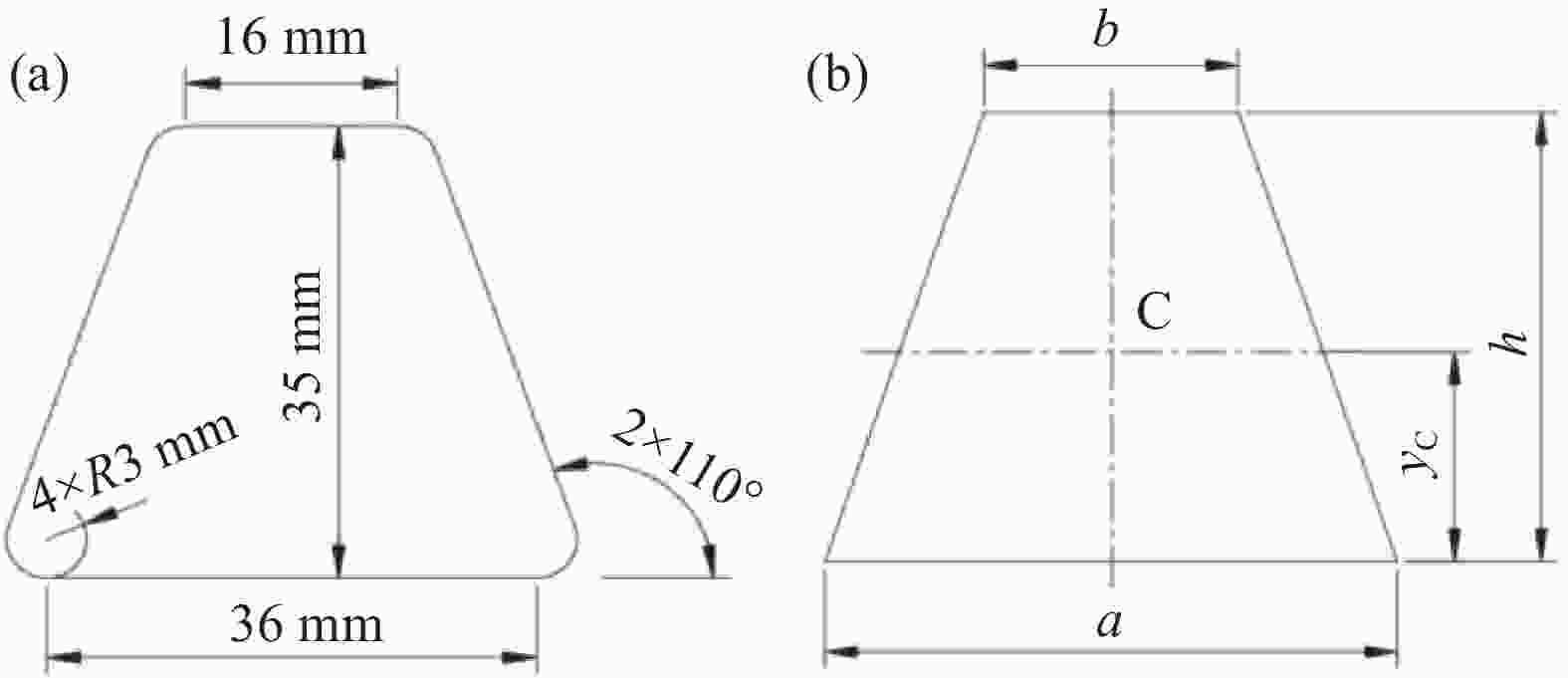
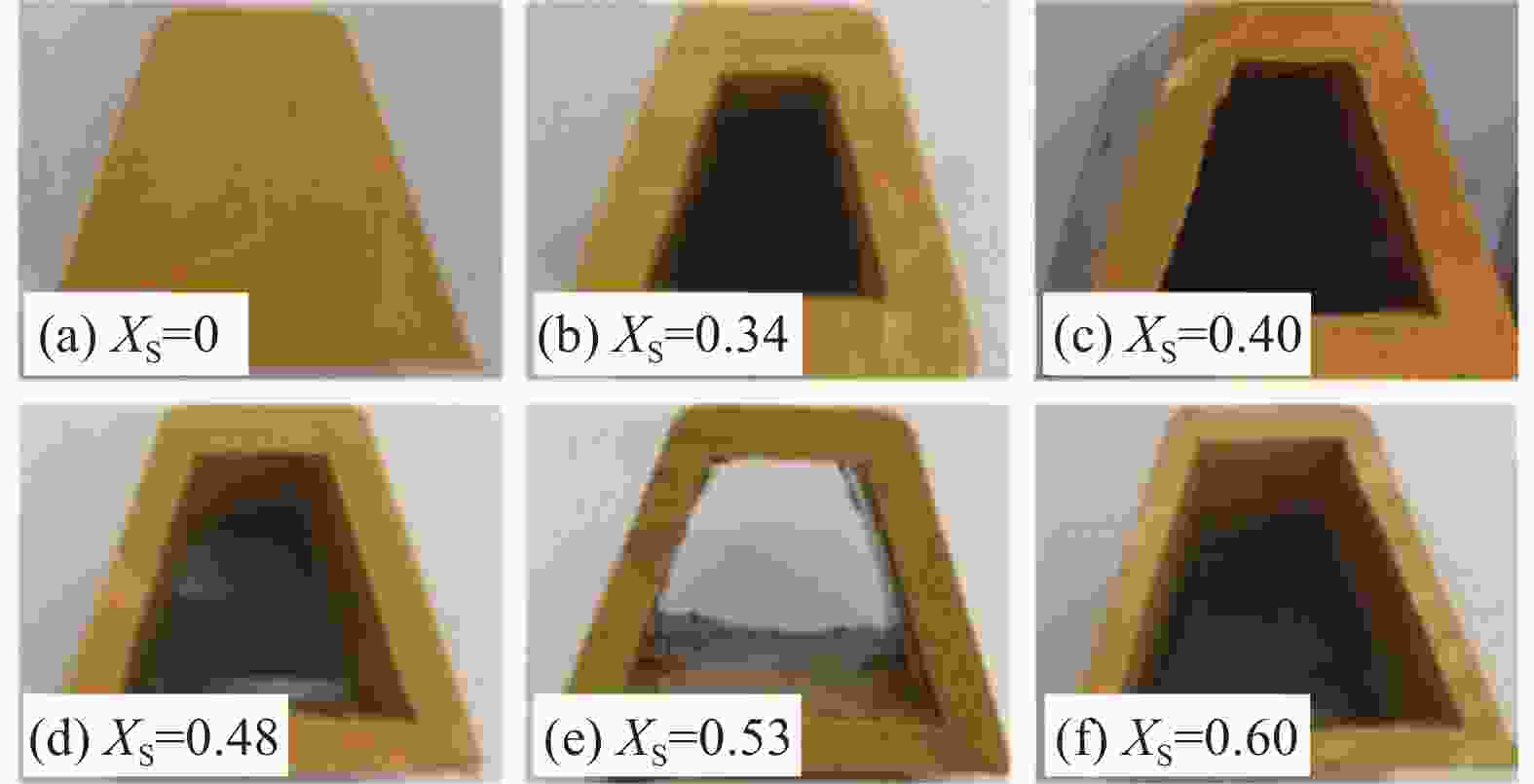
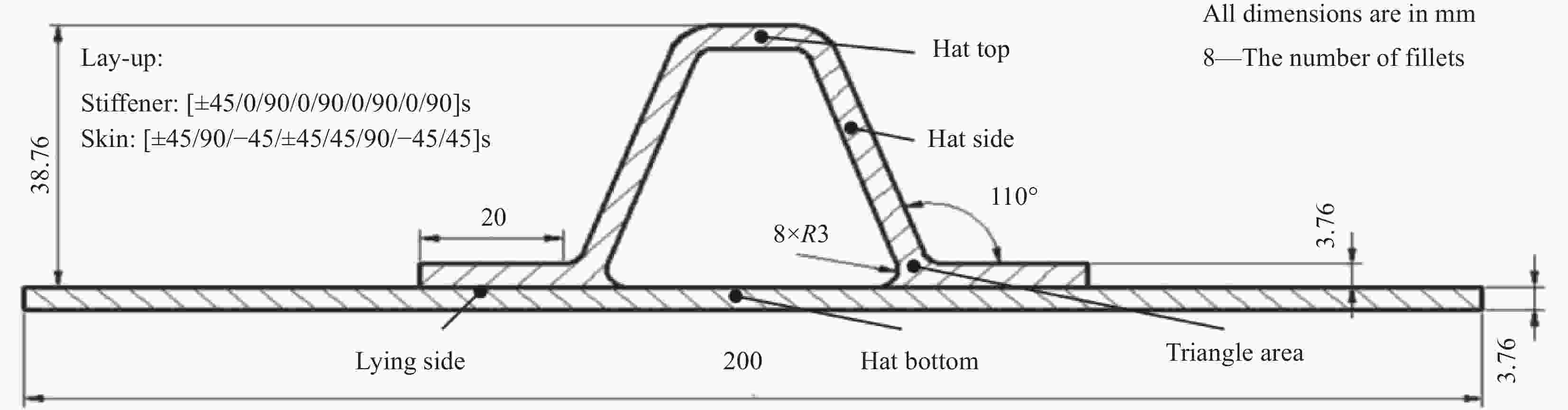
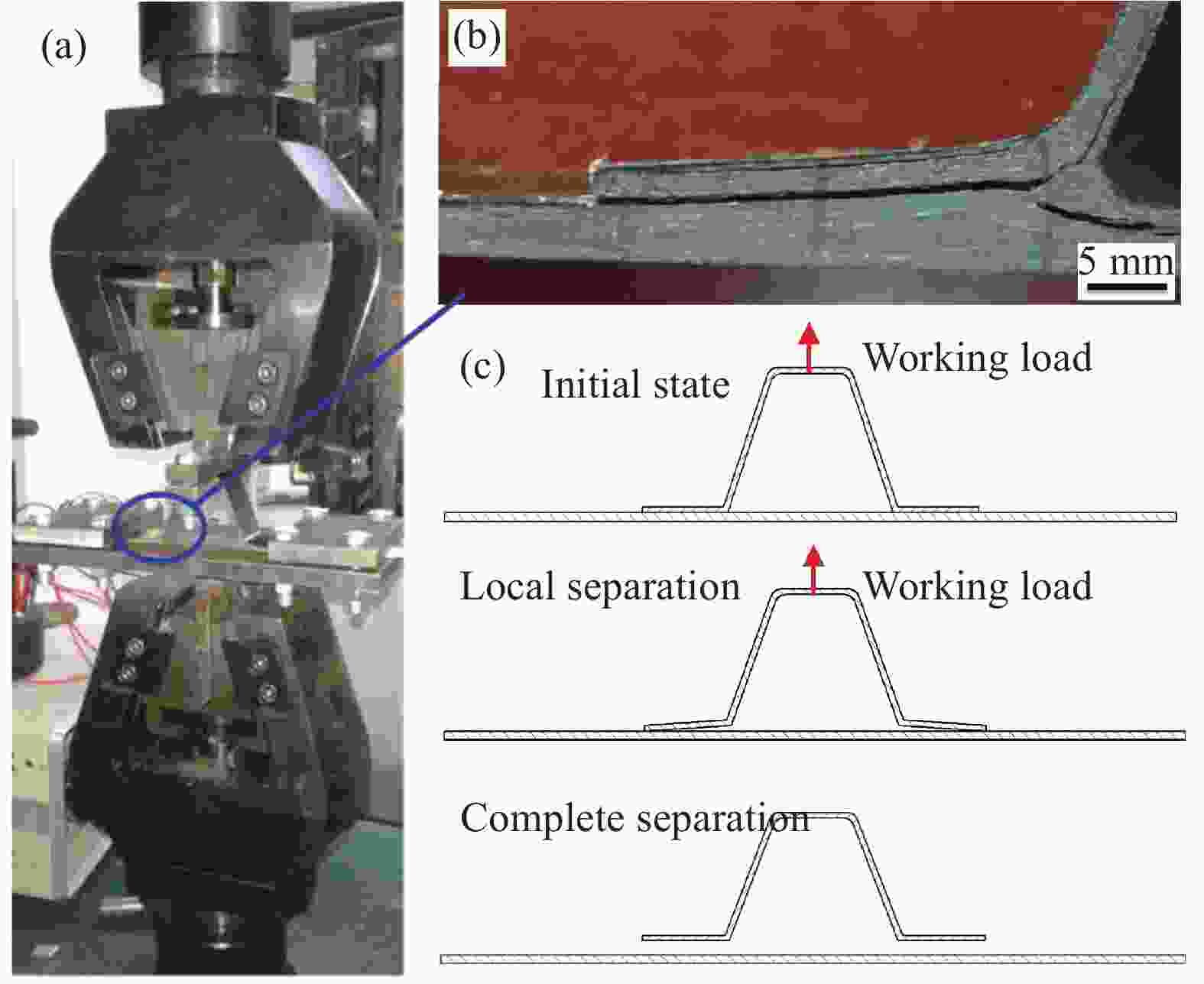
Pressure distribution and forming quality of composite hat-stiffened structures during curing process based on combined mandrel pressurization method
-
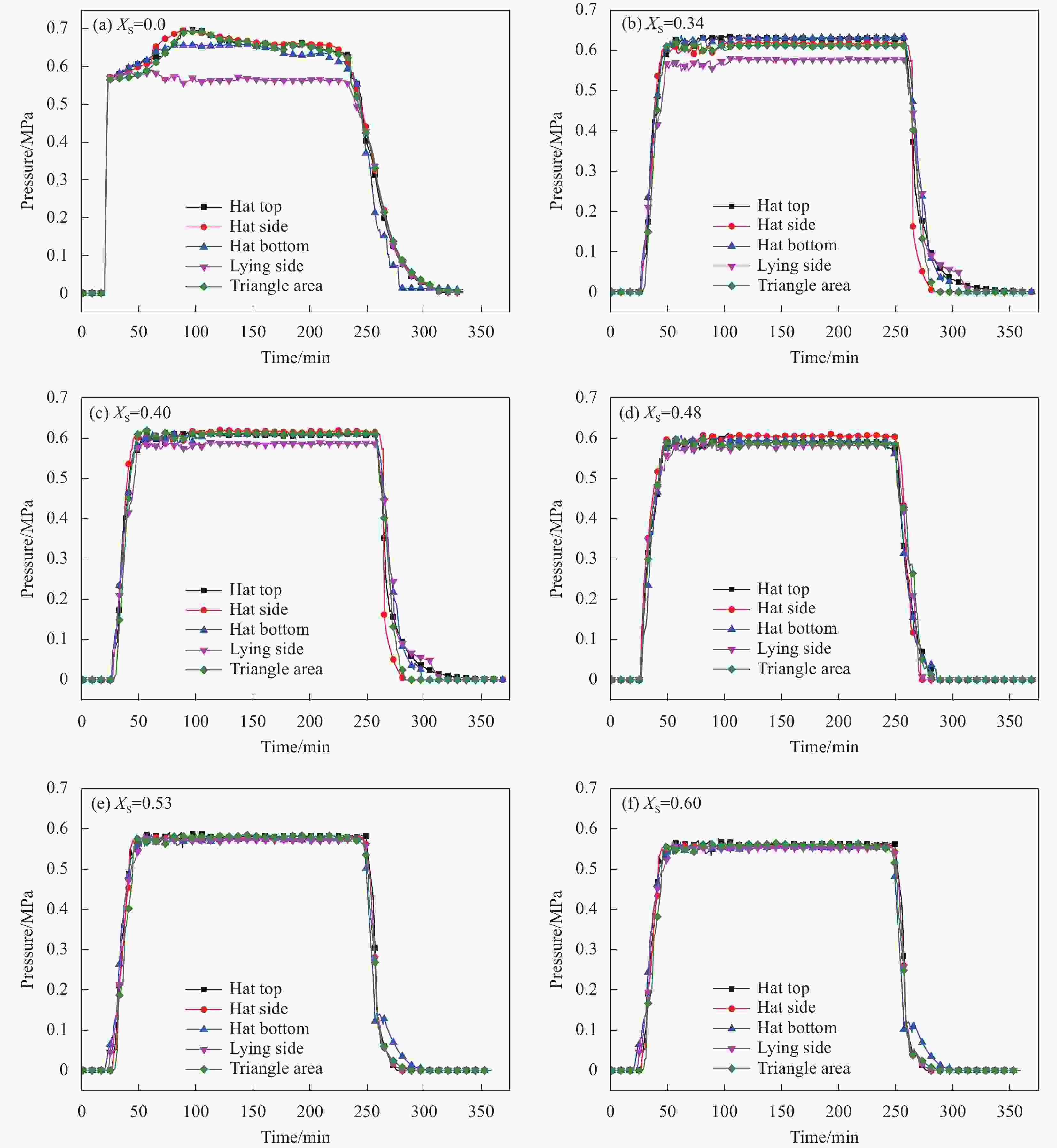
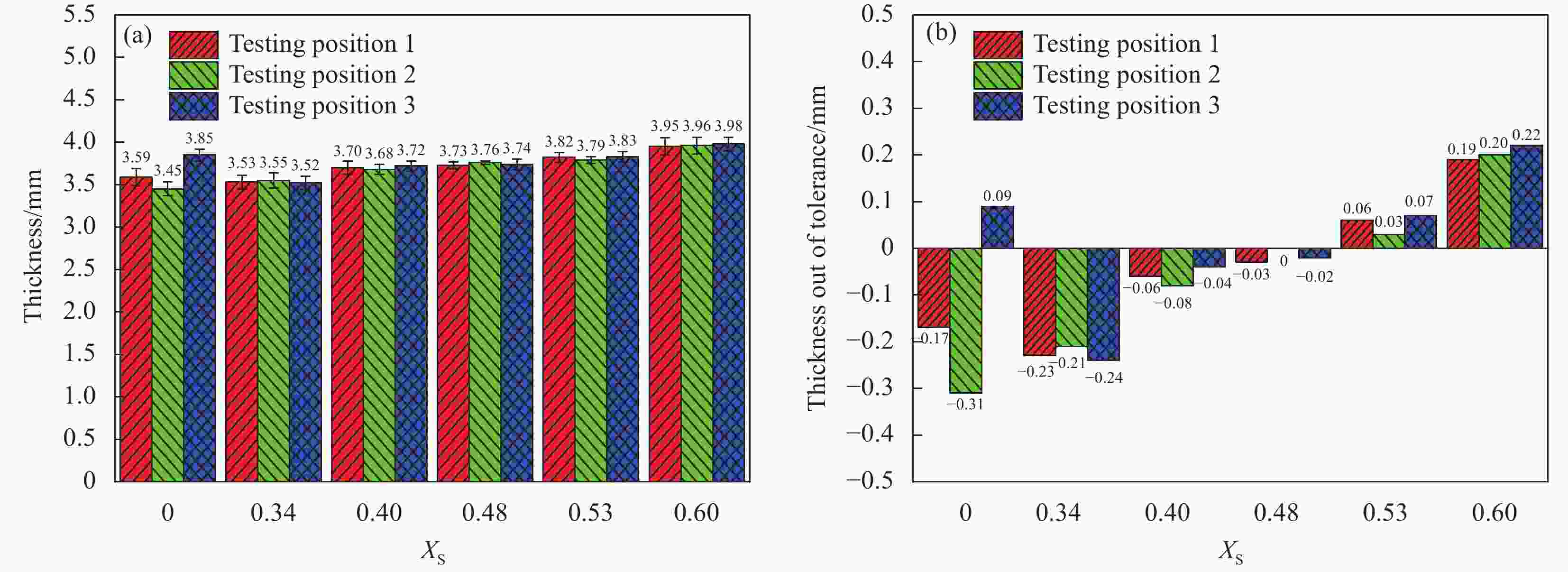
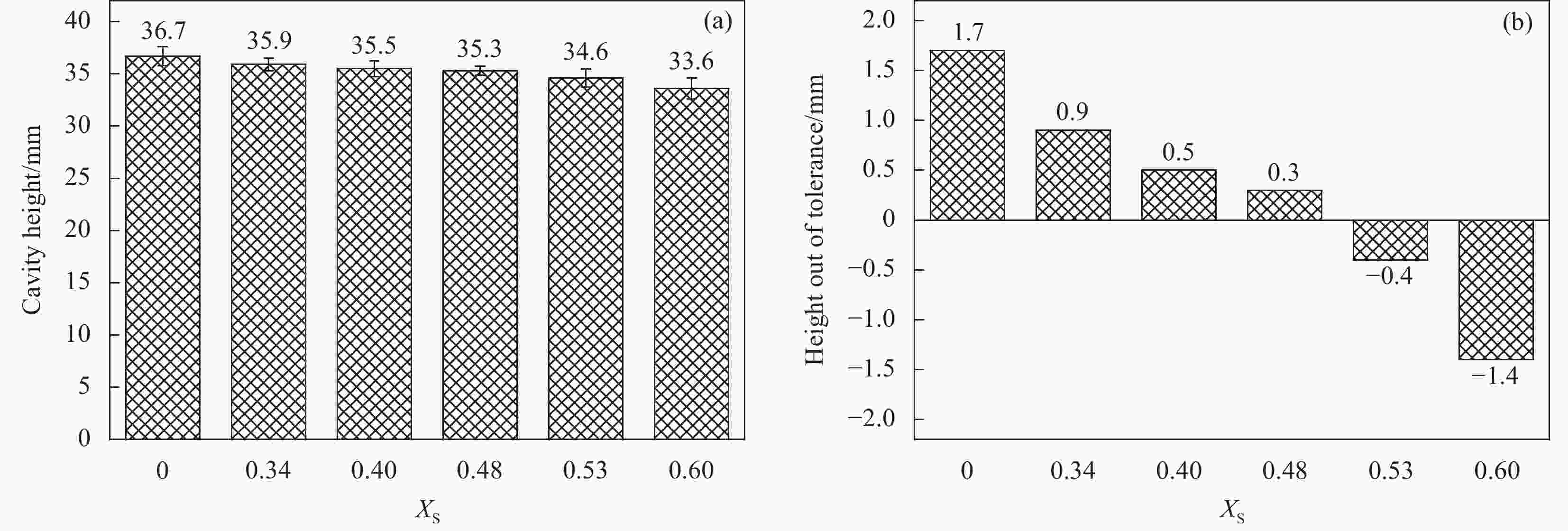
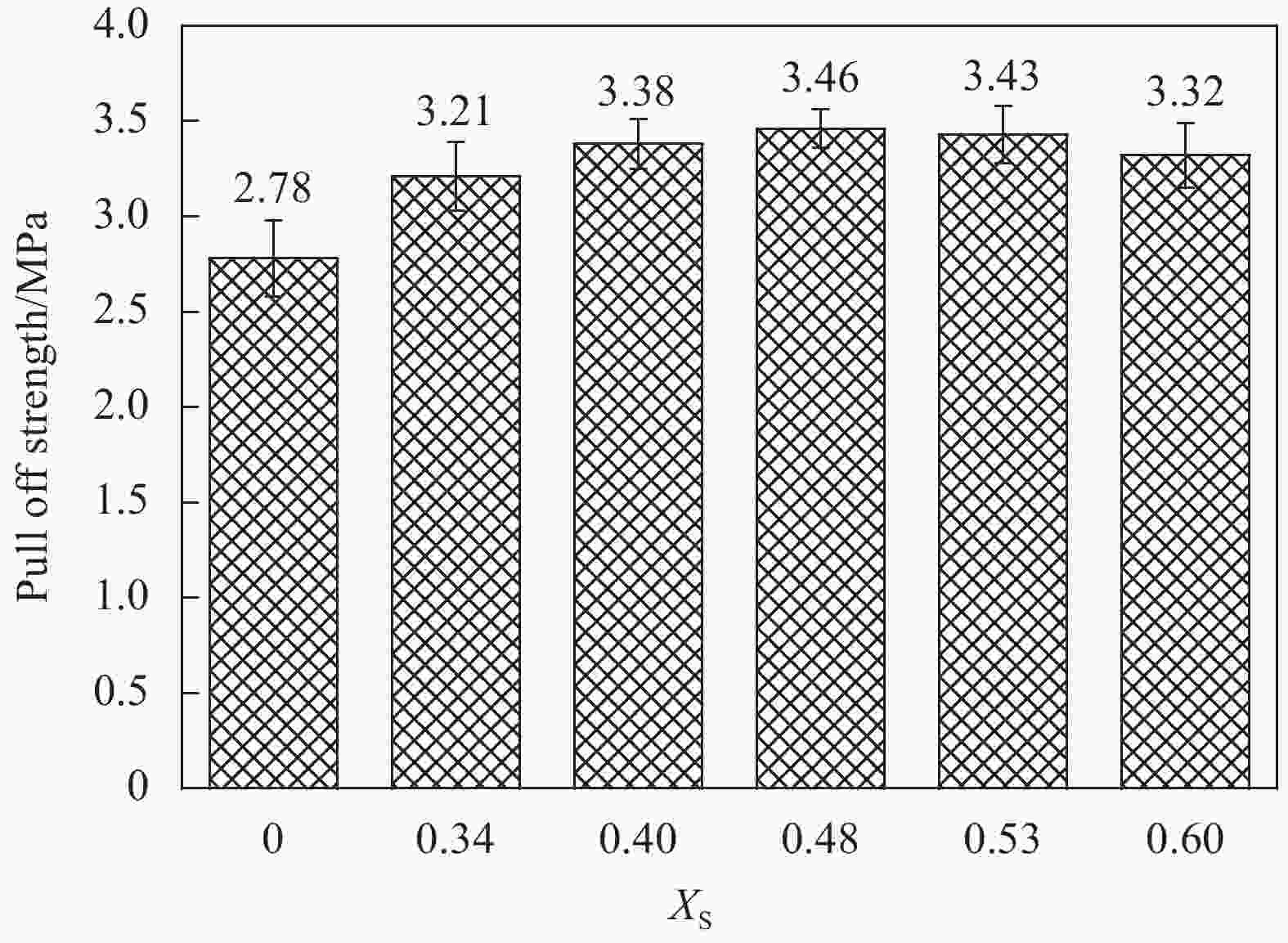
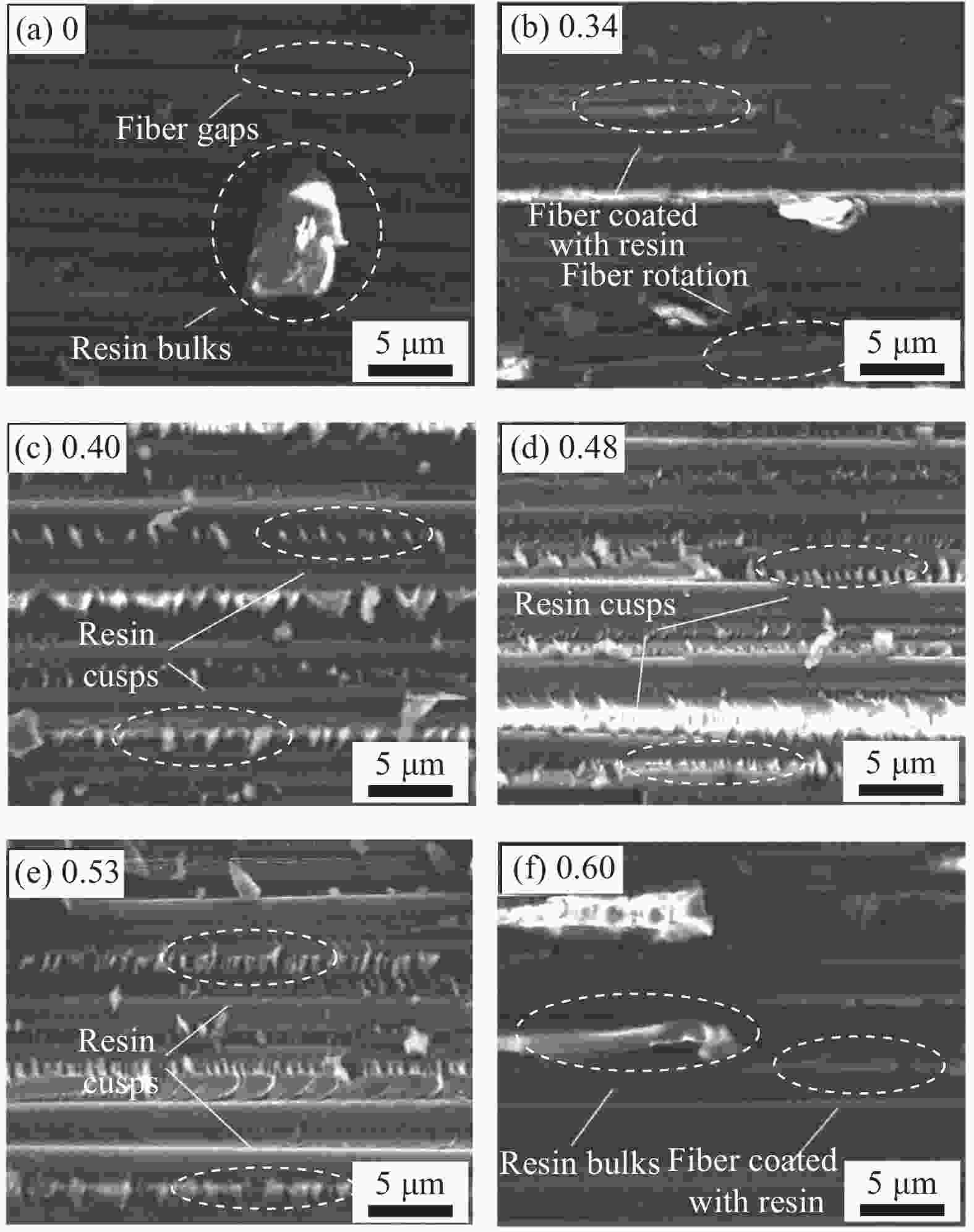
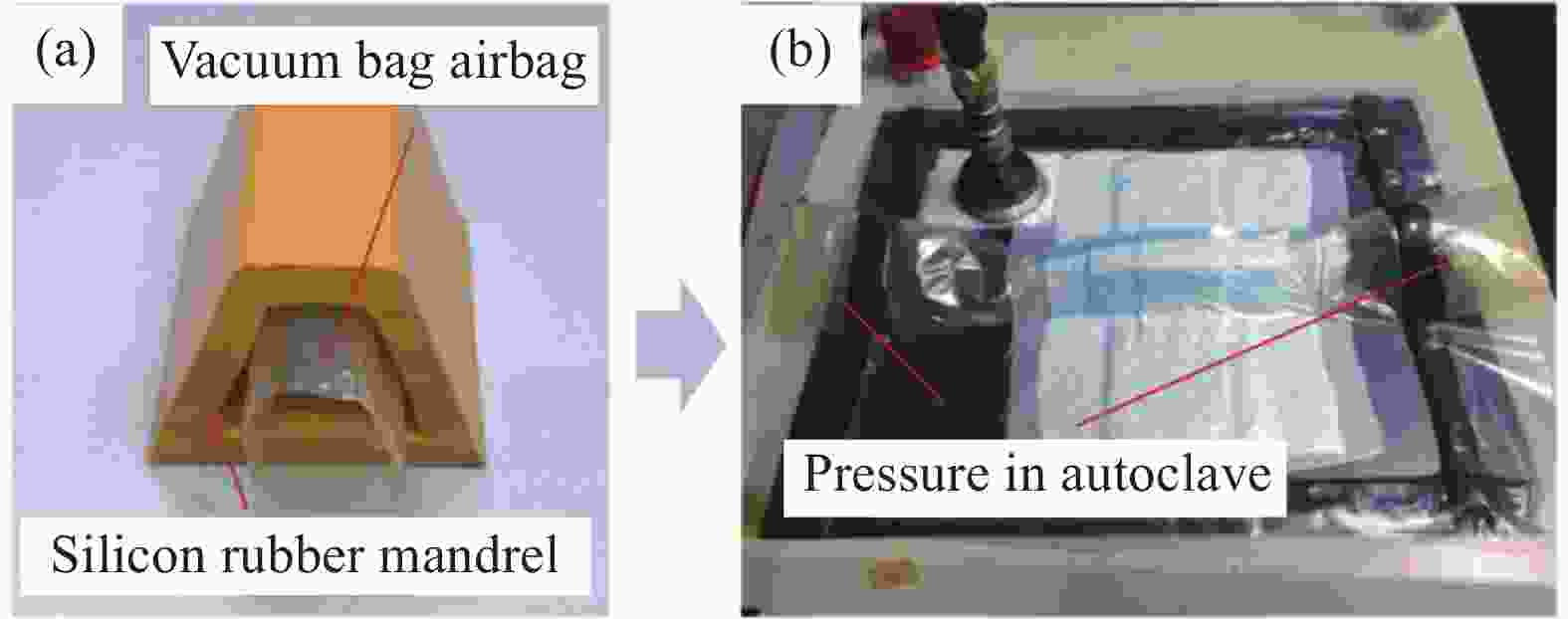
摘要: 为改善硅橡胶芯模辅助成型中调型孔工艺窗口过窄,导致复合材料帽型件成型质量对其敏感性过高问题,提出硅橡胶芯模&真空袋气囊组合新方法,并对不同调型孔硅橡胶芯模&真空袋气囊下成型的复合材料帽型件固化过程中压力分布和固化后成型精度、微观结构与力学性能进行了研究。结果表明:未开设调型孔&真空袋气囊,构件内部压力大小波动明显且不均分布,随着孔占比XS的增大,在XS=0.40~0.53内,构件内部压力均匀且稳定在所需压力0.6 MPa,同时,构件厚度和型腔高度平均差值仅为0.046 mm和0.40 mm,其三角区域微观结构质量较高,平均拉脱性能和增幅分别为3.42 MPa和23.02%。本文提出的方法具有更宽的调型孔工艺窗口,在复合材料帽型件固化成型领域具备一定应用潜力。Abstract: In order to improve the problem that the process window for the size of the silicone rubber mandrel was too narrow, which led to the high sensitivity of the forming quality of the composite hat-stiffened structure, a novel mandrel pressurization method combining silicon rubber mandrel and vacuum bag airbag was proposed, and the pressure distributions in the co-curing process and the forming accuracy, microstructure and mechanical properties of the composite hat-stiffened structures formed under the combined mandrel with different adjustable apertures were studied. The results show that the internal pressure fluctuates obviously and unevenly without the opening of adjustable aperture. With the increase of aperture proportion XS, the internal pressure is uniform and stable at the required pressure of 0.6 MPa within XS=0.40-0.53. At the same time, the average differences between the component thickness and the cavity height areonly 0.046 mm and 0.40 mm. The microstructure quality of the triangular area is high, and the average pull-off performance and increase rate are 3.42 MPa and 23.02% respectively. The method proposed in this study has a wider process window of adjustable aperture, which has a certain application potential in the forming manufacturing of composite hat-stiffened structures.
-
Key words:
- composite /
- hat-stiffened structures /
- co-curing /
- combined mandrel /
- forming quality
-
表 1 复合材料帽型加筋构件各监测点稳定阶段的压力分布
Table 1. Corresponding pressure in stable stage of the monitoring positions of composite hat-stiffened structure
XS Monitoring positions pressure/MPa Hat top Hat side Hat bottom Lying side Triangle area Pressure difference (Max) 0.00 0.681 0.665 0.669 0.671 0.573 0.108 0.34 0.631 0.615 0.630 0.577 0.610 0.054 0.40 0.614 0.610 0.602 0.595 0.612 0.019 0.48 0.591 0.586 0.594 0.588 0.592 0.008 0.53 0.578 0.582 0.576 0.575 0.583 0.008 0.60 0.556 0.558 0.550 0.548 0.553 0.010 -
[1] DEVARAJU S, ALAGAR M. Polymer matrix composite materials for aerospace applications[J]. Encyclopedia of Materials: Composites,2021,1:947-969. [2] 单忠德, 范聪泽, 孙启利, 等. 纤维增强树脂基复合材料增材制造技术与装备研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(2):221-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.02.007SHAN Zhongde, FAN Congze, SUN Qili, et al. Research on additive manufacturing technology and equipment for fiber reinforced resin composites[J]. China Mechanical Engnieering,2020,31(2):221-226(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.02.007 [3] 马立敏, 张嘉振, 岳广全, 等. 复合材料在新一代大型民用飞机中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(2):317-322. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20150122.001MA Limin, ZHANG Jiazhen, YUE Guangquan, et al. Application of composites in new generation of large civil aircraft[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(2):317-322(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20150122.001 [4] SUDHIN A, REMANAN M, AJEESH G, et al. Comparison of properties of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic and thermosrtting composites for aerospace applications[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2020,24(2):453-462. [5] ZHAO Y, SUN H, LI Z. Manufacturing technology and its application of aerospace advanced polymer matrix composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2016,46(4):1-7. [6] 沈真, 张晓晶. 复合材料飞机结构强度设计与验证概论[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2011: 25.SHEN Zhen, ZHANG Xiaojing. Introduction to strength design and verification of composite aircraft structure[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2011: 25. [7] XIE P P, ZHU S, PENG W F, et al. Feasibility analysis of autoclave co-curing polymer composite hat-stiffened panels with Silicone airbag mandrels[J]. Iranian Polymer Journals,2019,28:505-514. doi: 10.1007/s13726-019-00718-2 [8] 蒲永伟, 湛利华. 航空先进复合材料帽型加筋构件制造关键技术探究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2015, 4:78-81. doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2015.04.078PU Yongwei, ZHAN Lihua. Study on the key manufacturing technology of aeronautical advanced composite hat-stiffened structures[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2015,4:78-81(in Chinese). doi: 10.16080/j.issn1671-833x.2015.04.078 [9] SUN Z Y, LEI Z K, ZOU J C, et al. Prediction of failure behavior of composite hat-stiffened panels under in-plane shear using artificial neural network[J]. Composite Structures,2021,272(15):114238. [10] TARFAOUI M, MOURMEN A E. Dynamic behavior of top-hat bonded stiffened composite panels: Experimental characterization[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,149(15):216-226. [11] 张国凡, 孙侠生, 吴存利. 复合材料帽型加筋壁板的失效机制分析与改进设计[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(11):2479-2486.ZHANG Guofan, SUN Xiasheng, WU Cunli. Failure mecha-nism analysis and design of omega stiffened composite panel[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(11):2479-2486(in Chinese). [12] 戴征征, 余章杰, 张琪, 等. 含预填块复合材料帽型单筋板弯曲性能研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 54(1):103-113.DAI Zhengzheng, YU Zhangjie, ZHANG Qi, et al. Bending property of composite hat-stiffened panel with pre-filled blocks[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics,2022,54(1):103-113(in Chinese). [13] 李哲夫, 谈源, 张俭, 等. 热模压预成型工艺参数对复合材料帽型长桁质量的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10):3270-3280. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201215.004LI Zhefu, TAN Yuan, ZHANG Jian, et al. Effects of hot stamp forming process parameters on quality of the hat-shaped structure preforms of composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(10):3270-3280(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20201215.004 [14] SALA G. Advances in elastomeric tooling technology[J]. Material & Design,1996,17(1):33-42. [15] KIM G H, CHOI J H, KWEON J H. Manufacture and performance evaluation of the composite hat-stiffened panel[J]. Composite Structures, 2010, 92: 2276-2284. [16] 马成, 赵聪, 刘兴宇, 等. 气囊硬度对固化后帽型长桁厚度的影响[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(6):422667. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22667MA Cheng, ZHAO Cong, LIU Xingyu, et al. Effect of airbag hardness on thickness of hat-shaped stringer[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2019,40(6):422667(in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22667 [17] LI S J, PU Y W, ZHAN L H, et al. Effect of mandrel structures on co-curing quality for polymer composite hat-stiffened structures[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2015,16(9):1898-1907. doi: 10.1007/s12221-015-5051-1 [18] 邢丽英, 蒋诗才, 周正刚. 先进树脂基复合材料制造技术进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(2):1-9. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2013.02.028XING Liying, JIANG Shicai, ZHOU Zhenggang. Progress of manufacturing technology development of advanced polymer matrix composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(2):1-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2013.02.028 [19] XIN C B, GU Y Z, LI M, et al. Online monitoring and analysis of resin pressure inside composite laminate during zero-bleeding autoclave process[J]. Polymer Composites,2011,32(2):314-323. doi: 10.1002/pc.21048 [20] GU Y Z, XIN C B, LI M, et al. Resin pressure and resin flow inside tapered laminates during zero-bleeding and bleeding processes[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2012,31(4):205-214. doi: 10.1177/0731684411434149 [21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 碳纤维增强塑料孔隙含量和纤维体积含量试验方法: GB/T 3365—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.National Standardization Administration of China. Test method for void content and fiber volume content of carbon fiber reinforced plastics: GB/T 3365—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: