Research on microstructure and site preference of NiTi alloy coating on 316L by laser cladding
-
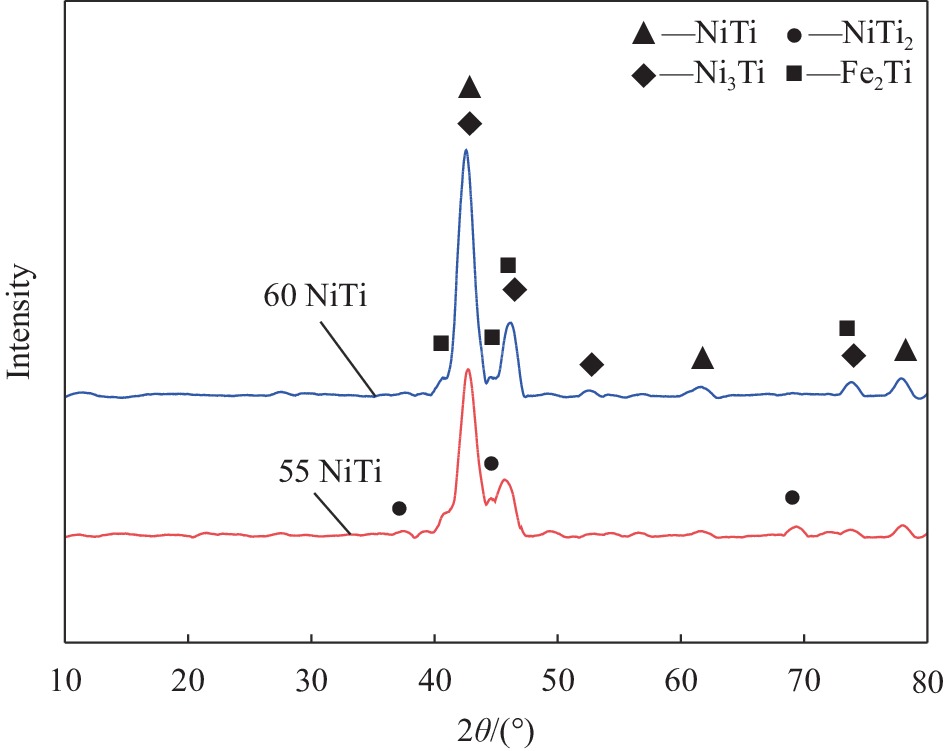
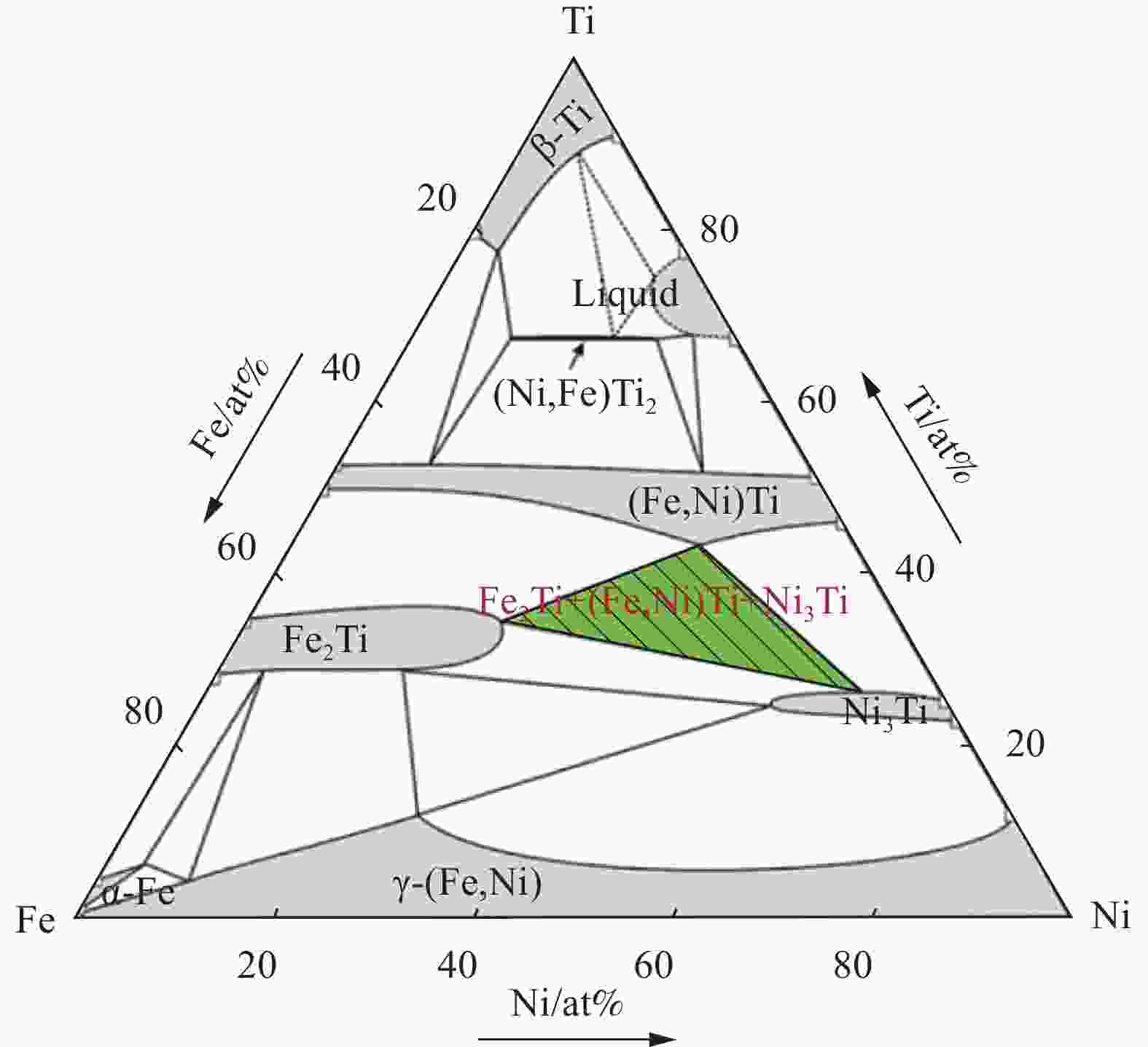
摘要: 60 NiTi (60wt%Ni-40wt%Ti)合金具有高硬度、高弹性模量及优异的耐磨和耐腐蚀性能,在许多领域有潜在的应用价值。本文对激光熔覆方法在316L不锈钢表面制备NiTi涂层的微观组织结构和物相组成进行了分析。结果表明:基材中主要成分Fe和Cr扩散到熔覆涂层中并显著地影响了镍钛涂层的组织结构和性能。熔覆涂层主要组成相为NiTi和Ni3Ti,提高Ni含量可抑制NiTi2析出。第一性原理计算结果显示,Fe和Cr元素易于固溶在B2结构的NiTi相中,并且都倾向于置换晶胞中的Ni原子。Ni3Ti晶胞结构中的Ni和Ti原子各有2个不同的晶位,Fe原子倾向于置换晶胞中Ni-1晶位的Ni原子,而Cr原子倾向于置换晶胞中Ni-2晶位的Ni原子。根据涂层的成分分析结合模拟可知,镍钛合金涂层中NiTi和Ni3Ti相的化学式分别为Ni5Ti8Fe2Cr和Ni9Ti4Fe2Cr。Abstract: 60 NiTi (60wt%Ni-40wt%Ti) alloy presents higher hardness, high elastic modulus, good abrasion performance and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various applications in different fields. This paper investigated the microstructure and phase composition of NiTi alloy coating on 316L stainless steel prepared by laser cladding. It shows that the main alloying elements Fe and Cr in the substrate are significantly doped into the cladding coating, which obviously affect the microstructure and properties of Ni-Ti coating. The main phases in the coating are NiTi and Ni3Ti phases. Increase the content of Ni can inhibit the precipitation of NiTi2. First-principles calculation based on density functional theory was used to study the phase preference and site preference occupations of the alloying elements Fe and Cr from substrate in NiTi and Ni3Ti phases. The microstructure and phase composition of the coatings were investigated as well. The results show that, NiTi and Ni3Ti are the major phases in the coating. Both Fe and Cr atoms prefer to substitute Ni atom in the NiTi (B2) crystal structure. However, in the Ni3Ti crystal structure, each Ni and Ti atom has two different crystal positions, Fe atom prefers to substitute position Ni-1 and Cr atom prefers to substitute position Ni-2 instead. Combined the experiment and calculation results, the major phases in the coatings after element doping are supposed to be Ni5Ti8Fe2Cr and Ni9Ti4Fe2Cr.
-
Key words:
- laser cladding /
- NiTi alloy /
- first-principles calculation /
- alloy doping /
- site preference /
- surface modification
-
表 1 基体材料316L不锈钢的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of 316L stainless steel substrate
Element Fe Cr Ni Mo Mn Si P C S Mass fraction/wt% Balance 16.320 10.120 2.040 0.920 0.340 0.026 0.016 0.015 表 2 Ni粉末和55 NiTi合金粉末的化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of Ni and 55 NiTi powders
Element Ni Ti Fe Nb Co C Si O Mass fraction of
Ni powder/wt%Balance — 0.003 — 0.020 0.020 0.003 0.006 Mass fraction of 55 NiTi powder/wt% 56.460 Balance 0.005 0.010 0.005 0.005 — 0.037 表 3 激光熔覆工艺参数
Table 3. Process parameters for laser cladding
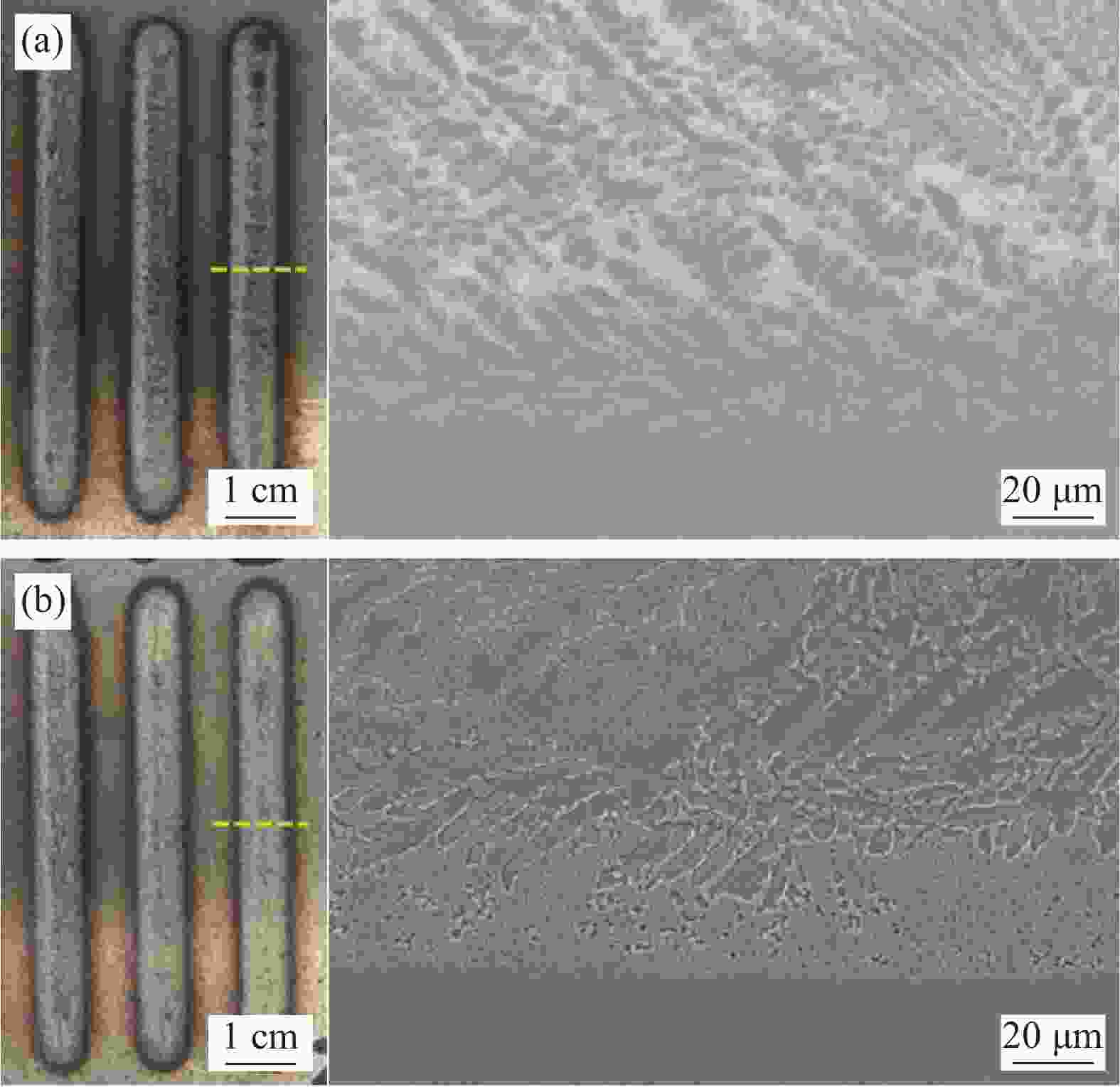
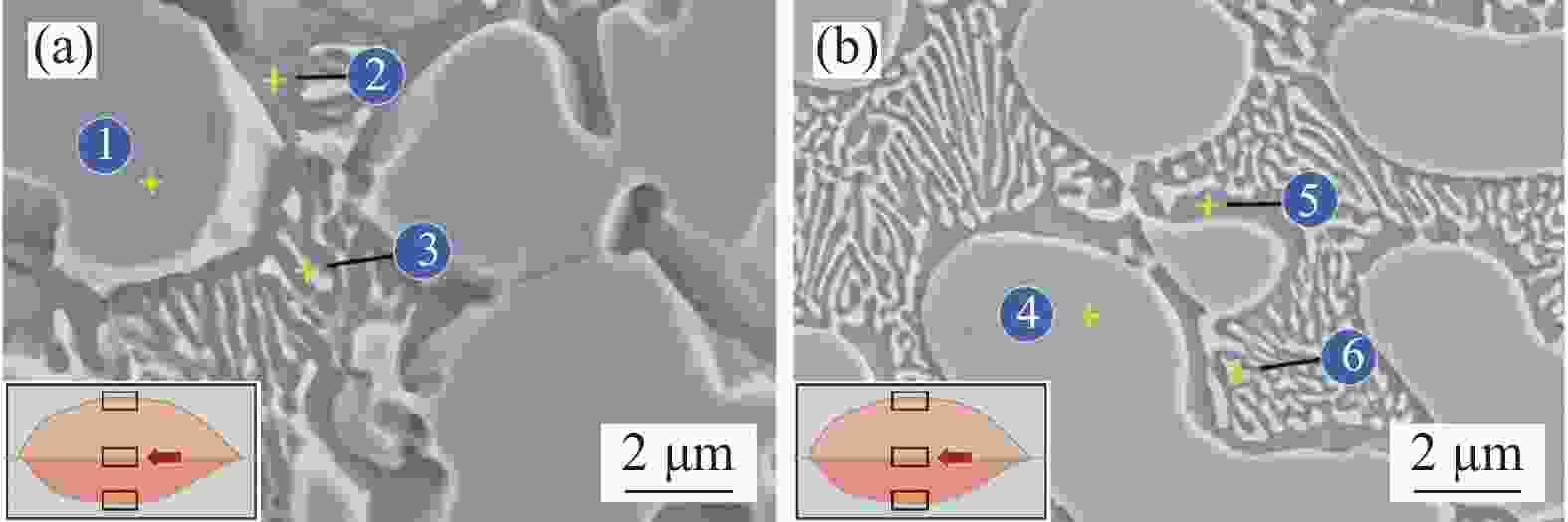
Parameter Value Laser power/kW 2.0 Scan speed/(mm·s–1) 2.0 Laser beam spot diameter/mm 7.2 Working distance/mm 10 Overlap ratio/% 55 Powder feed rate/(r·min–1) 50 Carrier gas flow rate/(L·min–1) 8 Shielding gas flow rate/(L·min–1) 5 Coating Position Ni/at% Ti/at% Fe/at% Cr/at% Major phase 55 NiTi 1 35.34 41.28 15.63 7.75 NiTi 2 59.59 25.74 10.32 4.35 Ni3Ti 3 45.10 34.77 14.52 5.61 Ni3Ti + NiTi 60 NiTi 4 38.48 42.89 13.42 5.21 NiTi 5 61.63 23.27 9.26 5.84 Ni3Ti 6 50.08 30.34 16.33 3.25 Ni3Ti + NiTi 表 5 NiTi相和Ni3Ti相的晶胞结构和原子位置
Table 5. Crystal structure and atom position of the NiTi and Ni3Ti phase
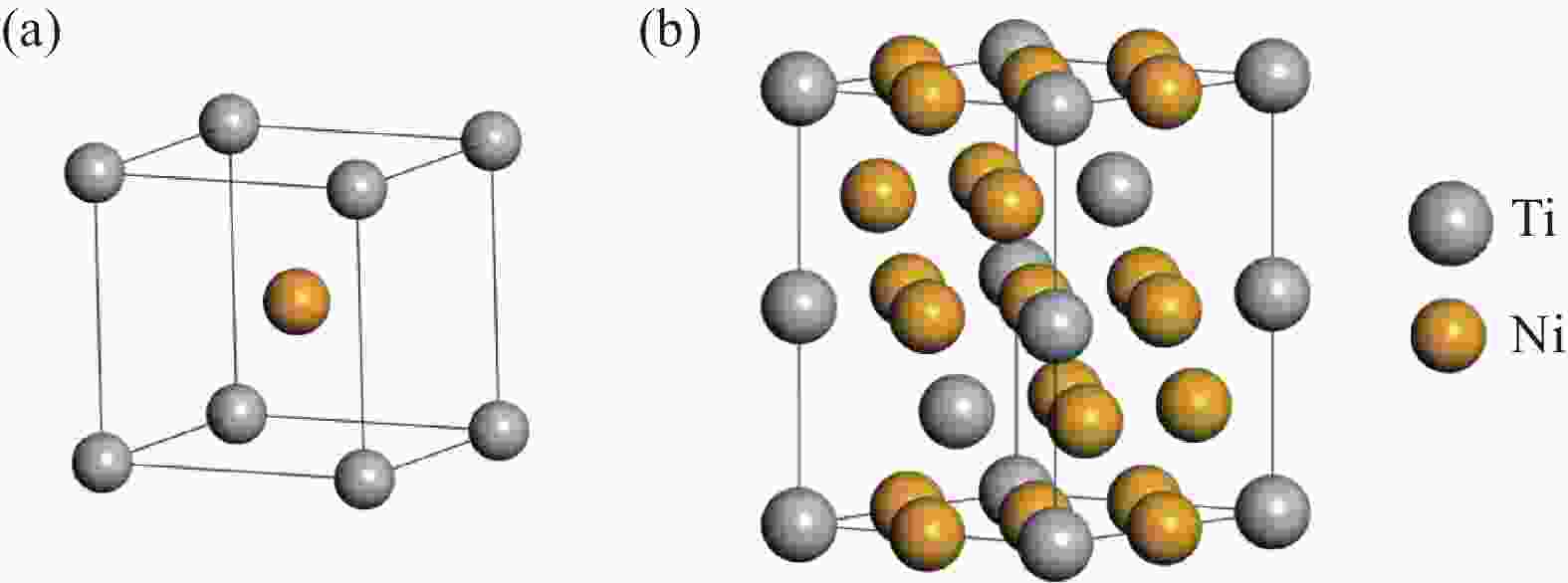
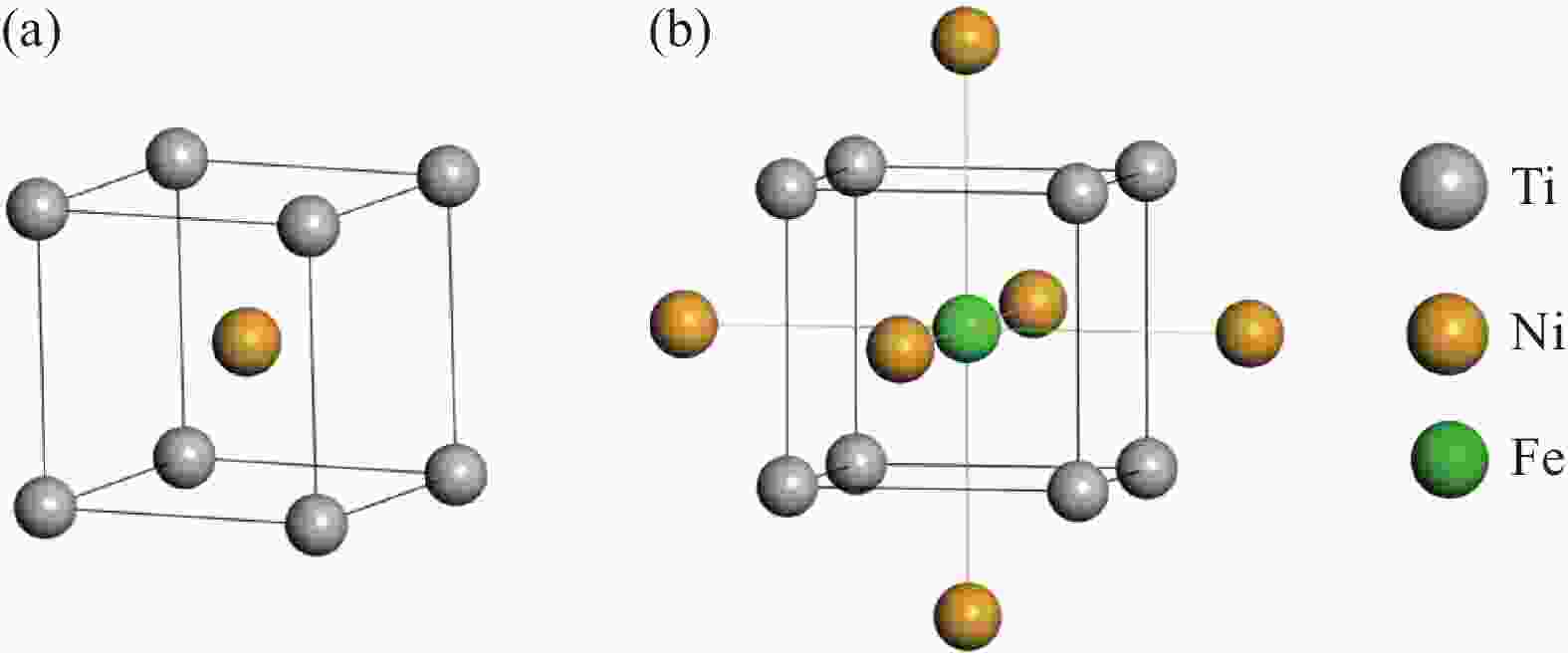
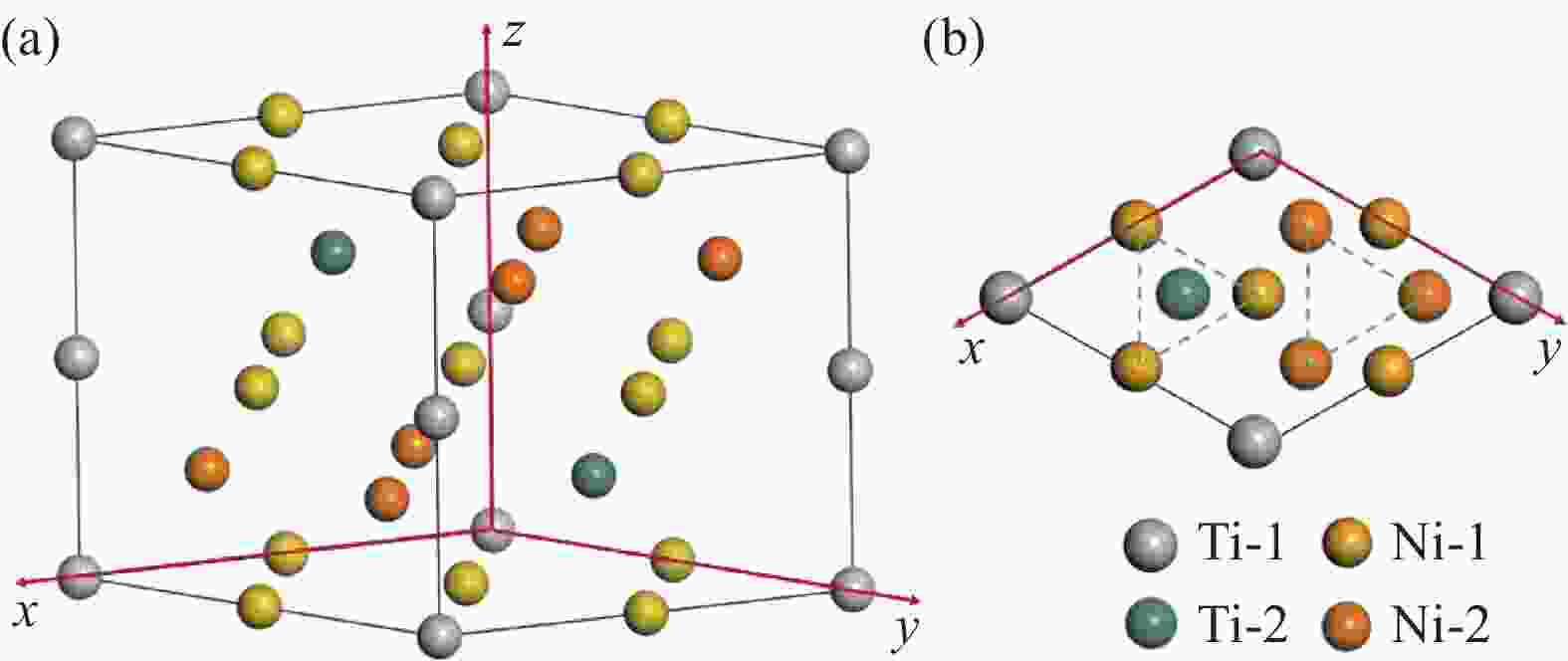
Compound Lattice category Lattice parameter Atom Position NiTi SP No.221 a=b=c=0.3005 nm Ni 1a α=β=γ=90° Ti 1b Ni3Ti SP No.194 a=b=0.5096 nm Ni-1 6g c=0.8304 nm Ni-2 6h α=β=90° Ti-1 2a γ=120° Ti-2 2c 表 6 Ni、Ti、Fe和Cr的原子半径及其电负性
Table 6. Atom radius and its electronegativity of Ni, Ti, Fe and Cr atom
Element Atomic radius/nm Atomic electronegativity/eV Ni 0.125 1.91 Ti 0.145 1.54 Fe 0.124 1.83 Cr 0.125 1.66 表 7 Ni3Ti相晶胞中原子坐标
Table 7. Atom coordinates in Ni3Ti crystal structure
Compound Atom x y z Ni3Ti Ni-1 0.5 0 0 Ni-2 0.8333 0.6667 0.25 Ti-1 0 0 0 Ti-2 0.3333 0.6667 0.25 表 8 Fe和Cr原子置换后Ni3Ti晶胞的晶格常数
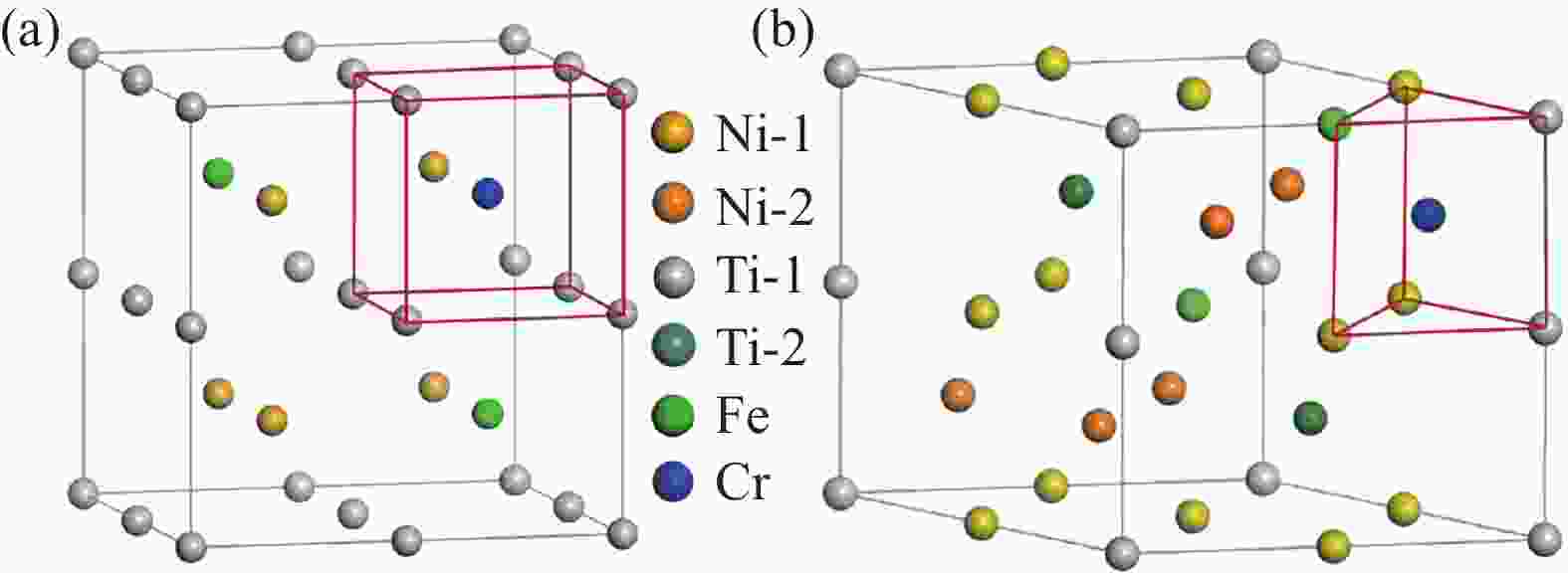
Table 8. Lattice parameters of Ni3Ti crystal after substitution of Fe and Cr atom
Atom Replaced position Composition a/nm b/nm c/nm Fe Ni-1 Ni11Ti4Fe 0.5118 0.4418 0.8316 Ni-2 Ni11Ti4Fe 0.5116 0.4419 0.8317 Ti-1 Ni12Ti3Fe 0.5068 0.4388 0.8286 Ti-2 Ni12Ti3Fe 0.5060 0.4385 0.8281 Cr Ni-1 Ni11Ti4Cr 0.5122 0.4434 0.8357 Ni-2 Ni11Ti4Cr 0.5129 0.4443 0.8377 Ti-1 Ni12Ti3Cr 0.5088 0.4407 0.8293 Ti-2 Ni12Ti3Cr 0.5085 0.4404 0.8293 表 9 Fe和Cr原子在NiTi和Ni3Ti结构中的原子占比
Table 9. Atomic proportion of Fe and Cr atom in NiTi and Ni3Ti crystal structure after substitution
Phase Composition after substitution Ni/at% Ti/at% Fe/at% Cr/at% NiTi (B2) Ni5Ti8Fe2Cr 31.25 50.00 12.50 6.25 Ni3Ti Ni9Ti4Fe2Cr 56.25 25.00 12.50 6.25 表 10 Fe和Cr原子置换后的形成能及晶格常数
Table 10. Formation energy and lattice parameters after substitution of Fe and Cr atoms
Crystal Composition Formation
energy/eVa/nm b/nm c/nm NiTi (B2) Ni5Ti8Fe2Cr −0.3286 0.5962 0.5962 0.6007 Ni3Ti Ni9Ti4Fe2Cr −0.3050 0.5128 0.4432 0.8362 -
[1] HASSAN M, MEHRPOUYA M, DAWOOD S. Review of the machining difficulties of nickel-titanium based shape memory alloys[J]. Advances in Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, 2014 , 564 : 533-537. [2] VELMURUGAN C, SENTHILKUMAR V, DINESH S, et al. Review on phase transformation behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2018,5(6):14597-14606. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.03.051 [3] WANG X, KUSTOV S, VAN HUMBEECK J. A short review on the microstructure, transformation behavior and functional properties of NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Materials (Basel),2018,11(9):1683. doi: 10.3390/ma11091683 [4] 王本力. 镍钛形状记忆合金的研究及其应用进展[J]. 新材料产业, 2021, 4(4):28-31.WANG Benli. Research and application progress of NiTi shape memory alloys[J]. Advanced Materials Industry,2021,4(4):28-31(in Chinese). [5] 杨建楠, 黄彬, 谷小军, 等. 形状记忆合金力学行为与应用综述[J]. 固体力学学报, 2021, 42(4):345-375.YANG Jiannan, HUANG Bin, GU Xiaojun, et al. A review of shape memory alloys: Mechanical behaviour and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics,2021,42(4):345-375(in Chinese). [6] SABURI T, YOSHIDA M, NENNO S. Deformation behavior of shape memory TiNi alloy crystals[J]. Scripta Metallurgica,1984,18(4):363-366. doi: 10.1016/0036-9748(84)90453-8 [7] ELAHINIA M, SHAYESTEH MOGHADDAM N, TAHERI ANDANI M, et al. Fabrication of NiTi through additive manufacturing: A review[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2016,83:630-663. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.08.001 [8] 任虔弘, 陈超越, 卢战军, 等. 激光选区熔化制备镍钛合金的研究进展[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2021, 15(3):276-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.03.013REN Qianhong, CHEN Chaoyue, LU Zhanjun, et al. Progress in the preparation of NiTi alloy by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Research and Application,2021,15(3):276-286(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.03.013 [9] 郭绍庆, 刘伟, 黄帅, 等. 金属激光增材制造技术发展研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2020, 22(3):56-62.GUO Shaoqing, LIU Wei, HUANG Shuai, et al. Development of laser additive manufacturing technology for metals[J]. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engi-neering,2020,22(3):56-62(in Chinese). [10] FENG Y, DU Z, HU Z. Study on the effect of Ni addition on the microstructure and properties of NiTi alloy coating on AISI 316L prepared by laser cladding[J]. Materials,2021,14(16):4373. doi: 10.3390/ma14164373 [11] DU Z, HU Z, FENG Y, et al. The effect of powder composition on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of laser cladding 60 NiTi alloy coatings on SS 316L[J]. Metals,2021,11(7):1104. doi: 10.3390/met11071104 [12] 肖斌, 吴雨沁, 刘轶. 基于第一性原理计算的镍基单晶高温合金掺杂的机器学习研究[J]. 上海金属, 2020, 42(3):97-104, 110.XIAO Bin, WU Yuqin, LIU Yi. Machine learning on doping of nickel-base single crystal superalloy based on first-principles calculation[J]. Shanghai Metals,2020,42(3):97-104, 110(in Chinese). [13] OHNO K, TSUCHIYA M, KUWAHARA R, et al. Study on Ni-Ti alloys around equiatomic composition by the first-principles phase field method [J]. Computational Materials Science, 2021, 191: 110284. [14] 孙浚晞, 杜婉, 肖斌, 等. 镍基单晶高温合金多组元置换的第一性原理研究[J]. 上海金属, 2021, 43(6):92-102.SUN Junxi, DU Wan, XIAO Bin, et al. First-principles study of multiple component subsititution in nickel-based single crystal superalloy[J]. Shanghai Metals,2021,43(6):92-102(in Chinese). [15] 席蒙, 尚家香. 过渡元素掺杂NiTi合金的第一性原理研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(8):2041-2045.XI Meng, SHANG Jiaxiang. First principle study on NiTi alloyed with transition elements[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2016,45(8):2041-2045(in Chinese). [16] YIN J Y, LI G F, SI Y L, et al. Micromechanism of Cu and Fe alloying process on the martensitic phase transformation of NiTi-based alloys: First-principles calculation[J]. Jour-nal of Structural Chemistry,2016,56(6):1051-1057. [17] OKAMOTO H, OKAMOTO H. Phase diagrams for binary alloys[M]. Ohio: ASM International Materials Park, 2000. [18] DUARTE L I, KLOTZ U E, LEINENBACH C, et al. Experimental study of the Fe-Ni-Ti system[J]. Intermetallics,2010,18(3):374-384. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2009.08.008 [19] 李梦龙. 化学数据速查手册[Z]. 北京: 化学工业出版社. 2003.LI Menglong. Concise handbook of chemical China[Z]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2003(in Chinese). [20] 陈志伟, 敬云兵, 甘春雷, 等. Fe含量对等原子比NiTi形状记忆合金微观组织、相变行为和显微硬度的影响[J]. 材料研究与应用, 2021, 15(2):118-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.02.006CHEN Zhiwei, JING Yunbing, GAN Chunlei, et al. Effect of Fe content on microstructure, phase transformation bevaviour and microhardness of the equiatomic NiTi shape memory alloy[J]. Materials Research and Application,2021,15(2):118-124(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2021.02.006 [21] BOZZOLO G, NOEBE R D, MOSCA H O. Site preference of ternary alloying additions to NiTi: Fe, Pt, Pd, Au, Al, Cu, Zr and Hf[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2005,389(1-2):80-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.07.051 [22] 张磊, 李世春. Ni-Ti系金属间化合物的电子结构与结合能计算[J]. 材料导报, 2011, 25(10):126-130.ZHANG Lei, LI Shichun. Calculations of valence electron structure and cohesive energy for intermetallic compounds in Ni-Ti alloys[J]. Materials Reports,2011,25(10):126-130(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: