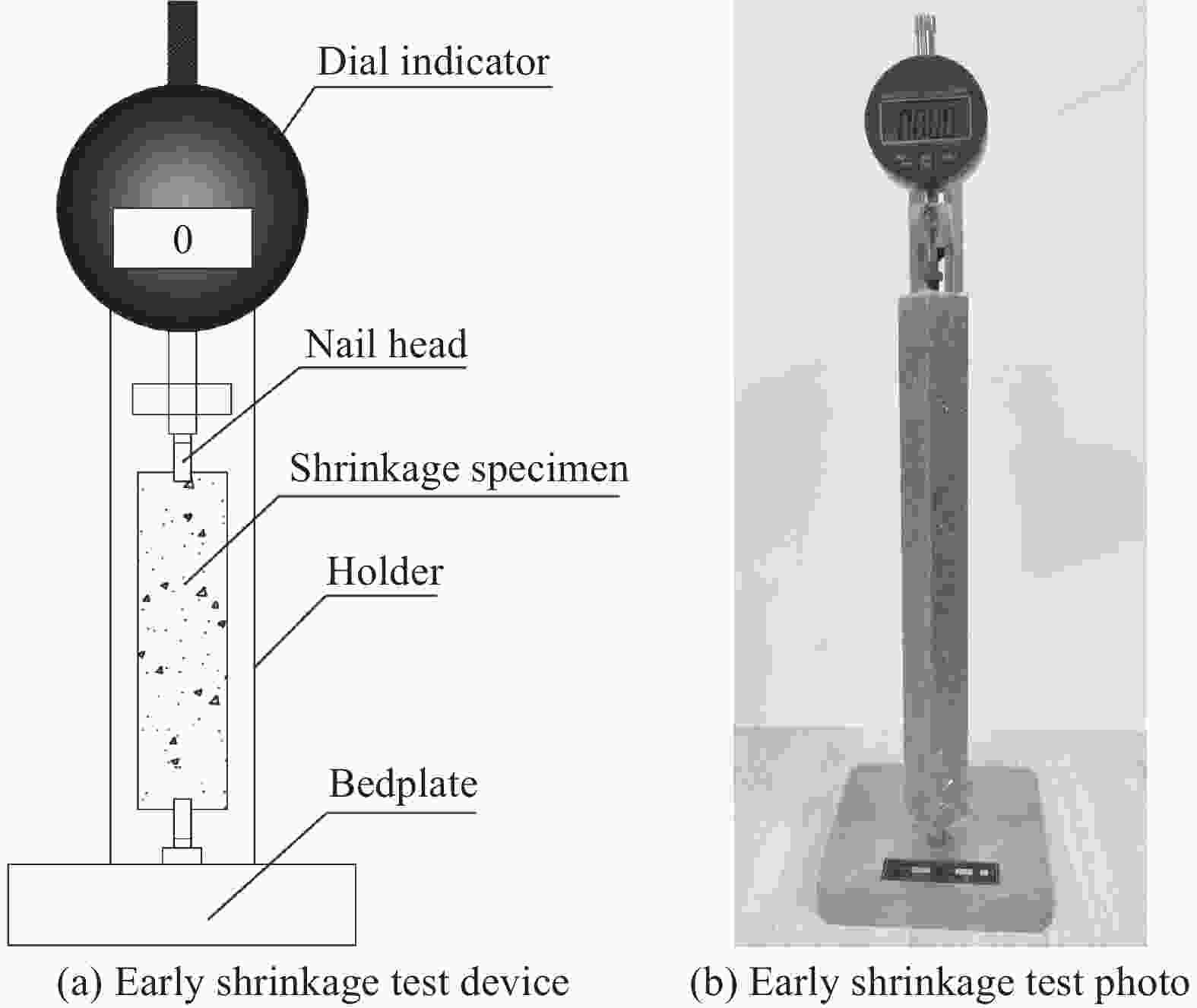
Early shrinkage characteristics of high performance geopolymer concrete
-
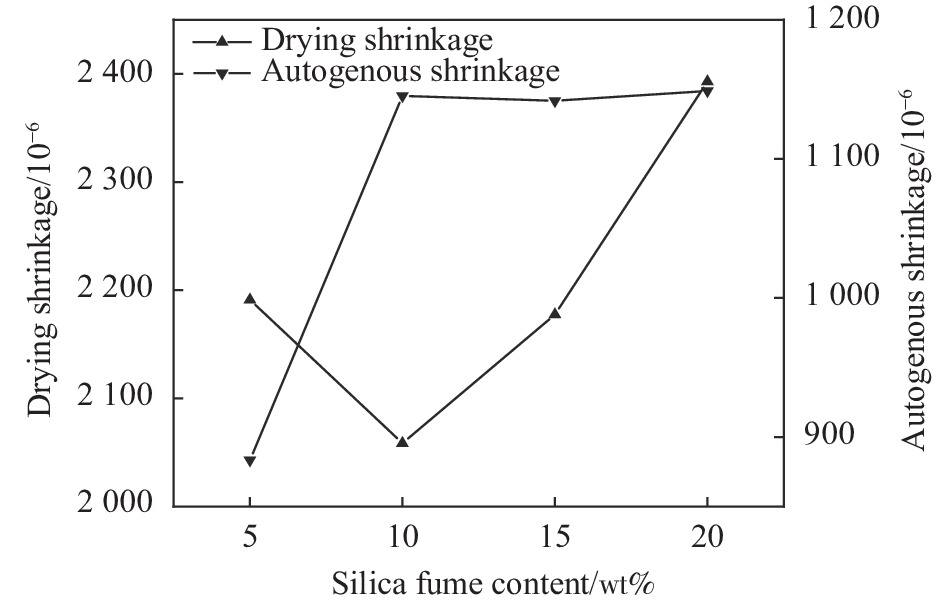
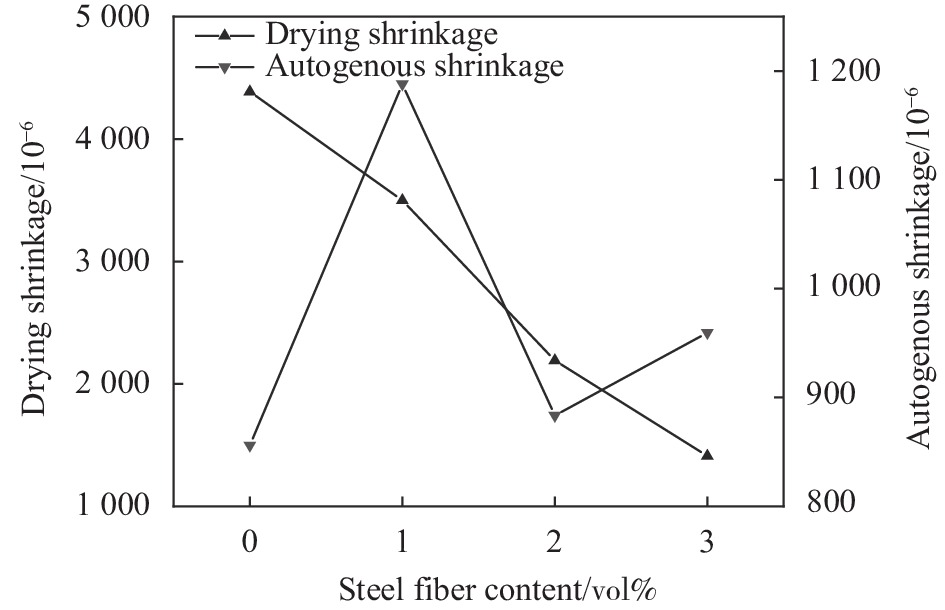
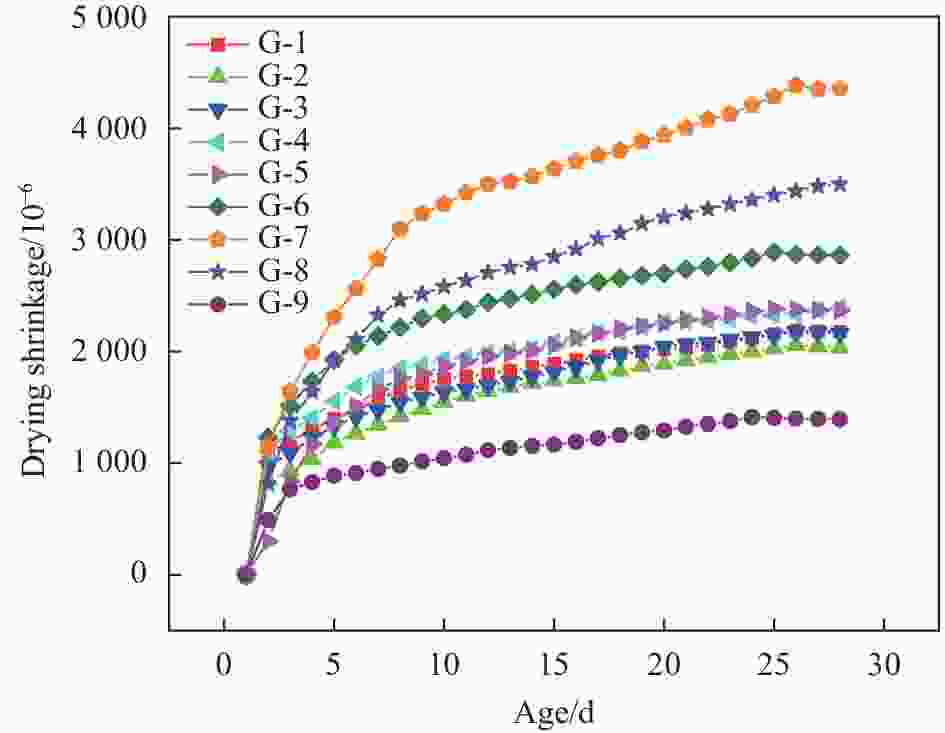
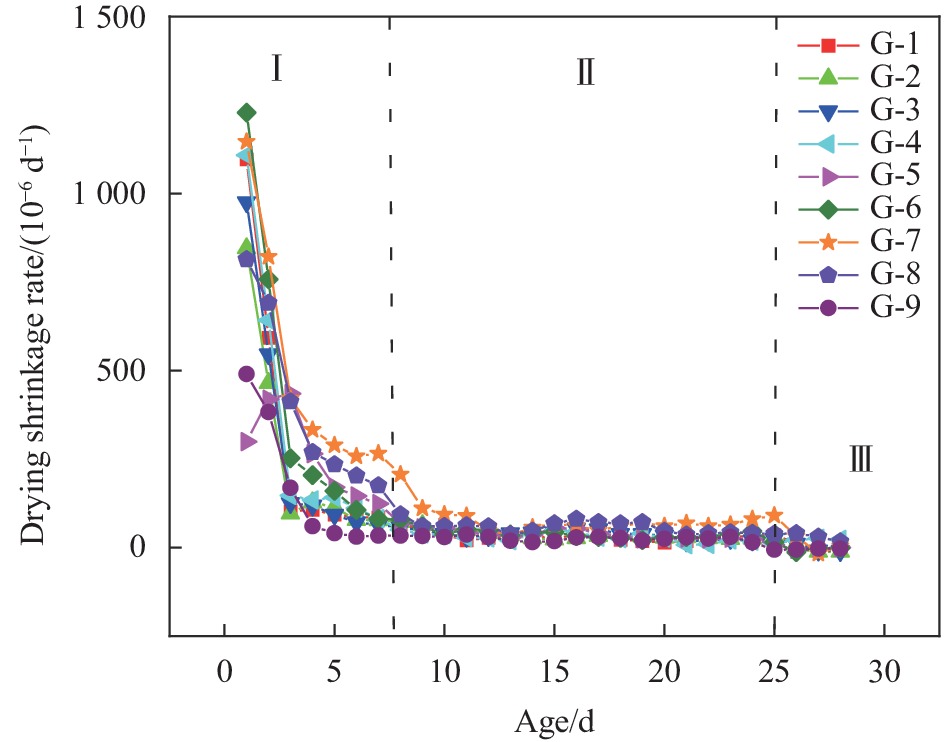
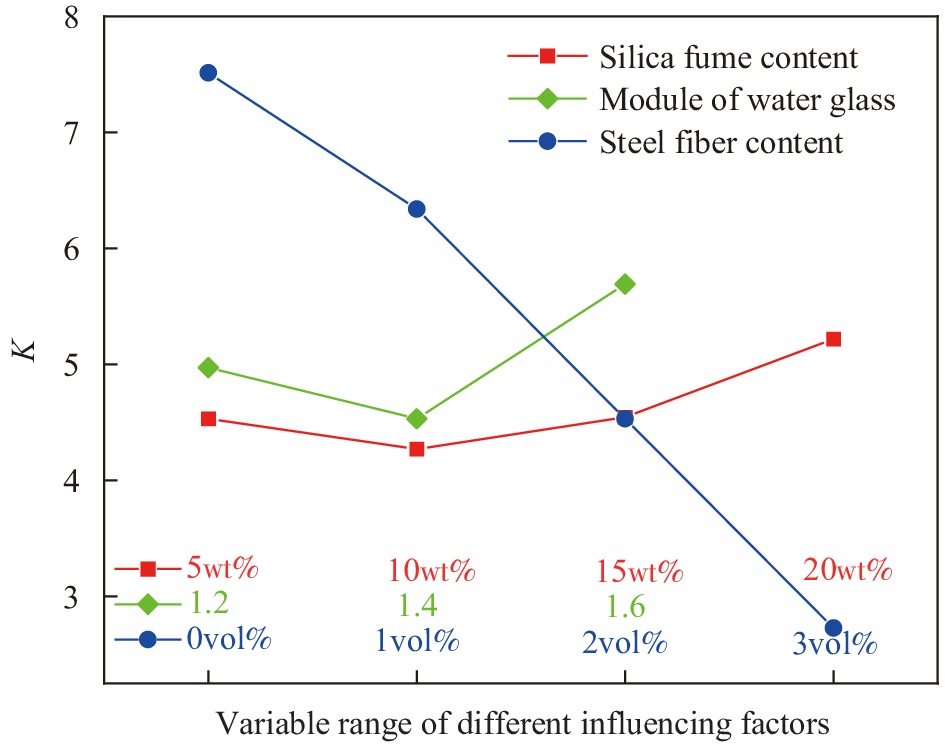
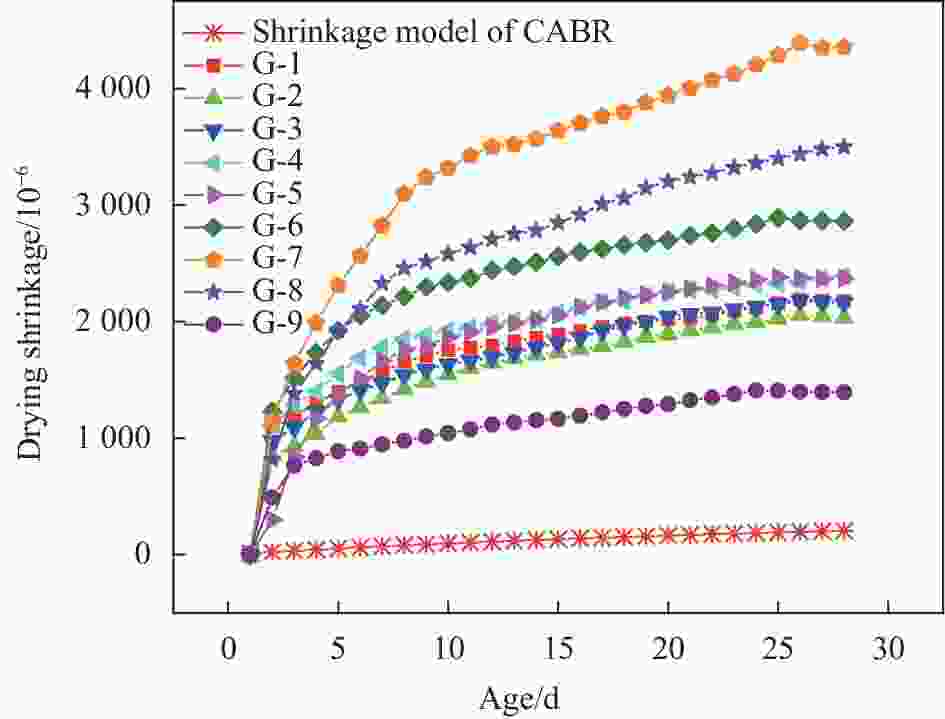
摘要: 为研究高性能地聚物混凝土的早期收缩性能,进行系列试验研究与分析。研究表明:在试验掺量变量范围内,硅灰掺量及水玻璃模数对高性能地聚物混凝土早期干燥收缩影响一致,均先减小后增大;硅灰掺量及钢纤维掺量对高性能地聚物混凝土早期自收缩影响一致,均先增大后减小,之后再增大。在水玻璃模数范围内,水玻璃模数对高性能地聚物混凝土早期自收缩均为负面影响,增大水玻璃模数,高性能地聚物混凝土早期自收缩均依次增大。在试验钢纤维掺量范围内,钢纤维掺量对高性能地聚物混凝土早期干燥收缩均为正面影响,增加钢纤维掺量,高性能地聚物混凝土早期干燥收缩均依次降低。高性能地聚物混凝土试件早期干燥收缩均在1411×10−6~4387×10−6之间,早期自收缩均在856×10−6~1188×10−6之间。随龄期增长,高性能地聚物混凝土干燥收缩初期增长较快,自收缩先略微减小后快速增长,之后均逐渐趋于平缓,并可将早期收缩曲线分为3个阶段(快速增长段、缓慢增长段和稳定段)。基于早期干燥收缩实测值,验证了GL2000模型对高性能地聚物混凝土早期干燥收缩曲线的适用性。Abstract: In order to study the early shrinkage performance of high performance geopolymer concrete, a series of experimental research and analysis were carried out. The results show that the influence of silica fume content and water glass modulus on the early drying shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete is consistent within the range of test content, which decreases first and then increases. The influence of silica fume content and steel fiber content on the early autogenous shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete is consistent, which increases first and then decreases, and then increases. In the range of water glass modulus, the water glass modulus has a negative effect on the early autogenous shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete. Increasing the water glass modulus, the early autogenous shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete increases in turn. In the range of steel fiber content in the test, the steel fiber content has a positive effect on the early drying shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete. With the increase of steel fiber content, the early drying shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete decreases in turn. The early drying shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete specimens is between 1411×10−6-4387×10−6, and the early autogenous shrinkage is between 856×10−6-1188×10−6. With the increase of age, the drying shrinkage of high performance geopolymer concrete increases rapidly in the early stage, and the autogenous shrinkage decreases slightly first and then increases rapidly, and then gradually tends to be gentle. The early shrinkage curve can be divided into three stages (rapid growth stage, slow growth stage and stable stage). Based on the measured values of early drying shrinkage, the applicability of GL2000 model to the early drying shrinkage curve of high performance geopolymer concrete was verified.
-
Key words:
- high performance /
- geopolymer concrete /
- silica fume /
- water glass modulus /
- steel fiber /
- drying shrinkage /
- self-shrinkage
-
表 1 钢纤维各项性能指标
Table 1. Performance indicators of steel fiber
Length/mm Diameter/μm Elastic modulus/GPa Tensile strength/MPa Elongation/% Density/(g·cm−3) 13 200 220 3000 3-5 7.5 表 2 水玻璃成分及性能指标
Table 2. Composition and performance index of water glass
SiO2/(kg·m−3) Na2O/(kg·m−3) H2O/(kg·m−3) °Bé Modulus Density/(g·cm−3) 26.8 8.5 64.7 40 3.22 1.38 Note: °Bé—Baume degree. 表 3 高性能地聚物混凝土配合比 (kg·m−3)
Table 3. Mix proportion of high performance geopolymer concrete (kg·m−3)
Slag Fly ash Silica fume Steel fiber Sand NaOH Na2O·nSiO2 Water 688 172 45 156 905 56 314 87 表 4 早期收缩性能试验配合比 (kg·m−3)
Table 4. Early shrinkage performance test mix proportion (kg·m−3)
Packet number Slag Fly ash Silica fume Steel fiber Sand NaOH Na2O·nSiO2 Water G-1 688 172 45 (5wt%) 150 (2vol%) 905 56 (1.4) 314 87 G-2 652 163 90 (10wt%) 150 905 56 314 87 G-3 616 154 135 (15wt%) 150 905 56 314 87 G-4 580 145 180 (20wt%) 150 905 56 314 87 G-5 688 172 45 150 905 72.53 (1.2) 314 87 G-6 688 172 45 150 905 43.65 (1.6) 314 87 G-7 688 172 45 0 (0vol%) 905 56 314 87 G-8 688 172 45 75 (1vol%) 905 56 314 87 G-9 688 172 45 225 (3vol%) 905 56 314 87 表 5 高性能地聚物混凝土28天龄期立方体抗压强度$ {f}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m}28} $值 (MPa)
Table 5. Measured value of 28 days compressive strength ($ {f}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m}28} $) of high performance geopolymer concrete (MPa)
Packet number ${f}_{\mathrm{c}\mathrm{m}28} $ G-1 104.3 G-2 110.0 G-3 109.9 G-4 114.4 G-5 106.0 G-6 91.7 G-7 77.1 G-8 86.5 G-9 94.9 -
[1] ASGHAR R, KHAN M A, ALYOUSEF R, et al. Promoting the green construction: Scientometric review on the mechanical and structural performance of geopolymer concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,368:130502. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130502 [2] 赵军, 王帅斌, 王自柯, 等. BFRP 筋与地聚物混凝土黏结性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2022, 43(6):245-256.ZHAO Jun, WANG Shuaibin, WANG Zike, et al. Experimental study on bonding properties between BFRP bars and geopolymer concrete[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2022,43(6):245-256(in Chinese). [3] ASSI L N, CARTER K, DEAVER E, et al. Review of availability of source materials for geopolymer/sustainable concrete[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,263:121477. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121477 [4] 张全超, 黄大建, 张小鹏, 等. 高掺量硅灰石纤维对偏高岭土基地聚物性能和微结构的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(8): 4694-4702.ZHANG Quanchao, HUANG Dajian, ZHANG Xiaopeng, et al. Effects of high content wollastonite fiber on properties and microstructure of metakaolin-based geopolymer[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(8): 4694-4702(in Chinese). [5] 陈宝春, 韦建刚, 苏家战, 等. 超高性能混凝土应用进展[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2019, 36(2):10-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2019.02.003CHEN Baochun, WEI Jiangang, SU Jiazhan, et al. State-of-the-art progress on application of ultra-high performance concrete[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering,2019,36(2):10-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2049.2019.02.003 [6] YOO Y D, BANTHIA N. Mechanical properties of ultra-high-performance fiber-reinforced concrete: A review[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2016,73:267-280. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.08.001 [7] 钟卿瑜, 粟淼, 彭晖. 偏高岭土-矿渣地聚物宏观性能试验及Lasso回归模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(11):5474-5485. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211230.001ZHONG Qingyu, SU Miao, PENG Hui. Macroscopic performance test and Lasso regression model of metakaolin-slag geopolymer[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(11):5474-5485(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211230.001 [8] 彭晖, 崔潮, 蔡春声, 等. 激发剂浓度对偏高岭土基地聚物性能的影响机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(12):2952-2960. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160315.003PENG Hui, CUI Chao, CAI Chunsheng, et al. The effect of activator concentration on the properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(12):2952-2960(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160315.003 [9] RANJBAR N, ZHANG M Z. Fiber-reinforced geopolymer composites: A review[J]. Cement and Concrete Compo-sites,2020,107(C):103498. [10] MORADIKHOU A B, ESPARHAM A, AVANAKI M J. Physical & mechanical properties of fiber reinforced metakaolin-based geopolymer concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,251(C):118965. [11] LIU Y W, ZHANG Z H, SHI C J, et al. Development of ultra-high performance geopolymer concrete (UHPGC): Influence of steel fiber on mechanical properties[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2020,112:103670. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103670 [12] 刘岩, 叶涛萍, 曹万林. 地聚物混凝土结构研究与发展[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2020, 29(4):8-19. doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0402LIU Yan, YE Taoping, CAO Wanlin. Research and development of geopolymer concrete structure[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2020,29(4):8-19(in Chinese). doi: 10.13577/j.jnd.2020.0402 [13] 章定文, 王安辉. 地聚合物胶凝材料性能及工程应用研究综述[J]. 建筑科学与工程学报, 2020, 37(5):13-38. doi: 10.19815/j.jace.2020.08041ZHANG Dingwen, WANG Anhui. Review on the properties and engineering application of geopolymer cementitious materials[J]. Journal of Architecture and Civil Engineering,2020,37(5):13-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.19815/j.jace.2020.08041 [14] OKOYE F N, PRAKASH S, SINGH N B. Durability of fly ash based geopolymer concrete in the presence of silica fume[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2017,149:1062-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.176 [15] 李三, 彭小芹, 苟菁, 等. 矿物掺合料对地聚合物抗冻性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(10):1711-1715. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.10.027LI San, PENG Xiaoqin, GOU Jing, et al. The effect of mineral admixtures on the frost resistance of geopolymer[J]. Materials Reports,2018,32(10):1711-1715(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.10.027 [16] 黄嘉钰, 刘元珍, 王朝旭, 等. 再生保温混凝土内部湿度与干燥收缩预测模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(10):4788-4800. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210928.003HUANG Jiayu, LIU Yuanzhen, WANG Zhaoxu, et al. Prediction model of internal humidity and drying shrinkage of recycled thermal insulation concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(10):4788-4800(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210928.003 [17] NEGAHBAN E, BAGHERI A, SANJAYAN J. One-year study of restrained shrinkage and creep behaviours of geopolymer concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,376:131057. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131057 [18] LONG G C, CHEN Y, TANG Z, et al. Drying shrinkage behavior of cement mortar under low vacuum conditions[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2023,374:130933. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130933 [19] WANG Z X, LIU Y Z, TU J S, et al. Effects of glazed hollow beads on the drying shrinkage value and trend of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2023,68:106021. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106021 [20] YANG T, ZHU H J, ZHANG Z H. Influence of fly ash on the pore structure and shrinkage characteristics of metakaolin-based geopolymer pastes and mortars[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,153:284-293. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.067 [21] XIANG J C, LIU L P, CUI X M, et al. Effect of fuller-fine sand on rheological, drying shrinkage, and microstructural properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer grouting materials[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2019,104:103381. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2019.103381 [22] MERMERDAŞ K, ALGIN Z, EKMEN Ş. Experimental assessment and optimization of mix parameters of fly ash-based lightweight geopolymer mortar with respect to shrinkage and strength[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2020,31:101351. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101351 [23] LIU Y W, SHI C J, ZHANG Z H, et al. Mechanical and fracture properties of ultra-high performance geopolymer concrete: Effects of steel fiber and silica fume[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2020,112:103665. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103665 [24] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 水泥胶砂干缩试验方法: JC/T 603—2004[S]. 北京: 中国建材工业出版社, 2004.National Development and Reform Commission of the People's Republic of China. Cement mortar shrinkage test method: JC/T 603—2004[S]. Beijing: China Building Materials Industry Press, 2004(in Chinese). [25] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Physical and mechanical properties test method standard for concrete: GB/T 50081—2019[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2019(in Chinese). [26] 吴志涛, 张云升, 刘乃东, 等. 玻璃纤维增强水泥基材料收缩性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(8):2570-2577. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2019.08.035WU Zhitao, ZHANG Yunsheng, LIU Naidong, et al. Study on shrinkage properties of glass fiber reinforced cement-based materials[J]. Silicate Bulletin,2019,38(8):2570-2577(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2019.08.035 [27] 刘翼玮, 张祖华, 史才军, 等. 硅灰对高强地聚物胶凝材料性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(11):1689-1699. doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200234LIU Yiwei, ZHANG Zuhua, SHI Caijun, et al. Effect of silica fume on properties of high strength geopolymer cementitious materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2020,48(11):1689-1699(in Chinese). doi: 10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.20200234 [28] 吴林妹. 超高性能混凝土早期收缩性能与长期稳定性研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2019.WU Linmei. Research on early shrinkage performance and long-term stability of ultra-high performance concrete[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2019. [29] KOVLER K, ZHUTOVSKY S. Overview and future trends of shrinkage research[J]. Materials and Structures,2006,39(9):827-847. doi: 10.1617/s11527-006-9114-z [30] 张恒春, 唐方宇, 季锡贤, 等. 超细矿物掺合料对高强混凝土干燥收缩影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(7):2514-2518. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2017.07.060ZHANG Hengchun, TANG Fangyu, JI Xixian, et al. Effects of ultrafine mineral admixtures on drying shrinkage of high strength concrete[J]. Silicate Bulletin,2017,36(7):2514-2518(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2017.07.060 [31] 曾昊, 詹培敏, 李增, 等. 矿物掺合料对水泥基材料干燥收缩影响的研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(9):2714-2723. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2020.09.003ZENG Hao, ZHAN Peimin, LI Zeng, et al. Research progress on the effect of mineral admixtures on the drying shrinkage of cement-based materials[J]. Silicate Bulletin,2020,39(9):2714-2723(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2020.09.003 [32] 徐仁崇, 李晓斌, 桂苗苗, 等. 矿物掺合料对C100混凝土早期收缩及干缩的影响[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2013(1):24-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2013.01.006XU Renchong, LI Xiaobin, GUI Miaomiao, et al. Effects of mineral admixtures on early shrinkage and dry shrinkage of C100 concrete[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products,2013(1):24-27(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4637.2013.01.006 [33] MAZLOOM M, RAMEZANIANPOUR A A, BROOKS J J. Effect of silica fume on mechanical properties of high-strength concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2004,26(4):347-357. doi: 10.1016/S0958-9465(03)00017-9 [34] AKCAY B, TASDEMIR M A. Performance evaluation of silica fume and metakaolin with identical finenesses in self compacting and fiber reinforced concretes[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,185:436-444. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.061 [35] ZHANG M H, TAM C T, LEOW M P. Effect of water-to-cementitious materials ratio and silica fume on the autogenous shrinkage of concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2003,33(10):1687-1694. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(03)00149-2 [36] 王东平, 陈佩圆, 王亮, 等. 粉煤灰掺量对碱激发矿渣砂浆减缩特性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2018, 37(2):701-705. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2018.02.052WANG Dongping, CHEN Peiyuan, WANG Liang, et al. Study on the shrinkage reduction characteristics of alkali-activated slag mortar with fly ash content[J]. Silicate Bulletin,2018,37(2):701-705(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2018.02.052 [37] RAVIKUMAR D, NEITHALATH N. Effects of activator characteristics on the reaction product formation in slag binders activated using alkali silicate powder and NaOH[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2012,34(7):809-818. doi: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.03.006 [38] 郑登登, 季韬, 王国杰. 水玻璃模数对AAS砂浆自收缩的影响[J]. 水利与建筑工程学报, 2019, 17(5):102-111.ZHENG Dengdeng, JI Tao, WANG Guojie. Effect of water glass modulus on autogenous shrinkage of AAS mortar[J]. Journal of Water Resources and Architectural Engineering,2019,17(5):102-111(in Chinese). [39] PEGADO L, LABBEZ C, CHURAKOV S V. Mechanism of aluminium incorporation into C-S-H from ab initio calculations[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2014,2(10):3477-3483. doi: 10.1039/C3TA14597B [40] 程红强, 高丹盈. 钢纤维混凝土的收缩性能试验研究[J]. 混凝土, 2009(2):57-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2009.02.018CHENG Hongqiang, GAO Danying. Experimental study on shrinkage performance of steel fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Concrete,2009(2):57-58(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2009.02.018 [41] WANG K J, SHAH S P, PHUAKSUK P. Plastic shrinkage cracking in concrete materials-influence of fly ash and fibers[J]. Materials Journal,2001,98(6):458-464. [42] 张佚伦, 詹树林, 钱晓倩, 等. 聚丙烯纤维混凝土早期收缩性能试验研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2006(1):25-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2006.01.009ZHANG Yilun, ZHAN Shulin, QIAN Xiaoqian, et al. Experimental study on early shrinkage of polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete[J]. New Building Materials,2006(1):25-28(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2006.01.009 [43] 龚建清, 周孜豪. 纤维和外加剂对泡沫混凝土收缩性能的影响[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(5):76-85. doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.05.009GONG Jianqing, ZHOU Zihao. Effects of fiber and admixture on shrinkage properties of foamed concrete[J]. Jour-nal of Hunan University (Natural Science Edition),2019,46(5):76-85(in Chinese). doi: 10.16339/j.cnki.hdxbzkb.2019.05.009 [44] 吴林妹, 史才军, 张祖华, 等. 钢纤维对超高性能混凝土干燥收缩的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2017, 31(23):58-65. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.023.007WU Linmei, SHI Caijun, ZHANG Zuhua, et al. Effect of steel fiber on drying shrinkage of ultra-high performance concrete[J]. Materials Reports,2017,31(23):58-65(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2017.023.007 [45] FANG C F, ALI M, XIE T Y, et al. The influence of steel fibre properties on the shrinkage of ultra-high performance fibre reinforced concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,242:117993. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117993 [46] 陈云鹤, 唐崇钊, 邓学钧. 配筋混凝土粘弹性参数的徐变试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2000(5):105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2000.05.017CHEN Yunhe, TANG Chongzhao, DENG Xuejun. Experimental study on creep of viscoelastic parameters of reinforced concrete[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2000(5):105-110(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2000.05.017 [47] 杨小兵. 混凝土收缩徐变预测模型研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2004.YANG Xiaobing. Study on prediction model of concrete shrinkage and creep[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2004(in Chinese). [48] GARDNER N J, LOCKMAN M J. Design provisions for drying shrinkage and creep of normal-strength concrete[J]. Materials Journal,2001,98(2):159-167. [49] ZHOU Y Q, CHEN W Y, YAN P Y. Measurement and modeling of creep property of high-strength concrete considering stress relaxation effect[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2022,56:104726. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104726 [50] 王铁梦. 工程结构裂缝控制[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017: 31-32.WANG Tiemeng. Crack control of engineering structures[M]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2017: 31-32(in Chinese). [51] 龚洛书, 惠满印, 杨蓓. 砼收缩与徐变的实用数学表达式[J]. 建筑结构学报, 1988(5):37-42. doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.1988.05.005GONG Luoshu, HUI Manyin, YANG Bei. Practical mathematical expressions for shrinkage and creep of concrete[J]. Journal of Building Structures,1988(5):37-42(in Chinese). doi: 10.14006/j.jzjgxb.1988.05.005 -





 下载:
下载: