Preparation and performance testing of amidation modified acoustic matching layer for air coupling ultrasonic transducer
-
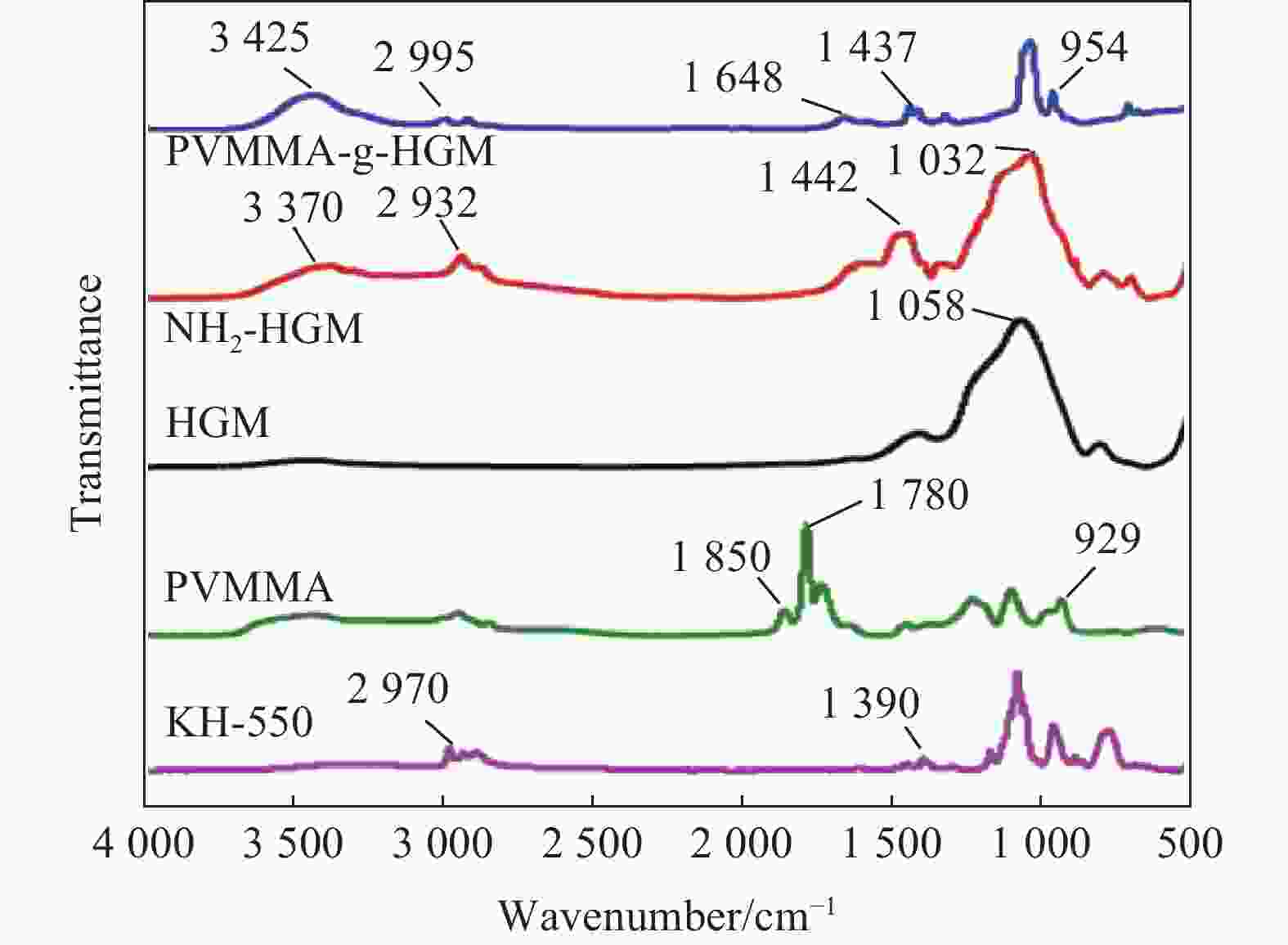
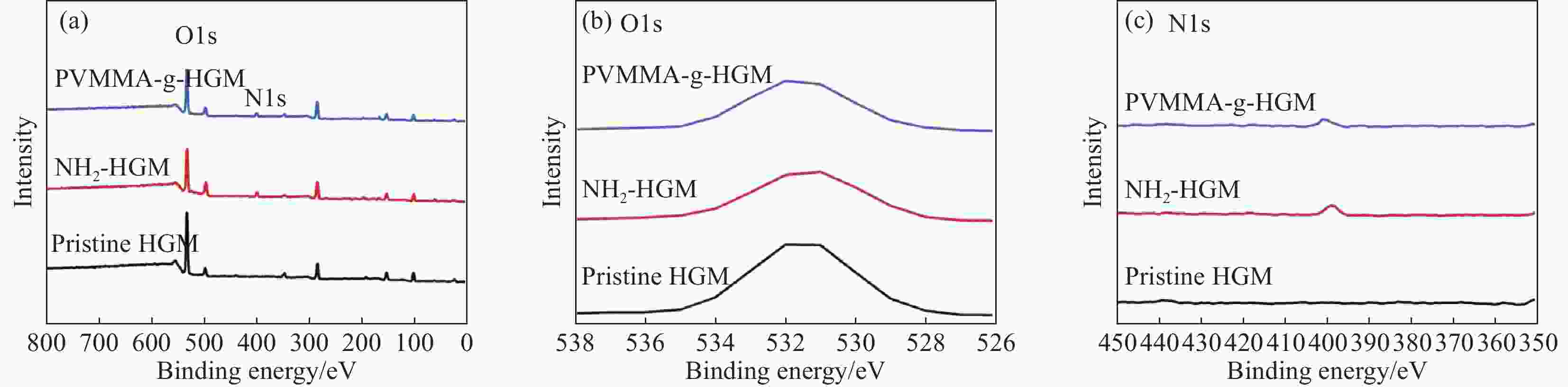
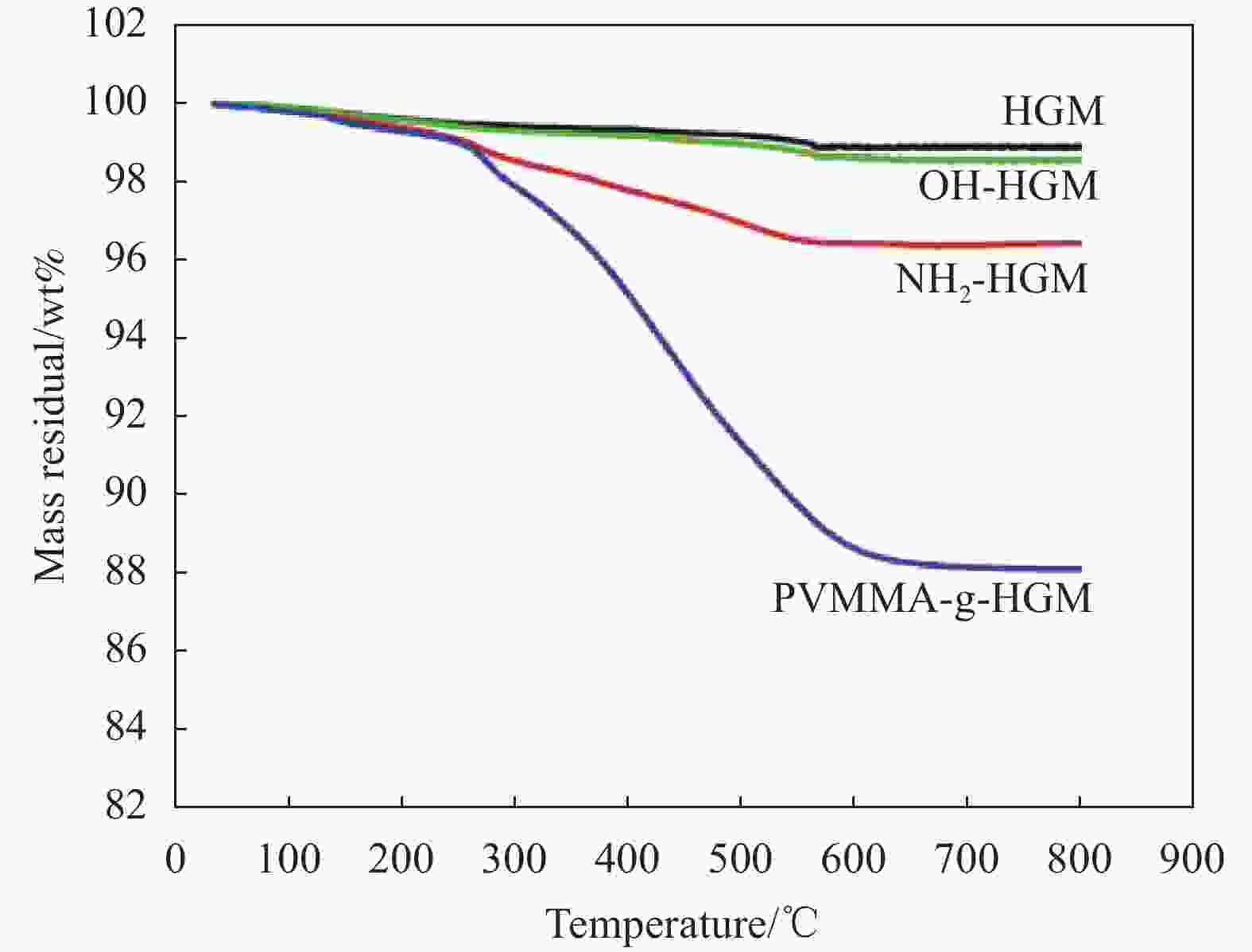
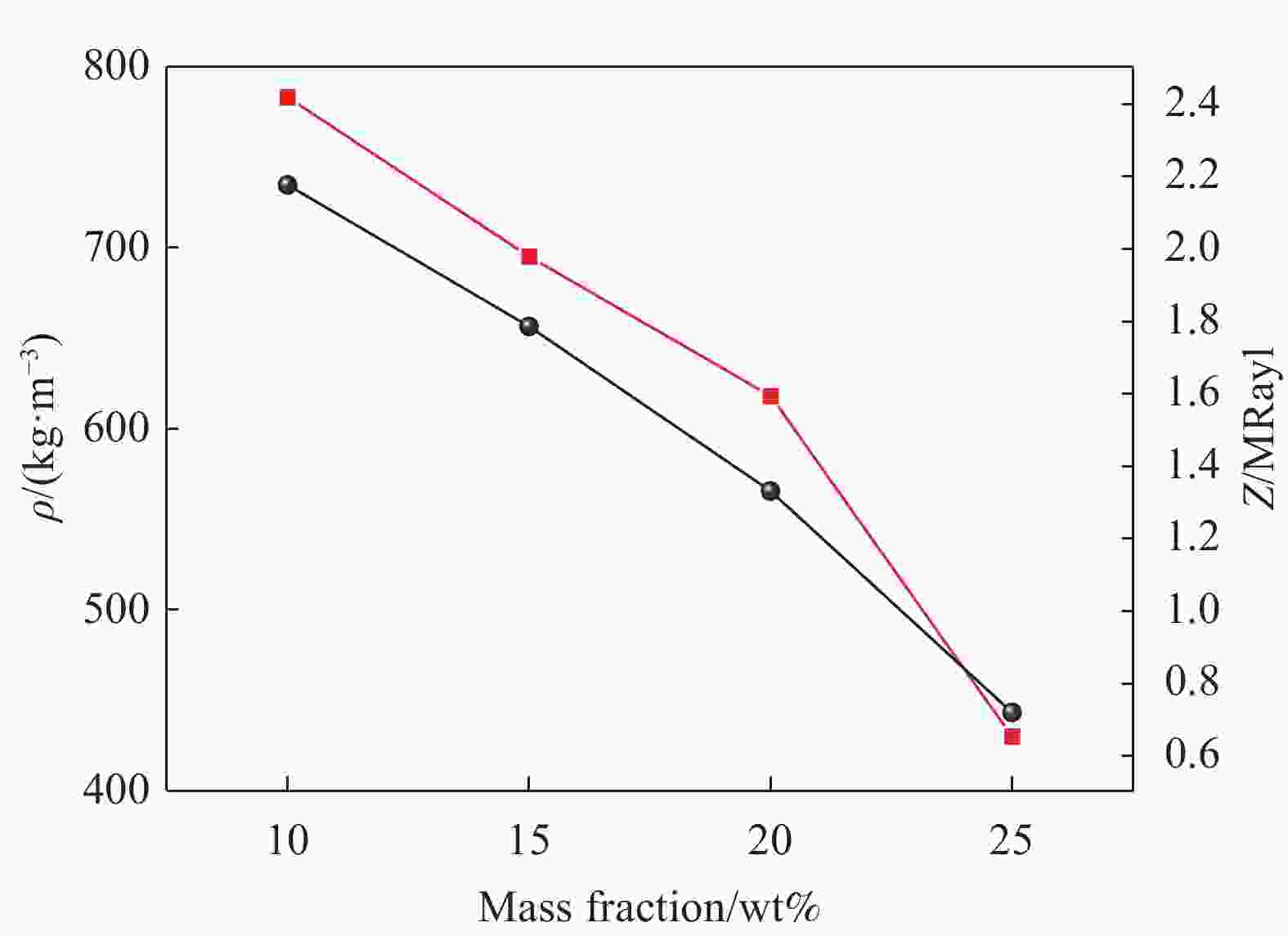
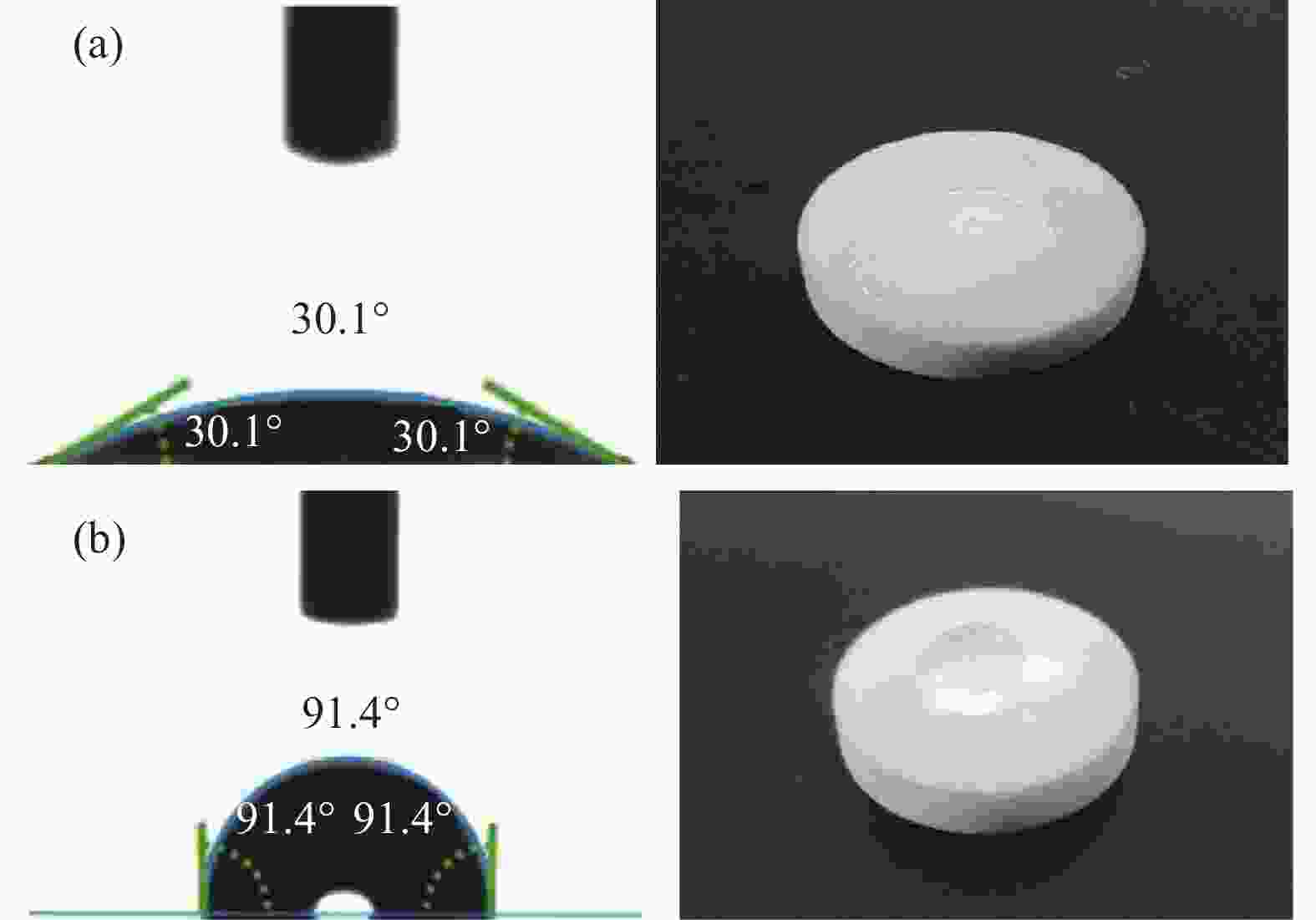
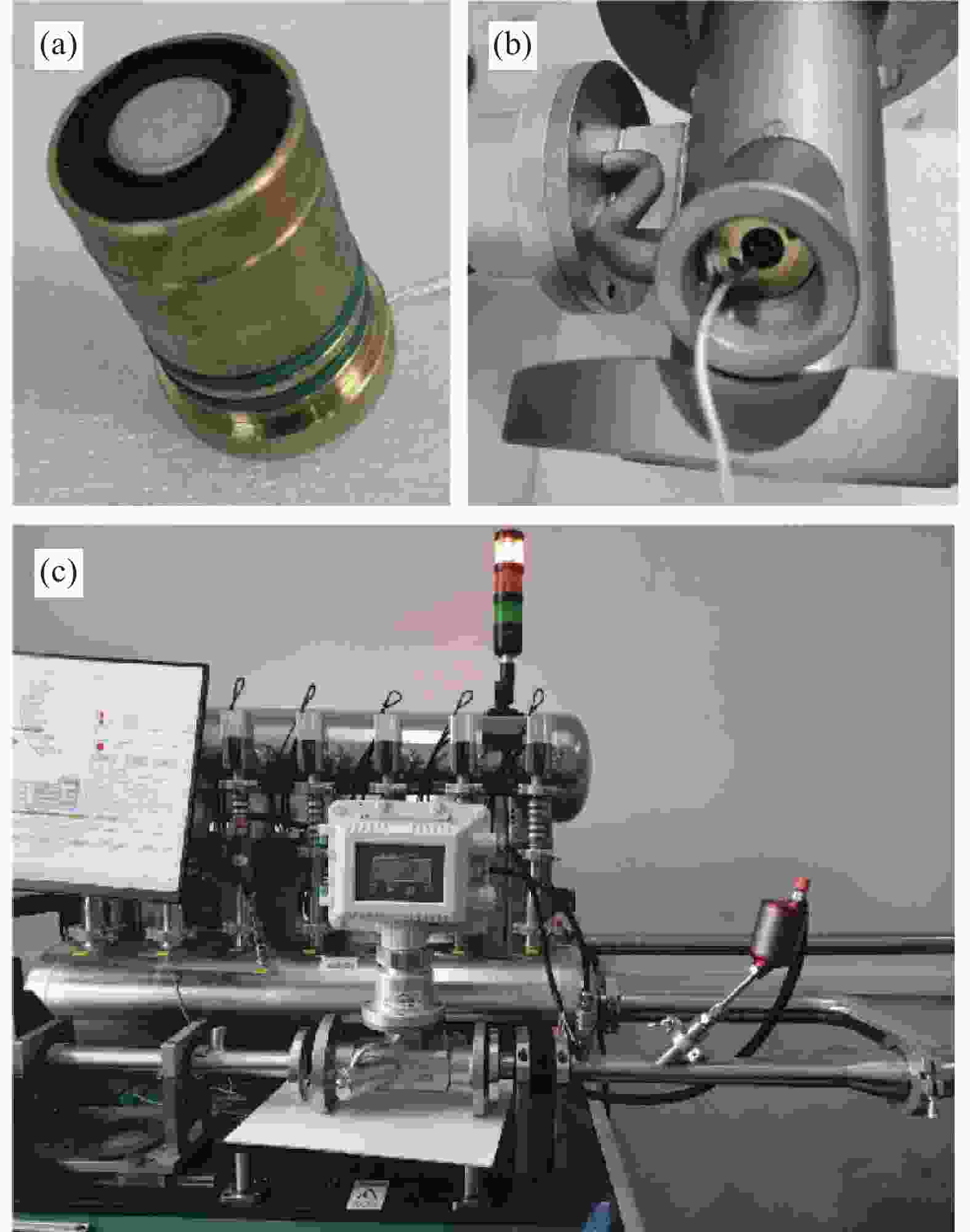
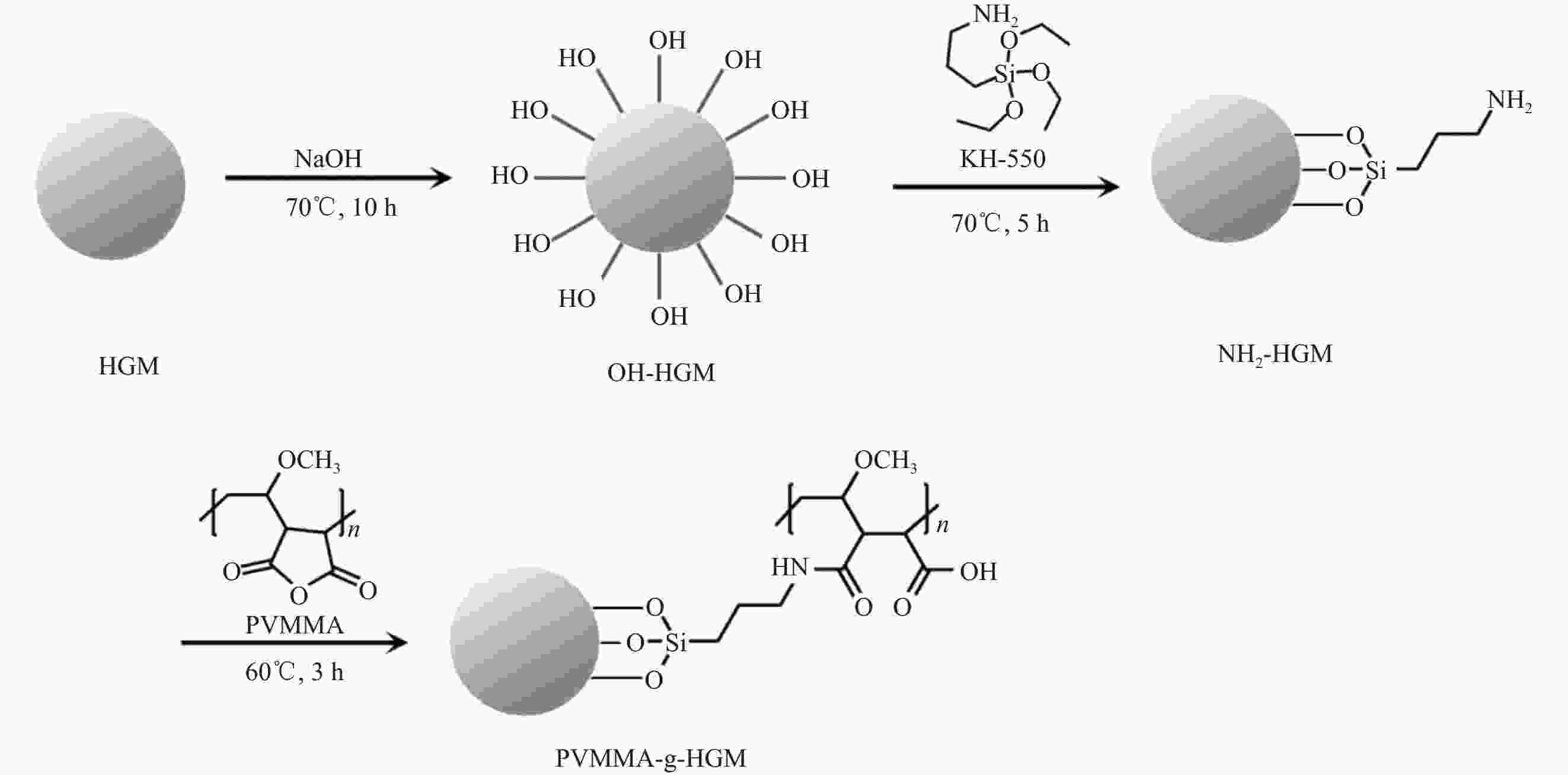
摘要: 基于空心玻璃微珠(HGM)/环氧树脂体系的声匹配层制备了高灵敏度的空耦超声波换能器。采用聚甲基乙烯基醚-马来酸酐共聚物(PVMMA)接枝到空心玻璃微珠表面(PVMMA-g-HGM),以提高低密度空心玻璃微珠在高密度环氧树脂基体中的分散性。结果表明:改性空心玻璃微珠/环氧树脂复合材料的致密度提升显著且无明显缺陷,具备了更好的声辐射性能,制备的空耦超声波换能器灵敏度达到4.88 V。此外,改进后超声波换能器装配的气体超声波流量计具备更好的流场适应性,相对误差绝对值低于1.0%。本文提出一种新的工艺以改进气体超声波流量计中超声换能器的性能。Abstract: A high-sensitivity air-coupled ultrasonic transducer with an acoustic matching layer based on epoxy resin/hollow glass microsphere (HGM) is investigated. In order to improve the dispersion of low-density HGM in high-density epoxy resin matrix, poly(methyl vinyl ether-alt-maleic anhydride) (PVMMA) was grafted onto the HGM surface (PVMMA-g-HGM). The morphology and surface chemical characteristics of modified HGM and HGM/epoxy resin composite were analyzed. An air-coupled ultrasonic transducer was fabricated with the improved matching layer, which achieved a peak-to-peak voltage of 4.88 V. In addition, the gas ultrasonic flowmeter equipped with the improved ultrasonic transducer had better flow field adaptability, and the relative error was less than 1.0%. This work is to propose a new technology to improve the performance of ultrasonic transducer in gas ultrasonic flowmeter.
-
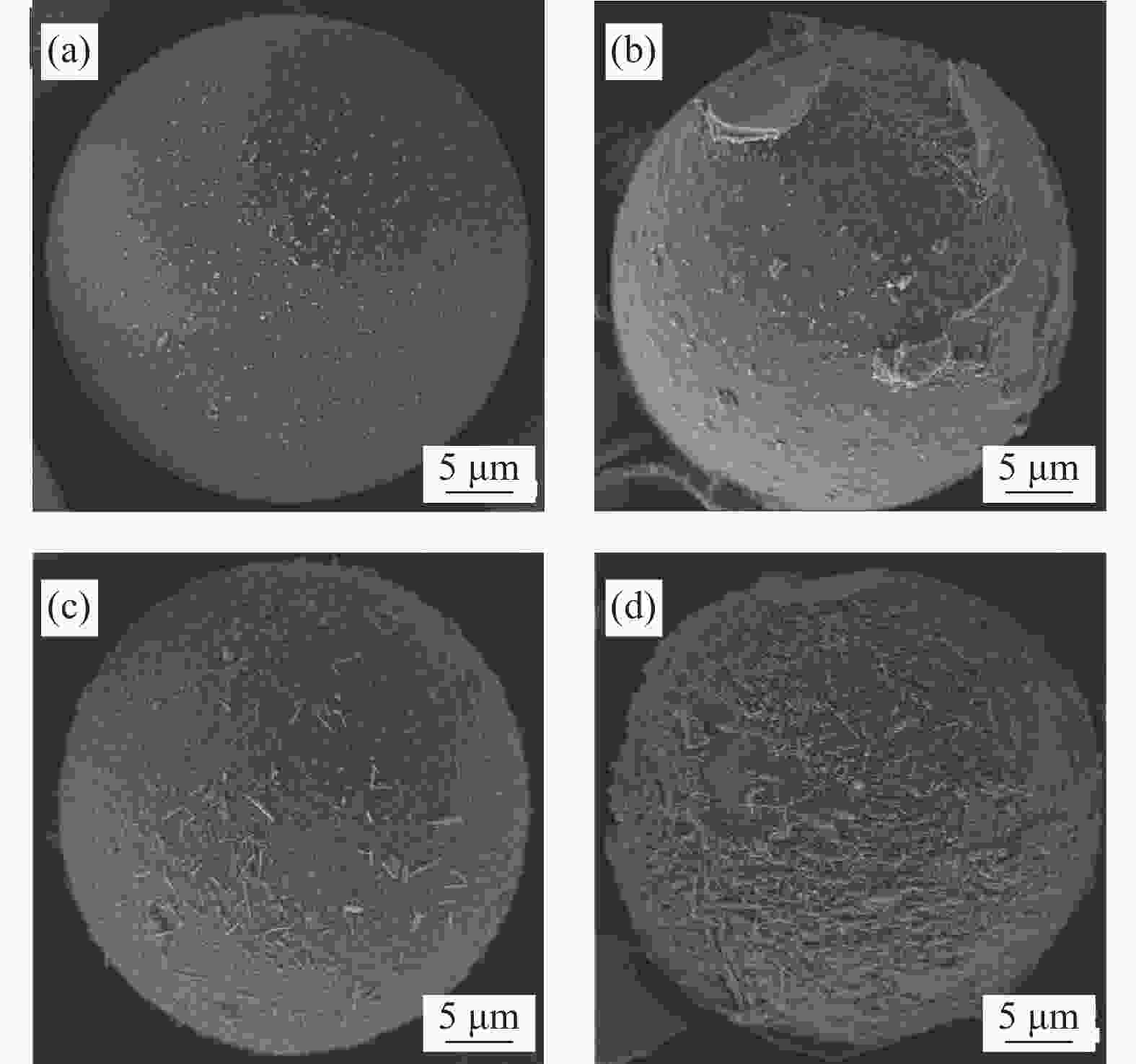
图 7 HGM/环氧树脂(EP)复合材料的表面形貌及SEM剖面图像:((a), (d)) 20wt%HGM/EP;((b), (e)) 20wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP;((c), (f)) 25wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP
Figure 7. Surface topography and cross-sectional SEM images of the fracture surface of HGM/epoxy resin (EP) composites: ((a), (d)) 20wt%HGM/EP; ((b), (e)) 20wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP; ((c), (f)) 25wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP
图 12 不同HGM/EP复合材料下超声波换能器的时域信号测试结果:(a) 20wt%HGM/EP;(b) 15wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP;(c) 20wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP;(d) 25wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP
Figure 12. Time-domain signal of ultrasonic transducers according to the different HGM/EP composites: (a) 20wt%HGM/EP;(b) 15wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP; (c) 20wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP; (d) 25wt%PVMMA-g-HGM/EP
-
[1] YIN X, WEN K, WU Y, et al. A machine learning-based surrogate model for the rapid control of piping flow: Application to a natural gas flowmeter calibration system[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2022, 98: 104384. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104384 [2] ABAD A R B, GHORBANI H, MOHAMADIAN N, et al. Robust hybrid machine learning algorithms for gas flow rates prediction through wellhead chokes in gas condensate fields[J]. Fuel, 2022, 308: 121872. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.121872 [3] FARZANEH-GORD M, RAHBARI H R. An intelligent approach for calculating natural gas compressibility factor and its application in ultrasonic flow meters[J]. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 76: 101833. doi: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2020.101833 [4] MOUSAVI S F, HASHEMABADI S H, JAMALI J. Calculation of geometric flow profile correction factor for ultrasonic flow meter using semi-3D simulation technique[J]. Ultrasonics, 2020, 106: 106165. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2020.106165 [5] YANG B, ZHANG Y, SHI L, et al. Optimize the rectifier structure to improve the accuracy of gas ultrasonic flowmeter under low flow conditions[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2023, 2458(1): 012031. [6] POP F, HERRERA B, RINALDI M. Lithium niobate piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers for high data-rate intrabody communication[J]. Nature Communications, 2022, 13(1): 1782. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29355-9 [7] LIU P, HU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Investigation of novel embedded piezoelectric ultrasonic transducers on crack and corrosion monitoring of steel bar[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 235: 117495. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117495 [8] SUN X H, MAN J J, CHEN D D, et al. Intelligent optimization of matching layers for piezoelectric ultrasonic transducer[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(12): 13107-13115. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3068041 [9] LI Z X, CHEN D D, FEI C L, et al. Optimization design of ultrasonic transducer with multimatching layer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 2021, 68(6): 2202-2211. doi: 10.1109/TUFFC.2021.3059671 [10] YANG X Y, FEI C L, LI D, et al. Multi-layer polymer-metal structures for acoustic impedance matching in high-frequency broadband ultrasonic transducers design[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2020, 160: 107123. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2019.107123 [11] CHEN D D, ZHAO J X, FEI C L, et al. Particle swarm optimization algorithm-based design method for ultrasonic transducers[J]. Micromachines, 2020, 11(8): 715. doi: 10.3390/mi11080715 [12] YANG X, LI Z X, FEI C L, et al. High frequency needle ultrasonic transducers based on Mn doped piezoelectric single crystal[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 832: 154951. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154951 [13] 王晓彧, 吴浩东, 公勋, 等. 多基元聚焦空气耦合超声换能器[J]. 应用声学, 2019, 38(3): 287-292.WANG Xiaoyu, WU Haodong, GONG Xun, et al. Multi-element focused air-coupled transducer[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2019, 38(3): 287-292(in Chinese). [14] WONG C M, CHAN S F, WU W C, et al. Tunable high acoustic impedance alumina epoxy composite matching for high frequency ultrasound transducer[J]. Ultrasonics, 2021, 116: 106506. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2021.106506 [15] LI Z, YANG D Q, LIU S L, et al. Broadband gradient impedance matching using an acoustic metamaterial for ultrasonic transducers[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 42863. doi: 10.1038/srep42863 [16] WANG X Y, GONG X, LI C C, et al. Low insertion loss air-coupled ultrasonic transducer with parallel laminated piezoelectric structure[J]. AIP Advances, 2020, 10(10): 105331. doi: 10.1063/5.0022598 [17] WU Q, CHEN Q Y, LIAN G X, et al. Investigation of an air-coupled transducer with a closed-cell material matching strategy and an optimization design considering the electrical input impedance[J]. Ultrasonics, 2021, 115: 106477. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2021.106477 [18] LIU S X, ZHANG Z, XU J L, et al. Optimizing dual-piezoelectric-layer ultrasonic transducer via systematic analysis[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2020, 315: 112336. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2020.112336 [19] SUN Y H, TAO J Y, GUO F F, et al. AZ31B magnesium alloy matching layer for Lens-focused piezoelectric transducer application[J]. Ultrasonics, 2023, 127: 106844. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2022.106844 [20] BAKHTIARI-NEJAD M, HAJJ M R, SHAHAB S. Dynamics of acoustic impedance matching layers in contactless ultrasonic power transfer systems[J]. Smart Materials and Structures, 2020, 29(3): 035037. doi: 10.1088/1361-665X/ab6fe5 [21] QIAO Y J, LI Q W, LI Q, et al. Improving thermal insulation properties of lightweight epoxy resin matrix composites with millimeter-sized hollow glass microspheres/epoxy hollow spheres[J]. Energy and Buildings, 2022, 277: 112546. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.112546 [22] DEWANGAN H C, THAKUR M, PATEL B, et al. Dynamic deflection responses of glass/epoxy hybrid composite structure filled with hollow-glass microbeads[J]. The European Physical Journal Plus, 2021, 136(7): 722. doi: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-01710-7 [23] YU Z B, DU X M, ZHU P L, et al. Surface modified hollow glass microspheres-epoxy composites with enhanced thermal insulation and reduced dielectric constant[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 32: 104046. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.104046 [24] ALTAY P, UÇAR N. Improvement of insulation properties of glass fiber fabric/epoxy composites modified by polymeric and inorganic fillers[J]. Polymer Composites, 2022, 43(1): 225-238. [25] 王奔, 于晓启, 赵国旗, 等. 微胶囊层间增韧碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料力学性能的超声导波评价[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(3): 788-796. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200619.002WANG Ben, YU Xiaoqi, ZHAO Guoqi, et al. Ultrasonic guided wave-based evaluation for mechanical properties of interlaminar toughening carbon fiber/epoxy composites with microcapsules[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(3): 788-796(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200619.002 [26] LI R, WANG P, ZHANG P, et al. Surface modification of hollow glass microsphere and its marine-adaptive composites with epoxy resin[J]. Advanced Composites Letters, 2020, 29: 2633366X20974682. [27] 安乐, 赵文哲, 金宸宇. 工业用环氧树脂及其复合材料的闭环回收再制造[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(5): 2575-2586.AN Le, ZHAO Wenzhe, JIN Chenyu. Closed-loop recycling and re-manufacturing of engineering epoxy and its composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(5): 2575-2586(in Chinese). [28] ZHANG X L, LIU M, CHEN Y, et al. Epoxy resin/hollow glass microspheres composite materials with low dielectric constant and excellent mechanical performance[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2022, 139(33): e52787. doi: 10.1002/app.52787 -





 下载:
下载: