Low-velocity impact of functional gradient honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets
-
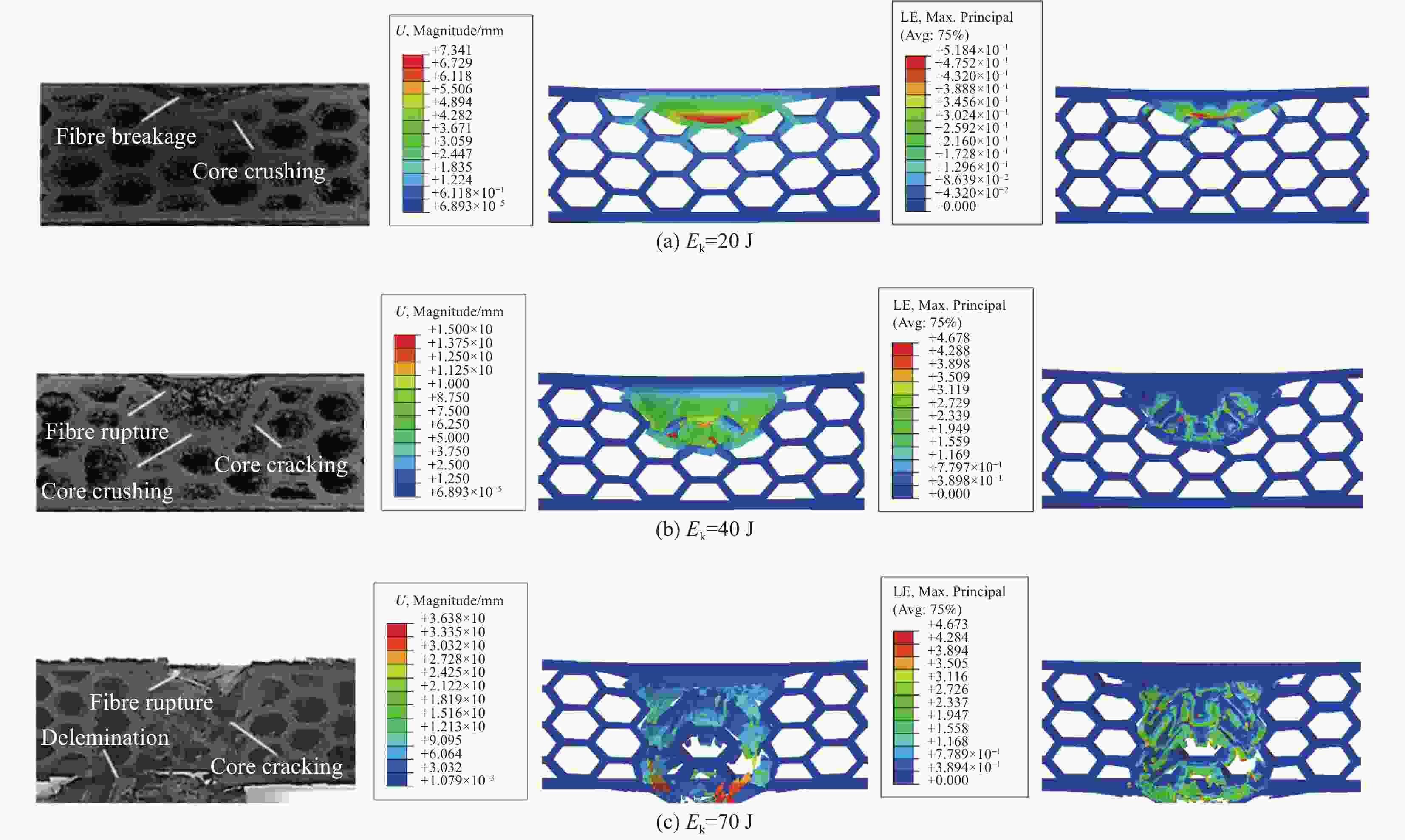
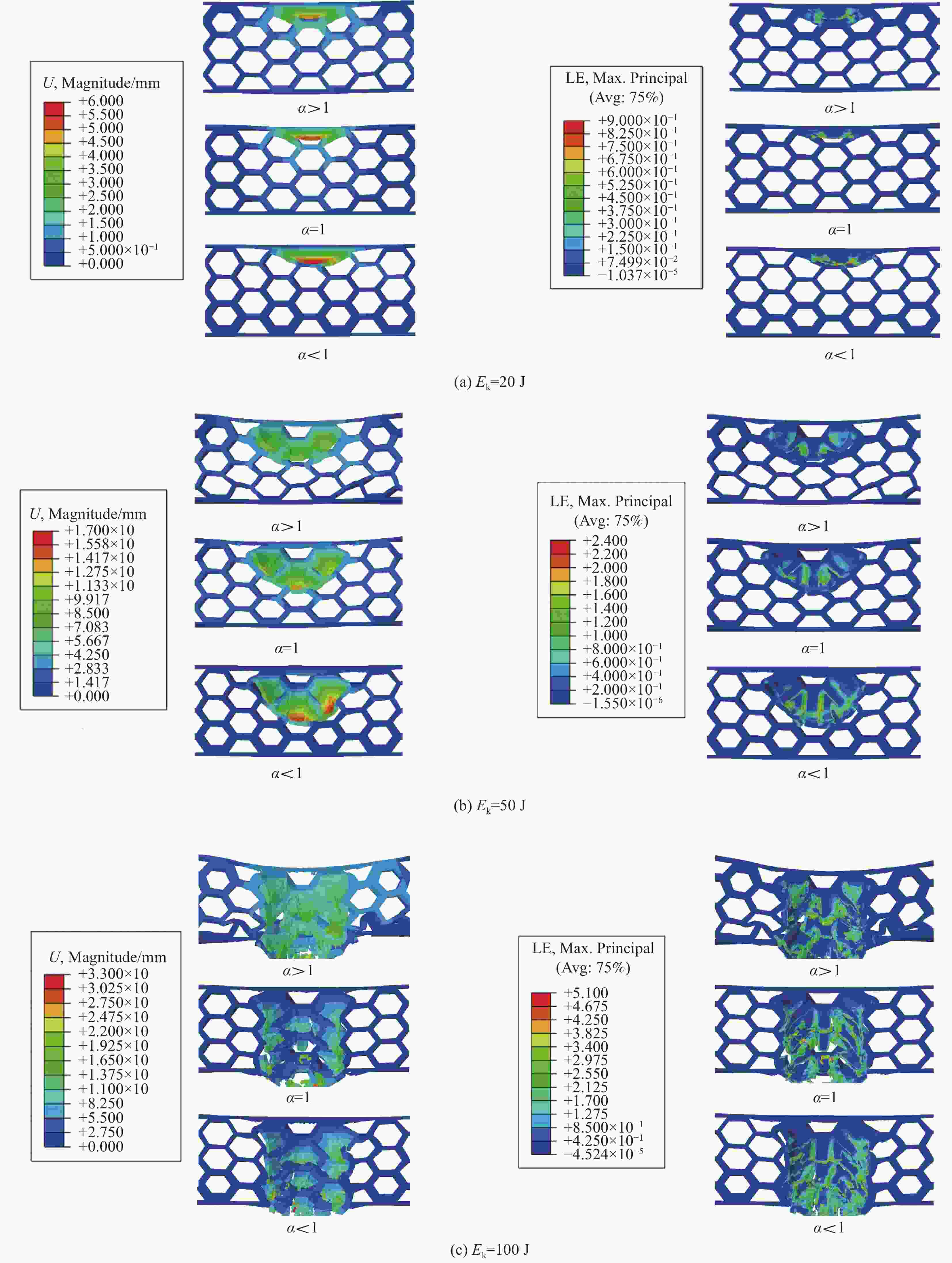
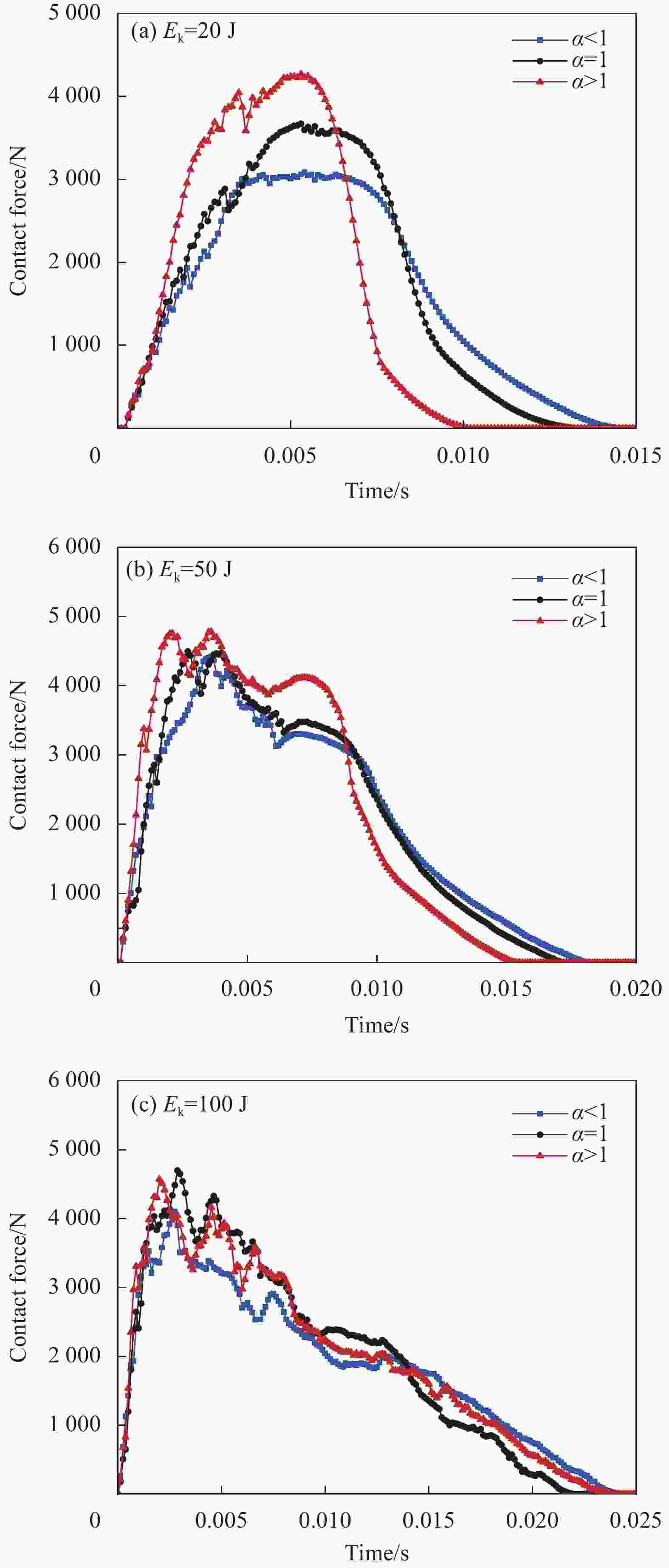
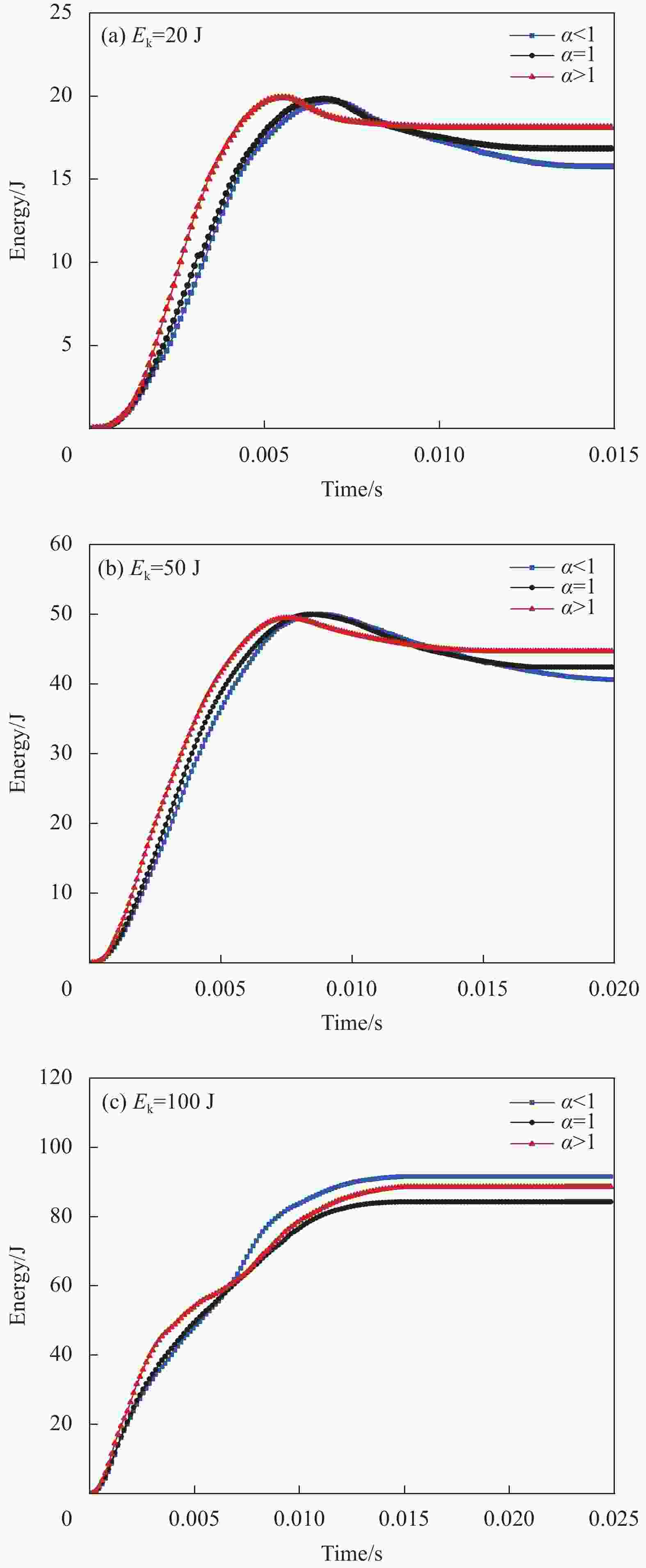
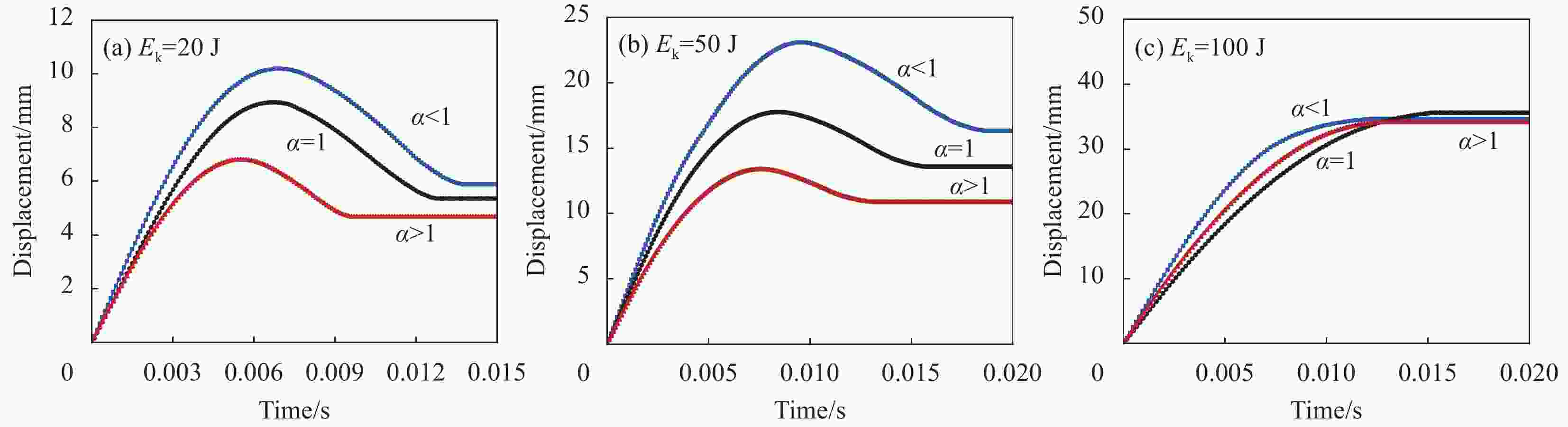
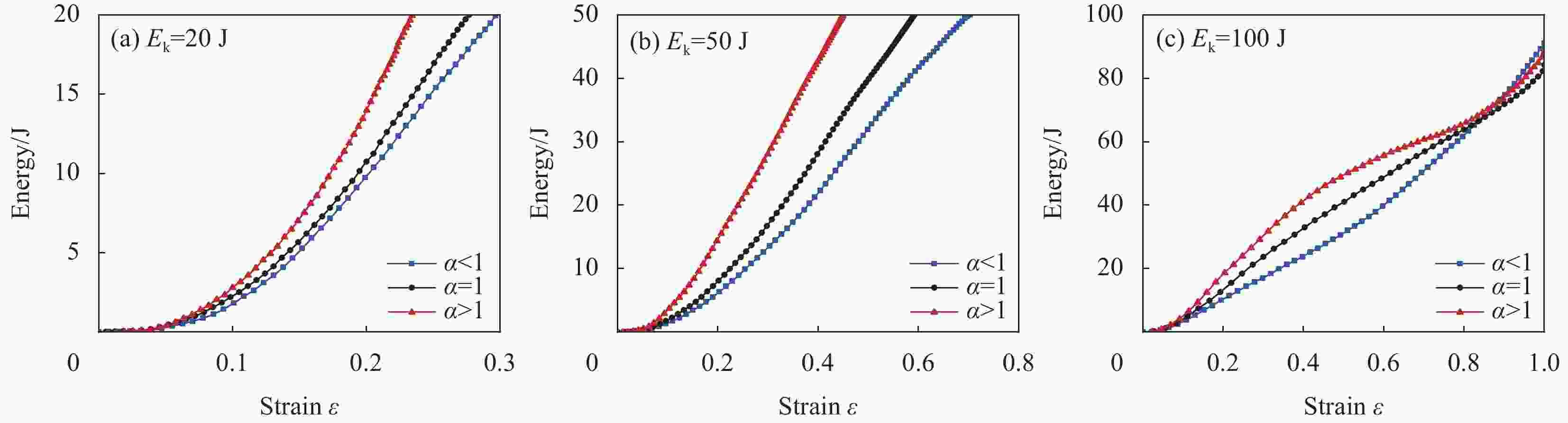
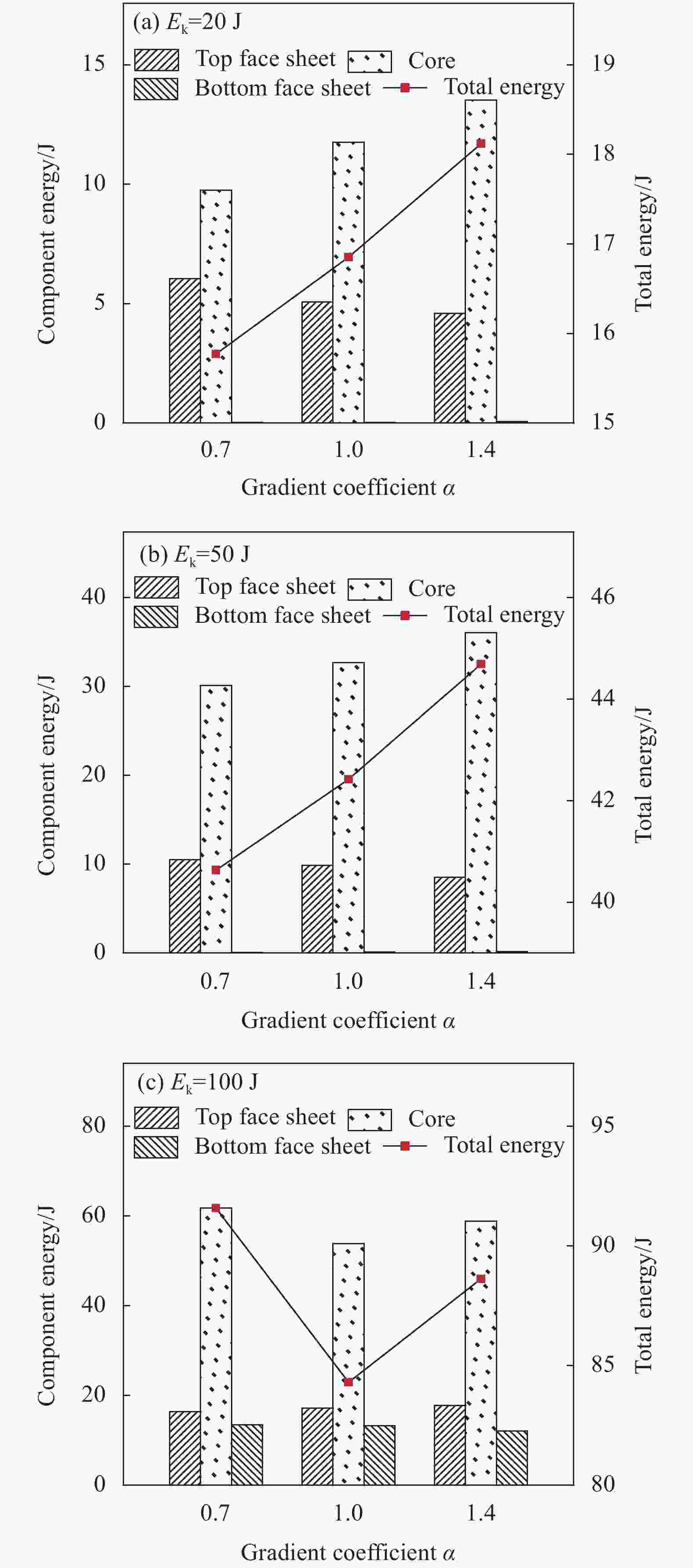
摘要: 针对蜂窝结构抗冲击性能进行有限元仿真,验证模型与实验结果的一致性,主要研究了碳纤维增强树脂基复合材 料(CFRP)面板-功能梯度蜂窝夹层板在低速冲击下的防护特性。通过改变壁厚在传统蜂窝结构中引入密度梯度,针对不同冲击能量和不同梯度系数α,对比研究了功能梯度夹层板和传统夹层板的吸能特性。结果表明,冲击能量较小时α>1的蜂窝夹层板具有更好的吸能特性,随着冲击能量的增大,具有吸能优越性的芯层从α>1逐渐向α<1转变,当冲击能量足够击穿整个夹层板时,α<1的夹层板具有更好的吸能特性。在20 J、50 J和100 J冲击能量下,同等质量下的功能梯度夹层板比传统夹层板吸能分别提升7.54%、5.33%和8.65%。Abstract: The impact process and resistance capability of honeycomb plate with carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) face sheets were studied by using finite element model (FEM), and the FEM was verified by comparing with impact experiment. The density gradient was introduced into the traditional honeycomb structure by changing the wall thickness and the protection characteristics of functional gradient (FG) honeycomb sandwich plate under low-velocity impact (LVI) were simulated under different impact energies and gradient coefficients α. The energy absorption characteristics of the FG and the traditional sandwich plate were compared through FEM. The results show that, under low impact energy, the honeycomb sandwich plate with α>1 has better energy absorption. With the increase of impact energy, the core with absorbing energy advantages changes gradually from α>1 to α<1, when the whole sandwich plate is penetrated, the sandwich plate with α<1 has better energy absorption characteristics. Under the impact energy of 20 J, 50 J and 100 J, the energy absorptions of functional gradient sandwich plates are 7.54%, 5.33% and 8.65% higher than that of traditional sandwich plates with the same mass.
-
Key words:
- functional gradient /
- low-velocity impact /
- energy absorption /
- sandwich plate /
- finite element model
-
表 5 抗冲击性能综合对比
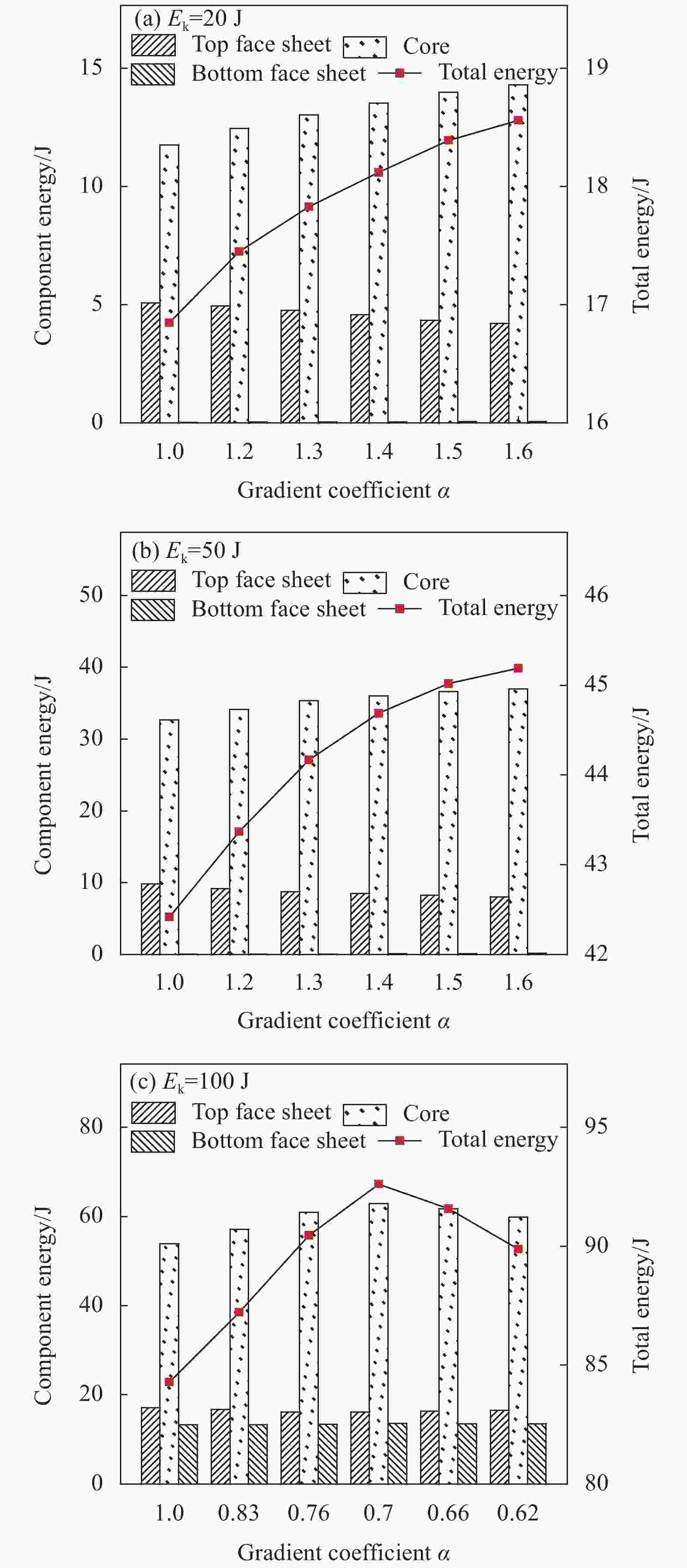
Impact energy /J α Peak contact force /N Total energy /J Core energy /J Total energy percentage increase (%) 20 0.7 3033.87 15.77 9.74 -6.14 1 3670.45 16.85 11.76 —— 1.4 4265.74 18.12 13.52 7.54 50 0.7 4420.25 40.63 30.11 -4.22 1 4496.30 42.42 32.66 —— 1.4 4781.43 44.68 36.03 5.33 100 0.7 4100.79 91.58 61.76 8.65 1 4700.03 84.29 53.88 —— 1.4 4570.88 88.63 58.78 5.15 表 1 CFRP材料参数
Table 1. Material properties of CFRP
Property Value Longitudinal stiffness E1/GPa 55.92 Transverse stiffness E2/GPa 54.40 Shear modulus G12/GPa 4.199 Poisson's ratio ν21 0.043 Longitudinal tensile strength Xt/MPa 910.1 Longitudinal compressive strength Xc/MPa 710.2 Transverse tensile strength Yt/MPa 772.2 Transverse compressive strength Yc/MPa 703.2 Shear strength Sc/MPa 131.0 表 2 ABS材料参数
Table 2. Material properties of ABS
Density/
(kg·m−3)Young's modulus/
MPaPoisson's ratio Yield strength/MPa Effective failure strain 1100 1741 0.35 39 0.015 表 3 网格收敛性分析
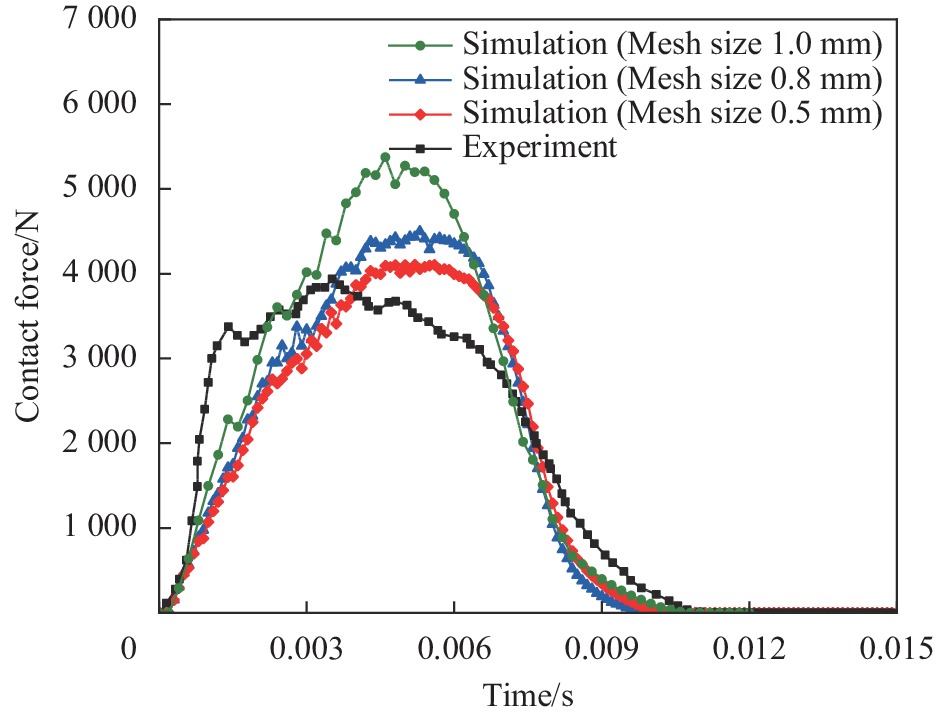
Table 3. Analysis of mesh convergence
Mesh size/mm Peak force/N Experimental difference/% FEM relative difference% 1.0 5374.09 36.45 — 0.8 4489.10 13.98 16.48 0.5 4103.61 4.19 8.59 表 4 不同Ek下CFRP面板-ABS蜂窝夹层板的接触力峰值和吸能及其相对误差
Table 4. Contact force peak and energy absorption and their relative errors of sandwich plate with ABS core and CFRP face sheets under different Ek
表 5 CFRP面板-功能梯度蜂窝夹层板壁厚与梯度值
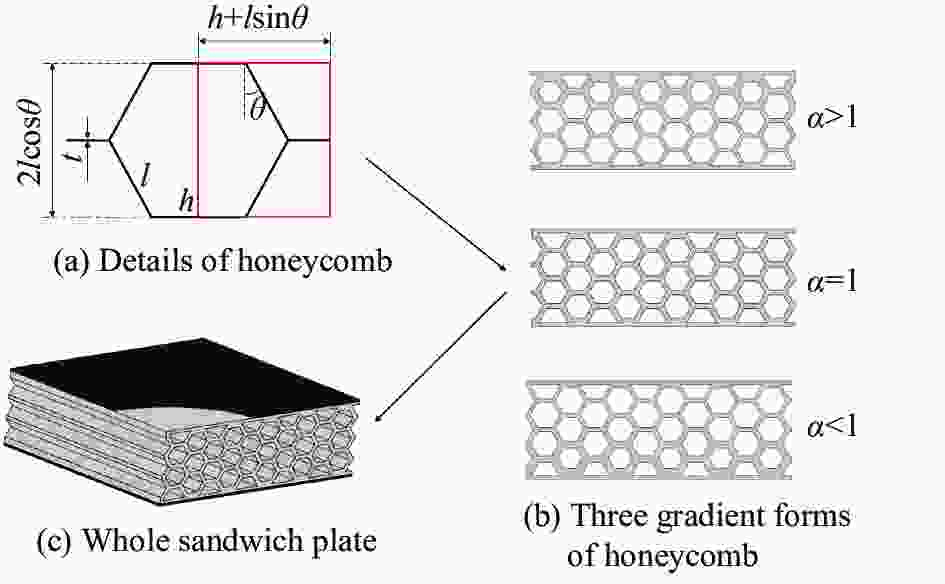
Table 5. Wall thickness and gradient values of functional gradient honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets
Gradient coefficient α Wall thickness/mm Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 1 1.50 1.50 1.50 1.2 1.94 1.62 1.35 1.3 2.13 1.64 1.26 1.4 2.29 1.64 1.17 1.5 2.43 1.62 1.08 1.6 2.56 1.60 1.00 0.7 1.17 1.64 2.29 表 6 CFRP面板-功能梯度蜂窝夹层板抗冲击性能综合对比
Table 6. Comprehensive comparison of impact resistance of functional gradient honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets
Ek/J α Peak contact
force/
NTotal
energy/
JCore
energy/
JTotal energy
percentage
increase/%20 0.7 3033.87 15.77 9.74 −6.14 1 3670.45 16.85 11.76 — 1.4 4265.74 18.12 13.52 7.54 50 0.7 4420.25 40.63 30.11 −4.22 1 4496.30 42.42 32.66 — 1.4 4781.43 44.68 36.03 5.33 100 0.7 4100.79 91.58 61.76 8.65 1 4700.03 84.29 53.88 — 1.4 4570.88 88.63 58.78 5.15 表 7 不同Ek下CFRP面板-功能梯度蜂窝夹层板吸能对比
Table 7. Comparison of energy absorption characteristics of functional gradient honeycomb sandwich plate with CFRP face sheets under different Ek
Ek/J Optimal α Total energy/J Total energy
percentage increase/%20 1.6 18.56 10.15 50 1.6 45.19 6.53 100 0.7 92.61 9.87 -
[1] FARSHIDI A, BERGGREEN C, SCHAUBLE R. Numerical fracture analysis and model validation for disbonded honeycomb core sandwich composites[J]. Composite Structures,2019,210:231-238. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.11.052 [2] GUNES R, ARSLAN K. Development of numerical realistic model for predicting low-velocity impact response of aluminium honeycomb sandwich structures[J]. Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,2016,18(1):95-112. [3] ZHANG X, XU F, ZANG Y, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation on damage behavior of honeycomb sandwich panel subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composite Structures,2020,236:111882. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.111882 [4] USTA F, TURKMEN H S, SCARPA F. Low-velocity impact resistance of composite sandwich panels with various types of auxetic and non-auxetic core structures[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2021,163:107738. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2021.107738 [5] 齐佳旗, 段玥晨, 铁瑛, 等. 结构参数对CFRP蒙皮-铝蜂窝夹层板低速冲击性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6):1352-1363. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190815.001QI Jiaqi, DUAN Yuechen, TIE Ying, et al. Effect of structural parameters on the low-velocity impact performance of aluminum honeycombsandwich plate with CFRP face sheets[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(6):1352-1363(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190815.001 [6] WANG Z. Recent advances in novel metallic honeycomb structure[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,166:731-741. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.02.011 [7] XING Y, YANG X, YANG J, et al. A theoretical model of honeycomb material arresting system for aircrafts[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2017,48:316-337. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2017.04.006 [8] QI C, SUN Y, YANG S. A comparative study on empty and foam-filled hybrid material double-hat beams under lateral impact[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2018,129:327-341. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2018.04.018 [9] AJDARI A, BABAEE S, VAZIRI A. Mechanical properties and energy absorption of heterogeneous and functionally graded cellular structures[J]. Procedia Engineering,2011,10:219-223. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.04.039 [10] 刘颖, 何章权, 吴鹤翔, 等. 分层递变梯度蜂窝材料的面内冲击性能[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2011, 31(3):225-231.LIU Ying, HE Zhangquan, WU Hexiang, et al. In-plane dynamic crushing of functionally layered metal honeycombs[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves,2011,31(3):225-231(in Chinese). [11] 张新春, 刘颖. 密度梯度蜂窝材料动力学性能研究[J]. 工程力学, 2012, 29(8):372-377.ZHANG Xinchun, LIU Ying. Research on the dynamic crushing of honeycombs with density gradient[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2012,29(8):372-377(in Chinese). [12] LIU Y, WU H, WANG B. Gradient design of metal hollew sphere (MHS) foams with density gradients[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2012,43(3):1346-1352. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.11.057 [13] 吴鹤翔, 刘颖. 梯度变化对密度梯度蜂窝材料力学性能的影响[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2013, 32(2):163-167.WU Hexiang, LIU Ying. Influences of density gradient variation on mechanical performances of density gradient honeycomb materials[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves,2013,32(2):163-167(in Chinese). [14] YU B, HAN B, SU P, et al. Graded square honeycomb as sandwich core for enhanced mechanical performance[J]. Materials and Design,2016,89:642-652. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.09.154 [15] SUN G, WANG E, WANG H, et al. Low-velocity impact behaviour of sandwich panels with homogeneous and stepwise graded foam cores[J]. Materials & Design,2018,160:1117-1136. [16] 乔及森, 孔海勇, 苗红丽, 等. 梯度铝蜂窝夹芯板的力学行为[J]. 材料工程, 2021, 49(3):167-174.QIAO Jisen, KONG Haiyong, MIAO Hongli, et al. Mechanical behavior of gradient aluminum honeycomb sandwich panels[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2021,49(3):167-174(in Chinese). [17] 王闯, 刘荣强, 邓宗全, 等. 铝蜂窝结构的冲击动力学性能的实验及数值研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2008, 27(11):56-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2008.11.012WANG Chuang, LIU Rongqiang, DENG Zongquan, et al. Experimental and numerical studies on aluminum honeycomb structure with various cell specifications under impact loading[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2008,27(11):56-61(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3835.2008.11.012 [18] MASTERS I G, EVANS K E. Models for the elastic deformation of honeycombs[J]. Composite Structures,1997,35:403-422. [19] 杜冰, 刘后常, 潘鑫, 等. 热塑性复合材料夹芯结构熔融连接研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3044-3058.DU Bing, LIU Houchang, PAN Xin, et al. Progress in fusion bonding of thermoplastic composite sandwich structures[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3044-3058(in Chinese). [20] GEDIKLI H, ASLAN M. Low-energy impact response of composite sandwich panels with thermoplastic honeycomb and reentrant cores[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2020,156:106989. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2020.106989 [21] ASTM. Standard test method for measuring the damage resistance of a fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136M—15[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM, 2015. [22] TIE Y, HOU Y, LI C, et al. Optimization for maximizing the impact-resistance of patch repaired CFRP laminates using a surrogate-based model[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2020,172:105407. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2019.105407 [23] 胡春幸, 侯玉亮, 铁瑛, 等. 基于遗传算法的CFRP层合板单搭胶接结构的多目标优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6):1847-1858.HU Chunxing, HOU Yuliang, TIE Ying, et al. Multi-objective optimization of adhesively bonded single-lap joints of carbon fiber reinforced olymer laminates based on genetic algorithm[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(6):1847-1858(in Chinese). [24] 孙振辉, 铁瑛, 侯玉亮, 等. 相对冲击位置和补片层数对胶接修理CFRP复合材料层合板抗冲击性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(5):1114-1123.SUN Zhenhui, TIE Ying, HOU Yuliang, et al. Effect of relative impact location and patch layer number on impact resistance of adhesive repaired CFRP composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(5):1114-1123(in Chinese). [25] TAO Y, DUAN S, WEN W, et al. Enhanced out-of-plane crushing strength and energy absorption of in-plane graded honeycombs[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,118:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.002 [26] 杨晶晶, 李成, 铁瑛. 铝褶皱夹层板的抗低速冲击性能[J]. 中国机械工程, 2022, 33(13): 1629-1637.YANG Jingjing, LI Cheng, TIE Ying. Low-velocity impact on sandwich plate with aluminum folded core[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(13): 1629-1637(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: