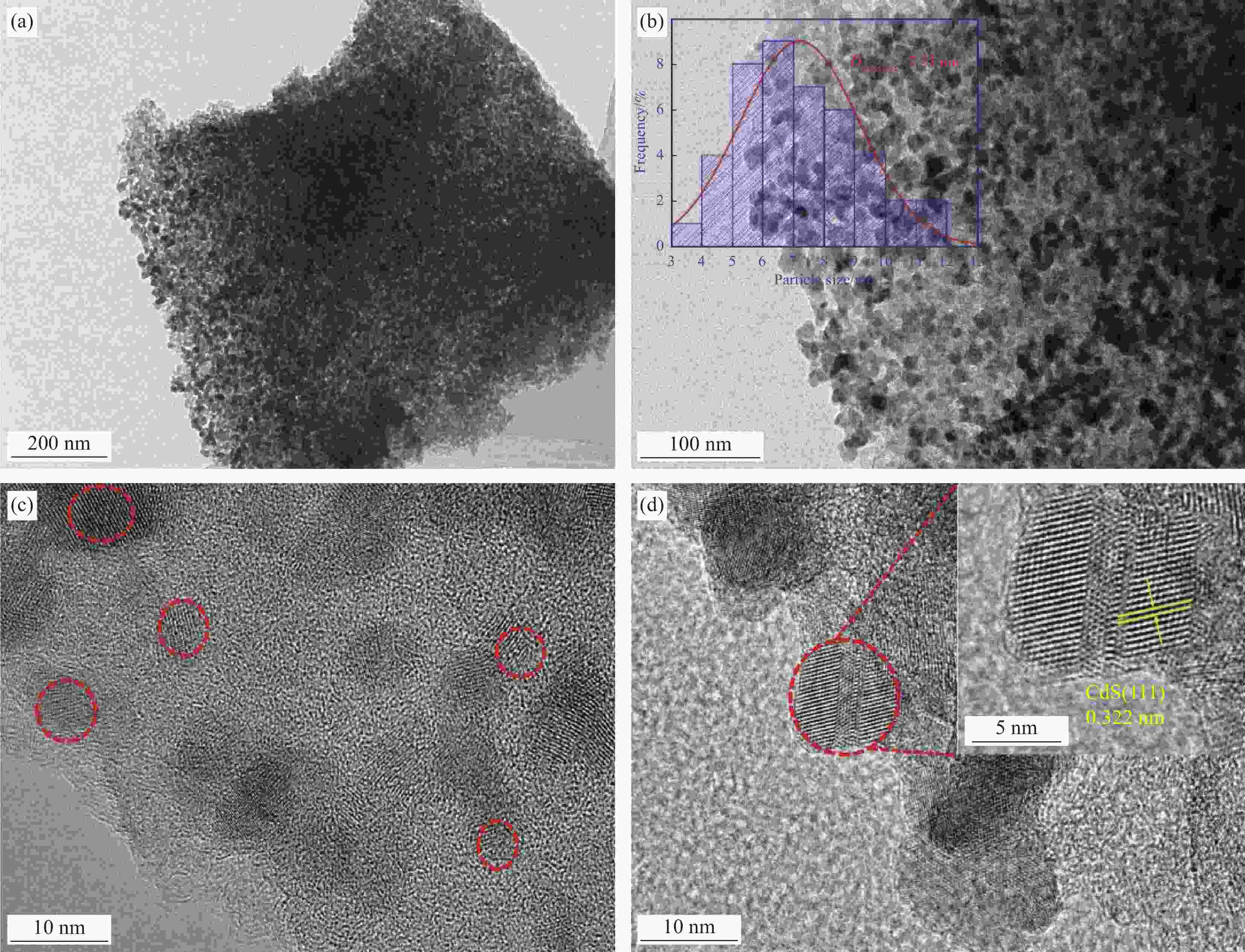
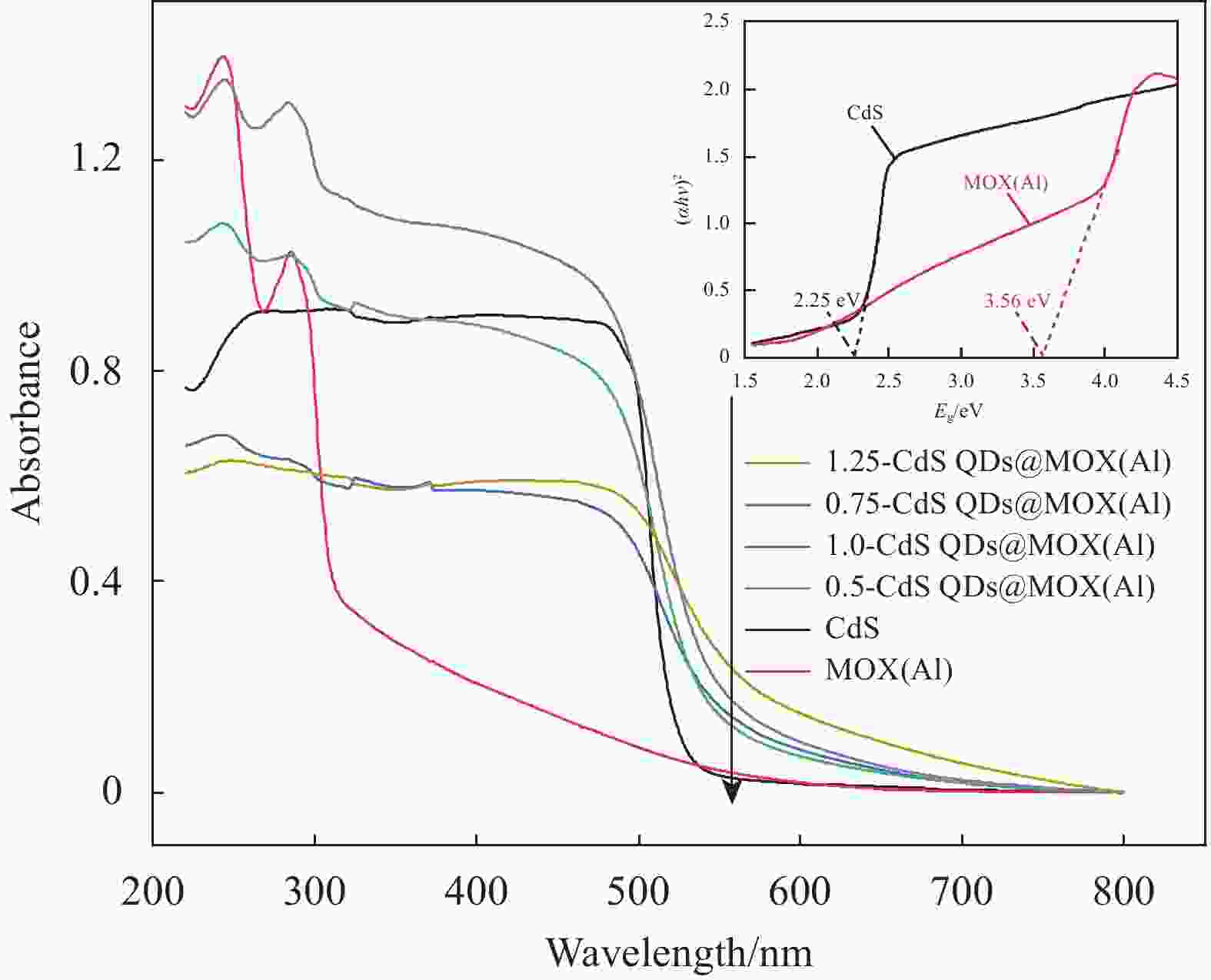
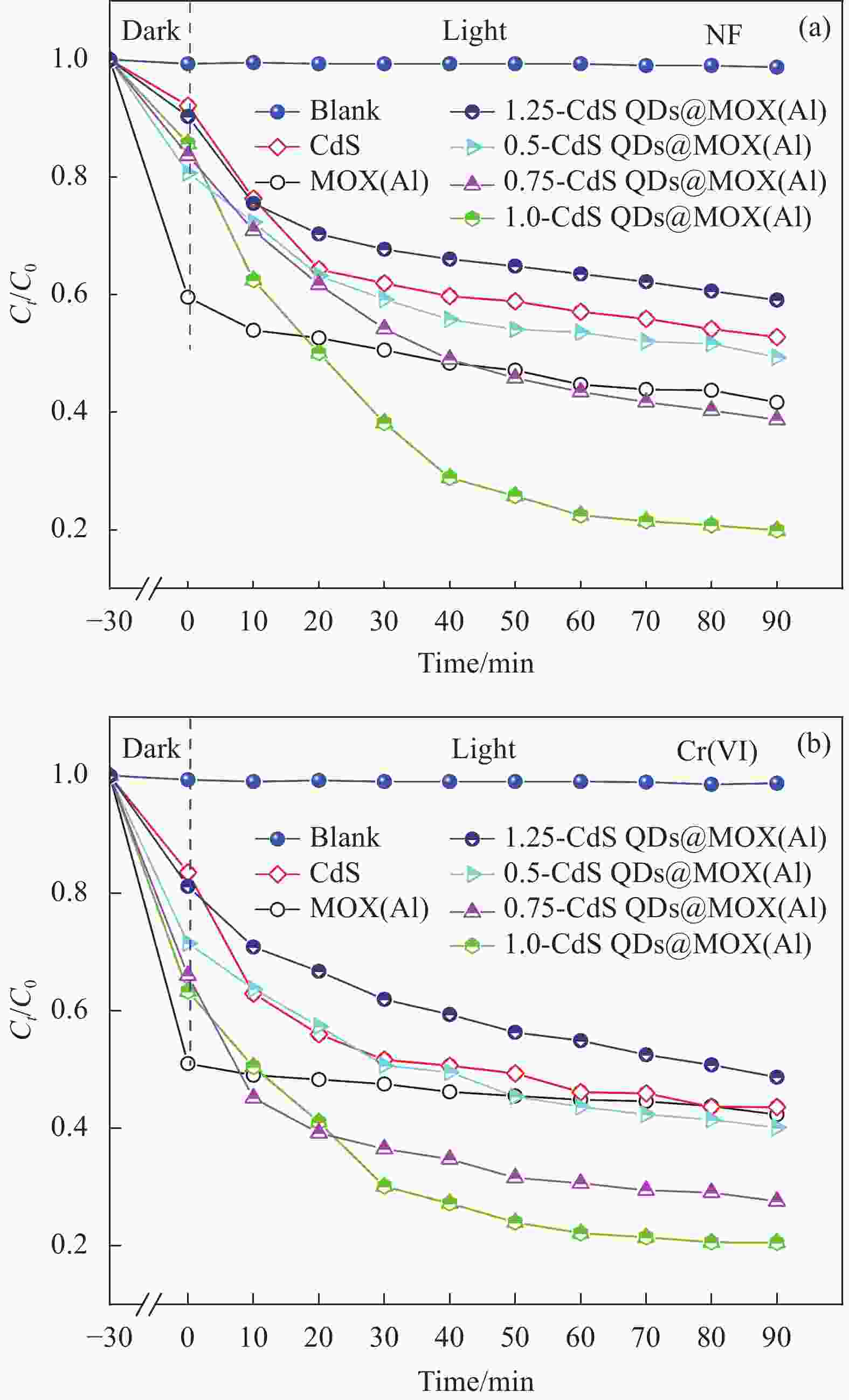
Synergistic degradation of norfloxacin and reduction of Cr(VI) by CdS QDs encapsulated in metal-organic gel heterojunction photocatalyst
-
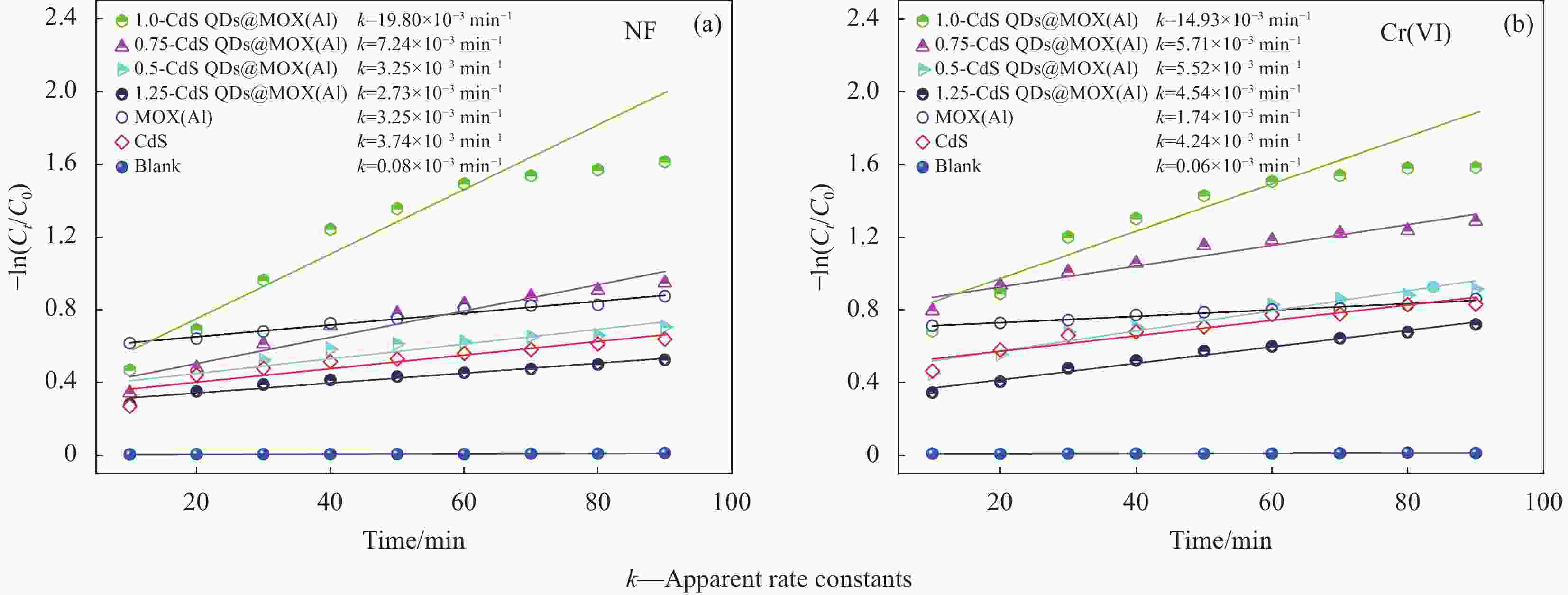
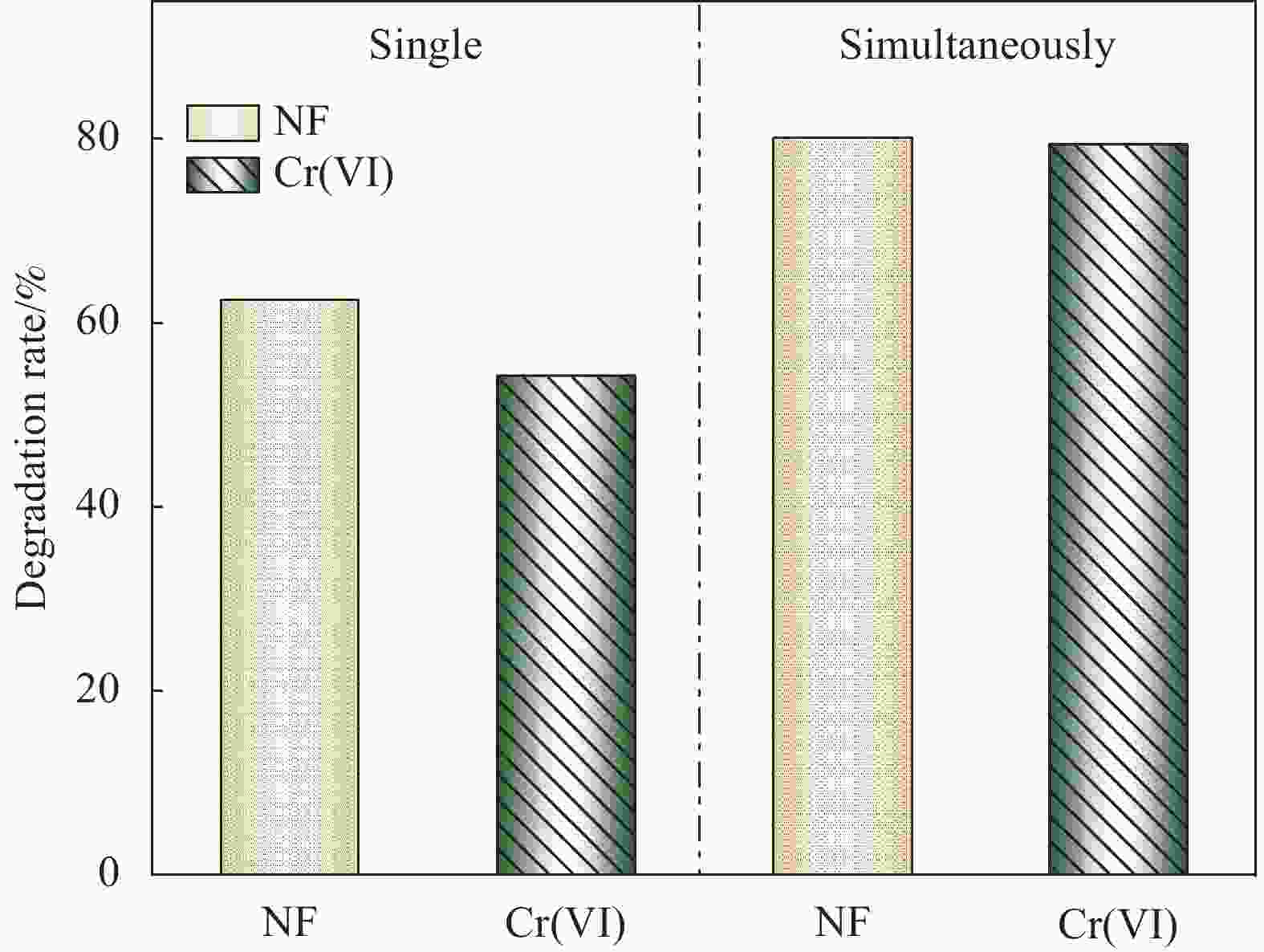
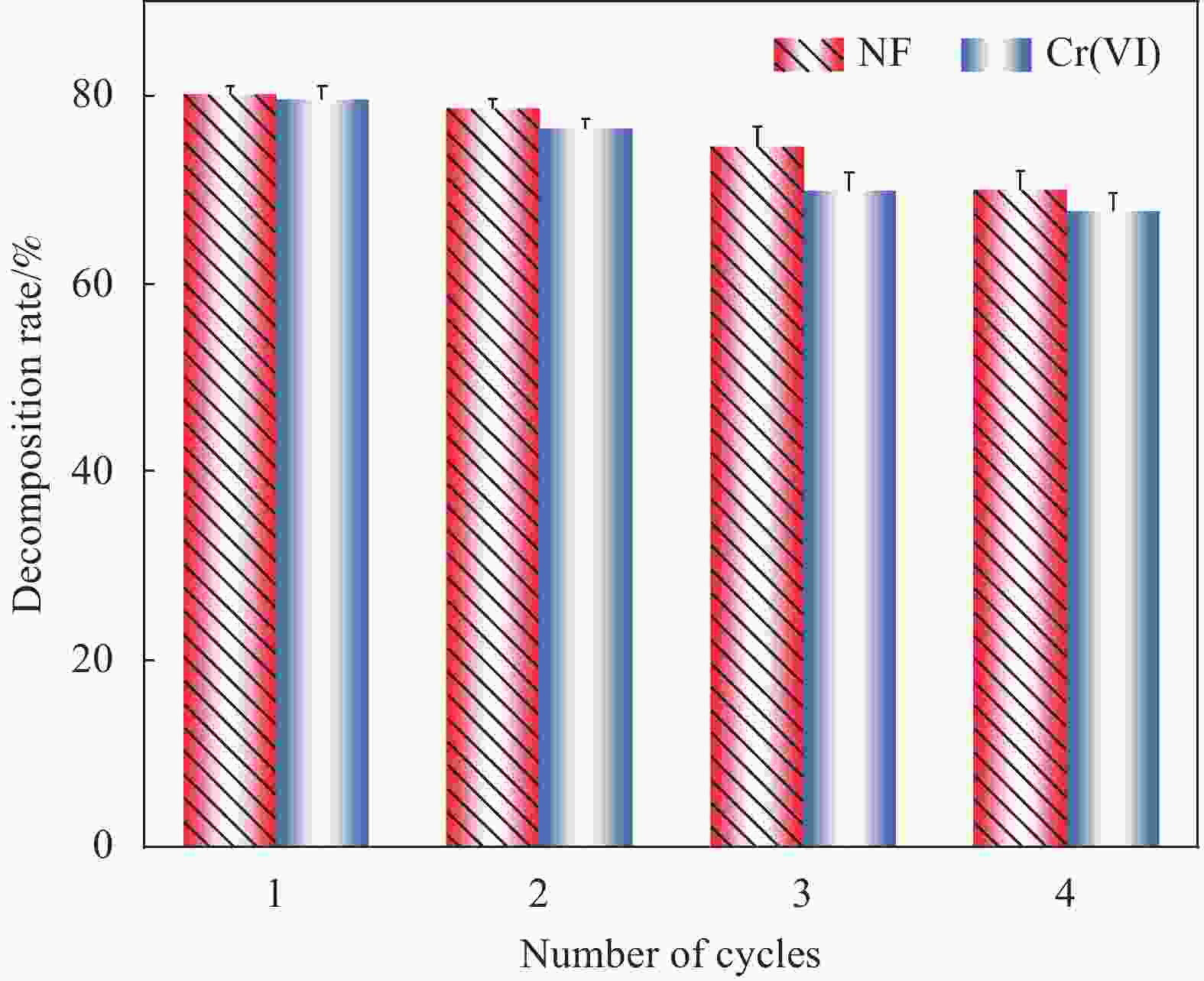
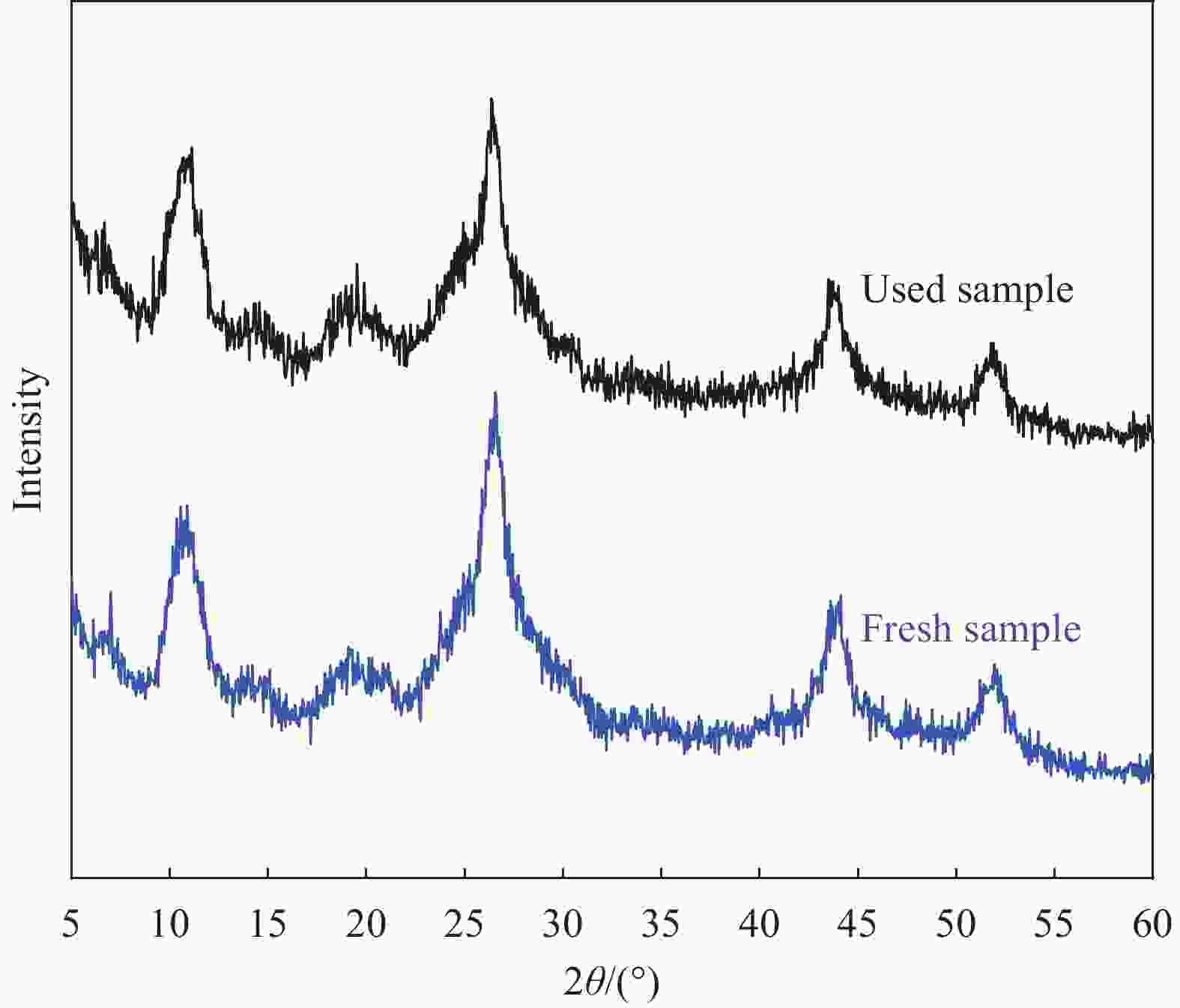
摘要: 构建具有高效电荷转移途径的异质结材料是光催化降解水体复合污染物的关键。采用凝胶限域法将CdS量子点(CdS QDs)分散在金属有机凝胶MOX(Al)中,制备出CdS QDs@MOX(Al)异质结光催化剂。通过 XRD、TEM、XPS、N2吸附-脱附等温曲线、UV-Vis DRS、瞬态光电流(TPC)响应和电化学阻抗谱(EIS)等手段对样品的组成结构和界面电荷传输效率进行了表征及分析,并探讨了在可见光下协同降解诺氟沙星(NF)和还原Cr(VI)的催化活性和机制。结果表明:1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al)对NF/Cr(VI)复合污染物体系表现出优异的光催化活性,降解过程符合伪一级动力学模型,表观速率常数k分别是纯MOX(Al)和CdS的6.1(8.5)倍和5.3(3.5)倍。与单一污染物体系相比,CdS QDs@MOX(Al)对NF/Cr(VI)复合污染物体系的光催化效率显著提高。活性物种捕获实验证实h+和•O2−为主要活性物种,光催化活性的增强主要归因于MOX(Al)和CdS QDs间形成的Type-II型异质结构,加速了光生电荷在异质结构界面处的有效分离和转移。Abstract: Construction of heterojunction materials with efficient charge transfer pathways is the key to photocatalytic degradation of composite pollutants in water. CdS QDs@MOX(Al) heterojunction photocatalyst was prepared by dispersion of CdS quantum dots (CdS QDs) in metal-organic gel MOX(Al) using the gel-confinement-method. The compositional structure and interfacial charge transfer efficiency of the samples were characterized and analyzed by XRD, TEM, XPS, N2 adsorption-desorption, UV-Vis DRS, transient photocurrent (TPC) response and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and the catalytic activity and mechanism for the synergistic degradation of norfloxacin (NF) and reduction Cr(VI) under visible light were investigated. The results show that 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) exhibite excellent photocatalytic activity for the NF/Cr(VI) complex pollutant system, the degradation process conforms to the pseudo-first-order kinetic model, and the apparent rate constants k are 6.1 (8.5) and 5.3 (3.5) times higher than those of pure MOX(Al) and CdS, respectively. Compared with the single pollutant system, the photocatalytic efficiency of CdS QDs@MOX(Al) for the NF/Cr(VI) complex pollutant system is significantly improved. The combination of active species capture experiments confirm that h+ and •O2− are the main active species. The enhanced photocatalytic activity is mainly attributed to the Type-II heterostructure formed between MOX(Al) and CdS QDs, which accelerates the effective separation and transfer of photogenerated charges at the interface of the heterostructure.
-
Key words:
- MOGs /
- CdS QDs /
- photocatalysis /
- heterojunction catalyst /
- mechanism
-
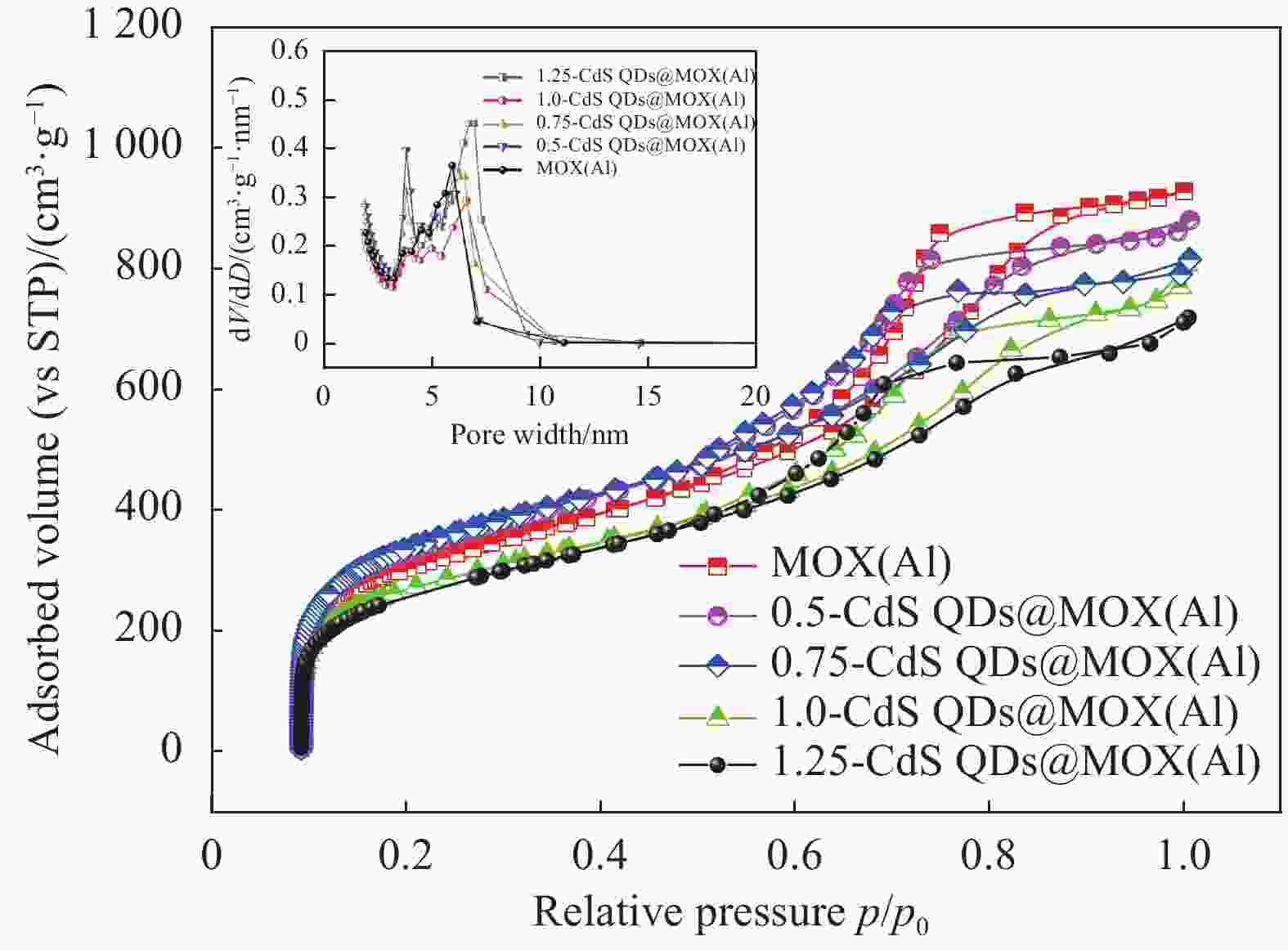
图 4 MOX(Al)和CdS QDs@MOX(Al)的N2吸附-脱附等温线和孔径分布曲线(插图)
V—Pore volume; D—Pore diameter; STP—In standard state; p—N2 partial pressure; p0—At the temperature of liquid nitrogen, the saturated vapor pressure of N2
Figure 4. N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and pore size distribution curves (illustration) of MOX(Al) and CdS QDs@MOX(Al)
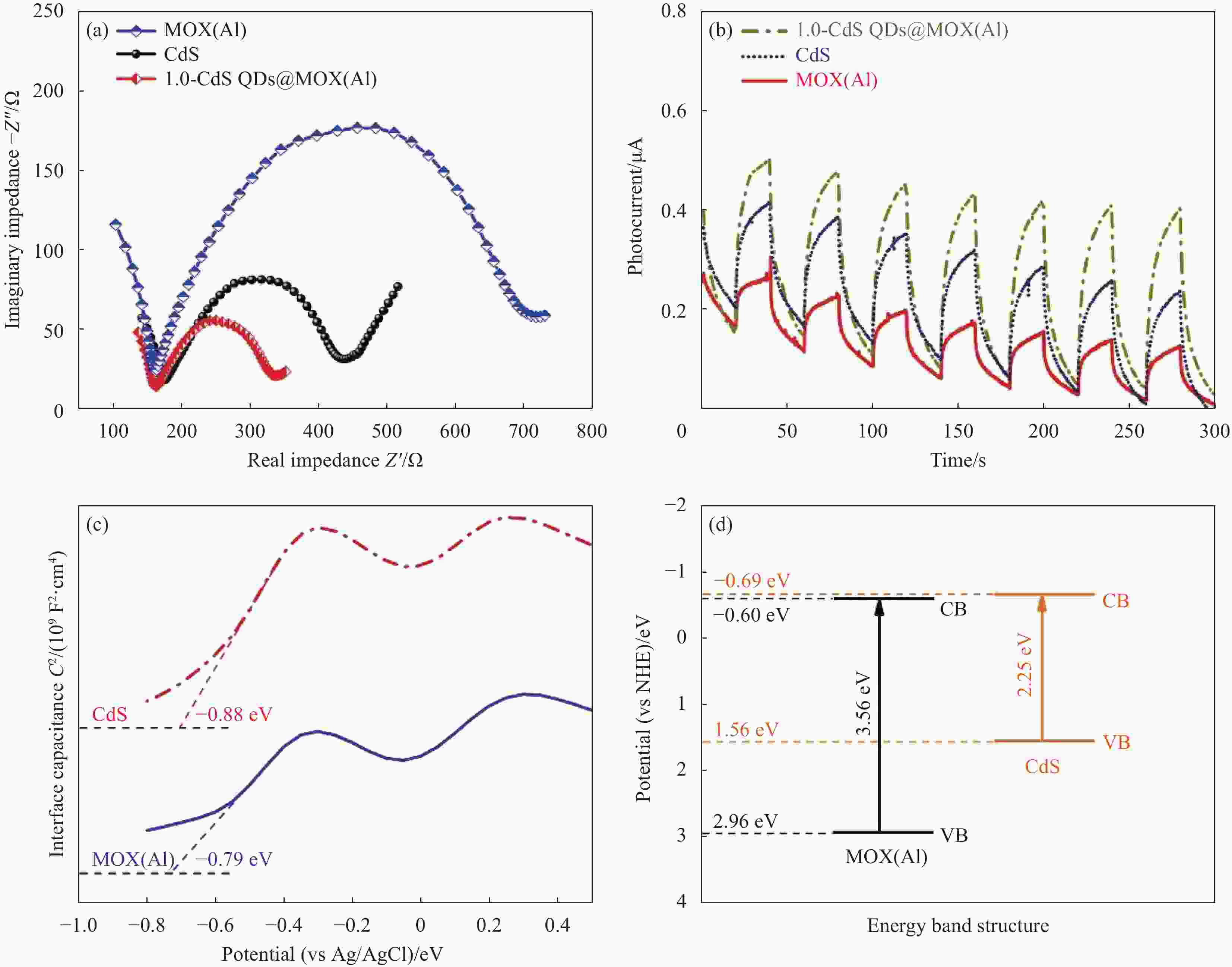
图 12 MOX(Al)、CdS和1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al)的电化学阻抗谱图 (a)、电流响应曲线 (b)、莫特-肖特基曲线 (c) 和能带结构示意图 (d)
VB—Valence band; CB—Conduction band; NHE—Normal hydrogen electrode
Figure 12. EIS Nyquist plots (a), transient photocurrent response curves (b), Mott-Schottky curves (c) and schematic diagram of energy band structure (d) for MOX(Al), CdS and 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al)
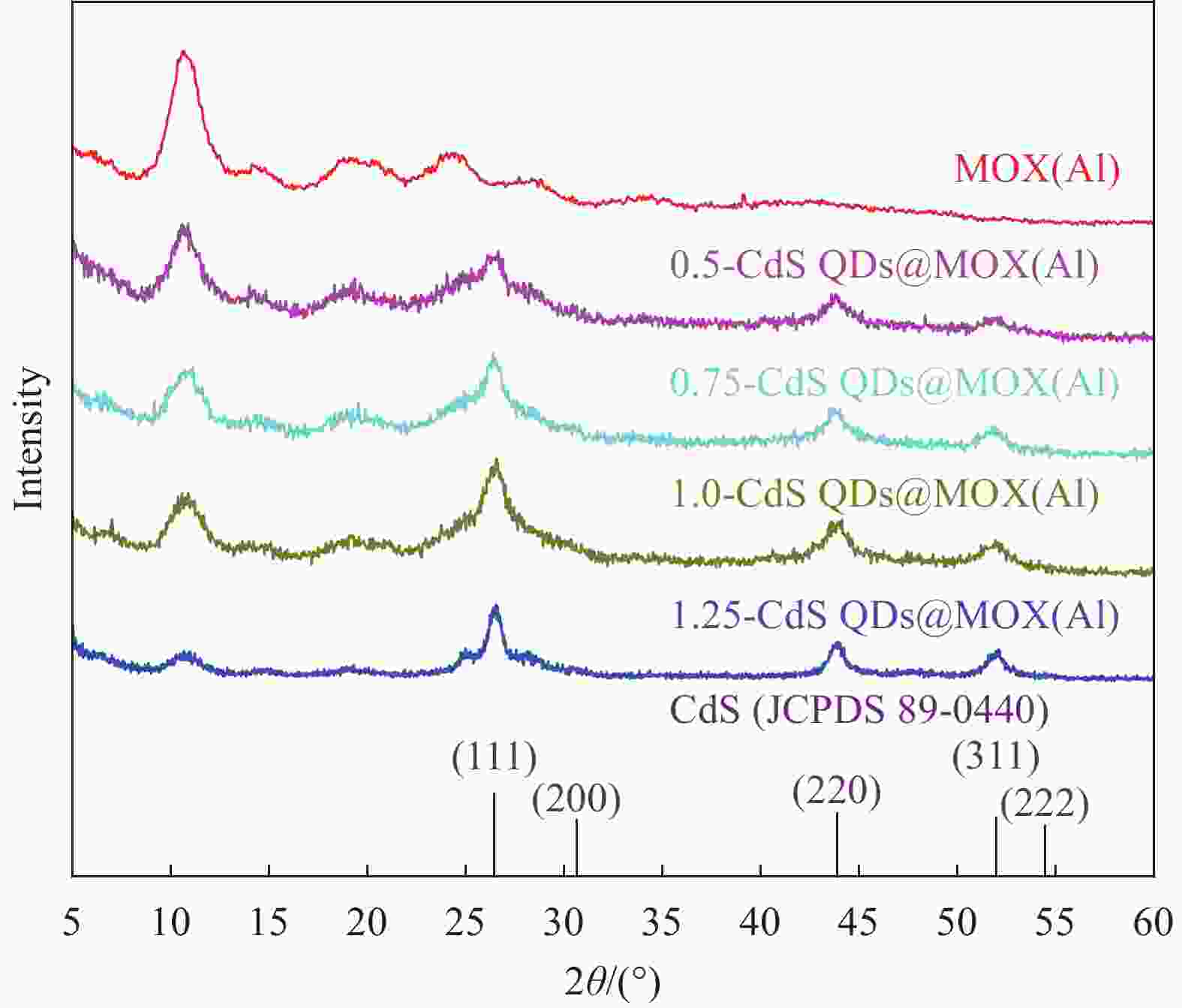
表 1 CdS量子点@金属有机凝胶(CdS QDs@MOX(Al))复合材料的命名
Table 1. Naming of CdS quantum dots@metal-organic gel (CdS QDs@MOX(Al)) composite
Sample Mole ratio of Cd2+ : MOX(Al) 0.5-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 0.50 0.75-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 0.75 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1.00 1.25-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1.25 表 2 MOX(Al)和CdS QDs@MOX(Al)的比表面积、孔体积和孔径
Table 2. Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface areas, pore volume and pore diameter of MOX(Al) and CdS QDs@MOX(Al)
Sample Surface aeraa/(m2·g−1) Pore volumeb/(cm3·g−1) Pore diameterc/nm MOX(Al) 1302.72 1.4345 4.79 0.5-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1288.56 1.3614 4.74 0.75-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1198.52 1.2617 4.35 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1052.80 1.2485 4.23 1.25-CdS QDs@MOX(Al) 1021.23 1.2111 3.97 Notes: a—BET multi-point method specific surface; b—BJH method desorption (Cylindrical pore model, 2.0-49.6 nm) pore volume; c—BJH method desorption (Cylindrical hole model) average hole diameter. 表 3 不同催化剂光催化性能的比较
Table 3. Comparison of photocatalytic properties of different catalysts
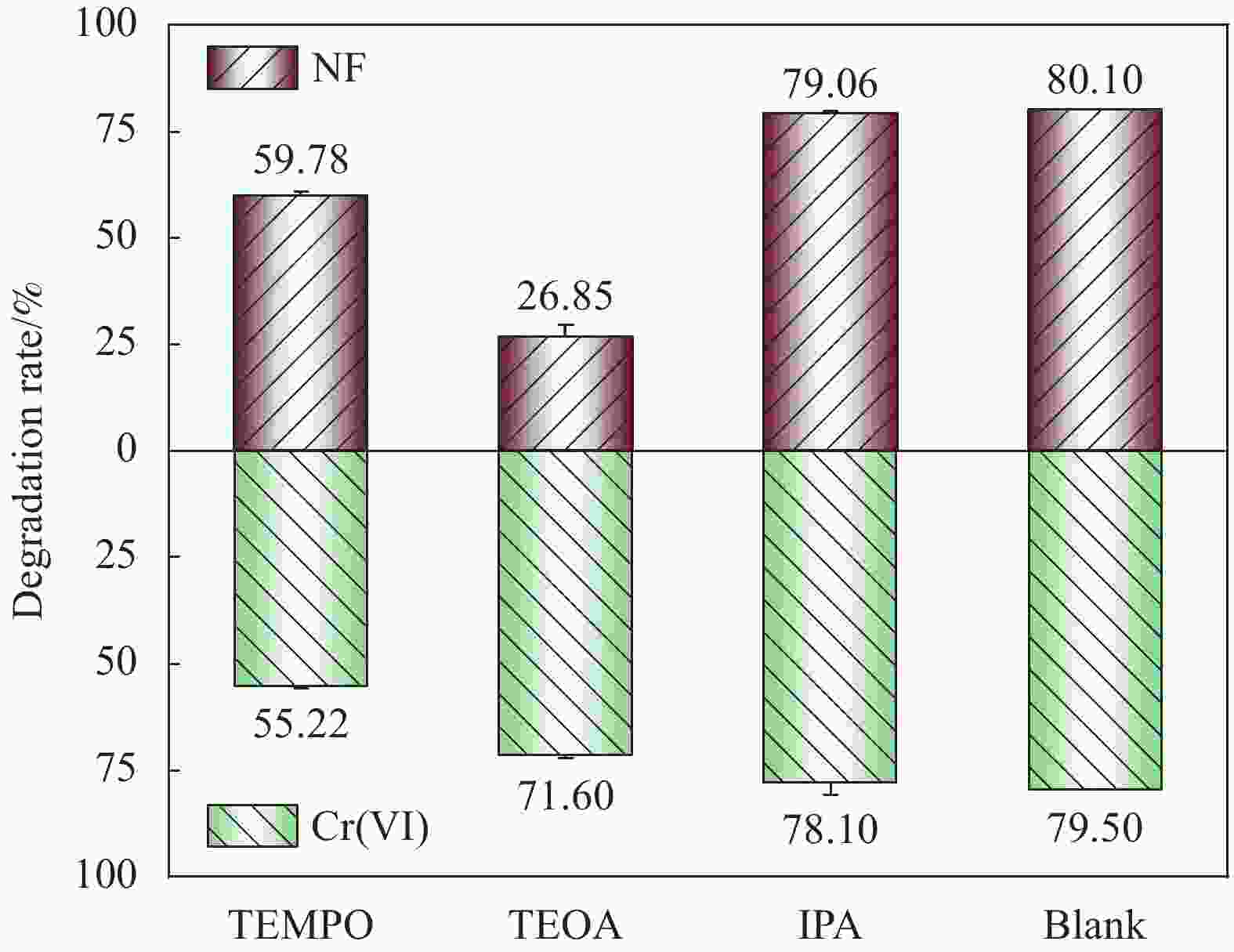
Photocatalyst/Amount(mg) Pollutants/V(mL)/C0(mg·L−1) Light source Time/h Efficiency/% Ref. GTSA/25 Cr(VI)/35/50 UV mercury light 3.0 79 [6] 3%CdS QDs/BiOI/Bi2MoO6/20 NF/20/20 Xe lamp 1.0 93 [9] 15%Co9S8/g-C3N4/20 Cr(VI)/50/10 500 W Xe lamp 3.0 87 [34] Bi2S3/Bi2WO6/20 Cr(VI)/20/10 500 W Xe lamp 1.0 88 [35] ZnO/Cu2O NF/20/10 Light intensity 50 mW/cm2 4.0 86 [36] 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al)/40 Cr(VI)/60/40 300 W Xe lamp 1.5 79.5 This work 1.0-CdS QDs@MOX(Al)/40 NF/60/100 300 W Xe lamp 1.5 80.1 This work Notes: GTSA—Thiourea/sodium alginate; V—Volume. -
[1] SONG X, REN C, ZHAO Q, et al. Simultaneous removal of Cr(VI) and triclosan from aqueous solutions through Fe3O4 magnetic nanoscale-activated persulfate oxidation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,381:122586. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122586 [2] 苏冰琴, 刘一清, 林昱廷, 等. Fe3O4活化过硫酸盐体系同步去除诺氟沙星和铅[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2):717-727. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.025SU Bingqin, LIU Yiqing, LIN Yuting, et al. Simultaneous removal of norfloxacin and Pb(II) via Fe3O4-activated persulfate oxidation[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(2):717-727(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.025 [3] 杨金辉, 胡世琴, 杨斌, 等. 氨化烟末生物碳吸附剂的制备及其对Cr(VI)的吸附行为[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(1):222-231.YANG Jinhui, HU Shiqin, YANG Bin, et al. Preparation of ammoniated tobacco leave powder residue biochar and its adsorption behavior on Cr(VI)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(1):222-231(in Chinese). [4] 王毅, 吴梦亚, 雷伟岩, 等. 氧化石墨烯负载 Ag3PO4@聚苯胺复合材料的制备及其光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(6):2740-2749.WANG Yi, WU Mengya, LEI Weiyan, et al. Preparation of grapheme oxide load Ag3PO4@polyaniline composite and its photocatalytic performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compo-sitae Sinica,2022,39(6):2740-2749(in Chinese). [5] CHERRIFI Y, BARRAS A, ADDAD A, et al. Simultaneous photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction and phenol degradation over copper sulphide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite under visible light irradiation: Performance and reaction mechanism[J]. Chemosphere,2021,268:128798. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128798 [6] 郝军杰, 郭成, 高翔鹏, 等. 硫脲/海藻酸钠对Cr(VI)的吸附和光催化还原协同去除机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(4):1657-1666.HAO Junjie, GUO Cheng, GAO Xiangpeng, et al. Synergistic removal mechanism of Cr(VI) by thiourea/sodium alginate adsorption and photocatalytic reduction[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(4):1657-1666(in Chinese). [7] 郭莉, 赵强, 张越诚, 等. 全固态Z-型 CdS/Au/Bi2MoO6 异质结的构筑及其光催化性能[J]. 无机化学学报, 2020, 36(1):11-20. doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2020.023GUO Li, ZHAO Qiang, ZHANG Yuecheng, et al. Design and construction of all-solid Z-scheme CdS/Au/Bi2MoO6 heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic performance[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2020,36(1):11-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.11862/CJIC.2020.023 [8] WANG S, LIU D, YU J, et al. Photocatalytic penicillin degradation performance and the mechanism of the fragmented TiO2 modified by CdS quantum dots[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(28):18178-18189. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02079 [9] KANDI D, BEHERA A, SAHOO S, et al. CdS QDs modified BiOI/Bi2MoO6 nanocomposite for degradation of quinolone and tetracycline types of antibiotics towards environmental remediation[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2020,253:117523. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117523 [10] SU Y, XU X, LI R, et al. Design and fabrication of a CdS QDs/Bi2WO6 monolayer S-scheme heterojunction confi-guration for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of trace ethylene in air[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2022,429:132241. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132241 [11] CHEN W, YAN R Q, ZHU J Q, et al. Highly efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen evolution by all-solid-state Z-scheme CdS QDs/ZnIn2S4 architectures with MoS2 quantum dots as solid-state electron mediator[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,504:144406. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144406 [12] LIANG Q, ZHANG C, XU S, et al. In situ growth of CdS quantum dots on phosphorus-doped carbon nitride hollow tubes as active 0D/1D heterostructures for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2020,577:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.053 [13] YIN J, ZHAN F, JIAO T, et al. Facile preparation of self-assembled MXene@Au@CdS nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity[J]. Science China Materials,2020,63(11):2228-2238. doi: 10.1007/s40843-020-1299-4 [14] LIANG R, HE Z, ZHOU C, et al. MOF-derived porous Fe2O3 nanoparticles coupled with CdS quantum dots for degradation of bisphenol A under visible light irradiation[J]. Nanomaterials,2020,10(9):1701. doi: 10.3390/nano10091701 [15] HUANG H, XU B, TAN Z, et al. A facile in situ growth of CdS quantum dots on covalent triazine-based frameworks for photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,833:155057. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155057 [16] WANG F, HOU T, ZHAO X, et al. Ordered macroporous carbonous frameworks implanted with CdS quantum dots for efficient photocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Advanced Materials,2021,33(35):2102690. doi: 10.1002/adma.202102690 [17] ALIEV S B, GURSKIY S I, ZAKHAROV V N, et al. Synthesis of novel nanoporous metal-organic gels with tunable poro-sity and sensing of aromatic compounds[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2018,264:112-117. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2018.01.001 [18] QIN Z S, DONG W W, ZHAO J, et al. Metathesis in metal-organic gels (MOGs): A facile strategy to construct robust fluorescent Ln-MOG sensors for antibiotics and explo-sives[J]. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2018,2018(2):186-193. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201701339 [19] MA Y, LI A, GAO X, et al. Effective separation of enantiomers based on novel chiral hierarchical porous metal-organic gels[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications,2019,40(8):1800862. doi: 10.1002/marc.201800862 [20] LIU M, ZOU D, MA T, et al. Simultaneous efficient adsorption and accelerated photocatalytic degradation of chlortetracycline hydrochloride over novel Fe-based MOGs under visible light irradiation assisted by hydrogen peroxide[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers,2019,6(6):1388-1397. doi: 10.1039/C9QI00046A [21] LIU M, ZOU D, MA T, et al. Stable cellulose-based porous binary metal-organic gels as highly efficient adsorbents and their application in an adsorption bed for chlortetracycline hydrochloride decontamination[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(14):6670-6681. doi: 10.1039/C9TA13818H [22] FU H G, YOU J. Novel porous rhodium metal-organic aerogel for efficient removal of organic dyes and catalysis of Si—H insertion reactions[J]. ACS Omega,2021,6(40):26766-26772. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04265 [23] GAO Z, SUI J, XIE X, et al. Metal-organic gels of simple chemicals and their high efficacy in removing arsenic(V) in water[J]. AIChE Journal,2018,64(10):3719-3727. doi: 10.1002/aic.16344 [24] ZHOU X, JI Y X, CAO J F, et al. Polyoxometalate encapsulated in metal-organic gel as an efficient catalyst for visible-light-driven dye degradation applications[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry,2018,32(3):e4206. doi: 10.1002/aoc.4206 [25] LE S, MA Y, HE D, et al. CdS/NH4V4O10 S-scheme photocatalyst for sustainable photo-decomposition of amoxicillin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,426:130354. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.130354 [26] QIN Z S, DONG W W, ZHAO J, et al. A water-stable Tb(III)-based metal-organic gel (MOG) for detection of antibiotics and explosives[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers,2018,5(1):120-126. doi: 10.1039/C7QI00495H [27] PAN J, LIU J, MA H, et al. Structure of flower-like hierarchical CdS QDs/Bi/Bi2WO6 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2018,42(9):7293-7300. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ00394G [28] WANG J, LIN W, DONG M, et al. Facile synthesize of CdS QDs decorated Bi2MoO6/Bi2Mo3O12 heterojunction photocatalysts and enhanced performance of visible light removal of organic pollutants[J]. Environmental Technology,2021,42(23):3581-3594. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2020.1737243 [29] XIANG X, ZHU B, CHENG B, et al. Enhanced photocataly-tic H2-production activity of CdS quantum dots using Sn2+ as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation[J]. Small,2020,16(26):2001024. doi: 10.1002/smll.202001024 [30] ARCHANA T, SREELEKSHMI S, SUBASHINI G, et al. The effect of graphene quantum dots/ZnS co-passivation on enhancing the photovoltaic performance of CdS quantum dot sensitized solar cells[J]. International Journal of Energy Research,2021,45(11):15879-15915. doi: 10.1002/er.6821 [31] 罗利军, 孟德梅, 戴建辉, 等. TiO2-NB/pg-C3N4可见光催化降解 17α-乙炔雌二醇的机制[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(2):654-664. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.018LUO Lijun, MENG Demei, DAI Jianhui, et al. The degradation mechanism study of 17α-ethinylestradiol by TiO2-NB/pg-C3N4 photocatalyst under visible light irradiation[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(2):654-664(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.02.018 [32] 郭冀峰, 李靖, 孙泽鑫, 等. Ag3PO4/Cu-BiVO4 p-n异质结的制备及其增强可见光催化降解四环素性能[J]. 中国环境科学, 2022, 42(1):146-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.01.017GUO Jifeng, LI Jing, SUN Zexin, et al. Synthesis of Ag3PO4/Cu-BiVO4 p-n heterojunction and enhancement of its visible-light photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline[J]. China Environmental Science,2022,42(1):146-159(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2022.01.017 [33] WANG Y J, WEI J H, LI S, et al. Convenient synthesis of polymetallic metal-organic gels for efficient methanol electro-oxidation[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers,2021,8(4):927-933. doi: 10.1039/D0QI01523G [34] GU J, CHEN H, JIANG F, et al. All-solid-state Z-scheme Co9S8/graphitic carbon nitride photocatalysts for simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid under simulated solar irradiation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,360:1188-1198. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.137 [35] RAUF A, SHER SHAH M S A, CHOI G H, et al. Facile synthesis of hierarchically structured Bi2S3/Bi2WO6 photocatalysts for highly efficient reduction of Cr(VI)[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2015,3(11):2847-2855. [36] MAMBA G, KIWI J, PULGARIN C, et al. Evidence for the degradation of an emerging pollutant by a mechanism involving iso-energetic charge transfer under visible light[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2018,233:175-183. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.03.109 [37] YUE Y, ZHANG P, WANG W, et al. Enhanced dark adsorption and visible-light-driven photocatalytic properties of narrower-band-gap Cu2S decorated Cu2O nanocompo-sites for efficient removal of organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,384:121302. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121302 [38] YANG W, ZHANG L, XIE J, et al. Enhanced photoexcited carrier separation in oxygen-doped ZnIn2S4 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2016,55(23):6716-6720. doi: 10.1002/anie.201602543 [39] MA Y, LV P, DUAN F, et al. Direct Z-scheme Bi2S3/BiFeO3 heterojunction nanofibers with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,834:155158. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155158 -





 下载:
下载: