Adsorption of heavy metals by agricultural solid waste based hydrogel: A review
-
摘要: 随着经济的快速发展,水中重金属离子污染对人类健康以及生态系统造成威胁。水凝胶以其良好的吸附性能、可再生性和低毒性在处理重金属离子方面具有很大的潜力。本文论述了近年来国内外以农业固体废弃物为原料制备水凝胶(纤维素基水凝胶、半纤维素基水凝胶、木质素基水凝胶等)吸附重金属的研究进展。同时,讨论了农业固废基水凝胶的合成,对重金属的吸附效果、吸附机制及分析方法,并列举了工业固废基和其他固废基水凝胶吸附重金属的效果,以期帮助研究者对农业固废基水凝胶吸附重金属的探究有更深刻的理解。Abstract: With the rapid development of economy, the pollution of heavy metal ions in water poses a threat to human health and ecosystem. Hydrogels have great potential in the treatment of heavy metal ions because of their good adsorption properties, renewability and low toxicity. This paper discusses the research progress in recent years on the preparation of hydrogels (cellulose-based hydrogels, hemicellulose-based hydrogels, lignin-based hydrogels, etc.) for the adsorption of heavy metals from agricultural solid wastes at home and abroad. The synthesis of agricultural solid waste based hydrogels, the adsorption effect, adsorption mechanism, and analytical methods for the removal of heavy metals are also discussed, and the effects of heavy metal adsorption by industrial solid waste based and other solid waste based hydrogels are enumerated. In order to help the researchers to have a deeper understanding of the investigation of heavy metal adsorption by agricultural solid waste based hydrogels.
-
Key words:
- hydrogel composites /
- agricultural waste /
- heavy metals /
- adsorption mechanism /
- water pollution control
-
表 1 重金属对人类健康的危害
Table 1. Hazards of heavy metals to human health
Heavy metal Harm to mankind Pb Accumulates in the bones, brain, kidneys and muscles of the body, leading to brain damage, mental
retardation, anemia and cancer[21]Hg Lung, kidney and chest pain, dyspnea injury[22] Cd Cadmium ions pose a threat to many organs such as kidneys, lungs and liver[23] Cu Leading to liver damage, insomnia and Wilson disease[24] Zn Zinc not only irritates the skin, but also causes headache, dry cough, dizziness and other symptoms[25] Cr Destroy human metabolism, stimulate skin and lung cancer[26] As Skin damage and affect the nervous system of the human body[27] Ni Dermatitis, nausea, chronic asthma, cough[27] Mn Excessive manganese can cause dizziness and fatigue, mental retardation, and cause neurotransmitter disorders[28] 表 2 农业固废基水凝胶的制备及特点
Table 2. Synthesis and characterization of agricultural solid waste-based hydrogels
Solid waste-based raw materials and other reagents Method Characteristic Ref. Cellulose base Soybean residue cellulose,
chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol,
nano-Fe3O4Freeze-thaw method The increase of cellulose content is beneficial to improve the mechanical strength and swelling properties of the hydrogel. [44] Licorice residue cellulose,
crosslinker epichlorohydrinSolution polymerization The adsorption capacity, chemical stability, pore size distribution and mechanical properties of the hydrogel are improved by using epichlorohydrin as cross-linking agent. [45] Bagasse cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol, crosslinker glutaraldehyde Microwave assisted irradiation Microwave assisted irradiation technology can save time and energy. [46] Wheat straw cellulose, monomer acrylic acid and acrylamide, crosslinker N, N'-methylene-bis-acrylamide, initiator ammonium persulfate Free radical graft copolymerization Hydrogel has good thermal stability at temperature below 392℃. [47] Poplar wood flour cellulose, 3-mercaptopropionic acid, L-cysteamine hydrochloride, initiator ammonium persulfate Ultraviolet photoinitiation The cellulose ester synthesized by esterification of anhydride with cellulose under homogeneous condition has higher reaction activity. [48] Banana cellulose, chitosan, crosslinker epichlorohydrin Solution polymerization There are a large number of hydrophilic groups of hydroxyl and amino groups in the synthesized hydrogel, and the surface distributes irregular pore structure. [49] Lignin based Wheat straw lignin, montmorillonite, monomer acrylic acid, crosslinker N, N'-methylene-bis-acrylamide, initiator
K2S2O8-Na2SO3Solution polymerization Montmorillonite is introduced into lignin nanocomposites to improve the adsorption and mechanical properties of lignin nanocomposites. [50] Mulberry lignin, monomer acrylic acid, intercalation agent citric acid modified montmorillonite, crosslinker N, N'-methylene-bis-acrylamide, initiator (NH4)S2O8 Graft intercalation method When the amount of lignin is too high, the excess lignin produces too many cross-linking points, which affects the gel strength and hinders the cross-linking reaction. [51] Rice husk lignin, chitosan, polyacrylamide Free radical polymerization Lignin and chitosan are mixed as the first network to provide active functional groups for the removal of heavy metals.
As a malleable second network, polyacrylamide forms a stable structural hydrogel adsorbent.[52] Hemicellulose group Corn kernel hemicellulose, monomers acrylic acid and N-isopropyl acrylamide, crosslinker N, N'-methylene-bis-acrylamide, photoinitiator benzoin dimethyl ether Ultraviolet photoinitiation Pb2+ solution pH in the range of 3.5-4.5 and elevated temperature favored the adsorption of hydrogels. [53] Reed hemicellulose, monomer acrylic acid, crosslinker N, N, N', N'-tetramethylethylenediamine Free radical polymerization After 8 cycles of adsorption-desorption, the hydrogel still has high adsorption efficiency for metal ions. [39] Xylan hemicellulose, carrageenan, initiator ammonium persulfate, polyvinylpyrrolidone Microwave assisted irradiation Compared with cellulose, xylan hemicellulose is amorphous and consists of branched chains of various sugars, which is easier to dissolve in common solvents. [54] Other types of agriculture Citrus peel pectin, crosslinker calcium chloride, metal organic frame (MOF) In-situ method MOFs can interact with other components or adjust the properties of hydrogel matrix. [55] Pomelo peel pectin, monomers acrylic acid and acrylamide, initiator ammonium persulfate, crosslinker N, N'-methylene-bis-acrylamide Graft copolymerization Microwave extraction-alcohol precipitation method for pectin extraction has the advantages of strong selectivity, short operation time, low solvent consumption and excellent quality of extracted pectin. [56] Livestock bone powder, sodium alginate Solution polymerization Adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherms indicate that adsorption is chemically and physically interactive. [57] 表 3 农业固废基水凝胶吸附重金属的优缺点
Table 3. Advantages and disadvantages of heavy metal adsorption on agricultural solid waste-based hydrogels
Common type Common ground Advantage Disadvantage Cellulose based hydrogel
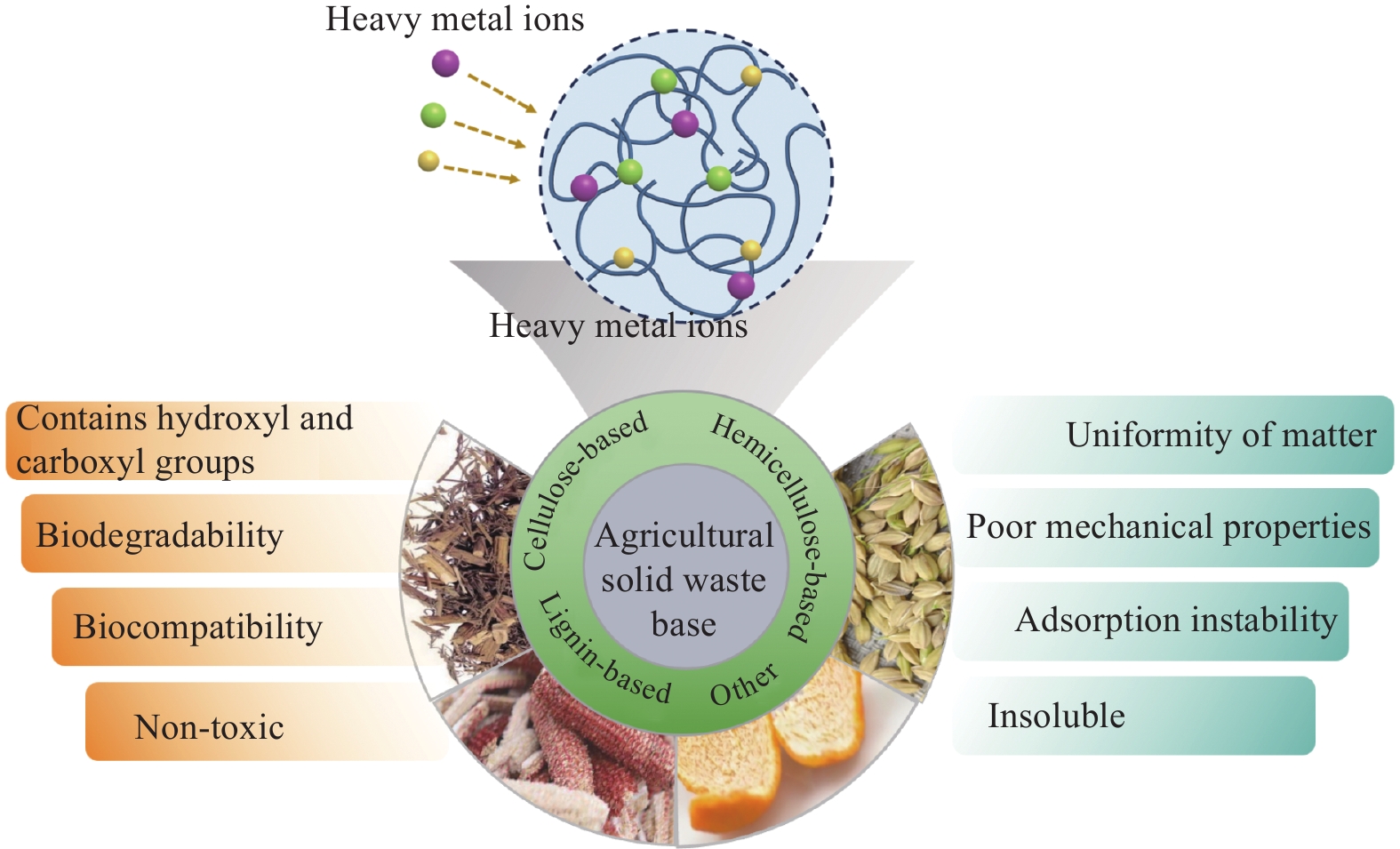
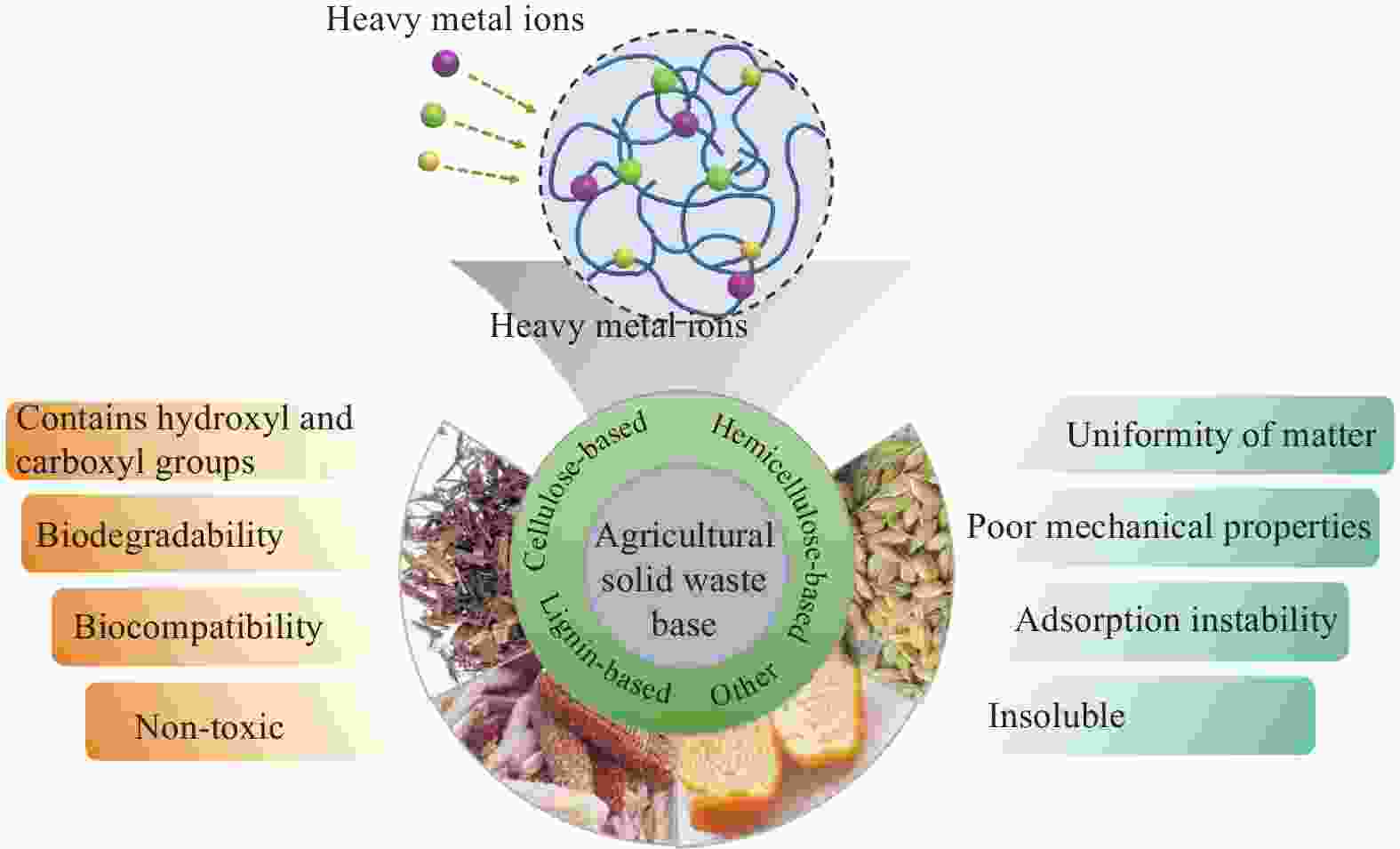
Advantages: The raw materials are non-toxic, biodegradable and low cost; Make the hydrogel biocompatible, biodegradable and improve its adsorption performance.
Disadvantages: Unhomogeneity of raw materials, structural complexity, and difficulty in obtaining pure substances, and poor mechanical strength of prepared hydrogels.Contains hydroxyl, carboxyl and hydrogen bonding to improve the adsorption and mechanical properties
of hydrogels.Refractory; After several cycles of use, the morphology and mechanical properties of the hydrogel will change considerably, resulting in an unstable adsorption capacity. Hemicellulose based hydrogel Contains functional groups such as hydroxyl, acetyl and carboxyl groups; Good water solubility. The mechanical strength of the prepared hemicellulose-based hydrogels is poor due to the small molecular weight of hemicellulose and low degree of polymerization. Lignin based hydrogel Hydroxyl and carbonyl groups can chelate with metal ions; Active site for chemical reactions. The inhomogeneity and structural complexity of lignin and the difficulty of obtaining pure lignin;And when the amount of lignin is too high, excess lignin produces too many cross-linking points, which affects the gel strength and hinders the cross-linking reaction. Other agricultural solid waste-based hydrogels Pectin contains reactive groups such as carboxyl and hydroxyl groups. Insoluble; Pectins from different sources have different gelling and adsorption capacities due to different sizes and chemical structures, and are less stable. 表 4 农业固废基水凝胶对重金属的吸附性能总结
Table 4. Summary of adsorption properties of agricultural solid waste-based hydrogels for heavy metals
Hydrogel Target
pollutantAdsorption
conditionMaximum adsorption capacity/(mg·g−1) Adsorption kinetic/
adsorption isothermRecycling rate Ref. Cellulose base Soybean residue cellulose magnetic hydrogel Cu(II) pH=5.0 15.94 Pseudo-second-order/
Freundlich4 times
>80%[44] Licorice residue cellulose hydrogel Pb(II)
Cr(III)
Cu(II)pH=5.0(Pb)
t=120 min,
pH=4.0(Cr)(Cu)
t=60 min591.8
458.3
121.4Pseudo-second-order/
Langmuir5 times
>75%[45] Bagasse carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel Cu(II) pH=5.0 2.3 — — [46] Wheat straw cellulose hydrogel Cu(II)
Mn(II)500 mg/L Co (Cu)
400 mg/L Co (Mn)238.1
176.9Pseudo-second-order — [47] Aspen cellulose methacrylate hydrogel Pb(II)
Hg(II)Hydrogel
dosage 0.2 g148.44
112.55Pseudo-second-order/
Langmuir— [48] Grapefruit peel cellulose-based hydrogel Cu(II)
Cr(VI)
Cd(II)Hydrogel dosage 10 g/L, pH=7.0, T=33℃, t=60 min, 10 mg/L Co Removal rate 96.21%, 98.02%,
95.43%— — [59] Banana fiber-chitosan hydrogel Cu(II)
Cd(II)
Pb(II)Hydrogel dosage 5 g/L, t=40 min Removal rate 98.35%, 79.22%,
77.3%Pseudo-second-order — [49] Lignin base Wheat straw lignin-montmorillonite hydrogel Cu(II) pH=6.5 74.35 Pseudo-second-order/
Freundlich5 times
>80%[50] Mulberry lignin hydrogel Mn(II)
Zn(II)
Pb(II)320 mg/L Co (Mn),
160 mg/L Co (Zn),
1000 mg/L Co (Pb),
t =720 min77.09
73.95
383.90— — [51] Hemicellulose based Reed hemicellulose-based hydrogel Pb(II)
Cd(II)
Zn(II)200 mg/L Co,
pH=5.5(Pb),
pH=6.5(Cd)(Zn)699
521
265Pseudo-second-order/
Langmuir— [39] Yellow bamboo xylan hemicellulose-acrylic hydrogel Pb(II)
Cd(II)
Zn(II)t=60 min,
pH=5.5(Pb),
pH=6.5(Cd)(Zn)859
495
274Pseudo-second-order/
Langmuir5 times
>90%[60] Other
categoriesMetal-organic frame composite citrus peel gum hydrogel Cr(VI)
Pb(II)pH=1(Cr),
pH=5(Pb)825.97
913.88Pseudo-second-order/
Langmuir8 times
>85%[55] Grapefruit peel pectin-based composite hydrogel Cu(II) pH=6.0 80.6 Pseudo-second-order/
Freundlich4 times
>90%[61] Bone hydrogel of abandoned livestock and poultry in rural area Cd(II) pH=4.0, t=720 min 1010.19 Pseudo-second-order and intra-particle diffusion models/
Langmuir and Freundlich3 times
>90%[57] Notes: T—Temperature; t—Time. 表 5 工业固废基水凝胶对重金属的吸附性能总结
Table 5. Summary of adsorption properties of industrial solid waste-based hydrogels for heavy metals
Hydrogel adsorption
materialTarget pollutant Adsorption condition Maximum adsorption
capacity/(mg·g−1)Ref. Red mud-sodium alginate hydrogel Pb(II) pH=6.0, T=25℃, t=900 min, 900 mg/L Co 454.54 [80] Fly ash-hydroxyethyl cellulose-chitosan hydrogel Cu(II) 100 mg/L Co 130.7 [81] Modified fly ash-sodium alginate crosslinked
acrylic hydrogelCu(II) 300 mg/L Co 131.09 [82] Magnetic attapulgite/fly ash/polyacrylic
acid hydrogelPb(II) pH=5.0, 100 mg/L Co, t=24 h 38 [83] Tobe mullite-starch hydrogel Cd(II) t=12 h, pH=5.21, T=25℃, hydrogel
dosage 0.05 g591.36 [84] -
[1] BHATNAGAR A, SILLANPÄÄ M, WITEK-KROWIAK A. Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification—A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 270: 244-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.135 [2] ZAMORA-LEDEZMA C, NEGRETE-BOLAGAY D, FIGUEROA F, et al. Heavy metal water pollution: A fresh look about hazards, novel and conventional remediation methods[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2021, 22: 101504. [3] ADEWUNMI A A, ISMAIL S, SULTAN A S. Laboratory scale study on rheological behavior, morphological and structural properties of crosslinked polyacrylamide composite hydrogels embedded with date seed powder[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2015, 132(28): 42110. doi: 10.1002/app.42110 [4] XU R, ZHOU G, TANG Y, et al. New double network hydrogel adsorbent: Highly efficient removal of Cd(II) and Mn(II) ions in aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015, 275: 179-188. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.040 [5] GOGOI N, BAROOAH M, MAJUMDAR G, et al. Carbon dots rooted agarose hydrogel hybrid platform for optical detection and separation of heavy metal ions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(5): 3058-3067. [6] ANITHA K, NAMSANI S, SINGH J K. Removal of heavy metal ions using a functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube: A molecular dynamics study[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 2015, 119(30): 8349-8358. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.5b03352 [7] ABDULLAH N, YUSOF N, LAU W J, et al. Recent trends of heavy metal removal from water/wastewater by membrane technologies[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2019, 76: 17-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2019.03.029 [8] FU F, WANG Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92(3): 407-418. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.11.011 [9] LIU X, MA R, WANG X, et al. Graphene oxide-based materials for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 62-73. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.050 [10] SUN H, ZHAN J, CHEN L, et al. Preparation of CTS/PAMAM/SA/Ca2+ hydrogel and its adsorption performance for heavy metal ions[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 607: 155135. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155135 [11] CHEN X, ZHOU S, ZHANG L, et al. Adsorption of heavy metals by graphene oxide/cellulose hydrogel prepared from NaOH/urea aqueous solution[J]. Materials, 2016, 9(7): 582. doi: 10.3390/ma9070582 [12] KHOZEMY E E, NASEF S M, MOHAMED T M. Radiation synthesis of superabsorbent hydrogel (wheat flour/acrylamide) for removal of mercury and lead ions from waste solutions[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2020, 30(5): 1669-1685. doi: 10.1007/s10904-019-01350-6 [13] WANG Z, LI T T, PENG H K, et al. Low-cost hydrogel adsorbent enhanced by trihydroxy melamine and β-cyclodextrin for the removal of Pb(II) and Ni(II) in water[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 411: 125029. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.125029 [14] 赵璐婷, 张健, 李娜, 等. 半纤维素基磁性水凝胶的制备及其对染料吸附性能的研究[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(11): 85-91. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000076ZHAO Luting, ZHANG Jian, LI Na, et al. Preparation of hemicellulose-based magnetic hydrogel and its adsorption properties for dye[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020, 48(11): 85-91(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.000076 [15] JAFARIGOL E, AFSHAR GHOTLI R, HAJIPOUR A, et al. Tough dual-network GAMAAX hydrogel for the efficient removal of cadmium and nickle ions in wastewater treatment applications[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2021, 94: 352-360. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2020.11.006 [16] GIWA A, HASAN S W. Nucleophilic-functionalized β-cyclodextrin-polyethersulfone structures from facile lamination process as nanoporous membrane active layers for wastewater post-treatment: Molecular implications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 563: 914-925. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2018.06.056 [17] PERUMAL S, ATCHUDAN R, EDISON T N J I, et al. A short review on recent advances of hydrogel-based adsorbents for heavy metal ions[J]. Metals, 2021, 11(6): 864. doi: 10.3390/met11060864 [18] 张玮玮, 柳荫, 常璐璐. 砷哭了, 不是重金属的“重金属”[J]. 金属世界, 2023(4): 18-21.ZHANG Weiwei, LIU Yin, CHANG Lulu. Arsenic cried, which is not heavy metal, but was mistaken for[J]. Metal World, 2023(4): 18-21(in Chinese). [19] 朱建龙, 徐伟杰, 郭硕铖, 等. 水体重金属污染危害及治理技术[J]. 现代农业科技, 2022(6): 129-132.ZHU Jianlong , XU Weijie, GUO Shuocheng, et al. Hazard of heavy metal pollution in water and its treatment technology[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022(6): 129-132(in Chinese). [20] PENG W, LI H, LIU Y, et al. Comparison of Pb(II) adsorption onto graphene oxide prepared from natural graphites: Diagramming the Pb(II) adsorption sites[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 364: 620-627. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.12.208 [21] MA S C, ZHANG J L, SUN D H, et al. Surface complexation modeling calculation of Pb(II) adsorption onto the calcined diatomite[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 359: 48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.09.133 [22] ZHOU Y, HU X, ZHANG M, et al. Preparation and characterization of modified cellulose for adsorption of Cd(II), Hg(II), and acid fuchsin from aqueous solutions[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(2): 876-884. [23] NAWROT T S, STAESSEN J A, ROELS H A, et al. Cadmium exposure in the population: From health risks to strategies of prevention[J]. BioMetals, 2010, 23(5): 769-782. doi: 10.1007/s10534-010-9343-z [24] BEKIARI V, LIANOS P. Poly(sodium acrylate) hydrogels as potential pH-sensitive sorbents for the removal of model organic and inorganic pollutants from water[J]. Global NEST Journal, 2013, 12(3): 262-269. doi: 10.30955/gnj.000720 [25] 杨瑶, 赵莹. 多微孔苄基化改性木粉的制备及其对废水中Cu2+、Pb2+和Zn2+的吸附性能研究[D]. 长沙: 中南林业科技大学, 2016.YANG Yao, ZHAO Ying. Preparation of microporous benzylated wood powder and study on adsorption ability of microporous benzylated wood powder to copper ions(II), lead ions(II) and zinc ions(II)[D]. Changsha: Central South Forestry University, 2016(in Chinese). [26] BALLAV N, MAITY A, MISHRA S B. High efficient removal of chromium(VI) using glycine doped polypyrrole adsorbent from aqueous solution[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 198-199: 536-546. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.05.110 [27] CHEN B, CHEN Y, XU L, et al. Research and development on industrial heavy metal wastewater treatment technology[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 585(1): 012051. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/585/1/012051 [28] 叶操. 水库重金属锰污染特征及原因分析[J]. 陕西水利, 2023(9): 92-93.YE Cao. Characterization of heavy metal manganese pollution in reservoirs and analysis of its causes[J]. Shaanxi Water Resources, 2023(9): 92-93(in Chinese). [29] 田长顺, 石亮. 农业废弃物吸附稀土离子的研究进展[J]. 有色金属科学与工程, 2019, 10(4): 113-122.TIAN Changshun, SHI Liang. Advances in adsorption of rare earth ions by agricultural wastes[J]. Nonferrous Metals Science and Engineering, 2019, 10(4): 113-122(in Chinese). [30] LIU Z, ZHOU X, CHEN X, et al. Biosorption of clofibric acid and carbamazepine in aqueous solution by agricultural waste rice straw[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(12): 2384-2395. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(12)60324-6 [31] SYAFTIKA N, MATSUMURA Y. Comparative study of hydrothermal pretreatment for rice straw and its corresponding mixture of cellulose, xylan, and lignin[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2018, 255: 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.01.085 [32] PENARANDA A J E, SABINO M A. Effect of the presence of lignin or peat in IPN hydrogels on the sorption of heavy metals[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2010, 65(5): 495-508. [33] SUN X F, ZENG Q, WANG H, et al. Preparation and swelling behavior of pH/temperature responsive semi-IPN hydrogel based on carboxymethyl xylan and poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)[J]. Cellulose, 2019, 26(3): 1909-1922. doi: 10.1007/s10570-018-2180-x [34] LIANG S, WU J, TIAN H, et al. High-strength cellulose/poly(ethylene glycol) gels[J]. ChemSusChem, 2008, 1(6): 558-563. doi: 10.1002/cssc.200800003 [35] FENG L, CHEN Z L. Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2008, 142(1-3): 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2008.06.007 [36] 景占鑫, 孙晓锋, 王海洪, 等. 环境敏感型纤维素水凝胶及其在药物控释方面的应用[J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(7): 83-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.07.019JING Zhanxin, SUN Xiaofeng, WANG Haihong, et al. Environment-sensitive cellulose hydrogels and its application in drug delivery aspects[J]. Materials Reports, 2012, 26(7): 83-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.07.019 [37] ZERPA A, PAKZAD L, FATEHI P. Hardwood kraft lignin-based hydrogels: Production and performance[J]. ACS Omega, 2018, 3(7): 8233-8242. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.8b01176 [38] 冯清华, 谌凡更. 含木质素水凝胶的研究进展[J]. 纤维素科学与技术, 2011, 19(4): 67-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2011.04.012FENG Qinghua, CHEN Fangeng. Advances in lignin-containing hydrogels[J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology, 2011, 19(4): 67-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2011.04.012 [39] 张文明, 黄莹, 朱厦, 等. 芦苇半纤维素基水凝胶的制备及对重金属离子的高效吸附[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2015, 35(4): 28-34.ZHANG Wenming, HUANG Ying, ZHU Sha, et al. Preparation of reed hemicelluloses-based hydrogels and its highly effective adsorption of heavy metal ions[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products, 2015, 35(4): 28-34(in Chinese). [40] XU Y, LIU K, YANG Y, et al. Hemicellulose-based hydrogels for advanced applications[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2023, 10: 1110004. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1110004 [41] FARHAT W, VENDITTI R, AYOUB A, et al. Towards thermoplastic hemicellulose: Chemistry and characteristics of poly-(ε-caprolactone) grafting onto hemicellulose backbones[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 153: 298-307. [42] GERSCHENSON L N, FISSORE E N, ROJAS A M, et al. Pectins obtained by ultrasound from agroindustrial by-products[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2021, 118: 106799. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106799 [43] 林彦萍, 任源, 王晓娥, 等. 农业生物质废弃物转化功能材料的研究进展[J/OL]. 环境科学, 2023: 1-29[2024-05-21]. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.202307264.LIN Yanping, REN Yuan, WANG Xiao'e, et al. Research progress of functional materials for conversion of agricultural biomass wastes[J/OL]. Environmental Science, 2023: 1-29[2024-05-21](in Chinese). [44] LI P, ZHOU M, LIU H, et al. Preparation of green magnetic hydrogel from soybean residue cellulose for effective and rapid removal of copper ions from wastewater[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2022, 10(5): 108213. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2022.108213 [45] YIN X, KE T, ZHU H, et al. Efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution using licorice residue-based hydrogel adsorbent[J]. Gels, 2023, 9(7): 559. doi: 10.3390/gels9070559 [46] BAIYA C, NANNUAN L, TASSANAPUKDEE Y, et al. The synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose-based hydrogel from sugarcane bagasse using microwave-assisted irradiation for selective adsorption of copper(II) ions[J]. Environmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 2019, 38(s1): S157-S165. [47] 吕晓萍, 王阳, 孙倩玉, 等. 麦秆水凝胶的制备及其对Cu(II)、Mn(II)的吸附[J]. 中国造纸, 2019, 38(11): 37-41. doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2019.11.006LYU Xiaoping, WANG Yang, SUN Qianyu, et al. Preparation of wheat straw hydrogel and its adsorption performance for Cu(II) and Mn(II)[J]. China Pulp & Paper, 2019, 38(11): 37-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.11980/j.issn.0254-508X.2019.11.006 [48] 陈旭, 王硕, 汤相宇, 等. 纤维素甲基丙烯酸酯水凝胶的制备及重金属离子吸附性能研究[J]. 森林工程, 2023, 39(1): 82-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2023.01.010CHEN Xu, WANG Shuo, TANG Xiangyu, et al. Study on preparation of cellulose methacrylate hydrogels and their adsorption performance of heavy metal ions[J]. Forest Engineering, 2023, 39(1): 82-91(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8023.2023.01.010 [49] 郑丽丽, 艾斌凌, 郑晓燕, 等. 香蕉纤维-壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及其吸附重金属离子性能研究[J]. 中国麻业科学, 2019, 41(3): 136-144.ZHENG Lili, AI Binling, ZHENG Xiaoyan, et al. Study on the preparation and heavy metal adsorption of banana fiber-chitosan hydrogels[J]. Plant Fiber Sciences in China, 2019, 41(3): 136-144(in Chinese). [50] SUN X F, HAO Y, CAO Y, et al. Superadsorbent hydrogel based on lignin and montmorillonite for Cu(II) ions removal from aqueous solution[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 127: 511-519. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.058 [51] 王莹, 王星敏, 熊杰, 等. 接枝插层合成木质素基水凝胶的制备因素解析[J]. 环境化学, 2020, 39(8): 2217-2226.WANG Ying, WANG Xingmin, XIONG Jie, et al. Analysis of preparation factors of lignin-based hydrogels synthesized by graft-intercalation[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2020, 39(8): 2217-2226(in Chinese). [52] MA J, LI T, LIU Y, et al. Rice husk derived double network hydrogel as efficient adsorbent for Pb(II), Cu(II) and Cd(II) removal in individual and multicomponent systems[J]. Bioresource Technology, 2019, 290: 121793. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121793 [53] 梁志. 玉米芯半纤维素基水凝胶对Pb2+吸附性能和机制[J]. 化工新型材料, 2023, 51(2): 202-206.LIANG Zhi. Adsorption properties and mechanisms of corn cobs hemicelluloses-based hydrogels for Pb2+[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2023, 51(2): 202-206(in Chinese). [54] MEENA R, LEHNEN R, SAAKE B. Microwave-assisted synthesis of kC/Xylan/PVP-based blend hydrogel materials: Physicochemical and rheological studies[J]. Cellulose, 2014, 21(1): 553-568. doi: 10.1007/s10570-013-0155-5 [55] MAHMOUD M E, MOHAMED A K. Novel derived pectin hydrogel from mandarin peel based metal-organic frameworks composite for enhanced Cr(VI) and Pb(II) ions removal[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 164: 920-931. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.090 [56] 张璇, 宋燕西. 柚子皮果胶的提取及其复合材料的制备及性能研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2019.ZHANG Xuan, SONG Yanxi. Extraction of pectin from grapefruit peel and preparation and properties of its composites[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2019(in Chinese). [57] LI J, CHEN M, YANG X, et al. Preparation of a novel hydrogel of sodium alginate using rural waste bone meal for efficient adsorption of heavy metals cadmium ion[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 863: 160969. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160969 [58] ZHENG X, ZOU M, ZHANG B, et al. Remediation of Cd-, Pb-, Cu-, and Zn-contaminated soil using cow bone meal and oyster shell meal[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2022, 229: 113073. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113073 [59] 黄铂扬. 柚子皮纤维素基水凝胶对重金属离子吸附效果的研究[J]. 菏泽学院学报, 2018, 40(2): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2103.2018.02.012HUANG Boyang. Adsorption effect of pomelo peel cellulose-based hydrogel on heavy metal ions[J]. Journal of Heze University, 2018, 40(2): 62-65(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2103.2018.02.012 [60] PENG X W, ZHONG L X, REN J L, et al. Highly effective adsorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions by macroporous xylan-rich hemicelluloses-based hydrogel[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(15): 3909-3916. doi: 10.1021/jf300387q [61] ZHANG W, SONG J, HE Q, et al. Novel pectin based composite hydrogel derived from grapefruit peel for enhanced Cu(II) removal[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2020, 384: 121445. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121445 [62] KUSHWAHA J, SINGH R. Cellulose hydrogel and its derivatives: A review of application in heavy metal adsorption[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 2023, 152: 110721. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2023.110721 [63] 李佶衡, 彭良琼, 郭丽君, 等. 固液吸附等温线模型与热力学参数计算[J]. 皮革科学与工程, 2023, 33(6): 36-43.LI Jiheng, PENG Liangqiong, GUO Lijun, et al. Solid-liquid adsorption isotherm model and thermodynamic parameter calculation[J]. Leather Science and Engineering, 2023, 33(6): 36-43(in Chinese). [64] MOHAMED W R, METWALLY S S, IBRAHIM H A, et al. Impregnation of task-specific ionic liquid into a solid support for removal of neodymium and gadolinium ions from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 236: 9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2017.04.013 [65] JIAO C, XIONG J, TAO J, et al. Sodium alginate/graphene oxide aerogel with enhanced strength-toughness and its heavy metal adsorption study[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2016, 83: 133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.061 [66] ZHOU D, ZHANG L, ZHOU J, et al. Cellulose/chitin beads for adsorption of heavy metals in aqueous solution[J]. Water Research, 2004, 38(11): 2643-2650. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2004.03.026 [67] YETIMOĞLU E K, KAHRAMAN M V, BAYRAMOĞLU G, et al. Sulfathiazole-based novel UV-cured hydrogel sorbents for mercury removal from aqueous solutions[J]. Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 2009, 78(2): 92-97. doi: 10.1016/j.radphyschem.2008.08.011 [68] ZHANG W, XU Y, MU X, et al. Research progress of polysaccharide-based natural polymer hydrogels in water purification[J]. Gels, 2023, 9(3): 249. doi: 10.3390/gels9030249 [69] DENG S, BAI, CHEN J P. Aminated polyacrylonitrile fibers for lead and copper removal[J]. Langmuir, 2003, 19(12): 5058-5064. doi: 10.1021/la034061x [70] 杨志林, 周勤. 花生壳木质纤维素基水凝胶对水体镉、铅的吸附性能与机制研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2023.YANG Zhilin, ZHOU Qin. Study on adsorption performance and mechanism of peanut husk lignocellulose-based hydrogel for cadmiumand lead in Water[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2023(in Chinese). [71] PEREIRA R C, ANIZELLI P R, DI MAURO E, et al. The effect of pH and ionic strength on the adsorption of glyphosate onto ferrihydrite[J]. Geochemical Transactions, 2019, 20(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/s12932-019-0063-1 [72] WEN Y, XUE C, JI D, et al. Eco-friendly enteromorpha polysaccharides-based hydrogels for heavy metal adsorption: From waste to efficient materials[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2023, 656: 130531. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130531 [73] BADSHA M A H, KHAN M, WU B, et al. Role of surface functional groups of hydrogels in metal adsorption: From performance to mechanism[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124463. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124463 [74] SHAN S, SUN X F, XIE Y, et al. High-performance hydrogel adsorbent based on cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin for copper(II) ion removal[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(18): 3063. doi: 10.3390/polym13183063 [75] 骆欣, 杨怡心, 徐东耀. 热改性粉煤灰对水中Cu(II)的吸附研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(9): 2242-2245, 2251. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.023LUO Xin, YANG Yixin, XU Dongyao. Study on adsorption of Cu(II) by thermal modified fly ash[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2020, 49(9): 2242-2245, 2251(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.09.023 [76] 刘畅, 张建斌. 电石渣基纳米碳酸钙的制备及吸附重金属的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2019.LIU Chang, ZHANG Jianbin. Studies on preparation of nano-CaCO3 from carbide slag and the adsorption of heavy metals[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [77] 孙道兴, 王馥琴. 赤泥脱除废水中重金属离子的研究[J]. 无机盐工业, 2008(8): 47-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2008.08.016SUN Daoxing, WANG Fuqin. Study on removal of heavy metal ions in wastewater by red mud[J]. Inorganic Chemicals Industry, 2008(8): 47-49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4990.2008.08.016 [78] 谢静怡, 赵晟锌, 陈忠林, 等. 粉煤灰基吸附剂去除水中重金属的研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2023, 46(S1): 116-124.XIE Jingyi, ZHAO Shengxin, CHEN Zhonglin, et al. Research progress on preparation of adsorbent based on fly ash and its application in the removal of heavy metals in water[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 46(S1): 116-124(in Chinese). [79] 雷小丽, 吴幼娥, 曾伟, 等. 改性赤泥吸附废水中典型重金属研究进展[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2021, 40(4): 1-8.LEI Xiaoli, WU You'e, ZENG Wei, et al. Research progress on adsorption of typical heavy metals in waste water by modified red mud[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2021, 40(4): 1-8(in Chinese). [80] 王威, 邓华, 胡乐宁, 等. 赤泥-海藻酸钠水凝胶对水中Pb(II)的吸附性能[J]. 广西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 41(5): 105-115.WANG Wei, DENG Hua, HU Lening, et al. Adsorption performance of red mud-sodium alginate hydrogel on Pb(II) in water[J]. Journal of Guangxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 41(5): 105-115(in Chinese). [81] 王昆. 羟乙基纤维素复合水凝胶的制备及性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2023.WANG Kun. Study on the preparation and properties of hydroxyethyl cellulose composite hydrogel[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2023(in Chinese). [82] 李露思, 赵梓年, 刘均科. 海藻酸钠交联丙烯酸基多元水凝胶的制备及性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2021.LI Lusi, ZHAO Zinian, LIU Junke. Preparation and properties of sodium alginaite cross-linked acrylate based multicomponent hydrogel[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [83] JIANG L, LIU P. Design of magnetic attapulgite/fly ash/poly(acrylic acid) ternary nanocomposite hydrogels and performance evaluation as selective adsorbent for Pb2+ ion[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2014, 2(7): 1785-1794. [84] HE C, MOU H, HOU W, et al. Drought-resistant and water-retaining tobermorite/starch composite hydrogel for the remediation of cadmium-contaminated soil[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2024, 255: 127534. [85] YUE X H, ZHANG F S, ZHANG C C, et al. Upcycling of blending waste plastics as zwitterionic hydrogel for simultaneous removal of cationic and anionic heavy metals from aqueous system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2022, 432: 128746. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.128746 [86] CHEN Y, LI L, LI Y, et al. Preparation of a double-network hydrogel based on wastepaper and its application in the treatment of wastewater containing copper(ii) and methylene blue[J]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(29): 18131-18143. [87] MAHMOUD M E, MOHAMED A K, SALAM M A. Self-decoration of N-doped graphene oxide 3-D hydrogel onto magnetic shrimp shell biochar for enhanced removal of hexavalent chromium[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 408: 124951. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124951 [88] MA J, LIU Y, ALI O, et al. Fast adsorption of heavy metal ions by waste cotton fabrics based double network hydrogel and influencing factors insight[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 1034-1042. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.041 [89] BI H, HUANG X, WU X, et al. Carbon microbelt aerogel prepared by waste paper: An efficient and recyclable sorbent for oils and organic solvents[J]. Small, 2014, 10(17): 3544-3550. doi: 10.1002/smll.201303413 [90] CHEN Y, LIU Y, LI Y, et al. Functional wastepaper-montmorillonite composite aerogel for Cd2+ adsorption[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(31): 38644-38653. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09907-6 -





 下载:
下载: