Research progress in preparation and performance of MXene and its composite absorbing materials
-
摘要: 信息时代迅猛发展的同时也给人们带来了日益严重的电磁污染问题,发展先进微波吸收材料不仅可以减少电磁波污染,也对军事安全有着重要意义。MXene是一种新型二维材料,独特的二维结构、丰富且可控的表面官能团、高比表面积、高导电率和低密度等特点使其成为一种理想的高性能微波吸收材料。本文讨论了MXene及其复合吸波材料的制备方法,介绍了和吸波性能密切相关的MXene的电磁性能,然后按照损耗机制对MXene及其复合材料的吸波性能进行总结与分析。最后从种类、结构、应用方面对MXene及其复合吸波材料的发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: The problem of electromagnetic pollution is becoming more and more serious with the rapid development of the information age. The development of advanced microwave absorbing materials can not only reduce electromagnetic pollution, but also have important implications for military security. MXene is a new type of two-dimensional material. The unique two-dimensional structure, abundant and controllable surface functional groups, high specific surface area, high conductivity and low density make it an ideal high-performance microwave absorbing material. This paper first discussed the preparation methods of MXene and its composite absorbing composites, then introduced the electromagnetic performance of MXene, which is closely related to the absorbing performance. In addition, MXene and its composite microwave absorbing materials are summarized and analyzed according to the loss mechanism. Finally, the development direction of MXene and its composite absorbing materials is prospected from the aspects of type, structure and application.
-
Key words:
- MXene /
- wave absorption /
- composites /
- electrical loss /
- magnetic loss
-
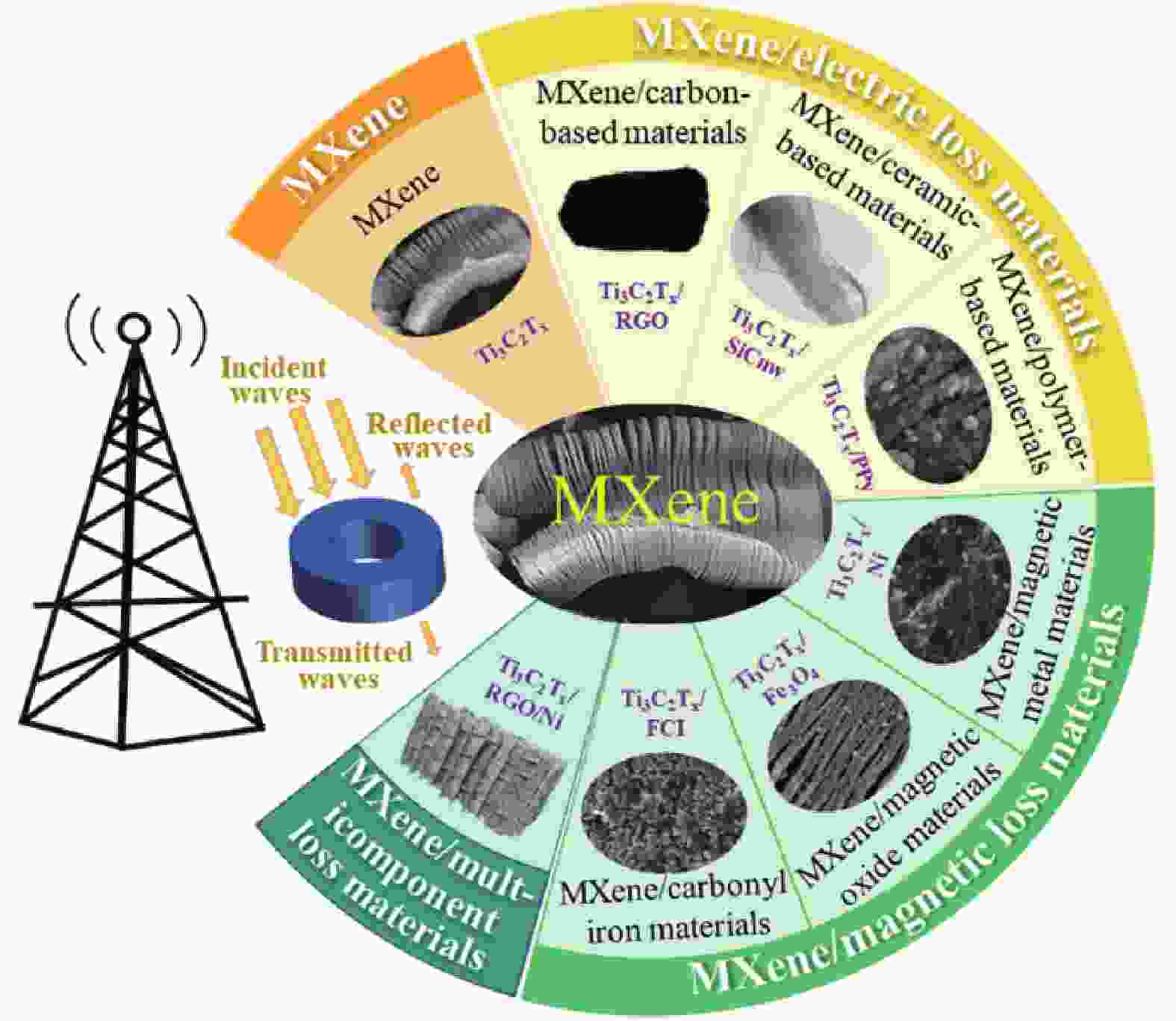
图 2 MXene微波吸收复合材料的分类:MXene、MXene/电损耗材料、MXene/磁损耗材料、MXene/多组分损耗材料
Figure 2. Classification of MXene microwave absorbing composites: Pure MXene, MXene/electric loss materials, MXene/magnetic loss materials, MXene/multicomponent loss materials
RGO—Reduced graphene oxide; SiCnw—SiC nanowire; PPy—Polypyrrole; FCI—Flaky carbonyl iron
图 4 静电自组装法制备聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)/SiCnw/MXene的示意图[50]
Figure 4. Schematic illustrations of the preparation process of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/SiCnw/MXene by electrostatic self-assembly method[50]
PDDA—Poly(diallyl dimethylammonium chloride); DI—Deionized; DMF—N, N-Dimethylformamide; PVDF—Poly(vinylidene fluoride)
图 7 原位聚合制备的Ti3C2Tx/PPy (a)[60]、CVD法制备的Ti3C2Tx/CNT (b)[62]和交替抽滤或喷涂法制备的Ti3C2Tx/TMO (c)[64]的工艺流程图
Figure 7. Schematic illustrations of the preparation process of Ti3C2Tx/PPy by in-situ polymerization (a)[60], Ti3C2Tx/CNT by CVD (b)[62] and Ti3C2Tx/TMO[64] by alternating filtration or spray coating methods (c)
APS—Ammonium persulfate; CVD—Chemical vapor deposition; TMO—Transition metal oxide
表 1 MXene及其复合材料的吸波性能
Table 1. Microwave absorption properties of MXene and its composite materials
Type Materials Methods Microwave absorbing performance Ref. RLmin/dB Band width/GHz Thickness/mm MXene Ti3C2Tx Etching MAX phase −17 5.6 (12.4-18) 1.4 [80] Ti3C2Tx Etching MAX phase −34.4 4.7 (12.4-17.1) 1.7 [81] Ti3C2Tx Etching MAX phase −45.2 3.66 1.68 [83] C/TiO2 Annealing process −50.3 4.7 2.1 [85] Ti3C2Tx/TiO2 Annealing process −40.07 3.6 1.5 [86] MXene/electric
loss materialsTi3C2Tx/CNTs Ultrasonic spray −45 4.9 1.9 [90] Ti3C2/CNTs Chemical vapor deposition −52.9 4.46 1.55 [62] Ti3C2Tx@GO Electrostatic-spinning + Freeze drying −49.1 2.9 (12.9-15.8) 1.2 [91] Ti3C2Tx@RGO Hydrothermal method + Freeze drying −31.2 5.4 (11.4-16.8) 2.05 [57] Ti3C2Tx/SiCnw Electrostatic self-assembly+
Freeze drying−55.7 4.2 (8.2-12.4) 3.5-3.8 [92] Ti3C2Tx/SiCnw Electrostatic self-assembly+
Solution casting+
Hot-pressing−75.8 5.0 1.5 [50] Ti3C2Tx@PPy In-situ polymerization −49.5 6.63 (8.55-15.18) 2.7 [93] Ti3C2Tx/PANI In-situ polymerization −56.3 5.95 2.4 [59] MXene/magnetic
loss materialsTi3C2/Ni Electroless plating −24.3 2.6 (8.66-11.26) 2.2 [94] Ti3C2Tx@Ni Co-solvothermal −52.6 6.1 3.0 [34] Ti3C2Tx/Ni chain Hydrothermal method −49.9 2.1 1.75 [96] FeCo−Ti3C2 Hydrothermal method −17.86 8.8 (9.2-18.0) 1.6 [95] Fe3O4@Ti3C2Tx Solvothermal method −57.2 1.4 4.2 [98] NiFe2O4−Ti3C2Tx Chemical coprecipitation −24.7 7.68 (10.32-18.0) 1.5 [100] CoFe2O4−Ti3C2 In-situ solvothermal −30.9 8.5 (8.3-16.8) 1.5 [102] Ti3C2/FCI Ultrasonic mixing −15.52 8.16 (9.84-18) 1.0 [103] MXene/
multicomponent
loss materialsTi3C2/Fe3O4/PANI Coprecipitation + In-situ polymerization −40.3 5.2 (12.8-18) 1.9 [104] RGO/Nb2CTx/Fe3O4 Hydrothermal method +
Electrostatic self-assembly−59.17 6.8 (9.76-16.56) 2.5 [105] PVB/Ti3C2/Ba3Co2Fe24O41 Tape casting −46.3 1.6 (4.9-6.5) 2.8 [106] Ni/TiO2/C Microwave heating −39.91 3.04 (14.24-17.28) 1.5 [107] Fe&TiO2@C Microwave heating +
Heat treatment−51.8 6.5 (11.5-18) 1.6 [108] Notes: RLmin—Minimum reflection loss; GO—Graphene oxide; CNTs—Carbon nanotubes; PVB—Polyvinyl butyral. -
[1] 刘顺华, 刘军民, 董星龙, 等. 电磁波屏蔽及吸波材料[M]. 第二版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2013.LIU Shunhua, LIU Junmin, DONG Xinglong, et al. Electromagnetic shielding and absorbing materials[M]. 2th ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2013(in Chinese). [2] YU G, YANG C, CHI H J, et al. Facile synthesis of FeCo/Fe3O4 nanocomposite with high wave-absorbing properties[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2013,14(7):14204-14213. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714204 [3] SUI M X, SUN X D, LOU H F, et al. Synthesis of hollow Fe3O4 particles via one-step solvothermal approach for microwave absorption materials: Effect of reactant concentration, reaction temperature and reaction time[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2018,29(9):7539-7550. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-8746-4 [4] PAN Y, MA G, LIU X, et al. Electromagnetic and microwave absorption properties of coatings based on spherical and flaky carbonyl iron[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2019,30(19):18123-18134. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-02165-4 [5] ONO K, SHINTANI H, YANO O, et al. Absorption of 10-MHz to 110-MHz ultrasonic waves by solutions of polystyrene[J]. Polymer Journal,1973,5(2):164-175. doi: 10.1295/polymj.5.164 [6] YE Z, LI Z, ROBERTS J A, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon nanotubes-epoxy compo-sites at microwave frequencies[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2010,108(5):054315. doi: 10.1063/1.3477195 [7] GREEN M, LIU Z, XIANG P, et al. Doped, conductive SiO2 nanoparticles for large microwave absorption[J]. Light: Science & Applications,2018,7(1):87-96. [8] MEI H, ZHAO X, ZHOU S, et al. 3D-printed oblique honeycomb Al2O3/SiCw structure for electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,372(31):940-945. [9] CUI L, HAN X, WANG F, et al. A review on recent advances in carbon-based dielectric system for microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2021,56(18):10782-10811. doi: 10.1007/s10853-021-05941-y [10] LI B, JI Z, XIE S, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of carbon black/cement-based composites filled with porous glass pellets[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2019,30(13):12416-12425. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-01600-w [11] XU J, QI X, LUO C, et al. Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties: A strongly hydrogenated TiO2 nanomaterial[J]. Nanotechnology,2017,28(42):425701. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aa81ba [12] DOSOUDIL R, FRANEK J, SLAMA J, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption performances of metal alloy/spinel ferrite/polymer composites[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,2012,48(4):1524-1527. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2011.2172779 [13] ABDALLA I, ELHASSAN A, YU J, et al. A hybrid comprised of porous carbon nanofibers and rGO for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2020,157(14):703-713. [14] YE Z, LIU W, LIU Z, et al. The effect of GO loading on electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide hybrids[J]. Ceramics International,2017,43(16):13146-13153. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.07.007 [15] NAGUIB M, KURTOGLU M, PRESSER V, et al. Two-dimensional nanocrystals: Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2[J]. Advanced Materials,2011,23(37):4248-4253. doi: 10.1002/adma.201190147 [16] VAHIDMOHAMMADI A, ROSEN J, GOGOTSI Y, et al. The world of two-dimensional carbides and nitrides (MXenes)[J]. Science, 2021, 372(6547): 1581 [17] LI Z, WANG L, SUN D, et al. Synthesis and thermal stability of two-dimensional carbide MXene Ti3C2[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B,2015,191:33-40. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2014.10.009 [18] XIE Y, NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N, et al. Role of surface structure on Li-ion energy storage capacity of two-dimensional transition-metal carbides[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2014,136(17):6385-6394. doi: 10.1021/ja501520b [19] KHAZAEI M, RANJBAR A, ARAI M, et al. Electronic pro-perties and applications of MXenes: A theoretical review[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2017,5(10):2488-2503. doi: 10.1039/C7TC00140A [20] LIU F, JIE Z, WANG S, et al. Preparation of high-purity V2C MXene and electrochemical properties as Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,2017,164(4):709-713. doi: 10.1149/2.0641704jes [21] SUN D, HU Q, CHEN J, et al. Structural transformation of MXene (V2C, Cr2C, and Ta2C) with O groups during lithiation: A first-principles investigation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(1):74-81. [22] ZHANG C J, KREMER M P, SERAL-ASCASO A, et al. Stamping of flexible, coplanar micro-supercapacitors using MXene lnks[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(9):1705506. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201705506 [23] HE H, XIA Q, WANG B, et al. Two-dimensional vanadium carbide (V2CTx) MXene as supercapacitor electrode in seawater electrolyte[J]. Chinese Chemical Letters,2020,31(4):984-987. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2019.08.025 [24] LIU S, LIU J, LIU X, et al. Hydrogen storage in incompletely etched multilayer Ti2CTx at room temperature[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2021,16(3):331-336. doi: 10.1038/s41565-020-00818-8 [25] YADAV A, DASHORA A, PATEL N, et al. Study of 2D MXene Cr2C material for hydrogen storage using density functional theory[J]. Applied Surface Science,2016,389:88-95. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.07.083 [26] WANG B, ZHOU A, LIU F, et al. Carbon dioxide adsorption of two-dimensional carbide MXenes[J]. Journal of Advanced Ceramics,2018,7(3):237-245. doi: 10.1007/s40145-018-0275-3 [27] ZHANG Y J, ZHOU Z J, LAN J H, et al. Theoretical insights into the uranyl adsorption behavior on vanadium carbide MXene[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,426:572-578. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.227 [28] DING L, WEI Y, WANG Y, et al. A two-dimensional lamellar membrane: MXene nanosheet stacks[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2017,56(7):1825-1829. doi: 10.1002/anie.201609306 [29] WANG K, LOU Z, WANG L, et al. Bioinspired interlocked structure-induced high deformability for two-dimensional titanium carbide (MXene)/natural microcapsule-based flexible pressure sensors[J]. ACS Nano,2019,13(8):9139-9147. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b03454 [30] LIU L, WANG L, LIU X, et al. High-performance wearable strain sensor based on MXene@cotton fabric with network structure[J]. Nanomaterials,2021,11(4):889-899. doi: 10.3390/nano11040889 [31] KIM S J, KOH H J, REN C E, et al. Metallic Ti3C2Tx MXene gas sensors with ultrahigh signal-to-noise ratio[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(2):986-993. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b07460 [32] WU M, HE M, HU Q, et al. Ti3C2 MXene-based sensors with high selectivity for NH3 detection at room tempera-ture[J]. ACS Sensors,2019,4(10):2763-2770. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.9b01308 [33] JIA X, SHEN B, ZHANG L, et al. Construction of compressible polymer/MXene composite foams for high-performance absorption-dominated electromagnetic shielding with ultra-low reflectivity[J]. Carbon,2021,173(5):932-940. [34] LIU Q, HE X, YI C, et al. Fabrication of ultra-light nickel/graphene composite foam with 3D interpenetrating network for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,182(11):107614. [35] LIANG L, YANG R, HAN G, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave-absorbing performance of magnetic nanoparticles-anchored 2D Ti3C2Tx MXene[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(2):2644-2654. [36] ZHANG Z, CAI Z, ZHANG Y, et al. The recent progress of MXene-based microwave absorption materials[J]. Carbon,2021,174(2):484-499. [37] PAN F, YU L, XIANG Z, et al. Improved synergistic effect for achieving ultrathin microwave absorber of 1D Co nanochains/2D carbide MXene nanocomposite[J]. Carbon,2021,172(19):506-515. [38] WU M, AN Y, YANG R, et al. V2CTx and Ti3C2Tx MXenes nanosheets for gas sensing[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2021,4(6):6257-6268. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.1c01059 [39] NAGUIB M, MOCHALIN V N, BARSOUM M W, et al. 25th Anniversary article: MXenes: A new family of two-dimensional materials[J]. Advanced Materials,2014,26(7):992-1005. doi: 10.1002/adma.201304138 [40] NAGUIB M, MASHTALIR O, CARLE J, et al. Two-dimensional transition metal carbides[J]. ACS Nano,2012,6(2):1322-1331. doi: 10.1021/nn204153h [41] GHIDIU M, LUKATSKAYA M, ZHAO M Q, et al. Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance[J]. Nature,2014,516(7529):78-81. doi: 10.1038/nature13970 [42] WANG L, ZHANG H, WANG B, et al. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of Ti3C2Tx with hydrothermal process[J]. Electronic Materials Letters,2016,12(5):702-710. doi: 10.1007/s13391-016-6088-z [43] WANG L, LIU D, LIAN W, et al. The preparation of V2CTx by facile hydrothermal-assisted etching processing and its performance in lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(1):984-993. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.11.038 [44] URBANKOWSKI P, ANASORI B, MAKARYAN T, et al. Synthesis of two-dimensional titanium nitride Ti4N3 (MXene)[J]. Nanoscale,2016,8(22):11385-11391. doi: 10.1039/C6NR02253G [45] LI M, LU J, LUO K, et al. Element replacement approach by reaction with lewis acidic molten salts to synthesize nanolaminated MAX phases and MXenes[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2019,141(11):4730-4737. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b00574 [46] LI T, YAO L, LIU Q, et al. Fluorine-free synthesis of high-purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via alkali treatment[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2018,57(21):6115-6119. doi: 10.1002/anie.201800887 [47] YANG S, ZHANG P, WANG F, et al. Fluoride-free synthe-sis of two-dimensional titanium carbide (MXene) using a binary aqueous system[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2018,130(47):15717-15721. doi: 10.1002/ange.201809662 [48] HU K, WANG H, ZHANG X, et al. Ultralight Ti3C2Tx MXene foam with superior microwave absorption performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,408:127283. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127283 [49] LI X, WEN C, YANG L, et al. MXene/FeCo films with distinct and tunable electromagnetic wave absorption by morphology control and magnetic anisotropy[J]. Carbon,2021,175(28):509-518. [50] MA L, HAMIDINEJAD M, LIANG C, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of polymer/SiC-nanowire/MXene (Ti3C2Tx) composites[J]. Carbon,2021,179(6304):408-416. [51] DENG B, LIU Z, PAN F, et al. Electrostatically self-assembled two-dimensional magnetized MXene/hollow Fe3O4 nanoparticle hybrids with high electromagnetic absorption performance and improved impendence matching[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2021,9(6):3500-3510. doi: 10.1039/D0TA10551A [52] HOU T, JIA Z, WANG B, et al. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber[J]. Chemical Engineering Jour-nal,2021,414(3):128875. [53] LIU H, LI L, CUI G, et al. Heterostructure composites of CoS nanoparticles decorated on Ti3C2Tx nanosheets and their enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Nanomaterials,2020,10(9):1666-1681. doi: 10.3390/nano10091666 [54] QIAN Y, WEI H, DONG J, et al. Fabrication of urchin-like ZnO-MXene nanocomposites for high-performance electromagnetic absorption[J]. Ceramics International,2017,43(14):10757-10762. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.082 [55] SONG Q, YE F, KONG L, et al. Graphene and MXene nanomaterials: Toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz band range[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(31):2000475. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202000475 [56] LIANG L, LI Q, YAN X, et al. Multifunctional magnetic Ti3C2Tx MXene/graphene aerogel with superior electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(4):6622-6632. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c09982 [57] WANG L, LIU H, LV X, et al. Facile synthesis 3D porous MXene Ti3C2Tx@RGO composite aerogel with excellent dielectric loss and electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,828:154251. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154251 [58] YANG M, YUAN Y, LI Y, et al. Anisotropic electromagnetic absorption of aligned Ti3C2Tx MXene/gelatin nanocomposite aerogels[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(29):33128-33138. [59] WEI H, DONG J, FANG X, et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene/polyaniline (PANI) sandwich intercalation structure composites constructed for microwave absorption[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,169(8):52-59. [60] TONG Y, HE M, ZHOU Y, et al. Hybridizing polypyrrole chains with laminated and two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx toward high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,434:283-293. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.140 [61] TAN K H, SAMYLINGAM L, ASLFATTAHI N, et al. Optical and conductivity studies of polyvinyl alcohol-MXene (PVA-MXene) nanocomposite thin films for electronic applications[J]. Optics & Laser Technology,2021,136:106772. [62] LI X, YIN X, HAN M, et al. Ti3C2 MXenes modified with in situ grown carbon nanotubes for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2017,5(16):4068-4074. doi: 10.1039/C6TC05226F [63] WANG Z, YANG L, ZHOU Y, et al. NiFe LDH/MXene derivatives interconnected with carbon fabric for flexible electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(14):16713-16721. [64] ZHAO M Q, TORELLI M, REN C E, et al. 2D Titanium carbide and transition metal oxides hybrid electrodes for Li-ion storage[J]. Nano Energy,2016,30:603-613. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2016.10.062 [65] HART J L, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, LANG A C, et al. Control of MXenes’ electronic properties through termination and intercalation[J]. Nature Communications,2019,10(1):522-532. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08169-8 [66] LIPATOV A, ALHABEB M, LUKATSKAYA M, et al. Effect of synthesis on quality, electronic properties and environmental stability of individual monolayer Ti3C2 MXene flakes[J]. Advanced Electronic Materials,2016,2(12):1600255. doi: 10.1002/aelm.201600255 [67] DU F, TANG H, PAN L, et al. Environmental friendly scalable production of colloidal 2D titanium carbonitride MXene with minimized nanosheets restacking for excellent cycle life lithium-ion batteries[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2017,235:690-699. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.03.153 [68] HALIM J, LUKATSKAYA M R, COOK K M, et al. Transparent conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide epitaxial thin films[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2014,26(7):2374-2381. doi: 10.1021/cm500641a [69] KHAZAEI M, ARAI M, SASAKI T, et al. Novel electronic and magnetic properties of two-dimensional transition metal carbides and nitrides[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2013,23(17):2185-2192. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201202502 [70] ZHU J, HA E, ZHAO G, et al. Recent advance in MXenes: A promising 2D material for catalysis, sensor and chemical adsorption[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2017,352:306-327. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2017.09.012 [71] XIONG K, WANG P, YANG G, et al. Functional group effects on the photoelectronic properties of MXene (Sc2CT2, T = O, F, OH) and their possible photocatalytic activities[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):15095. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15233-8 [72] CUI G, SUN X, ZHANG G, et al. Electromagnetic absorption performance of two-dimensional MXene Ti3C2Tx exfoliated by HCl + LiF etchant with diverse etching times[J]. Materials Letters,2019,252:8-10. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.05.053 [73] ZHANG Z, HE Y, LV Y, et al. Effect of surface structure and composition on the electromagnetic properties of Ti3C2Tx MXenes for highly efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2020,124(36):19666-19674. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c06115 [74] HAN M, YIN X, WU H, et al. Ti3C2 MXenes with modified surface for high-performance electromagnetic absorption and shielding in the X-band[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(32):21011-21019. [75] TONG Y, HE M, ZHOU Y, et al. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties in the centimetre-band of Ti3C2Tx MXenes with diverse etching time[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2018, 29(10): 8078–8088. [76] XIE Y, KENT P R C. Hybrid density functional study of structural and electronic properties of functionalized Ti(n+1)X(n) (X=C, N) monolayers[J]. Physical Review B,2013,87(23):235441. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.87.235441 [77] ZHANG Y, LI F. Robust half-metallic ferromagnetism in Cr3C2 MXene[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2017,433:222-226. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.03.031 [78] AKINOLA O, CHAKRABORTY I, CELIO H, et al. Synthesis and characterization of Cr2C MXenes[J]. Journal of Materials Research,2021,36(10):1980-1989. doi: 10.1557/s43578-021-00258-7 [79] ZHANG K, DI M, FU L, et al. Enhancing the magnetism of 2D carbide MXene Ti3C2Tx by H2 annealing[J]. Carbon,2020,157:90-96. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.10.016 [80] QING Y, ZHOU W, LUO F, et al. Titanium carbide (MXene) nanosheets as promising microwave absorbers[J]. Ceramics International,2016,42(14):16412-16416. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.150 [81] ZHANG J, XUE W, CHEN X Y. Ti3C2Tx MXenes as thin broadband absorbers[J]. Nanotechnology,2020,31(27):275301. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/ab80fd [82] FAN B, LI N, DAI B, et al. Investigation of adjacent spacing dependent microwave absorption properties of lamellar structural Ti3C2Tx MXenes[J]. Advanced Powder Technology,2020,31(2):808-815. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.11.035 [83] CUI G, ZHENG X, LV X, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption of Ti3C2Tx MXene with diverse reactant concentration, reaction time, and reaction temperature[J]. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(17): 23600-23610. [84] XU G, GONG S, WEI S, et al. Solvent-regulated preparation of well-intercalated Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets and application for highly effective electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Nanotechnology,2018,29(35):355201. doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/aac8f6 [85] LI X, YIN X, HAN M, et al. A controllable heterogeneous structure and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Ti2CTx MXene[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2017,5(30):7621-7628. doi: 10.1039/C7TC01991B [86] FAN B, SHANG S, DAI B, et al. 2D-Layered Ti3C2/TiO2 hybrids derived from Ti3C2 MXenes for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(10):17085-17092. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.04.004 [87] IQBAL A, SHAHZAD F, HANTANASIRISAKUL K, et al. Anomalous absorption of electromagnetic waves by 2D transition metal carbonitride Ti3CNTx (MXene)[J]. Science,2020,369(6502):446-450. doi: 10.1126/science.aba7977 [88] FENG W, LUO H, WANG Y, et al. Ti3C2 MXene: A promi-sing microwave absorbing material[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(5):2398-2403. doi: 10.1039/C7RA12616F [89] WANG Y, YANG J, CHEN Z, et al. A new flexible and ultralight carbon foam/Ti3C2Tx MXene hybrid for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(70):41038-41049. doi: 10.1039/C9RA09817H [90] CUI Y, WU F, WANG J, et al. Three dimensional porous MXene/CNTs microspheres: Preparation, characterization and microwave absorbing properties[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2021,145:106378. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2021.106378 [91] LI Y, MENG F, MEI Y, et al. Electrospun generation of Ti3C2Tx MXene@graphene oxide hybrid aerogel microspheres for tunable high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,391:123512. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123512 [92] LI X, YIN X, XU H, et al. Ultralight MXene-coated, interconnected SiCnws three-dimensional lamellar foams for efficient microwave absorption in the X-band[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(40):34524-34533. [93] LIU T, LIU N, AN Q, et al. Designed construction of Ti3C2Tx@PPY composites with enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,802:445-457. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.06.243 [94] LIU Y, ZHANG S, SU X, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2 MXene powders decorated with Ni particles[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(24):10339-10350. doi: 10.1007/s10853-020-04739-8 [95] HE J, SHAN D, YAN S, et al. Magnetic FeCo nanoparticles-decorated Ti3C2 MXene with enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2019,492:165639. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165639 [96] LIANG L, HAN G, LI Y, et al. Promising Ti3C2Tx MXene/Ni chain hybrid with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption and shielding capacity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(28):25399-25409. [97] HAN X, HUANG Y, DING L, et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheet/metal–organic framework composites for microwave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2021,4(1):691-701. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.0c02983 [98] ZHANG X, WANG H, HU R, et al. Novel solvothermal preparation and enhanced microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2Tx MXene modified by in situ coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,484:383-391. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.264 [99] GAO Y, DU H, LI R, et al. Multi-phase heterostructures of flower-like Ni(NiO) decorated on two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx/TiO2 for high-performance microwave absorption properties[J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(8):10764-10772. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.12.193 [100] SHAN D, HE J, DENG L, et al. The underlying mecha-nisms of enhanced microwave absorption performance for the NiFe2O4-decorated Ti3C2Tx MXene[J]. Results in Physics,2019,15:102750. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2019.102750 [101] HOU T, WANG B, MA M, et al. Preparation of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx) and NiCo2O4 compo-sites to achieve excellent microwave absorption properties[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,180:107577. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107577 [102] HE J, LIU S, DENG L, et al. Tunable electromagnetic and enhanced microwave absorption properties in CoFe2O4 decorated Ti3C2 MXene composites[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,504:144210. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144210 [103] YAN S, CAO C, HE J, et al. Investigation on the electromagnetic and broadband microwave absorption properties of Ti3C2 Mxene/flaky carbonyl iron composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2019,30(7):6537-6543. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-00959-0 [104] WANG Y, GAO X, ZHANG L, et al. Synthesis of Ti3C2/Fe3O4/PANI hierarchical architecture composite as an efficient wide-band electromagnetic absorber[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,480:830-838. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.03.049 [105] CUI C, GUO R, REN E, et al. MXene-based rGO/Nb2CTx/Fe3O4 composite for high absorption of electromagnetic wave[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,405(3):126626. [106] YANG H, DAI J, LIU X, et al. Layered PVB/Ba3Co2Fe24O41/Ti3C2 Mxene composite: Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties with high impedance match in a wide frequency range[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2017,200:179-186. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.05.057 [107] ZHOU C, WANG X, LUO H, et al. Rapid and direct growth of bipyramid TiO2 from Ti3C2Tx MXene to prepare Ni/TiO2/C heterogeneous composites for high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,383:123095. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123095 [108] DENG B, XIANG Z, XIONG J, et al. Sandwich-like Fe&TiO2@C nanocomposites derived from MXene/Fe-MOFs hybrids for electromagnetic absorption[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2020,12(1):55-71. doi: 10.1007/s40820-020-0398-2 -






 下载:
下载: