Mechanical properties and damage mechanisms of novel variable stiffness laminates
-
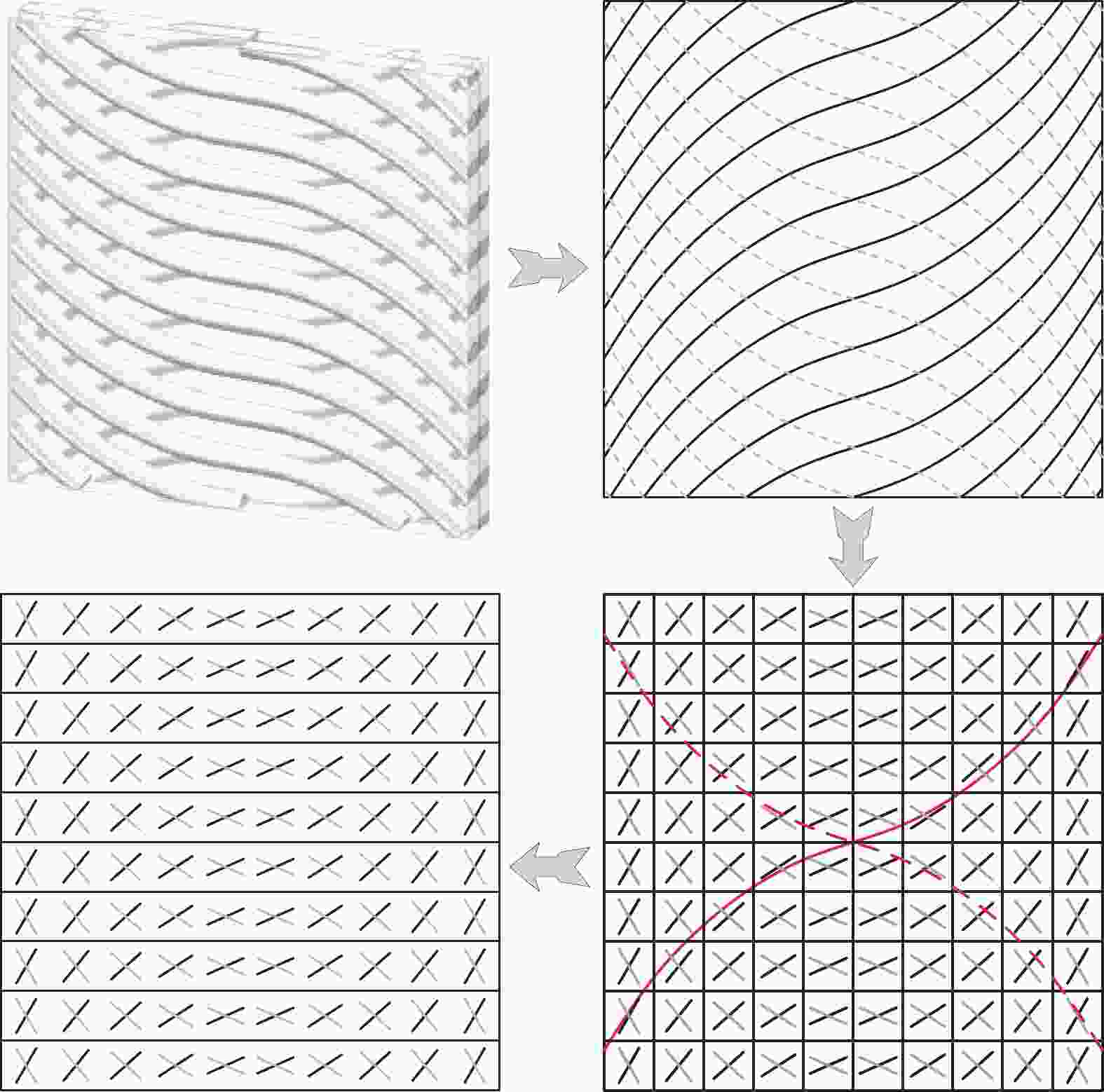
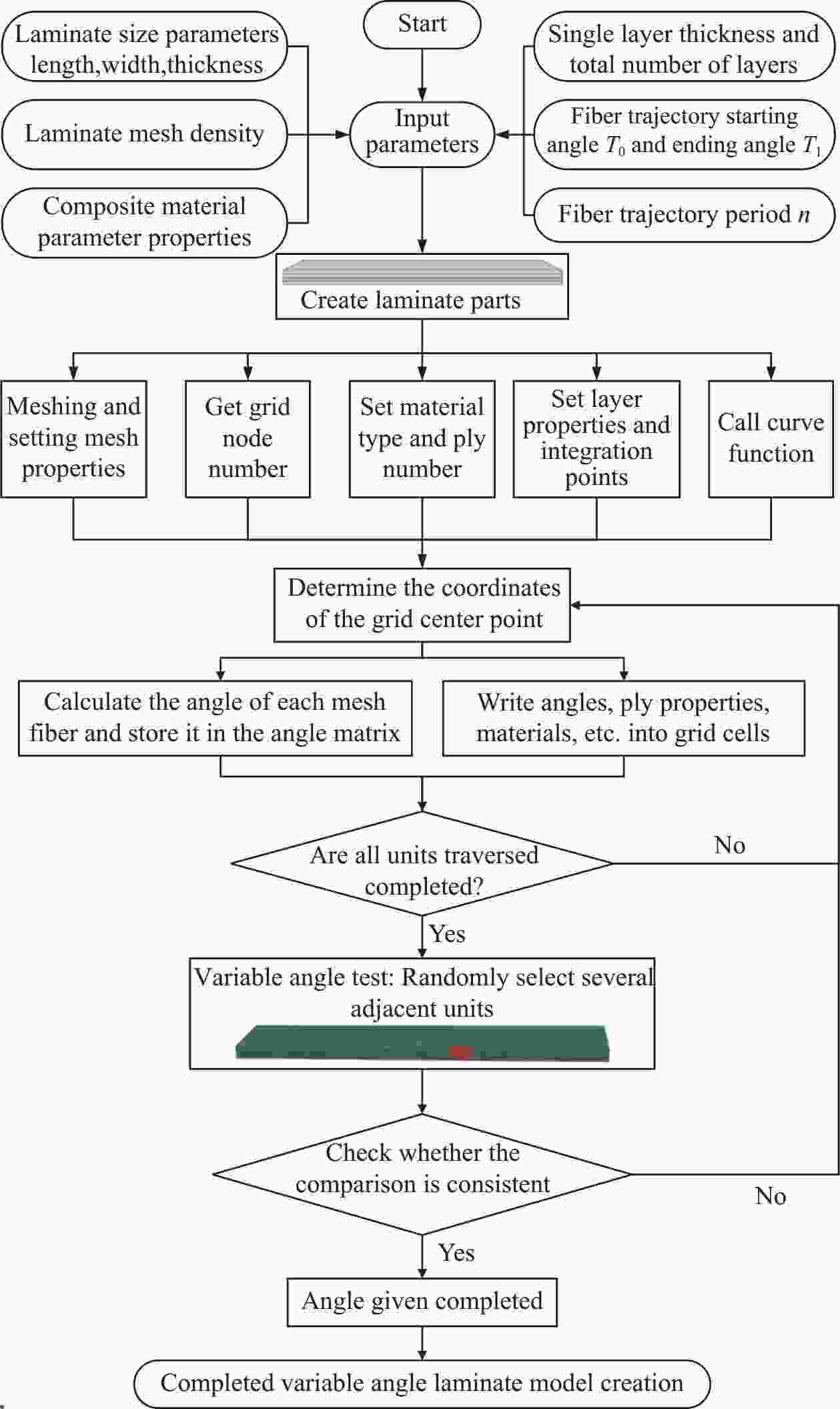
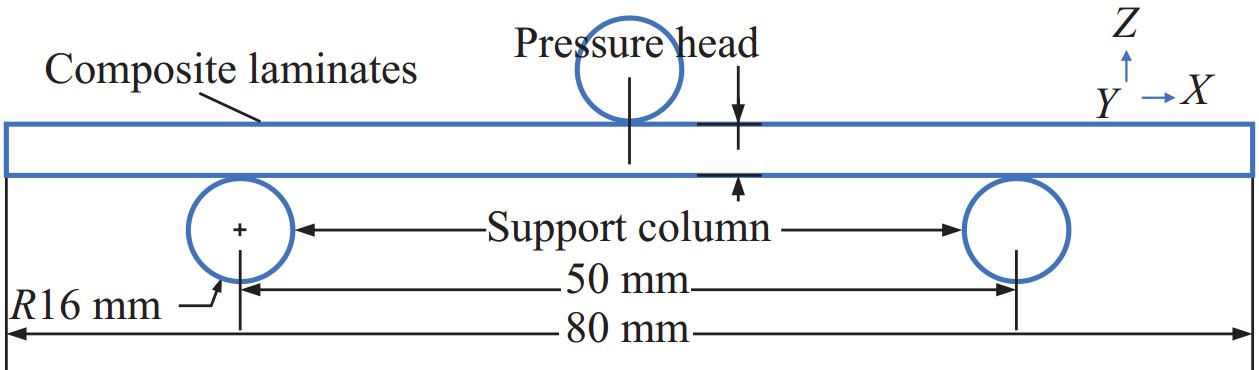
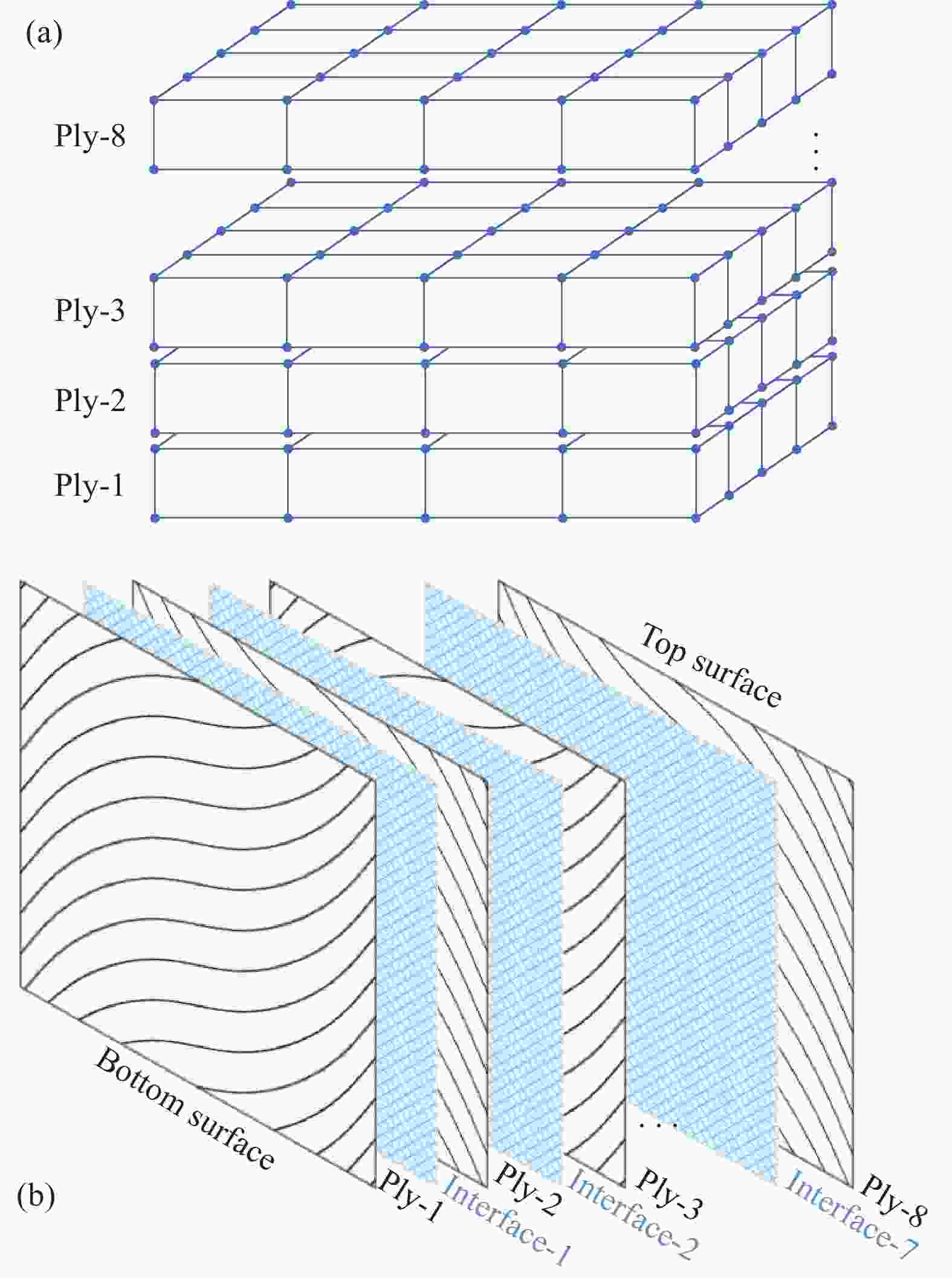
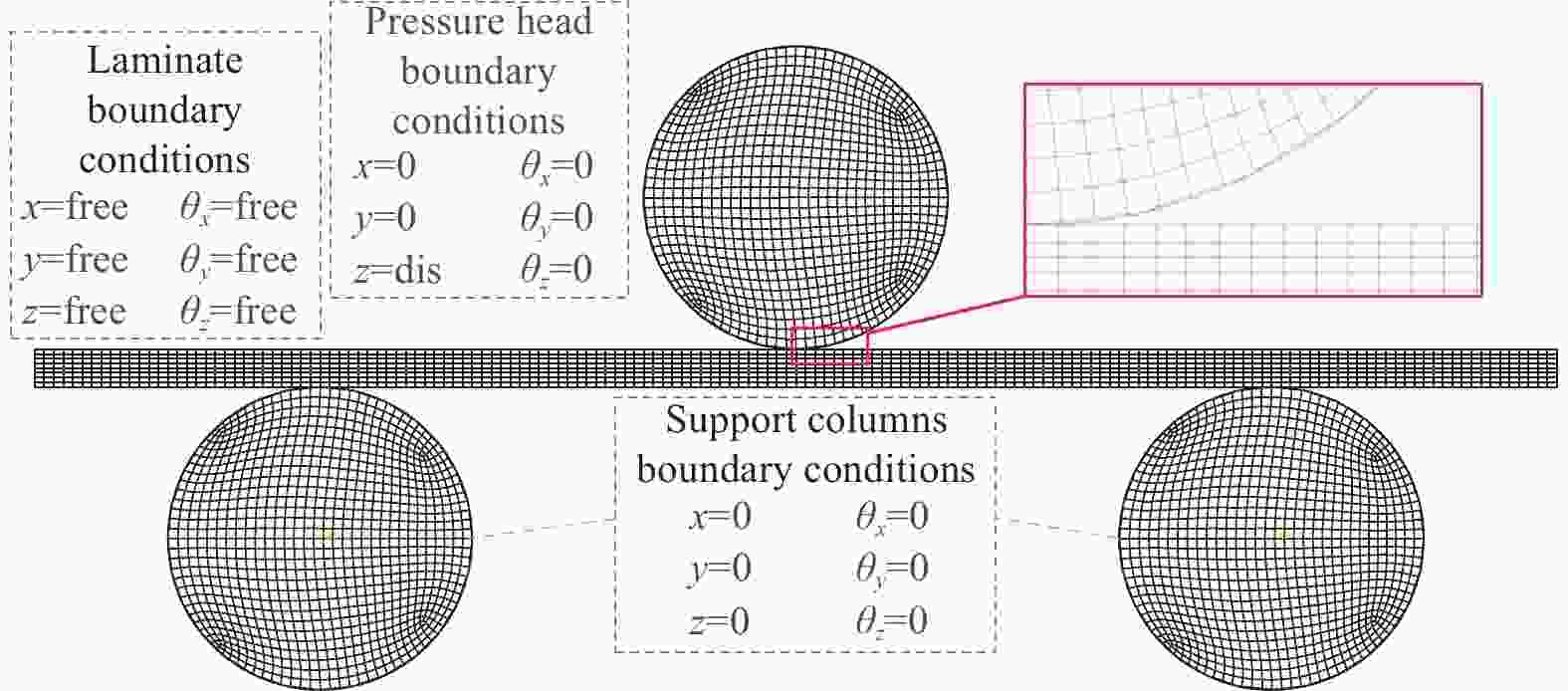
摘要: 广泛应用于航空航天、交通运输等领域的复合材料层合板在实际应用中存在着承载能力和稳定性方面的挑战,为解决上述问题,采用自动铺丝可变刚度层合板,并对其力学特性及失效机制进行研究。首先,在线性变角度函数的基础上,提出一种新型周期线性延拓函数算法,以优化复合材料纤维铺放路径,实现更为详细和精确的纤维轨迹变化。其次,通过Python/Abaqus联合构建新型变刚度层合板有限元模型。最后,分析了定/变刚度层合板三点弯曲下的损伤机制,揭示了不同纤维铺放角对层合板力学特性、应力分布和损伤情况的影响。研究结果表明:三点工况下中心纤维取向角对弯曲性能产生显著影响,0°有利于性能提升,90°则导致性能下降;在中心纤维取向角为5°的基础上,采用变角度设计可以有效抑制弯曲损伤进一步扩展,均匀层合板面内应力分布,同时进一步提高弯曲极限应力,最大提升幅度为28.31%。本研究为后续复合材料层合板的抗弯曲设计和优化提供了重要的研究思路和流程,具有一定参考意义。Abstract: Laminated composite panels, widely employed in aerospace, aviation and transportation, face challenges in terms of load-bearing capacity and stability in practical applications. To address these issues, this study adopts an automated variable stiffness layup approach and investigates the mechanical properties and failure mechanisms of the resulting laminated composite panels. Firstly, a novel periodic linear extrapolation algorithm was proposed based on a linear variable angle function to optimize the fiber placement paths, achieving more detailed and precise variations in fiber trajectories. Subsequently, a finite element model for the new variable stiffness laminated panel was constructed using Python/Abaqus. Finally, the damage mechanisms under three-point bending for both constant and variable stiffness laminated panels were analyzed, revealing the impact of different fiber orientation angles on the mechanical properties, stress distribution and damage scenarios. The research findings indicate that the orientation angle of the central fiber significantly influences bending performance under three-point conditions, with 0° favoring performance enhancement and 90° leading to a decline in performance. Compared to the baseline with a central fiber orientation angle of 5°, employing a variable angle design effectively suppresses further extension of bending damage, ensures a uniform stress distribution within the laminated panel, and further enhances the ultimate bending stress, with a maximum improvement of 28.31%. This study provides crucial insights and a systematic approach for the subsequent design and optimization of laminated composite panels, contributing to advancements in bending resistance design for composite materials.
-
Key words:
- composite laminate /
- variable stiffness /
- curve laying /
- mechanical properties /
- damage mechanism
-
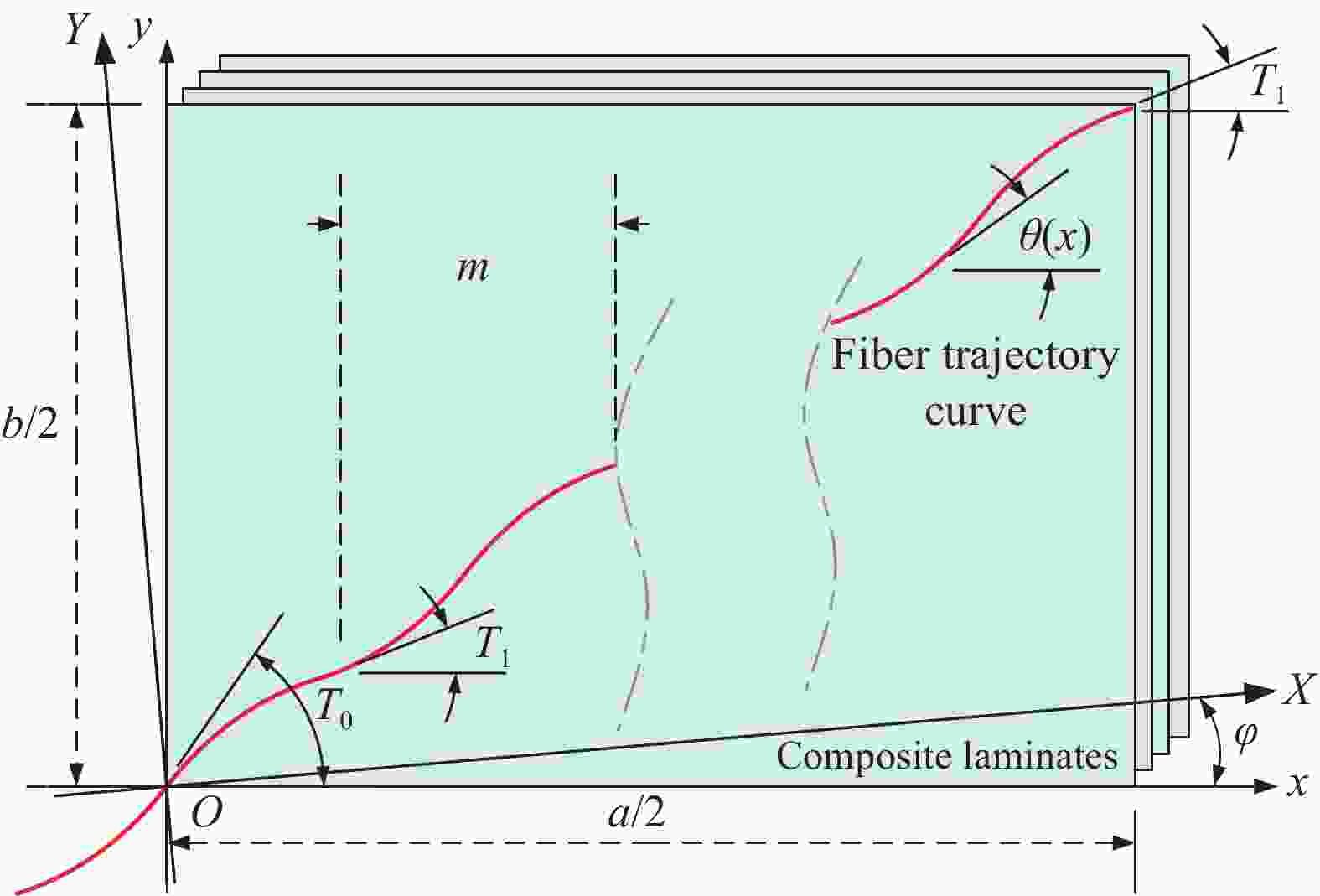
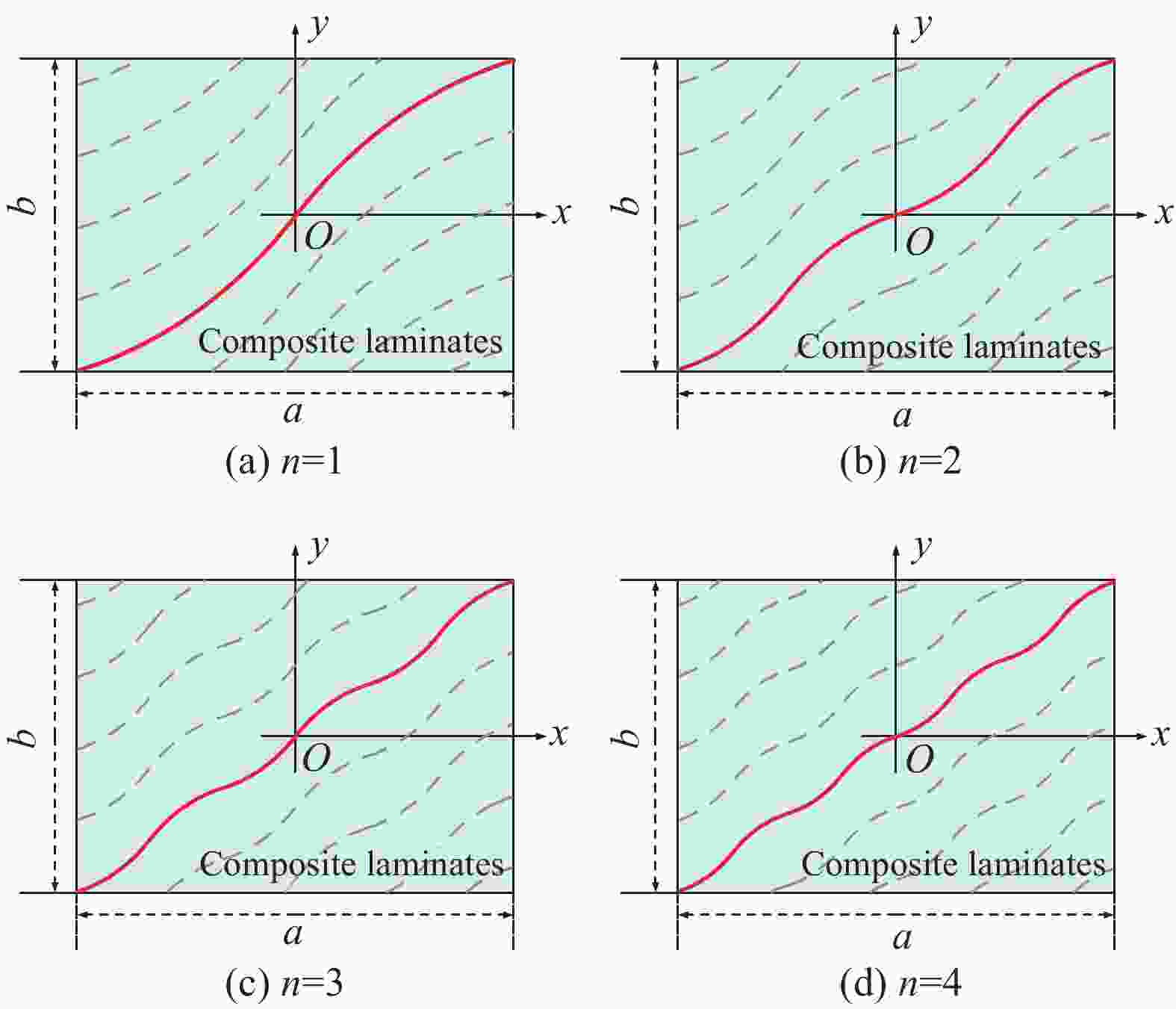
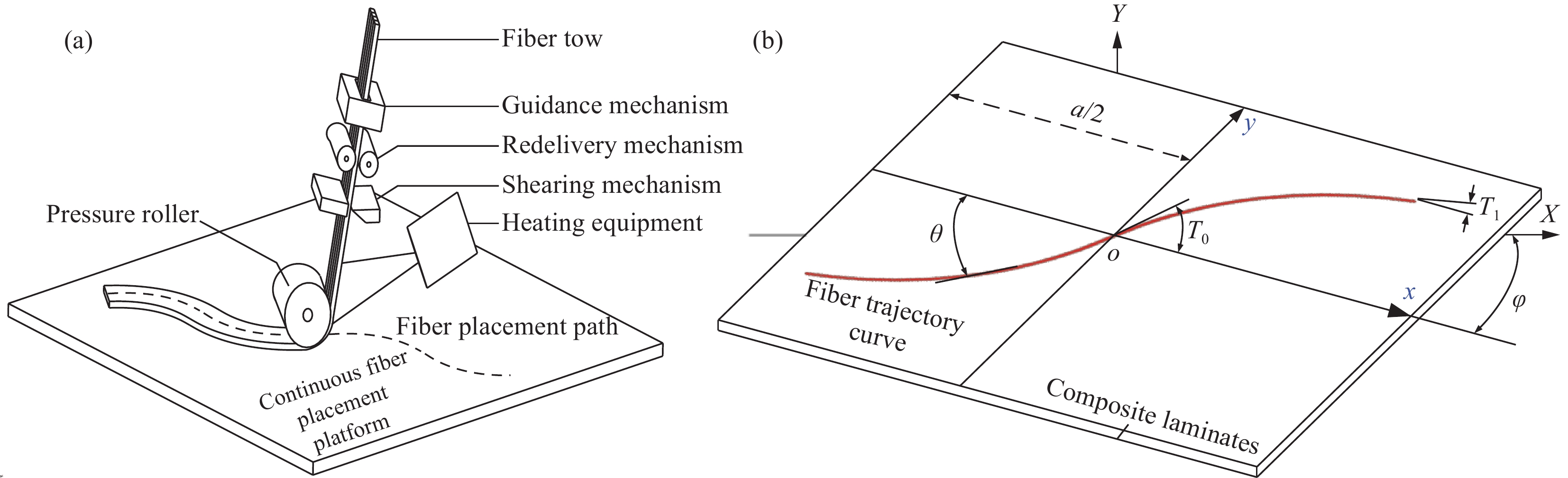
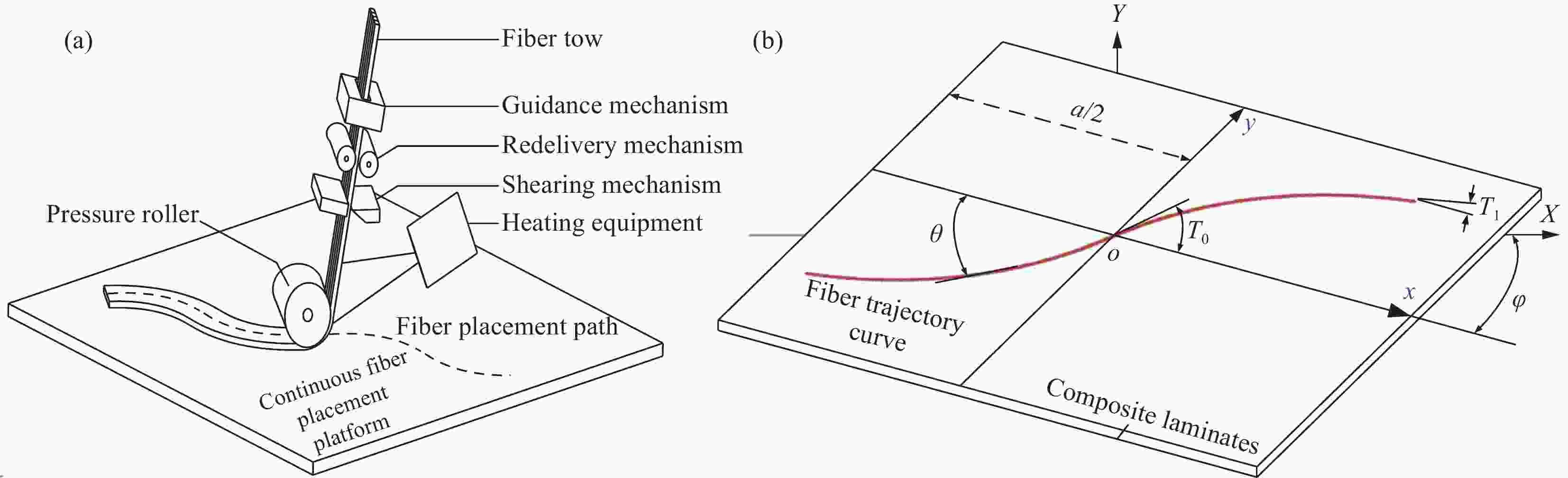
图 1 复合材料纤维铺放:(a)纤维自动铺放技术;(b)纤维铺放参考路径
Figure 1. Composite fiber placement: (a) Automatic fiber placement technology; (b) Fiber placement reference path
a—Length of laminate; T0—Starting angle of curved fiber; T1—Termination angle of curved fiber; θ—The angle between the tangent line at a certain point on the fiber and the x-axis; φ—Deflection angle of the reference coordinate system
表 1 程序算法有效性验证
Table 1. Algorithm validity verification
表 2 层合板材料属性
Table 2. Composite laminate material parameters
Lamina constants Constitutive damage model parameters of lamina E11/MPa 463 Longitudinal tensile strength/MPa XT 2080 E22/MPa 700 Longitudinal compressive strength/MPa XC 1250 E33/MPa 700 Transverse tensile strength/MPa YT 60 G12/MPa 4800 Transverse compressive strength/MPa YC 140 G13/MPa 4800 Longitudinal shear strength/MPa SL 60 G23/MPa 3800 Transverse shear strength/MPa ST 140 ν12 0.33 Longitudinal tensile fracture energy/(mJ·mm−2) GXT 133 ν13 0.33 Longitudinal compressive fracture energy/(mJ·mm−2) GXC 40 ν23 0.3 Transverse tensile fracture energy/(mJ·mm−2) GYT 0.6 Transverse compressive fracture energy/(mJ·mm−2) GYC 2.1 Notes: E11, E22, E33—Stiffness; G12, G13, G23—Shear modulus; ν12, ν13, ν23—Poisson's ratio. 表 3 层合板铺层方案
Table 3. Composite laminate laying methods
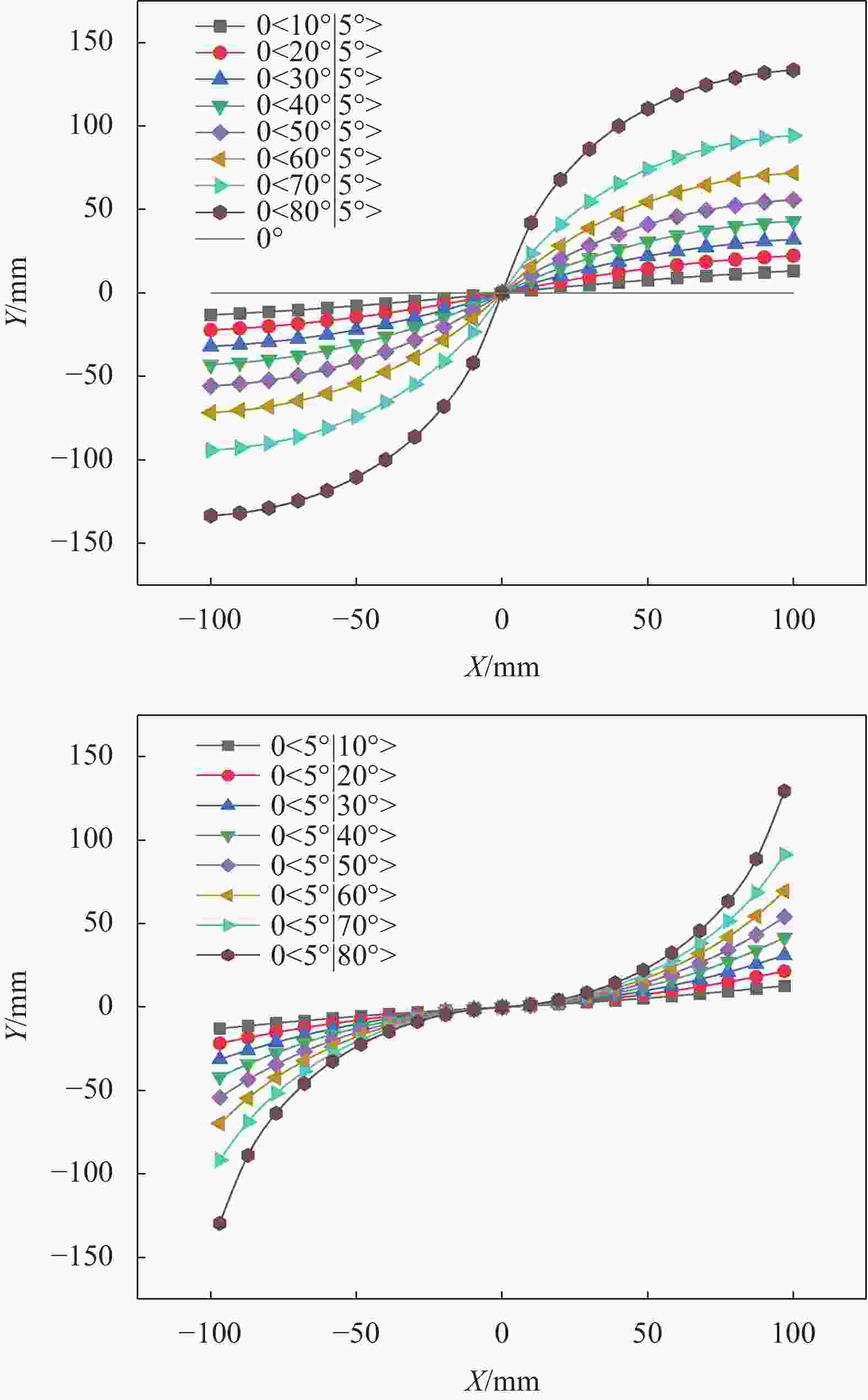
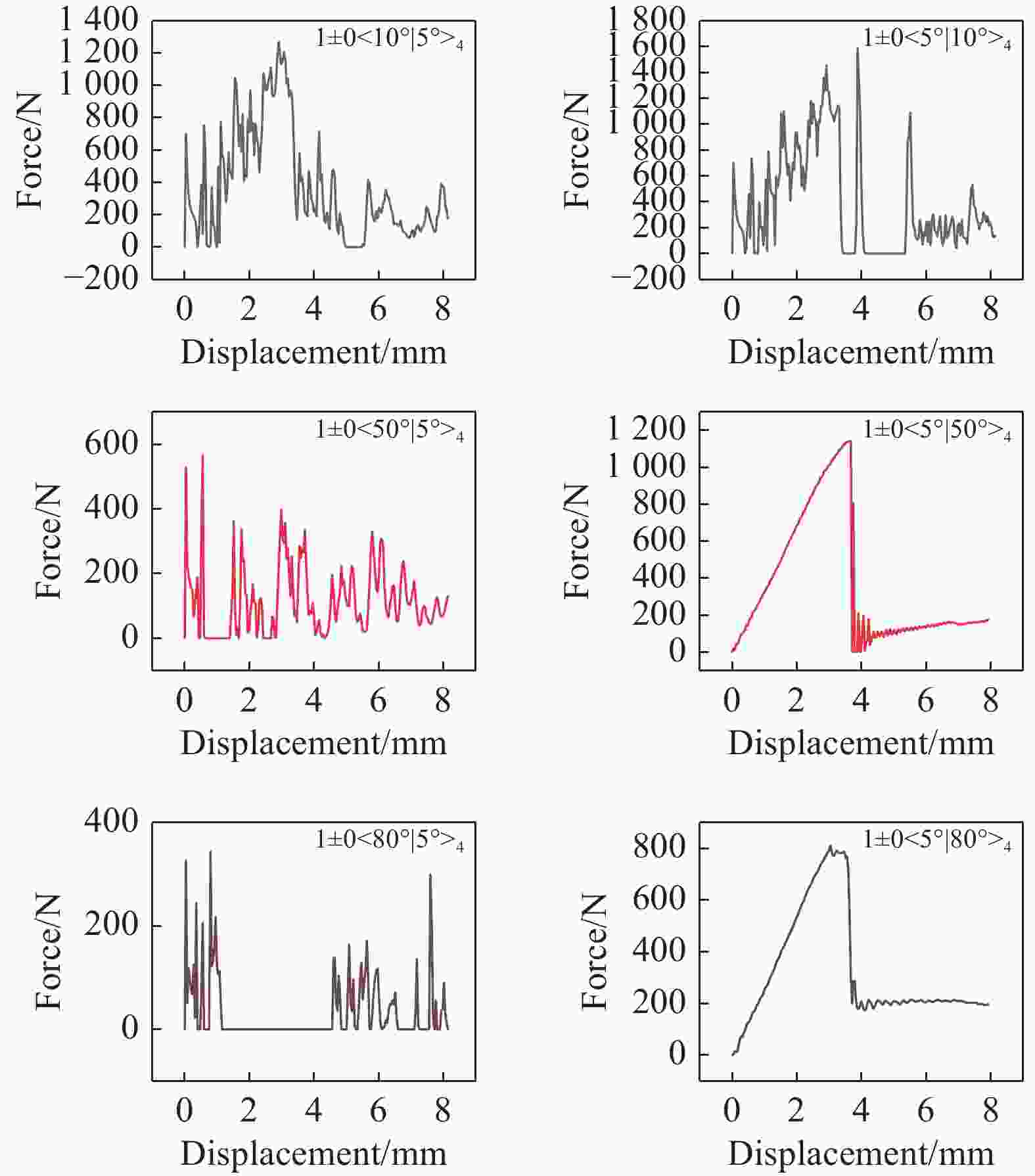
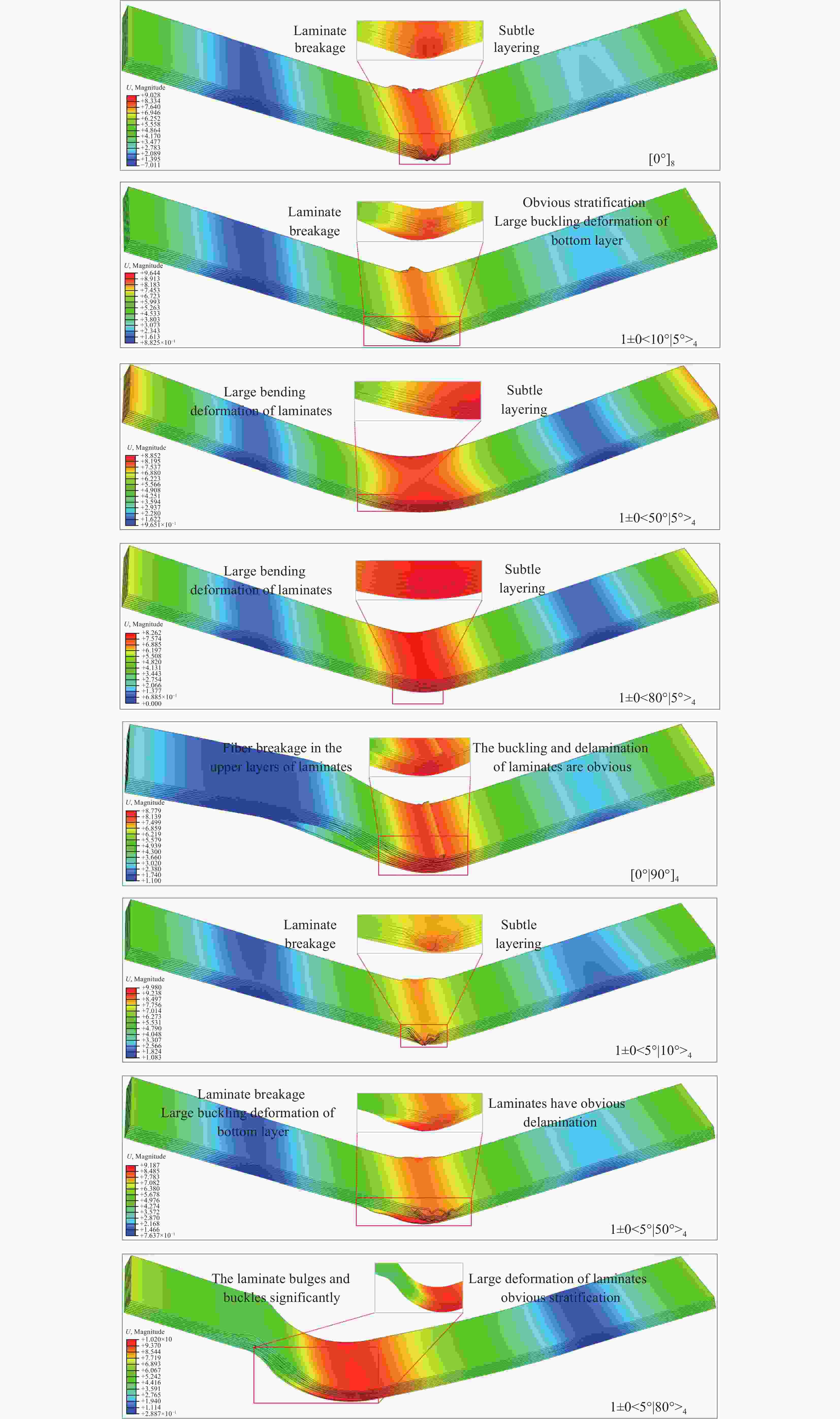
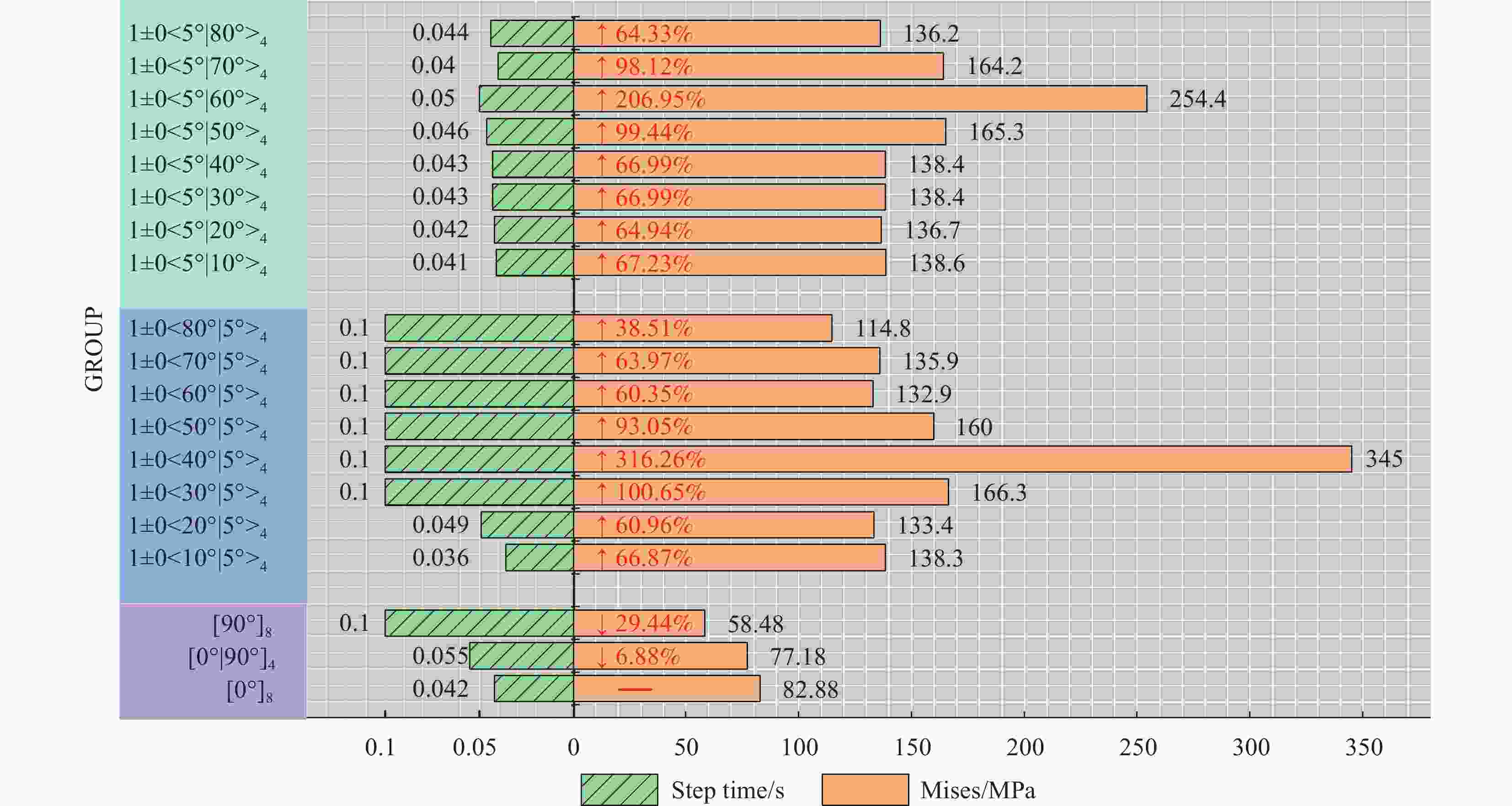
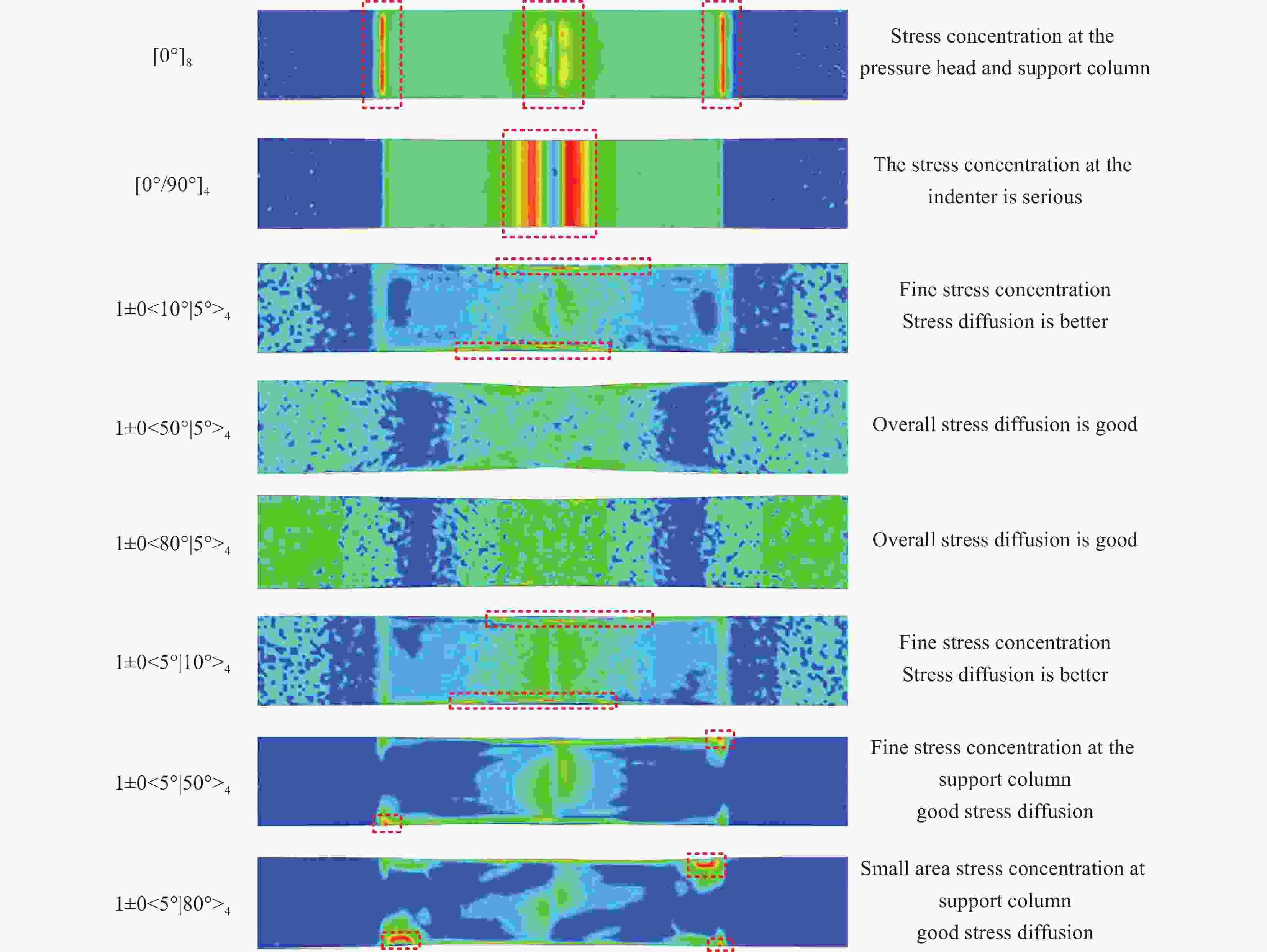
Type of laminate Layer representation method The constant stiffness [0°]8 [0°/90°]4 [90°]8 The variable stiffness T1 remains unchanged 1±0<10°|5°>4 1±0<20°|5°>4 1±0<30°|5°>4 1±0<40°|5°>4 1±0<50°|5°>4 1±0<60°|5°>4 1±0<70°|5°>4 1±0<80°|5°>4 T0 remains unchanged 1±0<5°|10°>4 1±0<5°|20°>4 1±0<5°|30°>4 1±0<5°|40°>4 1±0<5°|50°>4 1±0<5°|60°>4 1±0<5°|70°>4 1±0<5°|80°>4 表 4 三点弯曲工况下层合板极限应力对比
Table 4. Comparison of ultimate stress of laminates under three-point bending conditions
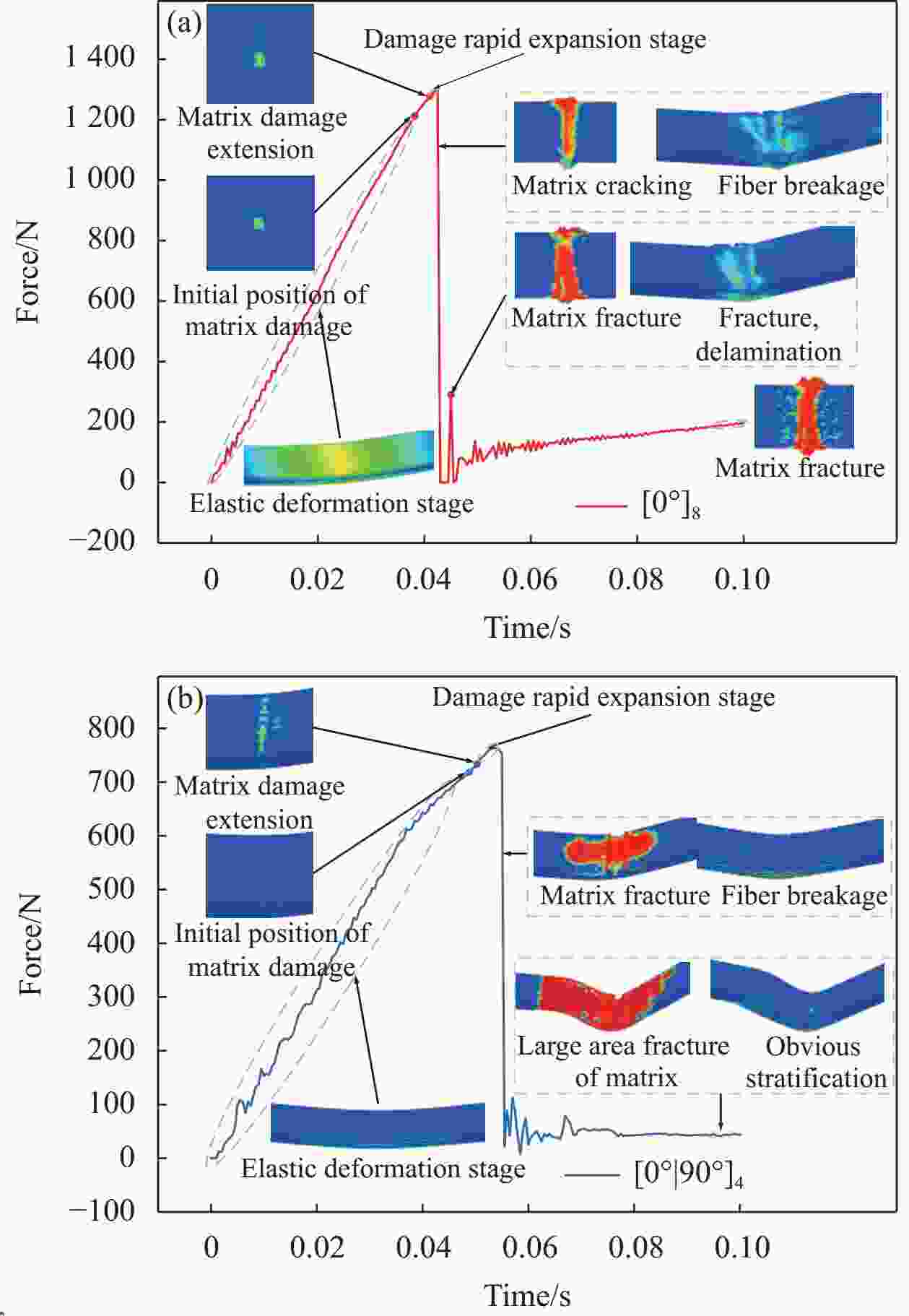
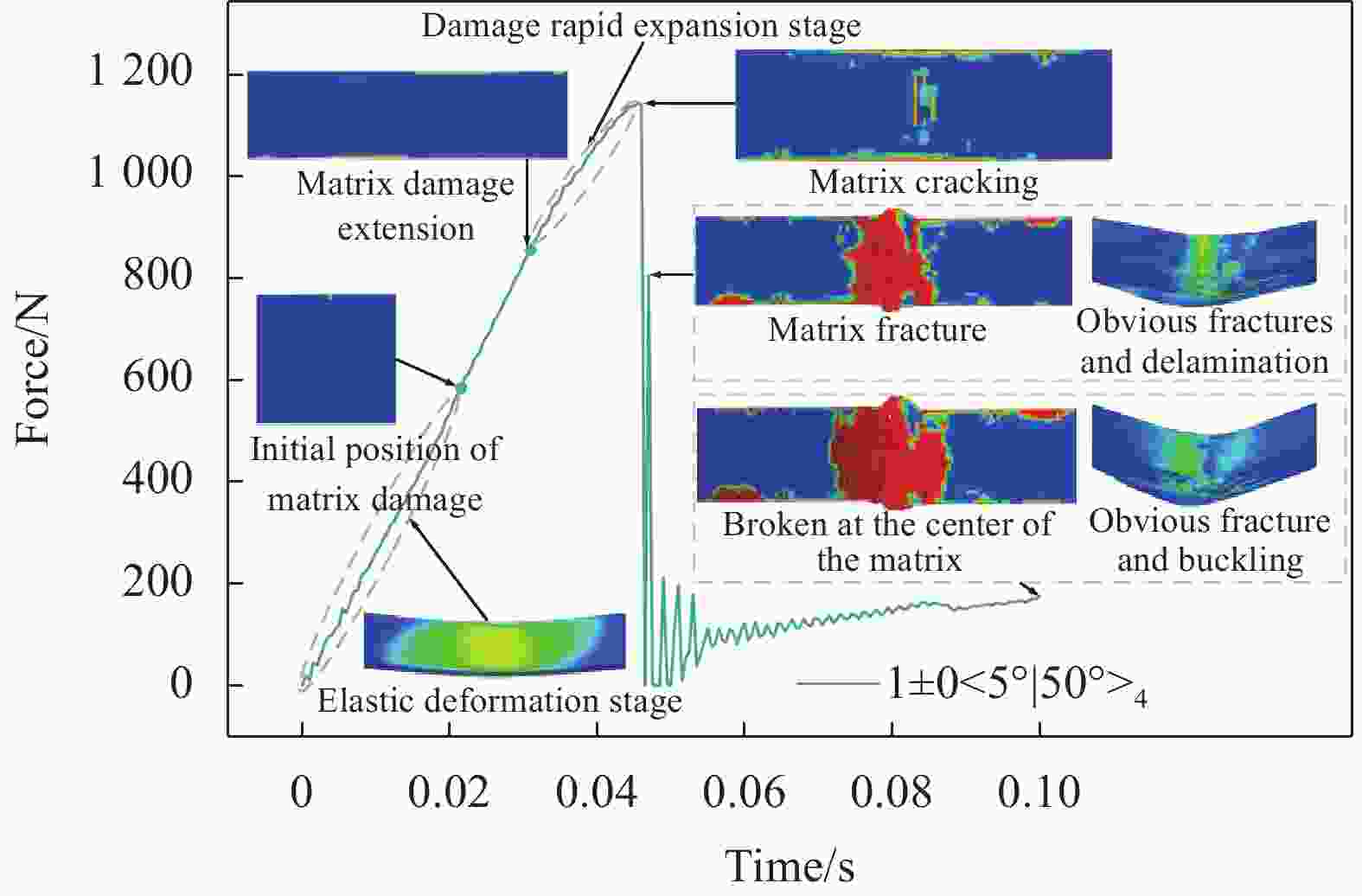
Layer Ultimate stress/MPa Compare Layer Ultimate stress/MPa Compare [0°]8 1618 – [0°/90°]4 1361 ↓ 15.884 1±0<10°|5°>4 2035 ↑ 25.773 1±0<5°|10°>4 2072 ↑ 28.059 1±0<20°|5°>4 2076 ↑ 28.307 1±0<5°|20°>4 2073 ↑ 28.121 1±0<30°|5°>4 2052 ↑ 26.823 1±0<5°|30°>4 2076 ↑ 28.307 1±0<40°|5°>4 861.5 ↓ 46.755 1±0<5°|40°>4 2076 ↑ 28.307 1±0<50°|5°>4 1149 ↓ 28.986 1±0<5°|50°>4 2072 ↑ 28.059 1±0<60°|5°>4 687.9 ↓ 57.485 1±0<5°|60°>4 2055 ↑ 27.009 1±0<70°|5°>4 493.4 ↓ 69.506 1±0<5°|70°>4 1656 ↑ 2.295 1±0<80°|5°>4 238.7 ↓ 85.247 1±0<5°|80°>4 2011 ↑ 24.289 [90°]8 58.48 ↓ 94.174 -
[1] 白瑞祥, 佟凯旋, 刘琛. 自动铺丝变刚度加筋板结构承载能力分析[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2019, 40(8): 1480-1487. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201807122BAI Ruixiang, TONG Kaixuan, LIU Chen. Load capacity analysis of plates stiffened through automated fiber placement with variable stiffness[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2019, 40(8): 1480-1487(in Chinese). doi: 10.11990/jheu.201807122 [2] 陈同海, 周正亮, 张守玉, 等. 夹层复合材料三点弯曲试验和有限元模拟分析对比[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2017, 45(7): 111-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2017.07.022CHEN Tonghai, ZHOU Zhengliang, ZHANG Shouyu, et al. Comparison of three point bending test and finite element simulation analysis of sandwich composites[J]. Engineering Plastics Application, 2017, 45(7): 111-114(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2017.07.022 [3] 张华伟, 吴佳璐. 三点弯曲工况下复合材料层合板的应力变化[J]. 纺织高校基础科学学报, 2020, 33(1): 32-37.ZHANG Huawei, WU Jialu. Stress change of composite laminates in three point bending[J]. Basic Sciences Journal of Textile Universities, 2020, 33(1): 32-37(in Chinese). [4] ULLAH H, HARLAND A R, LUCAS T, et al. Finite-element modelling of bending of CFRP laminates: Multiple delaminations[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 52(1): 147-156. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2011.02.005 [5] ULLAH H, HARLAND A R, SILBERSCHMIDT V V. Damage modelling in woven-fabric CFRP laminates under large-deflection bending[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 64: 130-135. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.05.036 [6] 杨慧. 复合材料层合板三点弯曲损伤失效数值研究[J]. 燃气涡轮试验与研究, 2006, 19(4): 38-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2006.04.009YANG Hui. Simulation of the damage progression of composite panels under three-point bending load[J]. Gas Turbine Experiment and Research, 2006, 19(4): 38-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2620.2006.04.009 [7] ZHOU H W, MISHNAEVSKY L, BRØNDSTED P, et al. SEM in situ laboratory investigations on damage growth in GFRP composite under three-point bending tests[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55: 1199-1208. doi: 10.1007/s11434-009-0560-1 [8] 庄蔚敏, 王楠, 吴迪, 等. 碳纤维复合材料层合板三点弯曲损伤仿真研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(10): 109-114. doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.10.109ZHUANG Weimin, WANG Nan, WU Di, et al. Simulation and analysis of the damage of carbon fiber composite laminates under three point bending load[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(10): 109-114(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2019.10.109 [9] 许良, 肖景厚, 宋万万, 等. 碳纤维复合材料层合板三点弯曲疲劳性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2024, 54(2): 400-409.XU Liang, XIAO Jinghou, SONG Wanwan, et al. Three-point bending fatigue properties of carbon fiber composite laminates[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2024, 54(2): 400-409(in Chinese). [10] 李辉, 赵春江, 梁建国, 等. 变刚度复合材料层合板力学特性及失效机理分析[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2022(7): 5-10, 24.LI Hui, ZHAO Chunjiang, LIANG Jianguo, et al. Analysis of mechanical properties and failure mechanism of variable stiffness composite laminates[J]. Composites Science and Engineering, 2022(7): 5-10, 24(in Chinese). [11] 叶辉, 李清原, 闫康康. 变刚度复合材料层合板的力学性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(3): 920-928.YE Hui, LI Qingyuan, YAN Kangkang. Mechanical properties of variable-stiffness carbon fiber composite laminates[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(3): 920-928(in Chinese). [12] 刘禹华, 高峰, 盛聪, 等. 变刚度复合材料夹芯板设计及模态分析[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2021, 51(2): 26-30.LIU Yuhua, GAO Feng, SHENG Cong, et al. Design and modal analysis of sandwich plates with variable stiffness[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2021, 51(2): 26-30(in Chinese). [13] CAO Z, FU H, HAN Z. Comparative study on bezier curve and linear variable angle method for variable stiffness laminates[J]. Polymer Composites, 2019, 40(3): 952-960. doi: 10.1002/pc.24769 [14] 潘杰, 原崇新, 李志远, 等. 考虑可制造性的变刚度复合材料加筋壁板的优化设计[J]. 航空科学技术, 2023, 34(3): 64-70.PAN Jie, YUAN Chongxin, LI Zhiyuan, et al. Optimization design of variable stiffness stiffened composites considering manufacturability[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2023, 34(3): 64-70(in Chinese). [15] GAO T, WANG X, LIU C, et al. Experimental study on the influence of lamination parameters on the vibration characteristics of variable stiffness composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures, 2023, 312: 116882. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.116882 [16] MARQUES F E C, MOTA A F S, LOJA M A R. Variable stiffness composites: Optimal design studies[J]. Journal of Composites Science, 2020, 4(2): 80. doi: 10.3390/jcs4020080 [17] 张雅会, 陈普会, 孔斌. 变刚度复合材料平板与开孔板屈曲性能试验验证与数值仿真[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(4): 2377-2389.ZHANG Yahui, CHEN Puhui, KONG Bin. Experimental verification and numerical simulation of buckling behavior of variable stiffness composite plates and open-hole plates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(4): 2377-2389(in Chinese). [18] ZHANG Y, KONG B, GU J, et al. Experimental investigation on the buckling and post-buckling behavior of variable stiffness laminates[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 184: 110450. [19] PINNA C, SOUTIS C. Modelling impact damage in composite laminates: A simulation of intra- and inter-laminar cracking[J]. Composite Structures, 2014, 114: 10-19. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2014.03.052 [20] RUSSELL B P, LIU T, FLECK N A, et al. The soft impact of composite sandwich beams with a square-honeycomb core[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2012, 48: 65-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2011.04.007 [21] 牛雪娟, 李辰阳, 刘江雨. 变刚度CFRP层合板在低速冲击下的分层失效分析[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2022, 45(3): 431-437. doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2022.03.015NIU Xuejuan, LI Chenyang, LIU Jiangyu. Delamination failure analysis of variable stiffness CFRP laninates under low-velocity impact[J]. Joumal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2022, 45(3): 431-437(in Chinese). doi: 10.7673/j.issn.1006-2793.2022.03.015 [22] 周俊杰, 王生楠. 低速冲击下碳纤维复合层合板数值模拟研究[C]//第二十一届全国复合材料学术会议(NCCM-21)论文集. 呼和浩特: 中国航空学会, 2020: 44-51.ZHOU Junjie, WANG Shengnan. Numerical simulation of carbon fiber composite laminates subject to low velocity impact [C]//Proceedings of the 21st National Conference on Composite Materials (NCCM-21). Hohhot: Chinese Society of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020: 44-51(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: