Enhanced solar steam generation using CNTs-HEC/PVDF porous composite membrane
-
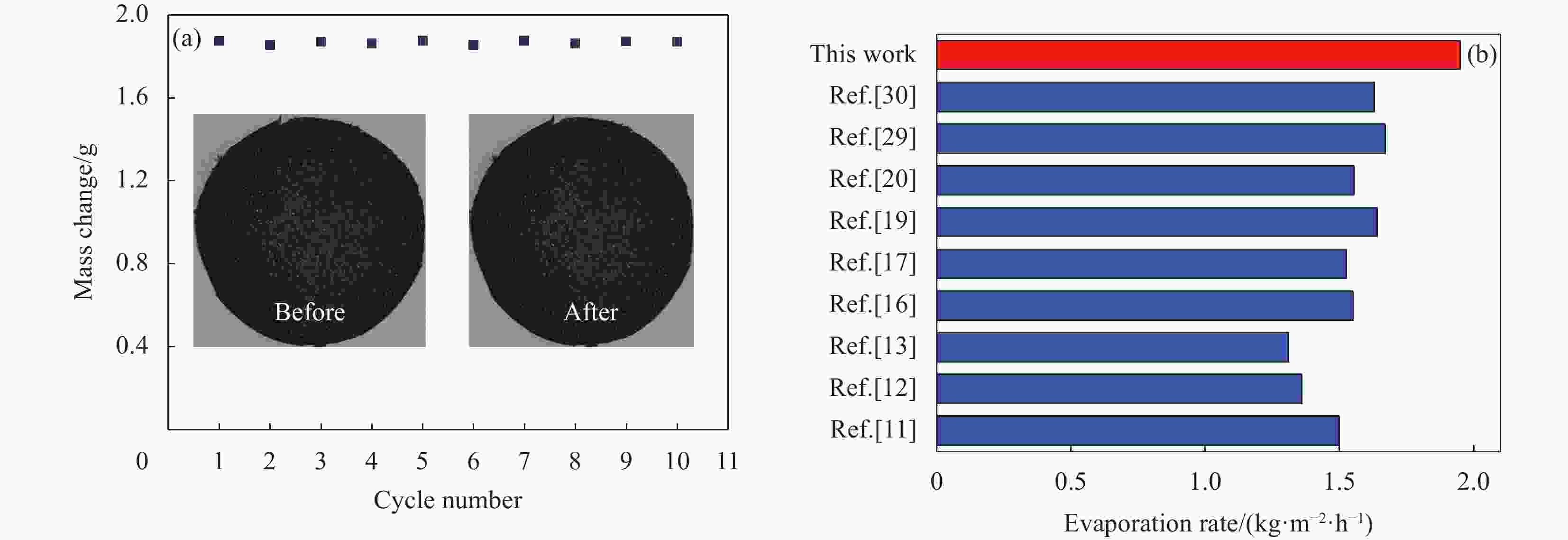
摘要: 太阳能界面水蒸发技术在解决目前人类所面临的能源和淡水资源短缺方面具有广阔的应用前景。水输运是太阳能水蒸发过程中十分重要的一环。理想状态下的水输运是输送适量的水来维持太阳能蒸发层高效、稳定的水蒸发。而蒸发层所拥有的多孔结构所产生的毛细管作用力决定了其水输运的能力。因此,蒸发层内部的孔隙结构非常重要。本文以聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)为基体,借助碳纳米管(CNTs)的优异光吸收能力,通过羟乙基纤维素(HEC)掺杂并与戊二醛进行交联制备了可用于太阳能界面水蒸发的CNTs-HEC/PVDF多孔复合膜。CNTs-HEC/PVDF复合膜的多孔结构形成的微通道提高了水输运和蒸汽逸出能力,从而增强了太阳能界面水蒸发性能。在1 kW·m−2的太阳光照射下,其水蒸发速率达到1.81 kg·m−2·h−1,相应的光热转化效率为95%。相关实验结果还展现出该复合膜具有优异的循环使用性能、化学稳定性和高效的污水净化能力。Abstract: Solar interface water evaporation technology has a broad application prospect in solving the shortage of energy and fresh water resources that mankind is currently facing. Water transport was a very important step in the solar steam generation process. The ideal water transport was to transport the right amount of water to maintain efficient and stable water evaporation from the solar evaporation layer. The capillary force generated by the porous structure of the evaporation layer determined its ability when transporting water. Therefore, the pore structure inside the evaporation layer was very important. In this paper, a porous carbon nanotubes-hydroxyethyl cellulose/polyvinylidene fluoride (CNTs-HEC/PVDF) composite membrane for solar interfacial water evaporation was produced, which was doped with HEC and cross-linking with glutaraldehyde on a PVDF depended on the excellent light absorption capacity of CNTs. The solar interfacial water evaporation performance was improved as the microchannels formed by the porous structure of CNTs-HEC/PVDF composite membranes enhanced water transport and vapor escape. The water evaporation rate reaches 1.81 kg·m−2·h−1 under 1 kW·m−2 of solar irradiation, and the corresponding photothermal conversion efficiency is 95%. The relevant experimental results also show that the composite membrane has excellent recycling performance, chemical stability and efficient sewage purification ability.
-
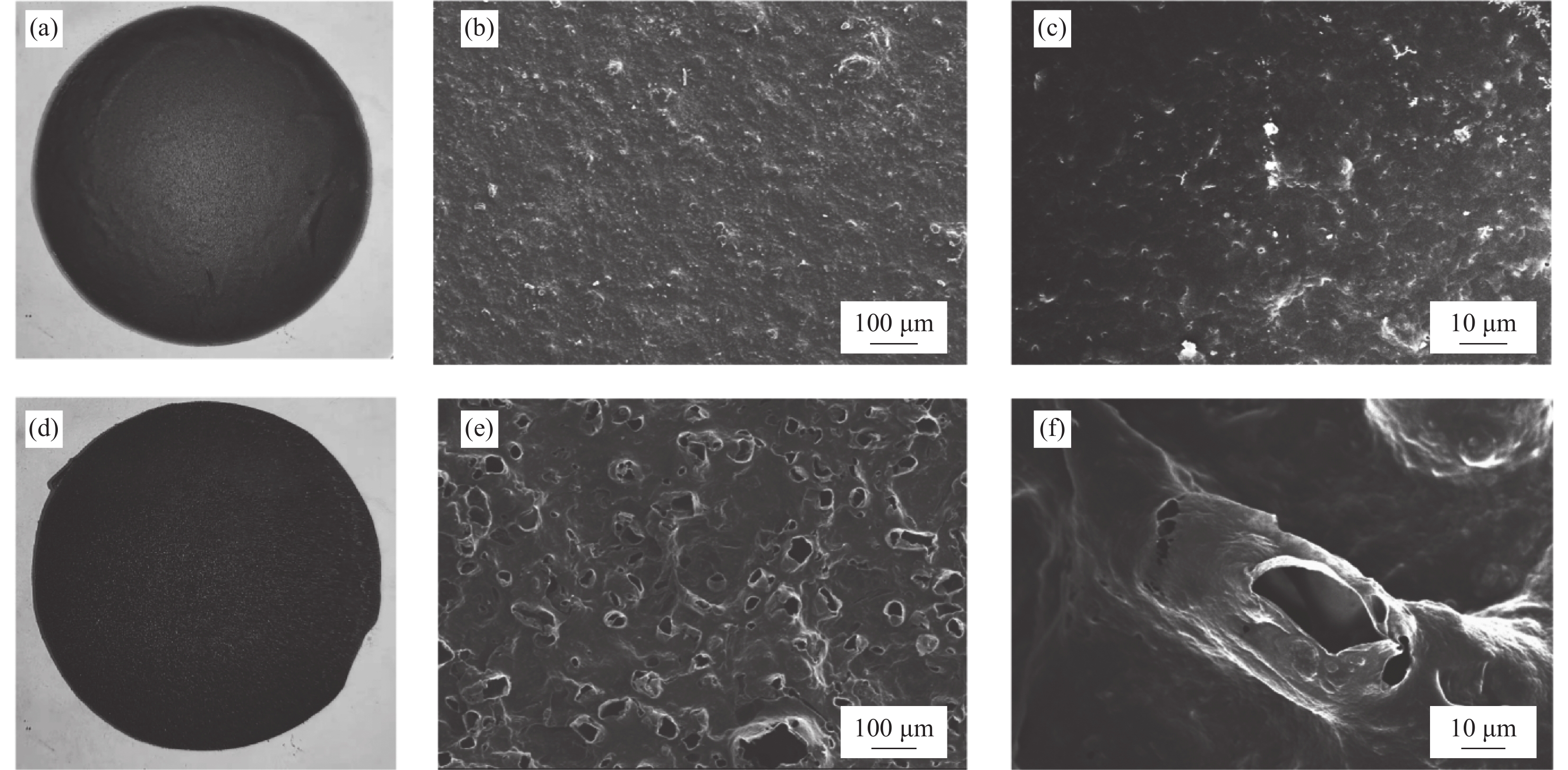
图 1 不含羟乙基纤维素(HEC)的碳纳米管/聚偏氟乙烯(CNTs/PVDF)样品图像(a)及其SEM图像((b), (c));含有HEC的CNTs-HEC/PVDF样品图像(d)及其SEM图像((e), (f))
Figure 1. Photographs of carbon nanotubes/polyvinylidene fluoride (CNTs/PVDF) sample without hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) (a) and SEM images ((b), (c)); Photographs of CNTs-HEC/PVDF with HEC (d) and SEM images ((e), (f))
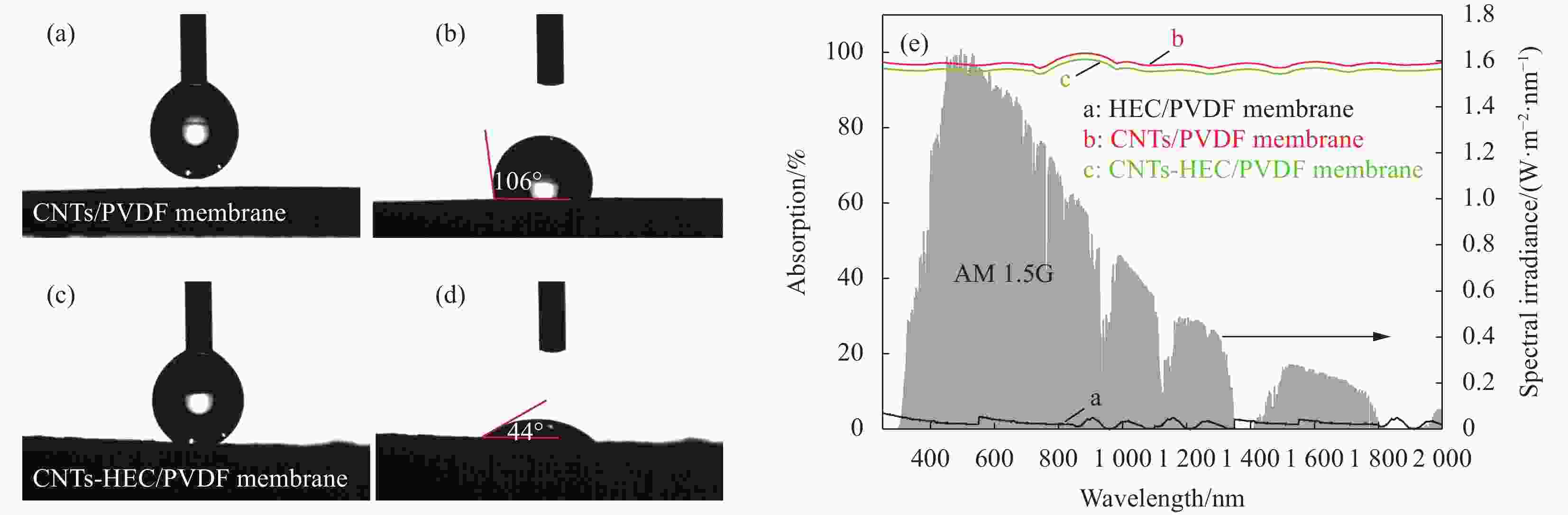
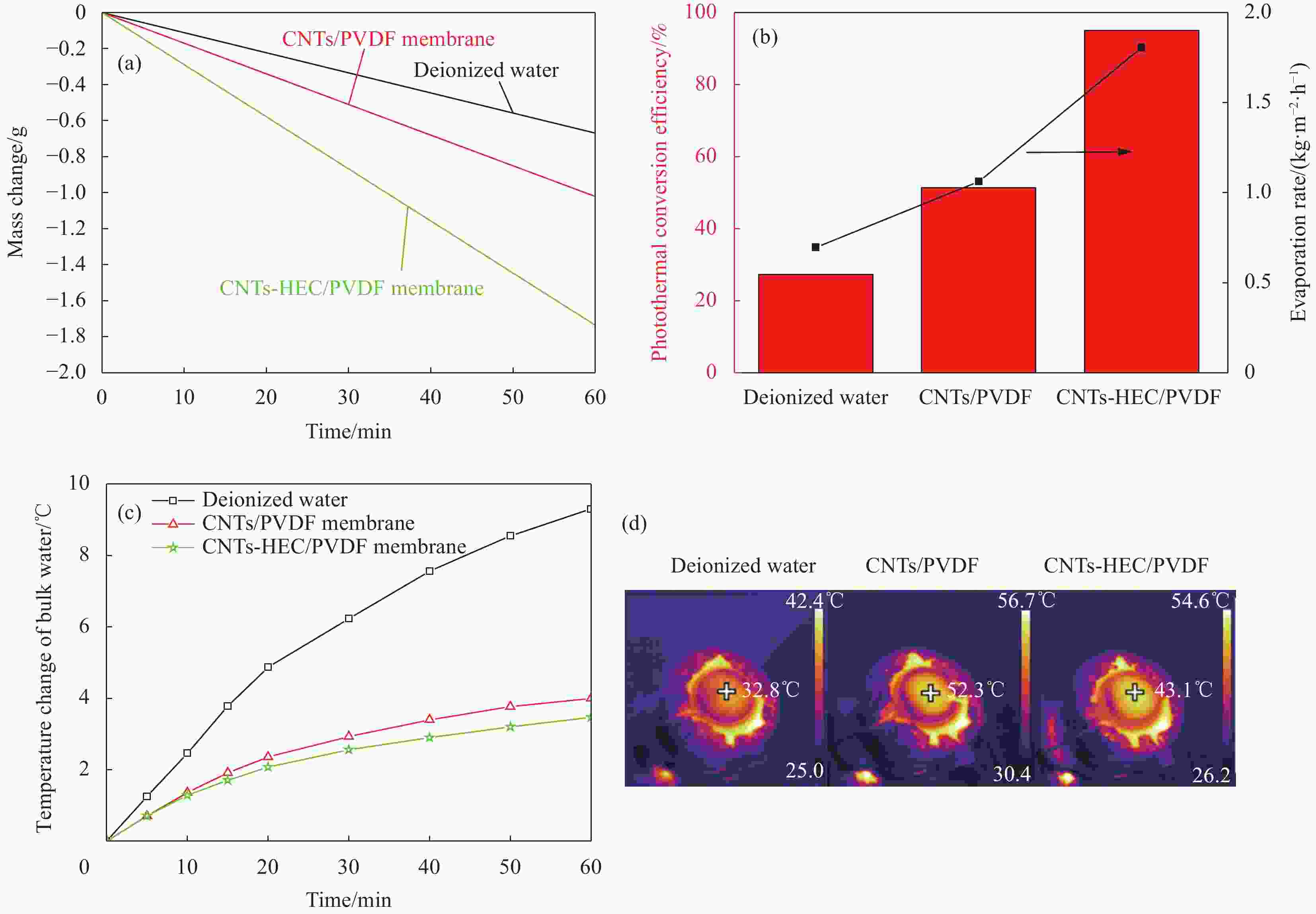
图 3 去离子水、CNTs/PVDF复合膜和CNTs-HEC/PVDF多孔复合膜界面的蒸发性能:(a)质量变化;(b)光热转换效率(左)和水蒸发率(右);(c)本体水温变化;(d)表面温度
Figure 3. Evaporation performance at the interface of pure water, CNTs/PVDF composite membrane and CNTs-HEC/PVDF porous composite membrane: (a) Mass change; (b) Photothermal conversion efficiency (Left) and water evaporation rate (Right); (c) Bulk water temperature change; (d) Surface temperature
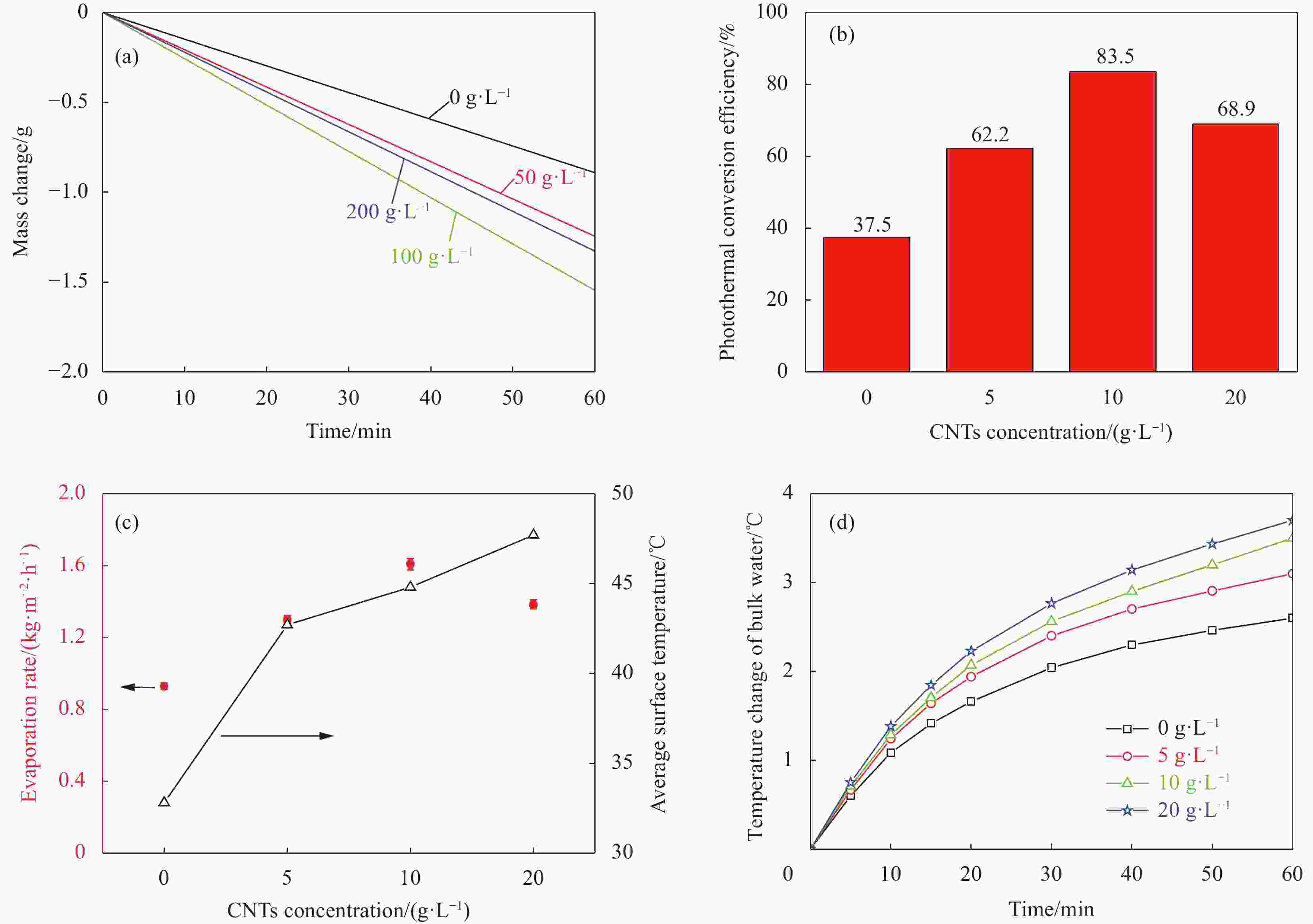
图 4 不同 CNTs浓度复合膜对太阳能水蒸发性能的影响:(a)质量变化;(b)光热转换效率;(c)蒸发率(左)和平均表面温度(右);(d) 整体水温变化
Figure 4. Effects of different CNTs concentration composite membranes on solar water evaporation performance: (a) Mass change; (b) Photothermal conversion efficiency; (c) Evaporation rate (Left) and average surface temperature (Right); (d) Bulk water temperature change
图 5 不同HEC浓度复合膜对太阳能水蒸发性能的影响:(a)质量变化;(b) 光热转换效率;(c) 蒸发率(左)和平均表面温度(右);(d) 整体水温变化
Figure 5. Effects of different HEC concentration composite membranes on solar water evaporation performance: (a) Mass change; (b) Photothermal conversion efficiency; (c) Evaporation rate (Left) and average surface temperature (Right); (d) Bulk water temperature change
-
[1] GREVE P, KAHIL T, MOCHIZUKI J, et al. Global assessment of water challenges under uncertainty in water scarcity projections[J]. Nature,2018,1(9):486-494. [2] VELDKAMP T, WADA Y, AERTS J, et al. Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8:15697. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15697 [3] ZHAO F, GUO Y, ZHOU X, et al. Materials for solar-powered water evaporation[J]. Nature Reviews Materials,2020,5(5):388-401. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-0182-4 [4] TAO P, NI G, SONG C, et al. Solar-driven interfacial evaporation[J]. Nature Energy,2018,3:1031-1040. doi: 10.1038/s41560-018-0260-7 [5] 梁平平, 刘帅, 李红艺, 等. PVDF-CNT自漂浮多孔微珠的制备及在高效太阳能驱动界面水蒸发中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8):2689-2693.LIANG Pingping, LIU Shuai, LI Hongyi, et al. Self-floating porous PVDF-CNT microbeads for highly efficient solar-driven interfacial water evaporation[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2021,42(8):2689-2693(in Chinese). [6] GUO C L, MIAO E D, ZHAO J X, et al. Paper-based integrated evaporation device for efficient solar steam generation through localized heating[J]. Solar Energy,2019,188:1283-1291. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.07.023 [7] MIAO E D, YE M Q, GUO C L, et al. Enhanced solar steam generation using carbon nanotube membrane distillation device with heat localization[J]. Applied Thermal Engi-neering,2019,149:1255-1264. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2018.12.123 [8] 汪日圆, 陈浩然, 陈芳琳, 等. 多巴胺@氮化硼-碳纳米管/聚酰亚胺复合气凝胶太阳能蒸发器的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 40(3):1494-1500. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220410.001WANG Riyuan, CHEN Haoran, CHEN Fanglin, et al. Preparation and performance of dopamine@boron nitride carbon nanotubes/polyimide composite aerogel solar-driven evaporator[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,40(3):1494-1500(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220410.001 [9] ZHOU L, TAN Y, WANG J, et al. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination[J]. Nature Photonics,2016,10(6):393-398. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.75 [10] YING X A, JM A, YU H A, et al. A simple and universal strategy to deposit Ag/polypyrrole on various substrates for enhanced interfacial solar evaporation and antibacterial activity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,384(C):123379. [11] REN P, LI J, ZHANG X, et al. Highly efficient solar water evaporation of TiO2@TiN hyperbranched nanowires-carbonized wood hierarchical photothermal conversion material[J]. Materials Today Energy,2020,18:100546. doi: 10.1016/j.mtener.2020.100546 [12] ZADA I, ZHANG W, SUN P, et al. Superior photothermal black TiO2 with random size distribution as flexible film for efficient solar steam generation[J]. Applied Materials Today,2020,20:100669. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2020.100669 [13] 薛超瑞, 李洋森, 黄蕊蕊, 等. BiOBr/Bi复合光热粉体的制备及其界面光热驱动水蒸发性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7):3271-3280. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210909.001XUE Chaorui, LI Yangsen, HUANG Ruirui, et al. Preparation of BiOBr/Bi composite photothermal powder and its interfacial photothermal driven water evaporation performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(7):3271-3280(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20210909.001 [14] HE J X, FAN Y K, XIAO C H, et al. Enhanced solar steam generation of hydrogel composite with aligned channel and shape memory behavior[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,204:108633. [15] SUN H, ZHOU P, ZHANG W, et al. Flexible and double-layered photothermal material based on resorcinol-formaldehyde foam for solar assisted water desalination[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2021,232:111350. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2021.111350 [16] CHANG C, TAO P, XU J, et al. High-efficiency superheated steam generation for portable sterilization under ambient pressure and low solar flux[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(20):18466-18474. [17] HE S, CHEN C, KUANG Y, et al. Nature-inspired salt resistant bimodal porous solar evaporator for efficient and stable water desalination[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2019,12(5):1558-1567. [18] GOH K, KARAHAN H E, LI W, et al. Carbon nanomaterials for advancing separation membranes: A strategic perspective[J]. Carbon,2016,109:694-710. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.08.077 [19] CHEN Y, SHI Y, KOU H, et al. Self-floating carbonized tissue membrane derived from commercial facial tissue for highly efficient solar steam generation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2019, 7(3): 2911-2915. [20] AIKIFA R, LU J Y, SAFA A, et al. Novel receiver-enhanced solar vapor generation: Review and perspectives[J]. Energies,2018,11(1):253. doi: 10.3390/en11010253 [21] WU X, ROBSON M E, PHELPS J L, et al. A flexible photothermal cotton-CuS nanocage-agarose aerogel towards portable solar steam generation[J]. Nano Energy,2018,56:708-715. [22] XU Y, LV B, YANG Y, et al. Facile fabrication of low-cost starch-based biohydrogel evaporator for efficient solar steam generation[J]. Desalination,2021,517:115260. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2021.115260 [23] LI Y, HONG W, LI H, et al. Solar absorber with tunable porosity to control the water supply velocity to accelerate water evaporation[J]. Desalination,2021,511(2):115113. [24] WANG Y, ZHANG L, WANG P. Self-floating carbon nanotube membrane on macroporous silica substrate for highly efficient solar-driven interfacial water evaporation[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2016,4(3):1223-1230. [25] XU W, YUN X, LIU J, et al. Efficient water transport and solar steam generation via radially, hierarchically structured aerogels[J]. ACS Nano,2019,13(7):7930-7938. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b02331 [26] GONG F, HAO L, WANG W B, et al. Scalable, eco-friendly and ultrafast solar steam generators based on one-step melamine-derived carbon sponges toward water purification[J]. Nano Energy,2019,58:322-330. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2019.01.044 [27] WANG X, HE Y, XING L, et al. Enhanced direct steam generation via a bio-inspired solar heating method using carbon nanotube films[J]. Powder Technology,2017,321:276-285. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.08.027 [28] CONG C, GAO M, XING G, et al. Carbon nanomaterials treated by combination of oxidation and flash for highly efficient solar water evaporation[J]. Chemosphere,2021,277(4):130248. [29] GUO Y H, LU H Y, ZHAO F, et al. Biomass-derived hybrid hydrogel evaporators for cost-effective solar water purification[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(11):e1907061. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907061 [30] ZHOU X, ZHAO F, GUO Y, et al. Architecting highly hydratable polymer networks to tune the water state for solar water purification[J]. Science Advances,2019,5(6):eaaw5484. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw5484 -





 下载:
下载: