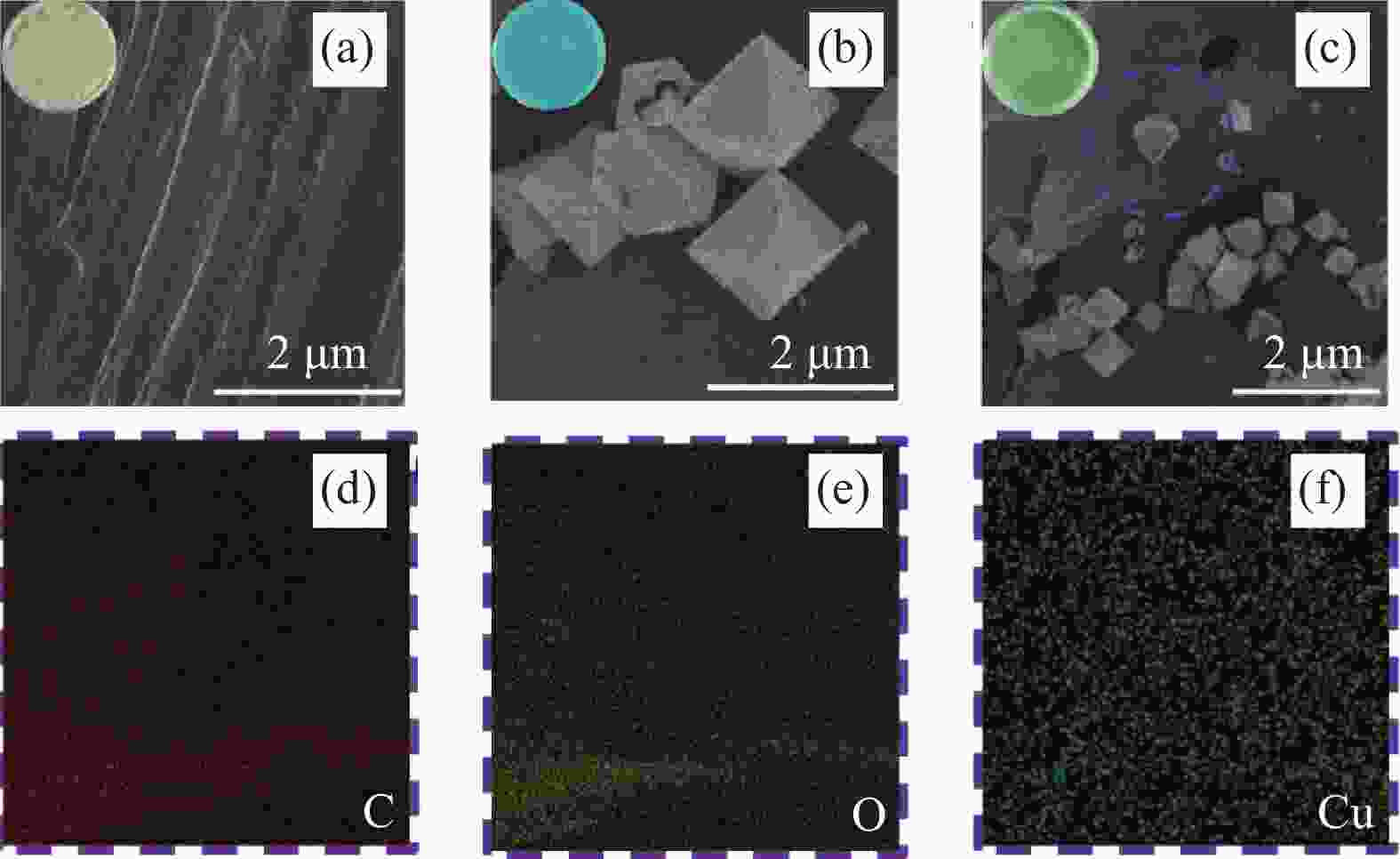
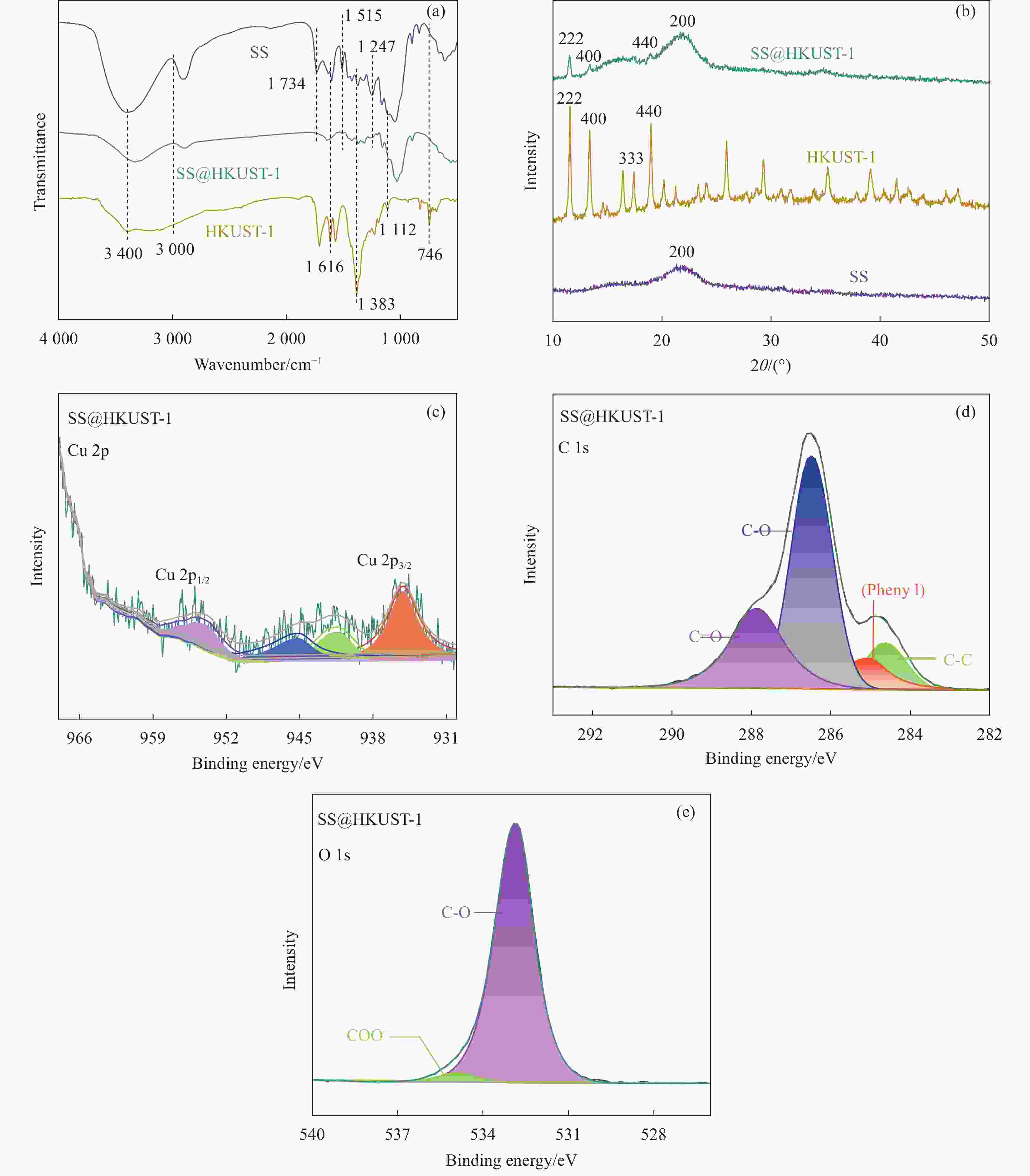
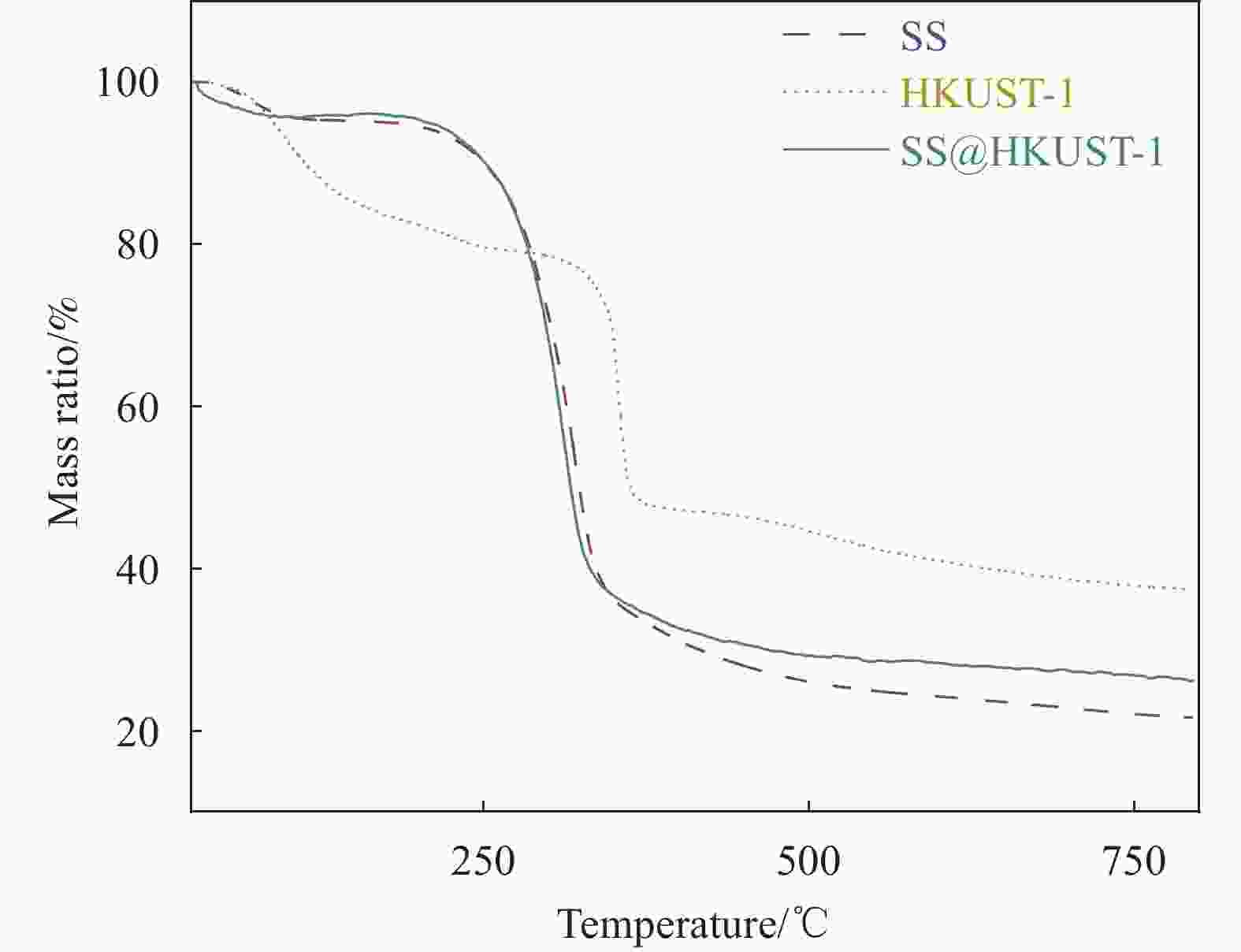
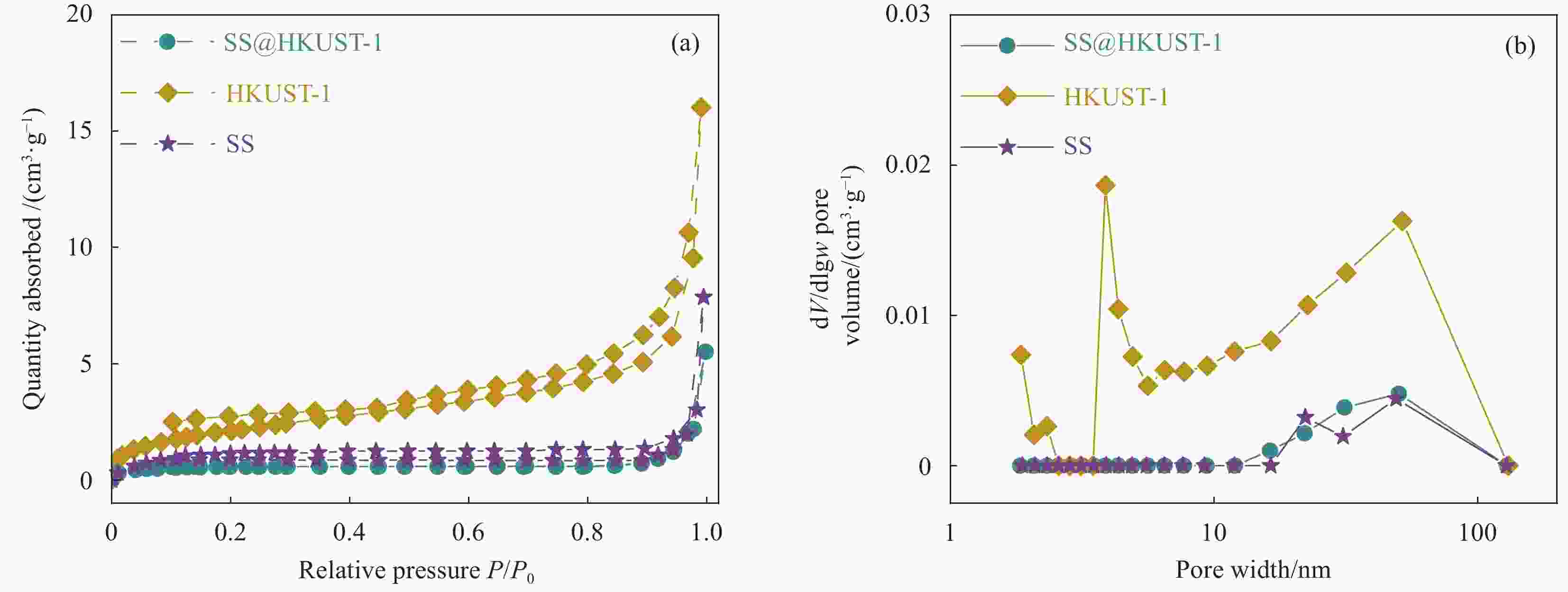
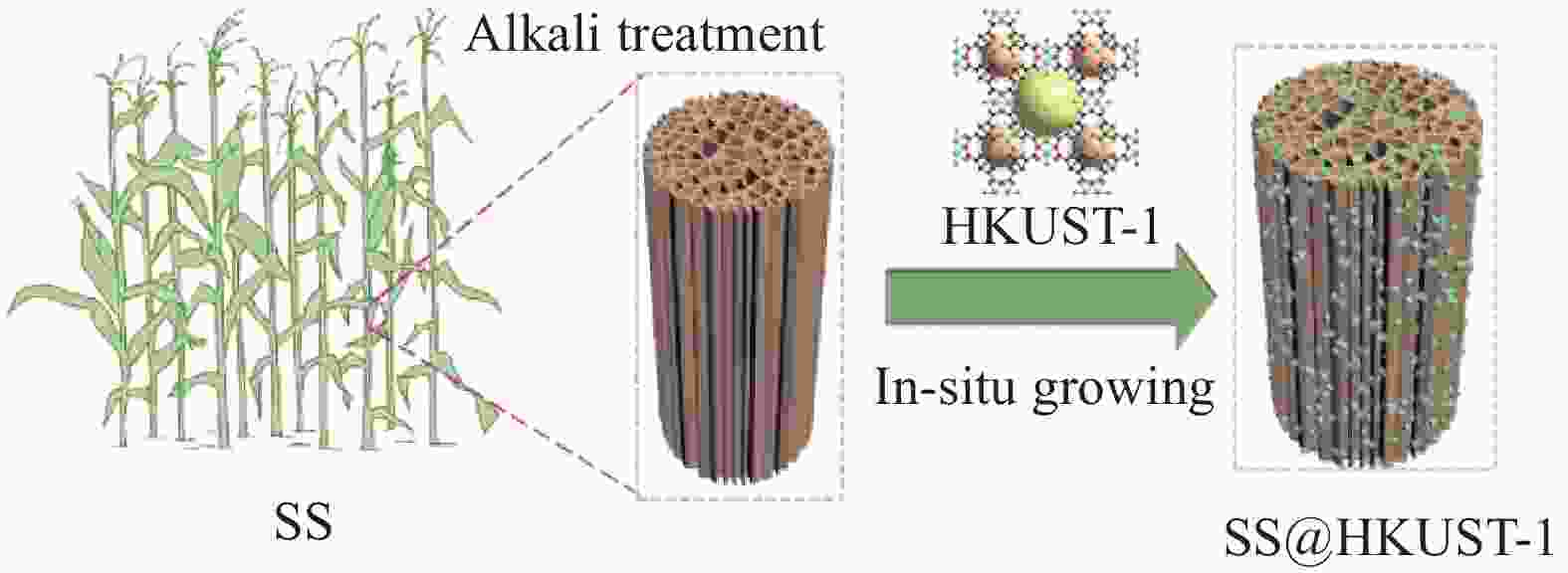
Adsorption behaviour and mechanism of tetracycline by sorghum straw-loaded HKUST-1
-
摘要: 四环素(TC)是一种难降解广谱抗生素,广泛存在于畜牧业排放的污废中,排放后会对水体生态环境造成严重的污染,通过吸附法可有效去除。本研究以高粱秸秆(SS)为基材,通过原位生长法在SS表面负载MOFs(HKUST-1)制备SS@HKUST-1复合材料,用于对TC的吸附去除,探究复合材料对TC的吸附行为及吸附机制。研究表明:当pH=7、T=25°C、HKUST-1的负载量为31%时,吸附容量达到95 mg/g。吸附过程符合准二级动力学模型,吸附等温线符合Freundlich模型,表明复合材料对TC吸附属于多分子层化学吸附。因此,SS@HKUST-1对水中TC的去除具有良好的应用前景。Abstract: Tetracycline (TC) is a refractory broad-spectrum antibiotic, that is widely present in the waste discharged from animal husbandry, which will cause serious pollution to the ecological environment of water bodies after discharge, and it can be effectively removed by adsorption. In this work, sorghum straw (SS) was used as the substrate to prepare SS@HKUST-1 composites by in-situ growth of MOFs (HKUST-1) on the surface of SS for the adsorption and removal of TC, investigating the adsorption behaviour and adsorption mechanism of composites on TC. The results showed that the adsorption capacity reached 95mg/g when pH=7, T=25℃ and the load capacity of HKUST-1 is 31%. The adsorption process conforms to the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the adsorption isotherm conforms to the Freundlich model, which suggested the existence of multimolecular layer chemisorption between TC and adsorbent. Therefore, SS@HKUST-1 had a good application prospect for tetracycline removal in water.
-
Key words:
- sorghum straw /
- HKUST-1 /
- In-situ growth /
- tetracycline /
- adsorption
-
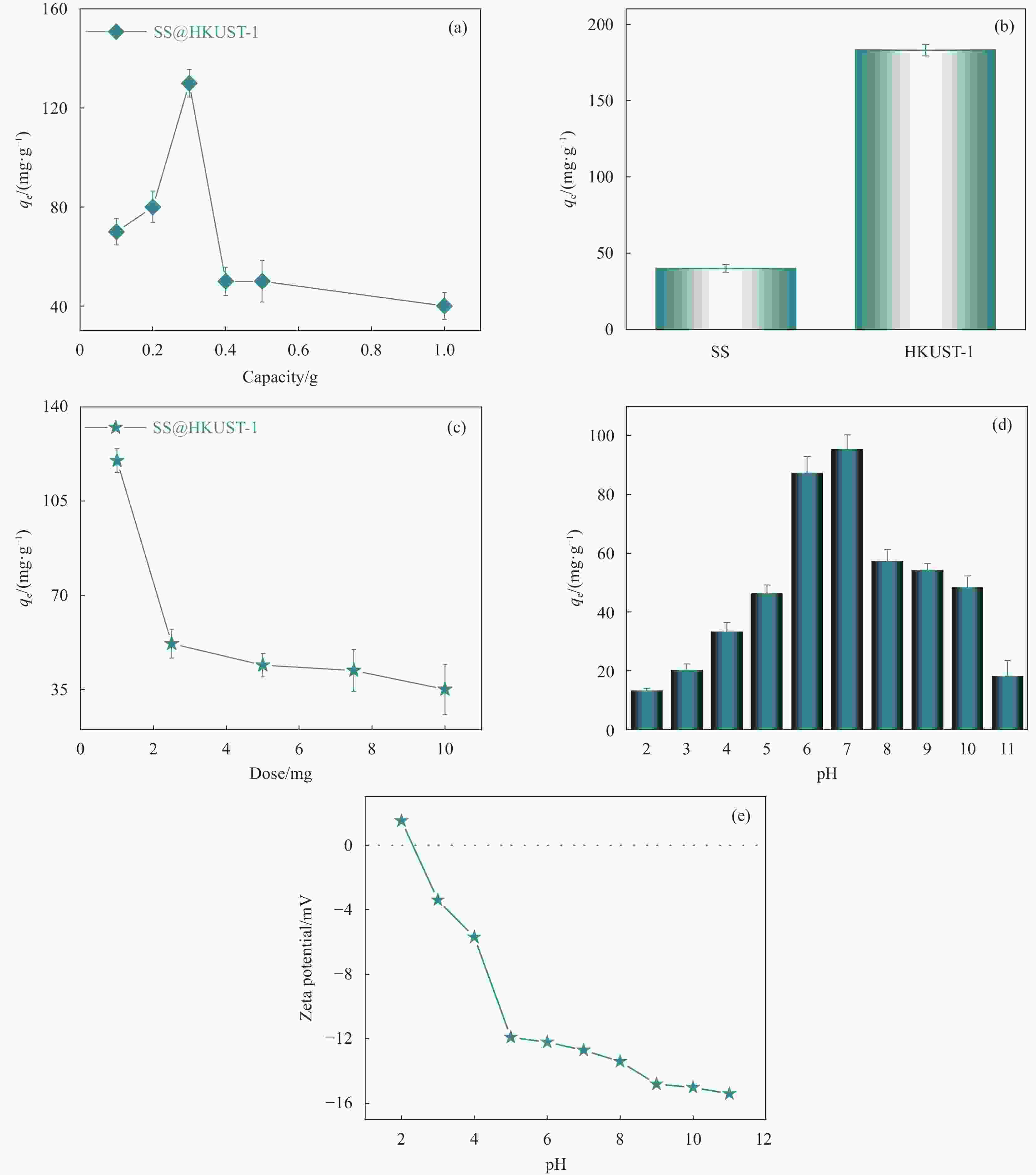
图 6 (a) 不同Cu(NO3)2质量对TC吸附的影响; (b) SS与HKUST-1对TC的吸附效果 (c) 吸附剂用量对SS@HKUST-1 TC吸附的影响; (d) 不同溶液pH值对SS@HKUST-1 TC吸附的影响; (e) 不同pH值下SS@HKUST-1的Zeta电位
Figure 6. (a) Effects of different Cu(NO3)2 monomer rations on TC adsorption; (b) Adsorption effects of SS and HKUST-1 on TC (c) Effects of adsorbent dosages on TC adsorption by SS@HKUST-1 composites; (d) Effects of different pH values on TC adsorption by SS@HKUST-1 composites; (e) Zeta potential of SS@HKUST-1 under different pH values
qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity
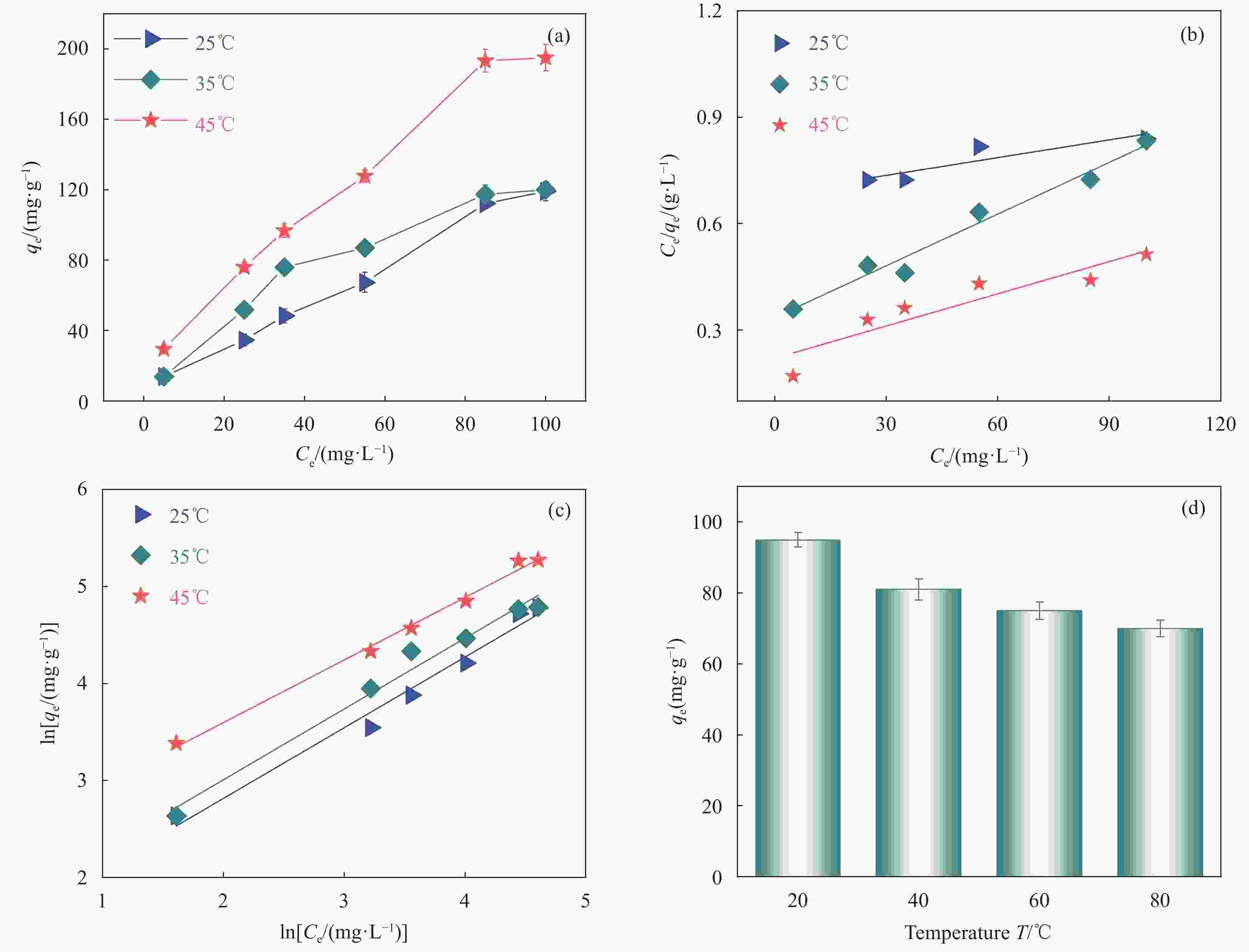
图 8 (a) TC在SS@HKUST-1表面的吸附等温线; (b) Langmuir吸附等温线; (c) Freundlich吸附等温线; (d) 不同温度处理SS@HKUST-1对吸附TC的影响
Figure 8. (a) Adsorption isotherms of TC onto the surfaces of SS@HKUST-1; (b) Langmuir adsorption isotherm; (c) Freundlich adsorption isotherm; (d) Effect of different temperature treatment SS@HKUST-1 on adsorbed TC
Ce—concentration at adsorption equilibrium; T—Temperature
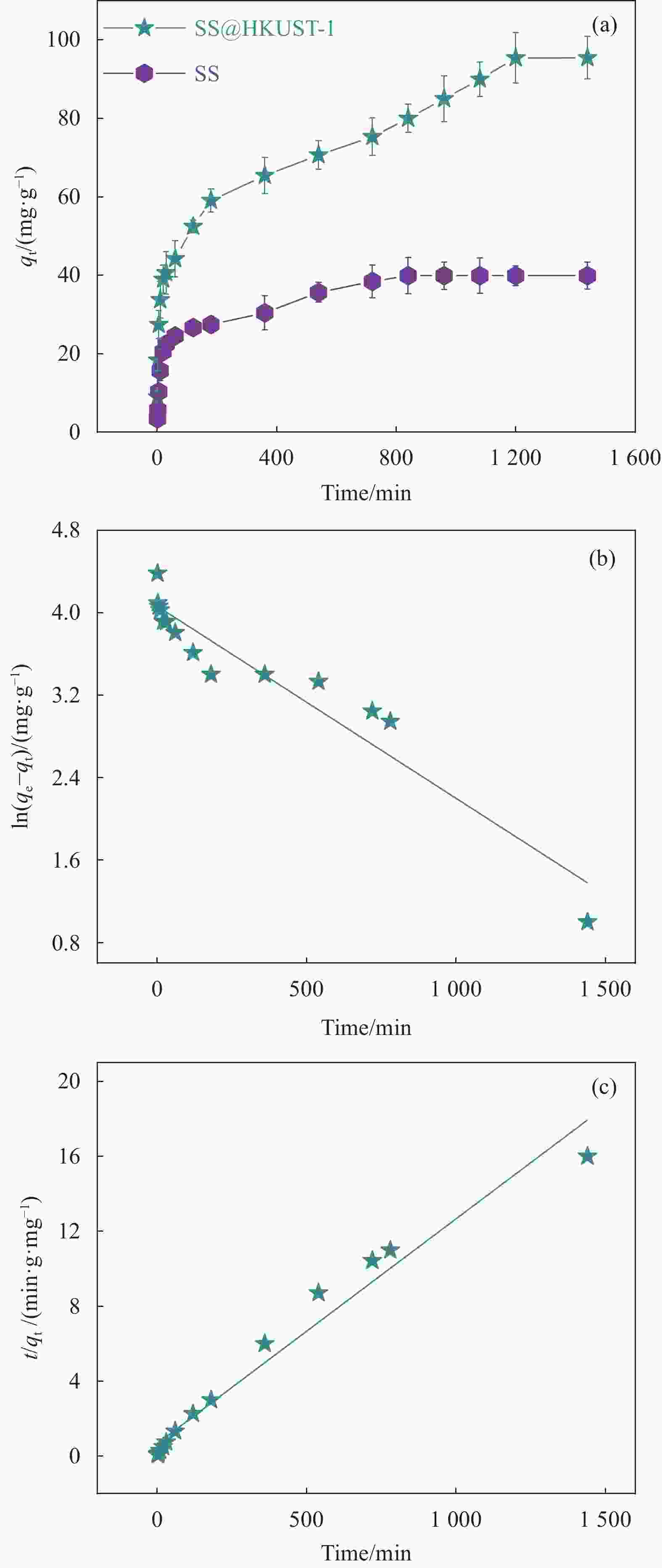
表 1 SS@HKUST-1吸附TC的动力学模型拟合参数
Table 1. parameters of kinetic model fitting for SS@HKUST-1 adsorbed TC
qe,exp/
(mg·g−1)Pseudo-first-order
kineticPseudo-second-order
kinetick1/
min−1qe,cal /
mg·g−1R2 k2/
(g·mg−1·min−1)qe,cal/
mg·g −1R2 95.44 0.002 65.06 0.947 0.010 1.87 0.994 Notes: qe,exp—The actual adsorption capacity at adsorption equilibrium; qe,cal—The calculated adsorption capacity at adsorption equilibrium; k1—Pseudo-first-order adsorption rate constant; k2—Pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constant; R2—The Correlation coefficient of Langmuir and Freundlich models 表 2 SS@HKUST-1的吸附等温线的拟合参数
Table 2. Fitting parameters to SS@HKUST-1 adsorption isotherms
Temperature/°C Langmuir model Freundlich model $ {q}_{\mathrm{m}} $/
(mg·g−1)b/
(L·mg−1)R2 $ {K}_{\mathrm{f}} $/
(mg·g−1)1/n R2 25 119.10 0.686 0.901 3.88 0.7291 0.989 35 120.00 0.335 0.987 4.69 0.7302 0.991 45 194.97 0.220 0.926 10.03 0.6453 0.997 Notes: qm—Maximum adsorption capacity; b—$ \dfrac{1}{{q}_{\mathrm{m}}{k}_{\mathrm{L}}} $, kL—Adsorption coefficient of Langmuir; Kf—Adsorption coefficient of Freundlich; 1/n—Empirical parameter varied with the degree of heterogeneity of adsorbing sites. 表 3 不同吸附剂对TC的吸附去除效果对比
Table 3. Comparison of adsorption and removal effects of different adsorbents for TC
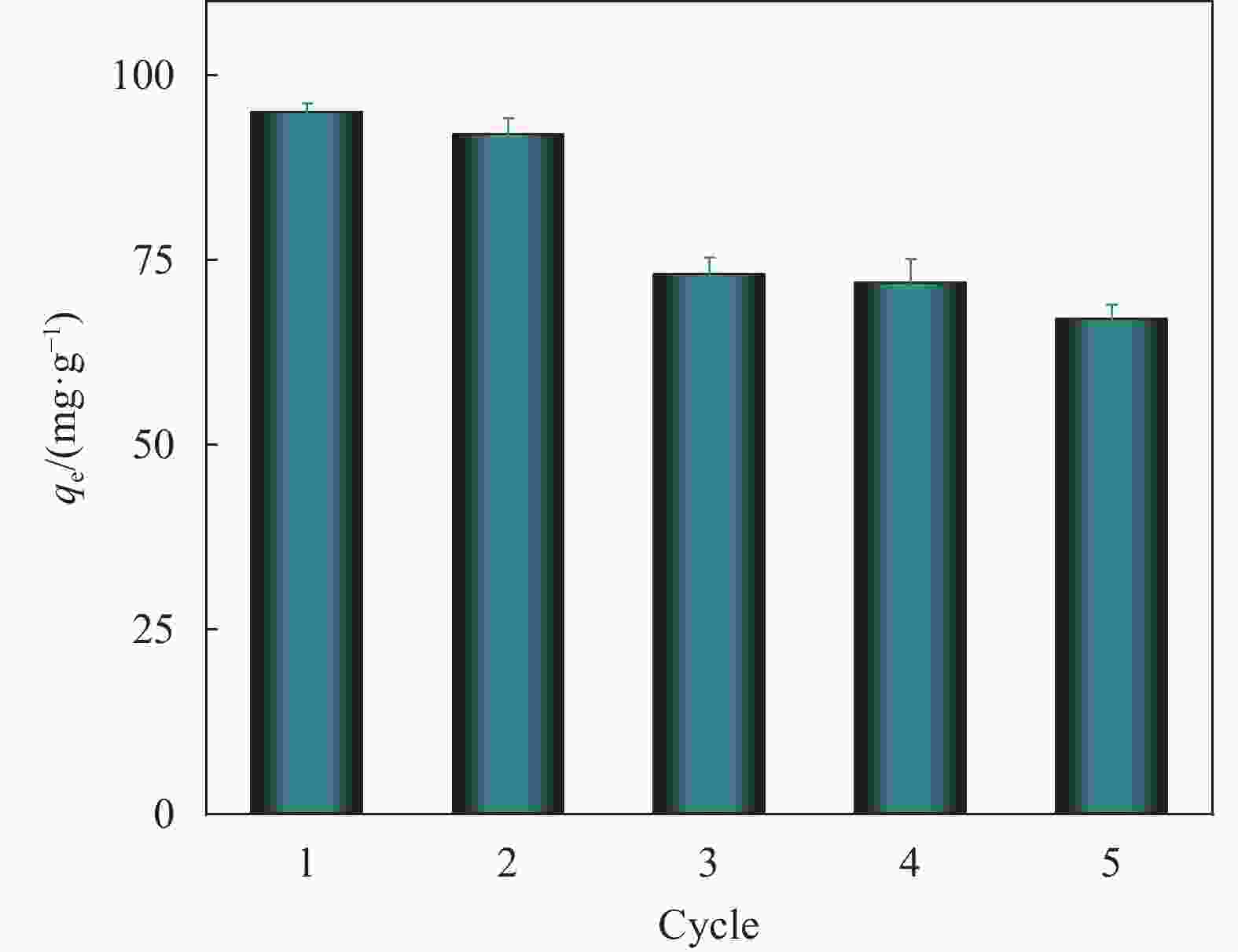
Sample qe(mg·g−1) Reference SS@HKUST-1 95 This work ZIF-8/CMC 78.75 37 CS biochar 53.191 38 WS biochar 66.67 38 MIL-100(Fe)/PEO 85.02 39 Fe3O4@RGO@C18 77.56 40 AG(Mn)-88 B-C 53.07 41 Notes: ZIF-8/CMC—The metal-organic skeleton hybrid foam ZIF-8/CMC with cellulose; CS biochar—Corn straw biochar; WS biochar—Wheat straw biochar; MIL-100(Fe)/PEO—Polyethylene oxide modified MIL-100(Fe); Fe3O4@RGO@C18—Fe3O4 magnetic particles were coated with a layer of RGO (graphene),and C18 was further modified on the surface of Fe3O4@RGO material; AG(Mn)-88 B-C—MIL-88 B(Fe)/sodium alginate composite aerogel. -
[1] 高艳林, 景红霞, 李龙祥等. 溶剂热法制备Bi2O3/BiOI复合光催化材料及对四环素的降解应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2): 677-684.GAO Yanlin, JING Hongxia, LI Longxiang et al. Preparation of Bi2O3/BiOI composite photocatalytic materials by solvothermal method and application to tetracycline degradation[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2022, 39(2): 677-684 (in Chinese). [2] WANG D, JIA F, WANG H, et al. Simultaneously efficient adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline by Fe-based MOFs[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science, 2018, 519: 273-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.02.067 [3] ZHANG X, LIN X, HE Y, et al. Study on adsorption of tetracycline by Cu-immobilized alginate adsorbent from water environment[J]. International journal of biological macromolecules, 2019, 124: 418-428. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.218 [4] 于晓雯, 索全义. 畜禽粪便中四环素类抗生素的残留及危害[J]. 北方农业学报, 2018, 46(3): 83-88.YU Xiaowen, SUO Quanyi. Residues and hazards of tetracycline antibiotics in livestock manure[J]. Northern Agricultural Journal, 2018, 46(3): 83-88 (in Chinese). [5] ZHU Y, LI B, WANG Y, et al. Preparation of Porous Ti/RuO2-IrO2@ Pt, Ti/RuO2-TiO2@ Pt and Ti/Y2O3-RuO2-TiO2@ Pt Anodes for Efficient Electrocatalytic Decomposition of Tetracycline[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(5): 2189. doi: 10.3390/molecules28052189 [6] GOPAL G, ALEX S A, CHANDRASEKARAN N, et al. A review on tetracycline removal from aqueous systems by advanced treatment techniques. RSC Adv 10: 27081–27095[J]. 2020. [7] YIN F, LIN S, ZHOU X, et al. Fate of antibiotics during membrane separation followed by physical-chemical treatment processes[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 759: 143520. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143520 [8] HU Z, WANG Y, WANG L, et al. Synthesis of S-type heterostructure π-COF for photocatalytic tetracycline degradation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023: 147534. [9] BHATT P, JEON C H, KIM W. Tetracycline bioremediation using the novel Serratia marcescens strain WW1 isolated from a wastewater treatment plant[J]. Chemosphere, 2022, 298: 134344. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134344 [10] 张甜, 姜博, 邢奕等. 吸附法去除水中抗生素研究进展[J]. 环境工程, 2021, 39(3): 29-39.ZHANG Tian, JIANG Bo, XING Yi et al. Research progress of antibiotic removal from water by adsorption[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2021, 39(3): 29-39 (in Chinese). [11] CHEN W, ZHAO B, GUO Y, et al. Effect of hydrothermal pretreatment on pyrolyzed sludge biochars for tetracycline adsorption[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9(6): 106557. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.106557 [12] LUO Q, REN T, LEI Z, et al. Non-toxic chitosan-based hydrogel with strong adsorption and sensitive detection abilities for tetracycline[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 427: 131738. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131738 [13] QIAO D, QU X, CHEN X, et al. Rational structural design of graphene oxide/W18O49 nanocomposites realizes highly efficient removal of tetracycline in water[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 619: 156630. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156630 [14] 陈刚. 功能化金属有机框架对抗生素的吸附研究[D]. 华东交通大学, 2021.CHEN G. Adsorption study of antibiotics by functionalized metal-organic frameworks [D]. East China Jiaotong University, 2021 (in Chinese). [15] 王艳萍, 房得珍, 路淼等. MOFs基材料对金属离子吸附分离的研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2023, 51(7): 68-73.WANG Yanping, FANG Dezhen, LU Miao et al. Advances in the adsorption and separation of metal ions by MOFs-based materials[J]. New Materials for Chemical Industry, 2023, 51(7): 68-73 (in Chinese). [16] YANG Y, XUE Y, LI J, et al. Efficient removal of organic dyestuff in water contamination over a MOF-derived Co-based adsorbent[J]. Reaction Chemistry & Engineering, 2023. [17] ZHANG M, LI Y, ZHOU X, et al. Preparation of ZIF-67/C3N4 composite material and adsorption of tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(41): 94112-94125. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28919-6 [18] MA X, XIONG Y, LIU Y, et al. When MOFs meet wood: From opportunities toward applications[J]. Chem, 2022, 8(9): 2342-2361. doi: 10.1016/j.chempr.2022.06.016 [19] 李钲, 王国栋, 陈日耀等. 椰壳炭吸附去除四环素性能及机理研究[J]. 福建师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 39(5): 117-123.LI Zheng, WANG Guodong, CHEN Riyao et al. Study on the performance and mechanism of tetracycline removal by adsorption on coconut shell carbon[J]. Journal of Fujian Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 39(5): 117-123 (in Chinese). [20] 王诗尧, 王少华, 孙强等. 玉米和小麦秸秆生物炭对四环素吸附效果研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2023, 48(8): 84-87.WANG Shiyao, WANG Shaohua, SUN Qiang et al. Study on the adsorption effect of tetracycline on corn and wheat straw biochar[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2023, 48(8): 84-87(in Chinese). [21] SHI Q, WANG W, ZHANG H, et al. Porous biochar derived from walnut shell as an efficient adsorbent for tetracycline removal[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2023, 383: 129213. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.129213 [22] ZHUO S N, DAI T C, REN H Y, et al. Simultaneous adsorption of phosphate and tetracycline by calcium modified corn stover biochar: Performance and mechanism[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2022, 359: 127477. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127477 [23] WANG K, HAN T, CHEN X, et al. Insights into behavior and mechanism of tetracycline adsorption on virgin and soil-exposed microplastics[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 440: 129770. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129770 [24] KANGRA B, JATRANA A, MAAN S, et al. Effective adsorption of chlorpyrifos pesticides by HKUST-1 metal-organic framework[J]. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 2022, 134(4): 104. doi: 10.1007/s12039-022-02099-1 [25] OLIVEIRA H, SCACCHETTI F, BEZERRA F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of HKUST-1 as an efficient adsorbent for textile dyes[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2023, 30(37): 87242-87259. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28455-3 [26] ZHAO L, AZHAR M R, LI X, et al. Adsorption of cerium (III) by HKUST-1 metal-organic framework from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science, 2019, 542: 421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.117 [27] BHORIA N, BASINA G, POKHREL J, et al. Functionalization effects on HKUST-1 and HKUST-1/graphene oxide hybrid adsorbents for hydrogen sulfide removal[J]. Journal of hazardous materials, 2020, 394: 122565. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122565 [28] PAN J, BAI X, LI Y, et al. HKUST-1 derived carbon adsorbents for tetracycline removal with excellent adsorption performance[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 205: 112425. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.112425 [29] ZHAO L, AZHAR M R, LI X, et al. Adsorption of cerium (III) by HKUST-1 metal-organic framework from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of colloid and interface science, 2019, 542: 421-428. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.01.117 [30] LUO J, FAN C, XIAO Z, et al. Novel graphene oxide/carboxymethyl chitosan aerogels via vacuum-assisted self-assembly for heavy metal adsorption capacity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 578: 123584. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123584 [31] JAGÓDKA P, MATUS K, ŁAMACZ A. On the HKUST-1/GO and HKUST-1/rGO composites: the impact of synthesis method on physicochemical properties[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(20): 7082. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207082 [32] DHYANI V, KUMAR J, BHASKAR T. Thermal decomposition kinetics of sorghum straw via thermogravimetric analysis[J]. Bioresource technology, 2017, 245: 1122-1129. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.189 [33] ZHANG S, HAN X, CAI H, et al. Aramid nanofibers/WS2 nanosheets co-assembled aerogels for efficient and stable Pb (II) adsorption in harsh environments[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 450: 138268. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138268 [34] 崔芳溪, 张蓬, 曹胜凯等. 不同pH溶液中四环素类抗生素与金属离子配合前后的光化学性质及毒性差异[J/OL]. 环境科学学报: 1-9.CUI Fanxi, ZHANG Peng, CAO Shengkai et al. Differences in photochemical properties and toxicity of tetracycline antibiotics before and after coordination with metal ions in different pH solutions[J/OL]. Journal of Environmental Science: 1-9 (in Chinese). [35] AL-JABARI M. Kinetic models for adsorption on mineral particles comparison between Langmuir kinetics and mass transfer[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2016, 6: 27-37. [36] CHEN X, HOSSAIN M F, DUAN C, et al. Isotherm models for adsorption of heavy metals from water-A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2022: 135545. [37] 李微, 郭孟雅, 刘宁. ZIF-8/CMC杂化泡沫吸附TC和Cu~(2+)研究[J/OL]. 环境工程, 1-16.LI Wei, GUO Mengya, LIU Ning. Adsorption of TC and Cu~(2+) by ZIF-8/CMC hybrid foam[J/OL]. Environmental Engineering, 1-16. (in Chinese). [38] 王诗尧, 王少华, 孙强等. 玉米和小麦秸秆生物炭对四环素吸附效果研究[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2023, 48(8): 84-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2023.08.017WANG Shiyao, WANG Shaohua, SUN Qiang et al. Study on the adsorption effect of tetracycline on corn and wheat straw biochar[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2023, 48(8): 84-87(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2023.08.017 [39] 李微, 宁雨阳, 刘宁等. PEO基MOFs杂化泡沫材料对四环素和Cu~(2+)吸附性能[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(7): 76-85.LI Wei, NING Yuyang, LIU Ning et al. Adsorption properties of PEO-based MOFs hybrid foams for tetracycline and Cu~(2+)[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(7): 76-85(in Chinese). [40] 李胜, 唐祝兴, 王英嘉等. 纳米复合材料Fe3O4@RGO@C18对四环素的吸附研究[J]. 辽宁化工, 2023, 52(4): 469-473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2023.04.003LI Sheng, TANG Zhuxing, WANG Yingjia et al. Adsorption study of tetracycline on nanocomposite Fe3O4@RGO@C18[J]. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2023, 52(4): 469-473(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2023.04.003 [41] 张晓东, 赵胜昊, 姜舜桐等. MIL-88B(Fe)/海藻酸钠气凝胶的制备及其吸附四环素性能研究[J]. 广州化学, 2023, 48(1): 10-18.ZHANG Xiaodong, ZHAO Shenghao, JIANG Suntong et al. Preparation of MIL-88B(Fe)/sodium alginate aerogel and its adsorption performance of tetracycline[J]. Guangzhou Chemistry, 2023, 48(1): 10-18(in Chinese). [42] 缪家鑫. Al掺杂UiO-66-NH2的制备及其对水体中四环素和Cu(Ⅱ)的吸附去除研究[D]. 四川农业大学, 2023.MIAO Jiaxin. Preparation of Al-doped UiO-66-NH2 and its adsorption and removal of tetracycline and Cu(II) from water[D]. Sichuan Agricultural University, 2023. (in Chinese). [43] 符佳佳. MOFs改性石墨烯气凝胶的制备及其对污水中四环素的去除研究[D]. 四川农业大学, 2022.FU Jiajia. Preparation of MOFs modified graphene aerogel and its removal of tetracycline from wastewater[D]. Sichuan Agricultural University, 2022. (in Chinese). [44] ABBASNIA A, ZAREI A, YEGANEH M, et al. Removal of tetracycline antibiotics by adsorption and photocatalytic-degradation processes in aqueous solutions using metal organic frameworks (MOFs): A systematic review[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2022, 145: 109959. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109959 [45] LI W, CAO J, XIONG W, et al. In-situ growing of metal-organic frameworks on three-dimensional iron network as an efficient adsorbent for antibiotics removal[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 392: 124844. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124844 -

 点击查看大图
点击查看大图
计量
- 文章访问数: 114
- HTML全文浏览量: 69
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: