Recent progress on 3D graphene aerogel based microwave absorbing materials
-
摘要: 随着信息技术的发展,电磁污染问题日益严重,开发具有“薄、轻、宽、强”特性的高性能吸波材料成为当务之急。石墨烯高电导率、高比表面积、低密度的优良特性受到研究人员的广泛关注。为解决单一石墨烯材料易引起的阻抗失配及损耗机制单一问题,引入其他组分制备多元复合材料,改善阻抗匹配、创造多样化的损耗机制是通用的设计方案。本文简要讨论了吸波机制,分述了介电型、磁复合型、有序型、压力诱导型4个类别,并通过材料选择(金属、陶瓷、铁氧体、导电聚合物、生物质材料等)、结构设计、机制分析等角度,结合领域内近年来的研究成果,总结了石墨烯基气凝胶吸波材料的研究进展,并对未来研究方向进行展望。Abstract: With the development of information technology, electromagnetic pollution has become increasingly severe. Therefore, the development of high-performance microwave absorbing materials with "thin, light, wide, and strong" characteristics has become a top priority. Graphene's excellent properties, such as high conductivity, high specific surface area, and low density, have attracted widespread attention from researchers. To solve the problem of impedance mismatch and single loss mechanism caused by single graphene material, other components are introduced to prepare multi-component composite materials, which improve impedance matching and create diverse loss mechanisms, making it a common design solution. This paper briefly discusses the absorption mechanism, describing four categories: Dielectric type, magnetic composite type, ordered type, and pressure-induced type. Through material selection (metals, ceramics, ferrites, conductive polymers, biomass materials, etc.), structural design, mechanism analysis, and combining with recent research results in the field, the research progress of graphene aerogel based microwave absorbing materials is summarized, and future research directions are also proposed.
-
Key words:
- graphene /
- aerogel /
- microwave absorption /
- structure design /
- impedance matching /
- electromagnetic pollution
-
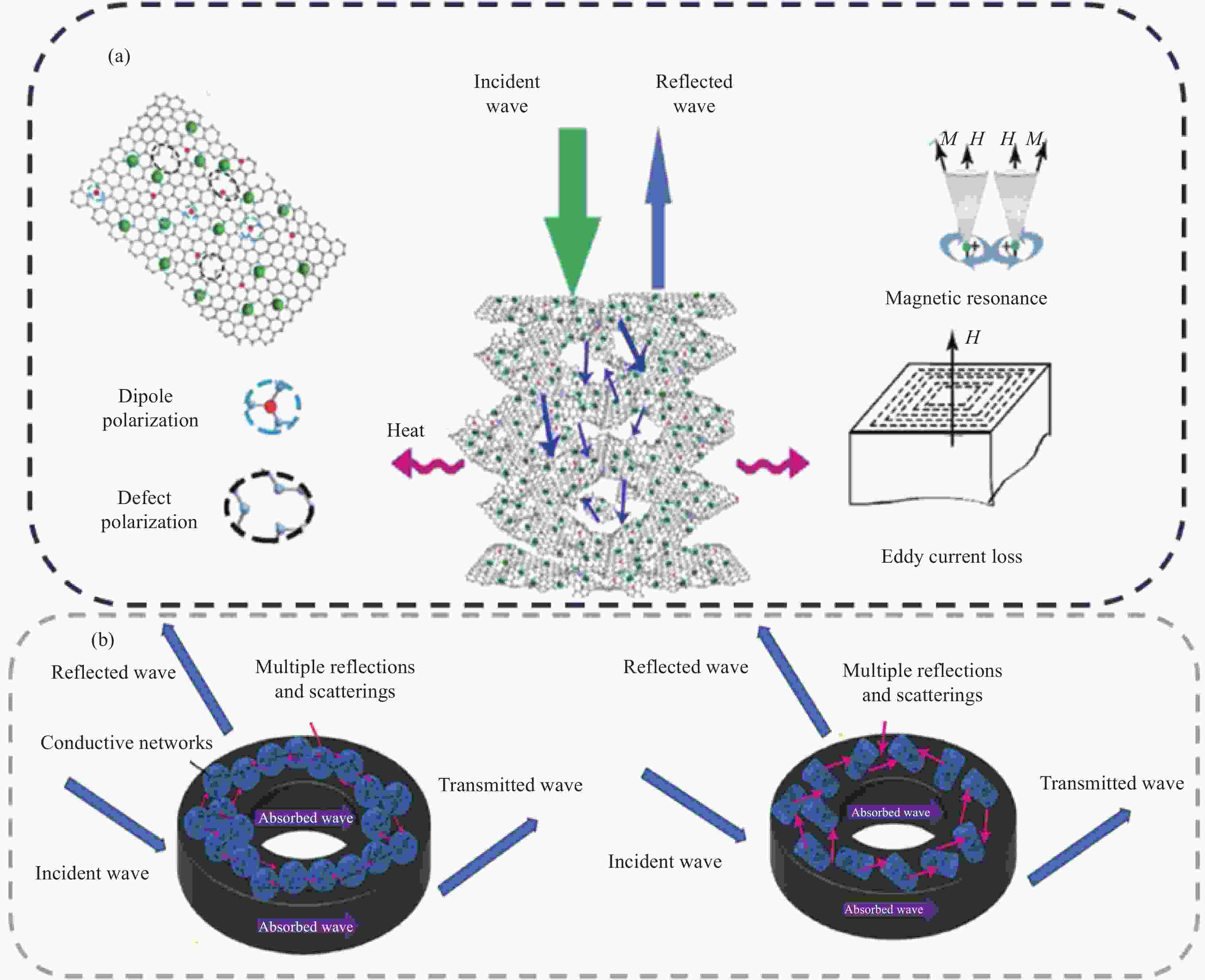
图 3 复合气凝胶的SEM图像及其微波吸收机制示意图:(a) Ti3C2Tx MXene@氧化石墨烯杂化气凝胶微球(M@GAMS)[25];((b), (c)) 聚苯胺(PANI)/GA[26];(d) 石墨烯芯(DG)/Si3N4气凝胶[27]
Pin—Incident electromagnetic wave; Pref—Reflected electromagnetic waves
Figure 3. SEM images of composite aerogel and schematic diagram of its microwave absorption mechanism: (a) Ti3C2Tx MXene@graphene oxide (M@GAMS)[25]; ((b), (c)) Polyaniline (PANI)/GA[26]; (d) Defect-engineered chemical vapor deposition graphene (DG)/Si3N4 aerogel[27]
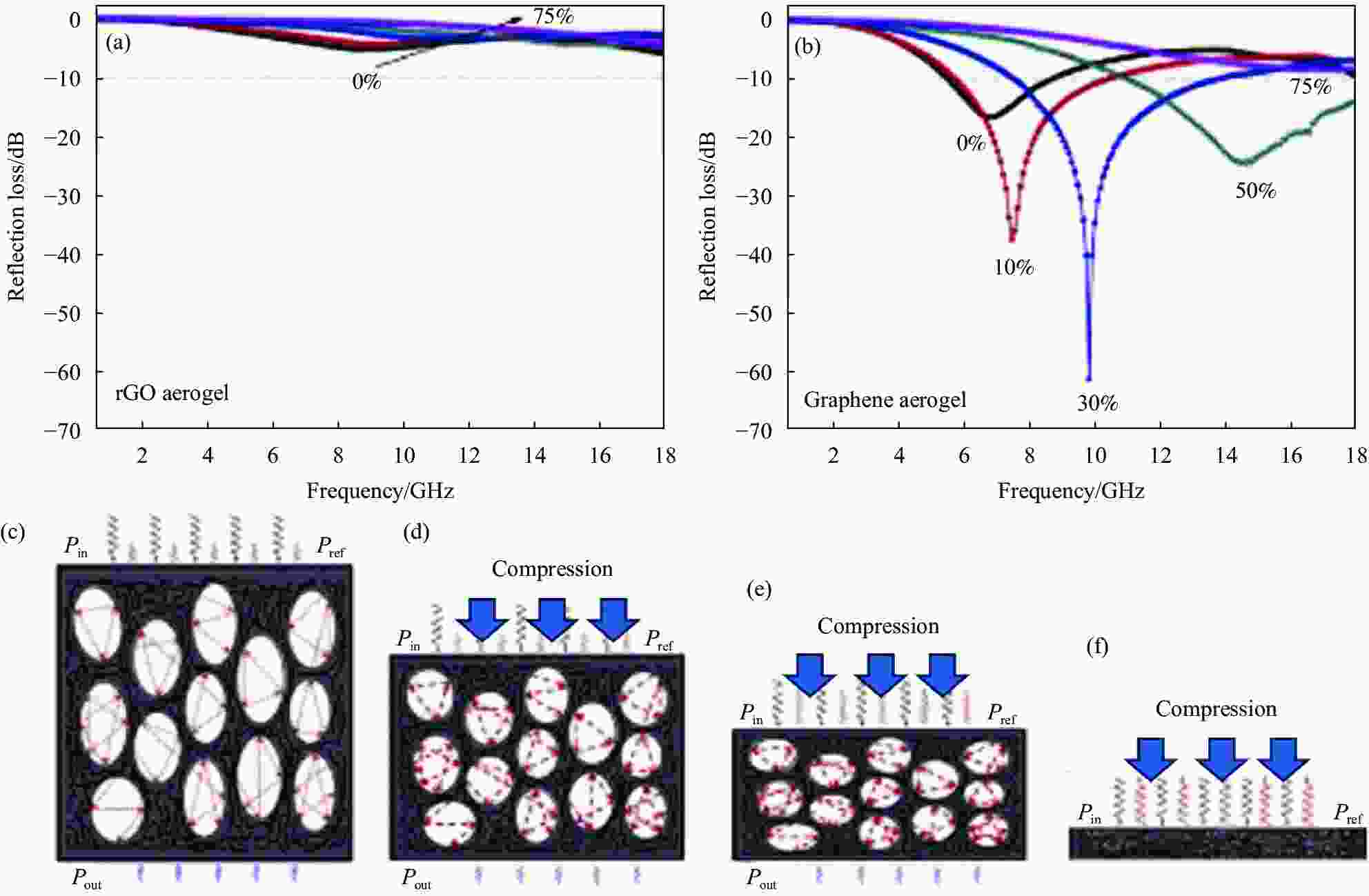
图 8 rGO气凝胶(6.91 mm) (a)和GA (6.87 mm) (b)在不同压缩应变下在0.5~18 GHz的频率范围内的微波RL曲线;((c)~(f)) GA在不同压缩应变下的微波吸收机制示意图[47]
Pout—Transmitted electromagnetic waves
Figure 8. Microwave RL curves in the frequency range of 0.5-18 GHz at different compression strains for rGO aerogel (6.91 mm) (a) and GA (6.87 mm) (b); ((c)-(f)) Schematic illustration of microwave absorption mechanism of GA under different compression strains[47]
表 1 不同吸波剂性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of performance for different absorber
Sample Filling ratio/wt% RLmin/dB EAB/GHz Thickness/mm Ref. M@GAMS 10 −49.1 2.9 (12.9-15.8) 1.2 [25] PANI/GA — −42.3 3.2 (8.7-11.9) 3.0 [26] DG/Si3N4 — −77.3 7.4 (10.6-18.0) 2.7 [27] GA@Ni 4.25 −52.3 6.5 (11.3-17.8) 3.0 [32] Fe3O4@C/rGO — −59.23 6.72 (−) 3.57 [33] CoFe2O4/N-rGO 20 − 60.4 6.48 (11.44-17.92) 2.1 [34] GA/Fe3O4@SiO2 5 −51.5 6.5 (6.2-12.7) 4.0 [35] Ni/MXene/rGO 0.64 −75.2 7.3 (−) 2.2 [38] Co@C/GA — −45.0 4.0 (13.1-17.1) 1.5 [39] GA — −61.09 6.3 (7.5-13.8) 4.81 [47] C/rGO 0.8 −46.11 5.8 (12.2-18.0) 2.70 [48] Notes: RLmin—Minimum reflection loss; EAB—Effective absorption bandwidth. -
[1] 黎昌金, 陈琦, 李建龙. 电磁辐射的危害与防护探讨[J]. 内江科技, 2018, 39(9):108-110.LI Changjin, CHEN Qi, LI Jianlong. Discussion on the hazard and protection of electromagnetic radiation[J]. Neijiang Science and Technology,2018,39(9):108-110(in Chinese). [2] SUN X, HE J, LI G, et al. Laminated magnetic graphene with enhanced electro-magnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2013,1(4):765-777. doi: 10.1039/C2TC00159D [3] XIA Y, GAO W, GAO C, et al. A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: Electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2022, 32(42): 2204591. [4] WANG P, WANG G, ZHANG J, et al. Excellent microwave absorbing performance of the sandwich structure absorber Fe@B2O3/MoS2/Fe@B2O3 in the Ku-band and X-band [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 382: 122804. [5] HU K, SZKOPEK T, CERRUTI M. Tuning the aggregation of graphene oxide dispersions to synthesize elastic, low density graphene aerogels[J]. Journal of Materials Che-mistry A,2017,5(44):23123-23130. doi: 10.1039/C7TA07006C [6] 许亚丽. 石墨烯纤维及其复合材料结构设计与电磁屏蔽性能[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2020.XU Yali. Structure design and electromagnetic shielding performance of graphene fibres and their composites[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2020(in Chinese). [7] 席嘉彬. 高性能碳基电磁屏蔽及吸波材料的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.XI Jiabin. Carbon-based materials for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding and microwave absorption[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018(in Chinese). [8] LIU D, DU Y, XU P, et al. Rationally designed hierarchical N-doped carbon nanotubes wrapping waxberry-like Ni@C microspheres for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(8):5086-5096. doi: 10.1039/D0TA10942H [9] HOU T, JIA Z, WANG B, et al. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,414:128875. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128875 [10] LYU H, ZHANG H, ZHAO J, et al. Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures[J]. Nano Research,2016,9:1813-1822. doi: 10.1007/s12274-016-1074-1 [11] WANG J, GAO C N, JIANG Y N, et al. Ultra-broadband and polarization-independent planar absorber based on multilayered graphene[J]. Chinese Physics B,2017,26(11):114102. doi: 10.1088/1674-1056/26/11/114102 [12] 王兰喜, 何延春, 卯江江, 等. 真空退火对氧化石墨烯纸的还原特性研究[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(10): 186-193.WANG Lanxi, HE Yanchun, MAO Jiangjiang, et al. Study on the reduction characteristics of oxygenated graphene paper by vacuum[J]. Surface Technology, 2021, 50(10): 186-193(in Chinese). [13] CAO Y, FATEMI V, FANG S, et al. Unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle graphene superlattices[J]. Nature, 2018, 556(7699): 43-50. [14] GUAN Z J, JIANG J T, YAN S J, et al. Sandwich-like cobalt/reduced graphene oxide/cobalt composite structure presenting synergetic electromagnetic loss effect[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2020, 561: 687-695. [15] ZHANG Y, HUANG Y, ZHANG T, et al. Broad-band and tunable high-performance microwave absorption of an ultralight and highly compressible graphene foam[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27(12):2049-2053. doi: 10.1002/adma.201405788 [16] CHEN C, XI J, ZHOU E, et al. Porous graphene microflowers for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Nano-micro Letters,2018,10:1-11. doi: 10.1007/s40820-017-0154-4 [17] 王军军, 王贤明, 吴连锋, 等. 石墨烯基复合吸波材料研究进展[J]. 中国涂料, 2019, 34(12): 1-7, 11.WANG Junjun, WANG Xianming, WU Lianfeng, et al. Research progress on graphene-based composite absorbing materials[J]. China Coatings, 2019, 34(12): 1-7, 11(in Chinese). [18] HUANG X, YU G, ZHANG Y, et al. Design of cellular structure of graphene aerogels for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,426:131894. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.131894 [19] LIU B, LI J, WANG L, et al. Ultralight graphene aerogel enhanced with transformed micro-structure led by polypyrrole nano-rods and its improved microwave absorption properties[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,97:141-150. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.03.001 [20] ZHANG K L, ZHANG J Y, HOU Z L, et al. Multifunctional broadband microwave absorption of flexible graphene composites[J]. Carbon, 2019, 141: 608-617. [21] SUN Y, HAN X, GUO P, et al. Slippery graphene-bridging liquid metal layered heterostructure nanocomposite for stable high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Nano, 2023, 17(13): 12616-12628. [22] WANG B X, XU C, DUAN G, et al. Review of broadband metamaterial absorbers: From principles, design strategies, and tunable properties to functional applications[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2023,33(14):2213818. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202213818 [23] 李俊. Fe基磁性金属及其石墨烯复合吸波材料研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2019.LI Jun. Study on Fe-based magnetic metal and its graphene composite absorbing materials[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019(in Chinese). [24] LIU Y, LU Q, WANG J, et al. A flexible sandwich structure carbon fiber cloth with resin coating composite improves electro-magnetic wave absorption performance at low frequency[J]. Polymers,2022,14(2):233. doi: 10.3390/polym14020233 [25] LI Y, MENG F, MEI Y, et al. Electrospun generation of Ti3C2Tx MXene@graphene oxide hybrid aerogel microspheres for tunable high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,391:123512. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123512 [26] WANG Y, GAO X, FU Y, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption performances of polyaniline/graphene aerogel by covalent bonding[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,169:221-228. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.008 [27] LIANG J, YE F, CAO Y, et al. Defect-engineered graphene/Si3N4 multilayer alternating core-shell nanowire membrane: A plainified hybrid for broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(22):2200141. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202200141 [28] TIAN Y, ZHI D, LI T, et al. Graphene-based aerogel microspheres with annual ring-like structures for broadband electromagnetic attenuation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,464:142644. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.142644 [29] ZHONG W, LI B, MA Z, et al. Double salt-template strategy for the growth of N, S-codoped graphitic carbon nanoframes on the graphene toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2023,202:235-243. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2022.10.086 [30] WANG G, GAO Z, WAN G, et al. High densities of magnetic nanoparticles supported on graphene fabricated by atomic layer deposition and their use as efficient synergistic microwave absorbers[J]. Nano Research,2014,7:704-716. doi: 10.1007/s12274-014-0432-0 [31] MENG F, WANG H, HUANG F, et al. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospec-tive[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,137:260-277. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.11.023 [32] XU D, YANG S, CHEN P, et al. Synthesis of magnetic graphene aerogels for microwave absorption by in-situ pyrolysis[J]. Carbon,2019,146:301-312. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.02.005 [33] ZHANG H, JIA Z, FENG A, et al. In situ deposition of pitaya-like Fe3O4@C magnetic microspheres on reduced graphene oxide nanosheets for electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,199:108261. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108261 [34] WANG X, LU Y, ZHU T, et al. CoFe2O4/N-doped reduced graphene oxide aerogels for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,388:124317. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124317 [35] MENG F, WANG H, WEI, et al. Generation of graphene-based aerogel microspheres for broadband and tunable high-performance microwave absorption by electrospinning-freeze drying process[J]. Nano Research,2018,11:2847-2861. doi: 10.1007/s12274-017-1915-6 [36] 刘鹏飞. 冰模板法构筑各向异性石墨烯三维结构及其应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2021.LIU Pengfei. The construction of three-dimensional anisotropic graphene aerogels by ice-templating method and their applications[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Che-mical Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [37] PAN D, YANG G, ABODIEF H M, et al. Vertically aligned silicon carbide nanowires/boron nitride cellulose aerogel networks enhanced thermal conductivity and electromagnetic absorbing of epoxy composites[J]. Nano-micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 118. [38] LIANG L, LI Q, YAN X, et al. Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(4):6622-6632. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09982 [39] XU J, ZHANG X, ZHAO Z, et al. Lightweight, fire-retardant, and anti-compressed honeycombed-like carbon aerogels for thermal management and high-efficiency electromagnetic absorbing properties[J]. Small,2021,17(33):2102032. doi: 10.1002/smll.202102032 [40] CHENG J B, ZHAO H B, CAO M, et al. Banana leaflike C-doped MoS2 aerogels toward excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(23): 26301-26312. [41] YANG C, ZHU X, WANG X, et al. Phase-field model of graphene aerogel formation by ice template method[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2019, 115(11): 111901. [42] HUANG J, WANG H, LIANG B, et al. Oriented freeze-casting fabrication of resilient copper nanowire-based aerogel as robust piezoresistive sensor[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,364:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.071 [43] WANG S, MENG W, LYU H, et al. Thermal insulating, light-weight and conductive cellulose/aramid nanofibers composite aerogel for pressure sensing[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,270:118414. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118414 [44] HU Y, CAO M, XU J, et al. Thermally insulating and electroactive cellular nanocellulose composite cryogels from hybrid nanofiber networks[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,455:140638. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.140638 [45] 于泓轩. 石墨烯气凝胶柔韧及传感特性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.YU Hongxuan. Study of graphene aerogel flexibility and sensing properties[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [46] CAO X, ZHANG J, CHEN S, et al. 1D/2D nanomaterials synergistic, compressible, and response rapidly 3D graphene aerogel for piezoresistive sensor[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(35):2003618. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202003618 [47] WANG Z, WEI R, GU J, et al. Ultralight, highly compressible and fire-retardant graphene aerogel with self-adjustable electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2018,139:1126-1135. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.08.014 [48] BAI T, GUO Y, WANG D, et al. A resilient and lightweight bacterial cellulose-derived C/rGO aerogel-based electromagnetic wave absorber integrated with multiple functions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(9):5566-5577. doi: 10.1039/D0TA11122H [49] HADI J M, AZIZ S B, MUSTAFA M S, et al. Role of nano-capacitor on dielectric constant enhancement in PEO: NH4SCN: xCeO2 polymer nano-composites: Electrical and electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(4): 9283-9294. [50] ZHENG Y, LI C, ZHAO Y, et al. Engineering of magnetic coupling in nanographene[J]. Physical Review Letters,2020,124(14):147206. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.124.147206 [51] 杨晴. 陶瓷基干涉型吸波材料的制备和性能研究[D]. 烟台: 烟台大学, 2022.YANG Qing. Preparation and performance study of ceramic-based interference absorbing material[D]. Yantai: Yantai University, 2022(in Chinese). [52] SHU R, WAN Z, ZHANG J, et al. Synergistically assembled nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite aerogels with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Compo-sites Science and Technology,2021,210:108818. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108818 -





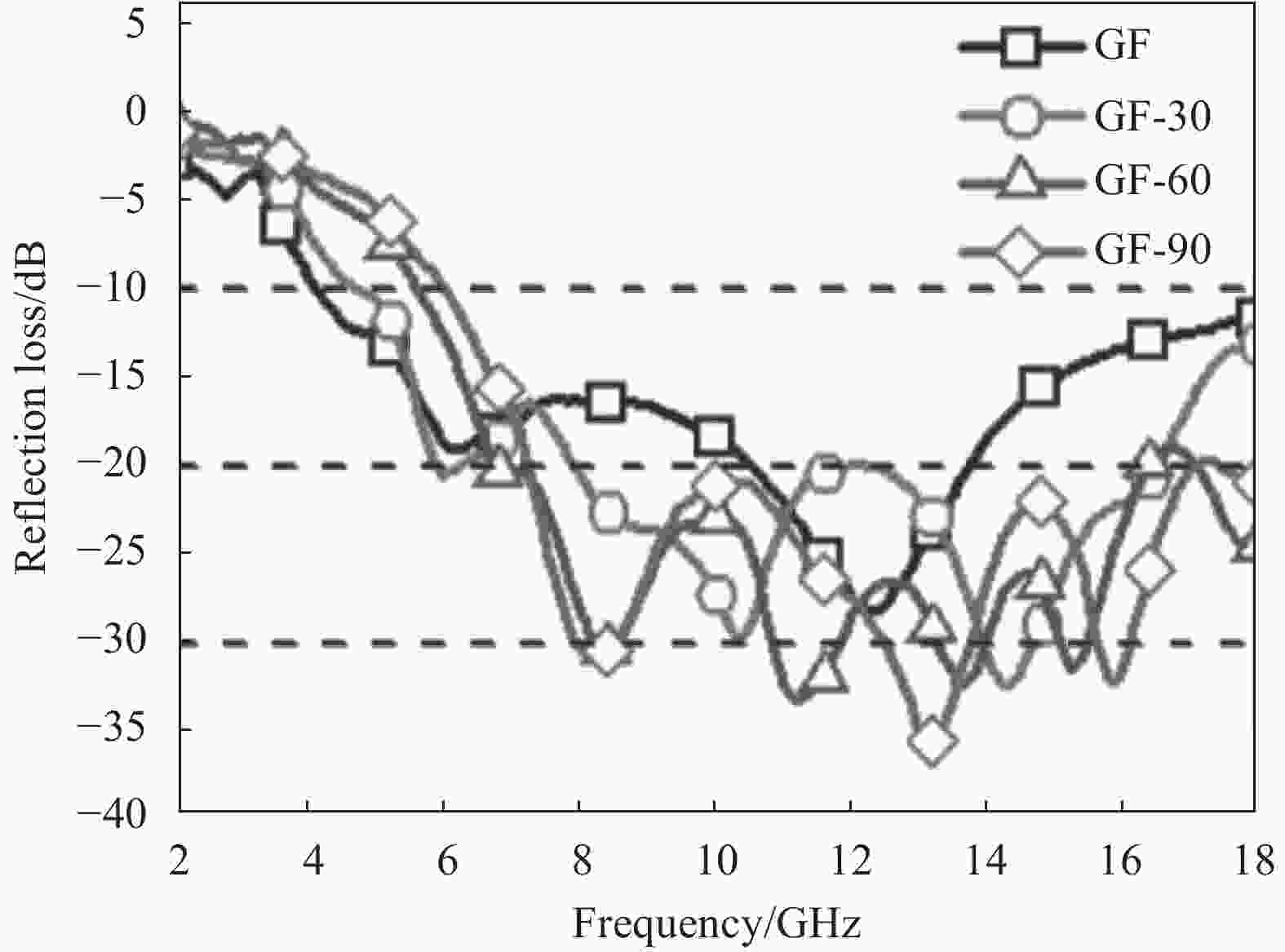
 下载:
下载: