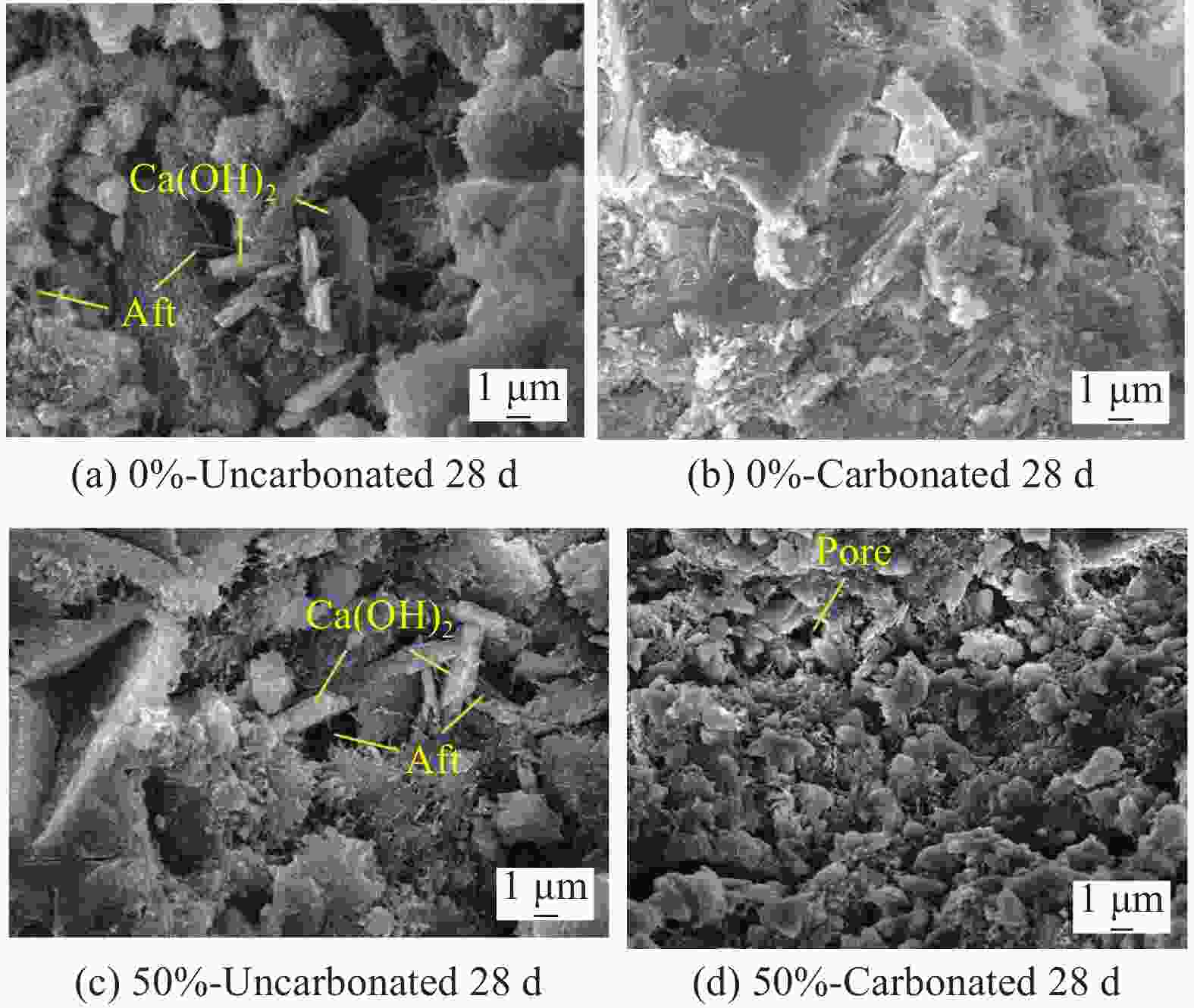
Effect of carbonation curing on the performance of cement paste added with carbide slag
-
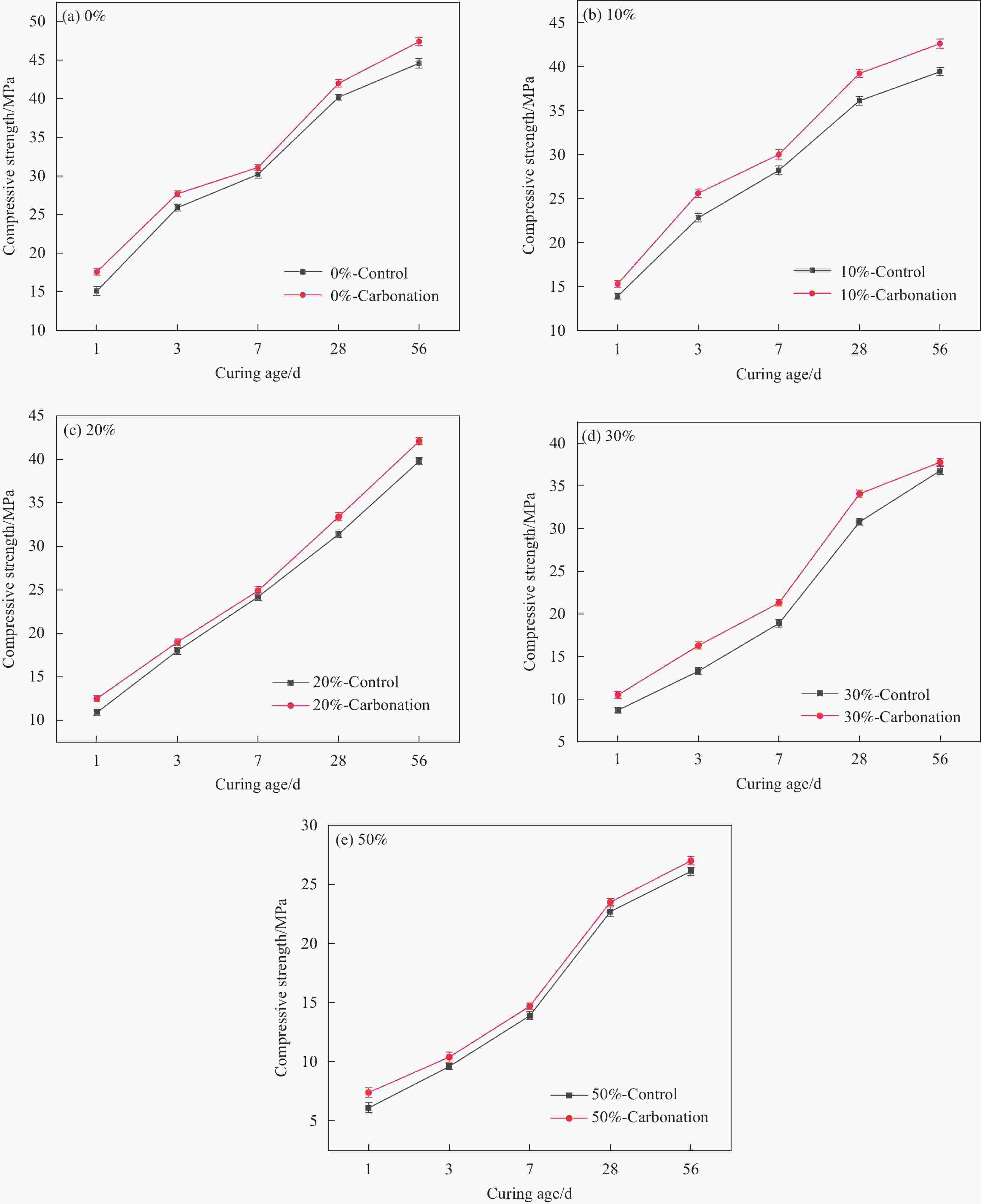
摘要: 为降低水泥行业的碳足迹同时回收利用电石渣,本文将电石渣作为掺合料加入碳化养护水泥中,研究了碳化养护对掺电石渣水泥石抗压强度、干燥收缩、氯离子渗透等性能的影响,并利用X射线衍射、热分析、压汞法、扫描电镜等测试手段对水泥石的微观结构进行了分析。结果表明:碳化养护提高了掺电石渣水泥石的抗压强度及抗氯离子侵蚀性能,使其电通量降低了38.17%~50.08%,56天干燥收缩率降低了8.8%~25.2%,细化了其孔结构。在保证水泥石强度不降低的前提下,约10%的电石渣可以被资源化利用,同时水泥石的固碳率可达11.19%~15.87%。利用碳化养护达到了捕捉固化二氧化碳、资源化利用电石渣、提升水泥石性能的目的。Abstract: In order to reduce the carbon footprint of cement industry and recycle carbide slag, carbide slag was added into carbonation curing cement as the mineral admixture. The influence of carbonation curing on the compressive strength, drying shrinkage, chloride ion penetration of cement paste added with carbide slag was studied, and the microstructure of cement paste was analyzed by X-ray diffraction, thermal analysis, mercury intrusion porosimetry, scanning electron microscopy, etc. The results show that carbonation curing can improve the compressive strength and chloride ion erosion resistance of cement paste added with carbide slag, reduce the electric flux by 38.17%-50.08%, reduce the 56 days drying shrinkage by 8.8%-25.2%, and refine the pore structure. About 10% of carbide slag can be used as resource under the premise that the strength of cement paste is not reduced, and the carbon fixation rate of cement paste can reach 11.19%-15.87%. The purpose of capturing and solidifying carbon dioxide, recycling carbide slag and improving the performance of cement paste are achieved by carbonation curing.
-
Key words:
- carbide slag /
- cement-based materials /
- carbonation curing /
- compressive strength /
- micro-structure
-
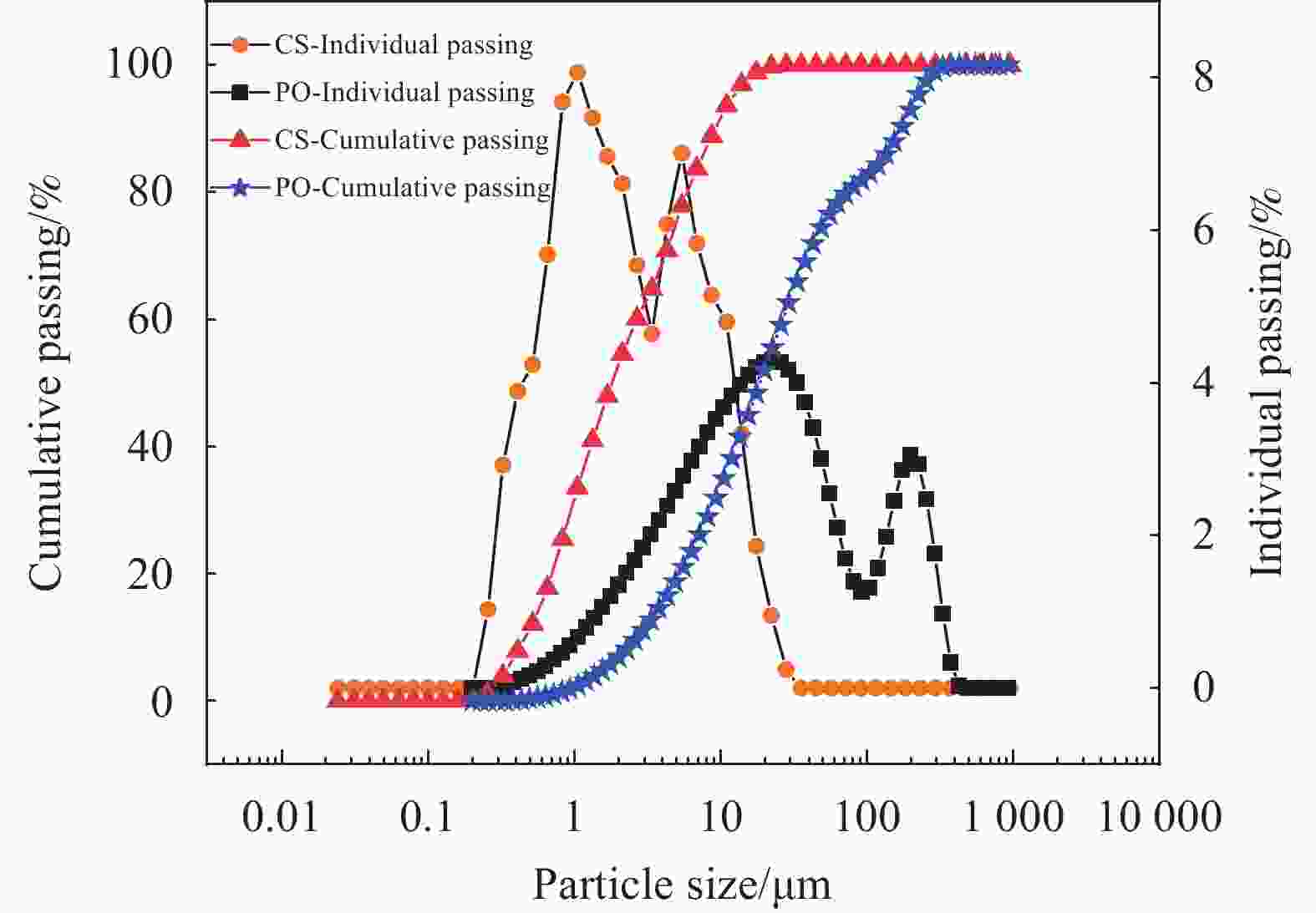
表 1 普通硅酸盐水泥(PO)和电石渣(CS)的化学组成 (wt%)
Table 1. Chemical composition of ordinary portland cement (PO) and carbide slag (CS) (wt%)
Composite CaO SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 MgO SO3 Na2O K2O TiO2 PO 58.36 21.34 8.22 4.12 3.50 1.23 0.78 0.47 0.35 CS 93.50 3.02 1.60 0.63 0.10 0.88 0.01 0.04 0.07 表 2 水泥石的加速碳化结果
Table 2. Accelerated carbonation results of cement paste
Items Curing
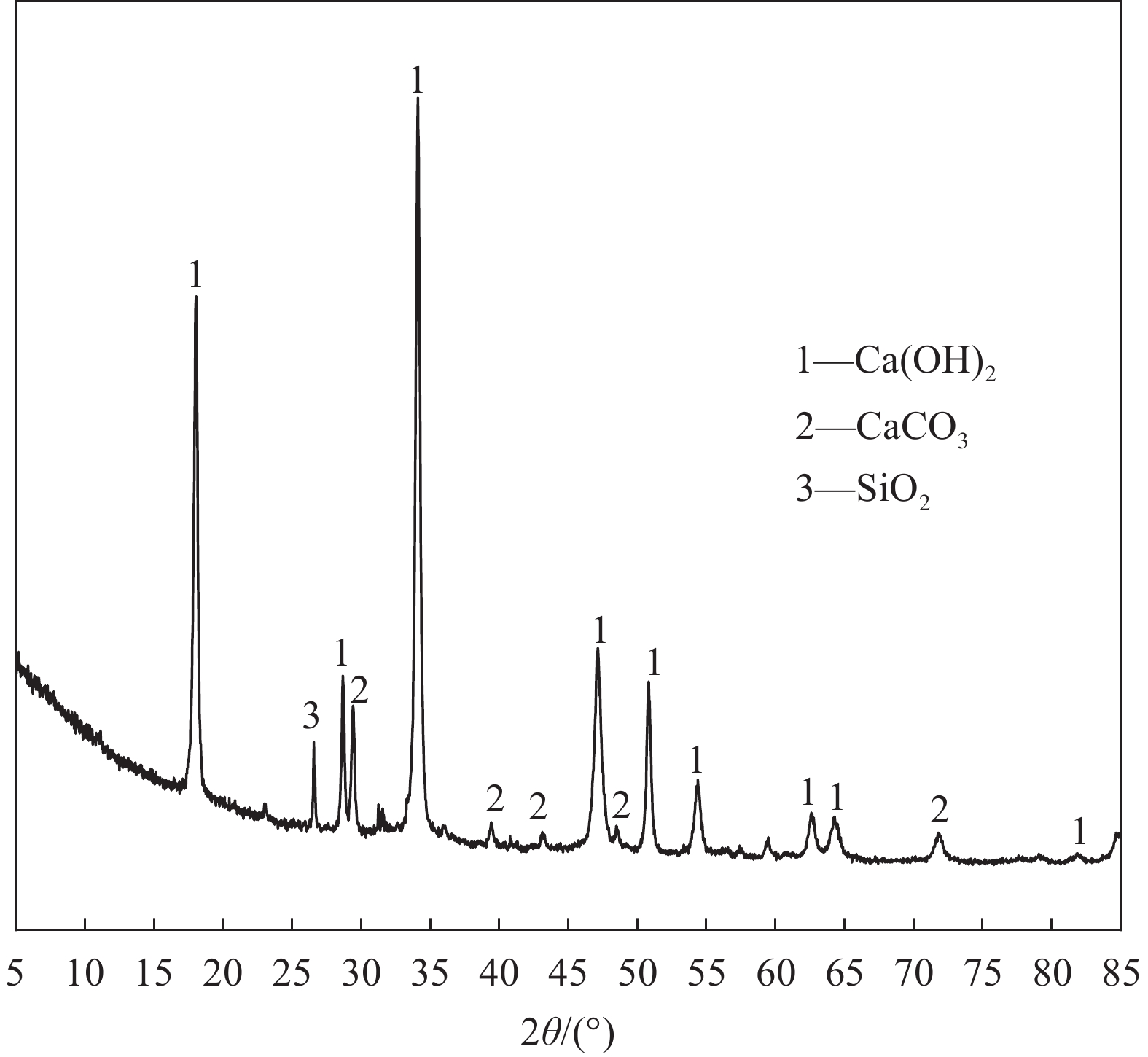
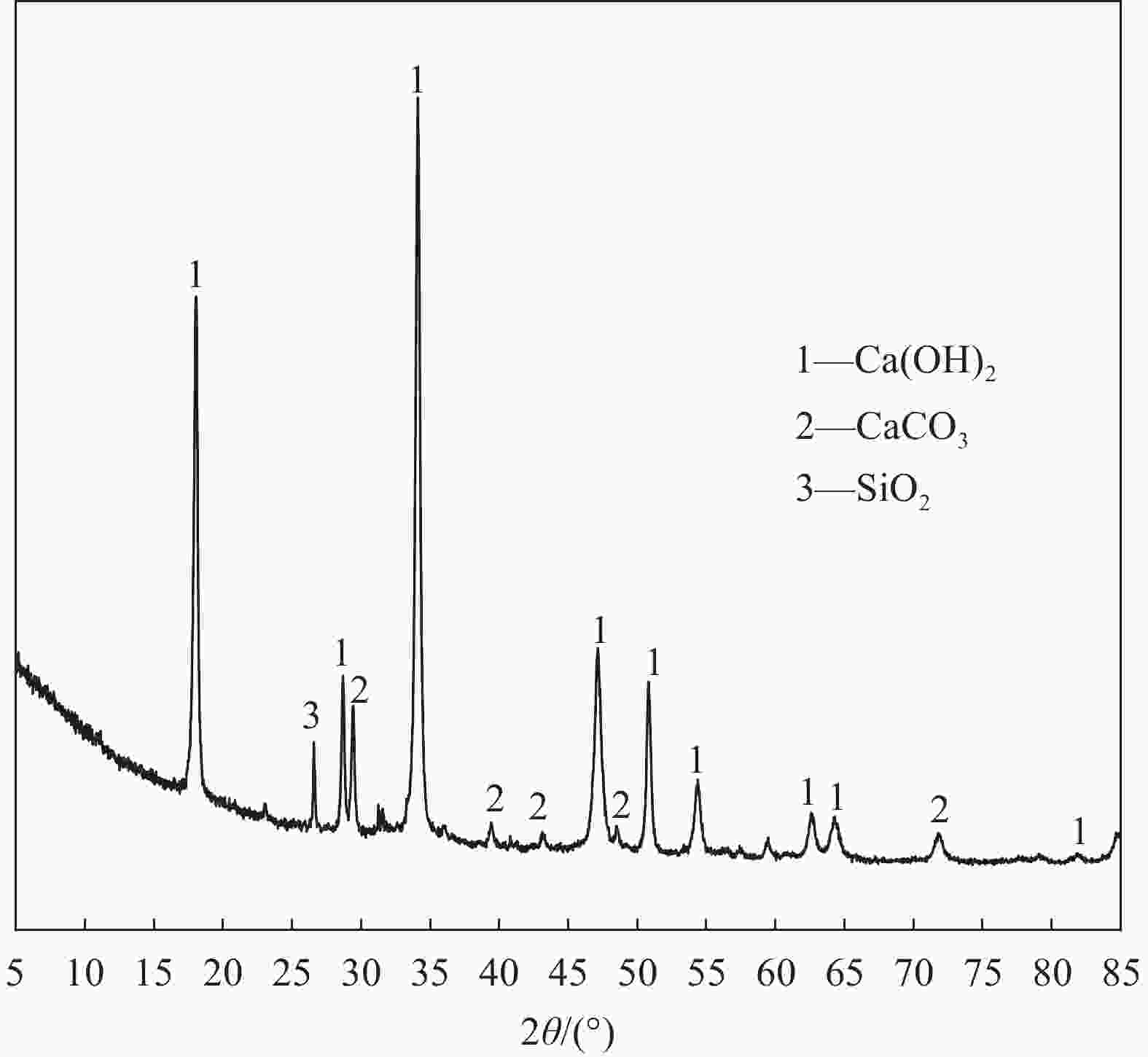
age/dUncarbonated (Control) Carbonated 0% 20% 50% 0% 20% 50% Ca(OH)2/wt% 1 2.23 2.93 5.72 2.08 2.71 5.61 7 2.31 3.69 6.66 2.18 3.58 5.87 28 2.61 4.71 7.52 2.48 4.11 6.89 Well-crystallinity CaCO3/wt% 28 4.17 5.78 6.35 4.91 7.72 8.55 Poor-crystallinity CaCO3/wt% 28 2.69 2.01 1.82 3.46 2.94 2.74 WC/PC 28 0.64 0.34 0.28 0.70 0.38 0.32 CO2 adsorption capacity/wt% — — — — 11.19 14.62 15.87 Notes: WC—Well-crystallinity; PC—Poor-crystallinity. 表 3 PO-CS 浆体孔结构参数
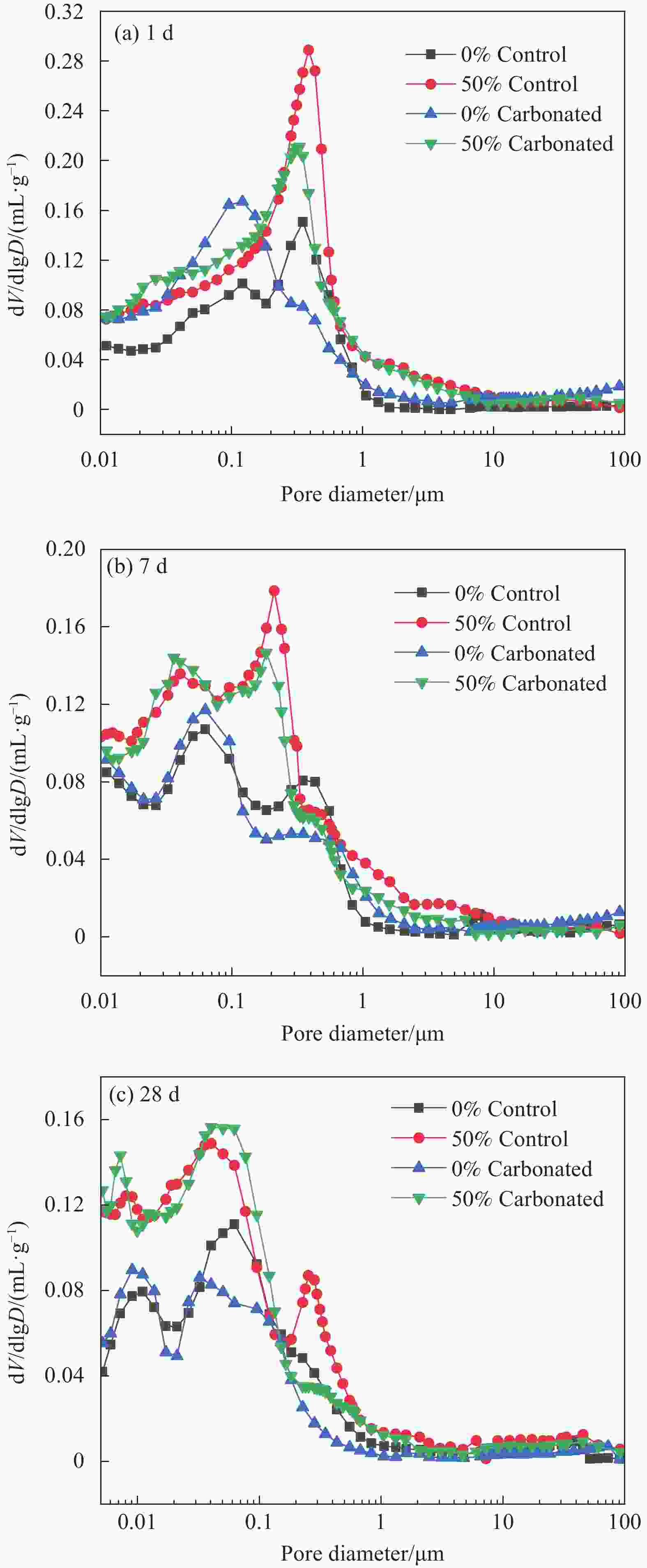
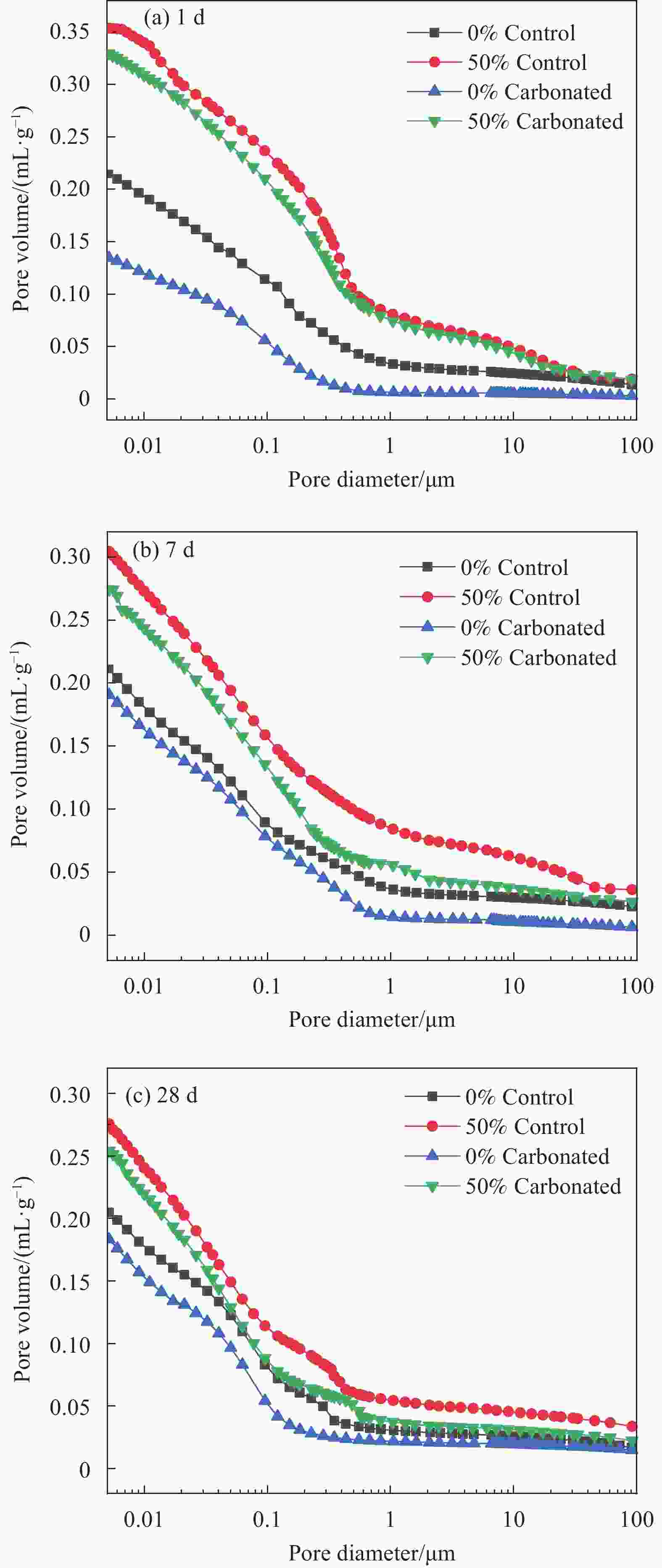
Table 3. Pore structure parameters of PO-CS pastes
Curing
age/dGroup Porosity
/%Pore size distribution/% <20 nm 20-50 nm 50-100 nm 100-1000 nm >1000 nm 1 Uncarbonated 0 26.7 21.3 16.3 13.4 39.5 9.5 50% 50.6 14.5 12.5 8.7 44.8 19.2 Carbonated 0 25.4 22.0 16.8 20.1 37.3 3.7 50% 43.7 14.7 13.5 10.5 42.0 18.9 7 Uncarbonated 0 21.1 28.7 16.9 15.9 34.1 4.4 50% 42.8 24.4 17.3 13.6 27.7 17.0 Carbonated 0 19.3 28.7 19.2 17.4 27.7 6.9 50% 40.2 24.1 18.5 15.4 30.1 11.9 28 Uncarbonated 0 18.7 26.3 18.7 21.4 24.0 9.6 50% 39.08 29.1 23.5 14.9 24.1 8.4 Carbonated 0 16.8 30.4 20.8 26.3 18.6 3.7 50% 37.1 31.4 23.9 17.3 21.0 6.3 -
[1] 赵雯涵, 吴水木, 李英杰. 钙基工业固废循环捕集CO2性能研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2022, 47(11):3926-3935.ZHAO Wenhan, WU Shuimu, LI Yingjie. Research progress on CO2 recycling performance of calcium-based industrial solid waste[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(11):3926-3935(in Chinese). [2] 万宗华, 张文芹, 刘志超, 等. 电石渣-矿渣复合胶凝材料性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2022, 41(5):1704-1714.WAN Zonghua, ZHANG Wenqin, LIU Zhichao, et al. Study on properties of carbide slag-slag composite cementitious materials[J]. Bulletinthe Chinese Ceramic Society,2022,41(5):1704-1714(in Chinese). [3] 赵立文, 朱干宇, 李少鹏, 等. 电石渣特性及综合利用研究进展[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2021, 27(3):13-26.ZHAO Liwen, ZHU Ganyu, LI Shaopeng, et al. Research progress on properties and comprehensive utilization of calcium carbide slag[J]. Clean Coal Technology,2021,27(3):13-26(in Chinese). [4] 李文秀, 杨宇航, 黄艳, 等. 二氧化碳矿化高钙基固废制备微细碳酸钙研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(4):2047-2057.LI Wenxiu, YANG Yuhang, HUANG Yan, et al. Research progress on preparation of fine calcium carbonate from high calcium base solid waste by carbon dioxide mineralization[J]. Chemical Industry Progress,2023,42(4):2047-2057(in Chinese). [5] JUN C, JUN H Z, JIAN Z L, et al. Physicochemical characterizations and desulfurization properties in coal combustion of three calcium and sodium industrial wastes[J]. Energy & Fuels,2009,23(3):2506-2516. [6] 王秋华, 吴嘉帅, 张卫风. 碱性工业固废矿化封存二氧化碳研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2023, 42(3):1572-1582.WANG Qiuhua, WU Jiashuai, ZHANG Weifeng. Research progress on carbon dioxide sequestration by alkaline industrial solid waste mineralization[J]. Chemical Industry Progress,2023,42(3):1572-1582(in Chinese). [7] 李英杰, 谢辛, 孙荣岳, 等. 流态化下电石渣循环煅烧/碳酸化捕集CO2特性[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2014, 34(26):4447-4453.LI Yingjie, XIE Xin, SUN Rongyue, et al. Characteristics of carbon dioxide capture by cyclic calcination/carbonation of calcium carbide slag under fluidization[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering,2014,34(26):4447-4453(in Chinese). [8] RIAD, AYECHE, OUALID, et al. Valorization of carbide lime waste, a by-product of acetylene manufacture, in wastewater treatment[J]. Desalination and Water Treat,2012,50(13):87-94. [9] YANG J, ZHANG Y, HE X, et al. Heat-cured cement-based composites with wet-grinded fly ash and carbide slag slurry: Hydration, compressive strength and carbonation[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,307:124916. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124916 [10] DD A, ENVELOPE H, FANG W A, et al. Solid waste-based dry-mix mortar using fly ash, carbide slag, and flue gas desulfurization gypsum[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,21(10):3636-3649. [11] 王勇, 张萌, 曹元辉, 等. 电石渣水泥生产对水泥行业碳减排的影响分析[J]. 水泥, 2022, 545(7):10-12.WANG Yong, ZHANG Meng, CAO Yuanhui, et al. Analysis of influence of carbide slag cement production on carbon emission reduction in cement industry[J]. Cement,2022,545(7):10-12(in Chinese). [12] REN Y, WANG Z, QU G, et al. Comprehensive performance study of aluminum ash and calcium carbide slag for brick making under ultra-high pressure[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,359:129526. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129526 [13] PANG L, PAN Y, DENG B, et al. Conjoint reuse of ceramic polishing waste and calcium carbide slag as mineral admixtures: Hydration and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2023,72:106741. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106741 [14] 张明星. 利用工业余热高产量/低能耗粉碎粉煤灰的动力学机制及关键控制技术[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2022.ZHANG Mingxing. Dynamic mechanism and key control technology of pulverizing fly ash with industrial waste heat at high yield/low energy consumption[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2022(in Chinese). [15] 张忠圆, 付神进. 国际水泥行业发展及碳减排现状简述[J]. 中国水泥, 2022, 246(11):20-23.ZHANG Zhongyuan, FU Shenjin. Development and carbon emission reduction of international cement industry[J]. China Cement Corporation,2022,246(11):20-23(in Chinese). [16] 秦玲. 水泥基材料早期碳化反应动力学和长期性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.QIN Ling. Study on early carbonation kinetics and long-term properties of cement-based materials[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [17] 曾海马, 刘志超, 王发洲. 碳化养护对大掺量钢渣砂浆的力学性能及显微结构的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(11):1801-1807.ZENG Haima, LIU Zhichao, WANG Fazhou. Effect of carbonization curing on mechanical properties and microstructure of steel slag mortar with large dosage[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(11):1801-1807(in Chinese). [18] 张丰, 莫立武, 邓敏. 碳化养护对钢渣混凝土强度和体积稳定性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2016, 44(5):640-646.ZHANG Feng, MO Liwu, DENG Min. Influence of carbonization curing on strength and volume stability of steel slag concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,44(5):640-646(in Chinese). [19] 管学茂, 魏红姗, 马小娥, 等. C3S2矿物的加速碳化硬化过程[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2018, 21(6):900-905.GUAN Xuemao, WEI Hongshan, MA Xiao'e, et al. Accelerated carbonization hardening process of C3S2 minerals[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2018,21(6):900-905(in Chinese). [20] 秦玲, 毛星泰, 高小建, 等. 碳化养护蒸压加气混凝土改性水泥的抗硫酸盐侵蚀性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(12):1269-1276.QIN Ling, MAO Xingtai, GAO Xiaojian, et al. Sulfate resistance of carbonized curing autoclaved aerated concrete modified cement[J]. Journal of Building Materials,2022,25(12):1269-1276(in Chinese). [21] XIAN X, MA H T, SHAO Y. Production of concrete pipes by carbonation curing in an inflatable enclosure[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,363:129861. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.129861 [22] ZHANG D, SHAO Y. Early age carbonation curing for precast reinforced concretes[J]. Construction Building Materials,2016,113(11):134-143. [23] 国家质量技术监督局. 水泥胶砂强度检验方法: GB/T 17671—1999[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1999.The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision of China. Test method for strength of cement mortar: GB/T 17671—1999[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 1999(in Chinese). [24] ZHANG D, GHOULEH Z, SHAO Y. Review on carbonation curing of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization,2017,21(7):119-131. [25] SHAO Y, ROSTAMI V, HE Z, et al. Accelerated carbonation of portland limestone cement[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2014,26(1):117-124. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0000773 [26] GAITERO J J, CAMPILLO I, GUERRERO A. Reduction of the calcium leaching rate of cement paste by addition of silica nanoparticles[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2008,38(8):1112-1118. [27] MO L W, ZHANG F, DENG M. Mechanical performance and microstructure of the calcium carbonate binders produced by carbonating steel slag paste under CO2 curing[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2016,88(5):217-226. -





 下载:
下载: