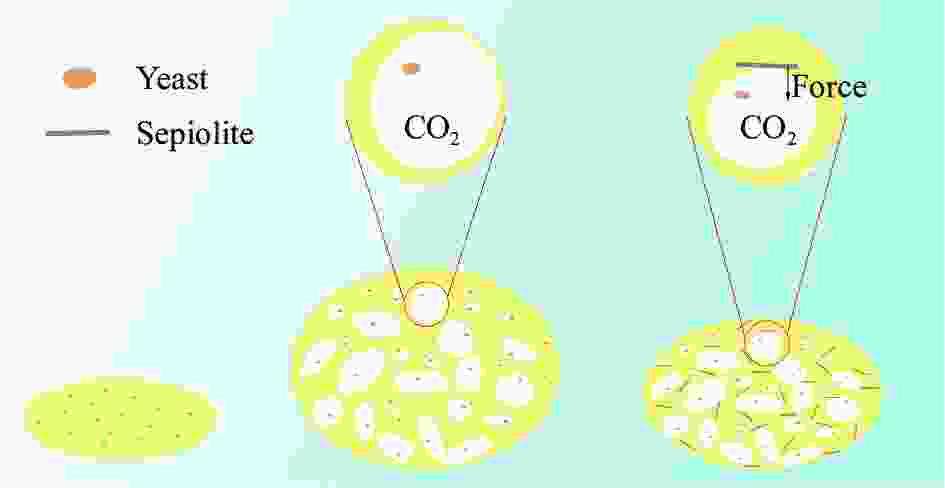
Sepiolite reinforced carbon foam composite toward phase change energy storage material and its light-thermal-electric conversion performance
-
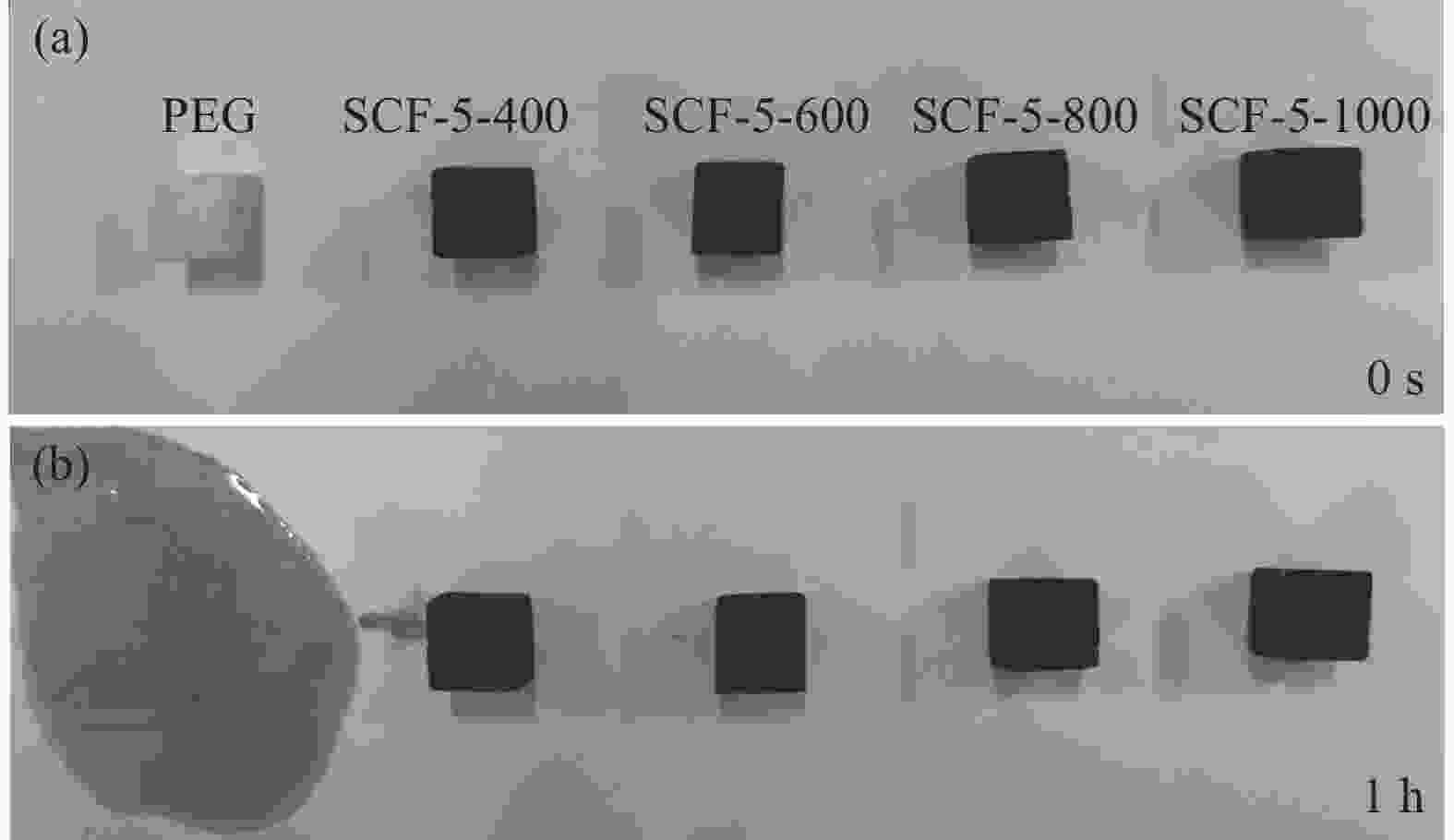
摘要: 聚乙二醇(PEG)具有高相变焓、可生物降解、无毒、耐腐蚀等优点,是一种优异的相变材料。但容易泄露和导热性差这两大缺点阻碍了它的大规模应用。为此,本文以小麦面粉作为基体,海泡石纤维为增强体,利用酵母发酵产气的微生物发泡技术和高温炭化工艺,制得海泡石增强的生物质炭泡沫复合材料SCF-X-Y (X 表示海泡石的添加量,Y 表示炭化温度) 作为PEG相变材料载体。实验结果显示,SCF-10-800的抗压强度可达5.42 MPa。负载PEG后制得的SCF-5-1000@PEG,导热系数达到0.39 W/(m·K),熔化焓和凝固焓分别为123.4 J·g−1和106.6 J·g−1,并具备优异的抗泄露能力。基于SCF-5-1000@PEG为光吸收源,所组装的光驱动热电转换系统具有63.2%光热转化效率,且可以实现大于400 s的稳定电流输出,彰显其在光-热能-电能转换系统的应用潜能。Abstract: Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is an excellent phase change material with high phase change enthalpy, biodegradability, non toxicity and corrosion resistance. However, the easy leakage and poor thermal conductivity hinder its large-scale application. Therefore, with wheat flour as the matrix, a biomass carbon foam composite SCF-X-Y reinforced by sepiolite, where X represents the amount of sepiolite added and Y represents the carbonization temperature) was prepared as the efficient carrier of PEG phase change material by using microbial foaming and high temperature carbonization technology. The experimental results show that the compressive strength of SCF-10-800 can reach 5.42 MPa. The thermal conductivity of SCF-5-1000@PEG reaches 0.39 W/(m·K), and its melting enthalpy and solidification enthalpy are 123.4 J·g−1 and 106.6 J·g−1, respectively. Meanwhile, it has excellent leakage resistance. Using SCF-5-1000@PEG as an optical absorption source, a light driven thermoelectric conversion system was assembled, which showed a light to heat conversion efficiency of 63.2% and could achieve a stable current output for more than 400 s, demonstrating its application potential in the light-thermal-electric energy conversion system.
-
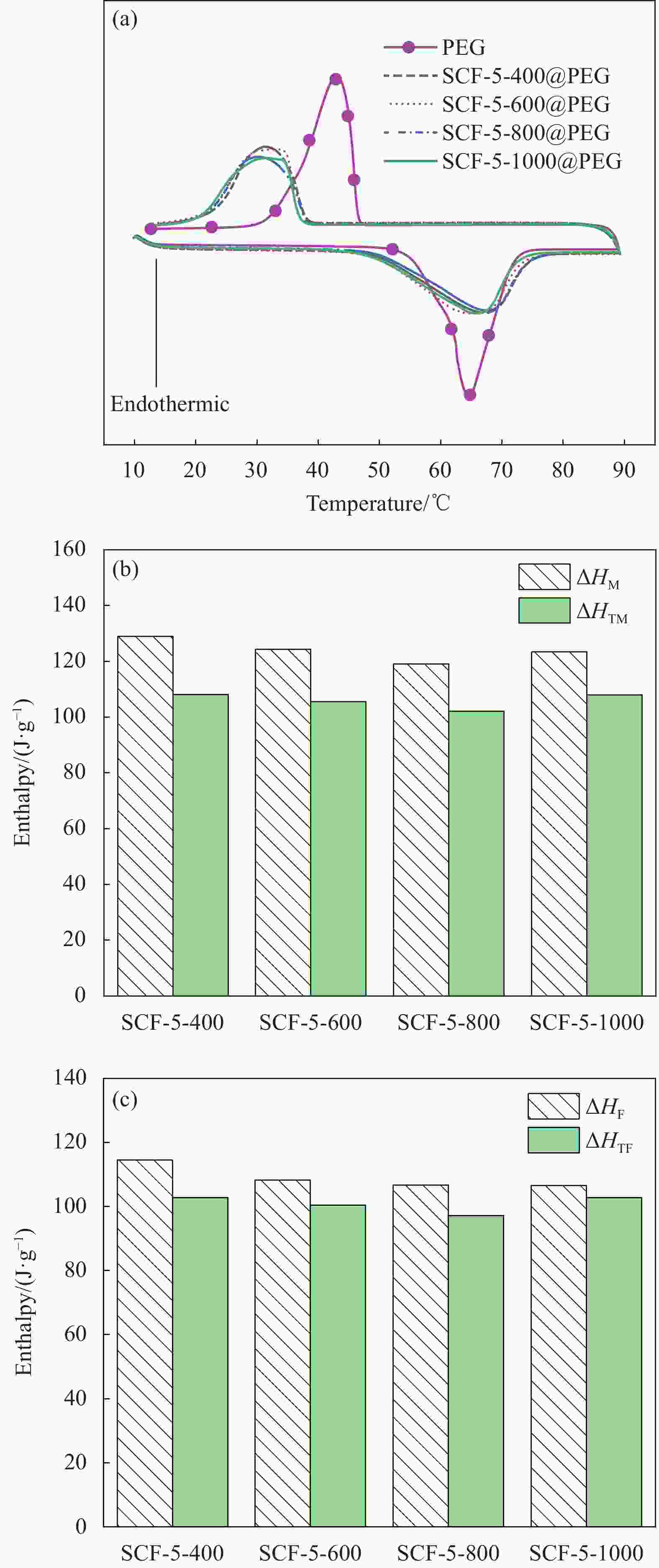
图 8 (a) PEG和SCF-5-Y@PEG的DSC 曲线;(b) SCF-5-Y@PEG的实际熔化焓ΔHM与理论熔化焓ΔHTM;(c) SCF-5-Y@PEG的实际凝固焓ΔHF与理论凝固焓ΔHTF
Figure 8. (a) DSC curves of PEG and SCF-5-Y@PEG; (b) Melting enthalpy (ΔHM) and theoretical melting enthalpy (ΔHTM) of SCF-5-Y@PEG; (c) Solidification enthalpy (ΔHF) and theoretical solidification enthalpy (ΔHTF) of SCF-5-Y@PEG
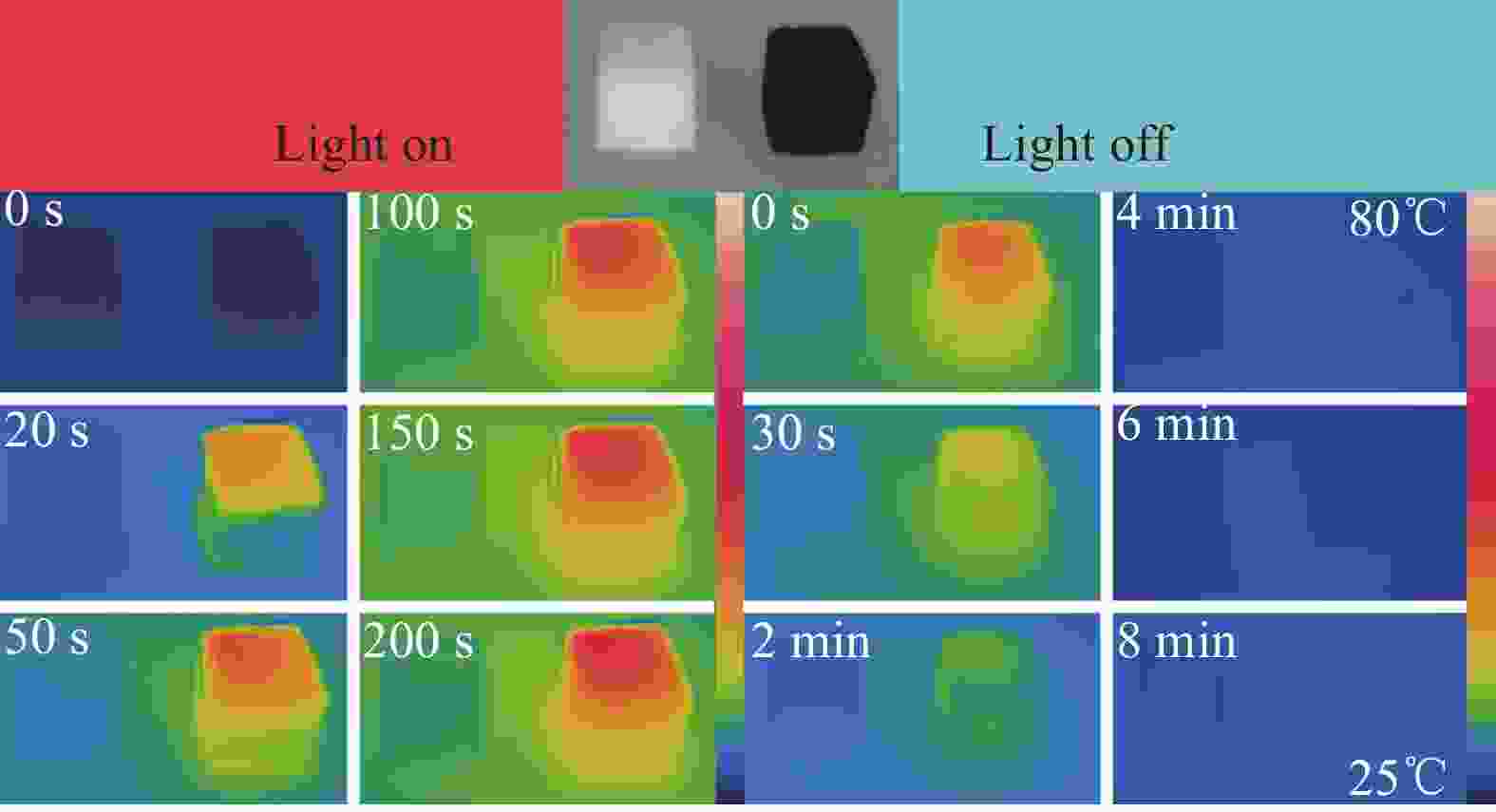
图 11 (a) 光驱动热电转换系统装置;(b) 基于SCF-5-1000@PEG的太阳能热电装置示意图;在300 mW·cm−2模拟太阳光照射下:(c) SCF-5-1000@PEG的电流/温度-时间曲线;(d) SCF-5-1000@PEG和PEG的温度-时间曲线
Figure 11. (a) Light-driven thermoelectric conversion device; (b) Schematic diagram of SCF-5-1000@PEG-based solar thermoelectric device; (c) Current/temperature-time curves of SCF-5-1000@PEG; (d) Temperature-time curves of SCF-5-1000@PEG and PEG under simulated sunlight irradiation of 300 mW·cm−2
表 1 样品命名
Table 1. Sample naming
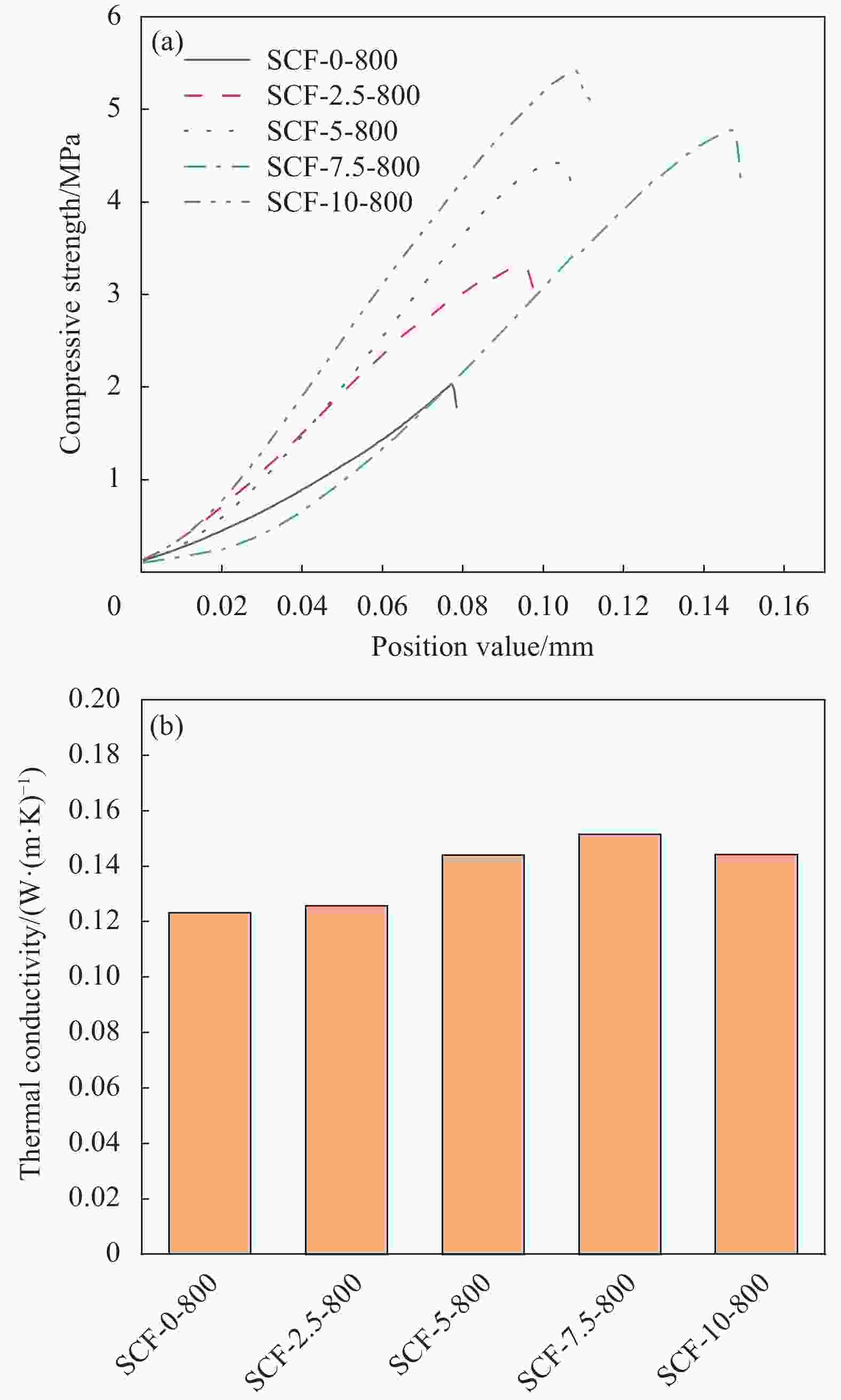
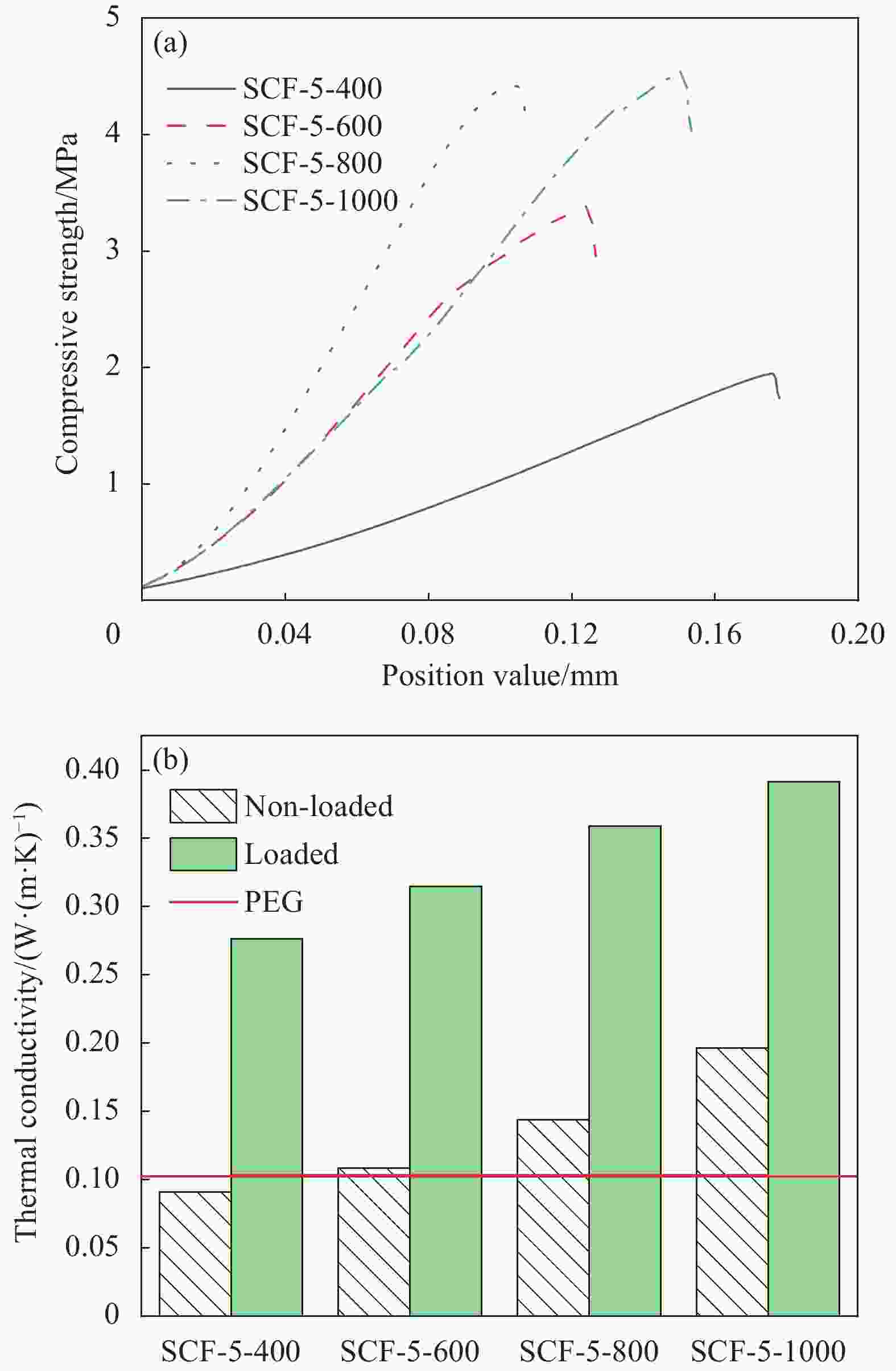
SCF-X-Y X/g Y/℃ SCF-0-800 0 800 SCF-2.5-800 2.5 800 SCF-5-800 5 800 SCF-7.5-800 7.5 800 SCF-10-800 10 800 SCF-5-400 5 400 SCF-5-600 5 600 SCF-5-1000 5 1000 Notes: SCF—Sepiolite/carbon foam; X—Amount of sepiolite added; Y—Carbonized temperature. 表 2 SCF-5-1000@PEG同近几年报道的不同相变储能材料的热学性能对比
Table 2. Thermal properties of SCF-5-1000@PEG comparison with different phase change energy storage materials reported in recent years
Sample PCM ΔHM/(J·g−1) ΔHF/(J·g−1) Ref. PGI-PEG 50 PEG 6000 86.93 83.65 [19] PGI/PEG PEG 6000 86.9 70.1 [20] PEG/BC-2 PEG 6000 71.17 68.43 [21] PCM PEG 6000 97.2 92.3 [22] Fe3O4-GNS/PCM-4 PEG 6000 101.5 55.7 [23] PCM-6000 PEG 6000 76.37 80.46 [24] SCF-5-1000@PEG PEG 6000 123.4 106.6 This work Notes: PCM—Phase change materials; PGI—Poly(glycerol-itaconic acid); BC—Bone char; GNS—Functionalised graphene nanosheets. -
[1] WU S F, YAN T, KUAI Z H, et al. Experimental and numerical study of modified expanded graphite/hydrated salt phase change material for solar energy storage[J]. Solar Energy,2020,205:474-486. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.05.052 [2] WANG C J, LIANG W D, YANG Y Y, et al. Biomass carbon aerogels based shape-stable phase change composites with high light-to-thermal efficiency for energy storage[J]. Renewable Energy,2020,153:182-192. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2020.02.008 [3] 宋佳音. 丝瓜基相变复合材料的制备及其在纺织品热防护中的应用研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021.SONG Jiayin. Preparation of towel gourd-based phase change composite material and its application in textile thermal protection [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021(in Chinese). [4] SU X L, JIA S K, LV G W, et al. A unique strategy for polyethylene glycol/hybrid carbon foam phase change materials: Morphologies, thermal properties, and energy storage behavior[J]. Materials,2018,11(10):2011. doi: 10.3390/ma11102011 [5] BAO Z J, BING N C, YAO H R, et al. Three-dimensional interpenetrating network phase-change composites with high photothermal conversion and rapid heat storage and release[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials,2021,4(8):7710-7720. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.1c01061 [6] 吴丽梅, 刘庆欣, 王晓龙, 等. 相变储能材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(S1):501-506.WU Limei, LIU Qingxin, WANG Xiaolong, et al. Review on phase change energy storage materials[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(S1):501-506(in Chinese). [7] XU B W, LI Z J. Paraffin/diatomite composite phase change material incorporated cement-based composite for thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Energy,2013,105:229-237. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.01.005 [8] LUO Y, XIONG S Y, HUANG J T, et al. Preparation, characterization and performance of paraffin/sepiolite composites as novel shape-stabilized phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2021,231:111300. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2021.111300 [9] DENG Y, LI J H, NIAN H G. Polyethylene glycol-enwrapped silicon carbide nanowires network/expanded vermiculite composite phase change materials: Form-stabilization, thermal energy storage behavior and thermal conductivity enhancement[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2018,174:283-291. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2017.09.013 [10] 王长远, 王功勋, 陶涛, 等. 海泡石功能化绿色建材研究进展与应用现状[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(10):3285-3291. doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2017.10.012WANG Changyuan, WANG Gongxun, TAO Tao, et al. Research progress and application status of sepiolite functional green building materials[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2017,36(10):3285-3291(in Chinese). doi: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2017.10.012 [11] LI C C, XIE B S, CHEN J, et al. Emerging mineral-coupled composite phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2019,183:633-644. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.021 [12] OLA O, CHEN Y, ZHU Y Q. Three-dimensional carbon foam nanocomposites for thermal energy storage[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2019,191:297-305. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2018.11.037 [13] INAGAKI M, QIU J S, GUO Q G. Carbon foam: Preparation and application[J]. Carbon,2015,87:128-152. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.02.021 [14] SHI T T, ZHANG X G, QIAO J X, et al. Preparation and characterization of composite phase change materials based on paraffin and carbon foams derived from starch[J]. Polymer,2021,212:123143. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2020.123143 [15] SONG J Y, CAI Y B, DU M Y, et al. 3D lamellar structure of biomass-based porous carbon derived from towel gourd toward phase change composites with thermal management and protection[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials,2020,3(12):8923-8932. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c01196 [16] ZHANG Y J, ZHAO M Y, WANG H, et al. Damaged starch derived carbon foam-supported heteropolyacid for catalytic conversion of cellulose: Improved catalytic performance and efficient reusability[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,288:121532. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121532 [17] QI F Q, WANG L, ZHANG Y L, et al. Robust Ti3C2Tx MXene/starch derived carbon foam composites for superior EMI shielding and thermal insulation[J]. Materials Today Physics,2021,21:100512. doi: 10.1016/j.mtphys.2021.100512 [18] 张磊. 聚乙二醇基复合储热材料的制备、性能及其相变传热过程研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2012.ZHANG Lei. Study on preparation, properties and phase change heat transfer process of polyethylene glycol-based composite thermal energy storage materials[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [19] YIN G Z, PALENCIA J L D, WANG D Y. Fully bio-based poly(glycerol-itaconic acid) as supporter for PEG based form stable phase change materials[J]. Composites Communications,2021,27:100893. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2021.100893 [20] YIN G Z, YANG X M, HOBSON J, et al. Bio-based poly(glycerol-itaconic acid)/PEG/APP as form stable and flame-retardant phase change materials[J]. Composites Communications,2022,30:101057. doi: 10.1016/j.coco.2022.101057 [21] WEN R L, JIA P Q, HUANG Z H, et al. Thermal energy storage properties and thermal reliability of PEG/bone char composite as a form-stable phase change material[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry,2018,132(3):1753-1761. doi: 10.1007/s10973-017-6934-8 [22] WANG R, XIAO Y, LEI J X. A solid-solid phase change material based on dynamic ion cross-linking with reprocessability at room temperature[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,390:124586. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124586 [23] WANG W T, UMAIR M M, QIU J J, et al. Electromagnetic and solar energy conversion and storage based on Fe3O4-functionalised graphene/phase change material nanocomposites[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2019,196:1299-1305. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.06.084 [24] YANG Y Y, KONG W B, CAI X F. Solvent-free preparation and performance of novel xylitol based solid-solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Energy and Buildings,2018,158:37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.09.096 [25] YANG H Y, LIU Y S, LI J, et al. Full-wood photoluminescent and photothermic materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,403:126406. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126406 [26] YU C, YANG S H, PAK S Y, et al. Graphene embedded form stable phase change materials for drawing the thermo-electric energy harvesting[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2018,169:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.001 -






 下载:
下载: