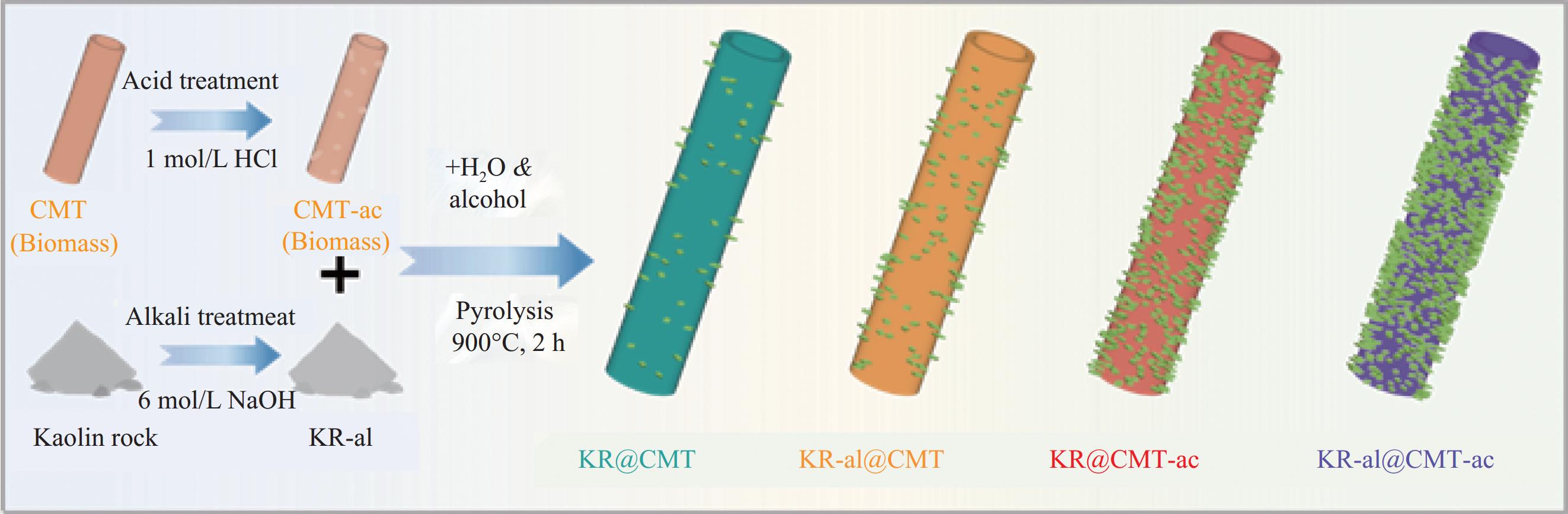
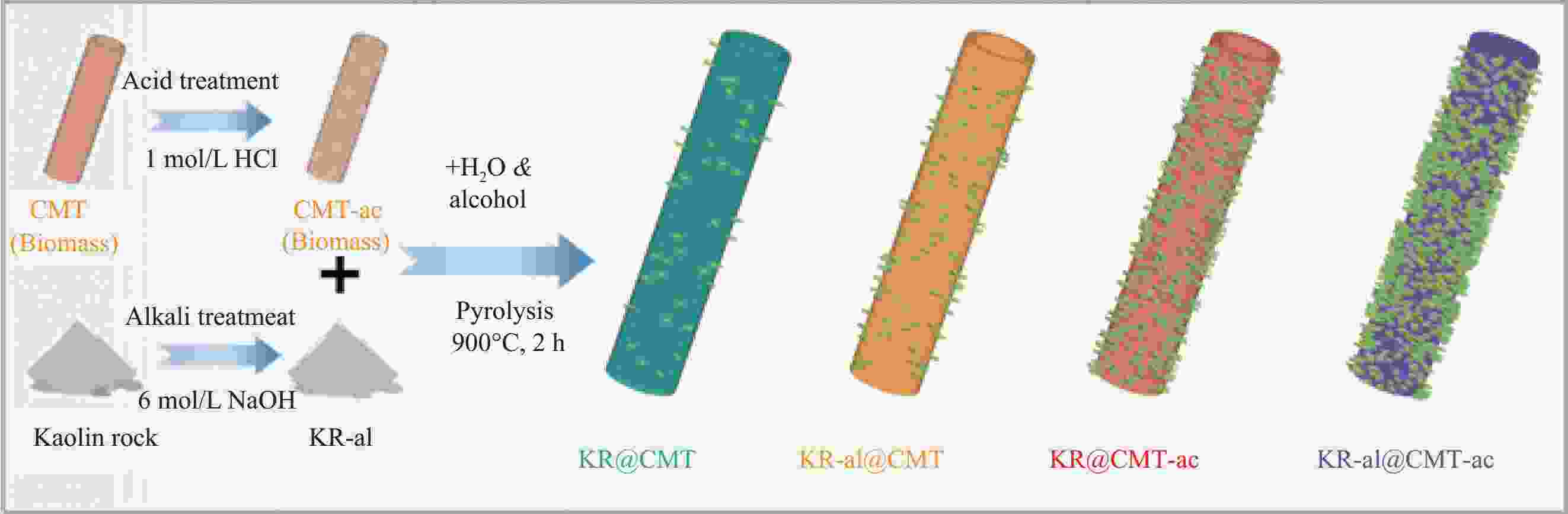
Biomass carbon tubes/kaolin rock-dual wastes derived composite for efficient microwave absorption
-
摘要: 低成本、高性能和具有良好的环境稳定性是微波吸收剂实现应用的关键因素。本文以废弃梧桐飘絮生物质为碳源,煤矿废弃资源高岭岩为负载,通过优化界面作用并结合高温热解的方法合成了具有优异微波吸收性能的碳管/高岭岩双废复合材料。实验结果表明,经过酸改性的碳微米管(Acid-treatment carbon microtubes,CMT-ac)和碱改性的高岭岩(Alkali-treatment kaolin rock,KR-al)在高温碳化后结合良好,两者之间形成了大量的异质界面,且由于两者电导率的差异并在电磁波的辐照下容易形成界面极化效应,从而大大衰减电磁波。最终得到的KR-al@CMT-ac碳基矿物复合样品在仅在2.0 mm的匹配厚度下有效吸收带宽达到6.3 GHz (11.7~18.0 GHz),厚度为3.0 mm时在8.08 GHz处达到最小反射损耗−51.5 dB。吸波性能的提升得益于增强的界面极化和本身高电导损耗的共同作用。本研究将为低成本和高性能的介电型吸波材料的设计提供有效的策略。Abstract: Low cost, high performance, and good environmental stability are the key factors to determine the application of microwave absorbent. In this study, the wasted platanus tree fruits were taken as raw biomass materials, which were combined with the kaolin rock, one kind of abandoned coal mine resources, to construct the dual wastes-derived composite for microwave absorption. The obtained carbon microtubes/kaolin rock composite was optimized by controlling their interfacial interaction followed by high-temperature pyrolysis to reach efficient absorbing capability towards microwave radiation. The experimental results show that the acid-modified carbon microtubes (CMT-ac) and the alkali-decorated kaolin rock (KR-al) combined well to supply a large number of heterogeneous interfaces to strengthen the interfacial polarization mechanism. As a result, their conductivity difference under the irradiation of electromagnetic wave enabled greatly attenuating electromagnetic wave. The final KR-al@CMT-ac sample achieved an effective absorption bandwidth of 6.3 GHz (11.7~18.0 GHz) at a matching thickness of only 2.0 mm and a minimum reflection loss of −51.5 dB at 8.08 GHz at a thickness of 3.0 mm. The improvement in microwave absorption performance is due to the enhanced interface polarization and conduction loss. This study will provide an effective strategy for the design of low-cost and high-performance dielectric absorbents.
-
Key words:
- kaolin rock /
- biomass /
- dielectric loss /
- interfacial polarization /
- microwave absorption
-
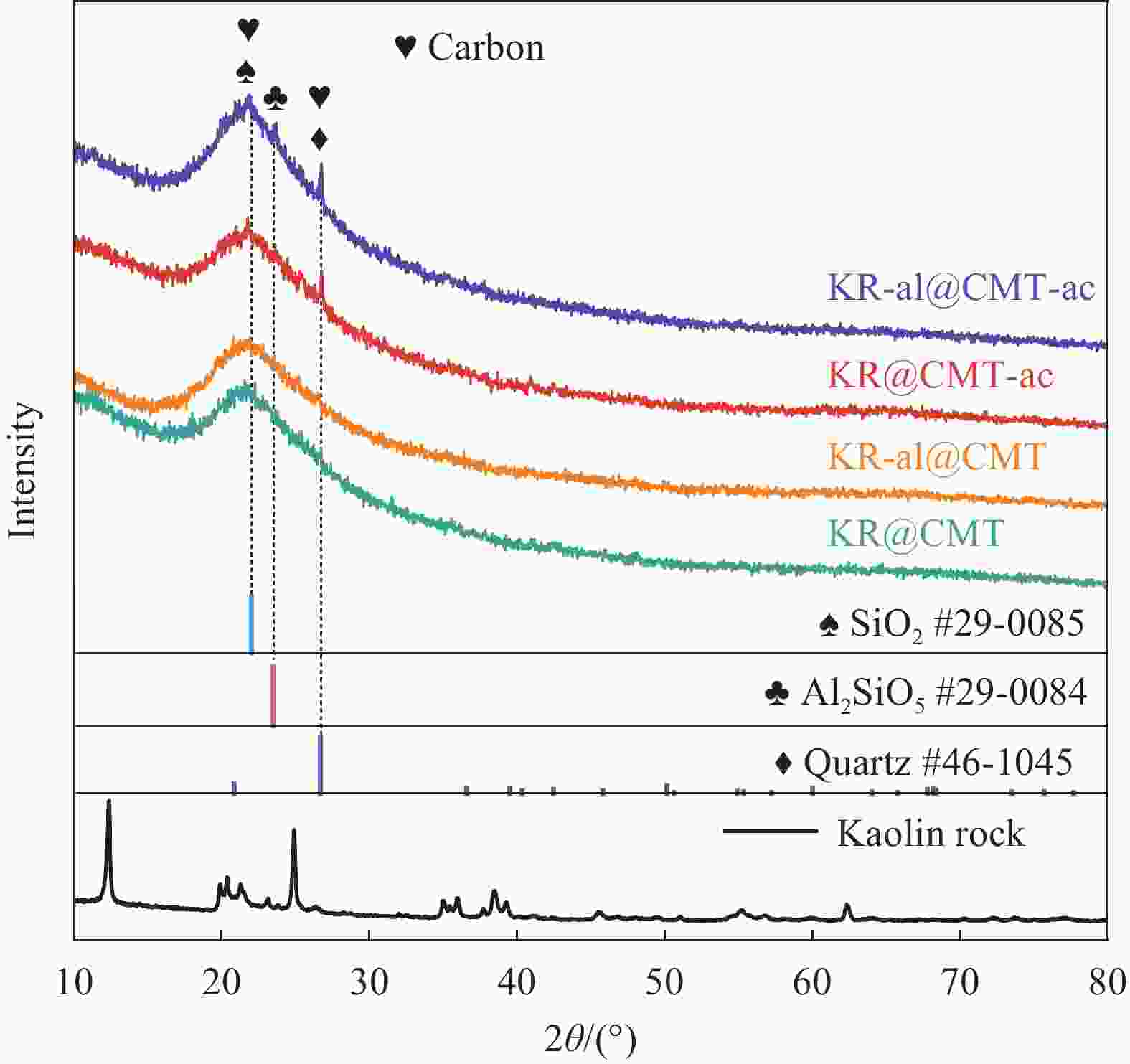
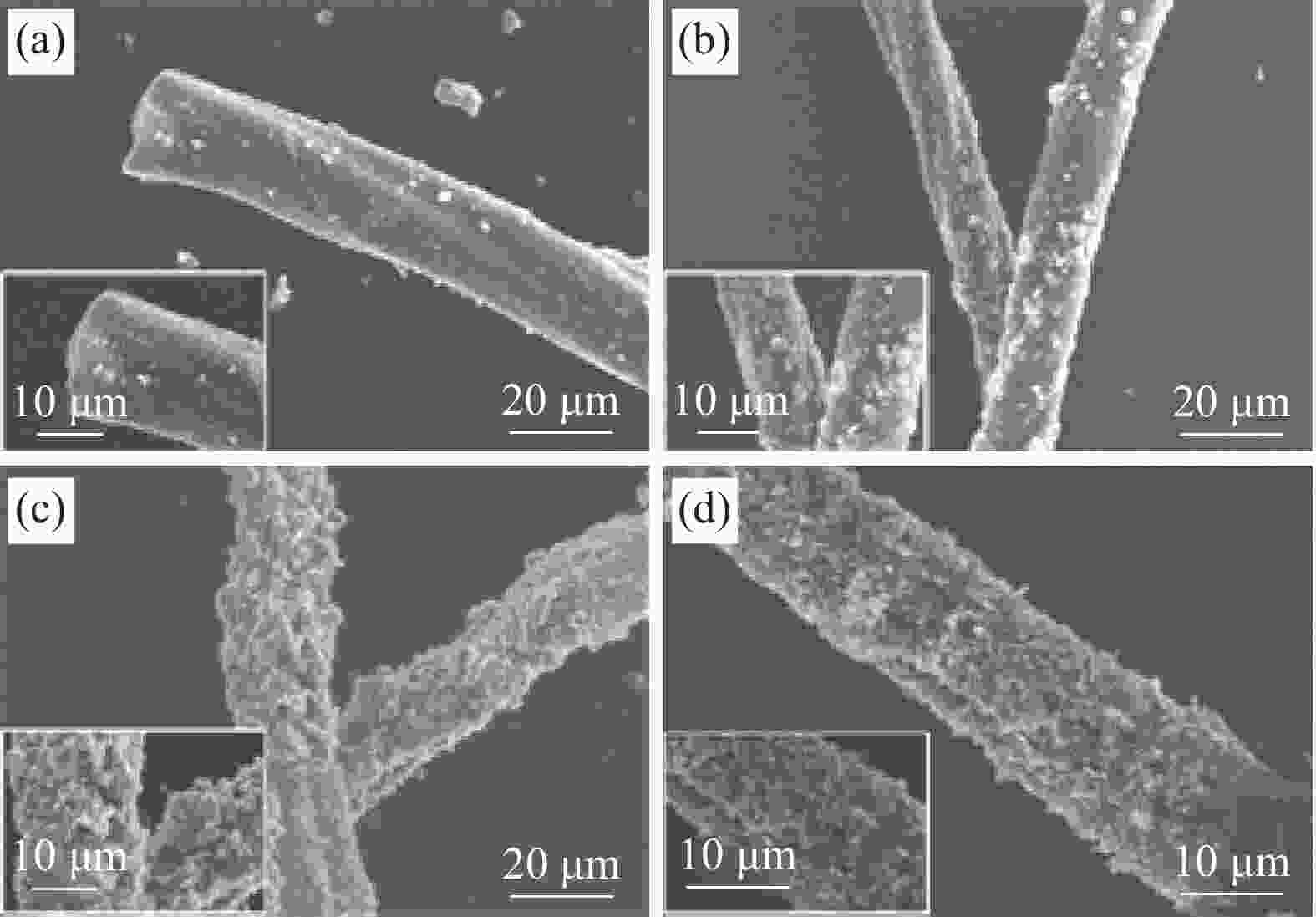
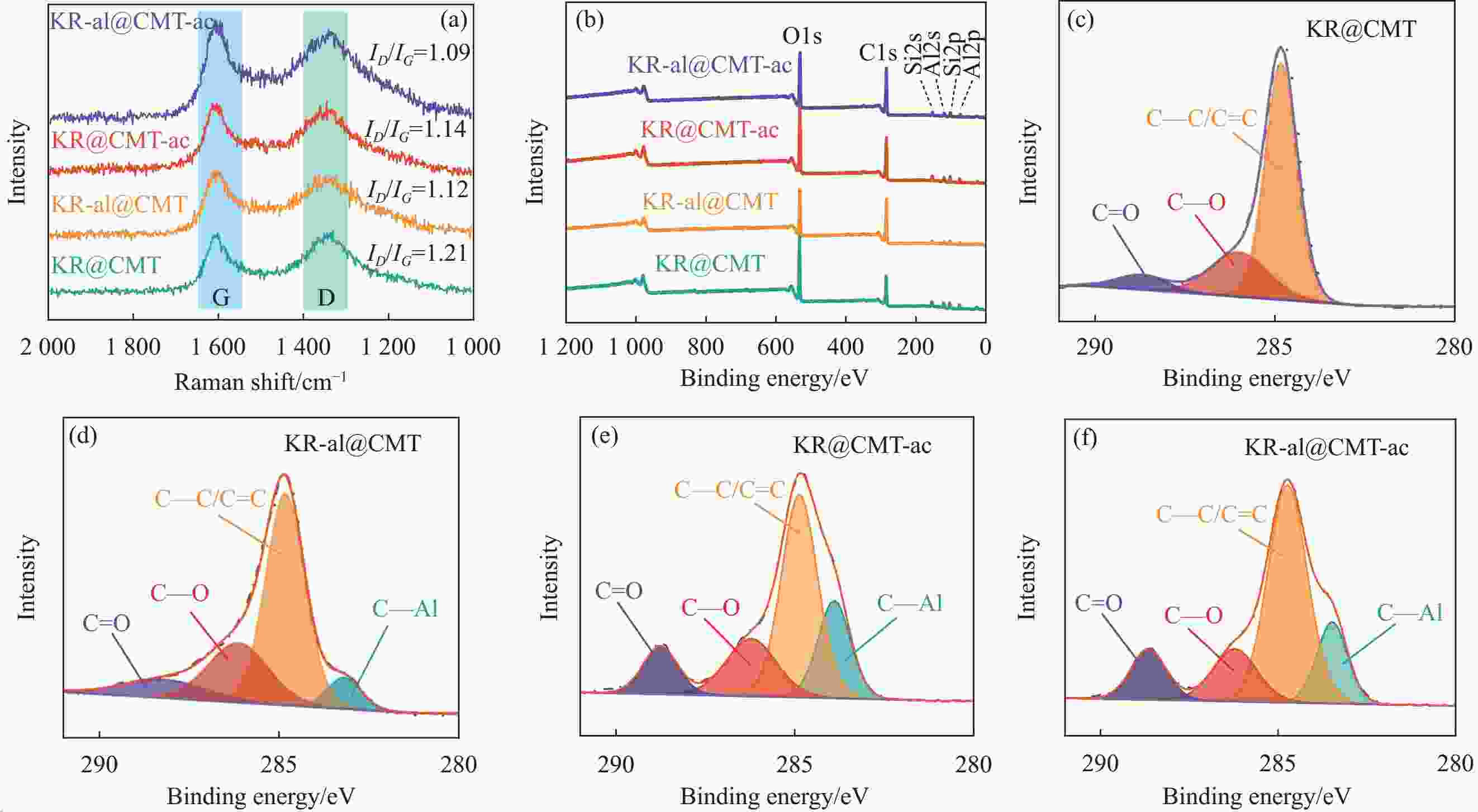
图 6 生物质碳微米管/高岭岩复合材料的Raman图谱(a)和XPS全谱(b);KR@CMT (c)、KR-al@CMT (d)、KR@CMT-ac (e)和KR-al@CMT-ac (f)样品的C1s窄谱
Figure 6. Raman spectra (a) and XPS survey spectra (b) of biomass carbon microtubes/kaolin rock composites; Narrow C1s spectra of KR@CMT (c), KR-al@CMT (d), KR@CMT-ac (e) and KR-al@CMT-ac samples (f)
ID/IG—Degree of defects and edges of carbon-based materials
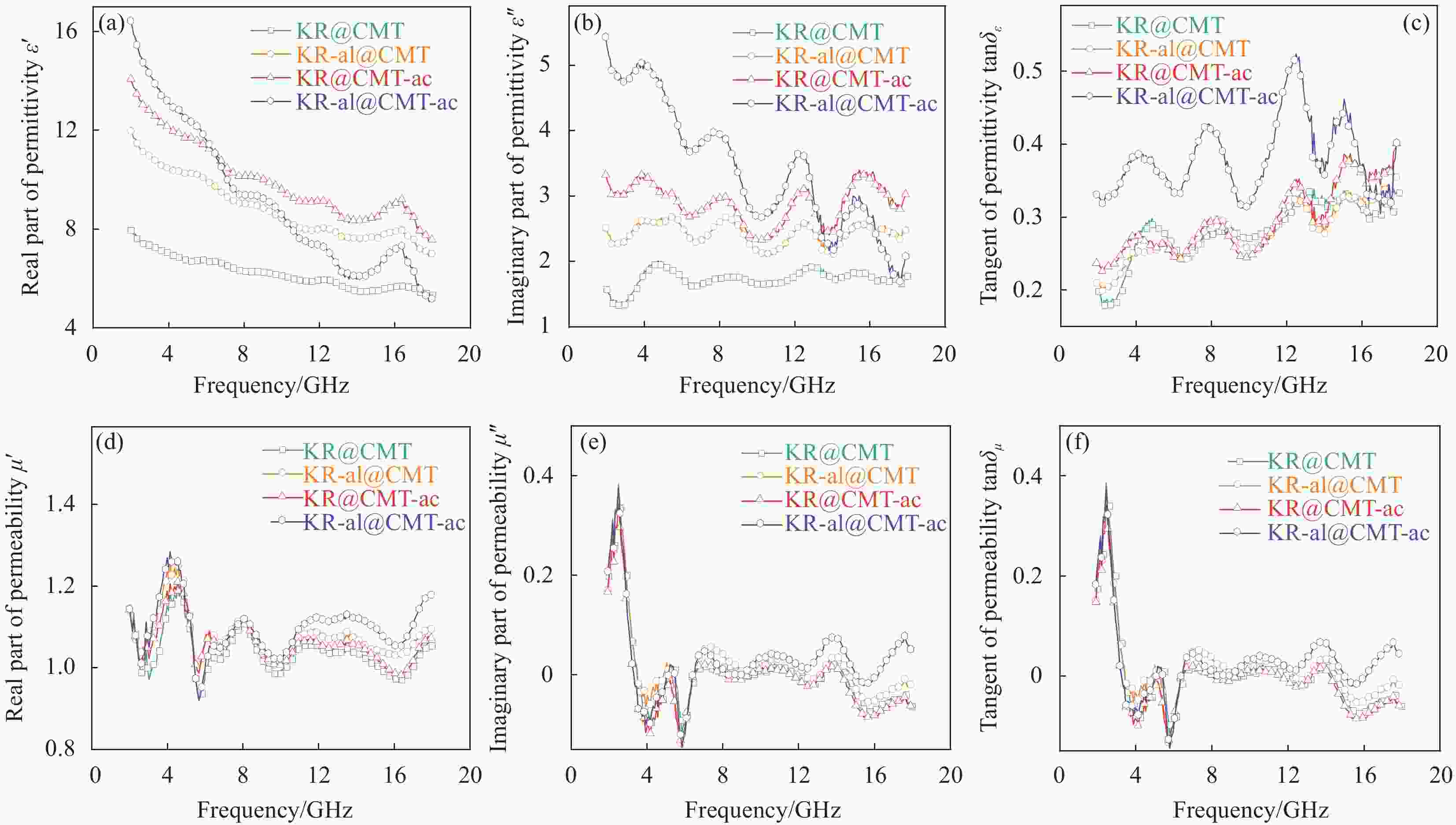
图 7 生物质碳微米管/高岭岩复合材料的电磁参数:(a)介电常数实部(ε');(b)介电常数虚部(ε'');(c)介电损耗角正切(tanδε);(d)磁导率实部(μ');(e)磁导率虚部(μ'');(f)磁损耗角正切(tanδμ)
Figure 7. Electromagnetic parameters of biomass carbon microtubes/kaolin rock composites: (a) Real part of permittivity (ε'); (b) Imaginary part of permittivity (ε''); (c) Tangent of permittivity (tanδε); (d) Real part of permeability (μ'); (e) Imaginary part of permeability (μ''); (f) Tangent of permeability (tanδμ)
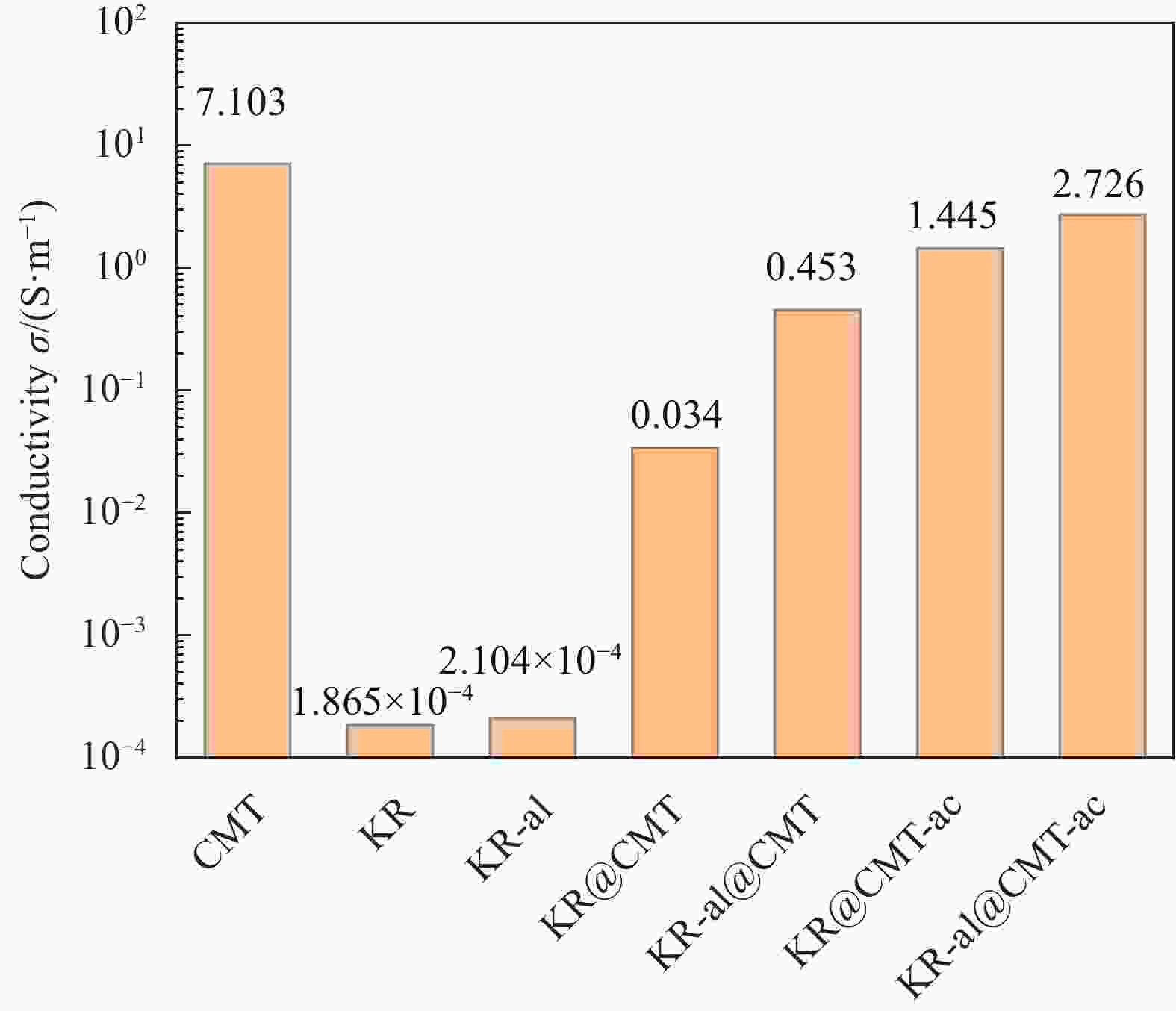
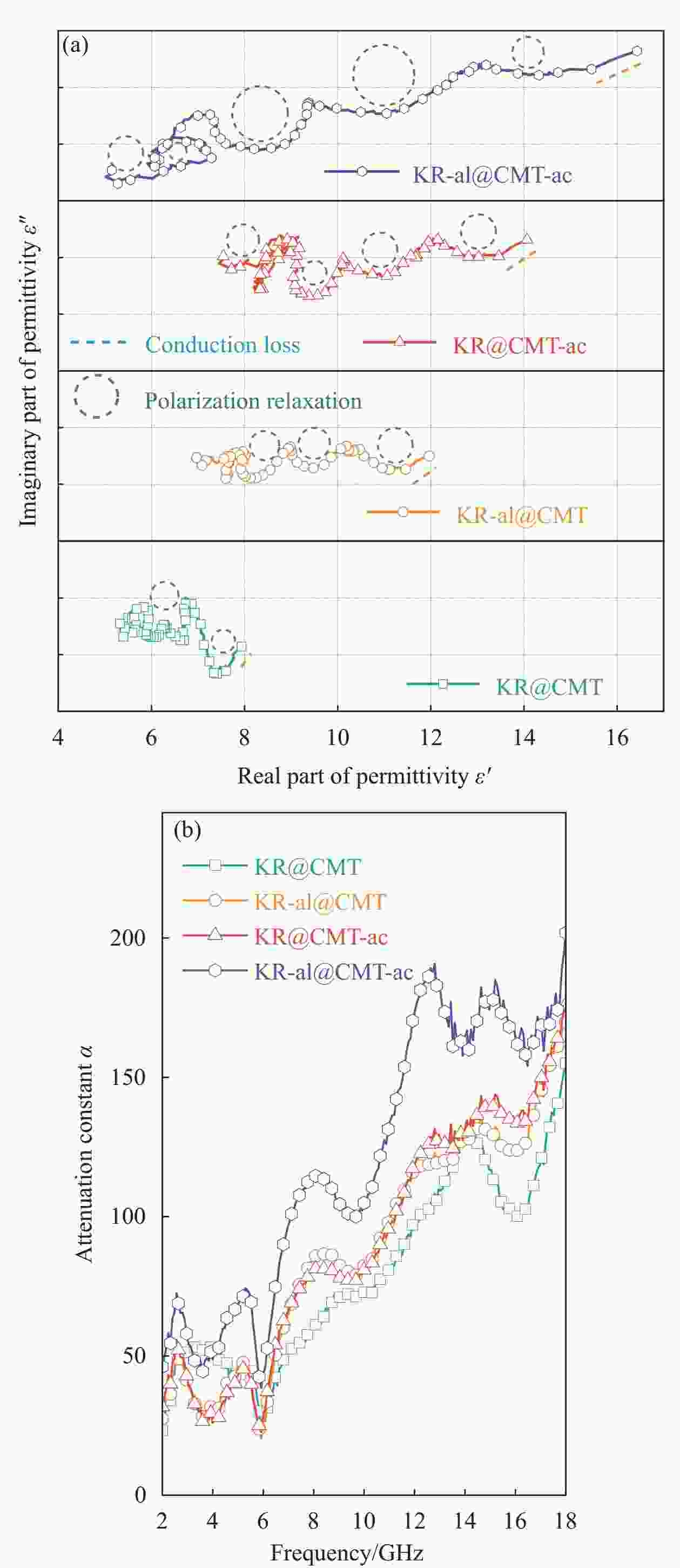
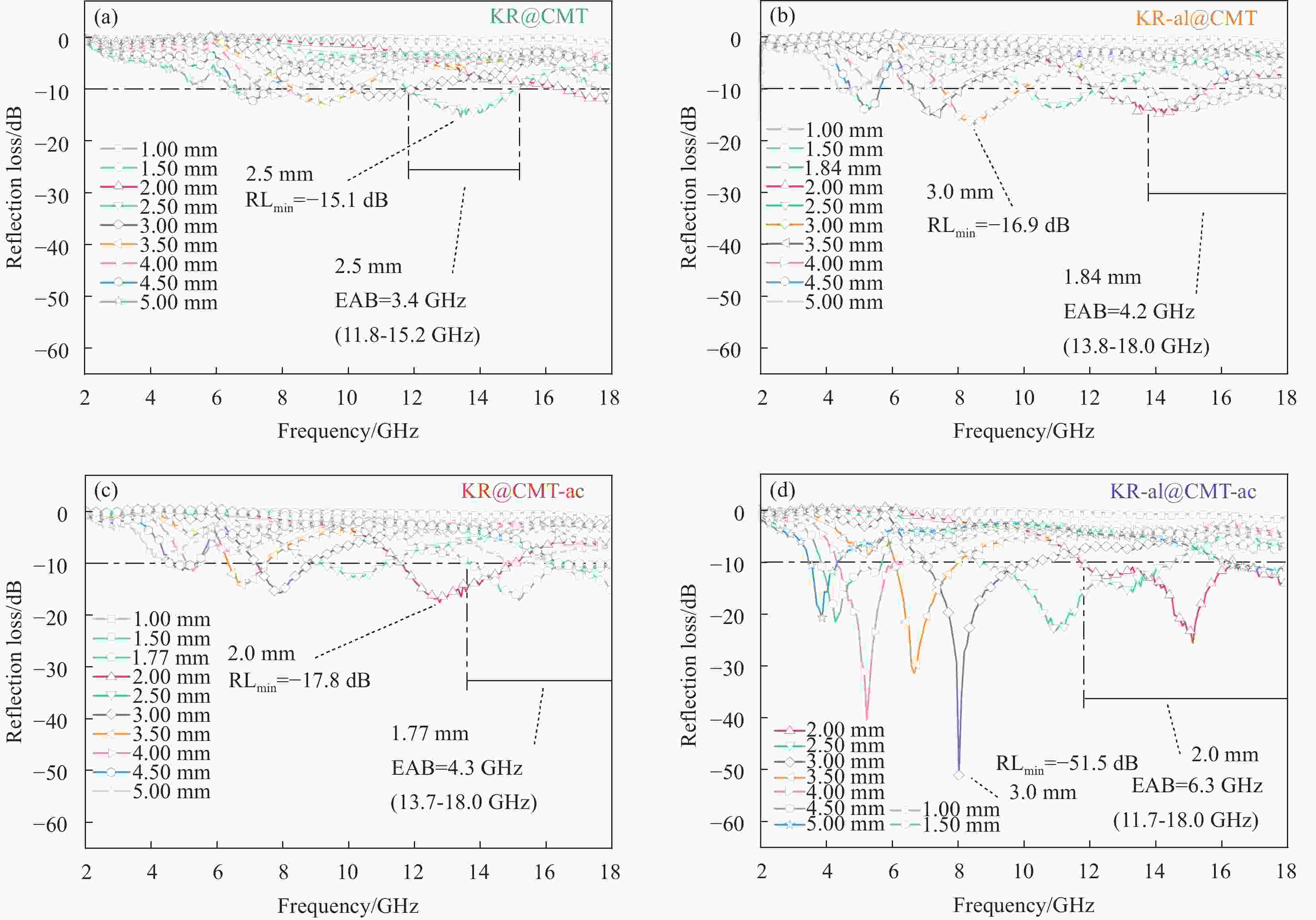
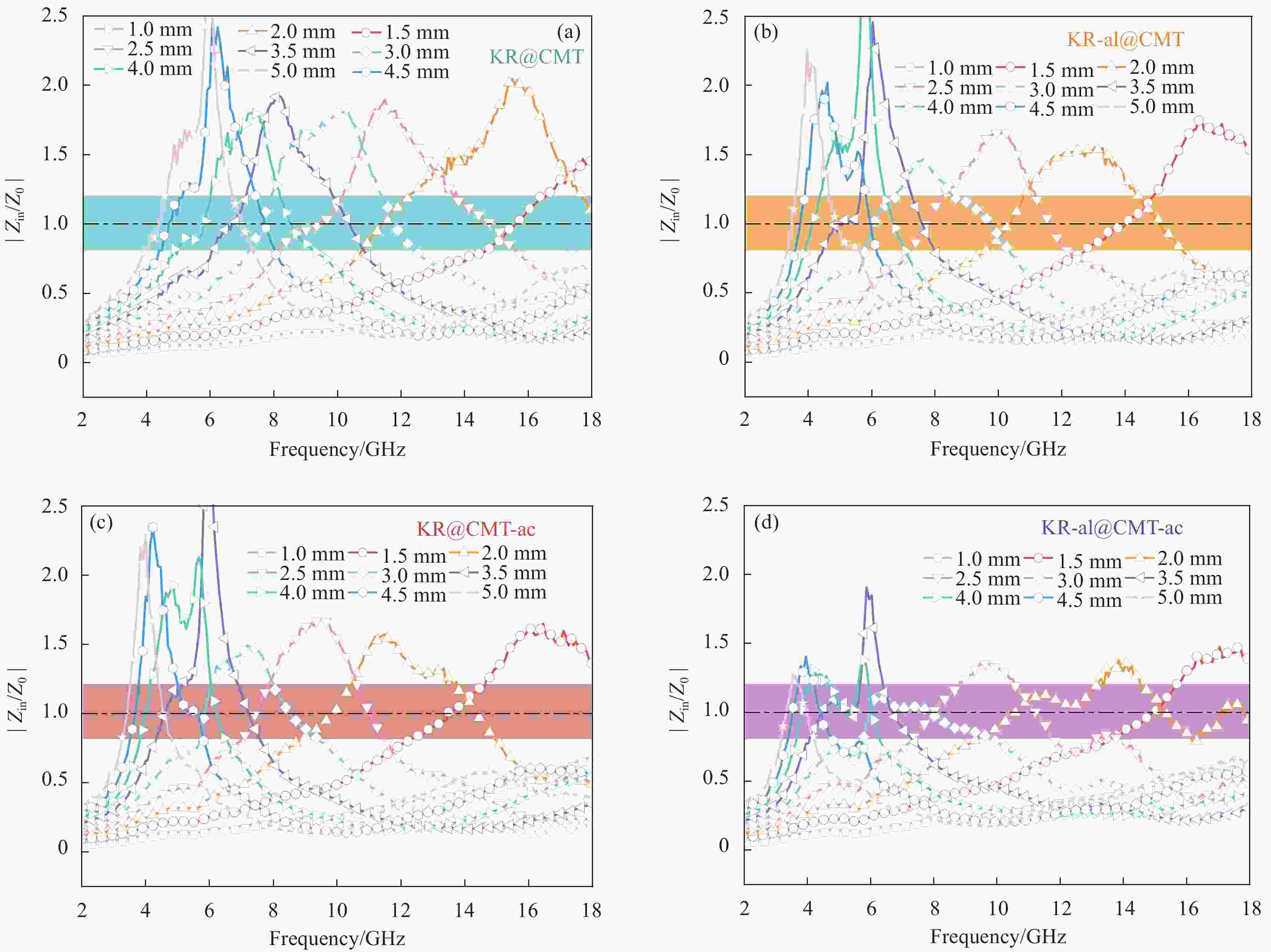
表 1 生物质碳微米管/高岭岩复合材料的吸波性能
Table 1. Microwave absorption properties of biomass carbon microtubes/kaolin rock composites
Sample RLmin/dB EAB/GHz Frequency/GHz T/mm KR@CMT −15.1 3.4 11.8-15.2 2.50/2.50 KR-al@CMT −16.9 4.2 13.8-18.0 3.00/1.80 KR@CMT-ac −17.8 4.3 13.7-18.0 2.00/1.77 KR-al@CMT-ac −51.5 6.3 11.7-18.0 3.00/2.00 Notes: RLmin, EAB, and T—Minimum reflection loss, effective absorption bandwidth, and thickness of the samples. -
[1] 梁丽萍, 高飞, 王亚珂, 等. 回收利用煤矸石低成本制备Ni/C/CG 复合型吸波材料[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2022, 50(1): 36-43.LIANG Liping, GAO Fei, WANG Yake, et al. Low-cost preparation of Ni/C/CG composites for microwave absorption by recycling coal gangue[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2022, 50(1): 36-43(in Chinese). [2] 陈博文, 强荣, 邵玉龙, 等. 香蒲衍生Fe/C 复合材料的制备及其吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(12): 6830-6840.CHEN Bowen, QIANG Rong, SHAO Yulong, et al. Cattail-derived Fe/C composites for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(12): 6830-6840(in Chinese). [3] ZHANG H Y, LI J Y, PAN Y, et al. Flexible carbon fiber-based composites for electro-magnetic interference shielding[J]. Rare Metals, 2022, 41(11): 3612-3629. doi: 10.1007/s12598-022-02057-3 [4] 王翊, 郭顺德, 刘元军, 等. 铁磁材料/石墨烯复合吸波涂层织物的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(17): 17178-17184.WANG Yi, GUO Shunde, LIU Yuanjun, et al. Research progress of ferromagnetic material/graphene composite wave absorbing coating fabrics[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(17): 17178-17184(in Chinese). [5] LIU D, YANG L, WANG F, et al. Hierarchical carbon nanotubes@Ni/C foams for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2022, 196: 867-876. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.05.057 [6] WU S, FU H, HU X, et al. High aspect-ratio sycamore biomass microtube constructed permittivity adjustable ultralight microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2022, 622: 719-727. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.04.128 [7] WU Z, TIAN K, HUANG T, et al. Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(13): 11108-11115. [8] LIU C, HAN M, LIN J, et al. Wood biomass-derived carbon for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing and shielding[J]. Carbon, 2023, 208: 255-276. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.03.067 [9] WU Z, PEI K, XING L, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption performance from magnetic coupling of magnetic nanoparticles suspended within hierarchically tubular composite[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(28): 1901448. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201901448 [10] YANG Y, CHENG J, PAN F, et al. Phragmites-derived magnetic carbon fiber with hollow assembly architecture toward full-covered effective bandwidth at Ku band[J]. Carbon, 2023, 213: 118228. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2023.118228 [11] LI Q, ZHU J, WANG S, et al. Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent[J]. Carbon, 2020, 161: 639-646. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.087 [12] WU F, YANG K, LI Q, et al. Biomass-derived 3D magnetic porous carbon fibers with a helical/chiral structure toward superior microwave absorption[J]. Carbon, 2021, 173: 918-931. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.088 [13] WU P, KONG X, FENG Y, et al. Phase engineering on amorphous/crystalline γ-Fe2O3 nanosheets for boosting dielectric loss and high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2024, 34(10): 2311983. [14] XU J, CHEN C, KONG X. Ru-O-Cu center constructed by catalytic growth of Ru for efficient hydrogen evolution[J]. Nano Energy, 2023, 111: 108403. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2023.108403 [15] HUANG W, GAO W, ZUO S, et al. Hollow MoC/NC sphere for electromagnetic wave attenuation: Direct observation of interfacial polarization on nanoscale hetero-interfaces[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2022, 10(3): 1290-1298. doi: 10.1039/D1TA09357F [16] 张含卓, 陈昭, 魏小亲, 等. 高岭土表面镀覆Co-P层及其微波吸收性能研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(8): 2244-2248.ZHANG Hanzhuo, CHEN Zhao, WEI Xiaoqin, et al. Microwave absorbing properties of modified kaolinite coated with Co-P by electroless plating[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2017, 46(8): 2244-2248(in Chinese). [17] ZHANG X, YAN F, ZHANG S, et al. Hollow N-doped carbon polyhedron containing CoNi alloy nanoparticles embedded within few-layer N-doped graphene as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(29): 24920-24929. [18] YANG T Z, QIAN T, WANG M F, et al. A sustainable route from biomass byproduct okara to high content nitrogen-doped carbon sheets for efficient sodium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(3): 539-545. doi: 10.1002/adma.201503221 [19] WANG S, JIAO Q, SHI Q, et al. Synthesis of porous nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by γ-Fe2O3 nanorings for enhancing microwave absorbing performance[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(1): 1002-1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.064 [20] WANG L, LI X, LI Q, et al. Oriented polarization tuning broadband absorption from flexible hierarchical ZnO arrays vertically supported on carbon cloth[J]. Small, 2019, 15(18): 1900900. doi: 10.1002/smll.201900900 [21] ZHAO X, NIE X, LI Y, et al. A layered double hydroxide-derived exchange spring magnet array grown on graphene and its application as an ultrathin electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(39): 12270-12277. doi: 10.1039/C9TC03254A [22] WANG J, LIU L, JIAO S, et al. Hierarchical carbon fiber@MXene@MoS2 core-sheath synergistic microstructure for tunable and efficient microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(45): 2002595. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002595 [23] GAO T, ZHAO R, LI Y, et al. Sub-nanometer Fe clusters confined in carbon nanocages for boosting dielectric polarization and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(31): 2204370. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202204370 [24] LI B, MA Z, ZHANG X, et al. NiO/Ni heterojunction on N-doped hollow carbon sphere with balanced dielectric loss for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2023, 19(12): 2207197. doi: 10.1002/smll.202207197 [25] LI Y, LIAO Y, JI L, et al. Quinary high-entropy-alloy@graphite nanocapsules with tunable interfacial impedance matching for optimizing microwave absorption[J]. Small, 2021, 18(4): 2107265. [26] LIANG J, YE F, CAO Y, et al. Defect-engineered graphene/Si3N4 multilayer alternating core-shell nanowire membrane: A plainified hybrid for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(22): 2200141. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202200141 [27] WU Y, CHEN L, HAN Y, et al. Hierarchical construction of CNT networks in aramid papers for high-efficiency microwave absorption[J]. Nano Research, 2023, 16(5): 7801-7809. doi: 10.1007/s12274-023-5522-4 [28] QIU J, LIAO J, WANG G, et al. Implanting N-doped CQDs into rGO aerogels with diversified applications in microwave absorption and wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 443: 136475. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136475 [29] WU Y, ZHAO Y, ZHOU M, et al. Ultrabroad microwave absorption ability and infrared stealth property of nano-micro CuS@rGO lightweight aerogels[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 171. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00906-5 [30] LIU C, QIAO J, ZHANG X, et al. Noncovalent self-assembly of a minuscule amount of nickel porphyrin on carbon nanotube for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2023, 164: 107281. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.107281 [31] CHENG J, ZHANG H, WANG H, et al. Tailoring self-polarization of bimetallic organic frameworks with multiple polar units toward high-performance consecutive multi-band electromagnetic wave absorption at gigahertz[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(24): 2201129. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202201129 [32] LI J, SUN H, YI S Q, et al. Flexible polydimethylsiloxane composite with multi-scale conductive network for ultra-strong electromagnetic interference protection[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 15(1): 15. [33] 黄才华, 黄陈, 吴海华, 等. 熔融沉积成型Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA微波吸收材料性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(4): 1954-1967.HUANG Caihua, HUANG Chen, WU Haihua, et al. Properties of microwave absorbers formed by fused deposition modeling with Fe3O4-MWCNTs/PLA composite wire[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(4): 1954-1967(in Chinese). [34] ZHAO H, CHENG Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Biomass-derived graphene-like porous carbon nanosheets towards ultralight microwave absorption and excellent thermal infrared properties[J]. Carbon, 2021, 173: 501-511. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.035 [35] 马茜, 强荣, 邵玉龙, 等. 空心铁基碳纤维复合材料的制备及吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(2): 1058-1069.MA Qian, QIANG Rong, SHAO Yulong, et al. Preparation and microwave absorption performance of hollow iron-based carbon fiber composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(2): 1058-1069(in Chinese). [36] YANG J, WANG J, LI H, et al. MoS2/MXene aerogel with conformal heterogeneous interfaces tailored by atomic layer deposition for tunable microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Science, 2022, 9(7): 2101988. doi: 10.1002/advs.202101988 [37] TAHIR M, MANCHON A, SABEEH K, et al. Quantum spin/valley hall effect and topological insulator phase transitions in silicene[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(16): 162412. doi: 10.1063/1.4803084 [38] SUN X, LI Y, HUANG Y, et al. Achieving super broadband electromagnetic absorption by optimizing impedance match of rGO sponge metamaterials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2021, 32(5): 2107508. [39] YAN X, HUANG X, ZHONG B, et al. Balancing interface polarization strategy for enhancing electromagnetic wave absorption of carbon materials[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 391: 123538. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123538 [40] PAN F, RAO Y, BATALU D, et al. Macroscopic electromagnetic cooperative network-enhanced MXene/Ni chains aerogel-based microwave absorber with ultra-low matching thickness[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 140. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00869-7 -





 下载:
下载: