Preparation and microwave absorption performance of hollow iron-based carbon fiber composites
-
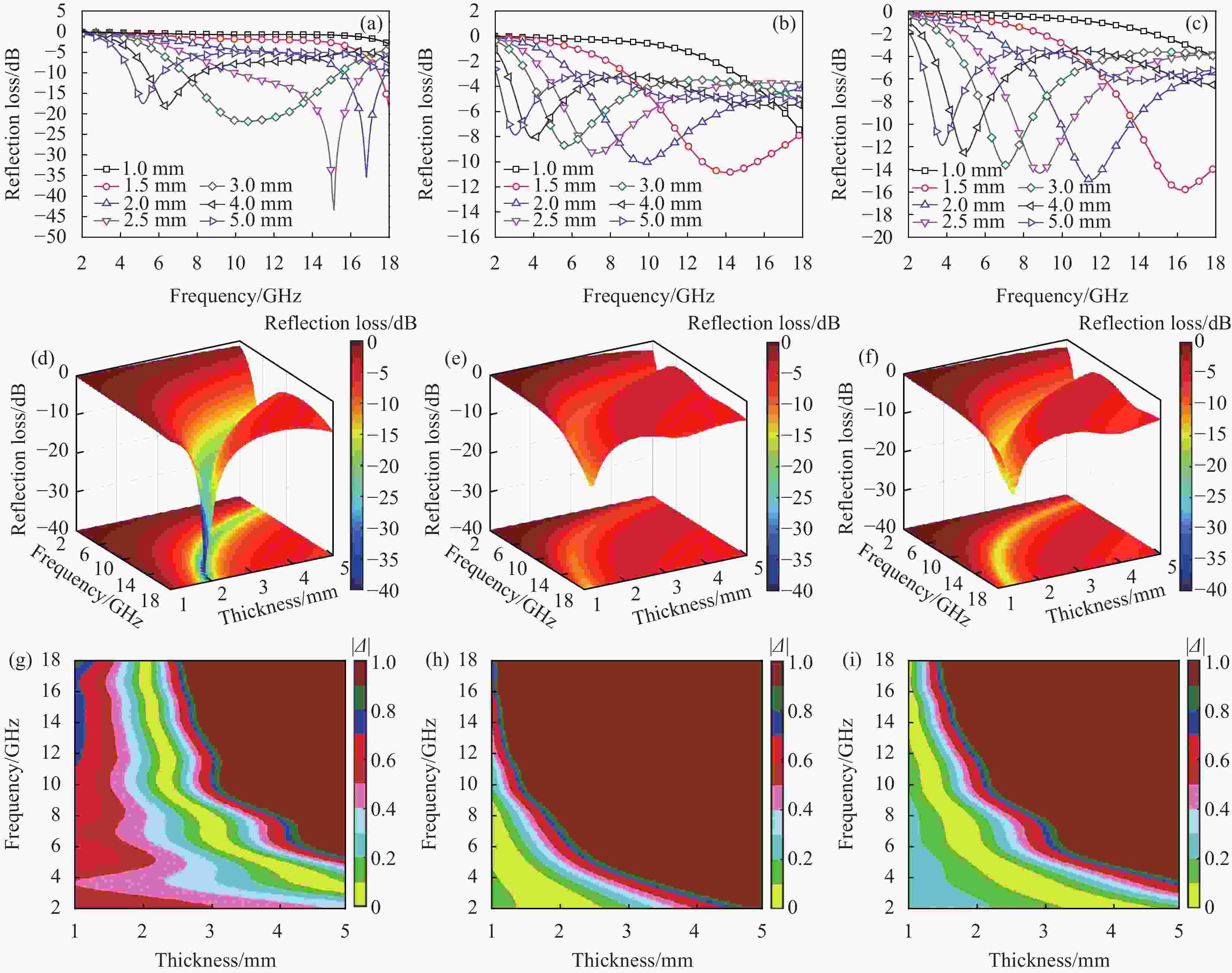
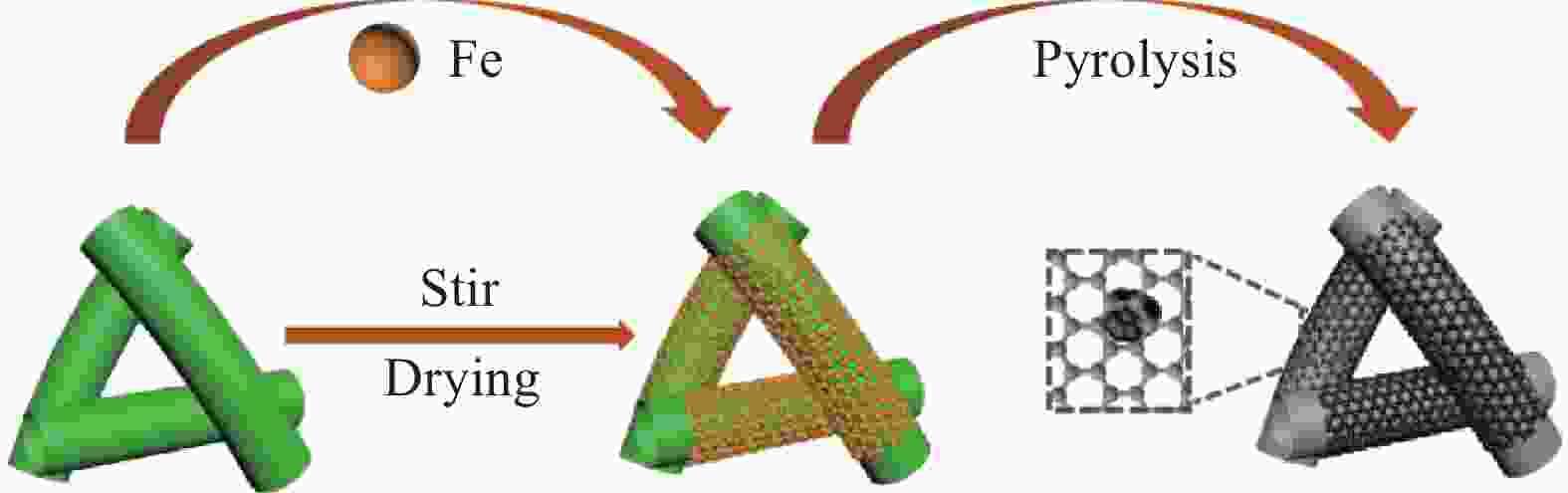
摘要: 为了改善因通信和电子设备的快速发展而造成的日益严重的电磁污染,解决磁性碳基吸波材料制备方法繁杂、能耗高等问题。提出了一种新型铁基碳纤维吸波材料的开发方法,以空心杨絮纤维为载体,Fe3+为金属源,采用湿式化学吸附和高温碳热还原的方法,得到了具有优良微波吸收性能的Fe-FexOy/C复合材料。实验结果表明:随煅烧温度升高,铁组分与杨絮中含氧基团结合生成不同的铁的氧化物(Fe/Fe3O4/FeO),材料的矫顽力和饱和磁化强度增强,铁磁特性明显;Fe-FexOy/C-600吸收剂厚度为3 mm 时,有效吸收带宽可达 8.4 GHz (7.2~15.6 GHz) ,复合材料优异的吸波性能归因于适宜的阻抗匹配和介电损耗与磁损耗的协同增强,相互搭载的纤维结构为电磁波构筑了适宜的衰减空间,并在碳纤维导电网络中快速衰减,研究将为新型铁基碳纤维吸波材料的设计开发提供借鉴。Abstract: In order to improve the increasingly serious electromagnetic pollution caused by the rapid development of communication and electronic devices, and solve the problems of complicated preparation methods and high energy consumption of magnetic carbon-based absorbing materials, this project proposes a new method for developing iron-based carbon fiber absorbing materials. Using hollow poplar catkin fibers as carriers, Fe3+ as the metal source, and wet chemical adsorption and high-temperature carbon thermal reduction methods, Fe-FexOy/C composite materials with excellent microwave absorption properties were obtained. The experimental results show that as the calcination temperature increases, different iron oxides (Fe/Fe3O4/FeO) are generated by combining the iron component with oxygen-containing groups in the Yangxu fibers, and the coercivity and saturation magnetization of the material are enhanced, and the ferromagnetic properties are obvious. Fe-FexOy/C-600 has the best absorption performance, and the effective absorption bandwidth can reach 8.4 GHz (7.2-15.6 GHz) when the thickness of the absorber is 3 mm. The excellent absorption performance of the composite material is attributed to the synergy of impedance matching and dielectric loss and magnetic loss, and the mutually carried fiber structure builds a suitable attenuation space for electromagnetic waves and quickly attenuates in the carbon fiber conductive network. The research will provide reference for the design and development of new iron based carbon fiber absorbing materials.
-
Key words:
- iron-based carbon fiber /
- porous structure /
- microwave absorption /
- polarization /
- dielectric loss /
- magnetic loss
-
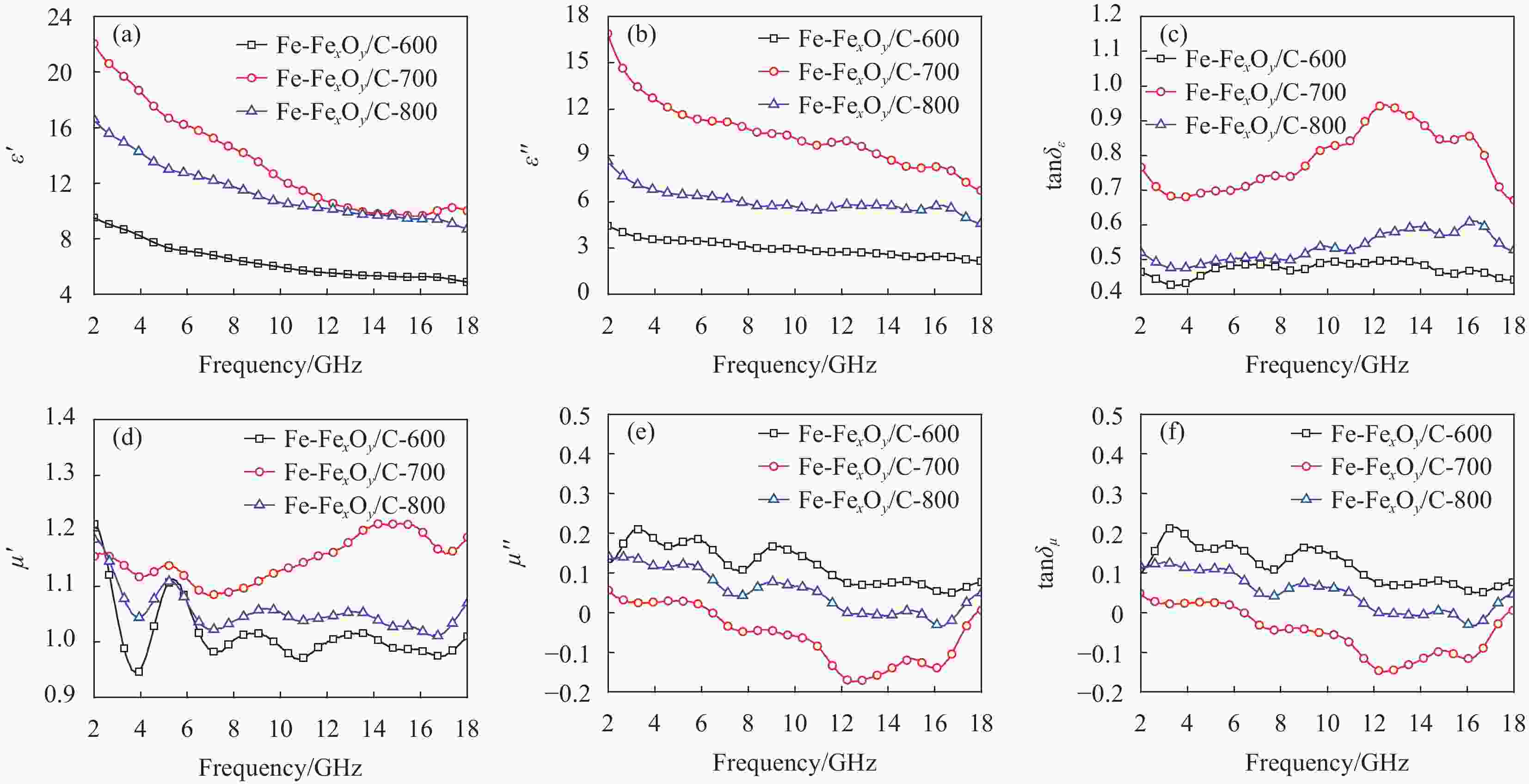
图 9 Fe-FexOy/C复合材料的介电常数实部ε' (a)、介电常数虚部ε'' (b)、介电损耗正切值tanδε (c)、复磁导率实部μ' (d)、复磁导率虚部μ'' (e)、复磁损耗正切值tanδμ (f)
Figure 9. Real part of the dielectric constant ε' (a), imaginary part of the dielectric constant ε'' (b), dielectric loss tangent tanδε (c), complex magnetic permeability real part μ' (d), complex magnetic permeability imaginary part μ'' (e), complex magnetic loss tangent tanδμ (f) of Fe-FexOy/C composite
表 1 不同煅烧温度后的样品
Table 1. Samples after different calcination temperatures
Material Calcination temperature/℃ Fe-FexOy/C-600 600 Fe-FexOy/C-700 700 Fe-FexOy/C-800 800 表 2 吸波性能对比
Table 2. Comparison of wave absorption performance
Microwave absorption materials Reflection loss/
dBMicrowave
absorption
bandwidth/GHzRef. CSBS-2.5 −20.0 6.4 [36] WPC-1 −50.0 4.8 [37] FK-SDC −18.0 4.8 [38] TiP2O7/C −32.4 6.0 [39] PRHC-900 −43.0 3.7 [40] Co@NPC −51.2 4.4 [41] Ni(OH)2/AC −23.2 — [42] Fe3O4/PBC −44.8 4.7 [43] HPMC-1.0 −52.0 — [44] Fe3O4/FeCo/C −37.4 5.9 [45] PPy/Fe3O4/CNTs −47.7 2.4 [46] G-LNL/ Fe3O4 −46.8 4.4 [47] Fe-FexOy/C-600 −43.5 8.4 This work Notes: CSBS—Coconut shell-based biomass carbon; WPC—Stirring watermelon pulp before carbonization; FK-SDC—High temperature carbonization of the treated soybean dregs; PRHC-900—Treated rice husk powder after high temperature carboni-zation; NPC—Nanoporous carbon; AC—Carbon; PBC—Porous biomass carbon; HPMC—Hierarchically porous magnetic carbon; PPy—Ternary polypyrrole; CNTs—Carbon nanotubes; G-LNL—3D graphene-like networks material. -
[1] QIANG R, FENG S B, CHEN Y, et al. Recent progress in biomass-derived carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,606:406-423. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.07.144 [2] LIANG L L, GU W H, WU Y, et al. Heterointerface engineering in electromagnetic absorbers: New insights and opportunities[J]. Advanced Materials,2022,34(4):2106195. doi: 10.1002/adma.202106195 [3] GAO T, ZHAO R Z, LI Y X, et al. Sub-nanometer Fe clusters confined in carbon nanocages for boosting dielectric polarization and broadband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(31):2204370. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202204370 [4] PAN F, CAI L, SHI Y Y, et al. Heterointerface engineering of β-chitin/carbon nano-onions/Ni-P composites with boosted maxwell-wagner-sillars effect for highly efficient electromagnetic wave response and thermal management[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,14(1):8501-8518. [5] ZHANG C, LI X A, SHI Y N, et al. Structure engineering of graphene nanocages toward high-performance microwave absorption applications[J]. Advanced Optical Materials,2022,10(2):2101904. doi: 10.1002/adom.202101904 [6] CHEN F, ZHANG S S, GUO R D, et al. 1D magnetic nitrogen doped carbon-based fibers derived from NiFe prussian blue analogues embedded polyacrylonitrile via electrospinning with tunable microwave absorption[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2021,224:109161. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109161 [7] LIANG X H, MAN Z M, QUAN B, et al. Environment-stable CoxNiy encapsulation in stacked porous carbon nanosheets for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2020,12(1):10201-10212. [8] HUANG W H, QIU Q, YANG X F, et al. Ultrahigh density of atomic CoFe-electron synergy in noncontinuous carbon matrix for highly efficient magnetic wave absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,14(1):9601-9614. [9] GOU G J, MENG F B, WANG H G, et al. Wheat straw-derived magnetic carbon foams: In-situ preparation and tunable high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Nano Research,2019,12(6):1423-1429. doi: 10.1007/s12274-019-2376-x [10] MARTINS A C, CAZETTA A L, PEZOTI O, et al. Sol-gel synthesis of new TiO2/activated carbon photocatalyst and its application for degradation of tetracycline[J]. Ceramics International,2017,43(5):4411-4418. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.12.088 [11] DUAN G G, ZHAO L Y, CHEN L A, et al. ZnCl2 regulated flax-based porous carbon fibers for supercapacitors with good cycling stability[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2021,45(48):22602-22609. doi: 10.1039/D1NJ04667E [12] LI H L, CAO L H, ZHANG H J, et al. Intertwined carbon networks derived from polyimide/cellulose composite as porous electrode for symmetrical supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,609:179-187. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.11.188 [13] WANG F, CHEN L, LI H L, et al. N-doped honeycomb-like porous carbon towards high-performance supercapacitor[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2020,31(7):1986-1990. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.02.020 [14] WANG H G, MENG F B, LI J Y, et al. Carbonized design of hierarchical porous carbon/Fe3O4@Fe derived from loofah sponge to achieve tunable high-performance microwave absorption[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(9):11801-11810. [15] DOLCET P, DIODATI S, ZORZI F, et al. Very fast crystallisation of MFe2O4 spinel ferrites (M = Co, Mn, Ni, Zn) under low temperature hydrothermal conditions: A time-resolved structural investigation[J]. Green Chemistry,2018,20(10):2257-2268. doi: 10.1039/C8GC00086G [16] FAN B X, XING L, YANG K X, et al. Synergistically enhanced heat conductivity-microwave absorption capabilities of g-C3N4@Fe@C hollow micro-polyhedra via interface and composition modulation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2023,451:138492. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.138492 [17] QIANG R, DU Y C, ZHAO H T, et al. Metal organic framework-derived Fe/C nanocubes toward efficient microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(25):13426-13434. doi: 10.1039/C5TA01457C [18] QIANG R, DU Y C, WANG Y, et al. Rational design of yolk-shell C@C microspheres for the effective enhancement in microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2016,98:599-606. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.11.054 [19] ZHOU Y Z, CHEN G B, WANG Q, et al. Fe-N-C electrocatalysts with densely accessible Fe-N4 sites for efficient oxygen reduction reaction[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(34):2102420. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202102420 [20] WANG X X, YOU F F, WEN X Y, et al. Doping Ce(OH)CO3 laminated dendrites with Fe, Co and Ni for defect steered wide-frequency microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,445:136431. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136431 [21] SULTAN S, TIWARI J N, JANG J H, et al. Highly efficient oxygen reduction reaction activity of graphitic tube encapsulating nitrided CoxFey alloy[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8(25):1801002. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201801002 [22] ZHANG X A, YAN F, ZHANG S, et al. Hollow N-doped carbon polyhedron containing CoNi alloy nanoparticles embedded within few-layer N-doped graphene as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(29):24920-24929. [23] LIU M M, YANG X F, SHAO W, et al. Superior microwave absorbing properties of O, S, N codoped carbon planar helixes via carbonization of polypyrrole spiral nanowires[J]. Carbon,2021,174:625-637. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.093 [24] DING D, WANG Y, LI X D, et al. Rational design of core-shell Co@C microspheres for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2017,111:722-732. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.10.059 [25] HE N, LIU M M, QI J Y, et al. Plasmon resonance strategy to enhance permittivity and microwave absorbing performance of Cu/C core-shell nanowires[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,378:122160. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122160 [26] YANG H J, CAO M S, LI Y, et al. Enhanced dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorption of SiC powders driven with NiO nanorings[J]. Advanced Optical Materials,2014,2(3):214-219. doi: 10.1002/adom.201300439 [27] YANG X F, FAN B X, TANG X, et al. Interface modulation of chiral PPy/Fe3O4 planar microhelixes to achieve electric/magnetic-coupling and wide-band microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,430:132747. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132747 [28] LIU M M, WU L W, FAN B X, et al. Governing the Ni content and size of 2D layered C/Ni nanoparticle composites for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science,2022,571:151273. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151273 [29] LIU P J, YAO Z J, ZHOU J T, et al. Small magnetic Co-doped NiZn ferrite/graphene nanocomposites and their dual-region microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2016,4(41):9738-9749. doi: 10.1039/C6TC03518C [30] LI Z X, LI X H, ZONG Y, et al. Solvothermal synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene decorated by superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their applications as enhanced synergistic microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2017,115:493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.01.036 [31] JI R, XING L, YANG K K, et al. Defect and interface co-steering ultra-wide microwave absorption and superior thermal conductance of TiO2/Fe/C nanocomposites[J]. Applied Surface Science,2023,608:155207. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155207 [32] ZHAO H B, FU Z B, CHEN H B, et al. Excellent electromagnetic absorption capability of Ni/carbon based conductive and magnetic foams synthesized via a green one pot route[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(2):1468-1477. [33] ZHANG X, CAI L, XIANG Z, et al. Hollow CuS microflowers anchored porous carbon composites as lightweight and broadband microwave absorber with flame-retardant and thermal stealth functions[J]. Carbon,2021,184:514-525. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.08.026 [34] LU Y, SHAO W, WU L W, et al. Controllable preparation and broadband high-frequency absorption capabilities of Co fibers and Co/Cu bimetallic core-shell fibers[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,847:156509. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156509 [35] HE N, HE Z D, LIU L, et al. Ni2+ guided phase/structure evolution and ultra-wide bandwidth microwave absorption of CoxNi1−x alloy hollow microspheres[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,381:122743. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122743 [36] WANG L H, GUAN H T, SU S L, et al. Magnetic FeOx /biomass carbon composites with broadband microwave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,903:163894. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163894 [37] SUN H, YANG Y X, CHEN J, et al. Biomass derived graphene-like multifold carbon nanosheets with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2022,644:128826. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128826 [38] YUE J Q, YU J, JIANG S H, et al. Biomass carbon materials with porous array structures derived from soybean dregs for effective electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2022,126:109054. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2022.109054 [39] HUANG Q, BAO C Z, WANG Q Y, et al. Tuning the microwave absorption capacity of TiP2O7 by composited with biomass carbon[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,515:145974. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145974 [40] LI Q S, ZHU J J, WANG S N, et al. Microwave absorption on a bare biomass derived holey silica-hybridized carbon absorbent[J]. Carbon,2020,161:639-646. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.087 [41] ZHAO H Q, CHENG Y, MA J N, et al. A sustainable route from biomass cotton to construct lightweight and high-performance microwave absorber[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,339:432-441. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.01.151 [42] GUAN H T, WANG H Y, ZHANG Y L, et al. Microwave absorption performance of Ni(OH)2 decorating biomass carbon composites from Jackfruit peel[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,447:261-268. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.225 [43] YANG Q X, SHI Y Y, FANG Y, et al. Construction of polyaniline aligned on magnetic functionalized biomass carbon giving excellent microwave absorption properties[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,174:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.02.031 [44] ZHAO H Q, CHENG Y, LYU H L, et al. A novel hierarchically porous magnetic carbon derived from biomass for strong lightweight microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2019,142:245-253. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.10.027 [45] BAO Y, GUO R Y, LIU C, et al. Design of magnetic triple-shell hollow structural Fe3O4/FeCo/C composite microspheres with broad bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(15):23932-23940. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.06.169 [46] SHANG T, LU Q S, ZHAO J J, et al. Novel three-dimensional graphene-like networks loaded with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for efficient microwave absorption[J]. Nanomaterials (Basel), 2021, 11(6): 1444. [47] ZHANG M, QIAN X, ZENG Q, et al. Hollow microspheres of polypyrrole/magnetite/carbon nanotubes by spray-dry as an electromagnetic synergistic microwave absorber[J]. Carbon,2021,175:499-508. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2021.01.013 -





 下载:
下载: