Recent advances in thermosetting resin-based composite phase change materials and enhanced phase change energy storage
-
摘要: 热固性树脂是一种能够在加热或辐射条件下发生交联反应而固化,逐渐硬化成型的树脂类材料,具有耐热性高,受压不易变形等优点,广泛应用于涂料、胶粘剂、电子封装等领域。现有研究表明,由于热固性树脂受热后的固化成型,可有效解决固-液相变材料相变储能过程中泄漏问题。本文从热固性树脂的分类出发,首次系统综述其在相变储能领域的应用研究现状,包括:(1) 基于酚醛树脂封装的定型相变材料研究进展;(2) 基于环氧树脂封装的定型相变材料研究进展;(3) 双环戊二烯石油树脂在相变储能领域应用的可能性。同时,从制备时改性与废弃时处置回收的角度,对热固性树脂强化的相变储能复合材料未来研究重点和发展趋势进行了展望,旨在为拓宽热固性树脂在相变储能领域的应用范围提供有益参考,为制备性能优异的定型相变材料提供更多研究思路。Abstract: Thermosetting resin is a kind of resin material that can be cured by cross-linking reaction under the condition of heating or radiation, and gradually hardened and molded, which has the advantages of high heat resistance and not easily deformed by pressure, and it was widely used in the fields of coating, adhesive and electronic packaging. Existing studies have shown that the problem of leakage during phase change energy storage of solid-liquid phase change materials can be effectively solved due to the curing and molding of thermosetting resin by heat. This paper presents the first review of the current research status of thermosetting resins in the field of phase change energy storage from the classification of thermosetting resins, including: (1) Research progress of stereotyped phase change materials based on phenolic resin encapsulation; (2) Research progress of stereotyped phase change materials based on epoxy resin encapsulation; (3) Possibilities of dicyclopentadiene petroleum resin for phase change energy storage applications. At the same time, the future research focus and development trend of thermoset resin-reinforced phase change energy storage materials are prospected from the perspectives of modification at preparation and disposal and recycling at disposal, aiming to provide useful references for broadening the application scope of thermoset resin in the field of phase change energy storage and to provide more research ideas for the preparation of stereotyped phase change materials with excellent performance.
-
Key words:
- phase change /
- renewable energy /
- polymers /
- thermosetting resin /
- energy storage
-
图 4 PEG/EP复合相变材料的相关研究[43]:(a) EP、PEG、PEG/EP的FTIR图谱;(b) PEG/EP的SEM图像;(c) PEG和PEG/EP的DSC曲线;(d) PEG和PEG/EP的静态热机械分析(TMA)曲线
Figure 4. Research related to PEG/EP composite phase change materials[43]: (a) FTIR spectra of EP, PEG and PEG/EP; (b) SEM image of PEG/EP composite; (c) DSC curves of PEG and PEG/EP; (d) Thermomechanicanalysis (TMA) curves of PEG/EP composite
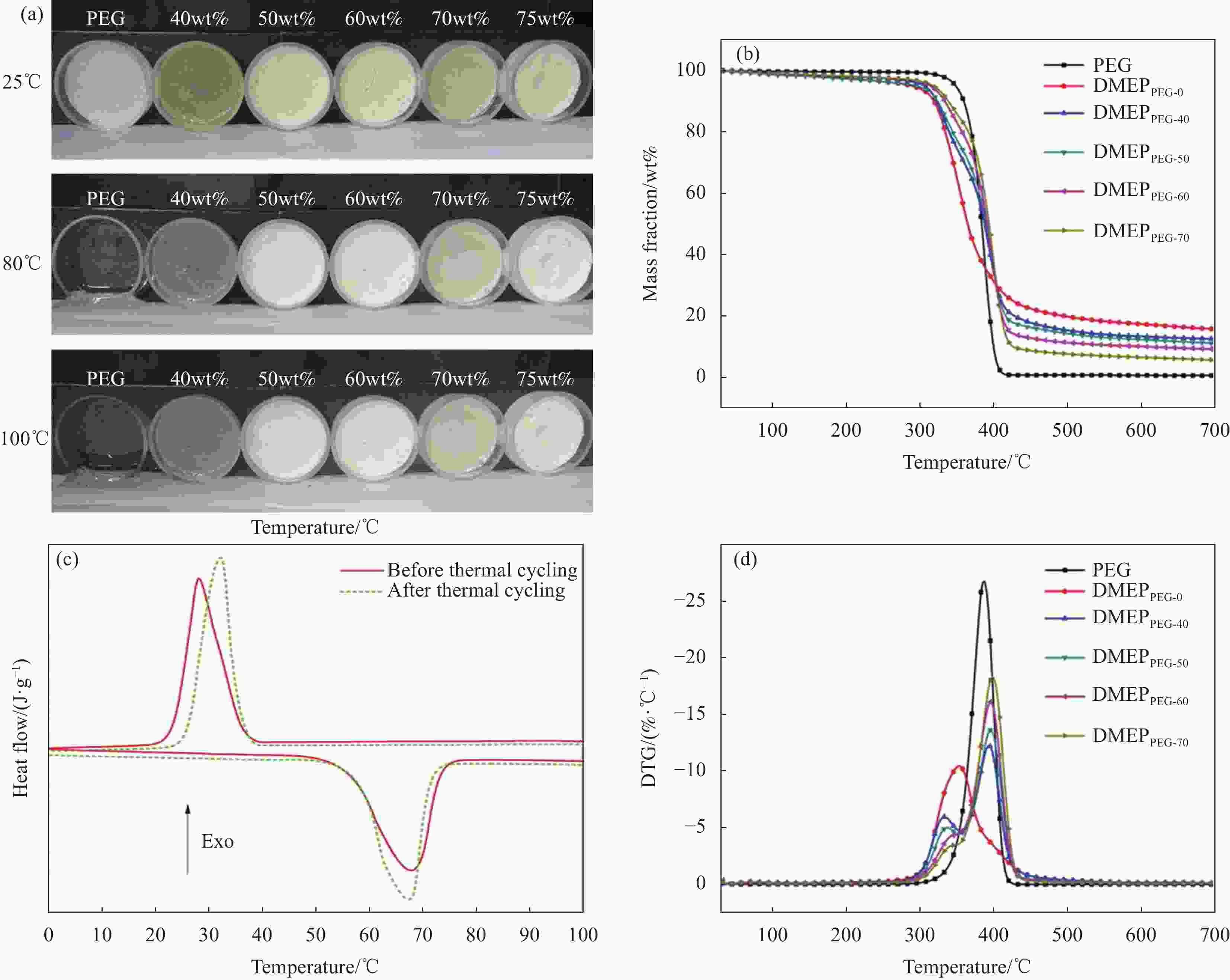
图 6 PEG/改性环氧树脂(DMEP)复合材料的相关研究[48]:(a) PEG和不同PEG质量分数的PEG/DMEP的稳型性能;(b) PEG和PEG/DMEP的TG曲线;(c) DMEPPEG-70 100次热循环前(实线)和后(虚线)的DSC曲线;(d) PEG和PEG/DMEP的DTG曲线
Figure 6. Correlation study on PEG/modified epoxy resin (DMEP) composites[48]: (a) Shape-stable properties of pristine PEG and PEG/DMEP with different mass fraction of PEG; (b) TG curves of pristine PEG and PEG/DMEP; (c) DCS curves of DMEPPEG-70 before (solid line) and after (dash dot line) 100 times thermal cycles; (d) DTG curves of pristine PEG and PEG/DMEP
x in DMEPPEG-x—Mass fraction of PEG
图 8 石蜡/EP复合材料中石蜡颗粒的相关研究[56-57]:(a) 乳化法制备石蜡颗粒的SEM图像;(b) 石蜡颗粒的SEM图像;(c) 石蜡颗粒的制备过程
Figure 8. Correlation study of paraffin particles in paraffin/EP composites materials[56-57]: (a) SEM image of paraffin particles produced by the emulsification method; (b) SEM image of paraffin particles; (c) Scheme representing synthesis of paraffin particles
图 9 费托蜡(FT蜡)/环氧树脂复合材料相关研究[62]:(a) 70/30 w/w环氧树脂/FT蜡断裂表面的SEM图像;(b) 70/30 w/w环氧树脂/FT蜡加热至140℃冷却后断裂表面的SEM图像;(c) 研究样品的DSC加热曲线;(d) 研究样品的DSC冷却曲线;(e) 研究样品的热重曲线(表内的T20wt%为质量损失20wt%时温度的平均值,括号内为标准差);(f) 储存模量随温度的变化
Figure 9. Correlation study on Fischer-Tropsch paraffin wax (wax FT)/epoxy resin composites[62]: (a) SEM image of fractured surfaces of 70/30 w/w wax FT/epoxy; (b) SEM image of fractured surfaces of 70/30 w/w wax FT/epoxy after heating to 140℃ and cooling; (c) DSC heating curves of the investigated samples; (d) DSC cooling curves of the investigated samples; (e) TGA curves of the investigated samples (T20wt% in table inset gives average values, with standard deviations in brackets, of temperatures at 20wt% mass loss); (f) Storage modulus as function of temperature of the investigated samples
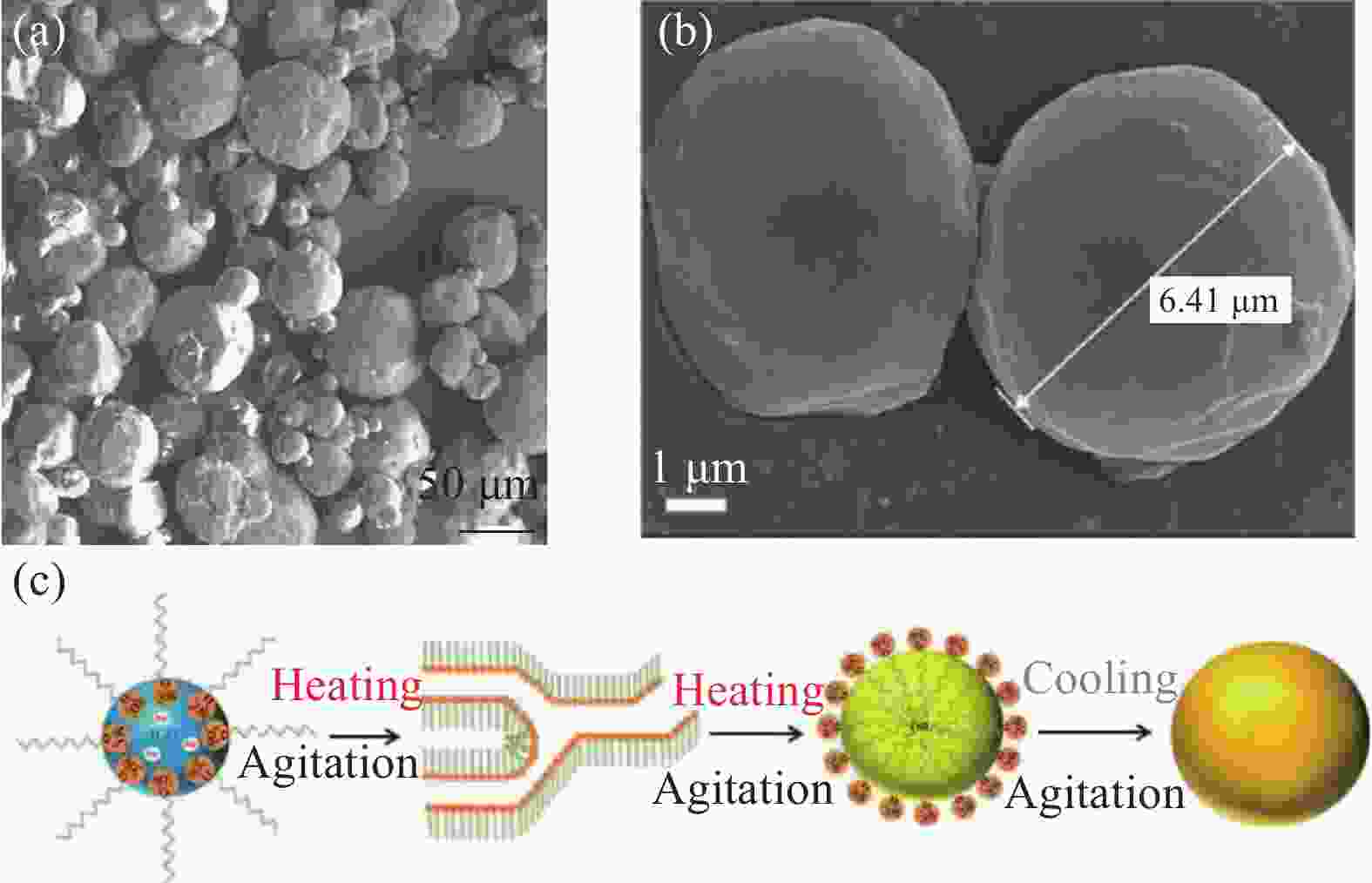
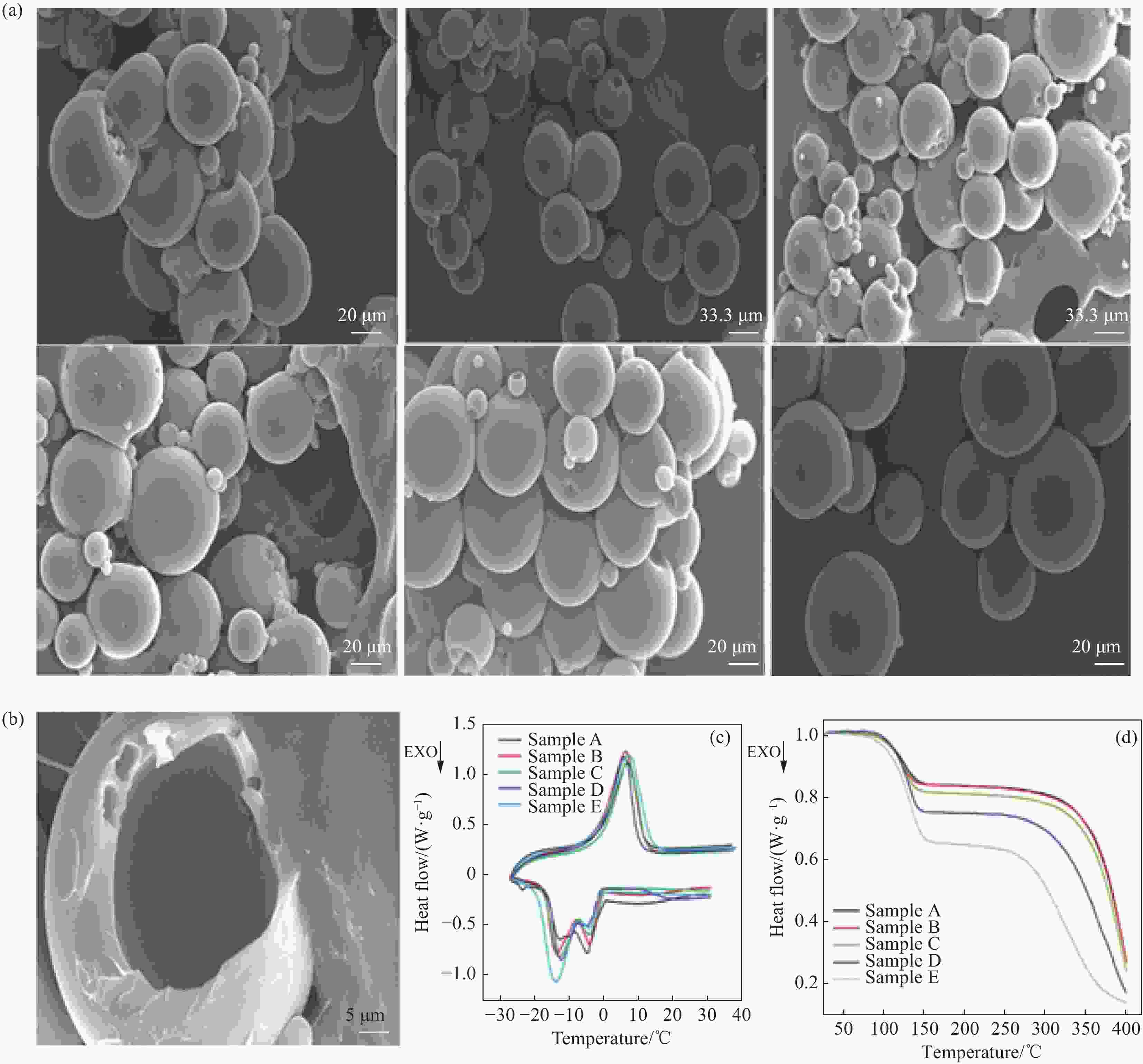
图 10 正十四烷-二甲苯@环氧树脂相变微胶囊的热性能[25]:(a) 样品A、B、C、D、E和G的SEM图像;(b) 微相变材料粉碎后(样品C)的SEM图像;样品A、B、C、D和E的DSC曲线 (c) 和TGA曲线 (d)
Figure 10. Thermal properties of n-tetradecane- dimethylbenzene@epoxy resin phase change microcapsules[25]: (a) SEM images of samples A, B, C, D, E and G; (b) SEM image of crushed micro phase change materials (sample C); DSC curves (c) and TGA curves (d) of samples A, B, C, D and E
图 11 新戊二醇(NPG)/环氧树脂复合相变储能材料的性能图[26]:(a) EP、NPG、NPG/EP复合材料的FTIR图谱;(b) NPG/EP复合材料的SEM图像;(c) NPG/EP复合材料的DSC曲线;(d) NPG/EP复合材料经过100次热循环试验后的DSC曲线
Figure 11. Performance diagram of neopentyl glycol (NPG)/epoxy resin composite phase change energy storage material[26]: (a) FTIR spectra of EP, NPG, NPG/EP composite; (b) SEM image of NPG/EP composite; (c) DSC curve of NPG/EP composite; (d) DSC curve of NPG/EP composite after 100 times thermal cycling test
△H—Latent heat of phase change; Te—Melting temperature
-
[1] WANG B, WANG Q, WEI Y, et al. Role of renewable energy in China’s energy security and climate change mitigation: An index decomposition analysis[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,90:187-194. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.03.012 [2] LIU J. China’s renewable energy law and policy: A critical review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2019,99:212-219. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2018.10.007 [3] 刘昌会, 刘红莉, 张天键, 等. 基于尿素/氯化胆碱低共熔溶剂体系纳米流体制备及其热物性研究[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(3):1333-1341.LIU C H, LIU H L, ZHANG T J, et al. Preparation and thermal physical properties of nanofluids based on a urea/choline chloride deep eutectic solvent system[J]. CIESC Journal,2021,72(3):1333-1341(in Chinese). [4] 蒯子函, 闫霆, 吴韶飞, 等. 硬脂醇/膨胀石墨复合相变材料的制备及储热性能[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(S1):301-310.KUAI Z H, YAN T, WU S F, et al. Fabrication and heat storage properties of stearyl alcohol/expanded graphite composite phase change materials[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(S1):301-310(in Chinese). [5] 陈赛, 陶丽娟, 李伟, 等. ZIF-8/丙烯酸十四-十六酯共聚物和PB/丙烯酸十四-十六酯共聚物形状稳定相变材料的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(11):3896-3903.CHEN S, TAO L J, LI W et al. Fabrication and characterization of shape-stabilized phase change materials of ZIF-8/P(tetradecyl acrylate-co-hexadecyl acrylate) and prussian blue/(tetradecyl acrylate-co-hexadecyl acrylate)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(11):3896-3903(in Chinese). [6] TANG F, CAO L, FANG G. Preparation and thermal properties of stearic acid/titanium dioxide composites as shape-stabilized phase change materials for building thermal energy storage[J]. Energy and Buildings,2014,80:352-357. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2014.05.030 [7] 吴韶飞, 闫霆, 蒯子函, 等. 高导热膨胀石墨/棕榈酸定形复合相变材料的制备及储热性能研究[J]. 化工学报, 2019, 70(9):3553-3564.WU S F, YAN T, KUAI Z H, et al. Preparation and thermal energy storage properties of high heat conduction expanded graphite/palmitic acid form-stable phase change materials[J]. CIESC Journal,2019,70(9):3553-3564(in Chinese). [8] 李海丽, 季旭, 冷从斌, 等. 膨胀石墨/五水硫代硫酸钠相变储能复合材料热性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(12):2941-2951.LI H L, JI X, LENG C B, et al. Thermal performance of expanded graphite/ Na2S2O3·5H2O phase change storage composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(12):2941-2951(in Chinese). [9] GOITANDIA A M, BEOBIDE G, ARANZABE E, et al. Development of content-stable phase change composites by infiltration into inorganic porous supports[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells,2015,134:318-328. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2014.12.010 [10] YAN Q, LIU C, ZHANG J. Experimental study on thermal conductivity of composite phase change material of fatty acid and paraffin[J]. Materials Research Express,2019,6(6):65507. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab0d5e [11] LI C, YU H, SONG Y, et al. Novel hybrid microencapsulated phase change materials incorporated wallboard for year-long year energy storage in buildings[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2019,183:791-802. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2019.01.036 [12] 马芹永, 白梅. 相变储能混凝土的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(3):676-683.MA Q Y, BAI, M. Preparation and properties phase-changing energy-storing concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(3):676-683(in Chinese). [13] GAO H, WANG J, CHEN X, et al. Nanoconfinement effects on thermal properties of nanoporous shape-stabilized composite PCMs: A review[J]. Nano Energy,2018,53:769-797. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.09.007 [14] SU W, DARKWA J, KOKOGIANNAKIS G. Review of solid–liquid phase change materials and their encapsulation technologies[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2015,48:373-391. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.044 [15] 周四丽, 张正国, 方晓明. 固-固相变储热材料的研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2021, 40(3):1371-1383.ZHOU S L, ZHANG Z G, FANG X M. Research progress of solid-solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(3):1371-1383(in Chinese). [16] YANG H, WANG S, WANG X, et al. Wood-based composite phase change materials with self-cleaning superhydrophobic surface for thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Energy,2020,261:114481. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114481 [17] LI C, YU H, SONG Y, et al. A n-octadecane/hierarchically porous TiO2 form-stable PCM for thermal energy storage[J]. Renewable Energy,2020,145:1465-1473. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.070 [18] SARI A, BICER A, AL-SULAIMAN F A, et al. Diatomite/CNTs/PEG composite PCMs with shape-stabilized and improved thermal conductivity: Preparation and thermal energy storage properties[J]. Energy and Buildings,2018,164:166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2018.01.009 [19] ABDEALI G, BAHRAMIAN A R, ABDOLLAHI M. Review on nanostructure supporting material strategies in shape-stabilized phase change materials[J]. Journal of Energy Storage,2020,29:101299. doi: 10.1016/j.est.2020.101299 [20] MA S, WEBSTER D C. Degradable thermosets based on labile bonds or linkages: A review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2018,76:65-110. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.07.008 [21] MASHOUF R G, MOHANTY A K, MISRA M. Green approaches to engineer tough biobased epoxies: A review[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2017,5(11):9528-9541. [22] MA S, LI T, LIU X, et al. Research progress on bio-based thermosetting resins[J]. Polymer International,2016,65(2):164-173. doi: 10.1002/pi.5027 [23] LIU J, WANG S, PENG Y, et al. Advances in sustainable thermosetting resins: From renewable feedstock to high performance and recyclability[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2021,113:101353. [24] SAMANI F, BAHRAMIAN A R, SHARIF A. Shape-stable phenolic/polyethylene glycol phase change material: Kinetics study and improvements in thermal properties of nanocomposites[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal,2018,27(7):495-505. doi: 10.1007/s13726-018-0626-5 [25] WEI K, MA B, WANG H, et al. Synthesis and thermal properties of novel microencapsulated phase-change materials with binary cores and epoxy polymer shells[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2017,74(2):359-367. doi: 10.1007/s00289-016-1718-z [26] MENG D, ZHAO K, ZHAO W, et al. Preparation and properties of neopentyl glycol/epoxy resin composite phase change material for thermal energy storage[C]//4th Annual International Conference on Material Science and Environmental Engineering (MSEE), Chengdu, 2016: 669-678. [27] MUC A, ROMANOWICZ P, CHWAŁ M. Description of the resin curing process—Formulation and optimization[J]. Polymers,2019,11(1):127. doi: 10.3390/polym11010127 [28] LIU J, ZHANG L, SHUN W, et al. Recent development on bio-based thermosetting resins[J]. Journal of Polymer Science,2021,59(14):1474-1490. doi: 10.1002/pol.20210328 [29] 陈杰, 马春柳, 刘邦, 等. 热固性树脂及其固化剂的研究进展[J]. 塑料科技, 2019, 47(2):95-102.CHEN J, MA C L, LIU B, et al. Research progress of thermosetting resins and their curing agents[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2019,47(2):95-102(in Chinese). [30] 王哲, 祖愿, 胡方圆, 等. 含杂萘联苯结构的环氧树脂固化动力学分析[J]. 化工学报, 2022, 73(02):681-688.WANG Z, ZU Y, HU F Y, et al. Kinetic analysis of curing of epoxy resin containing phthalazinone structure[J]. CIESC Journal,2022,73(02):681-688(in Chinese). [31] 钟辉, 黄红军, 王晓梅, 等. 环氧固化剂及其应用与发展[J]. 装备环境工程, 2016, 13(4):136-142.ZHONG H, HUANG H J, WANG X M, et al. Application and development of epoxy curing agent[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering,2016,13(4):136-142(in Chinese). [32] 吴丽梅, 刘庆欣, 王晓龙, 等. 相变储能材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(S1):501-506.WU L M, LIU Q X, WANG X L, et al. Review on phase change energy storage materials[J]. Materials Reports,2021,35(S1):501-506(in Chinese). [33] LIU Y, YU J K. Study on the curing process of allyl phenol-formaldehyde resin[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2011,282-283:143-146. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.282-283.143 [34] JIANG Y, WANG D, ZHAO T. Preparation, characterization, and prominent thermal stability of phase-change microcapsules with phenolic resin shell and n-hexadecane core[J]. Journal of applied polymer science,2007,104(5):2799-2806. doi: 10.1002/app.25962 [35] DOWDING P J, ATKIN R, VINCENT B, et al. Oil core/polymer shell microcapsules by internal phase separation from emulsion droplets. II: Controlling the release profile of active molecules[J]. Langmuir,2005,21(12):5278-5284. doi: 10.1021/la0470838 [36] DOWDING P J, ATKIN R, VINCENT B, et al. Oil core−polymer shell microcapsules prepared by internal phase separation from emulsion droplets. I. Characterization and release rates for microcapsules with polystyrene shells[J]. Langmuir,2004,20(26):11374-11379. doi: 10.1021/la048561h [37] ATKIN R, DAVIES P, HARDY J, et al. Preparation of aqueous core/polymer shell microcapsules by internal phase separation[J]. Macromolecules,2004,37(21):7979-7985. doi: 10.1021/ma048902y [38] LOXLEY A, VINCENT B. Preparation of poly(methylmethacrylate) microcapsules with liquid cores[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,1998,208(1):49-62. doi: 10.1006/jcis.1998.5698 [39] YANG H, FENG L, WANG C, et al. Confinement effect of SiO2 framework on phase change of PEG in shape-stabilized PEG/SiO2 composites[J]. European Polymer Journal,2012,48(4):803-810. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2012.01.016 [40] TANG B, WU C, QIU M, et al. PEG/SiO2-Al2O3 hybrid form-stable phase change materials with enhanced thermal conductivity[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2014,144(1-2):162-167. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.12.036 [41] ZHANG X, WEN R, TANG C, et al. Thermal conductivity enhancement of polyethylene glycol/expanded perlite with carbon layer for heat storage application[J]. Energy and Buildings,2016,130:113-121. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2016.08.049 [42] LIN F, ZHANG W, SHI T, et al. Thermally conductive and shape-stabilized polyethylene glycol/carbon foam phase-change composites for thermal energy storage[J]. Che-mistrySelect,2020,5(11):3217-3224. doi: 10.1002/slct.201904489 [43] FANG Y, KANG H, WANG W, et al. Study on polyethylene glycol/epoxy resin composite as a form-stable phase change material[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2010,51(12):2757-2761. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2010.06.012 [44] WANG T, WANG C, CHEN K, et al. Preparation, thermal, and mechanical properties of polyethylene glycol/expoxy resin composites as form-stable phase change materials[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2022, 62(2): 520-529. [45] ZHAO C S, LI N, WU L Y, et al. Preparation of epoxy/PEG shape-stabilized phase change materials by in situ reactive blending[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2012,430-432:1023-1027. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.430-432.1023 [46] SABAGH S, BAHRAMIAN A R, MADADI M H. Improvement in phase-change hybrid nanocomposites material based on polyethylene glycol/epoxy/graphene for thermal protection systems[J]. Iranian Polymer Journal,2020,29(2):161-169. doi: 10.1007/s13726-020-00783-y [47] LIU Z, WEI K, WANG S, et al. Effect of high-temperature-resistant epoxy resin/polyethylene glycol 2000 composite stereotyped phase change material particles on asphalt properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,300:124007. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124007 [48] WU B, JIANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Study on a PEG/epoxy shape-stabilized phase change material: Preparation, thermal properties and thermal storage performance[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2018,126:1134-1142. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.05.153 [49] LIN C H, WANG C S. Novel phosphorus-containing epoxy resins Part I. Synthesis and properties[J]. Polymer (Guilford),2001,42(5):1869-1878. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(00)00447-X [50] JIANG J, CHENG Y, LIU Y, et al. Intergrowth charring for flame-retardant glass fabric-reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(8):4284-4429. doi: 10.1039/C4TA06486K [51] WANG C S, LIN C H. Synthesis and properties of phosphorus-containing epoxy resins by novel method[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry,1999,37(21):3903-3909. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0518(19991101)37:21<3903::AID-POLA4>3.0.CO;2-X [52] SUNDARARAJAN S, KUMAR A, CHAKRABORTY B C, et al. Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-modified epoxy phase-change polymer with dual properties of thermal storage and vibration damping[J]. Sustainable Energy& Fuels,2018,2(3):688-697. [53] 王俊霞, 王军, 黄崇杏, 等. 多壁碳纳米管/硬脂酸-十八醇@脲醛树脂微胶囊的制备及表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(3):730-738.WANG J X, WANG J, HUANG C X, et al. Preparation and characterization of MWCNTs/stearic acid-octadecyl alcohol@ urea formaldehyde resin phase change microencapsules[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae sinica,2019,36(3):730-738(in Chinese). [54] LUO F, YAN P, QIAN Q, et al. Highly thermally conductive phase change composites for thermal energy storage featuring shape memory[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,129:105706. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105706 [55] WANG Z, SITU W, LI X, et al. Novel shape stabilized phase change material based on epoxy matrix with ultrahigh cycle life for thermal energy storage[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2017,123:1006-1012. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.179 [56] PENG S, FUCHS A, WIRTZ R A. Polymeric phase change composites for thermal energy storage[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2004,93(3):1240-1251. doi: 10.1002/app.20578 [57] KHAGOKPAM G K S, HALDER S. Paraffin wax microsphere embedded epoxy composites for potential thermal management in electronic devices[J]. High Performance Polymers,2018,31(7):767-777. [58] 刘昌会, 张海悦, 李业美, 等. 低共熔溶剂在储能与传热方面的研究进展[J]. 化工学报, 2021, 72(10):4973-4986.LIU C H, ZHANG H Y, LI Y M, et al. Recent advances of deep eutectic solvents in energy storage and heat transfer[J]. CIESC Journal,2021,72(10):4973-4986(in Chinese). [59] AGRAWAL R, HANNA J, GUNDUZ I E, et al. Epoxy-PCM composites with nanocarbons or multidimensional boron nitride as heat flow enhancers[J]. Molecules,2019,24(10):1883. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101883 [60] ARCE M, ALVAREZ F M, SUAREZ G A, et al. Novel formulations of phase change materials—Epoxy composites for thermal energy storage[J]. Materials,2018,11(2):195. doi: 10.3390/ma11020195 [61] ARCE E, AGRAWAL R, SUÁREZ A, et al. Modeling of energy demand and savings associated with the use of epoxy-phase change material formulations[J]. Materials,2020,13(3):639. doi: 10.3390/ma13030639 [62] LUYT A S, KRUPA I. Phase change materials formed by UV curable epoxy matrix and Fischer-Tropsch paraffin wax[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2009,50(1):57-61. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2008.08.026 [63] LIAN Q, LI Y, SAYYED A A S, et al. Facile strategy in designing epoxy/paraffin multiple phase change materials for thermal energy storage applications[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(3):3375-3384. [64] FREDI G, DIRÈ S, CALLONE E, et al. Docosane-organosilica microcapsules for structural composites with thermal energy storage/release capability[J]. Materials,2019,12(8):1286. doi: 10.3390/ma12081286 [65] WANG X, MA B, WEI K, et al. Thermal stability and mechanical properties of epoxy resin/microcapsule composite phase change materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,312:125392. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125392 [66] REN X, SHEN H, YANG Y, et al. Study on the properties of a novel shape-stable epoxy resin sealed expanded graphite/paraffin composite PCM and its application in buildings[J]. Phase Transitions,2019,92(6):581-594. doi: 10.1080/01411594.2019.1610174 [67] YOSHIDA K, KOZAKO M, ISHIBE S, et al. Dielectric properties of olefin-based thermosetting resin for application to electrical insulating material[C]//The Institute of Electrical Engineers. Niigata, 2014: 378-380. [68] YOSHIDA K, KOZAKO M, ISHIBE S, et al. Evaluation on applicability to electrical insulating material of hydrocarbon-based thermosetting resin[J]. Electronics and Communications in Japan,2017,100(4):83-90. doi: 10.1002/ecj.11953 [69] OHZUNO K, ABE K, KOZAKO M, et al. Estimation of electron trap in hydrocarbon-based thermosetting resin/fullerene composite by computational science[C]//2019 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP). Richland, 2019: 749-752. [70] KOVAČIČ S, KRAJNC P, SLUGOVC C. Inherently reactive polyHIPE material from dicyclopentadiene[J]. Chemical Communications,2010,46(40):7504. doi: 10.1039/c0cc02610g [71] KIEFER J, HILBORN J G, HEDRICK J L. Chemically induced phase separation: A new technique for the synthesis of macroporous epoxy networks[J]. Polymer,1996,37(25):5715-5725. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(96)00436-3 [72] DELLA M A, HILBORN J G, MÜHLEBACH A. Macroporous cross-linked poly(dicyclopentadiene)[J]. Macromolecules,2000,33(8):2916-2921. doi: 10.1021/ma990953l -





 下载:
下载: