Research progress of low-frequency radar absorbents
-
摘要: 随着米波、分米波低频雷达在军事领域的大规模应用,飞行器特别是远程战略轰炸机受到的空中威胁愈来愈大,为提高其生存能力,除对飞行器进行外形设计外,飞行器表面采用长波雷达吸波材料成为其隐身能力的关键措施之一。本文重点讨论了低频吸波机制,总结了传统吸波材料在低频下的应用,包括铁氧体、复合物、磁性金属微粉,分析了影响低频吸波性能的各种因素。最后讨论当前吸波材料的发展情况,并对未来低频吸波材料的发展方向进行了展望。Abstract: With the large-scale application of meter-wave and decimeter-wave low-frequency radars in the military field, aircraft, especially long-range strategic bombers, are facing increasing air threats. In order to improve their survive capabilities, low-frequency radars are used to absorb microwave except the external design. To overcome this difficult point, long-wave microwave absorption materials are one of the key measures for its stealth effectiveness. This article discusses the low-frequency absorbing mechanism, summarizes the applications of traditional absorbing materials at low frequencies, including ferrites, composites, magnetic metal powders, then analyzes various factors that affect low-frequency absorbing performance. Finally, the current development of absorbing materials is explored, and the future development direction of low-frequency absorbent is prospected.
-
Key words:
- low frequency absorbing /
- absorbent /
- absorbing mechanism /
- radar stealth /
- research progress
-
图 2 (a)溶胶凝胶-高温合成Ni-Zn铁氧体示意图[36];(b) Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4在不同烧结温度下的磁滞回线;(c) 不同烧结温度下的Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4反射损耗图;(d) 3种不同条件下得到样品的磁滞回线,左上为初始样品和在H2 600℃退火后得到样品的SEM图像[37]
Figure 2. (a) Schematic diagram of NiZn ferrites prepared by sol-gel and high temperature process [36]; (b) Hysteresis loops of Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4 sintered at different temperatures; (c) Reflection loss of Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4 sintered at different temperatures; (d) Hysteresis loops of the samples obtained under different conditions, upper left is the SEM image of the initial samples and the samples annealed at 600℃ in H2[37]
图 3 (a) CFG制备过程图[42];(b) 不同厚度下的CFG-50反射损耗;(c) ZCFO/MNFO@C-MWCNTs SEM图像[43];(d) 不同厚度的(ZCFO/MNFO)@CMWCNTs反射损耗;(e) 制备聚苯胺/Ba2Ni2Fe12O22复合物示意图[44];(f) 不同复合比例所得样品的SEM图像
Figure 3. (a) Process diagram of CFG preparation process [42]; (b) Reflection loss of CFG-50 with different thickness; (c) SEM images of ZCFO/MNFO@C-MWCNTs[43]; (d) Reflection loss of (ZCFO/MNFO)@CMWCNTs with different thickness; (e) Preparation process of polyaniline/Ba2Ni2Fe12O22 composite[44]; (f) SEM images of Ba2Ni2Fe12O22 composite
图 4 (a) MnFe2O4@C复合物制备过程示意图[47];(b) (I) S1、(II) S2、(III) S3、(IV) S4、(V) S5、(VI) S6样品SEM图;(c) (I) 2 mm的S1、S2、S3和S4反射损耗,(II) 2 mm的S1、S5、S3和S6反射损耗,(III) 不同厚度S3样品的反射损耗,(IV) 不同厚度S6样品的反射损耗;(d) MnFe2O4@C复合物电磁波吸波机制示意图
Figure 4. (a) Schematic diagram of the preparation process of MnFe2O4@C[47]; (b) SEM images of (I) S1, (II) S2, (III) S3, (IV) S4, (V) S5, (VI) S6; (c) (I) Reflection loss of S1, S2, S3, S4 under 2 mm, (II) Reflection Loss of S1, S5, S3, S6 under 2 mm, (III) Reflection loss of S3 with different thickness, (IV) Reflection loss of S6 with different thickness; (d) Electromagnetic absorption mechanisms of MnFe2O4@C composites
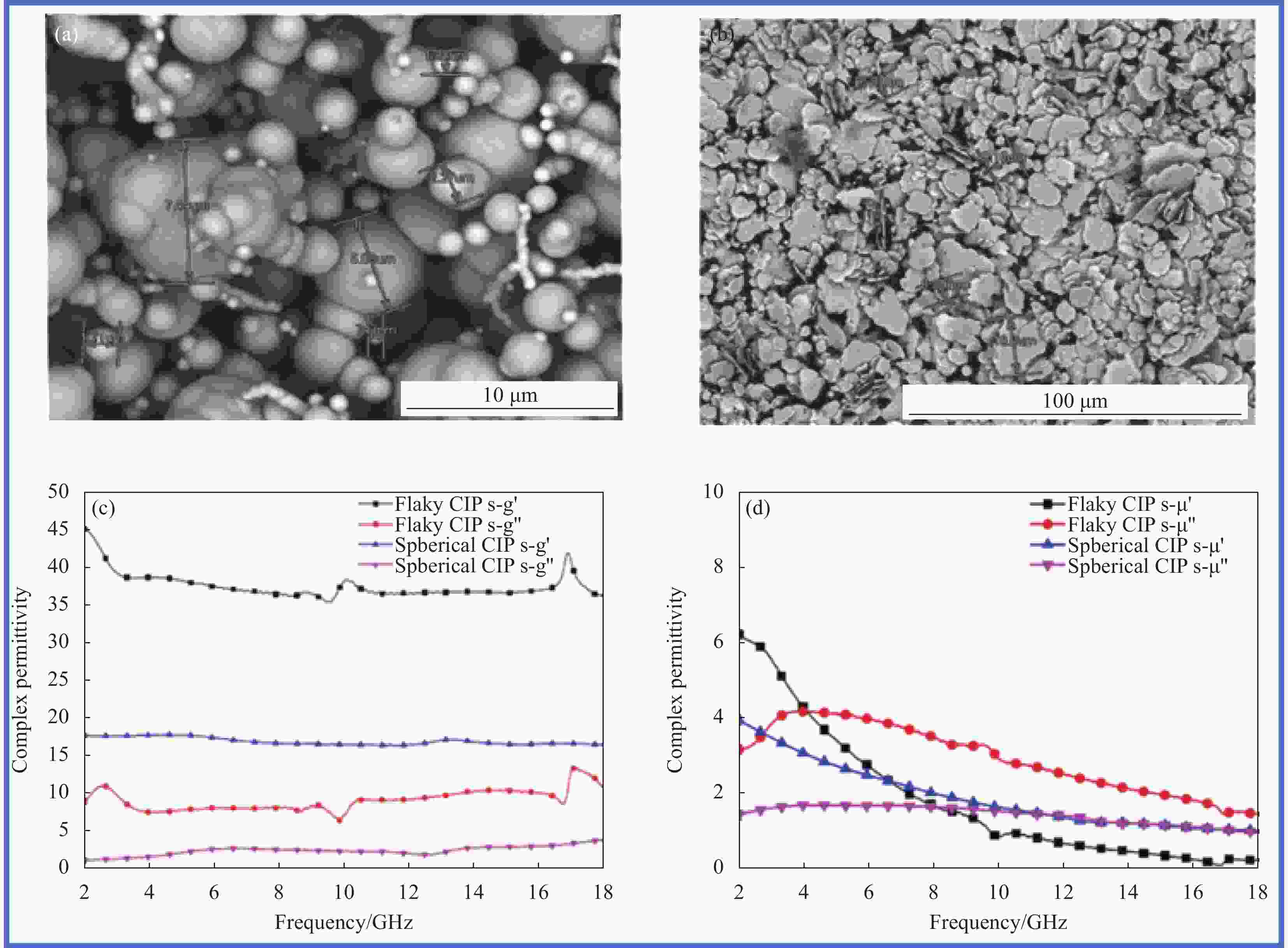
图 5 (a) 球状羰基铁SEM图像[49];(b) 片状羰基铁SEM图像;(c) 球状和片状羰基铁复介电常数;(d) 球状和片状羰基铁复磁导率常数
Figure 5. (a) SEM image of spherical carbonyl iron[49]; (b) SEM image of flake carbonyl iron; (c) Complex permittivity of spherical and flaky carbonyl iron; (d) Complex permeability constants of spherical and flaky carbonyl iron
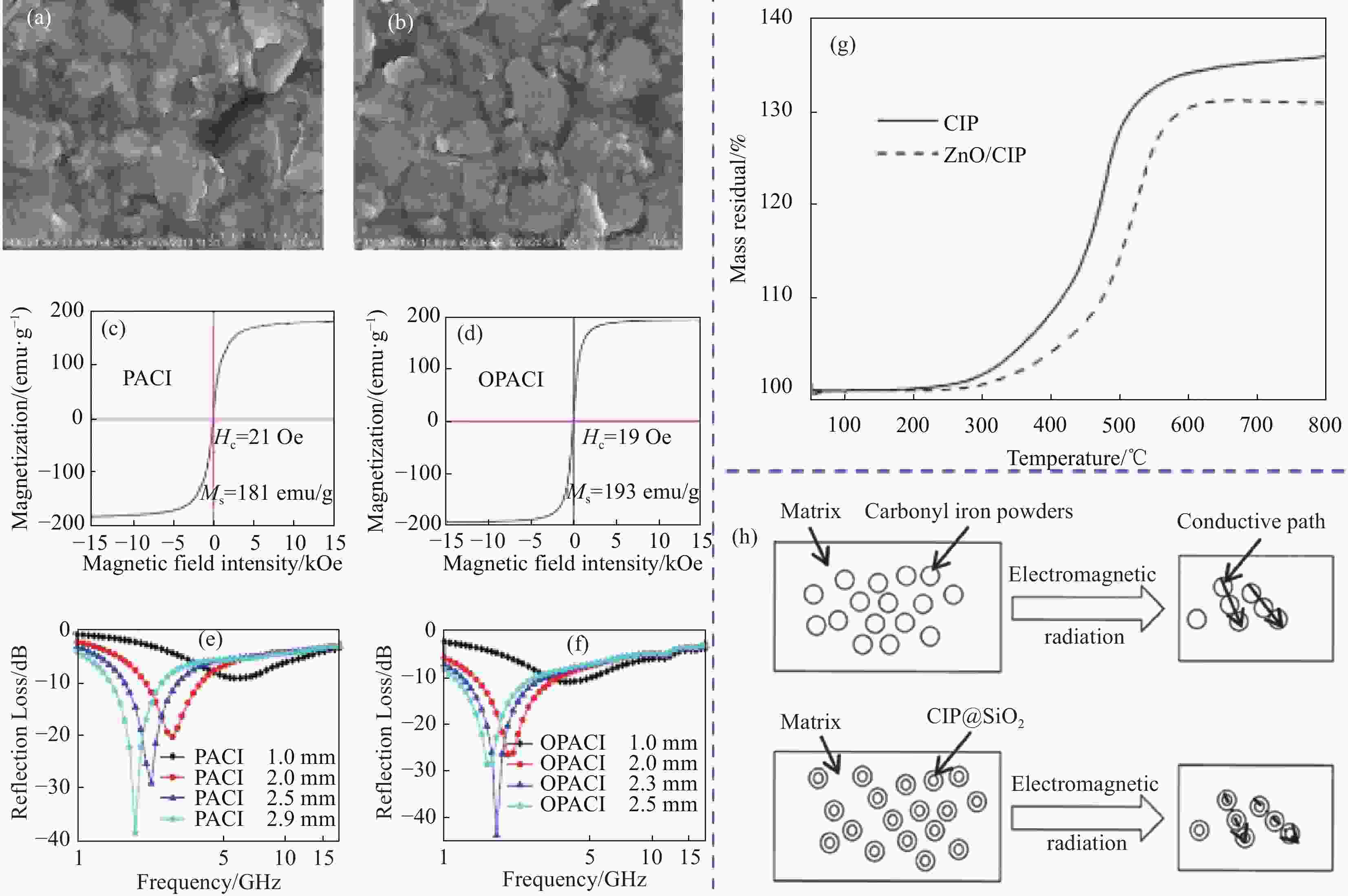
图 6 (a) 原始羰基铁SEM图像[52];(b) 取向后的羰基铁SEM图像;(c) 原始羰基铁的磁滞回线;(d) 取向后的羰基铁的磁滞回线;(e)不同厚度下原始羰基铁的反射损耗曲线;(f) 不同厚度下取向后的羰基铁反射损耗;(g) 羰基铁粉(CIP)和CIP/ZnO的热重曲线[53];(h) SiO2 包覆层对导电通路的阻碍机制[54]
Figure 6. (a) SEM images of original carbonyl iron particles [52]; (b) SEM image of carbonyl iron particles after orientation; (c) Hysteresis loops of original carbonyl iron particles; (d) Hysteresis loops of aligned carbonyl iron particles; (e) Reflection loss of original carbonyl iron particles with different thickness; (f) Reflection loss of carbonyl iron particles after orientation at different thickness; (g) TG cuvres of carbonyl-iron powders (CIP), CIP/ZnO [53]; (h) Barrier mechanism of SiO2 coating on conductive path[54]
PACI—Unoriented particle; OPACI—Magnetic particles; 1 Oe—79.57 A/m; HC—Coercive force; MS—Saturation magnetization
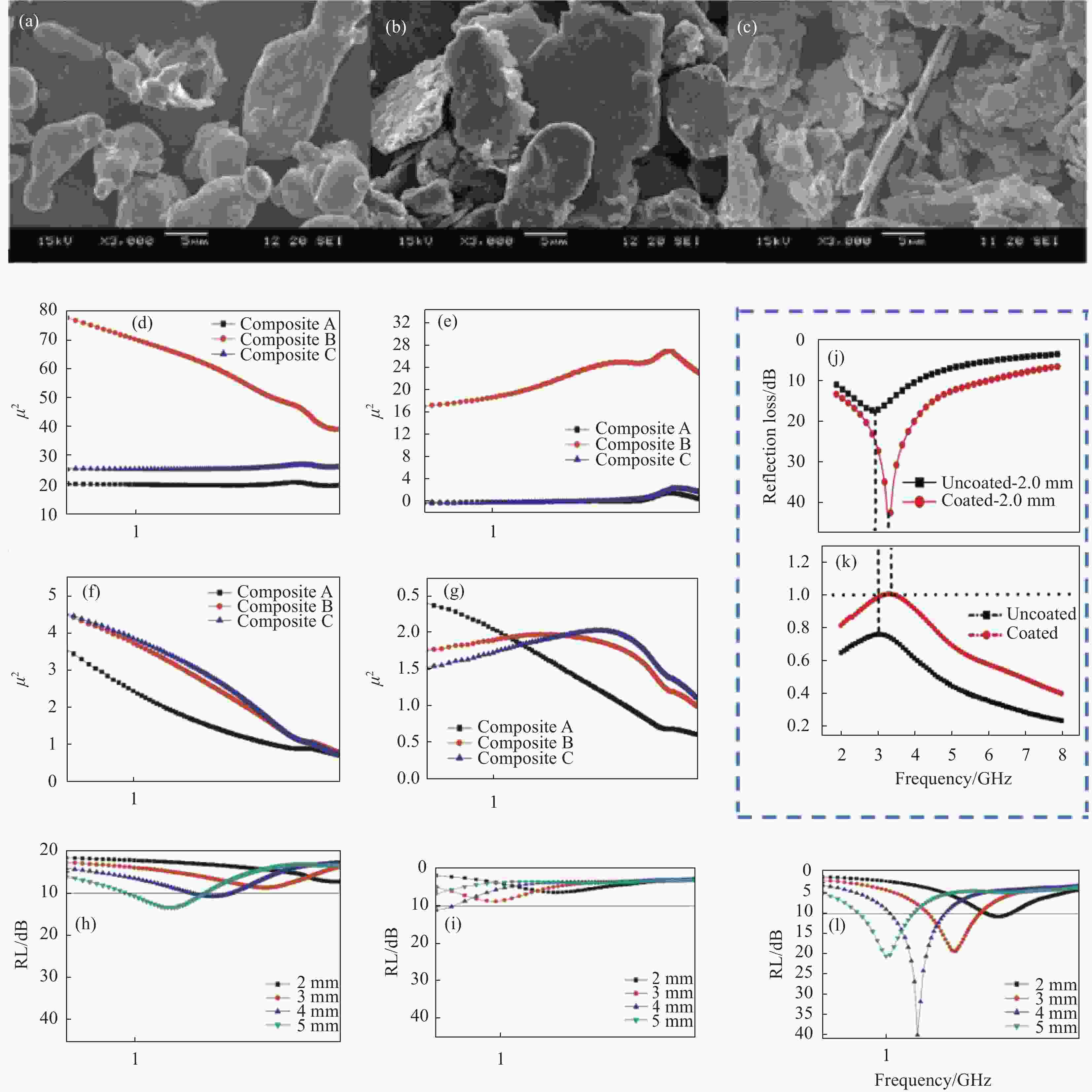
图 7 FeSiAl样品A (a)、样品B (b)、样品C (c)的SEM图像[62];(d) 样品A、B、C复介电常数实部;(e) A、B、C样品介电常数实部;(f) 样品A、B、C复磁导率实部;(g) 样品A、B、C复磁导率虚部;(h) 不同厚度的样品A反射损耗;(i) 不同厚度的样品B反射损耗;(j) 不同厚度的样品C反射损耗;(k) 无Fe3O4包覆与Fe3O4包覆样品的反射损耗[63];(l) 无Fe3O4包覆与Fe3O4包覆样品
$ {z}_{{\rm{in}}} $ /$ {z}_{0} $ 系数Figure 7. SEM images of sample A (a), sample B (b), sample C (c)[62]; (d) Real part of complex permittivity of sample A, B, C; (e) Real part of dielectric constant sample of A, B, C samples; (f) Real part of complex permeability of sample A, B, C; (g) Imaginary part of complex permeability of sample A, B, C; (h) Reflection loss of sample a with different thickness; (i) Reflection loss of sample B with different thickness; (j) Reflection loss of sample C with different thickness; (k) Reflection loss of samples without Fe3O4 coating and Fe3O4 coating[63]; (l)
$ {z}_{{\rm{in}}} $ /$ {z}_{0} $ coefficient of without Fe3O4 coating and Fe3O4 coating图 8 (a) FeSiAl与FeSiAlNi的磁滞回线[64];(b) 2 mm样品PrxHo2-xFe17反射损耗[65];(c) 2 mm 样品Pr0.3Ho1.7Fe17/Co(Co质量比=0、5、10、15、20%)反射损耗;(d) 不同厚度的Pr0.3Ho1.7Fe17/Co(10%)反射损耗;(e) 不同球磨时间FeNi合金复介电常数实部[68];(f) 不同球磨时间FeNi合金复介电常数虚部;(g) 不同球磨时间FeNi合金复磁导率实部;(h)不同球磨时间FeNi合金复磁导率虚部;((i)~(l)) 0 h、4 h、8 h和12 h球磨时间的Fe84Co4B11Nd的SEM图像[69]
Figure 8. (a) Hysteresis loops of FeSiAl and FeSiAlNi[64]; (b) Reflection loss of PrxHo2-xFe17 with 2 mm[65]; (c) Reflection loss of Pr0.3Ho1.7Fe17/Co (Co =0, 5, 10, 15, 20%) with 2 mm; (d) Reflection loss of Pr0.3Ho1.7Fe17/Co(10%) with different thickness; (e) Real part of complex permittivity of FeNi Alloy with different milling time[68]; (f) Imaginary part of complex permittivity of FeNi alloy with different milling time; (g) Real part of complex permeability of FeNi Alloy with different milling time; (h) Imaginary part of complex permeability of FeNi alloy with different milling time; ((i)-(l)) SEM images of Fe84Co4B11Nd with 0 h, 4 h, 8 h and 12 h milling time [69]
表 1 典型铁氧体低频吸波性能
Table 1. Microwave absorbing properties of typical ferrite
表 2 典型铁氧体复合材料低频吸波性能
Table 2. Low frequency microwave absorbing properties of typical ferrite composites
Material Absorption peak/
GHzMaximum reflection
loss/dBEffective
bandwidth/GHzThickness/
mmRef. ZnFe2O4@C/MWCNTs 0.81 −40.65 0.97 2.5 [40] CoFe2O4/FeCo/graphene 3.1 −30 1 5.5 [42] (Zn0.5Co0.5Fe2O4/
Mn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4)@C/MWCNTs0.56 −35.14 0.75 5 [43] Ba3Co2Fe24O21@SiO2 3.8 −9 — 3 [46] MnFe2O4@C 0.78 −48.92 1.4 2.5 [47] 表 3 典型金属微粉低频吸波性能
Table 3. Low frequency microwave absorbing properties of typical metal powders
Material Treatment method Absorption peak/GHz Maximum reflection loss/dB Effective bandwidth/GHz Thickness/mm Ref. Carbonyl iron Orientation 1.9 −40 1.1 2.9 [52] FeSiAl Flat design 2.25 −19 0.93 3 [59] FeSiAl Annealing 1.13 −22.64 0.8 5 [60] FeSiAl Ball milling, oxidation 1.4 −39.67 0.8 4 [62] FeSiAl @Fe3O4 Cladding 3.4 −43 4 2 [63] FeSiAlNi Doping 1.7 −11.9 0.5 2.5 [64] Ho0.6Ce1.4Co17 Doping 3.6 −12.74 0.48 3.5 [66] Nd0.3Ce1.7Co17 Doping 4.16 −13.85 0.64 3 [67] FeNi Ball milling 4.2 −21 2.5 — [68] Fe84Co4B11Nd Quenching, ball milling 3.9 −9.8 — 1.5 [69] -
[1] 张钊, 王峰, 张新全, 等. 低频宽带薄层吸波材料研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2019, 50(6):6038-6045.ZHANG Z, WANG F, ZHANG X Q, et al. Research progress of low frequency broadband thin layer absorbing materials[J]. Functional Materials,2019,50(6):6038-6045(in Chinese). [2] 索庆涛, 许宝才, 王建江, 等. 雷达吸波材料低频化研究现状及进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(4):25-28.SUO Q T, XU B C, WANG J J, et al. Research status and progress of low frequency radar absorbing materials[J]. New Chemical Materials,2019,47(4):25-28(in Chinese). [3] 吴岭, 邱彦文, 王枭. 美军反导预警体系电子目标研究[J]. 航天电子对抗, 2020, 36(1):28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.01.007WU L, QIU Y W, WANG X. Research on electronic target of us antimissile early warning system[J]. Space Electronic Countermeasures,2020,36(1):28-32(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2421.2020.01.007 [4] 刘顺华, 刘军民, 董星龙, 等. 电磁波屏蔽及吸波材料[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007.LIU S H, LIU J M, DONG X L, et al. Electromagnetic shielding and absorbing materials[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2007(in Chinese). [5] 陈光文. 空中霸主——美军F-22“猛禽”战斗机[J]. 知识就是力量, 2018(8): 80-83.CHEN G W. Air overlord-US air army F-22 raptor[J]. Knowledge is Power, 2018(8): 80-83(in Chinese). [6] 夹心. B-2隐形战略轰炸机[J]. 百科探秘(航空航天), 2020(4): 12-13.JIA X. B-2 stealth strategic bomber[J]. Encyclopaedic Mysteries (Aerospace), 2020(4): 12-13(in Chinese). [7] 马井军, 赵明波, 张开锋, 等. 飞机隐身技术及其雷达对抗措施[J]. 国防科技, 2009, 30(3):38-44, 64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2009.03.008MA J J, ZHAO M B, ZHANG K F, et al. Stealth technology and radar countermeasures[J]. National Defense Science and Technology,2009,30(3):38-44, 64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2009.03.008 [8] HUSNAIN Ahmad, ASRA Tariq, AMIR Shehzad, et al. Stealth technology-methods and composite materials-A review[J]. Polymer Composites,2019,40:4457-4472. doi: 10.1002/pc.25311 [9] LI M, CAO X, ZHENG S, et al. Ternary composites RGO/MoS2@Fe3O4: Synthesis and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorbing performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics,2017,28(22):16802-16812. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-7595-x [10] LV H, LIANG X, JI G, et al. Porous Three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(18):9776-9783. [11] CUI X, LIANG X, LIU W, et al. Stable microwave absorber derived from 1D customized heterogeneous structures of Fe3N@C[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,381:122589. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122589 [12] LIANG X, LIU W, CHENG Y, et al. Review: Recent process in the design of carbon-based nanostructures with optimized electromagnetic properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,749:887-899. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.03.344 [13] MA Z, MANG C, WENG X, et al. The influence of different metal ions on the absorption properties of nano-nickel zinc ferrite[J]. Materials,2018,11(4):11590. [14] SUN Y C, LI D P, YANG Y, et al. Achieving rough sphere-shaped ZnS with superior attenuation electromagnetic absorption performance[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(7):3907-3913. doi: 10.1039/C6RA26489A [15] PEYMANFAR R. AHMADI A, SELSELEH-ZAKERIN E. Evaluation of the size and medium effects on the microwave absorbing, magnetic, electromagnetic shielding, and optical properties using CuCo2S4 nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,848:156453. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156453 [16] 周聪俐. MXene复合物的合成及其在微波吸收中的应用[D]. 青岛: 青岛大学, 2020.ZHOU C L. Synthesis of MXene composite and its application in microwave absorption[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University, 2020 (in Chinese). [17] XU H, YIN X, LI M, et al. Ultralight cellular foam from cellulose nanofiber/carbon nanotube self-assemblies for ultrabroad-band microwave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(25):22628-22636. [18] DAS S, NAYAK G C, SAHU S K, et al. Development of FeCoB/graphene oxide based microwave absorbing materials for X-Band region[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2015,384:224-228. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.01.079 [19] WANG W J, ZANG C G, JIAO Q J. Magnetic ferrite/conductive polyaniline nanocomposite as electromagnetic microwave absorbing materials in the low frequency[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2013,333-335(2):1811-1815. [20] AGGARWAL N, NARANG S B. Magnetic characterization of Nickel-Zinc spinel ferrites along with their microwave characterization in Ku band[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2020,513:167052. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167052 [21] GUO Y, JIAN X, ZHANG L, et al. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core-shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high tempera-ture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,384:123371. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123371 [22] 葛超群, 汪刘应, 刘顾. 碳基/羰基铁复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2019, 47(12):43-54. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000220GE C Q, WANG L Y, LIU G. Research progress of carbon /carbonyl iron composite absorbing materials[J]. Material Engineering,2019,47(12):43-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000220 [23] ROZANOV K N. Ultimate thickness to bandwidth ratio of radar absorbers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation,2000,48(8):1230-1234. doi: 10.1109/8.884491 [24] SNOEK J L. Dispersion and absorption in magnetic ferrites at frequencies above one MC/S[J]. Physica,1948,14(4):207-217. doi: 10.1016/0031-8914(48)90038-X [25] ACHER O, DUBOURG S. Generalization of Snoek's law to ferromagnetic films and composites[J]. Physical Review B,2008,77(10):104440. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.77.104440 [26] MCHENRY M E, WILLARD M A, LAUGHLIN D E. Amorphous and nanocrystalline materials for applications as soft magnets[J]. Progress in Materials Science,1999,44(4):291-433. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6425(99)00002-X [27] KOTNALA R K, SHAH J. Handbook of magnetic materials[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2015: 291-379. [28] PARDAVI-HORVATH M. Microwave applications of soft ferrites[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2000,215:171-183. [29] LIU J L, ZHANG P, ZHANG X K, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of La-doped Sr-hexaferrite nanopowders via sol-gel auto-combustion method[J]. Rare Metals,2017,36(9):704-710. doi: 10.1007/s12598-015-0671-6 [30] 丁冬海, 白冰, 肖国庆, 等. 燃烧合成碳化硼粉体及其介电吸波性能[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(3):343-350.DING D H, BAI B, XIAO G Q, et al. Combustion synthesis of boron carbide powder and its microwave absorbing properties[J]. Acta silicate Sinica,2020,48(3):343-350(in Chinese). [31] 柏嘉玮, 杨静, 吕桢飞, 等. Ti4+掺杂M型六角铁氧体BaFe12-xTixO19陶瓷的磁学和介电特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1):43-48. doi: 10.15541/jim20200088BAI J W, YANG J, LV Z F, et al. Magnetic and dielectric properties of Ti4+ doped M-type hexagonal ferrite BaFe12-xTixO19 ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2021,36(1):43-48(in Chinese). doi: 10.15541/jim20200088 [32] ZHANG Y Z, KANG Z T, CHEN D. Synthesis and microwave absorbing properties of Mn-Zn nanoferrite produced by microwave assisted ball milling[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics,2014,25(10):4246-4251. doi: 10.1007/s10854-014-2156-z [33] REHMAN A U, SHAUKAT S F, AKHTAR M N, et al. Evaluations of structural, magnetic and various dielectric parameters of Ni-substituted Zn2W-type hexagonal ferrites for high frequency (1-6 GHz) applications[J]. Ceramics International,2019,45(18):24202-24211. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.129 [34] QIAN K, YAO Z, LIN H, et al. The influence of Nd substitution in Ni-Zn ferrites for the improved microwave absorption properties[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(1):227-235. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.255 [35] LIU P, NG V M H, YAO Z, et al. Facile synthesis and hierarchical assembly of flowerlike nio structures with enhanced dielectric and microwave absorption properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(19):16404-16416. [36] PRAVEENA K, SADHANA K, MATTEPPANAVAR S, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Ni0.4Zn0.2Mn0.4Fe2O4 potential for radar absorbing[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2017,423:343-352. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.09.129 [37] YOU C, FAN X, TIAN N, et al. Improved electromagnetic microwave absorption of the annealed pre-sintered precursor of Mn-Zn ferrite[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2015,381:377-381. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.12.089 [38] CAI X, WANG J, CUI K, et al. Crystallization processes and microwave absorption properties of amorphous LiZn ferrite hollow microspheres[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics,2017,28(13):9596-9605. doi: 10.1007/s10854-017-6708-x [39] 李保东, 李巧玲, 张存瑞, 等. 铁氧体复合吸波材料研究新进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008, 22(3):226-229.LI B D, LI Q L, ZHANG C R, et al. New development of ferrite composite absorbing materials[J]. Material Guide,2008,22(3):226-229(in Chinese). [40] TANG Y, YIN P, ZHANG L, et al. Novel carbon encapsulated zinc ferrite/MWCNTs composite: Preparation and low-frequency microwave absorption investigation[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(18):28250-28261. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.07.326 [41] CHEN Z, MU D, LIU T, et al. PANI/BaFe12O19@Halloysite ternary composites as novel microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,582:137-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.006 [42] SU X, WANG J, ZHANG X, et al. One-step preparation of CoFe2O4/FeCo/graphite nanosheets hybrid composites with tunable microwave absorption performance[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(8):12353-12363. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.286 [43] YIN P, ZHANG L, WU H, et al. Two-step solvothermal synthesis of (Zn0.5Co0.5Fe2O4/Mn0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4)@C-MWCNTs hybrid with enhanced low frequency microwave absorbing performance[J]. Nanomaterials,2019,9(11):1601. doi: 10.3390/nano9111601 [44] PACKIARAJ G, SAKTHIPANDI K, JOTANIA R B, et al. Dielectric and magnetic properties of polyaniline-blended Y-type Ba2Ni2Fe12O22 hexaferrite composites[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2020,49(5):3317-3324. doi: 10.1007/s11664-020-08051-8 [45] TAUBERT A, PALMS D, WEISS O, et al. Polymer-assisted control of particle morphology and particle size of zinc oxide precipitated from aqueous solution[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2002,14(6):2594-2601. doi: 10.1021/cm011670m [46] 陈柯宇, 何亚兵, 李良超, 等. Z型钡铁氧体/二氧化硅复合物的制备和吸波性能[C]//中国化学会2013年中西部地区无机化学化工学术研讨会论文集. 中国化学会, 2013: 2.CHEN K Y, HE Y B, LI L C, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of Z-type barium ferrite/silica composites[C]//Chinese Chemical Society. Proceedings of 2013 Central and Western Inorganic Chemistry and Chemical Engineering Symposium of Chinese Chemical Society. Chinese Chemical Society, 2013: 2. [47] YIN P, ZHANG L, SUN P, et al. Apium-derived biochar loaded with MnFe2O4@C for excellent low frequency electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(9):13641-13650. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.150 [48] WALSER R M, WIN W, VALANJU P M. Shape-optimized ferromagnetic particles with maximum theoretical microwave susceptibility[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,1998,34(4):1390-1392. doi: 10.1109/20.706558 [49] LE C, ZHAO Z G, MING X Z. Microwave absorbing property of thin coating in the broadband low-frequency range[J]. Materials Science Forum,2018,916:33-37. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.916.33 [50] WALSER R M, KANG W. Fabrication and properties of microforged ferromagnetic nanoflakes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,1998,34(4):1144-1146. doi: 10.1109/20.706419 [51] 刘琪, 朱冬梅, 周万城, 等. 高能球磨法制备片状羰基铁及其电磁性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2013, 42(2):1-4.LIU Q, ZHU D M, ZHOU W C, et al. Preparation of flake carbonyl iron by high energy ball milling and its electromagnetic properties[J]. Hot working process,2013,42(2):1-4(in Chinese). [52] ZHAO H, XU S, TANG D, et al. Thin magnetic coating for low-frequency broadband microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2014,116(24):243911. doi: 10.1063/1.4904443 [53] 郭飞, 杜红亮, 屈绍波, 等. 海胆状氧化锌/羰基铁粉核壳结构复合粒子的抗氧化及吸波性能[J]. 无机化学学报, 2015, 31(4):755-760.GUO F, DU H L, QU S B, et al. Antioxidant andmicrowave absorbing properties of sea urchin like ZnO/carbonyl iron powder core shell composite particles[J]. Journal of Inorganic Chemistry,2015,31(4):755-760(in Chinese). [54] 刘娜, 罗平, 刘朝辉, 等. 雷达波吸收剂羰基铁粉的改性研究进展[J]. 当代化工, 2019, 48(11):2671-2677. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.11.057LIU N, LUO P, LIU C H, et al. Research Progress on modification of carbonyl iron powder as radar wave absorber[J]. Modern Chemical Industry,2019,48(11):2671-2677(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0460.2019.11.057 [55] 谢建良, 梁波浪, 邓龙江. 二氧化硅包覆片状金属磁性微粉电磁特性分析[J]. 功能材料, 2008(1):41-43, 47. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2008.01.013XIE J L, LIANG B L, DENG L J. Analysis of electromagnetic characteristics of silicon dioxide coated sheet metal magnetic powder[J]. Functional Materials,2008(1):41-43, 47(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2008.01.013 [56] 高庆庆, 肖超, 张忠健, 等. 磷化处理对软磁铁粉性能影响[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2014, 36(2):7-11. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2014.02.002GAO Q Q, XIAO C, ZHANG Z J, et al. Effect of phosphating treatment on properties of soft magnetic iron powder[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2014,36(2):7-11(in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2014.02.002 [57] ZHENG D, LIU T, ZHOU L, et al. Electromagnetic absorbing property of the flaky carbonyl iron particles by chemical corrosion process[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2016,419:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.06.008 [58] TAKAHASHI M, ARAI H, WAKIYAMA T. Magnetostriction constants for Fe-Al-Si (Sendust) single crystals with DO3 ordered structure[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics,1987,23(5):3523-3525. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.1987.1065759 [59] 曹琦, 龚荣洲, 冯则坤, 等. Fe-Si-Al系合金粉微波吸收特性[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2006, 16(03):524-529. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2006.03.024CAO Q, GONG R Z, FENG Z K, et al. Microwave absorption characteristics of Fe Si Al alloy powder[J]. Chinese Jour-nal of Nonferrous Metals,2006,16(03):524-529(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2006.03.024 [60] 唐传明, 冯永宝, 丘泰. 扁平化及退火温度对FeSiAl合金吸波性能的影响[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2013, 32(2):43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.02.012TANG C M, FENG Y B, QIU T. Effect of flattening and annealing temperature on microwave absorbing properties of FeSiAl alloy[J]. Electronic Components and Materials,2013,32(2):43-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.02.012 [61] ZUO B, SARASWATI N, SRITHARAN T, et al. Production and annealing of nanocrystalline Fe-Si and Fe-Si-Al alloy powders[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing,2004,371(1-2):210-216. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2003.11.046 [62] FENG Y, TANG C, QIU T. Effect of ball milling and moderate surface oxidization on the microwave absorption properties of FeSiAl composites[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B-Advanced Functional Solid-State Materials,2013,178(16):1005-1011. [63] HE J, DENG L, LIU S, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4-modified flaky FeSiAl[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2017,444:49-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.07.097 [64] LI Q, FENG Z, YAN S, et al. Comparison of the magnetic and absorption properties of flaky super sendust and sendust alloys[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2015,44(10):3777-3782. doi: 10.1007/s11664-015-3847-9 [65] LUO J, PAN S, QIAO Z, et al. Electromagnetic and Microwave absorption properties of the flake-shaped Pr-Ho-Fe alloys in the C-band[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2018,47(1):751-759. doi: 10.1007/s11664-017-5833-x [66] HE Y, PAN S K, CHENG L C, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption property of Ho-Ce-Co alloy[J]. Physics of Metals and Metallography,2020,121(3):217-222. doi: 10.1134/S0031918X20020088 [67] HE Y, PAN S, CHENG L, et al. Effect of Nd content on microwave absorption property of Ce2Co17 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering,2019,48(10):3108-3112. [68] SUO Q, XU B, WANG J, et al. Effect of high energy ball milling on electromagnetic properties of FeNi absorbing materials[J]. Advances in Materials, Machinery, Electronics Ⅱ,2018,1955:020006. [69] WANG H, XIE G, XIE N, et al. Electromagnetic and absorbing properties of the composites based on iron, cobalt, B and rare earth Nd[J]. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics,2019,30(1):401-405. doi: 10.1007/s10854-018-0304-6 -





 下载:
下载: