Preparation of ZnO modified stainless steel mesh with controllable wettability and its oil-water separation performance
-
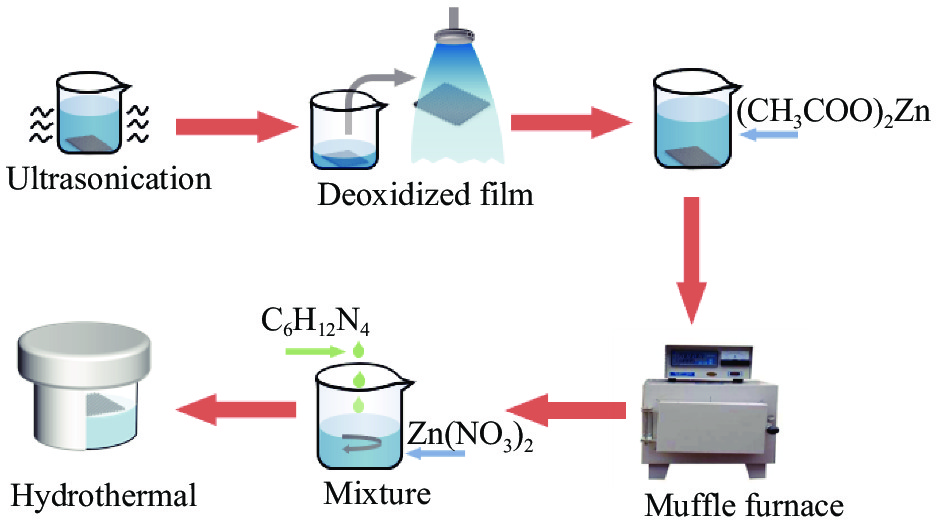
摘要: 为了制备出具有可控润湿性的不锈钢滤网,并根据其相关特性用于研究油水分离性能,本文通过水热法在不锈钢表面生长一层氧化锌,构造微纳米粗糙度,随后用不同链长的脂肪酸改性的方法,成功制备出具有可控润湿性的不锈钢滤网。采用接触角测量仪、FTIR、SEM及XRD等分别对样品的润湿性和表面形貌及成分进行分析,采用油水分离装置表征样品的油水分离效率及重复使用性。结果表明依据不同链长的脂肪酸改性的样品出现了从超亲水到超疏水的润湿性变化,范围为0°~158°,油始终保持在0°。油水分离效率在92%~98%,重复使用50次后,仍然具有油水分离的性能。因此,制备的不锈钢滤网具有优异的油水分离性能和良好的重复使用性能。Abstract: In order to prepare stainless steel filter with controllable wettability and oil-water separation property, a layer of zinc oxide was grown on the surface of stainless steel by hydrothermal method to construct micro-nano roughness. Then, a stainless steel filter with controllable wettability was successfully prepared by modification of fatty acids with different chain lengths. The wettability, surface morphology and composition of the samples were analyzed by contact angle measuring instrument, FTIR, SEM and XRD, respectively. The oil-water separation efficiency and reusability of the samples were characterized by oil-water separation device. The results show that the wettability of the samples modified by fatty acids with different chain lengths varie from superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic, ranging from 0° to 158°, and the oil remain at 0°. The oil-water separation efficiency is 92%-98%, and it still has oil-water separation performance after repeated use for 50 times. Therefore, the prepared stainless steel filter has excellent oil-water separation performance and good reuse performance.
-
Key words:
- manipulation of wettability /
- oil-water separation /
- stainless steel mesh /
- hydrothermal /
- ZnO /
- fatty acids
-
表 1 不同液体的表面张力及密度
Table 1. Surface tension and density of different liquids
Liquids Water 1,1-dichloromethane Chloroform Kerosene n-heptane Petrol Surface tension/(mN·m−1) 72 28 29 24 20 22 Density/(g·mL−1) 1 1.32 1.5 0.8 0.683 0.75 -
[1] YUAN J, GAO R, WANG Y Y, et al. A novel hydrophobic adsorbent of electrospun SiO2@MUF/PAN nanofibrous membrane and its adsorption behaviour for oil and organic solvents[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2018,53:16357-16370. doi: 10.1007/s10853-018-2795-1 [2] NGUYEN S T, FENG J D, LE N T, et al. Cellulose aerogel from paper waste for crude oil spill cleaning[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2013,52:18386-18391. [3] XIE H, WU Z, WANG Z, et al. Facile fabrication of acid-re-sistant and hydrophobic Fe3O4@SiO2@C magnetic particles for valid oil-water separation application[J]. Surfaces and Interfaces,2020,21:100651. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2020.100651 [4] ARNE J. How to defend against future oil spills[J]. Nature, 2010, 466: 182–183. [5] CHEN Y C, LI X F, XU Q, et al. SAR observation and model tracking of an oil spill event in coastal waters[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2011,62:350-363. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.10.005 [6] JANE H C Ø, FOSSEN M, FAROOQ U, et al. Study on how oil type and weathering of crude oils affect interaction with sea ice and polyethylene skimmer material[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2019, 145: 306-315. [7] JAGGI A, RADOVI'C J R, SNOWDON L R, et al. Oldenburg, composition of the dissolved organic matter produced during in situ burning of spilled oil[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2019,138:103926. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2019.103926 [8] LIU Z K, CALLIES U. A probabilistic model of decision making regarding the use of 1 chemical dispersants to combat oil spills in the German Bight[J]. Water Research, 2020, 169: 115196. [9] NAKAJIMA A, ABE K, HASHIMOTO K, et al. Preparation of hard super-hydrophobic films with visible light transmission[J]. Thin Solid Films,2000,376:140-143. doi: 10.1016/S0040-6090(00)01417-6 [10] WANG K X, LI X H, CHEN J S, et al. Surface and interface engineering of electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27:527-545. doi: 10.1002/adma.201402962 [11] ZHANG K J, LI X, MITLIN D, et al. Fundamental insight into Zr Modification of Li-and Mn-Rich cathodes: Combined transmission electron microscopy and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2018,30:2566-2573. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04861 [12] 李志文, 齐博浩, 刘长松, 等. 不锈钢表面润湿性的调控及其油水分离性能[J]. 中国表面工程, 2020, 33(5): 10-17.LI Zhiwen, QI Bohao, LIU Changsong, et al. Manipulation of surface wettability on stainless steel mesh and its oil-waterseparation performance[J]. China Surface Engineering, 2020, 33(5): 10-17(in Chinese). [13] 张容容. 超亲水及水下超疏油表面的制备及其油水分离性能的研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2016.ZHANG Rongrong. Preparation of superhydrophilic and underwater superhydrophobic surfaces and their oil-water separation properties[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2016(in Chinses). [14] WENZEL R N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1936,28(8):988-994. [15] YAN Y Y, GAO N, BARTHLOTT W. Mimicking natural super-hydrophobic surfaces and grasping the wetting process: A review on recent progress in preparing superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,2011,169(2):80-105. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2011.08.005 [16] SHUSTAK G, DOMB A J, MANDLER D, et al. Preparation and characterization of n-alkanoic acid self-assembled monolayers adsorbed on 316L stainless steel[J]. Langmuir,2004,20(18):7499-7506. doi: 10.1021/la036470z [17] GUSTAFSSON L, JANSSON R, HEDHAMMAR M, et al. Structuring of functional spider silk wires, coatings, and sheets by self-assembly on superhydrophobic pillar surfaces[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(3):1704325. doi: 10.1002/adma.201704325 [18] GAO A, WU Q, WANG D, et al. A superhydrophobic surface templated by protein self-assembly and emerging application toward protein crystallization[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(3):579-587. doi: 10.1002/adma.201504769 [19] CASSIE A B D, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surfaces[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1944,40:546-551. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [20] TAOY T. Structural comparison of self-assembled monolayers of n-alkanoic acids on the surfaces of silver, copper, and aluminum[J]. Journal of the American Chemi-cal Society,1993,115(10):4350-4358. doi: 10.1021/ja00063a062 [21] RAMAN A, GAWALT E S. Self-assembled monolayers of alkanoic acids on the native oxide surface of SS316L by solution deposition[J]. Langmuir,2007,23(5):2284-2288. doi: 10.1021/la063089g [22] RAMAN A, QUINONES R, BARRIGER L, et al. Understanding organic film behavior on alloy and metal oxides[J]. Langmuir, 2010, 26(3): 1747-1754. [23] NAKAMOTO K, FUJITA J, TANAKA S, et al. Infrared spectra of metallic complexes. IV. Comparison of the infrared spectra of unidentate and bidentate metallic complexes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1957,79(18):4904-4908. doi: 10.1021/ja01575a020 -






 下载:
下载: