Green multi-performances electromagnetic shielding material for 5G mm-wave
-
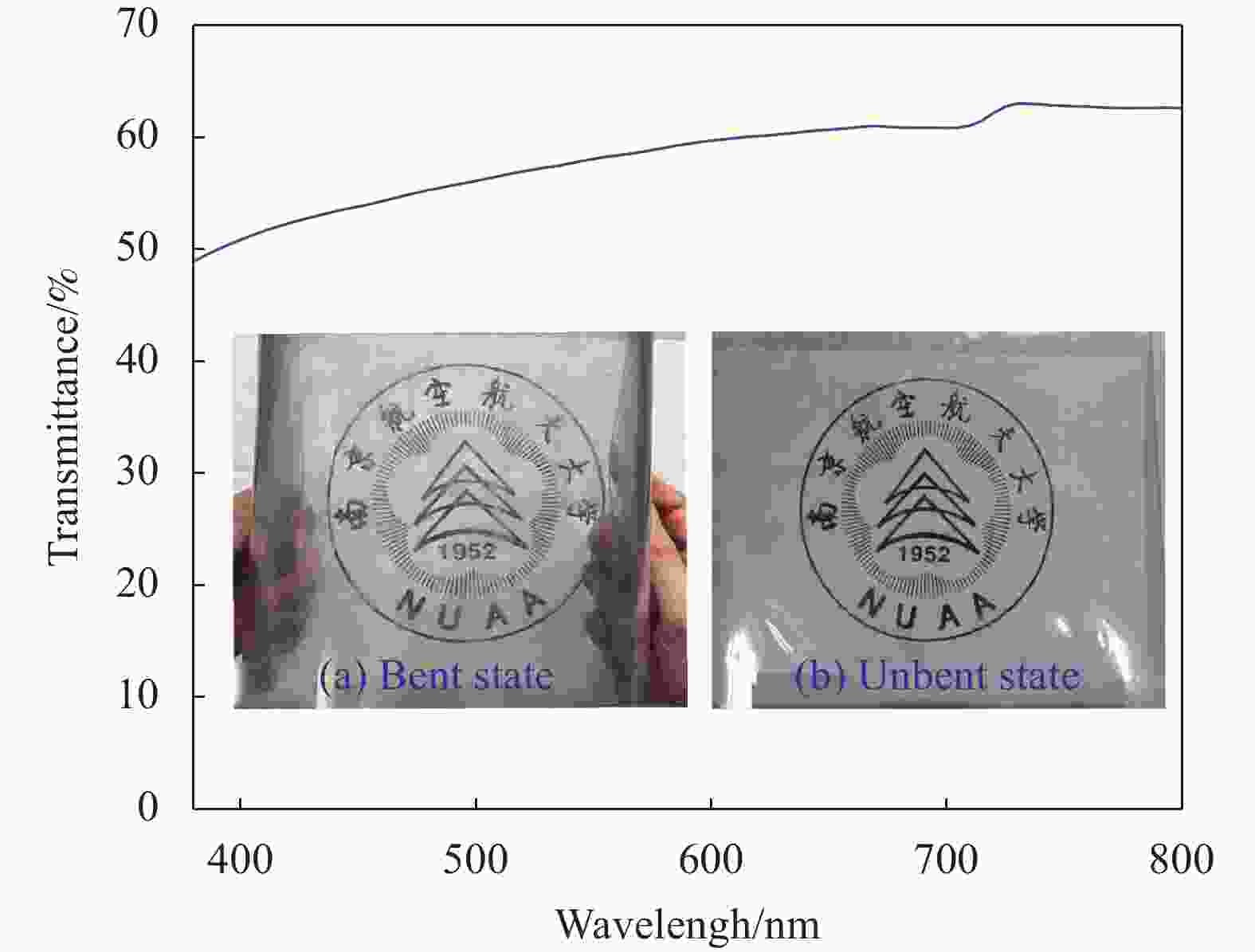
摘要: 为解决5G毫米波带来的电磁辐射及现有电磁屏蔽材料造成的环境二次污染、高雷达散射截面、光学不透明和难以共形等问题,本文以超材料吸波体为基础,提出了一个满足绿色屏蔽指数gs≥1的低雷达散射截面、光学透明和柔性多性能电磁屏蔽材料。该电磁屏蔽材料属于人工可设计的多层结构,使用透明导电材料氧化铟锡作为周期性谐振单元结构和底层铺地所用材料,透明材料聚对苯二甲酸乙二醇酯和聚氯乙烯作为介质层。仿真和实验结果一致性表明:该屏蔽材料在22~30 GHz频段内可实现未共形与共形角度60°状态>30 dB的绿色有效电磁屏蔽及>5 dB的雷达散射截面(RCS)缩减。理论推导的等效电路、等效参数和场分布论证了吸收屏蔽的原理。该绿色多性能电磁屏蔽材料精确覆盖了毫米波n257、n258和n261频段,可有效解决这些频段带来的电磁干扰问题。Abstract: In order to solve the electromagnetic radiation brought by 5G mm-wave, and environmental secondary pollution, high radar scattering cross section, optical opaque and difficult to conformal caused by the existing electromagnetic shielding materials. A multi-performances electromagnetic shielding material based on a metamaterial absorber was proposed in this paper, which can meet the green shielding index gs≥1 with low radar cross section (RCS), optical transparency, and flexible performances. This electromagnetic shielding material belongs to a manually designable multi-layer structure, in which the transparent conductive material indium tin oxide was used as the periodic resonant unit structure and the underlying floor material. The transparent materials polyethylene terephthalate and polyvinyl chloride were used as the dielectric layer. The consistency between simulation and experimental results shows that in the frequency range of 22-30 GHz, and un-conformal and conformal angle of 45° states, the proposed shielding material can achieve >30 dB green effective electromagnetic shielding and >5 dB RCS reduction. The equivalent circuit of theoretical derivation, and equivalent parameters, field distribution demonstrated the principle of absorption shielding. The green multi-performances electromagnetic shielding material accurately covers the 5G mm-wave n257, n258, and n261 frequency bands, which can effectively solve the electromagnetic interference problem caused by these frequency bands.
-
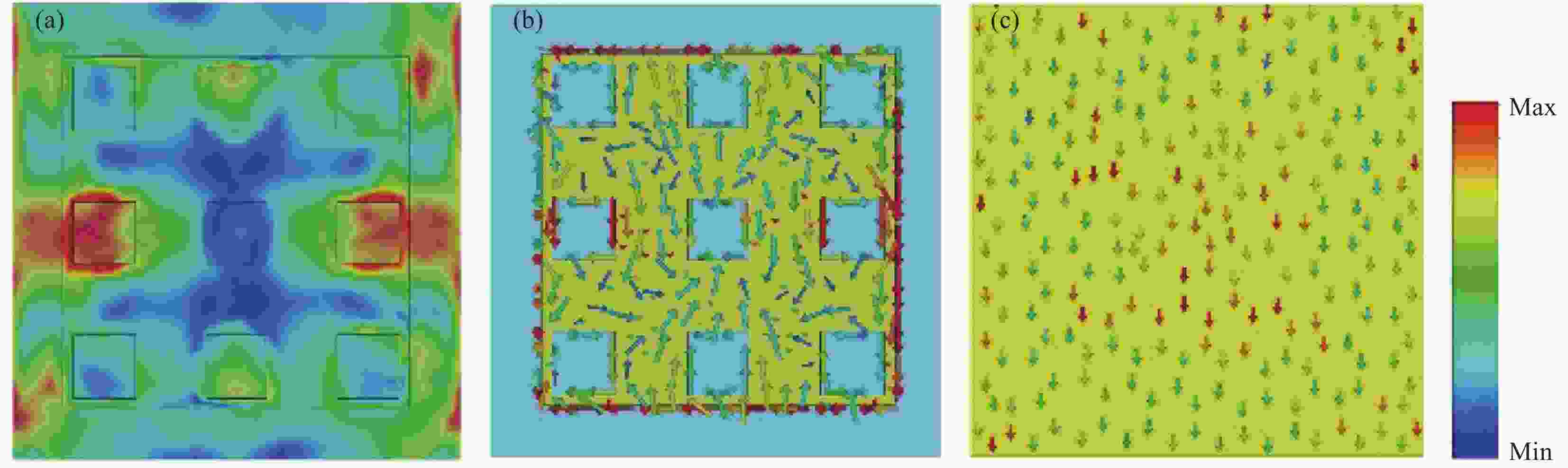
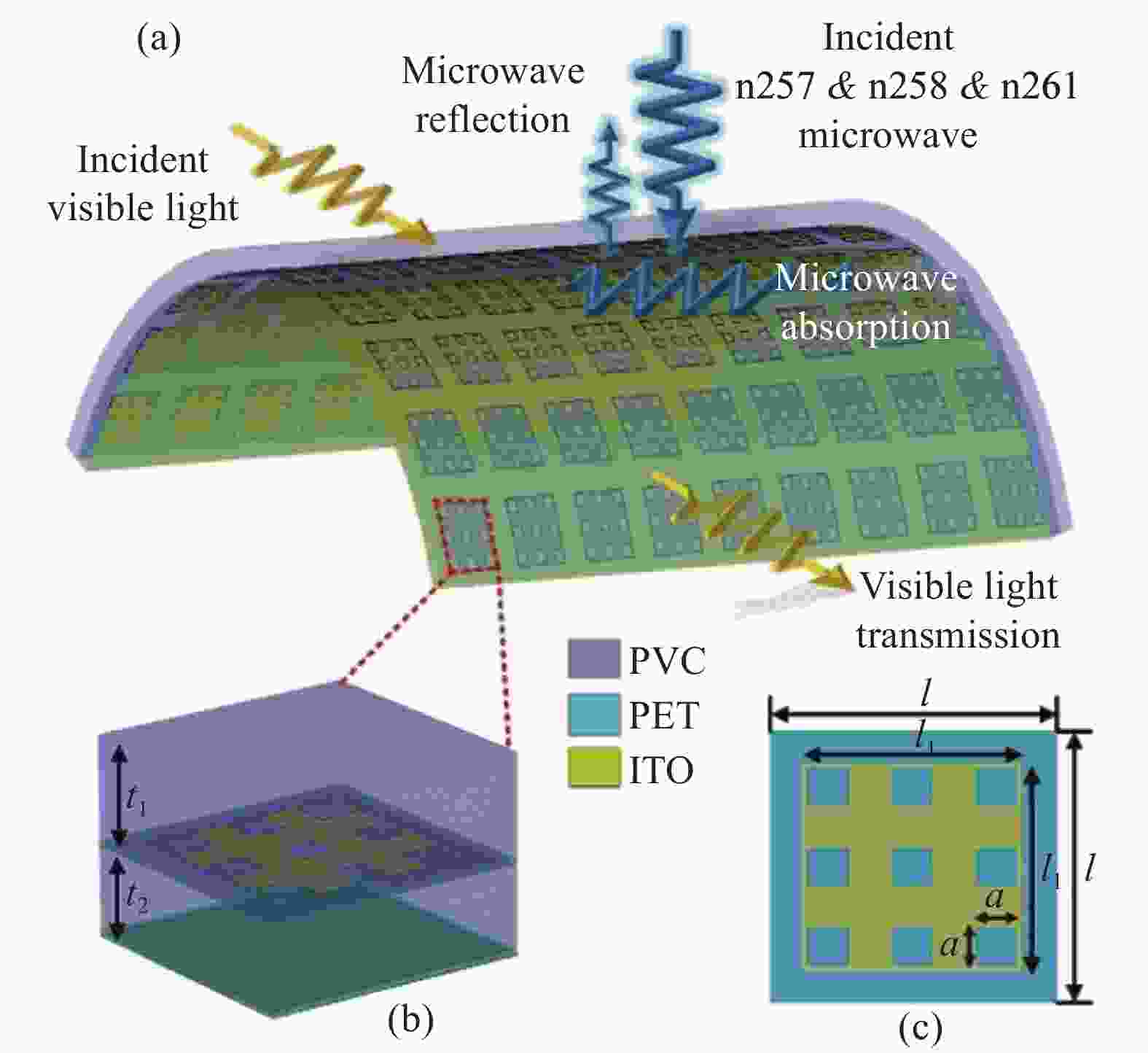
图 1 (a) 超材料吸波体的工作概念图;(b) 单元结构的3D视图;(c) 单元结构刻蚀氧化铟锡(ITO)层俯视图
PVC—Polyvinyl chloride; PET—Polyethylene terephthalate; l—Length; a—Side length; t—Thickness
Figure 1. (a) Working conceptual illustration of the proposed metamaterial absorber; (b) 3D-view of the unit cell; (c) Top view of the etched indium tin oxide (ITO) layer of the unit cell
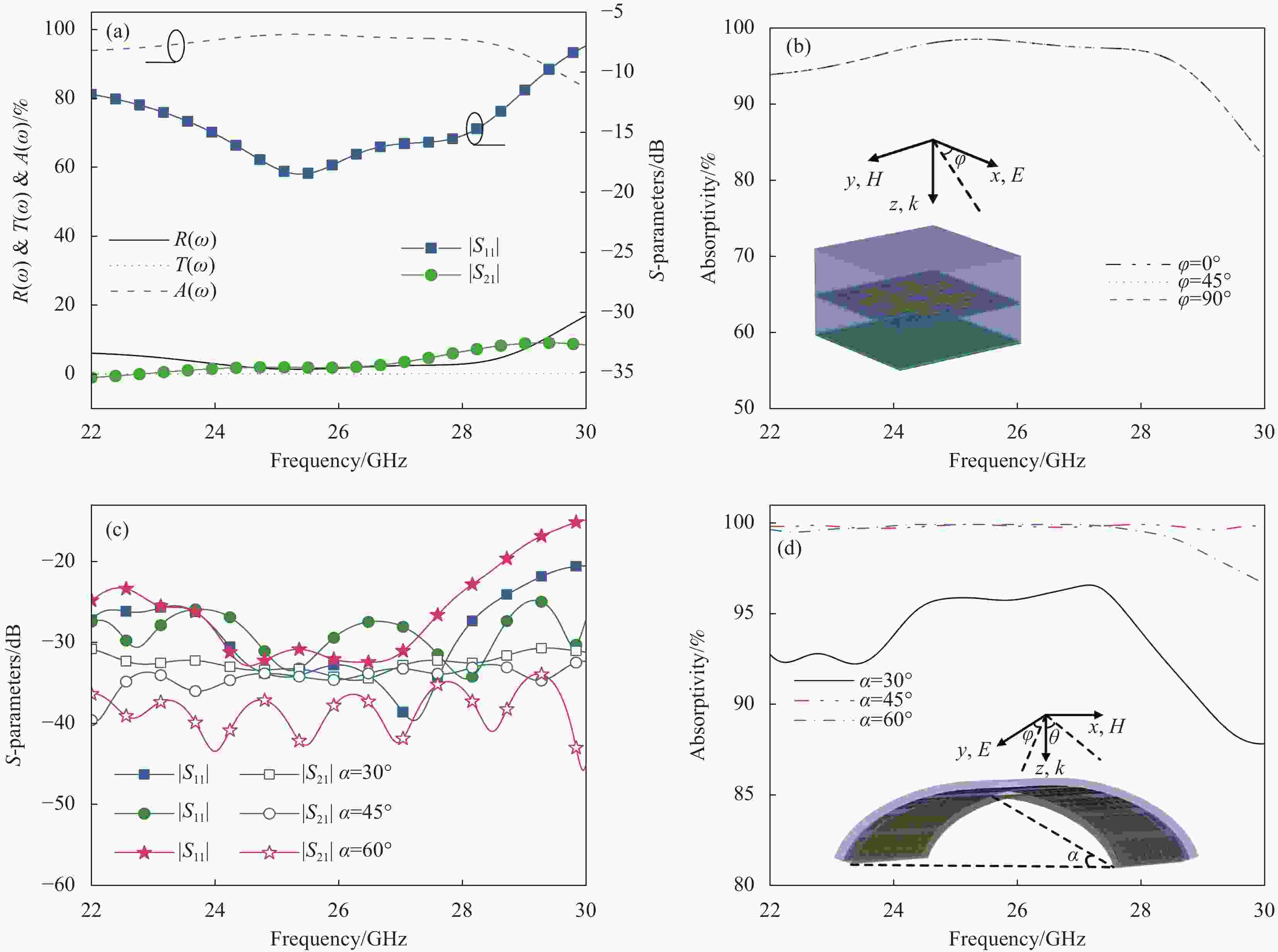
图 2 未共形状态超材料吸波体的S参数、反射率(R(ω))、透射比(T(ω))和吸收率(A(ω)) (a)及不同极化角下的A(ω) (b);不同共形角状态S参数(c) 和A(ω) (d)
Figure 2. In the non-conformal state of S-parameters, reflectivity (R(ω)), transmittance (T(ω)) and absorptivity (A(ω)) (a) and A(ω) at different polarization angles (b); In different conformal angles state of S-parameters (c) and A(ω) of the proposed metamaterial absorber (d)
|S11|—Reflection coefficient; |S21|—Transmission coefficient; α—Conformal angle; φ—Polarization angle; θ—Incident angle; E—Electric field; H—Magnetic field; k—Wave vector
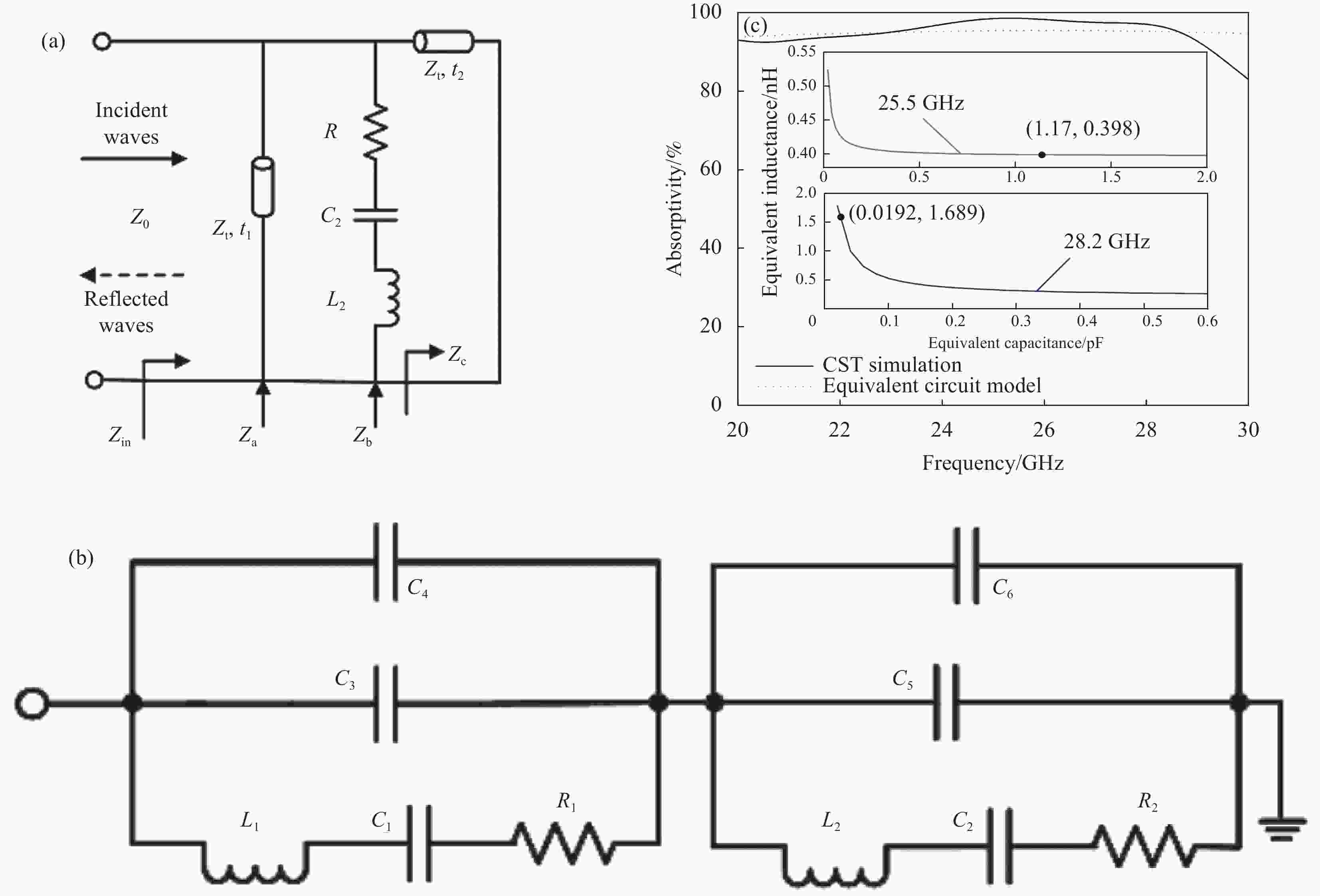
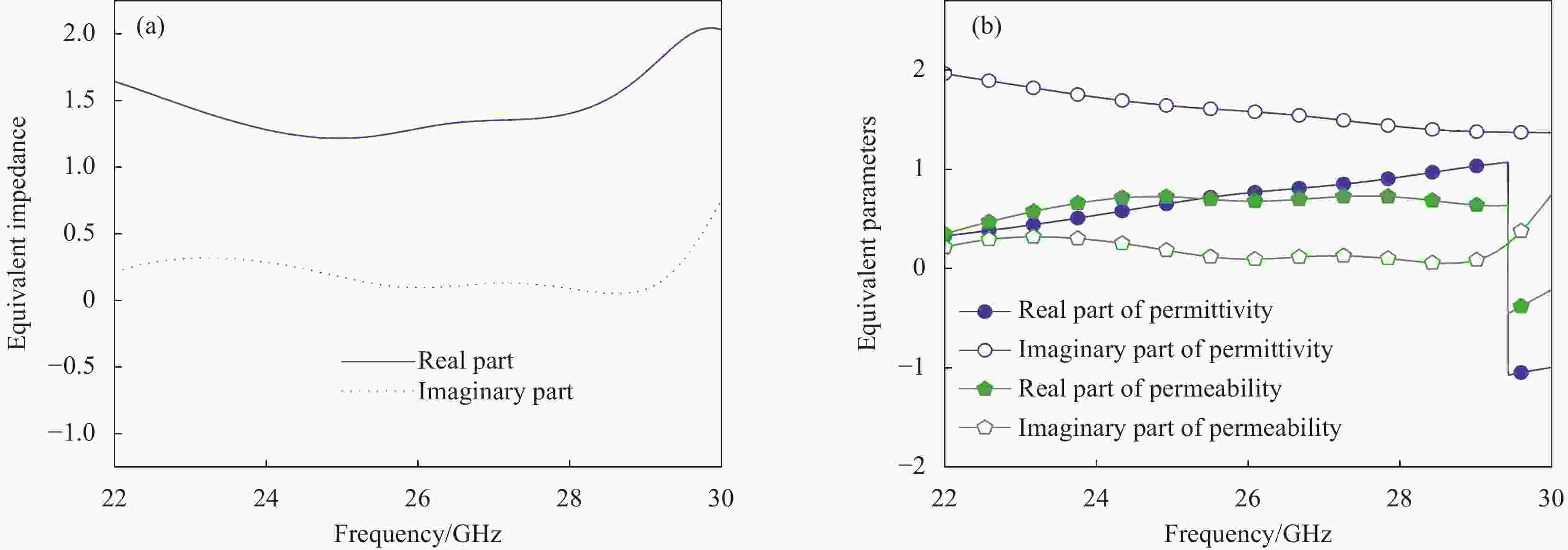
图 3 (a) 超材料吸波体的等效电路模型;(b) 具有双谐振点的ADS等效电路;(c) 垂直入射下仿真与等效电路吸收率对比(插图为L-C关系式)
Figure 3. (a) Equivalent circuit model of the proposed metamaterial absorber; (b) Equivalent circuit with double resonant points in ADS; (c) Comparison of absorptivity between simulation and equivalent circuit under vertical incidence (The inset shows L-C relation)
Z0—Wave impedance in free space; Zin—Input impedance of the absorber; Za—Impedance of top layer polyvinyl chloride (PVC) substrate; Zb—Impedance of the ITO layer with etched shape; Zc—Impedance of the bottom layer PVC substrate; Zt—Equal to Za and Zc; R1, R2—Calculated resistances;L1, L2—Calculated inductance; C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6—Calculated capacitance; t1—Thickness of the top layer PVC substrate; t2—Thickness of the bottom layer PVC substrate; CST—Computer simulation technology
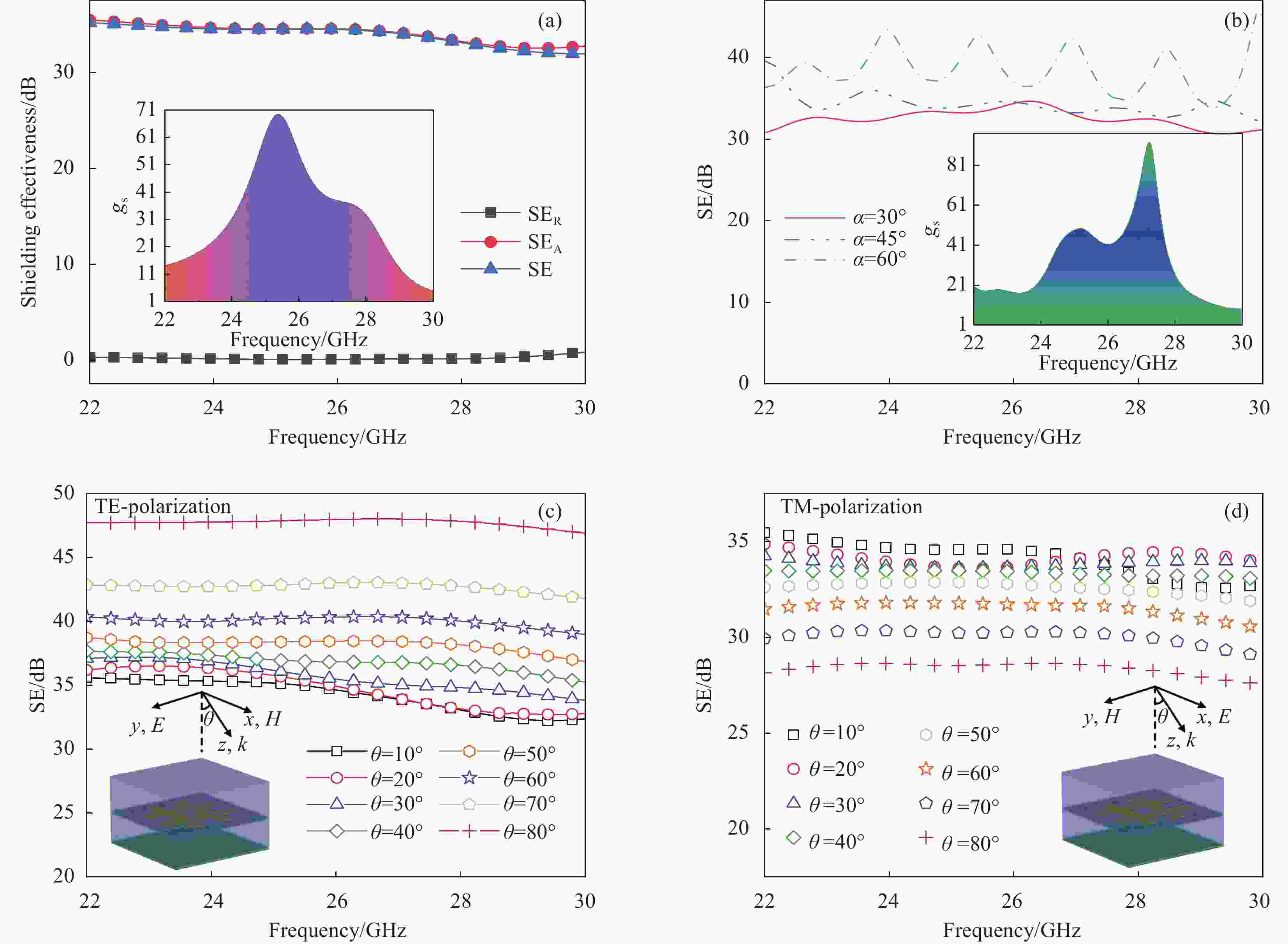
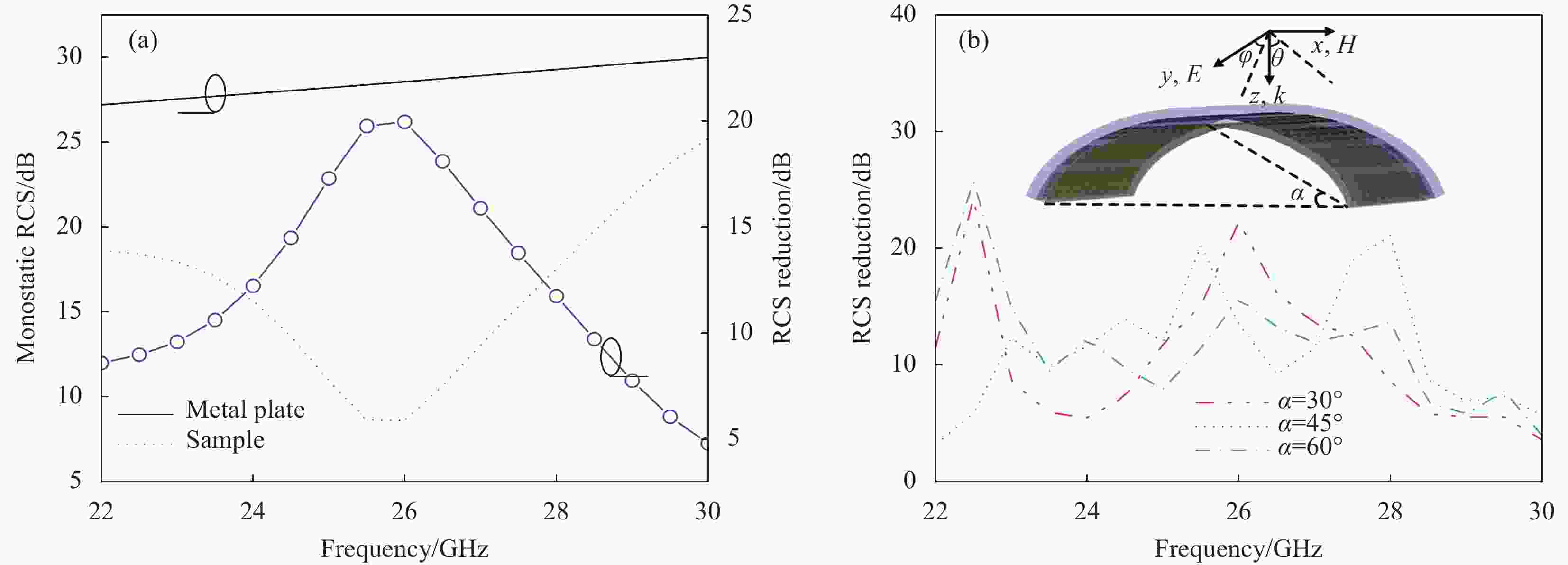
图 6 超材料吸波体的屏蔽效能:(a) 未共形状态;(b) 不同共形角状态(插图为绿色屏蔽指数);未共形状态不同入射角时的屏蔽效能横电波(TE) (c)和横磁波(TM)极化(d)
Figure 6. Shielding effectiveness of the proposed metamaterial absorber: (a) Un-conformal; (b) Different conformal angles states (The inset is green shielding index); Shielding effectiveness of the proposed metamaterial absorber at different incident angles in un-conformal state transverse electric wave (TE) (c) and transverse magnetic wave (TM) polarizations (d)
SER—Reflective shielding; SEA—Absorption shielding; SE—Total shielding; gs—Green shielding index
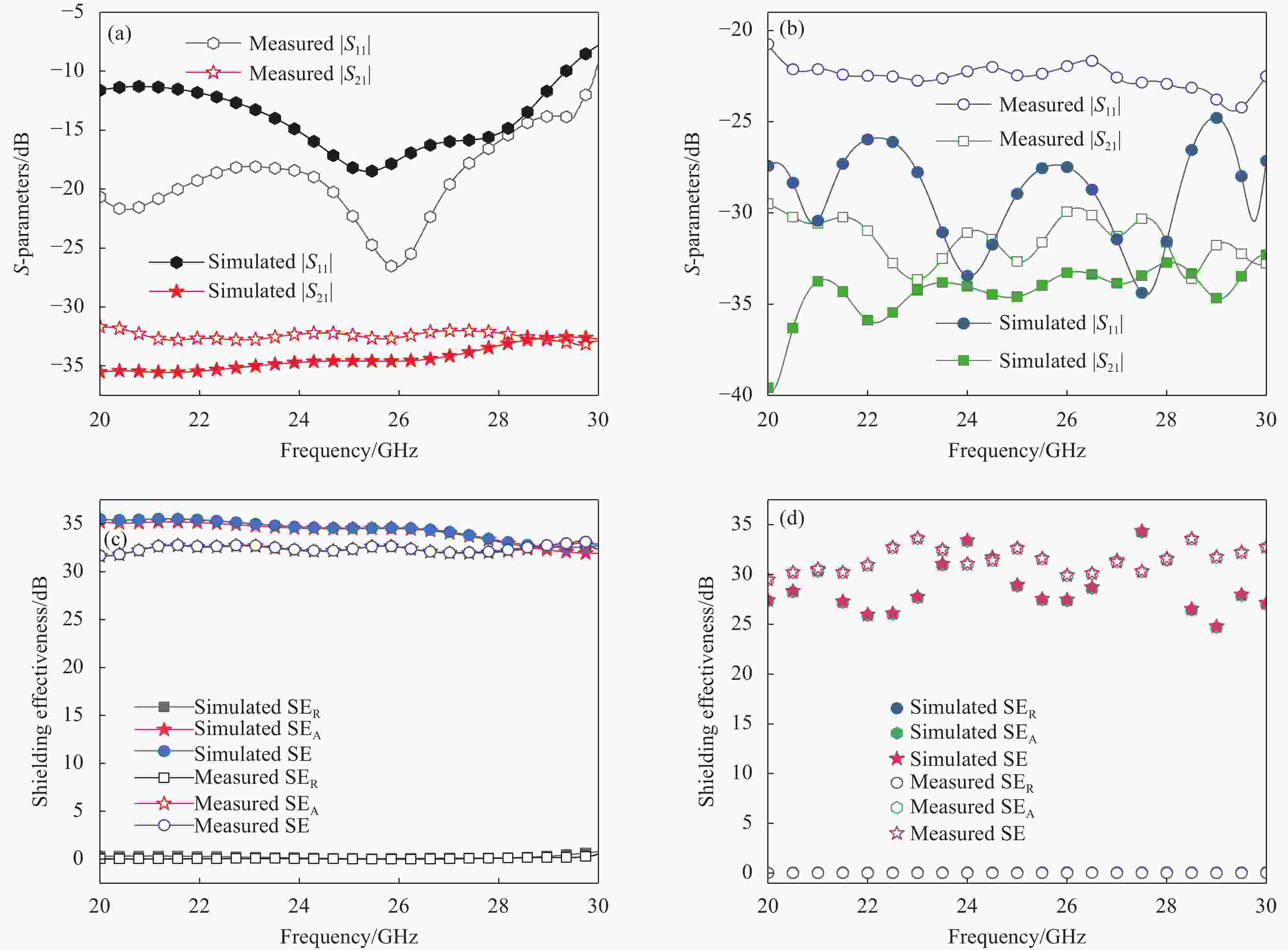
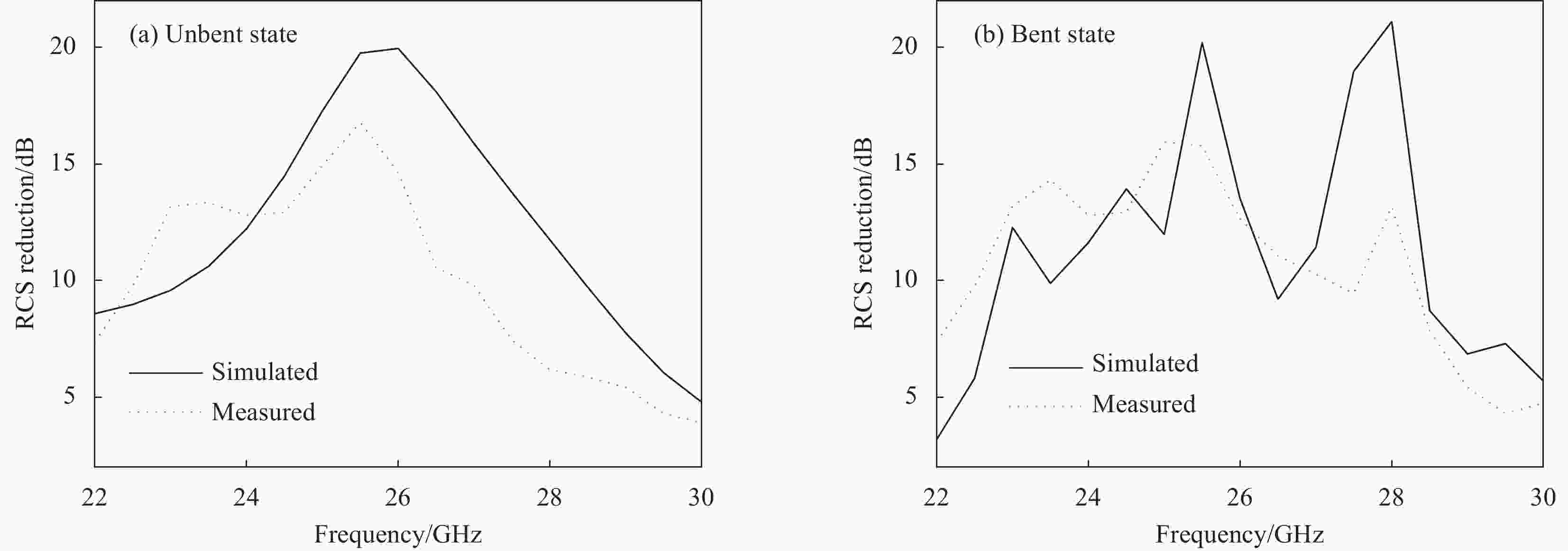
图 9 超材料吸波体的测试与仿真S参数对比:(a)未共形状态;(b)共形角45°状态;测试与仿真屏蔽效能对比:(c)未共形状态;(d)共形角45°状态
Figure 9. Comparison of S-parameters between measurement and simulation of proposed metamaterial absorber: (a) Un-conformal; (b) Conformal angle of 45° states; Comparison of shielding effectiveness between measurement and simulation: (c) Un-conformal; (d) Conformal angle of 45° states
表 1 本文与相关文献性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison between this paper and related literatures
Refs. Relative band/
GHzP-Ic O-Td Flexibility SE/dB gs≥1 [12] 8-12b No Yes Yes <16.36 No R(ω) [13] 8-12b No No Yes ~54 1.44 [15] 18-26.5b No No No 30 − [16] 18-26 b Yes No Yes 13 − [17] 12.4-18b Yes No No 32.6 − [21] 24, 28a No No No − − [23] 7.8-12.4a,b Yes Yes No >25 − [24] 7.8-18a,b Yes Yes No >18.25 − [25] 26.8-28.2a Yes Yes No − − This work 22-30a,b Yes Yes Yes >30 Yes Notes: a—Absorption bandwidth over 90%; b—Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding bandwidth; c—Polarization insensitive; d—Optical transparency. -
[1] 连俊杰, 刘润爱, 陈洪胜, 等. 双屏蔽(B4 C-W)/6061 Al层状复合板设计与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3387-3393.LIAN Junjie, LIU Run'ai, CHEN Hongsheng, et al. Design and properties of double shielding (B4 C-W)/6061 Al laminated composite board[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3387-3393(in Chinese). [2] BAAN R, GROSS Y, LAUBY-SECRETAN B, et al. Carcinogenicity of radio frequency electromagnetic fields[J]. Lancet Oncology,2011,12:624-626. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70147-4 [3] LI C B, LI Y J, ZHAO Q, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding of graphene aerogel with layered microstructure fabricated via mechanical compression[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12:30686-30694. [4] 中国新闻网. 工信部: 预计2020年底全国5G基站数超过60万个[EB/OL]. (2021-01-26) [2022-09-30]. https://baijhao.baidu.com/s?id=1689916049141199558&wfr=spider&for=pc.China News Network. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: The number of 5G base station in China is expected to exceed 600, 000 by the end of 2020[EB/OL]. (2021-01-26) [2022-09-30]. https://baijhao.baidu.com/s?id=1689916049141199558&wfr=spider&for=pc(in Chinese). [5] 通信世界. 5G毫米波机遇及挑战[EB/OL]. (2021-09-10) [2022-09-30]. https://baijhao.baidu.com/s?id=1710483343170185189&wfr=spider&for=pc.The Communication World. 5G millimeter wave opportu-nities and challenges[EB/OL]. (2021-09-10) [2022-09-30]. https://baijhao.baidu.com/s?id=1710483343170185189&wfr=spider&for=pc(in Chinese). [6] HWANG U, KIM J, SEOL M, et al. Quantitative interpretation of electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency: Is it really a wave absorber or a reflector?[J]. ACS Omega, 2022, 7: 4135-4139. [7] 管宇鹏, 齐晓俊, 李帅, 等. Pickering乳液技术制备纤维素纳米纤丝-还原氧化石墨烯/聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯电磁屏蔽复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8):1875-1883.GUAN Yupeng, QI Xiaojun, LI Shuai, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanofiber-reduced graphene oxide/poly(methyl methacrylate) electromagnetic interference shielding composites by Pickering emulsion technology[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(8):1875-1883(in Chinese). [8] XU Y D, LIN Z Q, RAJAVEL K, et al. Tailorable, lightweight and superelastic liquid metal monoliths for multifunctional electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,29:1-15. [9] 张梦辉, 马忠雷, 马建中, 等. 聚合物基电磁屏蔽复合材料的结构设计与性能研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(5):1358-1370. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201208.003ZHANG Menghui, MA Zhonglei, MA Jianzhong, et al. Research progress of structure design and performance of polymer-based electromagnetic shielding composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(5):1358-1370(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201208.003 [10] ZHANG D Q, LIU T T, SHU J C, et al. Self-assembly construction of WS2-rGO architecture with green EMI shielding[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11:26807-26816. [11] ZHU X Z, GUO A Q, YAN Z Y, et al. PET/Ag NW/PMMA transparent electromagnetic interference shielding films with high stability and flexibility[J]. Nanoscale,2021,13:8067-8076. doi: 10.1039/D1NR00977J [12] WANG J, HU Q, HUANG J H, et al. Multifuntional textiles enabled by simultaneous interaction with infrared and microwave electromagnetic waves[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces,2022,9(12):2102322. [13] WANG X X, SHU J C, CAO W Q, et al. Eco-mimetic nanoarchitecture for green EMI shielding[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,369:1068-1077. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.164 [14] YU Z, DAI T W, YUAN S W, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding performance of anisotropic polyimide/graphene composite aerogels[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12:30990-31001. [15] KWON S J, RYU S H, HAN Y K, et al. Electromagnetic interference shielding films with enhanced absorption using double percolation of poly(methyl methacrylate) beads and CIP/MWCNT/TPU composite channel[J]. Materials Today Communications,2022,31:103401. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103401 [16] RYU S H, PARK B, HAN Y K, et al. Electromagnetic wave shielding flexible films with near-zero reflection in the 5G frequency band[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2022,10:4446-4455. doi: 10.1039/D1TA10065C [17] MA L, HAMIDINEJAD M, ZHAO B, et al. Layered foam/film polymer nanocomposites with highly efficient EMI shielding properties and ultralow reflection[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(19): 1-18. [18] LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters,2008,100:207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402 [19] BIAN B, LIU S B, WANG S Y, et al. Novel triple-band polarization-insensitive wide-angle ultra-thin microwave metamaterial absorber[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2013,114:194511. doi: 10.1063/1.4832785 [20] OZDEN K, YUCEDAG O M, KOCER H. Metamaterial based broadband RF absorber at X-band[J]. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications,2016,70:1062-1070. [21] NAQVI S A, BAQIR M A, GOURLRY G, et al. A novel meander line metamaterial absorber operating at 24 GHz and 28 GHz for the 5G applications[J]. Sensors,2022,22:3764. doi: 10.3390/s22103764 [22] LEE J, LIM S. Bandwidth-enhanced and polarisation-insensitive metamaterial absorber using double resonance[J]. Electronics Letters, 2011, 47(1): 1-2. DOI: 10.1049/el.2010.2770 [23] LI S Y, LIU L L, JIANG Y Y, et al. Ultrathin optically transparent electromagnetic shielding window with broadband micro-wave absorption and ultrahigh optical transmittance[J]. International Journal of RF and Microwave Computeraided Engineering,2022,32(11):e23338. [24] ZHANG Y Q, DONG H X, MOU N L, et al. High-performance broadband electromagnetic interference shielding optical window based on a metamaterial absorber[J]. Optical Express,2020,28:26836-26849. doi: 10.1364/OE.401766 [25] JEONG H, TENTZERIS M M, LIM S, et al. Optically transparent metamaterial absorber using inkjet printing technology[J]. Materials,2019,12:3406. doi: 10.3390/ma12203406 [26] LI S Y, LIU L L, JIANG Y Y, et al. Ultrathin optically transparent metamaterial absorber for broadband microwave invisibility of solar panels[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,2022,55:045101. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/ac2bcc [27] XIONG Y, CHEN F, CHENG Y Z, et al. Rational design and fabrication of optically transparent broadband microwave absorber with multilayer structure based on indium tin oxide[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,920:166008. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.166008 [28] ZHANG C L, WU X Y, HUANG C, et al. Flexible and transparent microwave-infrared Bi-stealth structure[J]. Advanced Materials, 2020, 32: e1908496. [29] LIU T, KIM S S. Design of wide-bandwidth electromagne-tic wave absorbers using the inductance and capacitance of a square loop-frequency selective surface calculated from an equivalent circuit model[J]. Optics Communications,2016,359:372-377. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2015.10.011 [30] DENG R X, LI M L, MUNEER B, et al. Theoretical analysis and design of ultrathin broadband optically transparent microwave metamaterial absorbers[J]. Materials,2018,11(1):107. doi: 10.3390/ma11010107 [31] ZHANG F L, LIU Z J, QIU K P, et al. Conductive rubber based flexible metamaterial[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(6): 061906. [32] CHENG J Y, LI C B, XIONG Y F, et al. Recent advances in design strategies and multifunctionality of flexible electromagnetic interference shielding materials[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2022,80:1-31. [33] SHENG A, YU J, REN S Q. Printing nanostructured copper for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials,2022,4(4):2047-2052. doi: 10.1021/acsaelm.2c00199 [34] JIA X C, LI Y, SHEN B, et al. Evaluation, fabrication and dynamic performance regulation of green EMI-shielding materials with low reflectivity: A review[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2022,233:109652. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109652 -





 下载:
下载: