/PLA-0.1 D PPCU/PLA-0.2 D PPCU/PLA-0.3 D PPCU/PLA-0.4 D PPCU/PLA-0.5 D PPCU particle size/nm — 178±72 161±32 175±37 111±19 106±20 Hole diameter/nm 525±159 463±69 414±140 387±114 352±154 273±55 表 3 PPCU/PLA共混物热失重参数
Table 3. Thermal weight loss parameters of PPCU/PLA blends
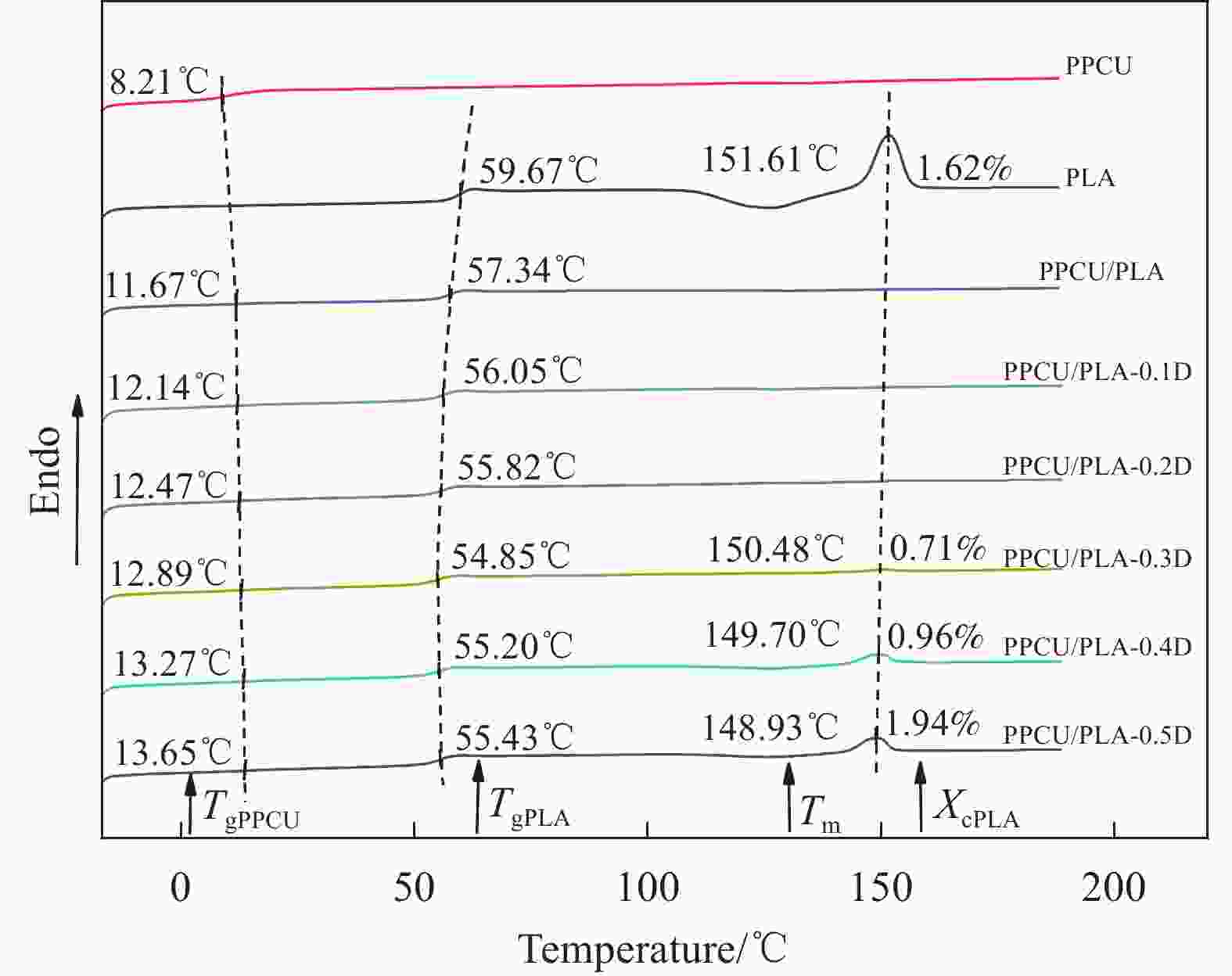
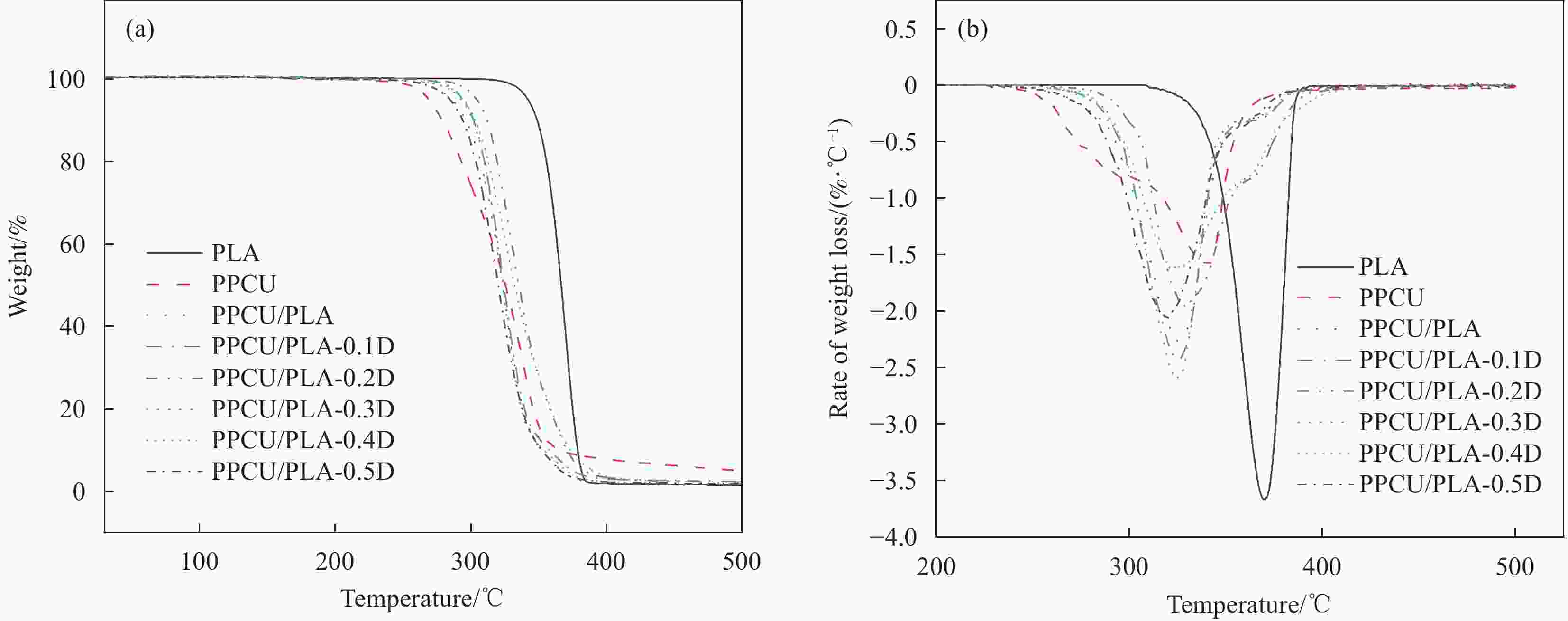
Sample T5%/℃ T50%/℃ Tmax/℃ PLA 342.3 366.7 369.8 PPCU 269.3 325.6 339.3 PPCU/PLA 285.4 323.5 325.1 PPCU/PLA-0.1 D 294.3 324.4 325.9 PPCU/PLA-0.2 D 305.0 335.5 330.1 PPCU/PLA-0.3 D 293.0 323.5 325.4 PPCU/PLA-0.4 D 294.7 332.3 325.7 PPCU/PLA-0.5 D 284.9 320.3 319.2 Notes:T5%, T50% and Tmax are the temperatures at which the weight loss of the sample is 5%, 50% and the weight loss rate is the highest, respectively. 表 4 PPCU/PLA共混物力学性能
Table 4. Mechanical properties of PPCU/PLA blends
Sample Tensile strength /MPa Elongation at break /% Notched impact strength
/(kJ·m2)PLA 68.61±0.74 7.06±0.63 2.25±0.18 PPCU/PLA 52.36±2.99 21.00±6.51 2.69±0.62 PPCU/PLA-0.1 D 44.84±1.32 122.12±13.53 3.20±0.60 PPCU/PLA-0.2 D 42.34±0.67 224.37±44.98 5.53±1.45 PPCU/PLA-0.3 D 43.19±1.63 173.80±20.37 6.33±0.94 PPCU/PLA-0.4 D 44.78±0.70 187.50±22.44 6.05±1.19 PPCU/PLA-0.5 D 43.78±0.57 22.69±3.82 7.91±2.19 -
[1] MACLEOD M, ARP H P H, TEKMAN M B, et al. The global threat from plastic pollution[J]. Science, 2021, 373(6550): 61-65. doi: 10.1126/science.abg5433 [2] RAMEZANI DANA H, EBRAHIMI F. Synth-esis, properties, and applications of polylactic acid-based polymers[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2023, 63(1): 22-43. [3] CASTRO-AGUIRRE E, IÑIGUEZ-FRANCO F, SAMSUDIN H, et al. Poly(lactic acid)—Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2016, 107: 333-366. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.03.010 [4] LI X, LIN Y, LIU M, et al. A review of research and application of polylactic acid composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2023, 140(7): e53477. doi: 10.1002/app.53477 [5] NOFAR M, SALEHIYAN R, SINHA RAY S. Rheology of poly (lactic acid)-based systems[J]. Polymer Reviews, 2019, 59(3): 465-509. doi: 10.1080/15583724.2019.1572185 [6] YANG J, PAN H, LI X, et al. A study on the mechanical, thermal properties and crystalli-zation behavior of poly(lactic acid)/thermop-lastic poly(propylene carbonate) polyurethane blends[J]. RSC Adv., 2017, 7(73): 46183-46194. doi: 10.1039/C7RA07424G [7] ZHANG Y, JIA S, PAN H, et al. Preparation, characterization and properties of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthala-te)/ther-moplastic poly(propylene carbonate) polyurethane blend films[J]. Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2021, 32(2): 613-629. doi: 10.1002/pat.5115 [8] 赵健雄, 何和智, 杨以科, 等. PLA/PPCU全降解复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 塑料, 2023, 52(6): 76-81.ZHAO Jianxion, HE Hezhi, YANG Yike, et al. Preparation and Properties of Biodegradable PLA/PPCU Composite[J]. PLASTICS, 2023, 52(6): 76-81(in Chinese). [9] ZHAO J-L, PAN H-W, YANG H-L, et al. Studies on Rheological, Thermal, and Mechanical Properties of Polylactide/Methyl Methacrylate-Butadiene-Styrene Copolymer/Poly(propylene carbonate) Polyurethane Ternary Blends[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2019, 37(12): 1273-1282. doi: 10.1007/s10118-019-2276-2 [10] JIA S, ZHAO L, WANG X, et al. Poly (lactic acid) blends with excellent low temperature toughness: A comparative study on poly (lactic acid) blends with different toughening agents[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2022, 201: 662-675. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.126 [11] ZHAO J, HE H, ZHU Z. Fabrication of Biodegradable Poly(Lactic Acid) Composites with High Toughness via In Situ Fibrillation Method and Facile Annealing Process[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2023, 62(9): 3952-3961. [12] 莫智翔, 刘小超, 刘跃军, 等. 苯乙烯-马来酸酐共聚物对PLA/PBAT共混物的相形态及其性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 2096-2106.MO Zhixiang, LIU Xiaochao, LIU Yuejun, et al. Effect of styrene-maleic anhydride on phase morphology and properties of PLA/PBAT blends[J]. Acta Mater Compos Sin, 2023, 40(4): 2096-2106(in Chinese). [13] AVERSA C, BARLETTA M, CAPPIELLO G, et al. Compatibilization strategies and analysis of morphological features of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT)/poly(lactic acid) PLA blends: A state-of-art review[J]. European Poly-mer Journal, 2022, 173: 111304. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2022.111304 [14] QIN S-X, YU C-X, CHEN X-Y, et al. Fully Biodegradable Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(propylene carbonate) Shape Memory Materials with Low Recovery Temperature Based on in situ Comp-atibilization by Dicumyl Peroxide[J]. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2018, 36(6): 783-790. doi: 10.1007/s10118-018-2065-3 [15] CAI K, LIU X, MA X, et al. Preparation of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blends with balanced toughness and strength by dynamic vulcanization process[J]. Polymer, 2024, 291: 126587. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2023.126587 [16] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料拉伸性能的测定: GB/T 1040−2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of tensile properties : GB/T 1040−2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese). [17] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料悬臂梁冲击强度的测定: GB/T 1843—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of izod impact strength: GB/T 1843—2008[S]. Bei-jing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese). [18] MA P, XU P, ZHAI Y, et al. Biobased Poly(lactide)/ethylene-co-vinyl Acetate Ther-moplastic Vulcanizates: Morphology Evolution, Superior Properties, and Partial Degradability[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3(9): 2211-2219. [19] 张也. 生物可降解聚己二酸对苯二甲酸丁二酯(PBAT)共混物及薄膜的制备与性能研究[D]. 长春: 长春工业大学, 2022.ZHANG Ye. Preparation and properties of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate tereph-thalate) (PBAT) blends and films[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Techn-ology, 2022. [20] YANG J, PAN H, LI X, et al. A study on the mechanical, thermal properties and crystal-lization behavior of poly(lactic acid)/thermop-lastic poly(propylene carbonate) polyurethane blends[J]. RSC Advances, 2017, 7(73): 46183-46194. doi: 10.1039/C7RA07424G [21] PRZYBYSZ-ROMATOWSKA M, HAPONIUK J, FORMELA K. Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Poly-(Lactic Acid) Blends Compatibilized by Peroxi-de Initiators: Comparison of Two Strategies, Polymers, 2020 , 12(1): 228. [22] 吴其晔, 巫静安. 高分子材料流变学(第二版)[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 351-373.WU Qiye, WU Jingan. Polymer Pheology (Second Edition)[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002: 351-373(in Chinese). [23] TESFAYE M, PATWA R, DHAR P, et al. Nanosilk-Grafted Poly(lactic acid) Films: Infl-uence of Cross-Linking on Rheology and The-rmal Stability[J]. ACS Omega, 2017, 2(10): 7071-7084. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.7b01005 [24] HUANG Y, ZHANG C, PAN Y, et al. Study on the Effect of Dicumyl Peroxide on Structure and Properties of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Natural Rubber Blend[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Envir-onment, 2013, 21(2): 375-387. doi: 10.1007/s10924-012-0544-0 [25] YAMOUM C, MAIA J, MAGARAPHAN R. Rheological and thermal behavior of PLA modified by chemical crosslinking in the pre-sence of ethoxylated bisphenol A dimeth-acrylates[J]. Polymers for Advanced Techn-ologies, 2017, 28(1): 102-112. doi: 10.1002/pat.3864 [26] ZHAO J, LI X, PAN H, et al. Rheological, thermal and mechanical properties of biode-gradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/poly(prop-ylene carbonate) po-lyurethane trinary blown films[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2020, 77(8): 4235-4258. doi: 10.1007/s00289-019-02942-5 [27] COLE K S, COLE R H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics I. Alternating Current Characteristics[J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1941, 9(4): 341-351. doi: 10.1063/1.1750906 [28] BALKAN O, EZDEŞIR A. Rheological behaviors of glass bead- and wollastonite-filled polypropylene composites modified with ther-moplastic elastomers[J]. Polymer Composites, 2012, 33(7): 1162-1187. doi: 10.1002/pc.22245 [29] ZHAO F, HUANG H-X, ZHANG S-D. Largely toughening biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/ thermoplastic polyurethane blends by adding MDI[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(48): 42511. doi: 10.1002/app.42511 [30] JIA S, CHEN Y, BIAN J, et al. Preparation and properties of poly(L-lactic acid) blends with excellent low-temperature toughness by blen-ding acrylic ester based impact resistance agent[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2021, 183: 1871-1880. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.177 [31] LAMNAWAR K, MAAZOUZ A, CABRERA G, et al. Interfacial Tension Properties in Biopolymer Blends: From Deformed Drop Retraction Method (DDRM) to Shear and Elongation Rheology-Application to Blown Film Extrusion[J]. International Polymer Processing, 2018, 33(3): 411-424. doi: 10.3139/217.3614 [32] CALDERÓN B A, MCCAUGHEY M S, THO-MPSON C W, et al. Evaluating the Influence of Specific Mechanical Energy on Biopolymer Blends Prepared via High-Speed Reactive Extrusion[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2019, 1(6): 1410-1419. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.9b00177 [33] HAN Y, SHI J, MAO L, et al. Improvement of Compatibility and Mechanical Performances of PLA/PBAT Composites with Epoxidized Soybean Oil as Compatibilizer[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020, 59(50): 21779-21790. [34] DI LORENZO M L, OVYN R, MALINCO-NICO M, et al. Peculiar crystallization kinetics of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(propy-lene carbonate) blends[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2015, 55(12): 2698-2705. [35] MONIKA, PAL A K, BHASNEY S M, et al. Effect of Dicumyl Peroxide on a Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS)/Func-tionalized Chitosan-Based Nanobiocomposite for Packaging: A Reactive Extrusion Study[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(10): 13298-13312. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b00907 [36] TIWARY P, KONTOPOULOU M. Tuning the Rheological, Thermal, and Solid-State Properties of Branched PLA by Free-Radical-Mediated Reactive Extrusion[J]. ACS Sustainable Chem-istry & Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 2197-2206. [37] YANG S-L, WU Z-H, YANG W, et al. Thermal and mechanical properties of chemical cross-linked polylactide (PLA)[J]. Polymer Testing, 2008, 27(8): 957-963. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2008.08.009 [38] ZHAO X, HU H, WANG X, et al. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: a comprehensive revi-ew[J]. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(22): 13316-13368. doi: 10.1039/D0RA01801E [39] RIGOUSSEN A, RAQUEZ J-M, DUBOIS P, et al. A dual approach to compatibilize PLA/ABS immiscible blends with epoxidized cardanol derivatives[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2019, 114: 118-126. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.02.017 [40] WANG X, PENG S, CHEN H, et al. Mechanical properties, rheological behaviors, and phase morphologies of high-toughness PLA/PBAT blends by in-situ reactive compatibilization[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 173: 107028. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107028 [41] WU B G, ZENG Q T, NIU D Y, et al. Design of Supertoughened and Heat-Resistant PLLA /Elastomer Blends by Controlling the Distribution of Stereocomplex Crystallites and the Morphology[J]. Macromolecules, 2019, 52(3): 1092-1103. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b02262 [42] CHEN X, ZENG Z, JU Y, et al. Design of biodegradable PLA/PBAT blends with balanced toughness and strength via interfacial compa-tibilization and dynamic vulcanization[J]. Polymer, 2023, 266: 125620. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2022.125620 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 41
- HTML全文浏览量: 16
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: