Synthesis of thermoreversible polyurethane based on D-A reaction and preparation and properties of its carbon fiber composites
-
摘要: 以二异氰酸酯(MDI)、聚醚多元醇(PTMG)和2, 5-呋喃二甲醇合成了含有呋喃结构的线型聚氨酯,与双马来酰亚胺基二苯甲烷(BMI)通过Diels-Alder反应制备了热可逆聚氨酯固化物,并制备了碳纤维单向复合材料。通过高温红外和DSC分析了聚氨酯树脂的热可逆行为,研究了树脂的溶解性、熔融再加工性及力学性能,分析了碳纤维复合材料的力学性能和动态机械性能。结果表明:热可逆聚氨酯固化物在热循环中有反复断键-交联行为,160℃左右可完成逆反应;采用高温溶剂溶解法或热熔法均可以进行再加工,再加工3次后仍能保持原有力学性能;碳纤维单向复合材料的层间剪切呈二次失效特点,层间剪切强度为34.85 MPa,玻璃化转变温度为93.73℃。Abstract: The line type polyurethane containing furan rings was prepared by diisocyanate (MDI), polyether polyols (PTMG) and 2, 5-furandimethanol. The cured thermoreversible polyurethane was synthesized by Diels-Alder reaction between bismaleimide (BMI) and the line type polyurethane containing furan rings, and the unidirectional carbon fiber composite was prepared. The thermal reversible behavior of the cured thermoreversible polyurethane was analyzed through high-temperature FTIR and DSC. The solubility, melt reprocessing ability and mechanical properties of the cured thermoreversible polyurethane were studied, the mechanical properties and dynamic mechanical properties of carbon fiber composites were also analyzed. The results show that the cured thermoreversible polyurethane has a repeated behavior of bond breaking and cross-linking during thermal cycling, and the reversible reaction is completed about 160℃. Both high-temperature dissolution process and hot-melt process can be used for reprocessing. After being reprocessed three times, the original mechanical properties of the cured thermoreversible polyurethane can still be maintained. The interlaminar shear of unidirectional carbon fiber composites was characterized by secondary failure, and the interlaminar shear strength is 34.85 MPa. The glass transition temperature of thermoreversible polyurethane is 93.73℃.
-
Keywords:
- thermoreversible polyurethane /
- D-A reaction /
- composite /
- recycling /
- secondary failure
-
分离过程在工业生产中占据重要地位,是化学工业的基础,传统的分离技术,如精馏、蒸发等需要消耗大量能源,占到工业总能耗的40%~70%[1]。新兴的膜分离技术由于具有低能耗、占地面积小、分离精度高、无二次污染等优势被认为是替代传统分离技术的新秀。膜材料是膜技术的核心,目前已经成功商业化的大多是有机聚合物膜,但其有渗透率-选择性权衡的限制及适用环境有限等问题。为了解决这一问题,开发和探索了碳分子筛、陶瓷及各种纳米材料及其与聚合物的复合膜[2]。完美的膜结构和高性能的膜材料一直是膜分离技术研究的核心,膜材料的结构组成和理化性质将直接影响膜分离技术的效率和经济性[3]。
近几年来,随着现代膜分离技术的不断发展,涌现出大批优异的膜材料,其中有众多纳米材料被开发出来应用于膜分离中,如氧化石墨烯(GO)[4-5]、二维氮化碳(g-C3N4)[6-7]、二维金属有机框架(MOFs)[8]、沸石分子筛(Zeolites)[9]、二维过渡金属硫化物(TMDs)[10]、二维氮化硼(BN)[11]和二维过渡金属碳/氮化物(MXene)[12]等。由于MXene具有类石墨烯结构,且具有出色的亲水性、柔韧性、热稳定性、抗菌性和丰富的表面末端基团(—OH、—O和—F等)等特性,推动了其在膜分离领域的开发和研究。
近年来,MXene纳滤膜取得了一系列重要进展,一些研究人员采用不同的纳米材料与MXene复合,调控层状结构的间距和排列方式,可以有效地提高复合膜的通量和分离效率[13-15]。此外,为了提升MXene复合纳滤膜的抗污染能力,研究人员通过表面改性、添加功能化纳米材料或设计新型支撑材料等方法,可以有效地减少污染物对复合膜的附着和堵塞,从而延长其使用寿命并提高稳定性[16-18]。虽然近年来已有许多综述聚焦于MXene基分离膜,但本文侧重描述MXene层状纳滤膜在纳滤领域的应用,特别强调了关于MXene层状复合纳滤膜的设计策略,同时还对其分离机制和在海水淡化、废水处理等领域应用的最新研究进展进行了总结(图1)。本文归纳总结了MXene层状复合纳滤膜面临的挑战,并概述了未来的发展方向,旨在有助于设计出高质量的MXene层状纳滤膜。
1. MXene材料
如图2所示,MXene材料的化学通式可以表示为Mn+1XnTx(n=1、2、3),M代表过渡金属,X代表碳或氮,T则代表其表面附着的活性基团(如—OH、—O和—F等)。另外,根据原子层数量和排列方式的不同,MXene可以分为M2XTx、M3X2Tx和M4X3Tx,分别对应3、5和7层原子层排列结构,例如Ti2CTx、Ti3C2Tx和Ti4N3Tx[19]。到目前为止已经报道了超过30个种类的MXene。其中研究最多的是Ti3C2Tx和Ti2CTx。通过选择不同的MAX (三元层状陶瓷材料)前驱体刻蚀及不同的刻蚀方法,能够制备出理化性质不同的MXene,从而构建出具有不同性能的膜[20]。
2. MXene层状纳滤膜的分类
作为二维材料中的一员,MXene材料被广泛应用于构筑高性能的分离膜。当前MXene纳滤膜的研究主要聚焦在MXene层状膜上,一般是通过真空或压力辅助过滤制备而成,其是MXene纳滤膜中研究最多的膜类型[20]。MXene层状膜是由相邻MXene纳米片堆叠而成,片层间的纳米级通道提供传质分离途径。因此,构建高度规则、致密且稳定的层间纳米通道是制备出高渗透选择性的MXene层状膜的前提[21]。MXene层状膜的类别主要可分为:(1)单一组分MXene层状纳滤膜;(2) MXene层状复合纳滤膜。复合方式一般是通过有机分子交联、不同维度纳米材料插层等方法制备出高渗透选择性的MXene层状膜。
2.1 单一组分MXene层状纳滤膜
单一组分MXene层状纳滤膜由MXene材料堆叠构建而成,常用于分离小分子有机物和离子。Han等[22]在聚醚砜(PES)超滤膜上通过简单的真空过滤方法制备出MXene层状膜,其具有115 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的渗透通量和对刚果红(CR)染料达92.3%的截留率。Li等[23]报道了一种由高横向尺寸的MXene纳米片(2~4 μm)组装的MXene层状膜,表现出优异的抗生素截留性能,其渗透通量比大多数具有类似抗生素分离作用的聚合物纳滤膜至少高一个数量级。Xiang等[24]通过控制离心的转速和时间,得到不同横向尺寸的MXene纳米片。由此制备出的不同横向尺寸的MXene层状膜在亚甲基蓝(MeB)染料的截留实验中显示,纳米片的横向尺寸越大,制备出的MXene膜的截留效果也越好。这些研究都证实了制备得到的MXene纳米片的横向尺寸对MXene层状膜分离性能的巨大影响,为高性能的MXene层状膜的设计提供了新的思路。由于MXene纳米片表面存在丰富的羟基,相邻纳米片之间的静电相互作用会导致纳米片无序堆叠,从而形成无序的层间纳米通道,影响膜的分离性能[21]。针对这一问题,Sun等[25]成功开发了一种厚度~100 nm的超薄MXene衍生膜,通过煅烧使MXene膜层内发生自交联去官能团化(—OH)反应,以此来提高MXene膜的分离性能。其中采用400℃的煅烧温度制备出的MXene-T400膜,对Na2SO4的最大脱盐率为75.9%,相应的渗透通量达3.5 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。这种简单的加热自交联去官能团化(—OH)的方法是提高MXene层状膜选择性的有效策略。
2.2 MXene层状复合纳滤膜
单一组分MXene层状纳滤膜存在纳米片堆叠严重及不规则的层间纳米通道等问题,为进一步提升膜的渗透选择性,研究人员利用MXene膜的可扩展性和可调性,在相邻的MXene纳米片之间嵌入不同尺寸的物质,如诸多有机分子[26-28]、零维颗粒[29-30]、一维纳米材料[31-34]和二维纳米材料[35-37]。这些层间复合材料的类型、尺寸、形貌对复合膜的形貌、孔隙率和机械强度等特性起着重要的作用[38]。因此,深入了解层间复合材料的物化性质对制备高渗透选择性的复合膜有重要意义。
2.2.1 层间有机分子交联
如图3(a)所示,Luo等[26]使用4种氨基酸(甘氨酸(Gly)、L-半胱氨酸(L-Cys)、L-谷氨酸(L-Glu)、L-赖氨酸(L-Lys))与MXene交联,其中由甘氨酸交联制备出Gly-3@MX-3膜表现出较高的盐截留性能和渗透通量,其对Na2SO4的截留率达到86.28%,相应的渗透通量为7.5 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。Tao等[27]使用MXene纳米片与羧甲基-β-环糊精分子交联,通过真空过滤的方法,制备出的MXene膜具有超过366 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的水渗透通量和对亚甲基蓝(MeB)、碱性红2 (BR2)、龙胆紫(CV)、罗丹明B (RhB)和甲基蓝(MB)染料超过97%的截留率。Zhang等[28]通过将MXene纳米片和带正电的聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)有机大分子交联,制备出MXene-PEI层状膜(图3(b)),其具有137.77 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的渗透通量和对刚果红(CR)染料高达99%的截留率。由此可见,将MXene纳米片与一些有机分子进行交联反应,能制备出具有高通量和优异截留效果的MXene复合纳滤膜。
2.2.2 零维层间复合材料
零维层间复合材料通常以零维纳米颗粒形式存在,零维颗粒的插层能有效扩展和稳定MXene层状膜的层间纳米通道,增强传质,提高膜的渗透性和选择性。Pandey等[29]利用MXene纳米片的还原性,将AgNO3溶液与MXene纳米片混合,成功地将Ag+离子还原成Ag零维颗粒并附着在MXene纳米片的层间,通过真空过滤制备出Ag@MXene膜。该膜表现出对甲基绿(MG)染料达92.32%的截留率及相应的354.29 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的优异渗透通量。此外该膜还兼具优异的抗菌性能。Long等[30]使用带正电荷的Al2O3零维颗粒,通过静电相互作用,插层在MXene膜的层间,如图4(a)所示。其中MXene与Al2O3零维颗粒质量比为1∶1的MXene/Al2O3复合膜表现出88.8 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的优异渗透通量和对罗丹明B (RhB)染料高达99.8%的截留率。因此,零维颗粒的插层是一种制备高性能的MXene层状膜的有效途径。
2.2.3 一维层间复合材料
一维纳米材料以纤维结构为特征,其内壁的长度与直径比呈现独特的特点。将这些一维纳米材料引入MXene膜中能有效阻止MXene纳米片之间的团聚现象并扩大层间距。尤其是一维碳纳米管具有独特的机械强度、出色的柔韧性,最重要的是,其密闭的传质通道允许水分子快速流动,从而能制备出高性能的MXene复合膜。Ding等[31]报道了一种由一维碳纳米管(CNTs)嵌入MXene膜层间,形成具有新型梭形通道的CNTs-MXene层状膜,表现出高的染料分子截留和超高的水渗透性。其对龙胆紫(CV)和玫瑰红(RB)染料的截留率分别为100%和97.3%,同时表现出优异的渗透通量,约为
1270 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。同时在水溶液中浸泡30 h后仍保持出色的分离性能,表现出良好的稳定性。如图4(b)所示,Sun等[32]报道了一种在MXene膜层间嵌入一维碳纳米管(CNTs),并通过真空过滤的方法在聚多巴胺(PDA)改性的Al2O3膜上制备出初始的MXene-CNT膜(PMCNM),随后通过热交联反应制备出MXene-CNT膜(MCNM)。该膜在错流过滤下对刚果红(CR)染料的截留率高达100%,相应的渗透通量为10.8 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1,且在50 h的错流过滤过程中表现出良好的稳定性。此外,Zhang等[33]也报道了一种由一维凹凸棒嵌入MXene膜层间的凹凸棒/MXene层状膜,在死端过滤下对亚甲基蓝(MeB)染料的截留率达90.67%,相应的水的渗透通量为46.51 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。2.2.4 二维层间复合材料
二维纳米材料因其表面积大、出色的机械强度和柔韧性及通过表面功能化可改变的众多表面位点而备受关注。以氧化石墨烯(GO)为代表的二维材料已被广泛用于分离膜制备[34]。将二维纳米材料(如GO)与MXene纳米片进行复合,不仅能有效地调控MXene膜的层间距,而且可发挥出两种二维材料的不同优势,从而制备出具有优异选择性和渗透性的MXene层状膜。Liu等[35]将一定质量比的GO纳米片和MXene纳米片混合均匀,通过真空过滤的方式制备出GO/MXene层状膜,其中GO与MXene质量比为1∶4的GO/MXene膜表现出对亚甲基蓝(MeB)和龙胆紫(CV)染料接近100%的截留率,同时具有71.9 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的优异水渗透通量,是纯GO膜的10倍。Gong等[37]通过静电自组装制备了不同比例的MXene/共价有机框架材料(COF)复合膜。其中COF与MXene质量比为1∶4的复合膜在甲基绿(MG)、乙基紫(EVT)、碱性品红(FB)、龙胆紫(CV)和亚甲基蓝(MeB)溶液中的渗透通量分别为217.6、185.3、203.9、169.3和190.7 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1,其对应截留率分别为99.7%、100%、100%、99.3%和99.8%。Wang等[37]通过将MoS2纳米片与使用木质素磺酸钠修饰的MXene纳米片进行复合,制备出的复合膜对刚果红(CR)和罗丹明B (RhB)染料的截留率分别为93%和99%。
目前将纳米材料与MXene材料复合,其层间中的位置都是随机的,通过功能化改性和膜制备方法调控,可控制纳米片分布的位置,实现层间有序排列。如图4(c)所示,本课题组通过使用乙酸铵(AA)修饰后的MXene (AA-Ti3C2Tx)与氧化石墨烯复合,通过慢速沉积法制备出了高渗透选择性的GO/AA-Ti3C2Tx复合纳滤膜[39]。在慢速沉积过程中,AA-Ti3C2Tx在GO层间能规则排列,形成有序的纳米孔道。该膜在错流过滤下对刚果红(CR)染料有着高达99.1%的截留率,与之相对应的水渗透通量为115.5 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。此外对于其他的染料,如活性艳红(X-3 B)、甲基蓝(MB)和伊文思蓝(EB)等染料的截留率分别达到84.7%、99.2%和99.9%。
本节讨论了几种关于MXene层状膜的设计策略,通过自交联、有机分子交联及不同维度纳米材料插层等方法来设计和调控MXene层状膜的传输通道。尽管制备和精确控制层间复合材料的尺寸仍然具有挑战性,但是通过优化层间复合纳米材料的尺寸参数,可有效提升复合膜的传质效率。
3. MXene层状纳滤膜的分离机制
目前,关于MXene层状纳滤膜的分离机制大致分为3种:(1)孔径筛分;(2)静电排斥;(3)吸附作用,如图5所示。
3.1 孔径筛分
MXene层状纳滤膜的显著特征之一就是由高纵横比MXene纳米片构建的层间纳米通道,这些纳米通道是由纳米片之间的内部间距及纳米片边缘之间的空隙形成[20]。孔径筛分是指制备出的膜在过滤的过程中可以截留比膜内层间纳米通道尺寸大的物质(如染料、盐等),而尺寸较小的物质(如水)则能从膜内渗透出去[40-41]。Sun等[25]通过在不同的煅烧温度下,制备出有着不同层间间距的MXene膜。实验结果显示,随着膜的层间间距变小,膜对盐的截留率也随之提高。表明了孔径筛分在MXene纳滤膜的分离过程中起到至关重要的作用。
3.2 静电排斥
由于MXene纳米片自身具有强负电荷的特性,因此可以通过Donnan效应实现对带电离子和染料的有效分离,具体来说,就是与MXene膜具有相同电荷的离子通过静电相互作用被膜排斥,同时为了保持溶液的电中性,具有相反电荷的离子也会被阻拦在膜的表面[38]。Zhang等[42]将聚丙烯酸(PAA)有机大分子与MXene纳米片交联,通过真空过滤的方法制备出PAA/MXene膜,测得PAA/MXene膜带负电荷。其实验结果显示,该膜对带负电的刚果红(CR)染料的截留率达95%,而对中性分子的截留却不理想,表明静电排斥作用对其选择性的影响。因此静电排斥对提高MXene纳滤膜的选择性起到重要的作用。
3.3 吸附作用
由于MXene材料具有高比表面积、可调的表面化学性质、独特的层状结构和表面丰富的官能团等特性,因此MXene材料被认为是很有前途的吸附剂。因此在过滤过程中,溶液中的重金属、染料等溶质在经过MXene纳滤膜层间时也会被其表面官能团吸附从而达到良好的去除效果[43]。
4. MXene层状纳滤膜的抗溶胀策略
MXene纳米片已经被证实了能够构建出具有高截留和高通量的纳滤膜。然而,MXene层状膜在过滤的过程中会吸收大量水分子,导致膜的层间距增加,即类似于石墨烯膜的溶胀问题[38]。这种膜溶胀的问题会导致层间距离增加,膜分离性能下降。目前,针对这一问题,能通过自交联、有机分子交联及不同维度纳米材料插层等方法,来稳定MXene膜在过滤过程中的层间距,从而避免溶胀问题并保持稳定的分离性能[44]。Sun等[25]使用自交联的方法制备MXene膜,其中在400℃下制备出的MXene膜能有效地将层间距控制在0.268 nm,并在长达100 h的错流过滤下中仍保持优异的分离性能且不会产生缺陷,显示出优异的抗溶胀性能。如图6(a)所示,Zhang等[45]将葫芦[5]脲与MXene纳米片铆接,以此来稳定和控制MXene膜的层间距,制备出的MXene层状膜在干湿状态下层间距的变化在0.05 nm左右,同时该膜在30个循环过滤中仍保持稳定的分离性能,显示出优异的抗溶胀性和可重复使用性。如图6(b)所示,Zhang等[46]通过插入一维的羧化纤维素纳米纤维(CNFs)来有效的稳定MXene膜的层间结构,并使用真空过滤的方法在聚醚砜(PES)膜上沉积以制备出MXene纳滤(NF)膜,其在干态下的层间距为0.4 nm,而在湿态下层间距为0.47 nm,仅变化0.07 nm,远远低于单一MXene膜的层间距在干湿状态下0.29 nm的变化幅度,同时该膜在长达76 h的错流过滤中,水渗透通量和染料截留率都没有明显变化,显示出其优秀的稳定性和抗溶胀性能。Sun等[32]通过自交联反应制备出MXene-CNT膜,其在干湿状态下的层间距变化在0.13 nm左右,同时在50 h的长期错流过滤中仍保持优异的渗透选择性,表现出优异的抗溶胀性,这种一维纳米材料复合和热交联的共同使用策略,为开发具有良好抗溶胀性能的MXene层状膜提供了新途径。通过不同的方法合理设计出具有稳定层间距的MXene层状膜,提高其在运行过程中的抗溶胀性能和稳定性,对推进MXene层状纳滤膜的工业化应用具有非常重要的作用。
5. MXene层状纳滤膜的应用
MXene材料有着诸多优异的特性,被广泛应用于膜分离的研究中。当前,MXene层状纳滤膜主要集中在海水淡化和废水处理等领域的应用,如表1所示。
表 1 MXene基纳滤膜的应用Table 1. Application of MXene-based nanofiltration membraneApplication Membrane Design strategy Permeance/
(L·m−2·h−1·bar−1)Rejection Ref. Seawater
desalinationMXene-T400 Self-crosslinking 3.5 75.9% for Na2SO4 [25] Gly-3@MX-3 Glycine crosslinking 7.5 86.28% for Na2SO4 [26] PEI/MXene Polyethylenimine crosslinking 9 82% for MgCl2 [47] HPEI-AgNP@Ti3C2Tx Hyperbranched polyethylenimine crosslinking+Silver zero-dimensional
particle composite24.55 84.15% for MgCl2 [48] MXene – ~59 ~70% for Na2SO4 [49] GO-MXene Graphene oxide composite+Self-crosslinking ~0.2 ~95% for MgCl2 [50] Wastewater
treatmentMXene/CM-β-CD Carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin crosslinking 431.37 99.7% for methylene blue [27] MXene-PEI Polyethylenimine crosslinking 137.77 99% for Congo red [28] Ag@MXene Silver zero-dimensional
particle composite354.29 92.32% for methyl green [29] MXene/Al2O3 Al2O3 zero-dimensional
particle composite88.8 99.8% for rhodamine B [30] CNTs-MXene Carbon nanotubes composite 1270 100% for crystal violet [31] GO/MXene Graphene oxide composite 71.9 ~100% for methylene blue [35] MoS2@LS-MXene Sodium lignosulfonate modified+
MoS2 composite77 93% for Congo red [37] GO/AA-Ti3C2Tx Ammonium acetate modification+
graphene oxide composite115.5 99.1% for Congo red [39] PEI-MXene Polyethylenimine crosslinking 441.3 99.82% for Congo red [54] MXene Fe(OH)3 zero-dimensional particle composite+HCl treatment 1084 90% for Evans blue [55] Ti3C2Tx-EDA Ethylenediamine crosslinking 20 93.2%-99.8% for Mn2+, Zn2+, Cd2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+ [56] Notes:MXene-T400—MXene-temperature-400℃; Gly-3@MX-3—Glycine-3@MXene-3; PEI/MXene—Polyethylenimine/MXene; HPEI-AgNP@Ti3C2Tx—Hyperbranched polyethylenimine-silver nanoparticle@Ti3C2Tx; GO-MXene—Graphene oxide-MXene; MXene/CM-β-CD—MXene/carboxymethyl-β-cyclodextrin; MXene-PEI—MXene-polyethylenimine; CNTs-MXene—Carbon nanotubes-MXene; GO/MXene—Graphene oxide/MXene; MoS2@LS-MXene—MoS2@sodium lignosulfonate-MXene; GO/AA-Ti3C2Tx—Graphene oxide/ammonium acetate-Ti3C2Tx; PEI-MXene—Polyethylenimine-MXene; Ti3C2Tx-EDA—Ti3C2Tx-thylenediamine. 5.1 海水淡化
目前水资源短缺严重,海水淡化是实现水资源增量的技术之一,一直受到广泛关注。其中设计高性能的膜以提高海水淡化效率是研究的热点。如图7(a)所示,Meng等[47]通过将聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)涂覆在MXene膜上,制备出了一种带正电的MXene复合膜,其具有9 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的渗透通量和对MgCl2约为82%的截留率。Li等[48]采用银零维颗粒复合和超支化聚乙烯亚胺(HPEI)交联相结合的策略,制备出的HPEI-AgNP@Ti3C2Tx MXene膜具有24.55 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的水渗透通量和对MgSO4达84.15%的截留率。同时该膜在长期的纳滤实验中仍保持优异的分离性能,具有良好的抗溶胀性能和稳定性。Liu等[49]报道了一种负载在聚合物中空纤维上的MXene层状膜,如图7(b)所示。制得的~90 nm厚的MXene层状膜具有纳滤脱盐性能,对Na2SO4的截留率为~70%,渗透通量为~59 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。Tiwary等[50]报道了一种在120℃下热交联制得的GO-MXene复合膜,该膜对0.00525 mol/L的MgCl2溶液的截留率为~95%,表现出了较好的截留效果。以上几项研究证明了基于MXene的层状纳滤膜在海水淡化方面的潜力。
5.2 废水处理
Xing等[51]将带正电的壳聚糖(CTS)和MXene纳米片混合,制备出CTS-MXene膜,利用壳聚糖和MXene纳米片之间的强相互作用力,克服膜溶胀的问题,使CTS-MXene膜具有0.433 nm的固定层间距,该膜对刚果红(CR)染料的截留率为99%,渗透通量达178.82 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。刘婷等[52]将二维材料MoS2插层到MXene膜的层间,制备出MXene/MoS2复合膜,同时使用FeCl3对MXene/MoS2复合膜进行轻微氧化,其中质量比为9.8∶0.2的膜对考马斯亮蓝(CBB)染料的截留率高达99.2%,同时还表现出良好的稳定性。如图8所示,Qiu等[53]通过使用单宁酸(TA)与MXene纳米片交联制得TA-MXene膜,随后将Fe3+离子插入TA-MXene膜中。该膜对阿尔新蓝8GX (AB8GX)、甲基蓝(MB)、刚果红(CR)、酸性品红(AF)、铬黑T (CBT)、甲基橙(MO)以及亚甲基蓝(MeB)染料具有较好的截留效果,其中对刚果红(CR)染料高达98.8%的截留率和90.5 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1的渗透通量。相较于纯MXene膜,该膜在水溶液中表现出长期的稳定性,为MXene膜的设计提供了新方案。Xing等[54]报道了一种PEI-MXene膜,通过使用聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)大分子与MXene纳米片交联,制备出的PEI-MXene膜的层间间距能够调控到0.415~0.452 nm。其中,PEI与MXene质量比为1∶1的PEI-MXene膜对阿尔新蓝8GX (AB8GX)、甲基橙(MO)、直接红80 (DR80)和刚果红(CR)等染料均表现出优异的截留效果,截留率分别为99.3%、99.9%和99.82%,渗透通量分别为282、266.8和441.3 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1,且在720 min的过滤过程中,染料的截留率仍保持在较高水平(>99%),显示出优异的长期稳定性和抗溶胀性能。Ding等[55]使用带正电的Fe(OH)3纳米颗粒与MXene纳米片复合,随后经真空过滤和盐酸溶液(HCl)处理以除去Fe(OH)3纳米颗粒,从而得到具有更多纳米通道的MXene膜。该膜在0.1 MPa的操作压力下对伊文思蓝染料(EB)的截留率达到90%,而水的渗透通量达到
1084 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。此外,对于重金属废水,MXene膜也表现出优异的去除能力。Jang等[56]报道了一种由Ti3C2Tx纳米片和乙二胺(EDA)水热反应制备出的Ti3C2Tx-EDA膜,乙二胺的引入改变了Ti3C2Tx纳米片的表面电荷,制备出的Ti3C2Tx-EDA膜的表面带正电荷,其对Mn2+、Zn2+、Cd2+、Cu2+、Ni2+和Pb2+等重金属离子的截留率在93.2%~99.8%左右,渗透通量约为20 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。该研究表明通过改变MXene膜的表面特性,使MXene膜在重金属离子去除中更具优势。王赛娣等[57]使用KOH溶液对MXene膜进行处理,制备出了表面羟基化的MXene膜,其中厚度为496 nm的羟基化的MXene膜对Cr6+、Pb2+、Cu2+和Cd2+等重金属离子的截留率分别为66.19%、76.57%、78.65%和79.21%,表现出较好的截留效果。6. MXene膜的规模化制备
目前,MXene膜在分子筛分方面显示出巨大的潜力,但所开发的膜的面积小,不足以用于实际应用。因此规模化制备是阻碍MXene膜产业化和实际应用的关键瓶颈。以下是一些报道的规模化制备技术,如图9(a)所示,Kim等[58]通过狭缝式涂布法制备出具有不同厚度的大面积MXene膜,该方法无需高浓度MXene分散液,同时在涂布过程中能防止污染物进入,制备出的膜均匀性好,对甲基红(MR)染料的截留率约为93.2%,水的渗透通量为200 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。但狭缝式涂布法存在设备和维护成本高的问题,且制备连续性还有待证明,需要进一步的研究与发展。如图9(b)所示,Li等[59]使用Meyer棒状涂布方法在聚醚砜(PES)底膜上制备出超过5 m的MXene膜,且厚度在纳米和微米尺寸之间可调。制备出的MXene膜对亚甲基蓝(MeB)染料的截留率为99.95%,相应的渗透通量为43.2 L·m−2·h−1·bar−1。虽然该方法能连续制备出大面积的MXene膜,工艺简单,但其需要高浓度MXene分散液,且该方法缺乏对膜结构的有效调节。后续还需要进一步扩展和改进。Deng等[60]采用电泳沉积的方法,在电场力的推动下,快速的将带负电荷的MXene纳米片堆积在带正电的基板上,从而形成超过500 cm2的大面积MXene膜。同时通过控制沉积时间,可以将膜的厚度控制在100 nm~1 μm之间。使用该方法能在10 min内制备出大面积MXene膜,简单快速,为MXene膜的规模化制备提供了一个可行的途径,但这种方法会受到导电基板的限制。当前用于分子筛分的大面积MXene膜的研究较少,需研究新型的制备方案和制造工艺设计,开发出简单连续的膜制备方法,制备出具有优异分离性能的大面积MXene膜,以满足未来MXene膜的实际应用。
7. 结 语
二维MXene材料的出现,为膜分离技术的研究注入了新鲜的血液,推动了膜分离技术的发展。虽然MXene层状纳滤膜的研究逐年深入和增多,也展现出优异的渗透选择性,但仍面临着一些挑战。
(1) MXene纳米片的制备。MXene层状纳滤膜的性能与MXene纳米片的尺寸大小、表面缺陷、表面官能团有着直接的关系。目前最常用的原位HF生成刻蚀法,无法精准调控MXene纳米片的尺寸大小、表面官能团和避免表面缺陷。因此需要探索出一种合适的刻蚀方法来调控MXene纳米片的结构和理化性质。
(2) MXene纳米片易氧化。单层MXene胶体溶液在15天内会从黑色变为混浊白色,发生严重的氧化现象。这种氧化受氧气和水的促进,导致了金红石型二氧化钛的形成,严重影响了复合膜性能,阻碍了实际应用。
(3) MXene层状纳滤膜的规模化制备。当前研究的MXene层状纳滤膜大都是实验室通过真空过滤的小规模制备,规模化制备MXene膜的研究较少,为了应对将来的工业化发展,开发新的能够规模化制备MXene膜的工艺和技术是有必要的。
(4) MXene层状纳滤膜的抗溶胀和稳定性。目前,自交联、有机分子交联及与不同维度的纳米材料插层的方法能制备出具有抗溶胀的MXene层状纳滤膜,但这一般是在理想的实验环境下,仍需研究出结构更稳定的MXene纳滤膜,以应对未来工业应用中高温、氧化和酸碱等恶劣的操作环境。
尽管面临这些挑战,但MXene层状纳滤膜在不同应用中仍展现出令人振奋的前景。未来MXene膜的技术发展领域应聚焦在开发兼具高渗透选择性和高稳定性的MXene膜上,以实现更高效的纳滤应用。到目前为止,通常对于渗透选择性强的MXene膜,水滴能快速通过其表面,但其稳定性不佳。相反,当MXene膜具有高稳定性时,很难获得高的渗透选择性,甚至不具渗透性。要突破这一应用瓶颈,就必须考虑如何保持这两个方面的平衡,即从渗透选择性和稳定性两个方面来设计高质量的纳滤膜。针对现有的MXene膜在纳滤应用中存在渗透选择性和稳定性之间的平衡效应的问题,相关的研究策略如下:(1)对MXene组分进行功能化改性,通过化学反应引入不同的功能基团增强MXene亲水性和化学稳定性;(2)设计新型的MXene复合膜,与新型二维材料、高分子材料等复合,利用不同材料的协同效应提高膜的综合性能。当前,探索不同类型、尺寸和维度的层间复合材料是关键焦点和研究趋势。随着持续努力,MXene层状纳滤膜有望在不久的将来在不同领域实现工业应用。
-
表 1 热可逆聚氨酯再加工后力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of thermoreversible polyurethane after reprocessing
High-temperature dissolution process Hot-melt process Tensile strength/MPa Break at elongation/% Tensile strength/MPa Break at elongation/% Original sample 25.2±3 76.7±15 25.2±3 76.7±15 1st reprocessed 27.3±3 72.3±15 23.4±3 75.5±15 2nd reprocessed 31.3±3 68.9±15 23.0±3 76.1±15 3rd reprocessed 30.0±3 69.2±15 23.0±3 74.2±15 -
[1] THAMIZH SELVAN R, VISHAKH RAJA P C, MANGAL P, et al. Recycling technology of epoxy glass fiber and epoxy carbon fiber composites used in aerospace vehicles[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2021,55(23):3281-3292. DOI: 10.1177/00219983211011532
[2] 王蒙娜, 王志强, 苏韬, 等. 聚酰亚胺改性耐高温透波邻苯二甲腈复合材料制备[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2020, 48(6):40-45. WANG Mengna, WANG Zhiqiang, SU Tao, et al. Preparation of high-temperature resistant wave-transmitting phthalonitrile based composites modified by polyimide[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2020,48(6):40-45(in Chinese).
[3] 张翼鹏, 颜春, 阮春寅, 等. 原位聚合法制备连续玻璃纤维增强PCBT复合材料及其性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(4):29-35. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2012.04.011 ZHANG Yipeng, YAN Chun, RUAN Chunyin, et al. Preparation and properties of continuous fiber reinforced PCBT composites by in-situ polymerization[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(4):29-35(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2012.04.011
[4] LIU L Z, XIA Y, WANG L, et al. Cyanate ester resin with high heat-resistance and degradable diacetal structure: Synthesis, polymerization, and properties[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2022,307(11):2200423. DOI: 10.1002/mame.202200423
[5] SONNENFELD C, MENDIL-JAKANI H, AGOGUÉ R, et al. Thermoplastic/thermoset multilayer composites: A way to improve the impact damage tolerance of thermosetting resin matrix composites[J]. Composite Structures,2017,171:298-305. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.03.044
[6] YAO S S, JIN F L, RHEE K Y, et al. Recent advances in carbon-fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites: A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,142:241-250. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.12.007
[7] 周天睿, 方立, 万明, 等. 连续CF增强PEEK复合材料层压板的制备工艺[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2016, 44(7):52-56. ZHOU Tianrui, FANG Li, WAN Ming, et al. Preparation process of continuous CF reinforced PEEK composite laminates[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2016,44(7):52-56(in Chinese).
[8] VALVERDE M A, BELNOUE J P H, KUPFER R, et al. Compaction behaviour of continuous fibre-reinforced thermoplastic composites under rapid processing conditions[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2021,149:106446.
[9] 刘锦成, 徐传昶, 姜侃, 等. 超高韧性聚氨酯复合材料性能影响因素[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2021, 49(4):104-108. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2021.04.020 LIU Jincheng, XU Chuanchang, JIANG Kan, et al. Influencing factors on the properties of ultra-high toughness polyurethane composite[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2021,49(4):104-108(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2021.04.020
[10] ECHEVERRIA-ALTUNA O, OLLO O, CALVO-CORREAS T, et al. Effect of the catalyst system on the reactivity of a polyurethane resin system for RTM manufacturing of structural composites[J]. Express Polymer Letters,2022,16(3):234-247. DOI: 10.3144/expresspolymlett.2022.19
[11] 孙海欧, 杜俊超, 于文杰, 等. 反应注射成型聚氨酯复合材料阻燃性研究[J]. 化学推进剂与高分子材料, 2013, 11(1):66-68. SUN Hai'ou, DU Junchao, YU Wenjie, et al. A study on flame retardant performance of reaction injection molding polyurethane composite materials[J]. Chemical Propellants & Polymeric Materials,2013,11(1):66-68(in Chinese).
[12] MOHAMED M, VUPPALAPATI R R, BHEEMREDDY V, et al. Characterization of polyurethane composites manufactured using vacuum assisted resin transfer molding[J]. Advanced Composite Materials,2015,24:13-31. DOI: 10.1080/09243046.2014.909975
[13] 李文斌, 陈洁, 黄金瑞, 等. 可降解热固性树脂及其碳纤维复合材料研究进展[J]. 热固性树脂, 2022, 37(5):60-69. LI Wenbin, CHEN Jie, HUANG Jinrui, et al. Research progress of degradable thermosetting resin and carbon fiber reinforced composites[J]. Thermosetting Resin,2022,37(5):60-69(in Chinese).
[14] ZHANG Y H, YUAN L, LIANG G Z, et al. Developing reversible self-healing and malleable epoxy resins with high performance and fast recycling through building cross-linked network with new disulfide-containing hardener[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(37):12397-12406.
[15] DI MAURO C, MALBURET S, GRAILLOT A, et al. Recyclable, repairable, and reshapable (3R) thermoset materials with shape memory properties from bio-based epoxidized vegetable oils[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials,2020,3(11):8094-8104. DOI: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01199
[16] LI Q T, JIANG M J, WU G, et al. Photothermal conversion triggered precisely targeted healing of epoxy resin based on thermoreversible Diels-Alder network and amino-functionalized carbon nanotubes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(24):20797-20807.
[17] 赵翰文, 冯利邦, 史雪婷, 等. 热可逆自修复环氧树脂的合成与修复行为[J]. 高分子学报, 2018(3):395-401. ZHAO Hanwen, FENG Libang, SHI Xueting, et al. Synthesis and healing behavior of thermo-reversible self-healing epoxy resins[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2018(3):395-401(in Chinese).
[18] 杨广杰, 潘李李, 李晓娟, 等. 基于可逆动态共价化学的新型可修复、可回收、可加工环氧树脂[J]. 功能高分子学报, 2017, 30(2):215-220. YANG Guangjie, PAN Lili, LI Xiaojuan, et al. New healable, recyclable and malleable epoxy resin based on dynamic imine bonding[J]. Journal of Functional Polymers,2017,30(2):215-220(in Chinese).
[19] ZHAO S, ABU-OMAR M M. Recyclable and malleable epoxy thermoset bearing aromatic imine bonds[J]. Macromolecules,2018,51(23):9816-9824. DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b01976
[20] MEMON H, LIU H Y, RASHID M A, et al. Vanillin-based epoxy vitrimer with high performance and closed-loop recyclability[J]. Macromolecules,2020,53(2):621-630. DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02006
[21] WANG Y Q, CUI X J, GE H, et al. Chemical recycling of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites via selective cleavage of the carbon-nitrogen bond[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2015,3(12):3332-3337.
[22] 张洋, 张隽爽, 马崇攀, 等. 碳纤维增强含酯键环氧树脂基复合材料的化学降解与回收[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(9):5026-5034. ZHANG Yang, ZHANG Junshuang, MA Chongpan, et al. Chemical degradation and recovery of carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin matrix composites containing ester bond[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(9):5026-5034(in Chinese).
[23] YU Q, LIANG Y Y, CHENG J, et al. Synthesis of a degradable high-performance epoxy-ended hyperbranched polyester[J]. ACS Omega,2017,2(4):1350-1359. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.7b00132
[24] BANERJEE P, KUMAR S, BOSE S. Thermoreversible bonds and graphene oxide additives enhance the flexural and interlaminar shear strength of self-healing epoxy/carbon fiber laminates[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2021,4(7):6821-6831. DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.1c00888
[25] KE X X, LIANG H B, XIONG L, et al. Synthesis, curing process and thermal reversible mechanism of UV curable polyurethane based on Diels-Alder structure[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2016,100:63-69. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2016.03.008
[26] YU S, ZHANG R C, WU Q, et al. Bio-inspired high-performance and recyclable cross-linked polymers[J]. Advanced Materials,2013,25(35):4912-4917.
[27] YU B F, FENG Y, ZHU W F, et al. Self-healing electromagnetic interference shielding composite based on Diels-Alder chemistry[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2019,30(22):19994-20001. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-019-02366-x
[28] SAI F T, ZHANG H T, QU J B, et al. Thermal-driven self-healing and green recyclable waterborne polyurethane films based on double reversible covalent bonds[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2023,178:107460. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2023.107460
[29] 王玉龙, 李雅琼, 王怡博, 等. 一种基于动态双硫键的自修复聚氨酯弹性体的制备与性能[J]. 聚氨酯工业, 2020, 35(2):22-25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2020.02.007 WANG Yulong, LI Yaqiong, WANG Yibo, et al. Preparation and properties of a self-healing polyurethane elastomer based on dynamic disulfide bond[J]. Polyurethane Industry,2020,35(2):22-25(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2020.02.007
[30] ZHANG X, CHEN P, ZHAO Y, et al. High-performance self-healing polyurethane binder based on aromatic disulfide bonds and hydrogen bonds for the sulfur cathode of lithium-sulfur batteries[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2021,60(32):12011-12020.
[31] WU D L, LIU L, MA Q H, et al. Biomimetic supramolecular polyurethane with sliding polyrotaxane and disulfide bonds for strain sensors with wide sensing range and self-healing capability[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2023,630:909-920. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.10.058
[32] GAINA C, URSACHE O, GAINA V. Re-mendable polyurethanes[J]. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering,2011,50(7):712-718. DOI: 10.1080/03602559.2010.551392
[33] HEO Y, SODANO H A. Self-healing polyurethanes with shape recovery[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2014,24(33):5261-5268. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201400299
[34] LI X P, YU R, HE Y Y, et al. Self-healing polyurethane elastomers based on a disulfide bond by digital light processing 3D printing[J]. ACS Macro Letters,2019,8(11):1511-1516.
[35] ZHANG R C, YU S, CHEN S L, et al. Reversible cross-linking, microdomain structure, and heterogeneous dynamics in thermally reversible cross-linked polyurethane as revealed by solid-state NMR[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2014,118(4):1126-1137. DOI: 10.1021/jp409893f
[36] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 528—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic—Determination of tensile stress-strain properties: GB/T 528—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009(in Chinese).
[37] 全国纤维增强塑料标准化技术委员会. 纤维增强塑料 短梁法测定层间剪切强度: JC/T 773—2010 [S]. 北京: 中国建材工业出版社, 2010. National Technical Committee on Fiber Reinforced Plastic of Standardization Administration of China. Fibre-reinforced plastics composites—Determination of apparent interlaminar shear strength by short-beam method: JC/T 773—2010[S]. Beijing: China Building Materials Press, 2010(in Chinese).
[38] 万里鹰, 肖洋, 张伦亮. 基于热可逆Diels-Alder动态共价键PU-DA体系的制备和性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2021, 35(10):752-760. WAN Liying, XIAO Yang, ZHANG Lunliang. Preparation and properties of PU-DA system based on thermoreversible Diels-Alder dynamic covalent bond[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2021,35(10):752-760(in Chinese).
[39] EHRHARDT D, VAN DURME K, JANSEN J F G A, et al. Self-healing UV-curable polymer network with reversible Diels-Alder bonds for applications in ambient conditions[J]. Polymer, 2020, 203: 122762.
[40] LIU Z Y, ZHU X Y, TIAN Y Z, et al. Bio-based recyclable form-stable phase change material based on thermally reversible Diels-Alder reaction for sustainable thermal energy storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,448(15):137749.
[41] 双超, 刘璐璐, 赵振华, 等. 湿热老化对T700/TDE-85复合材料层间剪切强度的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2018, 42(3):62-66. DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201803012 SHUANG Chao, LIU Lulu, ZHAO Zhenhua, et al. Effect of hygrothermal aging on interlaminar shear strength of T700/TDE-85 composite[J]. Materials for Mechanical Engineering,2018,42(3):62-66(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11973/jxgccl201803012
-
目的
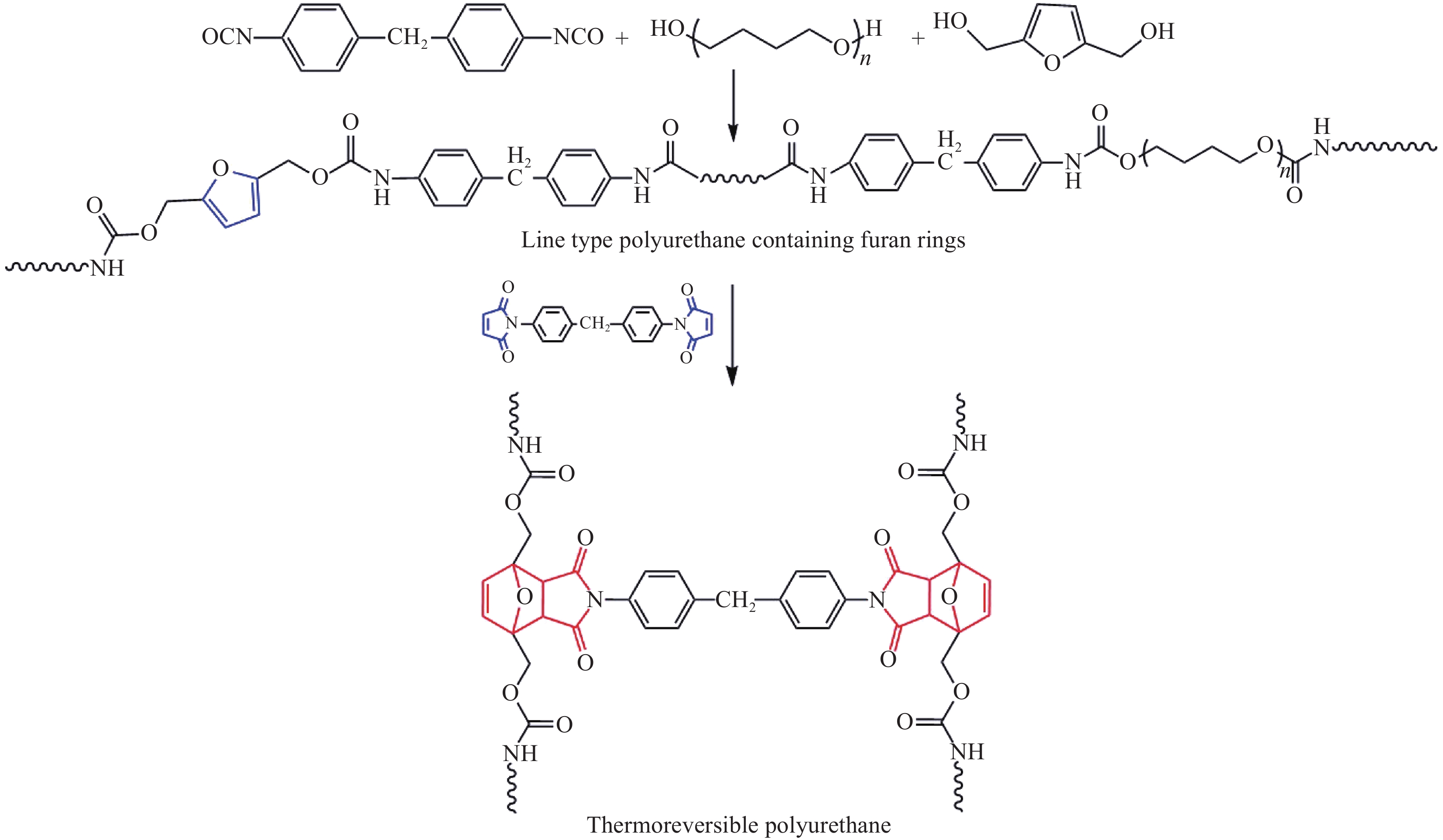
碳纤维树脂基复合材料多以热固性树脂为树脂基体,存在抗冲击强度低,无法加工和回收等问题。为实现碳纤维复合材料的高韧性和可回收性,本文利用Diels-Alder(D-A)反应制备了热可逆聚氨酯,并以其作为树脂基体制备了碳纤维复合材料。
方法在三口烧瓶中加入二苯基甲烷二异氰酸酯(MDI-50)、聚四氢呋喃二醇-1000(PTMG-1000)、2,5-呋喃二甲醇(摩尔比为3.15:1:2)及适量DMF,80℃反应4h,得到链上含呋喃环的线型聚氨酯。在室温下将溶解于DMF的4,4'-双马来酰亚胺基二苯甲烷(BMI)加入到所合成的含呋喃环线型聚氨酯中,其中双马来酰亚胺基团与呋喃环的摩尔比为1:1,混合均匀后得到热可逆聚氨酯胶液。将热可逆聚氨酯胶液浇注到聚四氟乙烯模具中,在80℃真空干燥箱中脱除DMF,再在95℃下固化2h,得到热可逆聚氨酯固化物。将热可逆聚氨酯胶液涂刷到T700-12k碳纤维表面,在80℃真空干燥箱中脱除DMF后放入预热好的模具中。在95℃下热压2h,制备单向碳纤维增强热可逆聚氨酯复合材料。
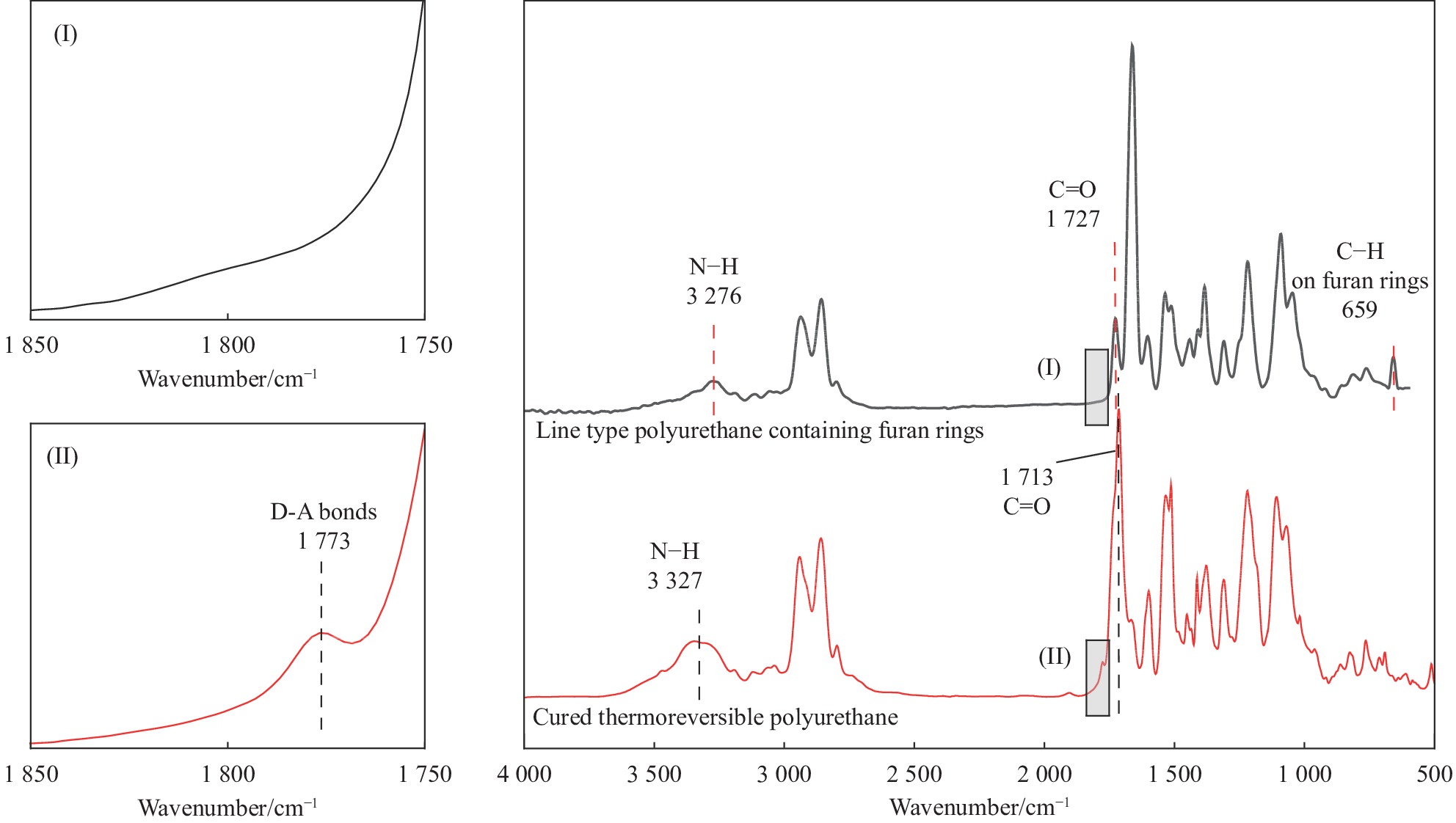
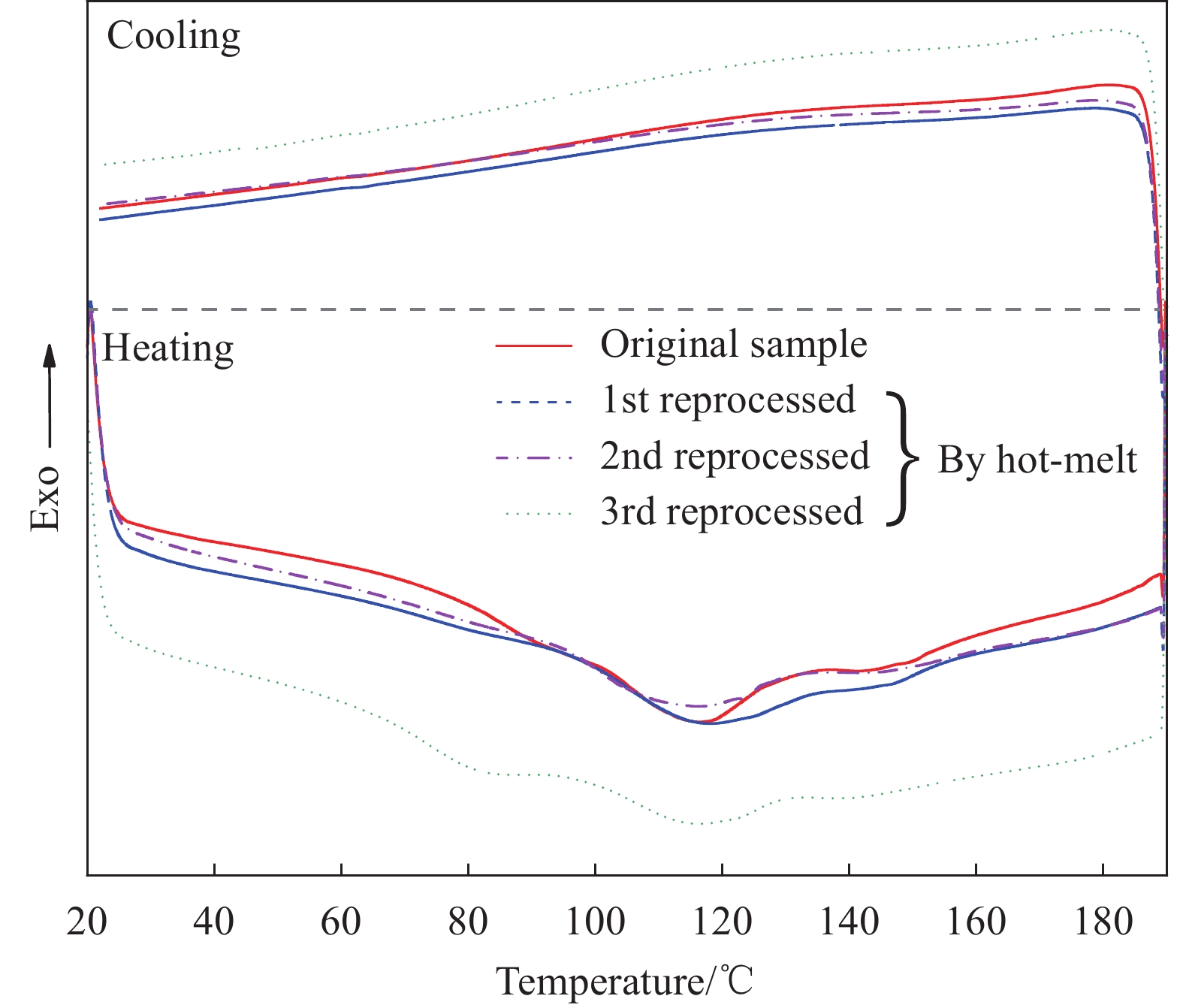
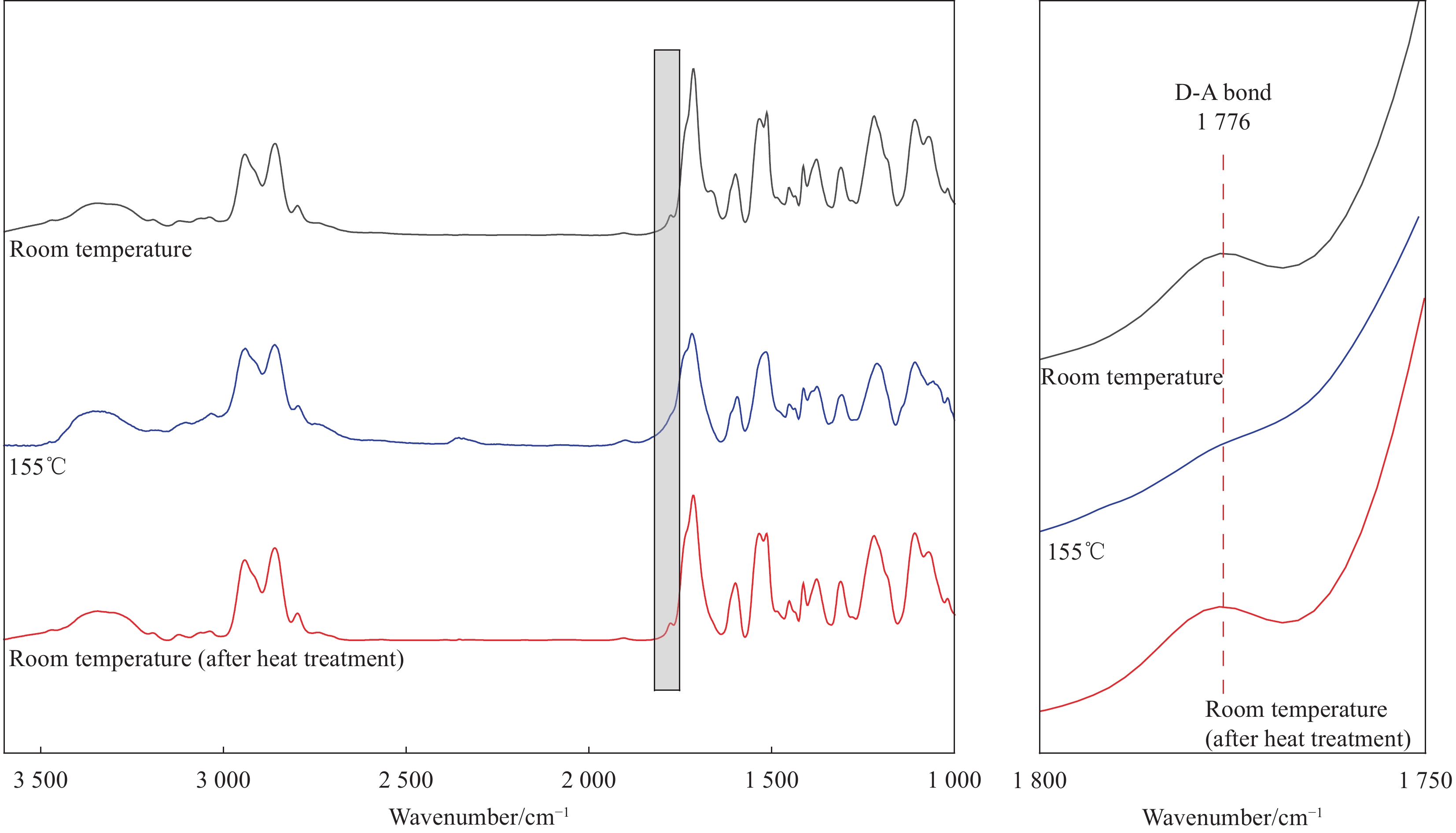
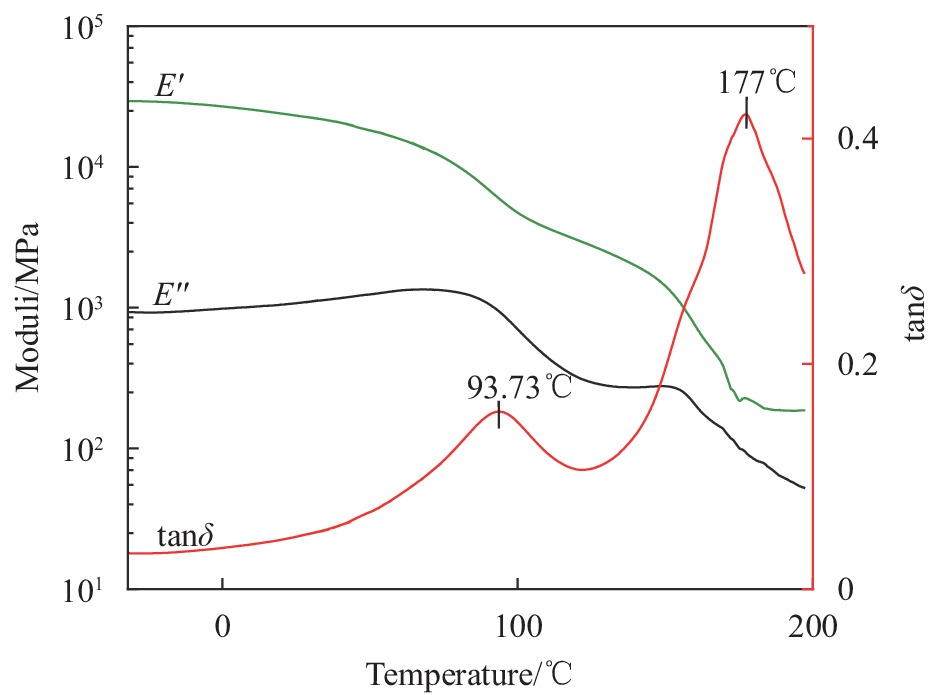
结果ϕ呋喃环线型聚氨酯的红外谱图中,在3276cm及1727 cm处存在氨基甲酸酯键中N—H及C═O特征峰,同时,在2300cm~2000cm处不存在—NCO特征峰,在1006cm附近不存在2,5-呋喃二甲醇伯醇上C—O伸缩振动特征峰,在659cm-处存在呋喃环上C—H面外弯曲振动特征峰。热可逆聚氨酯的红外谱图中未出现呋喃环上C—H面外弯曲振动特征峰,在3327cm及1713 cm处依旧存在典型聚氨酯特征峰,并且在1773cm处存在D-A结构特征峰,含呋喃环线型聚氨酯的红外谱图中并不存在该特征峰,表明合成出了目标产物。κ原始的热可逆聚氨酯样品拉伸强度为25.2MPa左右,断裂伸长率在76.7%左右。热可逆聚氨酯经高温溶解再加工三次后拉伸强度为30.0MPa左右;通过热熔法再加工则会使热可逆聚氨酯的强度轻微下降,再加工三次后拉伸强度在23.0MPa左右。通过两种方式进行再加工均不会使热可逆聚氨酯的断裂伸长率出现显著下降,且拉伸强度始终保持在较高值,具有良好再加工性能。λ原始的热可逆聚氨酯样品在加热过程中于101℃~157℃之间出现了明显的吸热峰,表明在此温度区间发生了rD-A反应,通过热熔法再加工一、二、三次的样品,分别在96℃~157℃、95℃~161℃、98℃~158℃出现吸热峰,吸热峰出现的温度范围基本一致,说明热可逆聚氨酯固化物中的D-A结构在循环加热及降温时会存在反复断键-交联的过程,使树脂具备热可逆特性。μ经155℃加热处理的热可逆聚氨酯在1776cm处不再出现D-A结构特征峰,而经加热处理再降至室温的热可逆聚氨酯在1776cm处又出现了D-A结构特征峰,表明所制备的热可逆聚氨酯固化物具有热可逆性。ν热可逆聚氨酯复合材料的层剪过程呈二次失效特点,在34.85MPa时出现第一个失效点,随后测试样条继续弯曲,应力持续增大,达到121MPa后应力下降,树脂基体表现出韧性材料的特性。热可逆聚氨酯复合材料在层剪测试中发生了多层剪切,为可接受的层剪失效模式,对应其首次失效;随应变增加,热可逆聚氨酯复合材料发生塑性剪切,对应其二次失效,但因塑性剪切为不可接受的层剪破坏模式,所以认定其层剪强度为34.85MPa。ο热可逆复合材料的储能模量E′在80℃以下有轻微下降,80℃后下降较快;tanδ曲线上出现2个峰值,其中93.73℃是复合材料的玻璃化转变温度(T)。在100℃~155℃之间,损耗模量E″曲线出现平台,可能与树脂的rD-A反应有关。随温度升高,热可逆聚氨酯发生高弹态向黏流态的转变,177℃为其黏流温度(T),可以作为热可逆聚氨酯二次加工及回收利用的最高温度。
结论ϕ以2,5-呋喃二甲醇为扩链剂将呋喃结构引入到聚氨酯分子链中,利用呋喃环与BMI之间发生的D-A反应制备了交联结构的热可逆聚氨酯,160℃左右可完成逆反应,具有反复加工性。κ热可逆聚氨酯采用高温溶剂溶解法或热熔法均可以进行再加工,再加工三次后的拉伸强度分别为30±3MPa和23±3MPa。λ碳纤维单向复合材料的层间剪切呈二次失效特点,层间剪切强度为34.85MPa。玻璃化转变温度93.73℃。





 下载:
下载: