Research progress in preparation and application of nanocellulose-based sensors
-
摘要: 可再生纳米纤维素近年来备受关注,纳米纤维素的优势在于来源广泛、制备方法多样、可生物降解、安全无毒、高比表面积、较高强度、较低密度和良好的热稳定性等。本论文主要针对纳米纤维素的制备方法、基于纳米纤维素制备的2D膜材料传感器与3D凝胶材料传感器的应用研究进展进行分析,重点介绍了纳米纤维素基传感器在接近传感、pH传感、电化学传感、葡萄糖传感以及离子传感检测等方面的应用。研究结果表明,纳米纤维素基传感器在灵敏度、力学性能、稳定性、特异性和环境友好性等方面优于一些传统材料制备的传感器,纳米纤维素基传感器具有广阔的潜在应用前景。Abstract: Renewable nanocellulose has attracted much attention in recent years. The advantages of nanocellulose include wide sources, diverse preparation methods, biodegradability, safe and non-toxic, high specific surface area, high strength, low density and good thermal stability. The preparation methods of nanocellulose, and the application research progress of 2D membrane material sensors and 3D gel material sensors based on nanocellulosic materials are mainly introduced. The applications of nanocellulose-based sensors in proximity sensing, pH sensing, electrochemical sensing, glucose sensing and ion sensing detection are highlighted. The results show that the sensitivity, mechanical properties, stability, specificity and environmental friendliness of nanocellulose based sensors are better than those prepared by some traditional materials. Nanocellulose based sensors have broad potential applications.
-
Key words:
- nanocellulose /
- preparation /
- sensor /
- application /
- detection
-
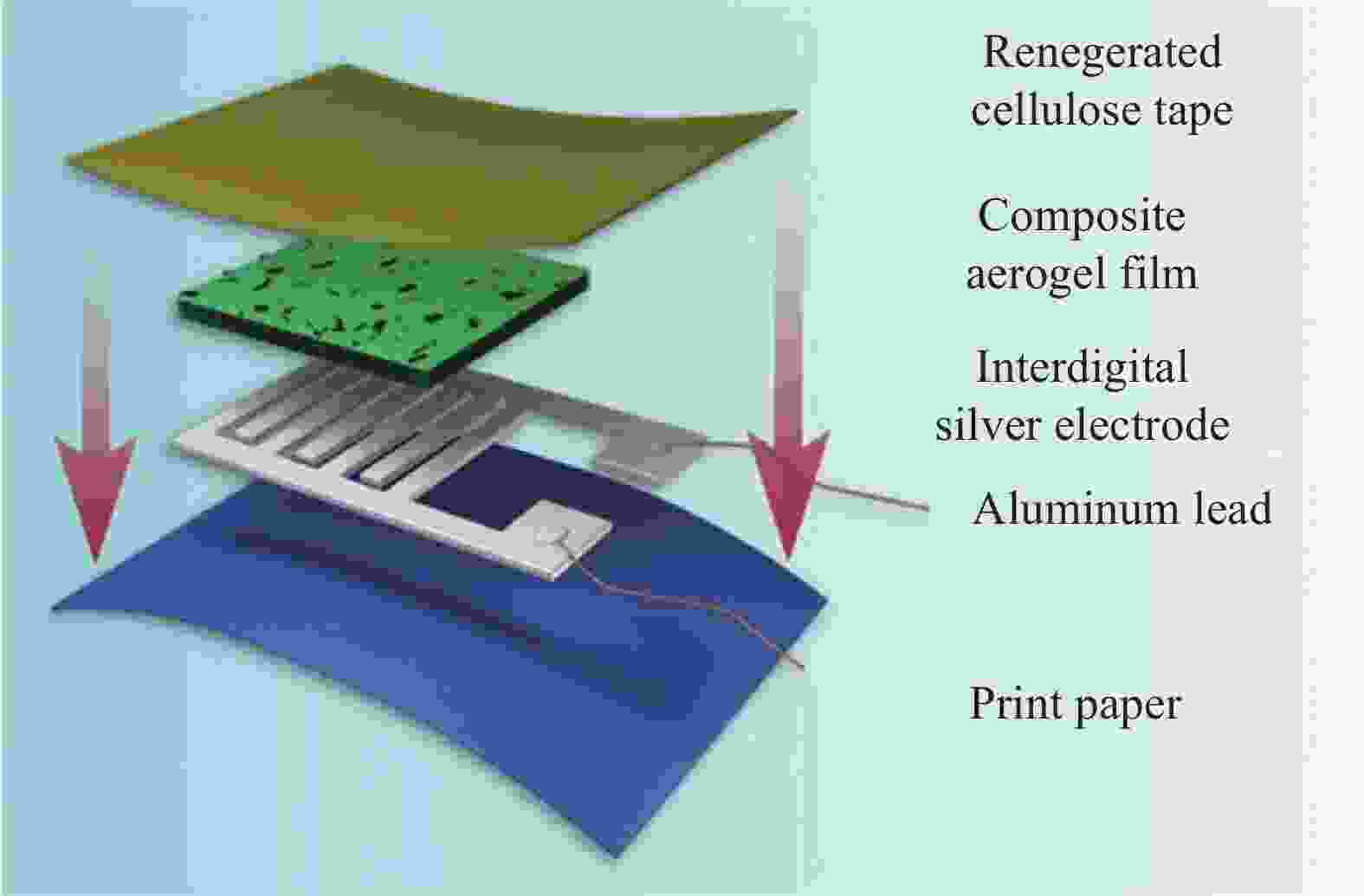
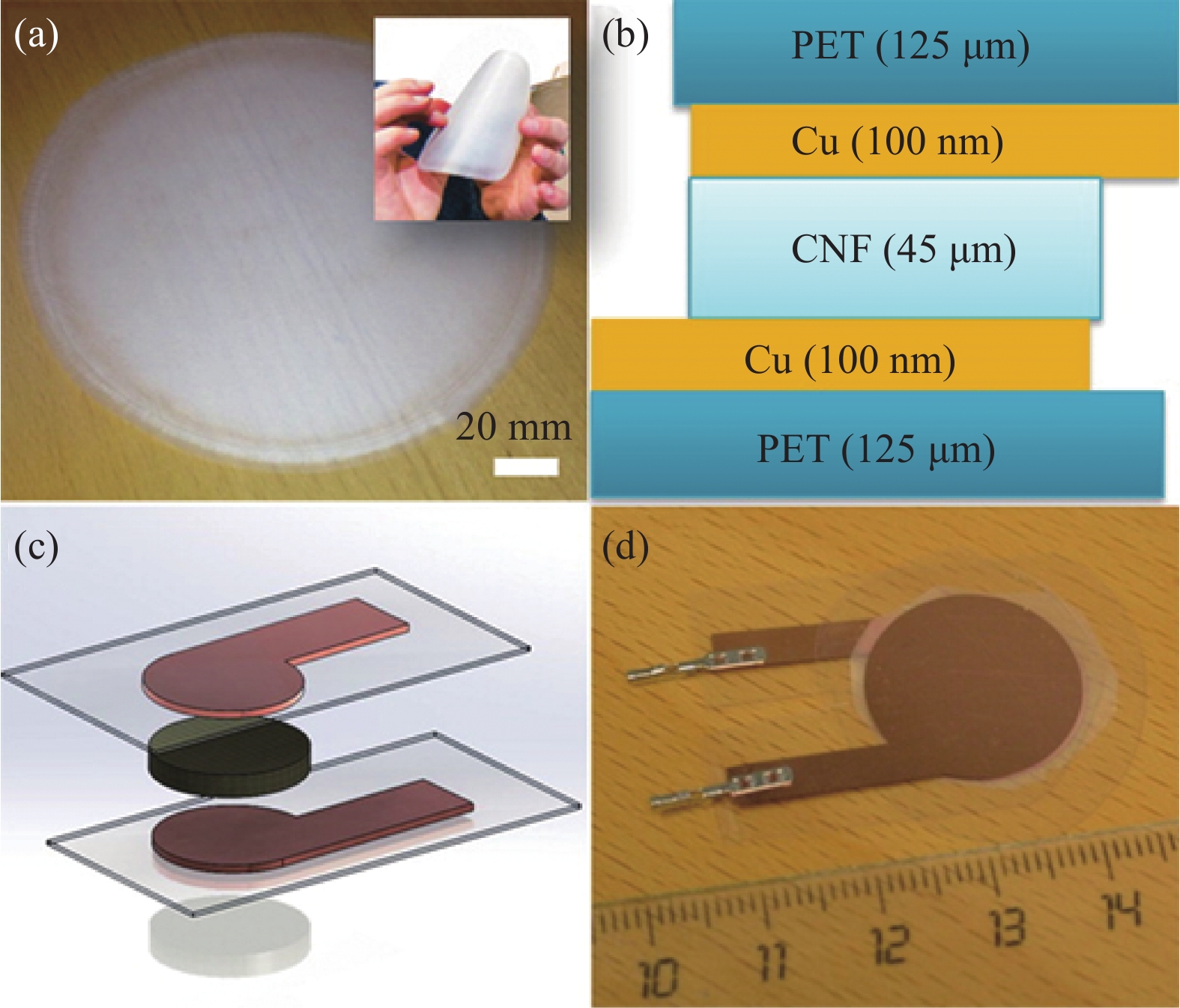
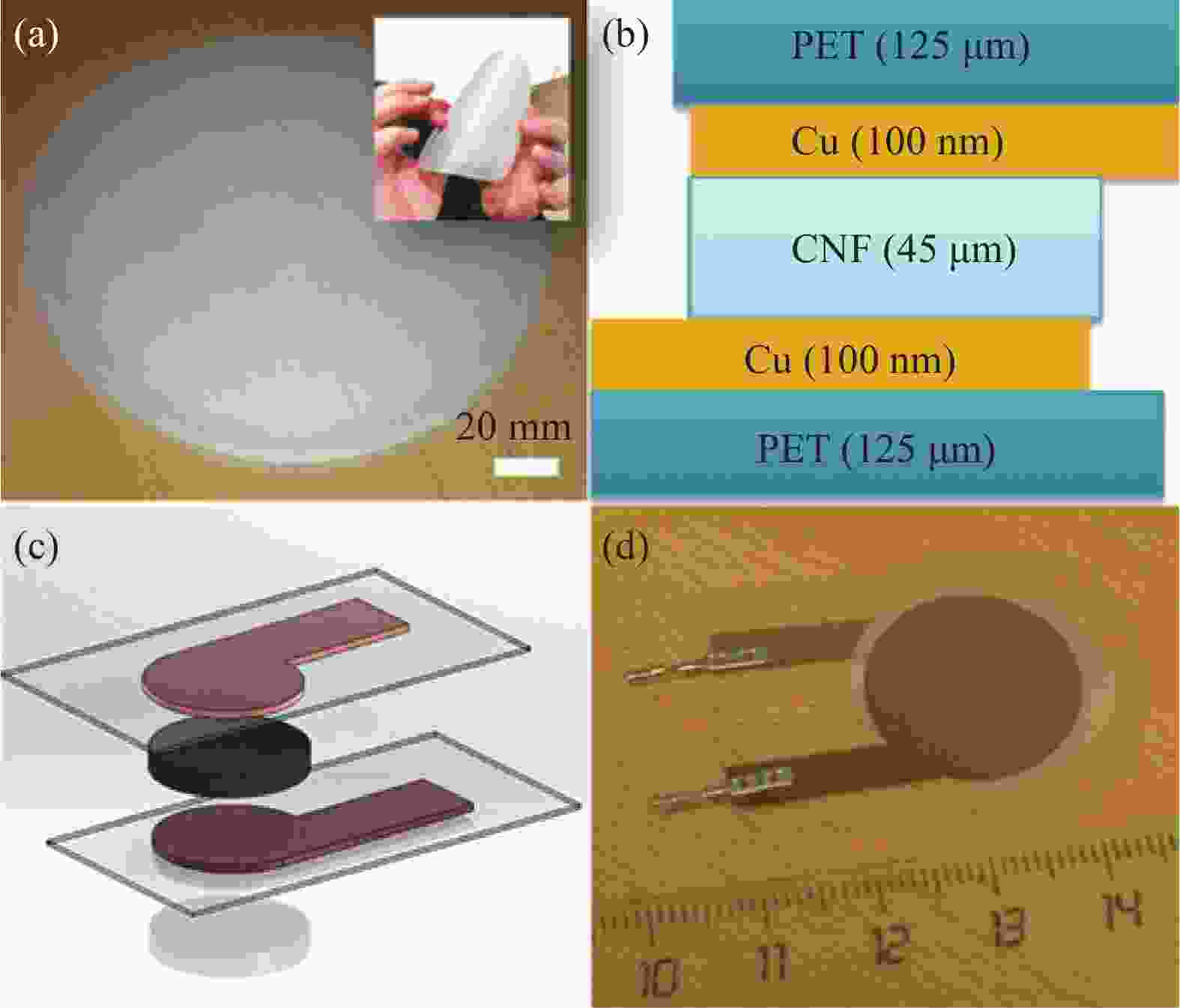
图 1 自支撑纤维素纳米纤丝(CNF) 薄膜及显示其弯曲强度的照片(a), 侧面示意图((b), (c))和组装传感器的照片(d)[30] (经许可转载)
Figure 1. Pictures of a fabricated self-standing cellulose nanofibril (CNF) film and its bending strength (a), schematic side view ((b), (c)) and a picture of assembled sensor (d)[30] (Reprinted with permission)
PET—Polyethylene terephthalate
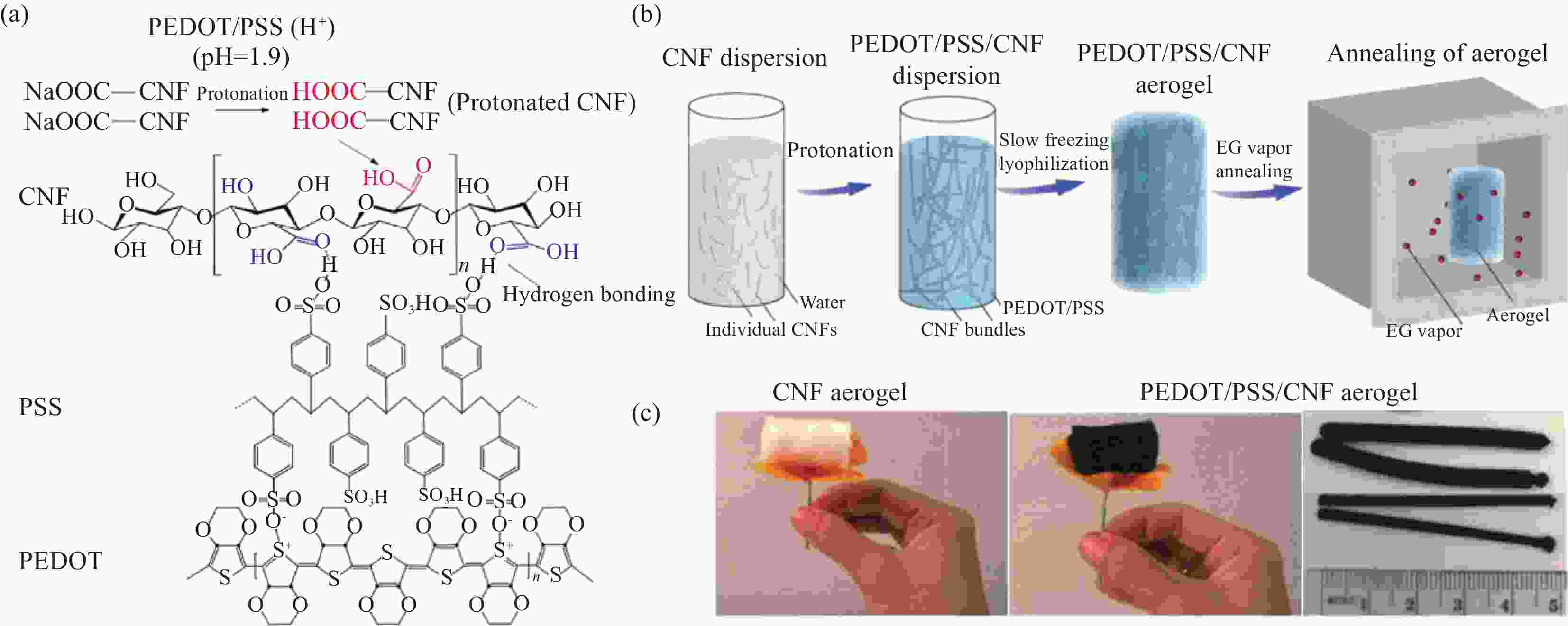
图 3 导电聚 3, 4-乙烯二氧噻吩/聚苯乙烯磺酸/纤维素纳米纤丝(PEDOT/PSS/CNF)气凝胶[45]:(a) PEDOT/PSS中CNF表面羧酸盐的质子化及其与PSS的氢键作用; (b)质子化、冷冻/冻干和乙二醇(EG)蒸汽退火工艺示意图;(c) CNF气凝胶和PEDOT/PSS/CNF气凝胶在加州罂粟上面的图片和不同直径的圆柱形PEDOT/PSS/CNF气凝胶的照片 (经许可转载)
Figure 3. Conductive poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrene sulfonate)/cellulose nanofibrils (PEDOT/PSS/CNF) aerogels[45]: (a) Protonation of CNF surface carboxylates and their hydrogen bonding with PSS in PEDOT/PSS; (b) Process schematic of protonation, freezing/lyophilization, and ethylene glycol (EG) vapor annealing processes; (c) Pictures of CNF and PEDOT/PSS/CNF aerogels on top of California poppy and cylindrical PEDOT/PSS/CNF aerogels in different diameters (Reprinted with permission)
图 4 纤维素纳米片增强的柔性多键交联聚丙烯酸水凝胶(Celn/PAA-Fem3+)的制备及其网络结构图解[53] (经许可转载)
Figure 4. Preparation of cellulose nanosheet enhanced flexible multibond cross-linked poly(acrylic acid) hydrogel (Celn/PAA-Fem3+) and their network structure diagram[53] (Reprinted with permission)
AA—Acrylic acid; MBA—N, N′-Methylenebisacrylamide; CNS—Cellulose nanosheet; PAA—Poly(acrylic acid)
-
[1] BRINCHI L, COTANA F, FORTUNATI E, et al. Production of nanocrystalline cellulose from lignocellulosic biomass: Technology and applications[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,94(1):154-169. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.01.033 [2] 黄彪, 卢麒麟, 唐丽荣. 纳米纤维素的制备及应用研究进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2016, 1(5):1-9.HUANG Biao, LU Qinlin, TANG Lirong. Research progress of nanocellulose manufacture and application[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2016,1(5):1-9(in Chinese). [3] 李媛媛. 纳米纤维素及其功能材料的制备与应用[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2014.LI Yuanyuan. Preparation and application of nanocellulose and nanocellulose based functional materials[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2014(in Chinese). [4] ABITBOL T, RIVKIN A, CAO Y F, et al. Nanocellulose, a tiny fiber with huge applications[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology,2016,39:76-88. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2016.01.002 [5] KLEMM D, KRAMER F, MORITZ S, et al. Nanocelluloses: A new family of nature-based materials[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2011,50(24):5438-5466. doi: 10.1002/anie.201001273 [6] 吕少一, 傅峰, 王思群, 等. 纳米纤维素基导电复合材料研究进展[J]. 林业科学, 2015, 51(10):117-125.LV Shaoyi, FU Feng, WANG Siqun, et al. Advances in nanocellulose-based electroconductive composites[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2015,51(10):117-125(in Chinese). [7] SEGEV-BAR M, HAICK H. Flexible sensors based on nanoparticles[J]. ACS Nano,2013,7(10):8366-8378. doi: 10.1021/nn402728g [8] XIA K L, JIAN M Q, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Advances in wearable and flexible conductors based on nanocarbon materials[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2016,32(10):2427-2446. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201607261 [9] 褚夫强, 张志广, 刘闯. 纳米纤维素在印刷电子中的应用研究进展[J]. 数字印刷, 2021,(3):66-74.CHU Fuqiang, ZHANG Zhiguang, LIU Chuang. Research progress on the application of nanocellulose in printed electronics[J]. Digital Printing,2021,(3):66-74(in Chinese). [10] 付菁菁, 何春霞, 陈永生, 等. 纳米纤维素增强SiO2气凝胶力学性能与微观结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(9):2593-2599.FU Jingjing, HE Chunxia, CHEN Yongsheng, et al. Mecha-nical properties and microstructure of SiO2 aerogels reinforced with cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(9):2593-2599(in Chinese). [11] GOLMOHAMMADI H, MORALES-NARVÁEZ E, NAGHDI T, et al. Nanocellulose in sensing and biosensing[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2017,29(13):5426-5446. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b01170 [12] 刘慰, 司传领, 杜海顺, 等. 纳米纤维素基水凝胶的制备及其在生物医学领域的应用进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2019, 4(5):11-19.LIU Wei, SI Chuanling, DU Haishun, et al. Advance in preparation of nanocellulose-based hydrogels and their biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2019,4(5):11-19(in Chinese). [13] SAITO T, KIMURA S, NISHIYAMA Y, et al. Cellulose nano-fibers prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation of native cellulose[J]. Biomacromolecules,2007,8(8):2485-2491. doi: 10.1021/bm0703970 [14] 黄健, 林春香, 陈瑞英, 等. 离子液体辅助纳米纤维素吸附剂的制备及其吸附性能[J]. 材料研究学报, 2020, 34(9):674-682.HUANG Jian, LIN Chunxiang, CHEN Ruiying, et al. Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of nanocellulose adsorbent and its adsorption properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2020,34(9):674-682(in Chinese). [15] SIRVIÖ J A, VISANKO M, LIIMATAINEN H, et al. Deep eutectic solvent system based on choline chloride-urea as a pre-treatment for nanofibrillation of wood cellulose[J]. Green Chemistry,2015,17(6):3401-3406. doi: 10.1039/C5GC00398A [16] WANG H Q, ZUO M, DING N, et al. Preparation of nanocellulose with high-pressure homogenization from pretreated biomass with cooking with active oxygen and solid alkali[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(10):9378-9386. [17] KHAWAS P, DEKA S C. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from culinary banana peel using highintensity ultrasonication combined with chemical treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:608-616. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.020 [18] WANG Q Q, ZHU J Y, GLEISNER R, et al. Morphological development of cellulose fibrils of a bleached eucalyptus pulp by mechanical fibrillation[J]. Cellulose,2012,19(5):1631-1643. doi: 10.1007/s10570-012-9745-x [19] WEN Y B, YUAN Z Y, LIU X L, et al. Preparation and characterization of lignin-containing cellulose nanofibril from poplar high-yield pulp via TEMPO-mediated oxidation and homogenization[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engi-neering,2019,7(6):6131-6139. [20] 郑丁源, 李梦扬, 张显权, 等. 橡胶木纤维素纳米纤丝的制备[J]. 包装工程, 2019, 40(3):100-107.ZHENG Dingyuan, LI Mengyang, ZHANG Xianquan, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanofibrils from rubber wood[J]. Packaging Engineering,2019,40(3):100-107(in Chinese). [21] 张坤, 刘金刚, 胡云. 羧乙基化法制备纳米纤化纤维素[J]. 纸和造纸, 2015, 34(2):30-33.ZHANG Kun, LIU Jingang, HU Yun. Preparation of nanofibrillated cellulose by carboxyethylation[J]. Paper and Paper Making,2015,34(2):30-33(in Chinese). [22] 马光瑞, 和铭, 杨桂花, 等. 低共熔溶剂体系预处理制备纤维素纳米纤丝及其性能研究[J]. 林产化学与工业, 2021, 41(4):69-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2021.04.010MA Guangrui, HE Ming, YANG Guihua, et al. Preparation of cellulose nanofibril by the pretreatment with deep eutectic solvent system[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2021,41(4):69-76(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2021.04.010 [23] LI B, XU W Y, KRONLUND D, et a1. Cellulose nanocrystals prepared via formic acid hydrolysis followed by TEMPO-mediated oxidation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,133:605-612. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.07.033 [24] 张会, 邵秋娟, 何建新, 等. 竹纤维素纳米晶须的结构与性质[J]. 纤维素科学与技术, 2012, 20(3):27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2012.03.005ZHANG Hui, SHAO Qiujuan, HE Jianxin, et al. The structure and properties of bamboo cellulose nanowhiskers[J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology,2012,20(3):27-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8405.2012.03.005 [25] LIU Y F, WANG H S, YU G, et a1. A novel approach for the preparation of nanocrystalline cellulose by using phosphotungstic acid[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,110:415-422. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.04.040 [26] LIU W, DU H S, LIU H Y, et al. Highly efficient and sustainable preparation of carboxylic and thermostable cellulose nanocrystals via FeCl3-catalyzed innocuous citric acid hydrolysis[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2020,8(44):16691-16700. [27] BROWN A J. XLIII. —On an acetic ferment which forms cellulose[J]. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions,1886,49:432-439. doi: 10.1039/CT8864900432 [28] 朱昌来, 李峰, 尤庆生, 等. 纳米细菌纤维素的制备及其超微结构镜观察[J]. 生物医学工程研究, 2008, 27(4):287-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6278.2008.04.015ZHU Changlai, LI Feng, YOU Qingsheng, et al. Preparation of nanometer biomaterial bacterial cellulose and observation of its ultra-structure[J]. Journal of Biomedical Engi-neering Research,2008,27(4):287-290(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6278.2008.04.015 [29] 武宝利, 张国梅, 高春光, 等. 生物传感器的应用研究进展[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2004, 24(7):65-69.WU Baolai, ZHANG Guomei, GAO Chunguang, et al. Application and development of biosensors[J]. Chinese Biotechnology,2004,24(7):65-69(in Chinese). [30] RAJALA S, SIPONKOSKI T, SARLIN E, et al. Cellulose nanofibril film as a piezoelectric sensor material[J]. ACS App-lied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(24):15607-15614. [31] FARJANA S, TOOMADJ F, LUNDGREN P, et al. Conductivity-dependent strain response of carbon nanotube treated bacterial nanocellulose[J]. Journal of Sensors,2013,2013(20):77-84. [32] ZHANG L F, LYU S Y, ZHANG Q J, et al. Dual-emitting film with cellulose nanocrystal-assisted carbon dots grafted SrAl2O4, Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors for temperature sensing[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,206:767-777. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.031 [33] 段建瑞, 李斌, 李帅臻. 常用新型柔性传感器的研究进展[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2015, 34(11):1-4.DUAN Jianrui, LI Bin, LI Shuaizhen. Research progress on common novel flexible sensor[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies,2015,34(11):1-4(in Chinese). [34] DAI L, WANG Y, ZOU X J, et al. Ultrasensitive physical, bio, and chemical sensors derived from 1-, 2- and 3-D nanocellulosic materials[J]. Small,2020,16(13):1906567. doi: 10.1002/smll.201906567 [35] TANG L R, CHEN W X, CHEN B, et al. Sensitive and renewable quartz crystal microbalance humidity sensor based on nitrocellulose nanocrystals[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2021,327:128944. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2020.128944 [36] XU S M, YU W J, YAO X L, et al. Nanocellulose-assisted dispersion of graphene to fabricate poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene nanocomposite for humidity sensing[J]. Compo-sites Science & Technology,2016,131:67-76. [37] EYEBE G A, BIDEAU B, BOUBEKEUR N, et al. Environmentally-friendly cellulose nanofibre sheets for humidity sensing in microwave frequencies[J]. Sensors and Actuators B Chemical,2017,245:484-492. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.130 [38] 周静, 童欣, 沈文浩. 拟用于可穿戴气敏传感器的二氧化钛/纳米纤维素复合膜制备及表征[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2020, 36(3):149-157.ZHOU Jing, TONG Xin, SHEN Wenhao. Preparation and characterization of titanium dioxide/nanocellulose composites film for wearable gas sensor[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering,2020,36(3):149-157(in Chinese). [39] NGUYEN L H, NAFICY S, MCCONCHIE R, et al. Polydiacetylene-based sensors to detect food spoilage at low temperatures[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2019,7:1919-1926. doi: 10.1039/C8TC05534C [40] SADASIVUNI K K, PONNAMMA D, KO H U, et al. Flexible NO2 sensors from renewable cellulose nanocrystals/iron oxide composites[J]. Sensors & Actuators B Chemical,2016,233:633-638. [41] SCHYRR B, PASCHE S, VOIRIN G, et al. Biosensors based on porous cellulose nanocrystal−poly (vinyl alcohol) scaffolds[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(15): 12674−12683. [42] ZHANG T J, WANG W, ZHANG D Y, et al. Biotemplated synthesis of gold nanoparticle–bacteria cellulose nanofiber nanocomposites and their application in biosensing[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2010,20(7):1152-1160. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200902104 [43] WU Z Y, LI C, LIANG H W, et al. Ultralight, flexible, and fire-resistant carbon nanofiber aerogels from bacterial cellulose[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2013,52:2925-2929. doi: 10.1002/anie.201209676 [44] CHEN S, CHEN Y L, LI D Q, et al. Flexible and sensitivity-adjustable pressure sensors based on carbonized bacterial nanocellulose/wood-derived cellulose nanofibril composite aerogels[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(7):8754-8763. doi: 10.1021/acsami.0c21392 [45] ZHOU J, HSIEH Y L. Conductive polymer protonated nanocellulose aerogels for tunable and linearly responsive strain sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(33):27902-27910. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b10239 [46] YANG Y T, SU G T, LI Q L, et al. Performance of the highly sensitive humidity sensor constructed with nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene oxide/polydimethylsiloxane aerogel via freeze drying[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11(3):1543-1552. doi: 10.1039/D0RA08193K [47] EDWARDS J V, FONTENOT K R, PREVOST N T, et al. Preparation, characterization and activity of a peptide-cellulosic aerogel protease sensor from cotton[J]. Sensors,2016,16(11):1789. doi: 10.3390/s16111789 [48] 董凤霞, 戴磊. 纤维素纳米纤丝基水凝胶及其在废水处理中的应用进展[J]. 中国造纸, 2020, 39(5):63-69.DONG Fengxia, DAI Lei. Research progress on cellulose nanofibrils-based hydrogel and its application in waste-water treatment[J]. China Pulp and Paper,2020,39(5):63-69(in Chinese). [49] 杨帆, 马建中, 鲍艳. 纳米纤维素及其在水凝胶中的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(7):1227-1233.YANG Fan, MA Jianzhong, BAO Yan. Advances in nanocellulose and its application in hydrogels[J]. Materials Reports,2019,33(7):1227-1233(in Chinese). [50] PAN X F, WANG Q H, NING D W, et al. Ultra-flexible self-healing guar gum-glycerol hydrogel with injectable, anti-freeze, and strain-sensitive properties[J]. ACS Biomater-ials Science & Engineering,2018,4(9):3397-3404. [51] ZHOU H W, JIN Z Y, YUAN Y, et al. Self-repairing flexible strain sensors based on nanocomposite hydrogels for whole-body monitoring[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,592:124587. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2020.124587 [52] JING X, LI H, MI H Y, et al. Highly transparent, stretchable, and rapid self-healing polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nano-fibril hydrogel sensors for sensitive pressure sensing and human motion detection[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2019,295:159-167. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.082 [53] LU F X, WANG Y Y, WANG C, et al. Two-dimensional nanocellulose-enhanced high-strength, self-adhesive and strain-sensitive poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels fabricated by radical-induced strategy for skin sensor[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2020,8(8):3427-3436. [54] ZHENG C X, YUE Y Y, GAN L, et al. Highly stretchable and self-healing strain sensors based on nanocellulose-supported graphene dispersed in electro-conductive hydrogels[J]. Nanomaterials,2019,9(7):937. doi: 10.3390/nano9070937 [55] CHEN Y Y, LU K Y, SONG Y H, et al. A skin-inspired stretchable, self-healing and electro-conductive hydrogel with a synergistic triple network for wearable strain sensors applied in human-motion detection[J]. Nanomaterials,2019,9(12):1737. doi: 10.3390/nano9121737 [56] SONG M L, YU H Y, ZHU J Y, et al. Constructing stimuli-free self-healing, robust and ultrasensitive biocompatible hydrogel sensors with conductive cellulose nanocrysals[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,398:125547. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125547 [57] RUIZ-PALOMERO C, BENÍTEZ-MARTÍNEZ S, SORIANO M L, et al. Fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogels based on graphene quantum dots for sensing laccase[J]. Analytica Chimica Acta,2017,974:93-99. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2017.04.018 [58] ZHANG B N, ZHANG J Q, ZHANG K H, et al. A non-contact proximity sensor with low frequency electromagnetic field[J]. Sensors and Actuators A: Physical,2007,135(1):162-168. doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2006.06.068 [59] SADASIVUNI K K, KAFY A, ZHAI L D, et al. Transparent and flexible cellulose nanocrystal/reduced graphene oxide film for proximity sensing[J]. Small,2015,11(8):994-1002. doi: 10.1002/smll.201402109 [60] CHEN L, CAO W, GRISHKEWICH N, et al. Synthesis and characterization of pH-responsive and fluorescent poly (amidoamine) dendrimer-grafted cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2015,450:101-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.03.002 [61] TANG J T, SONG Y, BERRY R M, et al. Polyrhodanine coated cellulose nanocrystals as optical pH indicators[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4(104):60249-60252. doi: 10.1039/C4RA09043H [62] ZHU C Z, YANG G H, LI H, et al. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2015,87(1):230-249. doi: 10.1021/ac5039863 [63] BOCANEGRA-RODRÍGUEZ S, MOLINS-LEGUA C, CAMPÍNS-FALCÓ P, et al. Monofunctional pyrenes at carbon nanotube electrodes for direct electron transfer H2O2 reduction with HRP and HRP-bacterial nanocellulose[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2021,187:113304. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113304 [64] 毕青. 电化学手性传感器的制备及应用[D]. 兰州: 西北师范大学, 2016.BI Qing. Preparation and application of electrochemical chiral sensor[D]. Lanzhou: Northwest Normal University, 2016(in Chinese). [65] SILVA R R, RAYMUNDO-PEREIRA P A, CAMPOS A M, et al. Microbial nanocellulose adherent to human skin used in electrochemical sensors to detect metal ions and biomarkers in sweat[J]. Talanta,2020,218:121153. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121153 [66] ESMAEILI C, ABDI M M, MATHEW A P, et al. Synergy effect of nanocrystalline cellulose for the biosensing detection of glucose[J]. Sensors,2015,15(10):24681-24697. doi: 10.3390/s151024681 [67] WANG S W, SUN J S, JIA Y X, et al. Nanocrystalline cellulose-assisted generation of silver nanoparticles for non-enzymatic glucose detection and antibacterial agent[J]. Biomacromolecules,2016,17(7):2472-2478. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00642 [68] 禚晓. 纳米纤维素纸基生物传感器设计[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018.ZHUO Xiao. Design of nanocellulose paper-based biosensors[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2018(in Chinese). [69] 付俊俊. 纳米纤维素/纳米金复合材料的制备及其应用研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.FU Junjun. Preparation and application of nanocellulose/AuNPs nanocomposites[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [70] ZHANG L Z, LI Q, ZHOU J P, et al. Synthesis and photophysical behavior of pyrene-bearing cellulose nanocrystals for Fe3+ sensing[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry & Physics,2012,213(15):1612-1617. [71] RAM B, JAMWAL S, RANOTE S, et al. Highly selective and rapid naked-eye colorimetric sensing and fluorescent studies of Cu2+ ions derived from spherical nanocellulose[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials,2020,2(11):5290-5299. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.0c01025 -





 下载:
下载: