Morphology modulation and photo-Fenton degradation of RhB properties in spinel-structured ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals
-
摘要: 水资源短缺和人类生产生活需水量的增加使污水净化处理这一话题变热。高级氧化工艺因其高效、环境友好且没有二次污染成为一种行之有效的处理污水方法。其中最具代表性的就是光催化技术和芬顿技术。通过调整工艺参数,采用水热法和煅烧法制备了3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4纳米晶,即微球状(ZFO-1)、空心球状(ZFO-2)和正六边形状(ZFO-3)。通过XRD、SEM、HRTEM、UV-vis、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)和瞬态光电流响应测试等,对样品的微观结构、形貌、元素组成和光电化学性能进行表征。此外,ZnFe2O4纳米晶光芬顿性能是通过对罗丹明B (RhB)的降解所得出的。结果表明:所制备的3种ZnFe2O4纳米晶均具有立方尖晶石结构和良好的结晶度。ZFO-2表现出优异的可见光吸收能力和最窄的带隙,并发生红移现象。EIS测试表明,ZFO-2的转移内阻最小且瞬态光电流最大,具有优异的光生载流子的迁移和分离能力。ZFO-1、ZFO-2、ZFO-3催化剂的光芬顿降解效率依次为88.2%、97.6%和48.1%,表明具有良好的降解性能。综合得到,ZFO-2具备优异的光降解性能。并探讨了可能的光芬顿降解RhB催化机制。Abstract: The shortage of water resources and the increase of water demand for human production and life have made the topic of wastewater purification and treatment hot. The advanced oxidation process has become a proven method to treat wastewater because it is efficient, environmentally friendly and free of secondary pollution. The most representative ones are photocatalytic technology and Fenton technology. Three different morphologies of ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals, namely microspherical (ZFO-1), hollow spherical (ZFO-2) and orthohexagonal (ZFO-3), were prepared by hydrothermal and calcination methods by adjusting the process parameters. The microstructure, morphology, elemental composition and photoelectrochemical properties of the samples were characterized by XRD, SEM, HRTEM, UV-vis, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and transient photocurrent response tests. Furthermore, the ZnFe2O4 nanocrystal photo-Fenton properties were derived from the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB). The results show that all three prepared ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals have cubic spinel structure and good crystallinity. ZFO-2 exhibits excellent visible light absorption and the narrowest band gap with red-shift phenomenon. EIS tests show that ZFO-2 has the lowest internal resistance to transfer and the highest transient photocurrent, with excellent migration and separation of photogenerated carriers. The photo-Fenton degradation efficiencies of ZFO-1, ZFO-2 and ZFO-3 catalysts are 88.2%, 97.6% and 48.1% in order, indicating good degradation performance. The comprehensive obtained, ZFO-2 has excellent photodegradation performance. And the possible catalytic mechanism of photo-Fenton degradation of RhB was discussed.
-
Keywords:
- ZnFe2O4 /
- shape control /
- photoelectrochemical properties /
- photo-Fenton /
- dye RhB
-
近几十年来,随着世界人口的快速增长和现代工农业的迅速发展,人类社会面临着日益严重的淡水资源短缺和环境水污染问题,对生态环境和人类健康构成了严重威胁[1-4]。尤其纺织和印染等工业排放的染料废水,由于其有机物含量高、成分复杂且难以生物降解,引起了研究人员的广泛关注[5-7]。目前对工业废水中有机污染物处理方法主要有化学氧化、物理吸附过滤、生物降解、芬顿氧化和光催化降解等技术[8-11]。其中光芬顿技术作为一种适用范围广、反应条件温和、效率高、二次污染少的降解方法,将铁基氧化物光催化技术与芬顿氧化技术相结合,提高强氧化性基团的产生效率,促进 Fe3+/Fe 2+的循环,可有效去除废水中有机污染物,提高光芬顿降解效率[12-16]。
ZnFe2O4是一种典型的尖晶石结构铁基金属氧化物半导体材料,禁带宽度较窄(约为1.9 eV),属于Fd3m空间群[17]。尖晶石结构混合金属氧化物的通式为AB2O4,其中A和B分别为二价和三价金属阳离子,氧离子的密集排布形成两种间隙,由4个氧原子和A形成AO4四面体单元,由6个氧原子和B形成BO6八面体单元。ZnFe2O4具有较高的热稳定性和化学稳定性、烧结温度低、量子产率高等特性[18-20]。对可见光吸收范围广,光催化活性较强[21-23],在电介质材料、传感器、光催化、高温陶瓷材料、光电转换、抗菌剂和微波磁性材料等方面应用前景广阔[24-28]。
半导体光催化剂的光催化性能不仅受到物理性质(能带结构、晶体结构、形貌、粒度和比表面积等),也受外界因素的影响,如温度、溶液pH值、光催化剂用量、污染物浓度、光源及照明时间等[29-32]。其中,微观结构是影响光催化剂性能的关键因素。迄今为止,有关形貌控制对ZnFe2O4光芬顿性能的影响的文章很少。因此本文的主要目的是研究尖晶石结构ZnFe2O4的形貌调控和光芬顿性能。
在本工作中,采用水热法和煅烧法对ZnFe2O4进行形貌调控,制备了正六面体状、微球状和空心球状3种不同形貌的 ZnFe2O4纳米晶。并对样品的微观结构、形貌和光电化学性能进行表征。此外,通过降解染料罗丹明B (RhB)来研究不同形貌ZnFe2O4的光芬顿性能的影响,提出了可能增强可见光催化活性的机制。
1. 实验部分
1.1 微球状(ZFO-1)的制备
采用水热法和煅烧法制备了不同形貌的 ZnFe2O4纳米晶。本实验所用原料均为分析纯,具体合成工艺如下:根据ZnFe2O4金属阳离子的摩尔配比,分别称取化学计量的Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和Fe(NO3)2·9H2O为原料,溶解于去离子水中,并在室温下通过磁力搅拌使之混合均匀。然后将NaOH溶液滴加到上述两种混合金属盐溶液中,调节混合溶液pH值为13。再将混合溶液转移至反应釜中,放入180℃恒温干燥箱中,水热反应13 h。待反应釜自然冷却至室温后洗涤干燥得到前驱体。最后将前驱体在400℃条件下煅烧2 h后得到小球状的ZnFe2O4,命名为ZFO-1。
1.2 空心球状(ZFO-2)的制备
同样以Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和Fe(NO3)2·9H2O为原料,分别溶解在由一定量的甘油和异丙醇组成的混合溶液中,通过磁力搅拌使之充分混合。再将混合溶液转入到反应釜,在180℃恒温干燥箱中反应6 h,然后对反应沉淀物洗涤并干燥。最后将前驱体以10℃/min的升温速率在350℃ 退火处理2 h得到空心球状ZnFe2O4,命名为ZFO-2。
1.3 正六边形状(ZFO-3)的制备
另外以Zn(NO3)2·6H2O和FeSO4·7H2O为原料,分别溶解于去离子水中,然后缓慢加入一定量的尿素和NH4F溶解到混合溶液中,通过超声振荡使其混合均匀。然后将得到的混合溶液转入反应釜中以200℃ 下加热24 h。冷却至室温后洗涤干燥。将所得黑色沉淀研磨转移至管式炉在通氩气的情况下 600℃ 的高温下煅烧4 h最终得到正六边形状ZnFe2O4,命名为ZFO-3。
1.4 测试与表征
通过X射线衍射(XRD,D/Max-2400型,Cu-Ka辐射,波长λ=0.154056 nm,扫描范围10°~90°,步长0.02°,日本理学Rigaku公司)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM,JSM-6701F,日本JEOL公司)、高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM,JEM-1200EX,日本JEOL公司)、能量色散 X 射线光谱仪(EDS,北京普析通用仪器仪器有限公司)和紫外可见漫反射光谱(UV-vis,PERSEE TU-1901,北京普析通用仪器仪器有限公司)表征材料的结构、形貌和光学特性。通过电化学工作站(CorrTest,CS 350,武汉科思特仪器股份有限公司),测试电化学阻抗谱(EIS)、瞬态光电流响应和莫特-肖特基(M-S)曲线,以评估所制备材料的光生载流子的复合、电子传输性能、半导体类型和能带位置。
1.5 光芬顿实验
通过氙灯模拟太阳光降解RhB评估催化剂光芬顿性能。称取 0.02 g 所制样品在黑暗中加入配制的RhB (10 mg·L−1)水溶液中超声分散均匀。开灯前,悬浮液在黑暗中持续搅拌0.5 h,以确保建立吸附-解吸平衡。在降解过程中每20 min取少量溶液通过使用UV-vis分光光度计 (λ=554 nm) 进行监测溶液吸光度。对于光芬顿实验,开灯前在上述光催化实验的悬浮液中添加适量 H2O2并调节pH后每10 min取少量溶液监测吸光度。根据郎伯-比尔定律分析降解率:
(Ct−C0)C0×100%=(At−A0)A0×100% (1) 其中:C0 和 Ct 分别代表初始和光照t时间溶液浓度;A0 和 At 分别是初始和光照t时间溶液的相应吸光度。
活性物种捕获实验分别使用对苯醌(BQ)、异丙醇(IPA)、乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)作为•O2−、•OH、h+的捕获剂,通过观测加入捕获剂后光芬顿降解效率与未加入捕获剂的光芬顿降解效率对比,了解该捕获剂捕获的自由基在光芬顿反应中所起的作用。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 不同形貌ZnFe2O4的物相分析
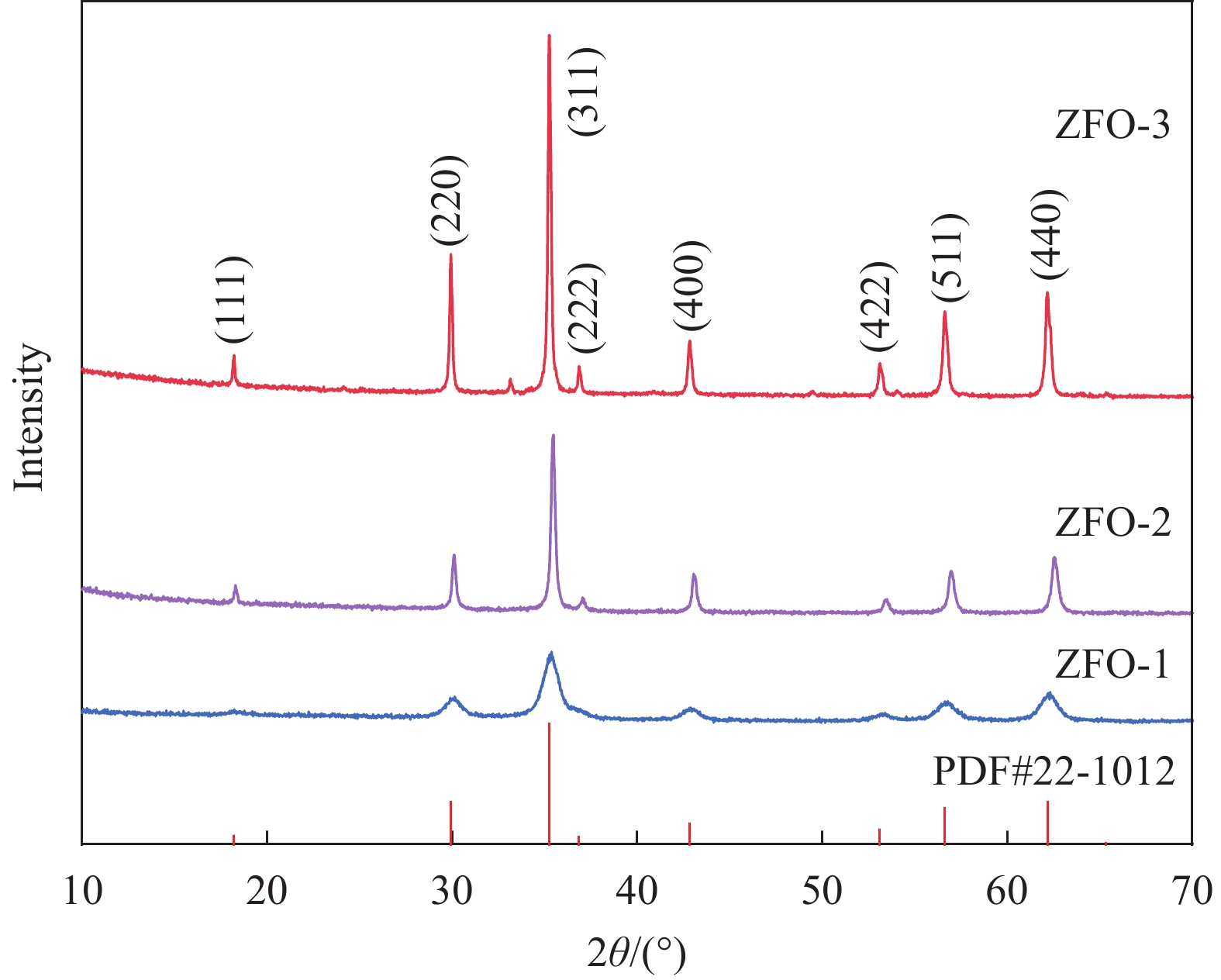
图1为不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品的X射线衍射图谱。可以看出ZnFe2O4样品在2θ=18.32°、29.92°、35.26°、36.88°、43.05°、53.62°、56.94°和62.21° 位置表现出明显的8个特征衍射峰,与尖晶石结构立方相ZnFe2O4 (JCPDS#22-1012)相匹配, 分别对应于(111)、(220)、(311)、(222)、(400)、(422)、(511)和(440)晶面,可以看出一个最明显的衍射峰,表明ZnFe2O4沿着(311)晶面生长。此外,不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品在 XRD 检测中未出现标准卡片以外的杂峰,表明成功制备出不同形貌的纯相ZnFe2O4。
2.2 ZnFe2O4的形貌对比
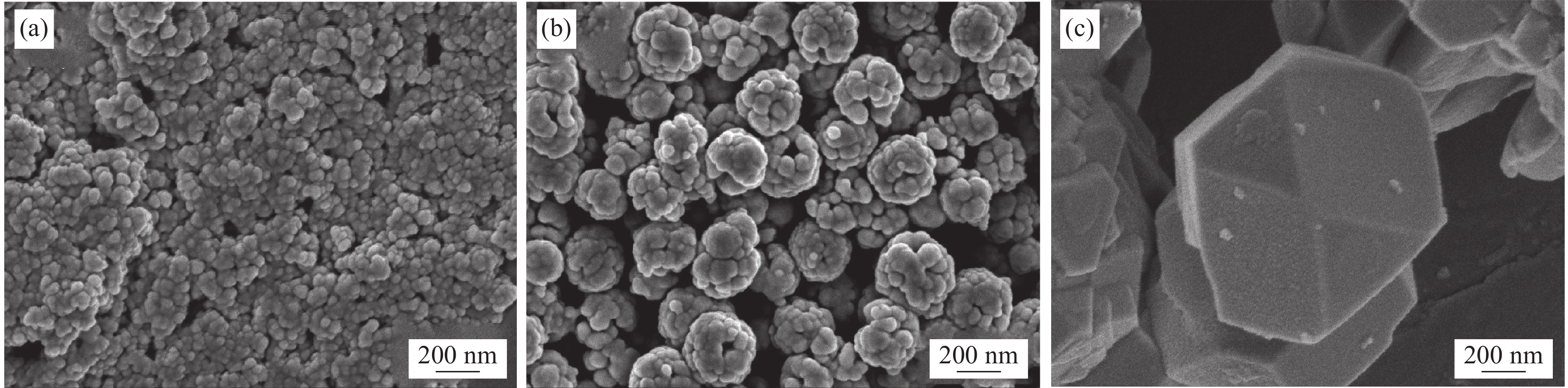
图2为3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品的SEM图像。从图2(a)可以看出,ZFO-1样品主要呈规则的微球形,颗粒表面光滑,尺寸比较均匀,平均粒径大约为50 nm。如图2(b)所示,ZFO-2中ZnFe2O4的表面上分别由许多小的纳米粒子生长在一起形成表面粗糙的空心结构球,球体的直径约为 200 nm。球体表面粗糙有利于提高光催化剂的吸附能力,因此三维空心结构对提高ZnFe2O4纳米材料的光催化活性具有积极作用。 ZFO-3样品的SEM图像如图2(c)所示,形貌为正六边形结构,表面光滑,边缘清晰,边长大概为1 μm。从图中分析得到通过调节反应体系的制备参数可以有效地调节纳米材料的形态形貌。
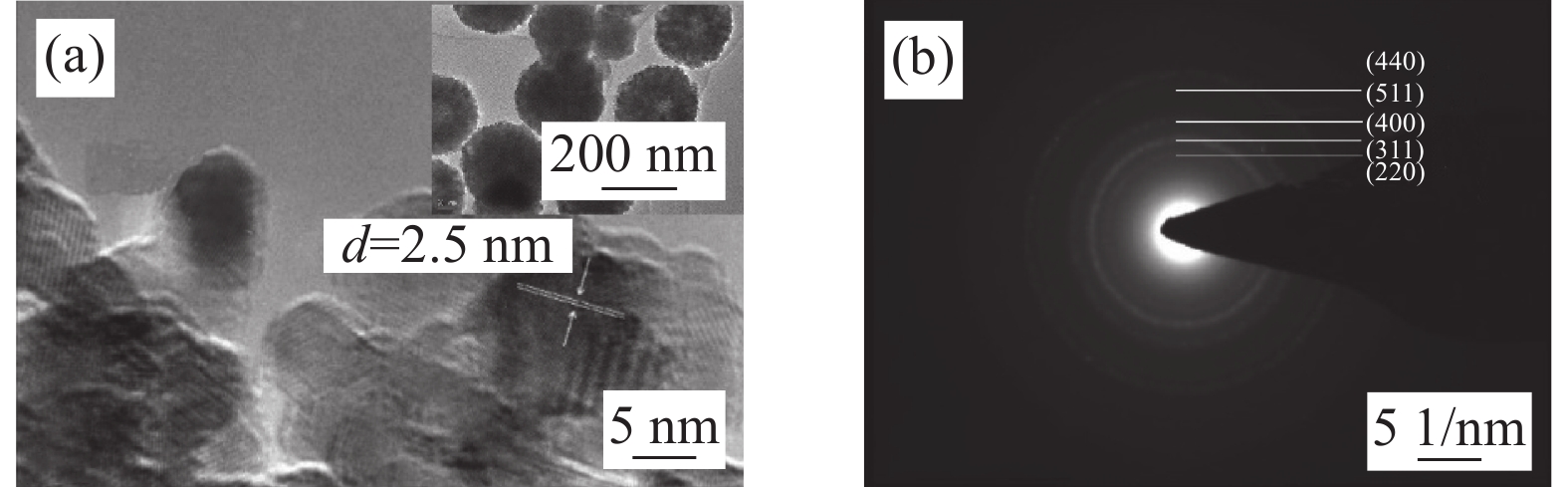
通过HRTEM进一步分析了三维空心球状ZnFe2O4的微观结构,如图3(a)插图所示,可以清晰地观察到由许多小纳米粒子团聚在一起形成三维疏松多孔的空心球状结构,单个球体的直径约为200 nm。且球体的边缘颜色较重而中间部分颜色较浅,表明ZFO-2样品为中空结构。
图3(a)为ZFO-2样品的局部放大HRTEM图像,可以清晰地观察到排列整齐的晶格条纹。经过测量得到晶面间距约为0.25 nm,对应于立方尖晶石结构ZnFe2O4上的(311)晶面,这与XRD结果一致。图3(b)为ZFO-2的选区电子衍射(SAED)图,由一系列半径不同的同心圆环组成,表明样品为多晶结构。这些衍射环从内到外分别对应立方相ZnFe2O4的(220)、(311)、(400)、(511)和(440)晶面。SAED和HRTEM结果进一步表明,ZnFe2O4样品具有立方尖晶石结构,这与XRD分析结果一致。
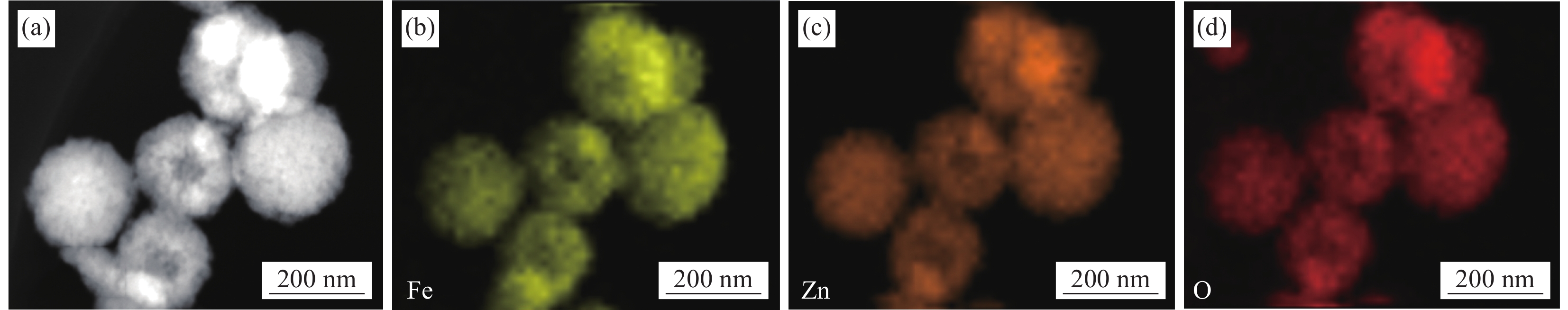
ZFO-2样品的元素映射图谱如图4所示,可以看出样品中的Zn、Fe和O元素均匀地分布在整个光催化剂上,没有富集现象,说明本方法在反应过程中成功合成了纯的ZnFe2O4纳米材料。
2.3 空心球状ZnFe2O4的比表面积
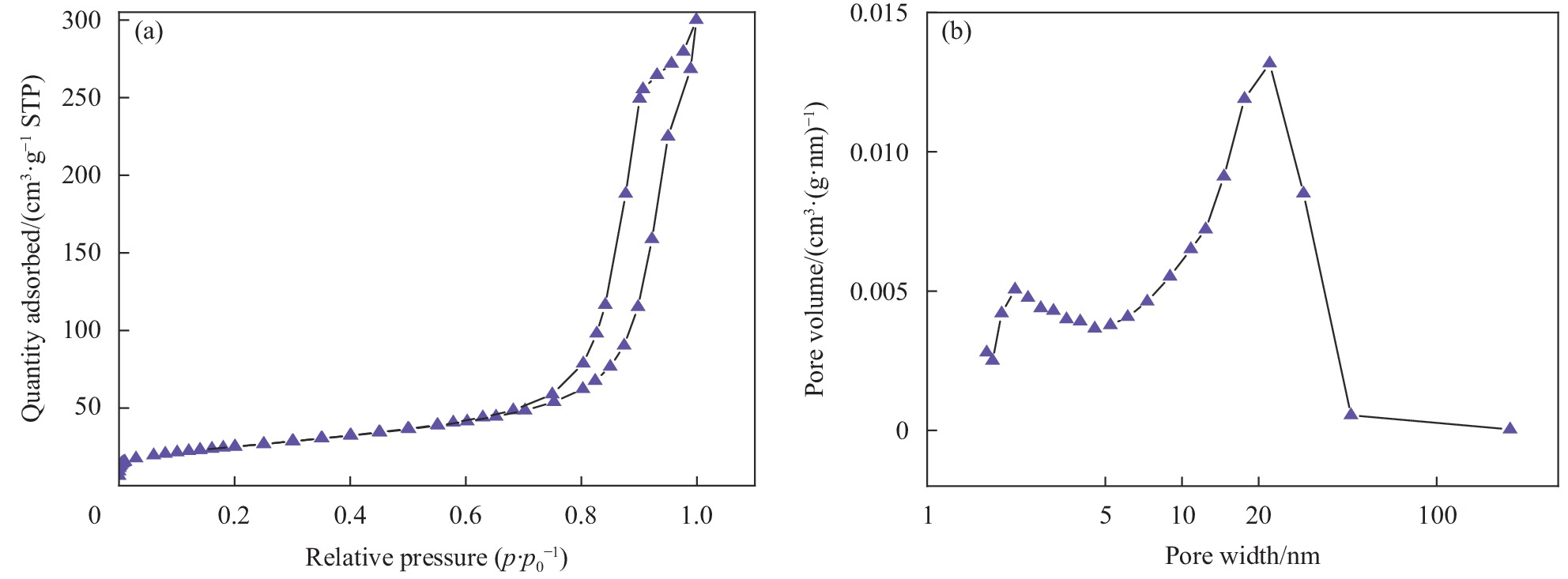
采用比表面分析仪和孔隙率分析仪研究了纯 ZnFe2O4的比表面积和孔径分布。如图5所示,纯ZnFe2O4光催化剂的氮气吸附-脱附等温线存在明显的IV型H3滞后环,表明样品具有介孔结构。这与SEM和HRTEM结果一致。此外,根据 Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET)模型计算,纯ZnFe2O4的比表面积为88.988 m2·g−1。用比表面积(BJH)法测定样品对应的孔径分布,ZnFe2O4的平均吸附孔径为10.26 nm。
2.4 不同形貌ZnFe2O4的UV-vis DRS性能
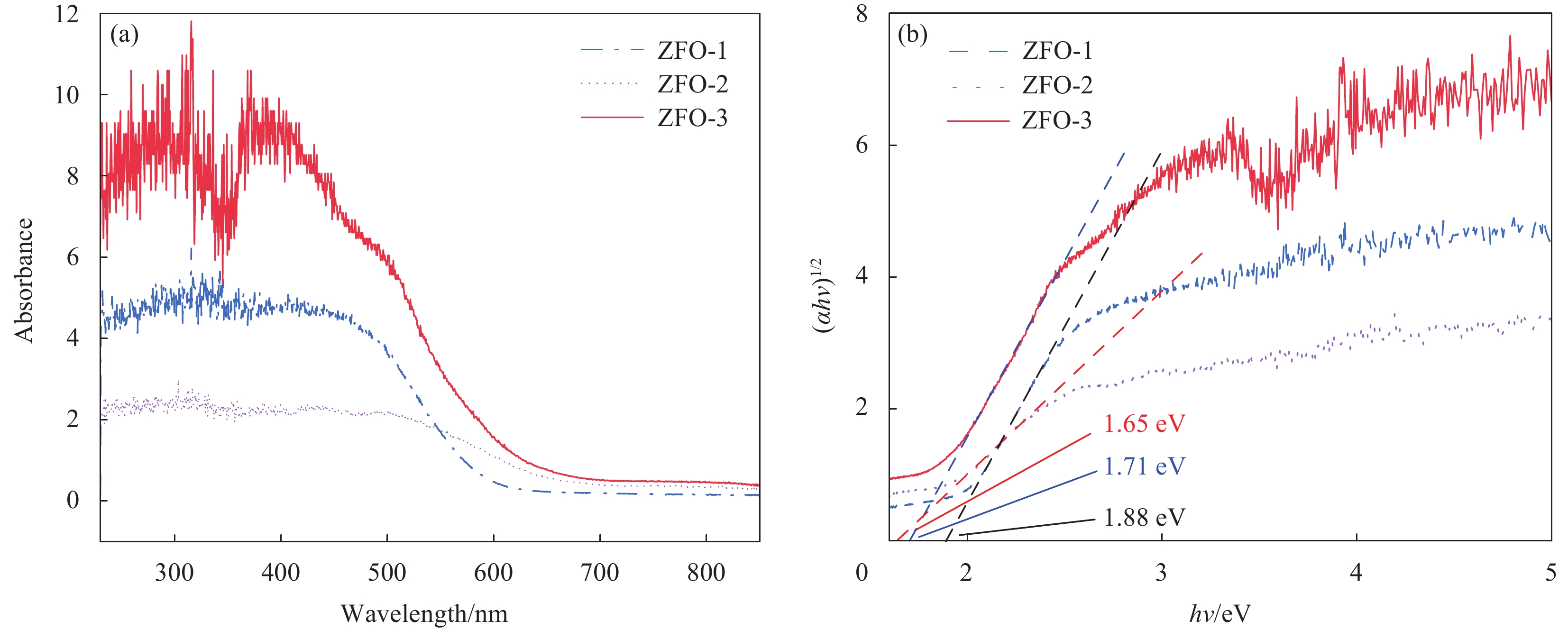
分别对微球状、空心球和正六边形3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品进行紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis)测试,研究其光响应能力和带隙,如图6(a)所示。三者在250~550 nm的可见光范围内均具有较好的可见光吸收特性和较强的光响应能力。与ZFO-1和ZFO-3相比,ZFO-2的吸收边在600 nm附近出现,向长波方向偏移,呈现出红移现象。
ZnFe2O4为直接带隙半导体材料,光学吸收系数与带隙Eg满足Tauc法则[33]:
(αhv)2=A(hv−Eg) (2) 其中:α、h、ν、A和Eg分别是吸收系数、普朗克常数、光子频率、常数和带隙。(αhν)2与hν的关系曲线如图6(b)所示,由此可得到ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3这3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品的带隙分别为1.71、1.65和1.88 eV,其中ZFO-2的带隙最小。
2.5 空心球状ZnFe2O4的电化学性能
图7显示了3000 Hz和5000 Hz下获得的ZFO-2样品的Mott-Schottky曲线。Mott-Schottky曲线在线性区域的斜率为正,表明ZnFe2O4是n型半导体。线性部分与横轴相交,横轴截距为平带电位VFB=−0.76 eV (vs SCE),n型半导体的导带电位VCB近似为平带电位VFB,根据下式[34]将相对标准甘汞电极电位(V(SCE))转换为标准氢电极电位(V(NHE)):
V(NHE)=V(SCE)+0.059pH+0.24(pH=7) (3) 结合UV-Vis测量ZFO-2样品的带隙Eg=1.65 eV,由此计算出ZFO-2的价带和导带电势分别为+1.54 eV和–0.11 eV。
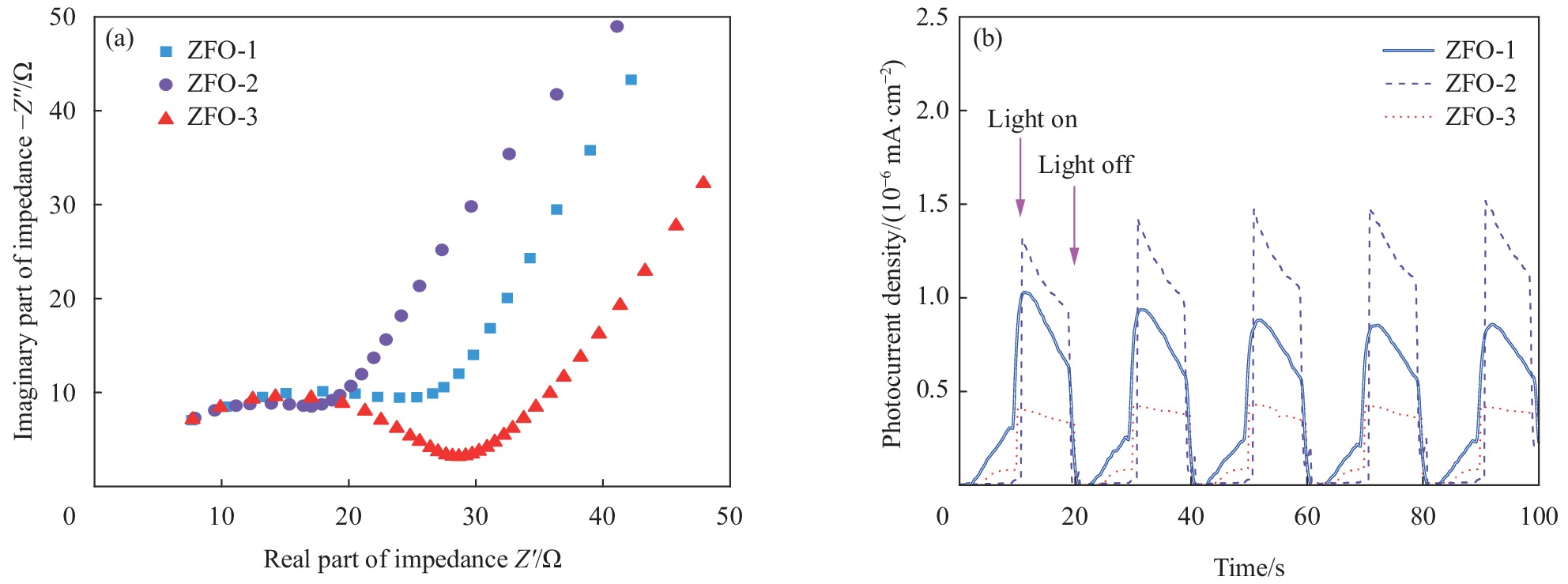
为了进一步研究3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品的光生载流子的转移和分离情况,对ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3样品进行Nyquis阻抗和瞬态光电流响应测试研究。由图8(a)可见,所有样品的Nyquis阻抗图在高频区域近似为半圆。Nyquist图的半圆形半径的相对大小代表光生载流子在电极和电解质之间的界面载流子转移电阻[35]。图8(a)中ZFO-2样品显示出圆半径最小,表明空心球状ZnFe2O4界面电荷转移电阻较低,有利于提高其光催化活性。图8(b)为3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品5个开/关循环下样品的瞬态光电流响应。光电流随光的开关而快速升降,表明样品具有快速的光响应,关灯后,光电流减小到初始值。与ZFO-1和ZFO-3相比,ZFO-2样品的光电流密度显著提高,说明其具有较好的光生电荷分离和迁移能力,进而表明ZFO-2催化剂具有较好的光芬顿活性。
2.6 不同形貌ZnFe2O4光催化和光芬顿降解RhB
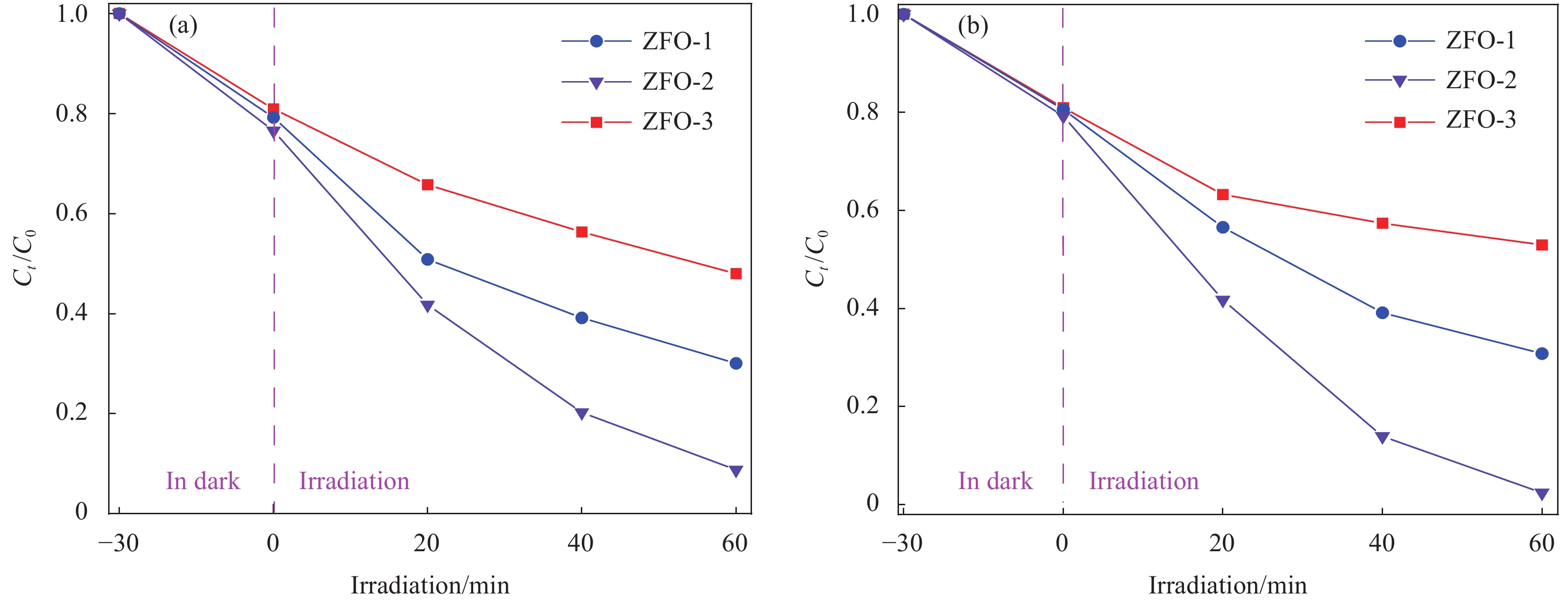
3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4样品的光催化效率通过模拟太阳光下降解RhB染料进行测试。图9(a)为ZnFe2O4光催化剂的光催化降解曲线。每次辐照反应前,先将悬浮液在黑暗中搅拌30 min后,以建立吸附-解吸平衡,可见所有样品的吸附率都在12.1%左右。打开氙灯模拟可见光辐射60 min后,ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3样品光降解污染物的效率依次是81.9%、91.3%和51.9%。图9(b)是在上述光催化实验中添加H2O2并调节pH后,30 min后ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3样品的光芬顿降解曲线,光芬顿降解污染物的效率依次是88.2%、97.6%和48.1%。相比之下,ZnFe2O4光催化剂在相同实验条件添加H2O2的光芬顿降解效率要比光催化降解效率高,ZFO-2样品的光催化和光芬顿降解效率明显优于ZFO-1和ZFO-3。
图10(a)为ZFO-2样品光催化降解RhB随辐照时间60 min (每20 min取样) UV光谱的变化。图10(b)为其光芬顿降解RhB随辐照时间为30 min(每10 min取样) UV光谱的变化。可以看到RhB浓度变化对应图中特征吸收峰(554 nm),随着时间的变化,特征吸收峰值逐渐降低并趋近0。以上分析可知ZFO-2催化剂的光催化和光芬顿降解能力明显优于其他形貌。与ZFO-1和ZFO-3相比,ZFO-2可能归因于其具有空心结构,光吸收能力增强,反应位点增多及更有效的光生电荷分离和迁移。
2.7 ZnFe2O4降解RhB光芬顿机制
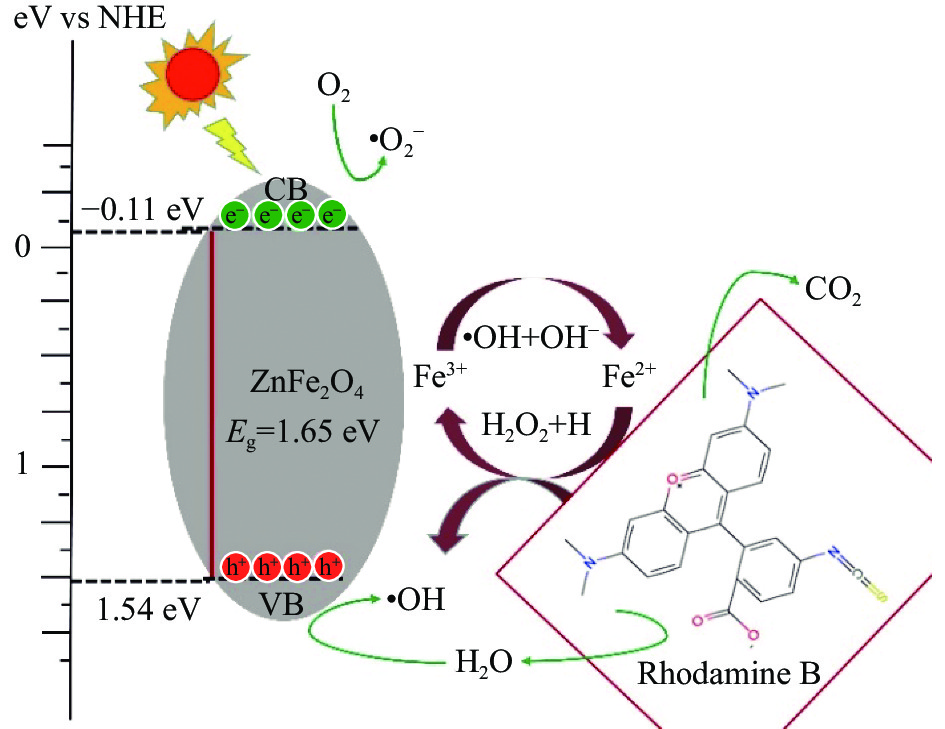
基于以上实验结果,ZFO-2在模拟可见光照射下可能的光催化降解机制如图11所示。n型ZnFe2O4半导体的带隙能Eg、导带能VCB和价带能VVB分别为1.65 eV、−0.11 eV和1.54 eV。光照射半导体表面时,当吸收能量大于Eg时,ZnFe2O4的价带中的电子被激发到导带,产生光生电子-空穴对[36]。导带中的电子被水中溶解氧捕获产生超氧自由基•O2−,而价带中的空穴可与OH–或H2O反应生成羟基自由基•OH,•OH和•O2−具有较强的氧化性,空穴本身也是氧化剂,在室温下可将RhB氧化为CO2和H2O等。此外,在光芬顿反应过程中,Fe3+作为受体捕获导带中的电子并还原为Fe2+,有效地抑制了光生电子和空穴的复合。然后Fe2+与H2O2反应,将Fe2+氧化为 Fe3+,同时产生大量•OH。在整个过程中,RhB被分解成小的无机分子,如CO2和H2O等其他小分子。
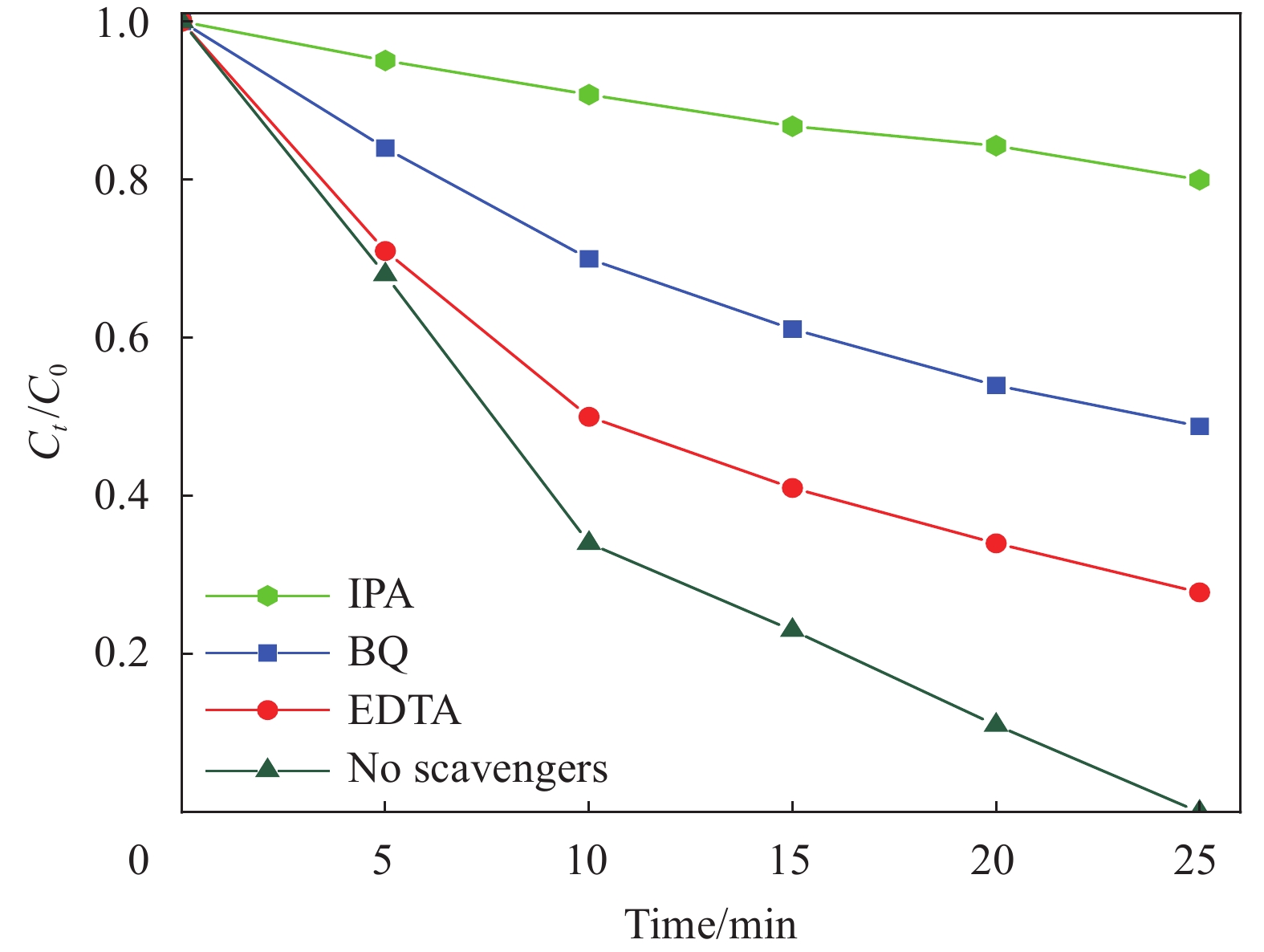
图12显示了氙灯在30 min (间隔5 min)的辐照下不同的活性物种捕获剂对ZFO-2样品光芬顿降解RhB的影响。图中在加入3种捕获剂后光芬顿降解速率都有所降低,值得注意的是,抑制光催化剂进行降解反应效果由强到弱依次为异丙醇(IPA)、苯醌(BQ)和乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA),其分别对应•OH、•O2−和h+自由基。由此可知,在光芬顿反应过程中自由基起最主要作用为•OH,其次是•O2−,最后为 h+。
3. 结 论
(1) 通过水热法和煅烧法,调整工艺参数制备了微球状(ZFO-1)、空心球(ZFO-2)和正六边形(ZFO-3) 3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4纳米晶。通过 XRD、SEM、TEM和EDS等表征材料的微观结构、形貌、元素组成。
(2) 3种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4纳米晶在可见光范围内均具有较好的可见光吸收特性和较强的可见光响应能力。与ZFO-1和ZFO-3相比,ZFO-2的带隙最窄,并出现红移现象。ZFO-2催化剂的转移内阻最小且瞬态光电流最大,表明具有优异的光生载流子的迁移和分离能力。
(3) 模拟可见光下催化剂对罗丹明B (RhB)的降解效率,探究不同形貌ZnFe2O4光催化剂的光催化和光芬顿活性。结果表明,ZFO-2型光催化剂具有最优异的降解性能,其在光催化实验中60 min将RhB几乎完全降解,而在光芬顿实验中仅30 min内RhB的降解率达到98.9%。自由基捕获实验表明,在光芬顿反应过程中自由基起最主要作用为•OH,其次是•O2−,最后为h+。
-
-
[1] LI X, XIE S Y, ZENG G M, et al. Research progress on application of magnetic nanomaterials in water pollution control[J]. Mini-Reviews in Organic Chemistry,2023,20(3):240-249. DOI: 10.2174/1570193X19666220328162619
[2] 马金环, 魏智强, 赵继威, 等. FeOCl光芬顿催化剂的表征及其降解罗丹明B的效果[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2023, 31(6): 9-18. MA Jinhuan, WEI Zhiqiang, ZHAO Jiwei, et al. Characterization of FeOCl photo-Fenton catalyst and its degradation effect of rhodamine B[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2023, 31(6): 9-18(in Chinese).
[3] WAN L, WANG H B. Control of urban river water pollution is studied based on SMS[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2021,22:101468.
[4] LI C, WEI Z Q, CHEN Y R, et al. Photo-electrochemical and enhanced photocatalytic activity of CdS/rGO nanocomposites prepared by hydrothermal method[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2021,32(17):22093-22105.
[5] DANG M, DENG Q L, TIAN Y Y, et al. Synthesis of anionic ionic liquids@TpBd-(SO3)2 for the selective adsorption of cationic dyes with superior capacity[J]. RSC Advances,2020,10(9):5443-5453. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA10035K
[6] GUO Q F, SUN H R, ZHANG L Y, et al. Fabric-based rGO/BiVO4 recyclable photocatalytic nanocomposites for dye degradation under visible light[J]. Composites Communications,2021,27:100846.
[7] LIU Q. Pollution and treatment of dye waste-water[J]. Earth and Environmental Science,2020,514(5):052001-052007.
[8] 梁家浩, 魏智强, 朱学良, 等. 尖晶石结构Ni掺杂ZnFe2O4纳米颗粒的性能表征[J]. 材料工程, 2019, 47(10):113-119. DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000042 LIANG Jiahao, WEI Zhiqaing, ZHU Xueliang, et al. Pro-perty characterization of spinel structure Ni-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2019,47(10):113-119(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000042
[9] TAO Y Q, CAI J, HUAI X L, et al. A novel antibiotic wastewater degradation technique combining cavitating jets impingement with multiple synergetic methods[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistryz,2018,44:36-44. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.02.008
[10] ZHU X L, WEI Z Q, ZHAO W H, et al. Preparation and characterization of Zn1-xNixFe2O4 nanoparticles with spinel structure synthesized by hydrothermal method[J]. Current Nanoscience,2018,14(6):474-480. DOI: 10.2174/1573413714666180528074117
[11] CUI Y, ZHANG D A, SHEN K L, et al. Biomimetic anchoring of Fe3O4 onto Ti3C2 MXene for highly efficient removal of organic dyes by Fenton reaction[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2020,8(5):104369. DOI: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104369
[12] YOU J Q, ZHANG X H, CHEN J L. Degradation of antibiotics by Fenton-like reaction catalyzed by iron oxide[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering,2022,2022:6849818.
[13] ZHU X Y, LIU L, DONG Z, et al. Confining Fe2O3 in silicalite-1 for effective catalytic activity in bias-assisted photo-Fenton system for nitrobenzene degradation[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2023,383:135525. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135525
[14] RUAN Y, KONG L J, ZHONG Y W, et al. Review on the synthesis and activity of iron-based catalyst in catalytic oxidation of refractory organic pollutants in wastewater[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,321:128924. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128924
[15] LUO Y, HAN H R, LI J J, et al. Fe doped Bi2O2S nanosheets for improved organic pollutants photo-Fenton degradation and CO2 photoreduction[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2023,306:122734. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122734
[16] LI C, WEI Z Q, LU Q, et al. Photoelectrochemical and photo-Fenton mechanism of enhanced visible light-driven nanocatalyst synthesis of ZnFe2O4/BiOI[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2022,29(23):34930-34942. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-022-18682-5
[17] KENFOUD H, NASRALLAH N, MEZIANI D, et al. Photoelectrochemical study of the spinel CaFe2O4 nanostructure: Application to basic blue 41 oxidation under solar light[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry,2021,25(6):1815-1823. DOI: 10.1007/s10008-021-04952-8
[18] BHOWMIK R. Tuning of composite cubic spinel structure in Co1.75Fe1.25O4 spinel oxide by thermal treatment and its effects on modifying the ferrimagnetic properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2016,680:315-327. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.163
[19] ZHAO W H, WEI Z Q, ZHANG X D, et al, Magnetic recyclable MnFe2O4/CeO2/SnS2 ternary nano-photocatalyst for photo-Fenton degradation[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2020, 593: 117443.
[20] KEFENI K K, MAMBA B B. Photocatalytic application of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and nanocomposites in wastewater treatment: Review[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies,2020,23:e00140. DOI: 10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00140
[21] 马金环, 魏智强, 梁家浩, 等. 水热法合成rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2超级电容器电极复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4580-4589. MA Jinhuan, WEI Zhiqiang, LIANG Jiahao, et al. Hydrothermal method of rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2 nanocomposites for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4580-4589(in Chinese).
[22] ZHAI B G, YANG L, MA Q L, et al. Visible light driven photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped ZnO nanocrystals[J]. Functional Materials Letters,2016,10(2):1750002.
[23] ARIMI A, MEGATIF L, GRANONE L I, et al. Visible-light photocatalytic activity of zinc ferrites[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2018,366:118-126. DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2018.03.014
[24] ANIS-UR-REHMAN M. Facile preparation approaches and prospective applications for nanostructured ferrites[J]. Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism,2017,30(11):3327-3331. DOI: 10.1007/s10948-016-3797-3
[25] DIPPONG T, LEVEI E A, CADAR O. Recent advances in synthesis and applications of MFe2O4 (M = Co, Cu, Mn, Ni, Zn) nanoparticles[J]. Nanomaterials,2021,11(6):1560. DOI: 10.3390/nano11061560
[26] RASHEED T, RIZWAN K, BILAL M, et al. Metal-organic framework-based engineered materials—Fundamentals and applications[J]. Molecules,2020,25(7):1598. DOI: 10.3390/molecules25071598
[27] SHOBANA M K, NAM H S, CHOE H. The effects of lithium and yttrium substitution on the optical and structural properties of cobalt ferrites[J]. Indian Journal of Physics,2019,93(3):307-313. DOI: 10.1007/s12648-018-1292-3
[28] LU Q, WEI Z Q, LI C, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by noble metal Ag modified semiconductor Zn2SnO4[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2022,138:106290. DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2021.106290
[29] ARELLANO C M, RAMIRIREZ M E, PAL U, et al. pH dependent morphology and texture evolution of ZnO nanoparticles fabricated by microwave-assisted chemical synthesis and their photocatalytic dye degradation activities[J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(19):27469-27478. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.06.170
[30] HU J H, DING J E, AI J P, et al. Room temperature growth of ZnO with highly active exposed facets for photocatalytic application[J]. Nanotechnology Reviews,2021,10(1):919-932. DOI: 10.1515/ntrev-2021-0057
[31] KAJITVICHYANUKUL P, NGUYEN V H, BOONUPARA T, et al. Challenges and effectiveness of nanotechnology-based photocatalysis for pesticides-contaminated water: A review[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 212(part C): 113336.
[32] ZANGIABADI M, SALJOOQI A, SHAMSPUR T, et al. Evaluation of GO nanosheets decorated by CuFe2O4 and CdS nanoparticles as photocatalyst for the degradation of dinoseb and imidacloprid pesticides[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(5):6124-6128. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.11.076
[33] REVATHI J, ABEL M J, ARCHANA V, et al. Synthesis and characterization of CoFe2O4 and Ni-doped CoFe2O4 nanoparticles by chemical Co-precipitation technique for photo-degradation of organic dyestuffs under direct sunlight[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter,2020,587:412136. DOI: 10.1016/j.physb.2020.412136
[34] LEE D U, LI J D, PARK M G, et al. Self-assembly of spinel nanocrystals into mesoporous spheres as bifunctionally active oxygen reduction and evolution electrocatalysts[J]. ChemSusChem,2017,10(10):2258-2266. DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201700369
[35] LI L, WEI Z Q, LIU W Z, et al. Selenium-doped Se-CoSe2@ZnSe heterojunction structure derived from ZIF-8 metal organic skeleton is used in high-performance asymmetric supercapacitors[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,927:167100. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.167100
[36] WEI Z Q, HUANG S P, ZHANG X D, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and photo-Fenton degradation of magnetic MnFe2O4/rGO nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2020,31(7):5176-5186. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-020-03077-4
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 颜秀花,房娟,唐兰勤. 磁性纳米ZnFe_2O_4/Ag_3PO_4复合材料的合成及光催化降解性能. 环境科学学报. 2025(01): 135-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 蒋莉萍,张雪乔,钟晓娟,魏于凡,肖利,郭旭晶,羊依金. 钒渣酸浸提铁工艺优化及复合光催化剂的制备. 化工进展. 2025(01): 538-548 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-
目的
水资源短缺和人类生产生活需水量的增加使得污水净化处理这一话题变热。高级氧化工艺因其高效、环境友好且没有二次污染成为一种行之有效的处理污水方法。其中最具代表性的就是光催化技术和芬顿技术。通过降解罗丹明模拟污水处理。研制成本小,效率高的纳米光催化剂具有重大的意义。
方法通过调整工艺参数,采用水热法和煅烧法制备了三种不同形貌的ZnFeO纳米晶,即微球状(ZFO-1)、空心球状(ZFO-2)和正六边形状(ZFO-3)。通过X射线衍射(XRD)分析物相结构,元素组成;利用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察形貌特点;高分辨率透射电子显微镜(HRTEM)计算晶面间距以及分析结构;用紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-vis)、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)和瞬态光电流响应测试等,对光电化学性能进行表征。通过降解罗丹明B(RhB)探究ZnFeO纳米晶光芬顿性能。
结果1从X射线衍射图谱中可以看出ZnFeO样品在2=18.32°,29.92°、35.26°、36.88°、43.05°、53.62°、56.94°和62.21° 位置表现出明显的8个特征衍射峰,与尖晶石结构立方相ZnFeO(JCPDS #22-1012)相匹配, 分别对应于(111)、(220)、(311)、(222)、(400)、(422)、(511)和(440)晶面,可以看出一个最明显的衍射峰,表明ZnFeO沿着(311)晶面生长。此外,不同形貌的ZnFeO样品在 XRD 检测中未出现标准卡片以外的杂峰,表明成功制备纯相ZnFeO。2SEM图可以看出,ZFO-1样品主要呈规则的微球形,颗粒表面光滑,尺寸比较均匀,平均粒径大约为50 nm。ZFO-2 中 ZnFeO的表面上分别由许多小的纳米粒子生长在一起形成表面粗糙的空心结构球,球体的直径约为 200 nm。球体表面粗糙有利于提高光催化剂的吸附能力,因此,三维空心结构对提高ZnFeO纳米材料的光催化活性具有积极作用。 ZFO-3样品形貌为正六边形结构,表面光滑,边缘清晰,边长大概为1μm。因此,通过调节反应体系的制备参数可以有效地调节纳米材料的形态形貌。3ZFO-2样品局部放大HRTEM图像观察到排列整齐的晶格条纹。经过测量得到晶面间距约为0.25 nm,对应于立方尖晶石结构ZnFeO上的(3 1 1)晶面,这与XRD结果一致。4ZFO-2光催化剂的氮气吸附-脱附等温线存在明显的 IV 型 H3 滞后环,表明样品具有介孔结构。此外,根据 Brunauer-Emmett-Teller(BET) 模型计算,纯ZnFeO的比表面积为 88.988 m g。用BJH法测定样品对应的孔径分布,ZnFeO的平均吸附孔径为102.6 。5对其进行紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis)测试,研究其光响应能力和带隙得到三者在250-550 nm的可见光范围内均具有较好的可见光吸收特性和较强的光响应能力。与ZFO-1和ZFO-3相比,ZFO-2的吸收边在600 nm附近出现,向长波方向偏移,呈现出红移现象。计算ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3三种不同形貌的ZnFeO样品的带隙分别为1.71、1.65和1.88 eV,其中ZFO-2的带隙最小。6在进行 Nyquis阻抗测量中。所有样品的Nyquis阻抗图在高频区域近似为半圆。ZFO-2样品显示出圆半径最小,表明空心球状ZnFeO界面电荷转移电阻较低,有利于提高其光催化活性。7降解RhB染料测试表明ZnFeO光催化剂在打开氙灯模拟可见光辐射60 min后,ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3样品光降解污染物的效率依次是81.9、91.3和51.9 %。添加HO并调节pH后,30 min后ZFO-1、ZFO-2和ZFO-3光芬顿降解污染物的效率依次是88.2、97.6和48.1 %。8对其做捕获实验证明抑制光催化剂进行降解反应效果由强到弱依次为异丙醇 (IPA)、苯醌 (BQ) 和乙二胺四乙酸 (EDTA),其分别对应·OH、·O和h自由基。
结论本文成功合成了三种不同形貌纳米光催化剂,在污水处理方面具有一定的意义。用许多测试对样品的微观结构、形貌、元素组成和光电化学性能进行表征。结果表明,所制备的三种ZnFeO纳米晶均具有立方尖晶石结构和良好的结晶度。ZFO-2表现出优异的可见光吸收能力和最窄的带隙,并发生红移现象。EIS测试表明,ZFO-2的转移内阻最小且瞬态光电流最大,具有优异的光生载流子的迁移和分离能力。ZFO-1、ZFO-2、ZFO-3催化剂的光芬顿降解效率依次为88.2、97.6和48.1 %,表明具有良好的降解性能。综合得到,ZFO-2具备优异的光降解性能。并探讨了可能的光芬顿降解RhB催化机理。
-
探索绿色发展、解决水污染已成为近年来商业发展的趋势。高级氧化工艺因其高效、环境友好且没有二次污染成为一种行之有效的处理污水方法。其中最具代表性的就是光催化技术和芬顿技术。调整工艺参数,我们采用水热法和煅烧法制备了三种不同形貌的ZnFe2O4纳米光催化剂,通过对样品的微观结构、形貌、元素组成和光电化学性能进行表征。此外,通过对罗丹明B(RhB)的降解研究ZnFe2O4纳米晶光芬顿性能。结果表明,所制备的三种ZnFe2O4纳米晶均具有立方尖晶石结构和良好的结晶度。空心球状(ZFO-2)表现出优异的可见光吸收能力和最窄的带隙,并发生红移现象。其阻抗测试表明,ZFO-2的转移内阻最小且瞬态光电流最大,具有优异的光生载流子的迁移和分离能力。三种催化剂的光芬顿降解效率体现出其具有良好的降解性能。综合得到,ZFO-2具备优异的光降解性能。并探讨了可能的光芬顿降解RhB催化机理。
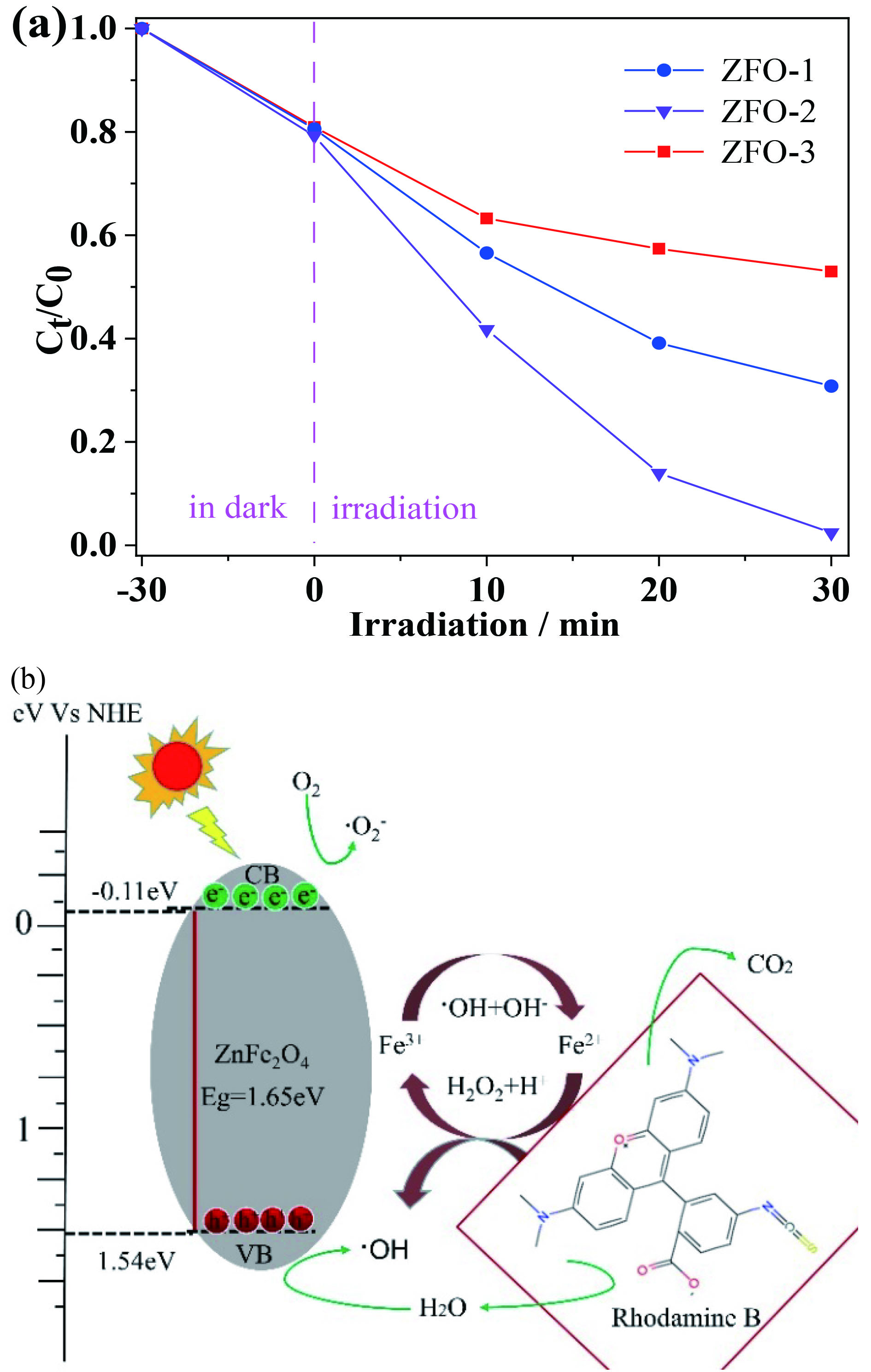
(a)光芬顿降解 RhB 随时间变化曲线 和光催化机理图




 下载:
下载: