Preparation and thermal conductivity study of hydroxylated boron nitride nanosheets/nanocellulose composite
-
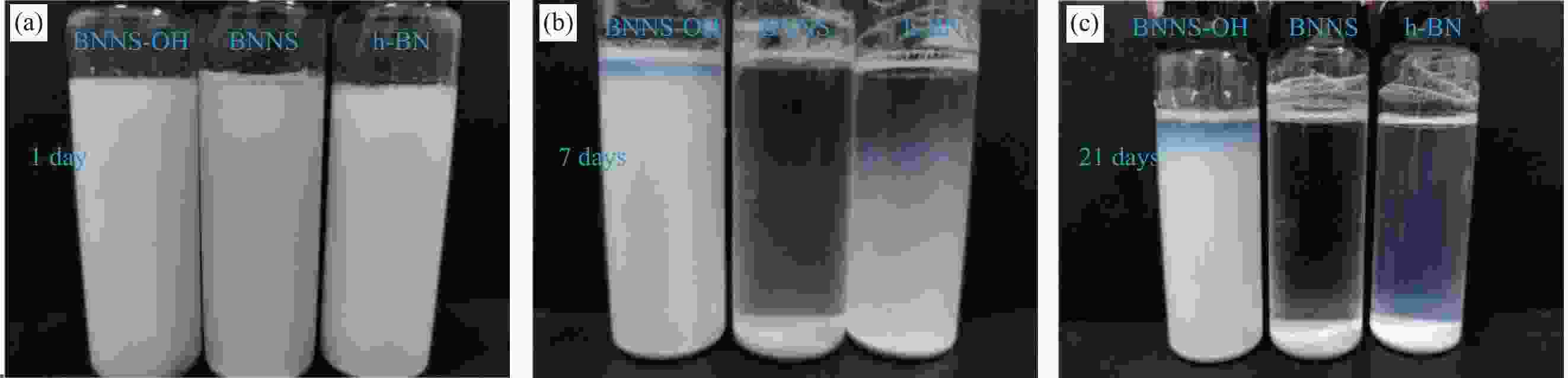
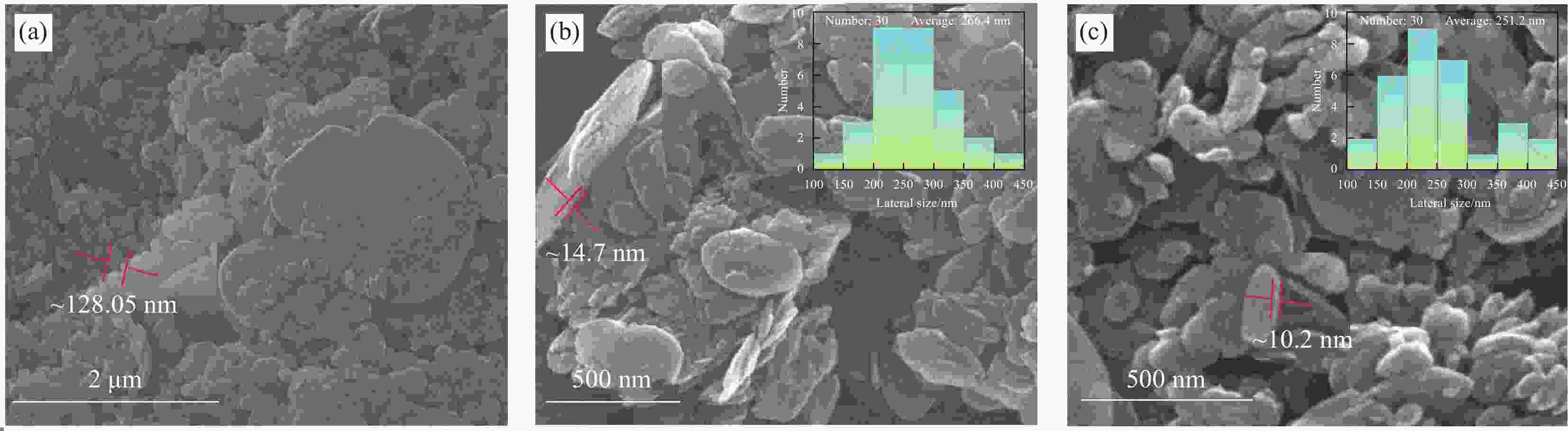
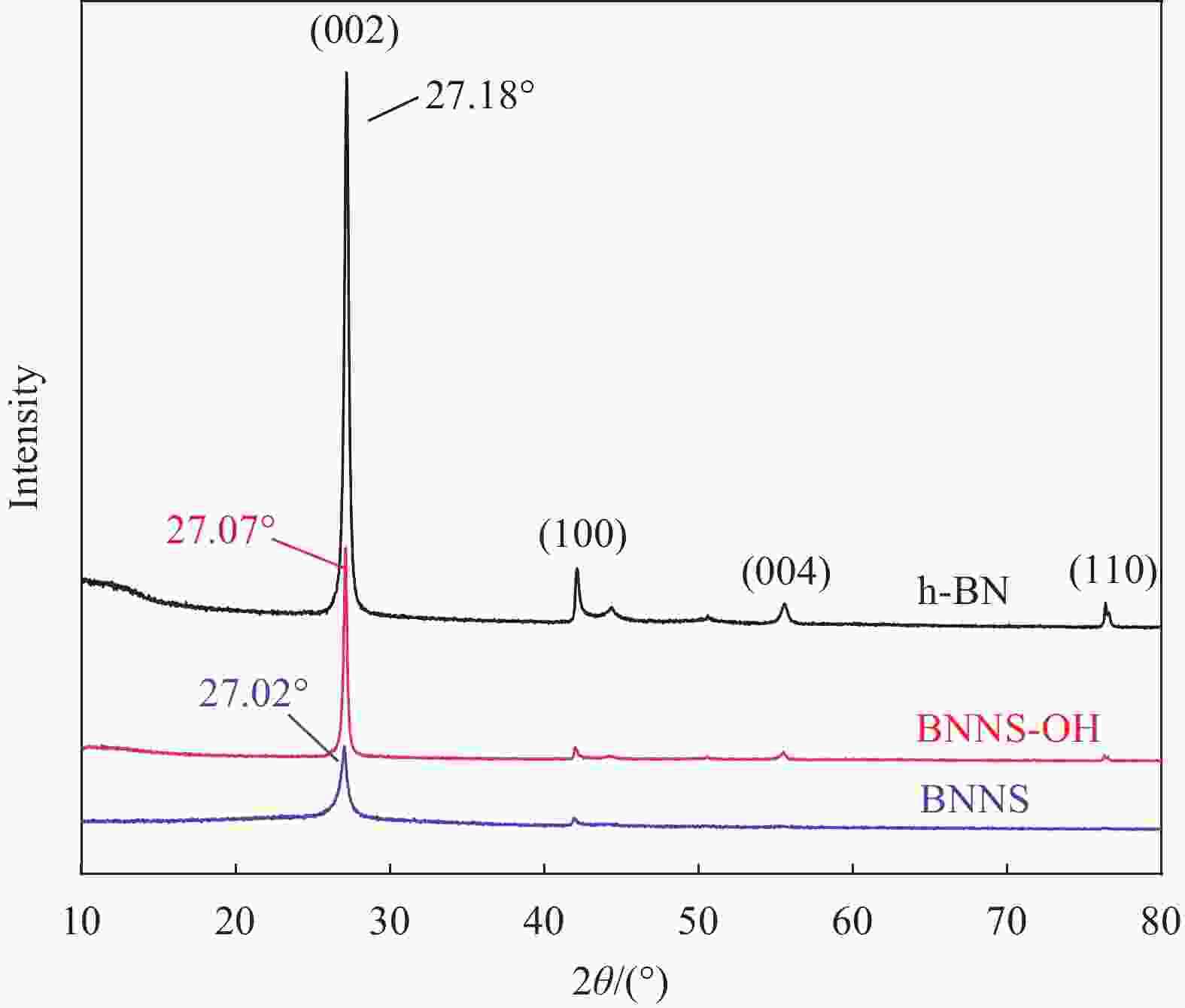
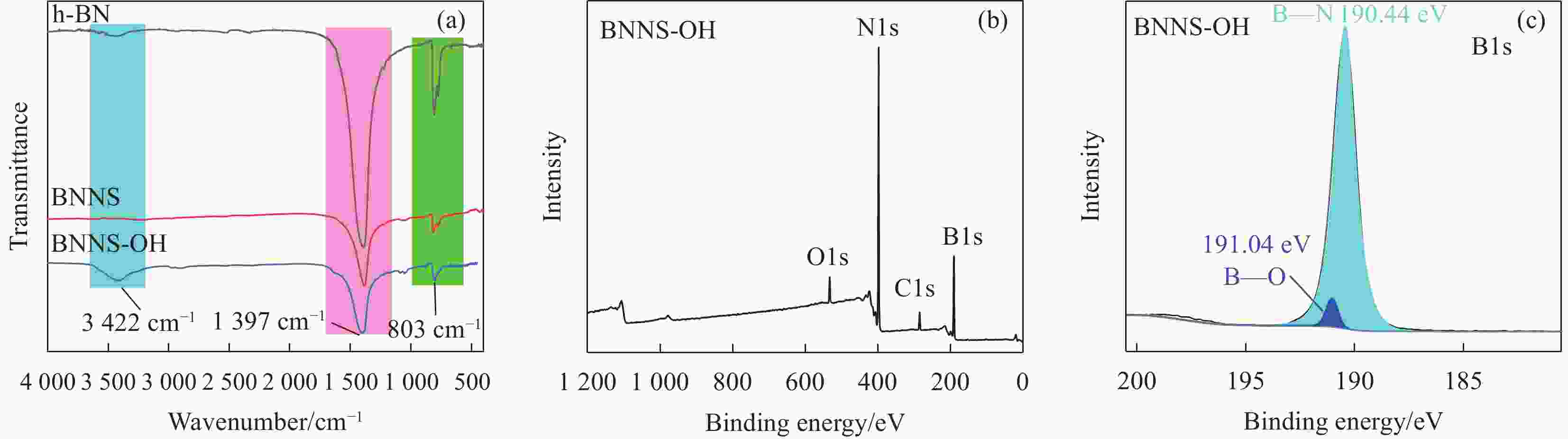
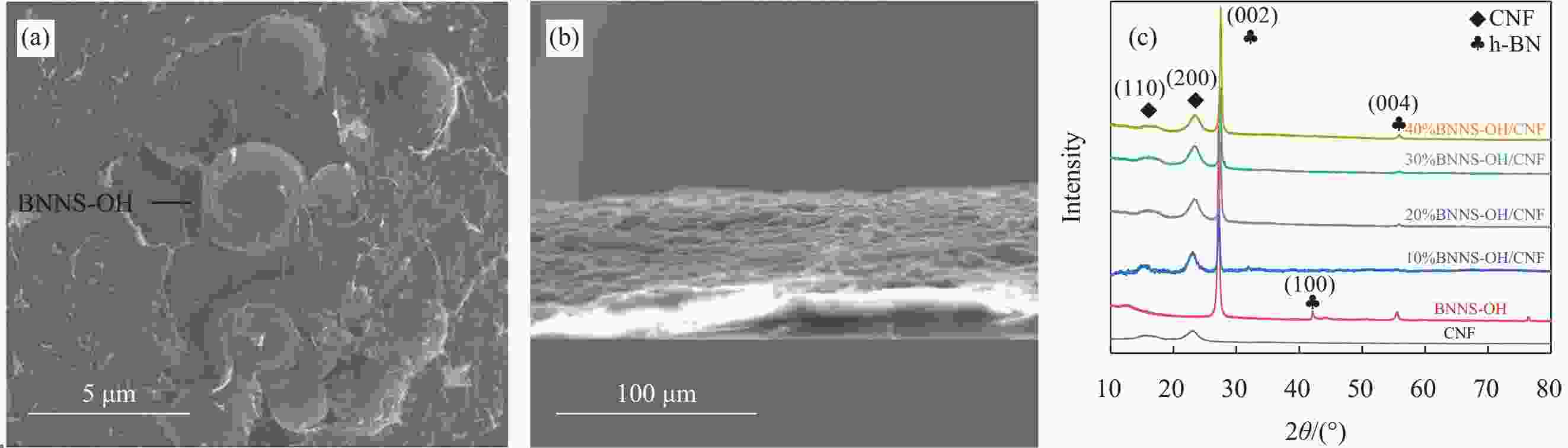
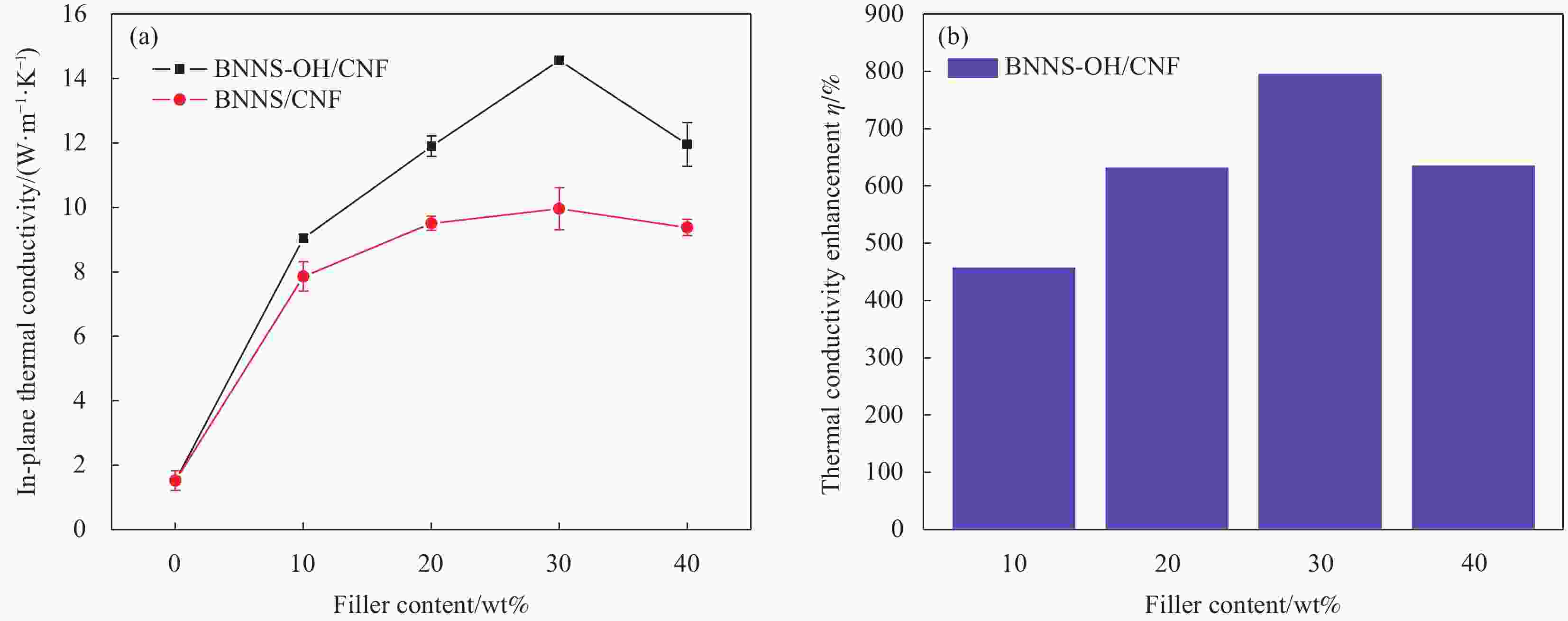
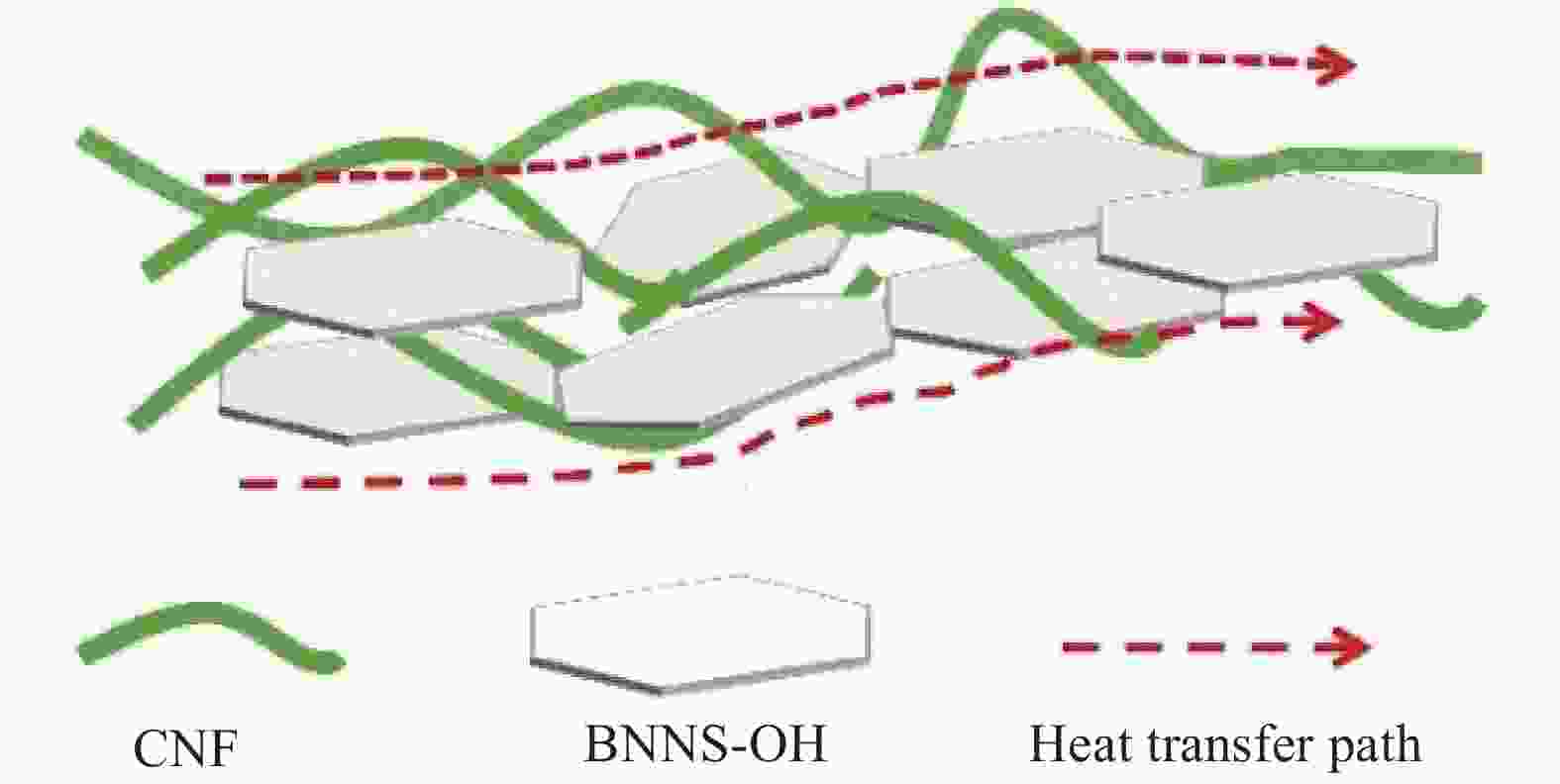
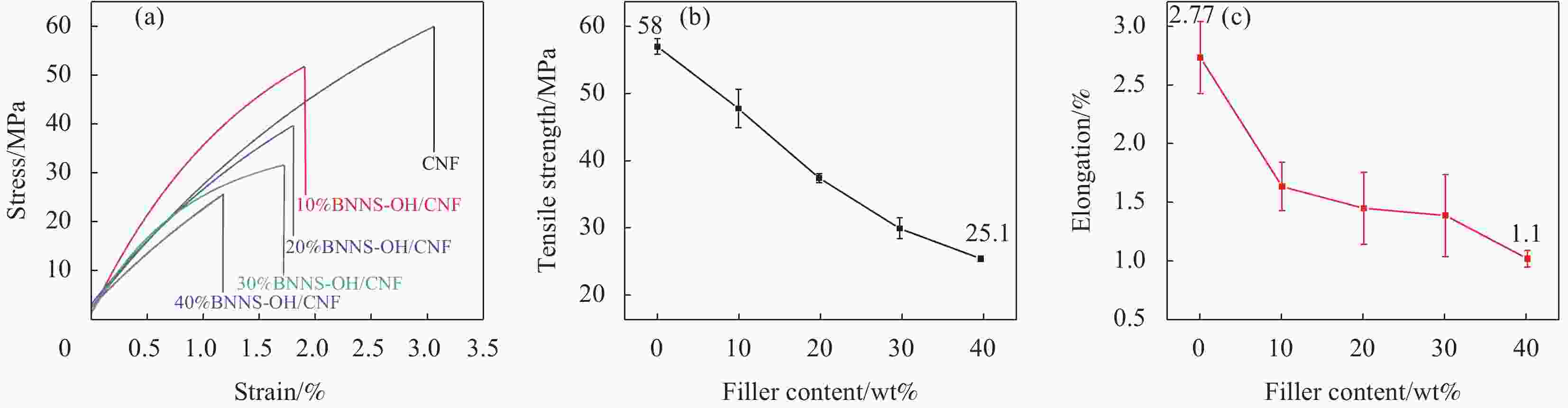
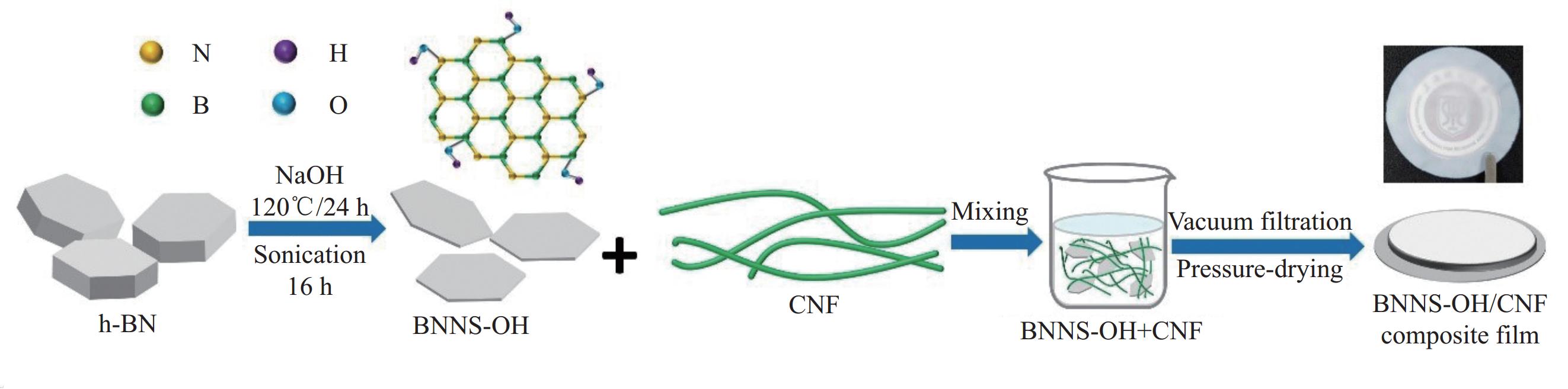
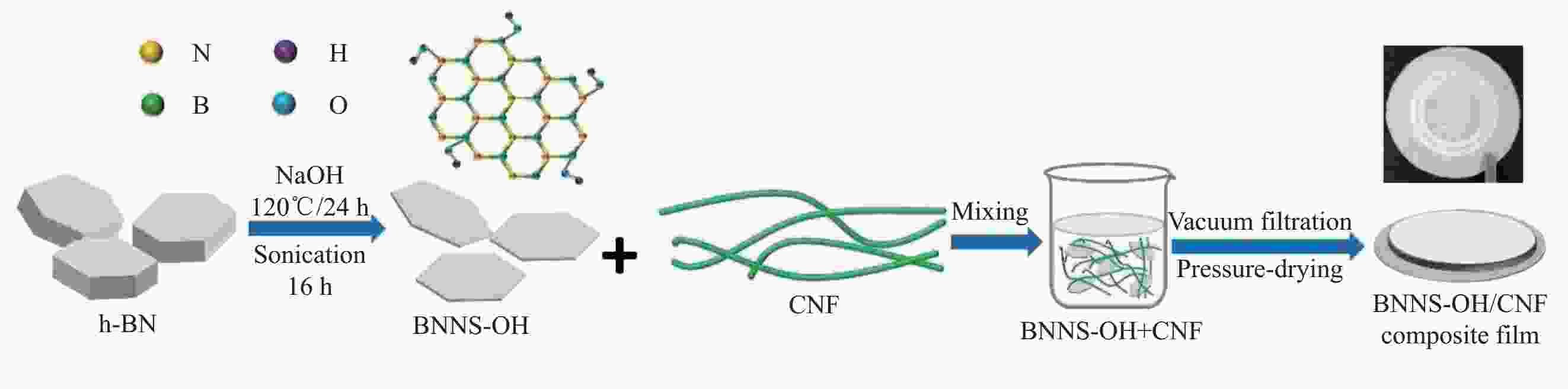
摘要: 氮化硼纳米片(BNNS)/聚合物复合材料因其高导热性能和电绝缘性能在热管理材料领域具有很大的潜力,但是由于BNNS表面化学惰性造成较高的界面热阻,导致BNNS 的优越性尚未得到充分发挥。通过高温碱处理结合液相辅助超声的方法成功制备羟基化氮化硼纳米片(BNNS-OH),然后采用真空抽滤结合压制干燥方法将BNNS-OH与纤维素纳米纤维(CNF)结合制备BNNS-OH/CNF高导热复合材料。氮化硼纳米片表面修饰的羟基有利于增强与CNF之间的相容性和BNNS的分散性,从而减少界面热阻;并且一维结构的CNF不会完全覆盖导热填料,压制干燥方法可以进一步减少填料与聚合物之间的空隙,形成致密的层状结构,有利于填料间更好接触,形成连续热传导通道,这都有利于提高复合材料热导率。在负载30wt%BNNS-OH填料下,BNNS-OH/CNF的热导率高达14.571 W·m−1·K−1,比纯CNF薄膜大约高出819%。在实际散热应用中,与CNF薄膜相比,使用BNNS-OH/CNF复合薄膜的LED芯片在150 s内温度降低了29.5℃。Abstract: The potential of boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS) in thermal management materials is significantly hindered by the inherent surface chemical inertness that leads to a substantial interfacial thermal resistance. To overcome this limitation, hydroxyl-functionalized boron nitride nanosheets (BNNS-OH) were successfully synthesized through a high-temperature alkali treatment coupled with liquid-phase assisted ultrasonication. Subsequently, a vacuum filtration combined with compression drying technique was employed to fabricate BNNS-OH/CNF composites. The hydroxyl groups on the surface of BNNS enhance compatibility with CNF and improve the dispersion of BNNS, thereby reducing the interfacial thermal resistance. Furthermore, the one-dimensional structure of CNF does not fully cover the thermal fillers, and the compression drying method effectively minimizes the voids between the fillers and polymer, resulting in a dense layered structure. This facilitates better contact between fillers, forming continuous thermal conduction pathways and enhancing the thermal conductivity of the composite material. When loaded with 30wt%BNNS-OH, the thermal conductivity of the BNNS-OH/CNF composite reaches as high as 14.571 W·m−1·K−1, approximately 819% higher than that of pure CNF films. In practical heat dissipation applications, compared to CNF films, LED chips encapsulated with BNNS-OH/CNF composite films exhibited a temperature reduction of 29.5℃ within 150 s.
-
Key words:
- thermal conductivity /
- boron nitride nanosheets /
- surface modification /
- nanocellulose /
- composite
-
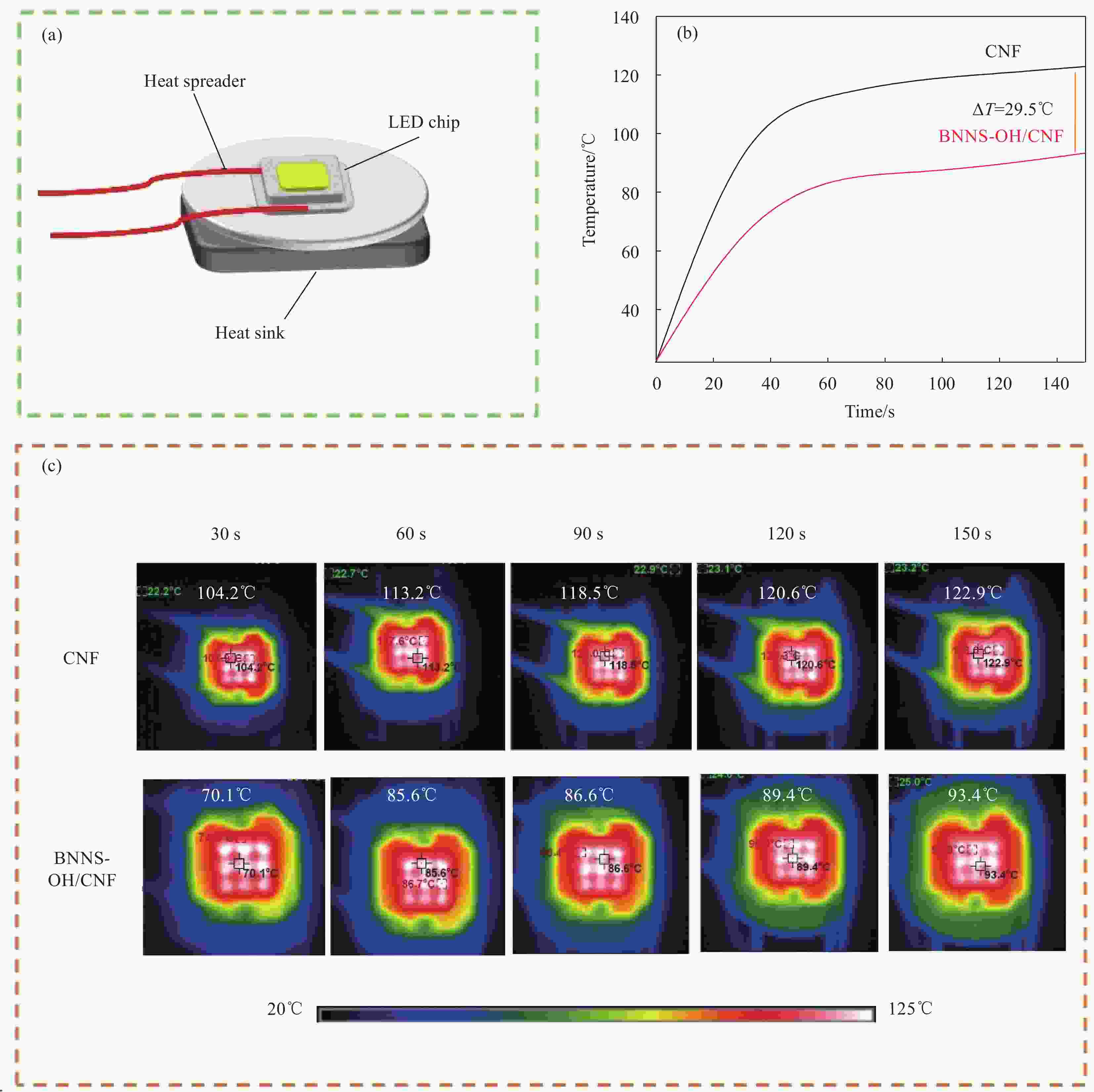
图 10 (a)用于测试CNF、BNNS-OH/CNF薄膜在LED芯片散热中的传热性能的实验配置;(b) LED芯片温度随运行时间的变化;(c)纯CNFs薄膜、30%BNNS-OH/CNF复合材料温度分布的相应红外图像
Figure 10. (a) Experimental configuration for testing the heat transfer performance of CNF and BNNS-OH/CNF films in LED chip heat dissipation; (b) LED chip temperature changes with running time; (c) Corresponding infrared images of the temperature distribution of pure CNFs films and 30%BNNS-OH/CNF composites
表 1 其他文献中聚合物基复合材料热导率比较
Table 1. Comparison of thermal conductivity of polymer-based composites in other literature
Filler Matrix Loading/wt% TC/(W·m−1·K−1) Year BNNS-Gly CNF 70 16.200 2021[21] BNNS-p-APP CNF 50 9.300 2021[31] APTES-BNNS
BNNS-OHEpoxy
CNF40
305.860
14.5712020[32]
This workNotes: BNNS-Gly—Glycine-functionalized BNNS; APP—Ammonium polyphosphate; APTES—3-aminopropyl triethoxysilane; TC—Thermal conductivity. -
[1] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, CHEN J, et al. Thermally conductive but electrically insulating polybenzazole nanofiber/boron nitride nanosheets nanocomposite paper for heat dissipation of 5G base stations and transformers[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(9): 14323-14333. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.2c04534 [2] WANG B, LI G, XU L, et al. Nanoporous boron nitride aerogel film and its smart composite with phase change materials[J]. ACS Nano, 2020, 14(12): 16590-16599. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c05931 [3] LI Q, CHEN L, GADINSKI M R, et al. Flexible high-temperature dielectric materials from polymer nanocomposites[J]. Nature, 2015, 523(7562): 576-579. doi: 10.1038/nature14647 [4] MOORE A L, SHI L. Emerging challenges and materials for thermal management of electronics[J]. Materials Today, 2014, 17(4): 163-174. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.04.003 [5] LI Y, QIAN Y, JIANG Q, et al. Thermally conductive polymer-based composites: Fundamentals, progress and flame retardancy/anti-electromagnetic interference design[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2022, 10(39): 14399-14430. doi: 10.1039/D2TC03306B [6] XU Y, WANG X, HAO Q. A mini review on thermally conductive polymers and polymer-based composites[J]. Composites Communications, 2021, 24: 100617. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2020.100617 [7] HUANG X, ZHI C, LIN Y, et al. Thermal conductivity of graphene-based polymer nanocomposites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2020, 142: 100577. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2020.100577 [8] XU X, CHEN J, ZHOU J, et al. Thermal conductivity of polymers and their nanocomposites[J]. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(17): 1705544. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705544 [9] 田恐虎, 吴阳, 盛绍顶, 等. 聚合物基绝缘导热复合材料中碳系填料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4): 1054-1065.TIAN Konghu, WU Yang, SHENG Shaoding, et al. Research progress of carbon-based fillers in polymer matrix insulating and thermally conductive composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(4): 1054-1065(in Chinese). [10] YU B, ZHOU Y, LUO Z, et al. Highly thermally conductive flexible insulated PI/BNNS@rGO nanocomposite paper with a three-dimensional network bridge structure[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 630: 157457. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157457 [11] 周正荣, 颜秀文, 何峰, 等. 三维网络填料增强聚合物基复合材料导热性能的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(7): 3301-3321.ZHOU Zhengrong, YAN Xiuwen, HE Feng, et al. Research progress on thermally conductive polymer matrix composites reinforced by three-dimensional network fillers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(7): 3301-3321(in Chinese). [12] GONG P, LI L, LI M, et al. Significantly thermally conductive cellulose composite film with graphene/boron nitride heterojunction structure achieved by combustion synthesis[J]. Composites Communications, 2023, 40: 101596. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2023.101596 [13] LI X, WU B, CHEN P, et al. Covalently interconnected carbon nanotubes network enhancing thermal conductivity of EP-based composite[J]. Composites Communications, 2023, 40: 101591. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2023.101591 [14] GUERRA V, WAN C, MCNALLY T. Thermal conductivity of 2D nano-structured boron nitride (BN) and its composites with polymers[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2019, 100: 170-186. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.10.002 [15] AN L, YU Y, CAI Q, et al. Hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets: Preparation, heat transport property and application as thermally conductive fillers[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2023, 138: 101154. [16] WONG T L, VALLÉS C, NASSER A, et al. Effects of boron-nitride-based nanomaterials on the thermal properties of composite organic phase change materials: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2023, 187: 113730. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2023.113730 [17] HU D, LIU H, YANG M, et al. Construction of boron nitride nanosheets-based nanohybrids by electrostatic self-assembly for highly thermally conductive composites[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials, 2022, 5(4): 3201-3211. doi: 10.1007/s42114-022-00463-w [18] CHEN K, PENG L, FANG Z, et al. Dispersing boron nitride nanosheets with carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibrils for strong and thermally conductive nanocomposite films with improved water-resistance[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2023, 321: 121250. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121250 [19] XU Y, CHEN X, ZHANG C, et al. Enhancing thermal conductivity and toughness of cellulose nanofibril/boron nitride nanosheet composites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2022, 296: 119938. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.119938 [20] E S F, ZHAO R, NING D, et al. Highly water-dispersed composite of cellulose nanofibers and boron nitride nanosheets[J]. Cellulose, 2022, 29(18): 9657-9670. doi: 10.1007/s10570-022-04857-3 [21] TIAN X, WU N, ZHANG B, et al. Glycine functionalized boron nitride nanosheets with improved dispersibility and enhanced interaction with matrix for thermal composites[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 408: 127360. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127360 [22] HU D, LIU H, GUO Y, et al. Interfacial design of nanocellulose/boron nitride nanosheets composites via calcium ion cross-linking for enhanced thermal conductivity and mechanical robustness[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2022, 158: 106970. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2022.106970 [23] MOON R J, MARTINI A, NAIRN J, et al. Cellulose nanomaterials review: Structure, properties and nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(7): 3941-3994. doi: 10.1039/c0cs00108b [24] LEI W, MOCHALIN V N, LIU D, et al. Boron nitride colloidal solutions, ultralight aerogels and freestanding membranes through one-step exfoliation and functionalization[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 8849. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9849 [25] MA Z, LIU Z, CHENG Z. Scalable exfoliation for few-layered hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets (BNNSs) by microwave-assisted expansion and liquid nitrogen intercalation[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters, 2020, 31(7): 1936-1940. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.01.019 [26] SUN J, YAO Y, ZENG X, et al. Preparation of boron nitride nanosheet/nanofibrillated cellulose nanocomposites with ultrahigh thermal conductivity via engineering interfacial thermal resistance[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2017, 4(17): 1700563. doi: 10.1002/admi.201700563 [27] 王海花, 冯佳, 赵敏. 氮化硼纳米片的制备及其增强环氧树脂复合材料导热性能的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3): 956-968.WANG Haihua, FENG Jia, ZHAO Min. Research progress on the preparation of boron nitride nanosheets and its reinforcement on the thermal conductivity of epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 956-968(in Chinese). [28] SHANG Y, JI Y, DONG J, et al. Sandwiched cellulose nanofiber/boron nitride nanosheet/Ti3C2T x MXene composite film with high electromagnetic shielding and thermal conductivity yet insulation performance[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2021, 214: 108974. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108974 [29] ZHU Z, XU X, YAO Y, et al. Liquid metal-assisted high-efficiency exfoliation of boron nitride for electrically insulating heat-spreader film[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(48): 54256-54265. [30] HU D, MA W, ZHANG Z, et al. Dual bio-inspired design of highly thermally conductive and superhydrophobic nanocellulose composite films[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(9): 11115-11125. [31] HU D, LIU H, DING Y, et al. Synergetic integration of thermal conductivity and flame resistance in nacre-like nanocellulose composites[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2021, 264: 118058. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118058 [32] LIU Z, LI J, LIU X. Novel functionalized BN nanosheets/epoxy composites with advanced thermal conductivity and mechanical properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(5): 6503-6515. -





 下载:
下载: