Preparation and application of cellulose-based metal nanoparticles composite catalysts
-
摘要: 纤维素是一种来源广泛、比表面积大、多羟基且环境友好型的生物高分子材料,其水悬浮液可形成三维网络缠结结构,从而为具有催化活性的金属纳米粒子提供负载位点,使其均匀分散并固定于基底内部或表面构建复合催化剂材料,进而有效提高催化性能。本文综述了纤维素基金属纳米粒子复合催化剂的制备及应用的相关研究,重点介绍了不同纤维素基材料作为基底制备金属纳米粒子复合催化剂的方法及其优缺点,归纳了金属纳米粒子在纤维素基材料中的负载途径及原理,重点阐述了纤维素基材料在复合催化剂中的主要作用,最后对纤维素基材料在金属纳米粒子复合催化剂领域的研究工作进行了总结与展望,为纤维素基复合催化剂材料的制备和应用提供参考。Abstract: Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer in nature, with many advantages like broad resource of raw material, large specific surface area, abundant hydroxyl groups and environmentally friendly. Besides, cellulose can form three-dimensional network structure in aqueous suspension, which provides loading sites for metal nanoparticles to make them disperse well and binds well with cellulose and prepares the composite catalysts with improved catalytic performance. Herein, the preparation and application of cellulose-based composite catalysts with metal nanoparticles were summarized, the methods and merits of the composite catalysts with various cellulosic materials were highlighted. Furthermore, the loading methods and principles of metal nanoparticles were generalized, and the main functions of cellulosic materials in composite catalysts were elaborated. Finally, the researches of cellulose-based composite catalysts with metal nanoparticle were summarized. This work can be a reference for the preparing and applying of cellulosic composite catalysts.
-
Key words:
- cellulose /
- metal nanoparticles /
- load /
- composite catalysts /
- catalytic performance
-
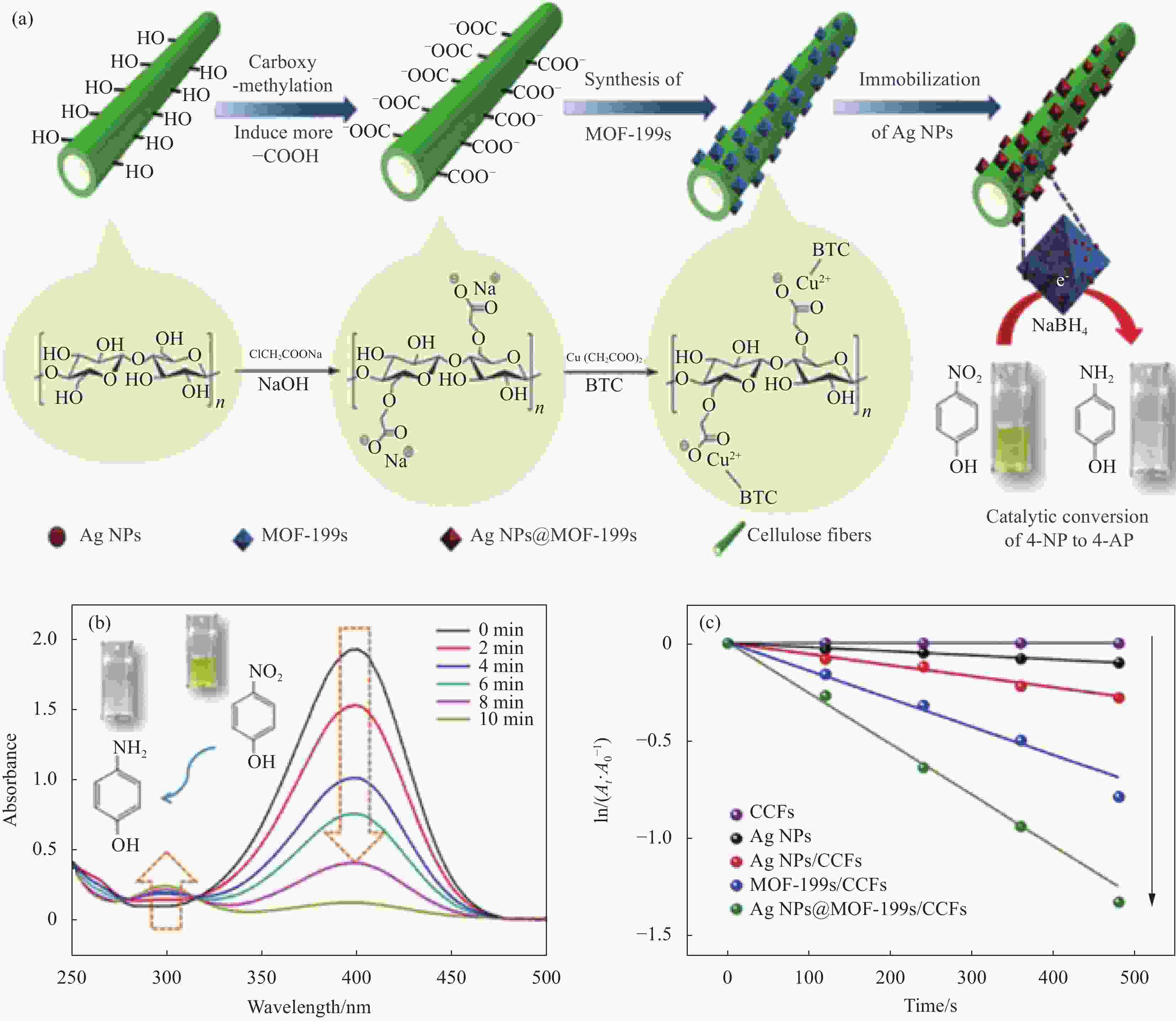
图 2 纤维素纤维(CF)基金属纳米粒子(NPs)复合催化剂合成路线示意图 (a)、加入催化剂后在不同反应时间下催化4-硝基苯酚(4-NP)降解的UV-vis (b) 及ln(At/A0)与反应时间t在400 nm处的关系 (c)[47]
Figure 2. Synthesis route of cellulose fiber (CF)-based metal nanoparticles (NPs) composite catalyst (a), UV-vis absorption spectra of 4-nitrophenol (4-NP) after adding the composite catalyst at different time (b) and ln(At/A0) versus reaction time (at 400 nm) (c)[47]
BTC—1,3,5-Benzenetricarboxylic acid; CCF—Carboxymethyl cellulose fiber; MOF—Metal-organic frame materials; A0—Absorbance of the mixture at the initial moment of reaction; At—Absorbance at 400 nm (4-NP) after reaction time t
图 4 纳米纤维素晶体(CNC)基NPs复合催化剂的制备流程图 (a)、不同时间下催化4-NP降解的紫外-可见光谱与At/A0 (b) 及ln(At/A0) (c) 随时间变化图[64]
Figure 4. Schematic of preparation of crystal nanocellulose (CNC)-based NPs composite catalyst (a), UV-vis absorption spectra after adding the composite catalyst at different time (b) and In(At/A0) versus reaction time (at 400 nm) (c)[64]
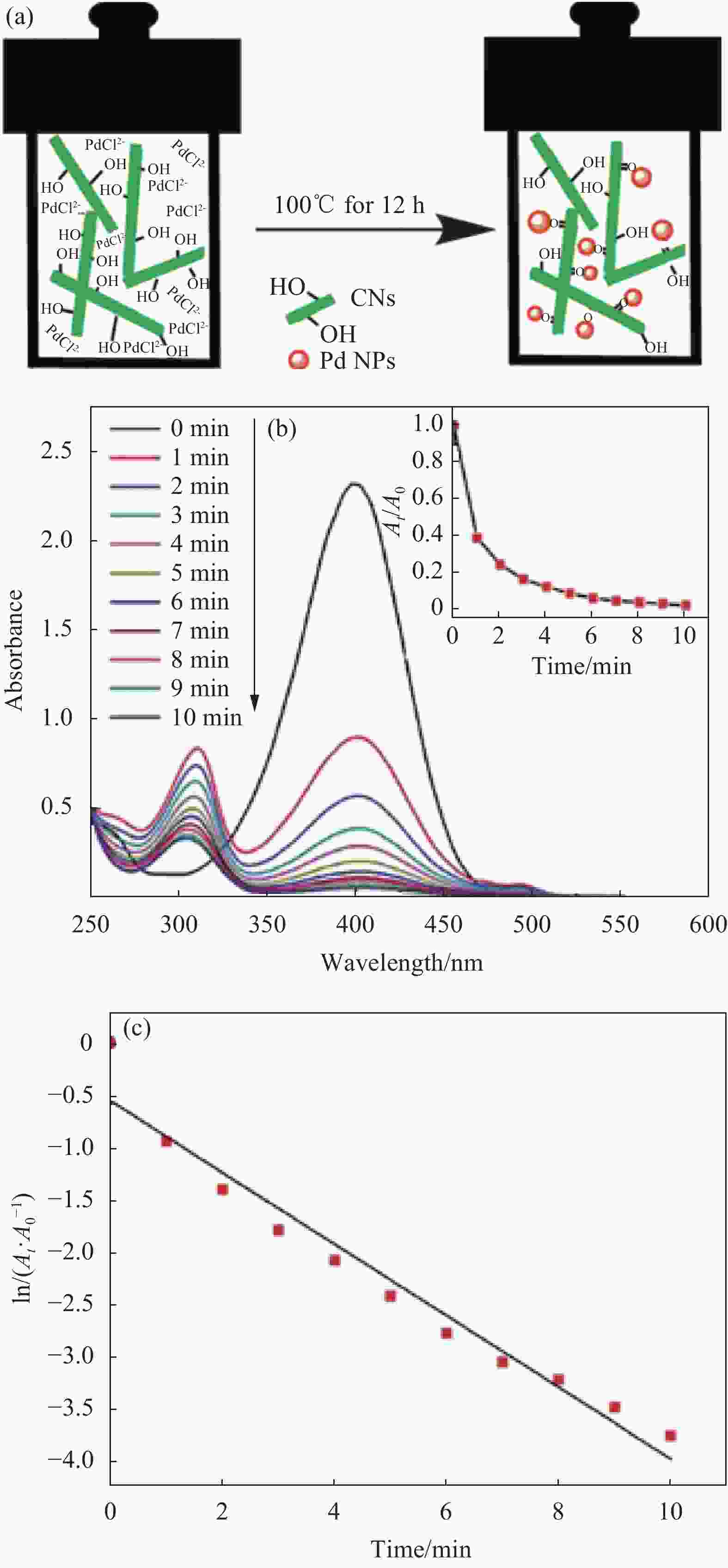
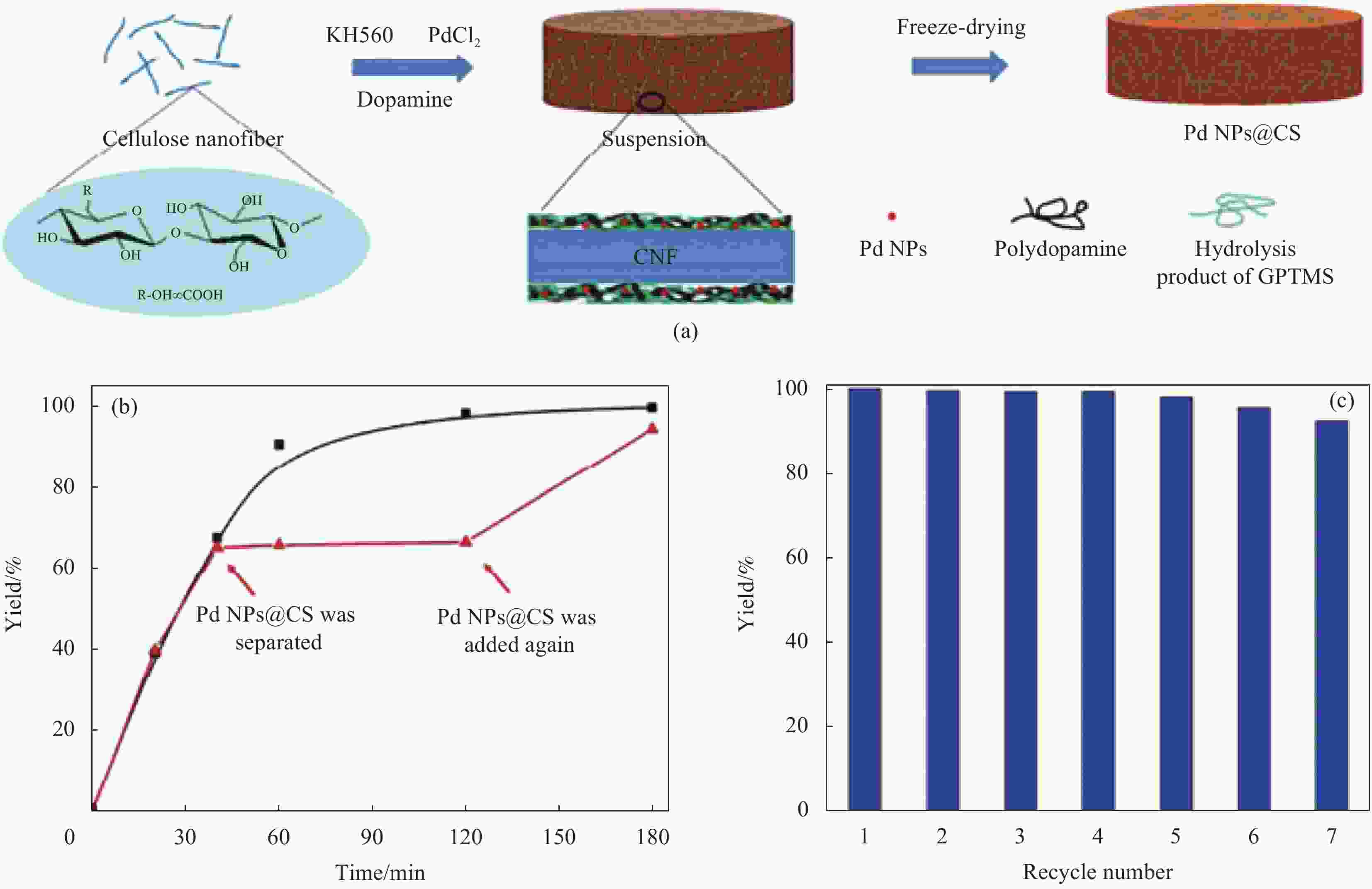
图 6 纳米纤维素纤维(CNF)基纳米复合催化剂的制备流程图 (a)、Pd NPs@纤维素海绵(CS)在芳基卤化物与芳基硼酸的交叉耦合反应中的催化活性 (b) 及可回用性 (c)[75]
Figure 6. Schematic of preparation of cellulose nanofibers (CNF) based mental nanoparticles composite catalyst (a), catalytic performance (b) and recyclability (c) of Pd NPs@cellulose sponge (CS) in the cross-coupling reaction between aryl halide and aryl boric acid[75]
GPTMS—γ-(2,3-Epoxypropoxypropyl) propyl trimethoxy silane
-
[1] 黄元元. 金属纳米颗粒的生长和表面结构调控的研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2014.HUANG Yuanyuan. Study on the growth and surface structure control of metal nanoparticles[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2014(in Chinese). [2] 神祥娜. 金属纳米颗粒的性质研究及其应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2011.SHEN Xiangna. Properties of metal nanoparticles and their applications[D]. Ji'nan: Shandong University, 2011(in Chinese). [3] 龚君佐, 屠重棋. 纳米粒子在恶性肿瘤治疗中的研究进展[J]. 华西医学, 2008, 23(2):415-416.GONG Junzuo, TU Zhongqi. Research progress of nanoparticles in the treatment of malignant tumors[J]. West China Medical Journal,2008,23(2):415-416(in Chinese). [4] 吴小龑, 刘琳琳, 解增旗, 等. 金属纳米粒子增强有机光电器件性能研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3):210-212.WU Xiaoyan, LIU Linlin, XIE Zengqi, et al. Advance in metal-based nanoparticles for the enhanced performance of organic optoelectronics devices[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2016,37(3):210-212(in Chinese). [5] ARIF U K. 贵金属纳米粒子的生物合成及其在生物医药和催化方面的应用[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2016.ARIF U K. Biosynthesis of noble metal nanoparticles and their biomedical and catalytic applications[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [6] 魏静仁, 张匆, 袁伟忠, 等. 纳米粒子表面ATRP修饰及其在生物医学领域中的应用[J]. 塑料, 2011, 40(5):110-112.WEI Jingren, ZHANG Cong, YUAN Weizhong, et al. Surface modification and functionlization of nanoparticles via atom transfer radical polymerization[J]. Plastics,2011,40(5):110-112(in Chinese). [7] 熊斌. 金属纳米粒子在生物成像与生物医学上的应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2013.XIONG Bin. Applications of metal nanoparticles in bioimaging and biomedical science[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2013(in Chinese). [8] 杭乐. 基于DNA修饰界面原位生长吸附金属纳米材料的电化学生物传感器[D]. 漳州: 闽南师范大学, 2015.HANG Le. Electrochemical biosensors based on in-situ growth of metal nanometerials on the DNA modified interfaces[D]. Zhangzhou: Minnan Normal University, 2015(in Chinese). [9] 李光照. 金纳米粒子传感器用于检测DNA和金属离子及核壳纳米材料制备[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011.LI Guangzhao. The synthesis of core-shell structure nanocomposites and gold nanoparticle sensors for the detection of DNA and metal ions[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011(in Chinese). [10] 李旺. 金属纳米粒子与DNAzyme在电化学与比色传感中的研究与应用[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2006.LI Wang. The research and application of metal nanoparticles and DNAzyme in electrochemical and colorimetric sensor[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2006(in Chinese). [11] 李贵安. 纳米粒子与染料超分子结构复合材料的设计及其吸收红移机理[J]. 陕西师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006(1):38-41.LI Guian. Design of composites based on supramolecular structure of nanoparticles dye and mechanism of absorption red shift[J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Natural Science Edition),2006(1):38-41(in Chinese). [12] 王建伟. 介孔二氧化硅包覆的贵金属纳米粒子催化还原阳离子染料[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2016.WANG Jianwei. Reduction cationic dye catalyzed by noble metal nanoparticles coated with mesoporous silica[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [13] 徐秋红. 青霉辅助光化学合成银纳米粒子及催化还原有机染料的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2014.XU Qiuhong. Photochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles assisted by penicillium and its use for catalytic reduction of organic dye[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2014(in Chinese). [14] NAMASIVAYAM D, TA W L, PITCHAIMANI V, et al. Metal nanoparticles anchored on rhenium disulfide nanosheets as catalysts for the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds[J]. Chemnanomat,2018,3(53):1-25. [15] 郑丽清. 金属纳米颗粒的团聚和催化机理的研究及其分析应用[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015ZHENG Liqing. Study of the aggregation and catalytic mechanisms of metal nanoparticles and their analytical applications[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015(in Chinese). [16] KALANTARI K, AFIFI A B M, Bayat S, et al. Heterogeneous catalysis in 4-nitrophenol degradation and antioxidant activities of silver nanoparticles embedded in Tapioca starch[J]. Arabian Journal of Chemistry,2019,12(8):5246-5252. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.12.018 [17] GENTA H, HIROMI S, MICHIO M M, et al. Preparation and characterization of gold nano-particles chemisorbed by π-radical thiols[J]. Chemistry Letters,2002(1):1030-1031. [18] FINK J, KIELY C J, BETHELL D, et al. Self-organization of nanosized gold particles[J]. Chemistry of Materials,1998,10(3):922-926. doi: 10.1021/cm970702w [19] YOKOTA S, KITAOKA T, OPIETNIK M, et al. Synthesis of gold nanoparticles for in situ conjugation with structural carbohydrates[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2010,120(51):10014-10017. [20] GUIBAL E. Heterogeneous catalysis on chitosan-based materials: A review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2005,30(1):71-109. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2004.12.001 [21] LIU S, LIU Y, DENG F, et al. Comparison of the effects of microcrystalline cellulose and cellulose nanocrystals on Fe3O4/C nanocomposites[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(1):74198-74205. [22] SONG J, KAHVECI D, CHEN M, et al. Enhanced catalytic activity of lipase encapsulated in PCL nanofibers[J]. Langmuir,2012,28(14):6157-6162. doi: 10.1021/la300469s [23] NATHANIEL C C, JASON L B, AARON D S. Copper-based nanostructured coatings on natural cellulose: Nanocomposites exhibiting rapid and efficient inhibition of a multi-drug resistant wound pathogen, A. baumannii, and mammalian cell biocompatibility in vitro[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2011,12(13):2506-2514. [24] STIJN V D V, GEBOERS J, JACOBS P A, et al. Recent advances in the catalytic conversion of cellulose[J]. ChemCatChem,2011,3(1):82-94. doi: 10.1002/cctc.201000302 [25] ROMAN Maren. Toxicity of cellulose nanocrystals: A review[J]. Industrial Biotechnology,2015,11(1):25-33. doi: 10.1089/ind.2014.0024 [26] 刘金萱. 纳米金属/聚合物复合粉体的制备及性能研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2008.LIU Jinxuan. The characteristic and preparation of metal/polymer nanocomposities[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2008(in Chinese). [27] MEHDI Y, IMAN G, HASSAN N, et al. Synthesis and characterization of antibacterial carboxymethylcellulose/CuO bio-nanocomposite hydrogels[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,73(1):109-114. [28] THAVASI V, SINGH G, RAMAKRISHNA S. Electrospun nano-fibers in energy and environmental applications[J]. Energy & Environmental Science,2008,1(2):205-221. [29] CAO X, DONG H, LI C M. New Nanocomposite materials reinforced with flax cellulose nanocrystals in waterborne polyurethane[J]. Biomacromolecules,2007,8(3):899-904. doi: 10.1021/bm0610368 [30] LABET M, THIELEMANS W, DUFRESNE A. Polymer grafting onto starch nanocrystals[J]. Biomacromolecules,2007,8(9):2916-2927. doi: 10.1021/bm700468f [31] 房美. 高分散负载钯纳米金属催化剂制备及其性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2013.FANG Mei. Preparation of high dispersed supported nanocrystals and catalytic performance[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [32] 匡尹杰. 基于贵金属纳米颗粒/碳纳米材料复合物的燃料电池电催化剂研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2012.KUANG Yinjie. Study on electrocatalysts of fuel cell based on nobel metal nanoparticles/carbon nanomaterial hybrids[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2012(in Chinese). [33] 杜庆伟, 郑长青, 李毅群. 四乙烯五胺功能化纤维素负载纳米钯催化剂的制备及其对Suzuki反应催化性能的研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2012, 24(1):63-68.DU Qingwei, ZHENG Changqing, LI Yiqun. Tetraethylenepentamine-functionalized cellulose supportednano-palladium for Suzuki reaction[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2012,24(1):63-68(in Chinese). [34] XIONG R, LU C, WANG Y, et al. Nanofibrillated cellulose as the support and reductant for the facile synthesis of Fe3O4/Ag nanocomposites with catalytic and antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2013,1(47):14910-14918. doi: 10.1039/c3ta13314a [35] ISLAM M T, DOMINGUEZ N, AHSAN M A, et al. Sodium rhodizonate induced formation of gold nanoparticles supported on cellulose fibers for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol and organic dyes[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5(1):4185-4193. [36] 章政. 天然高分子的电沉积技术及其纳米复合物的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2018.ZHANG Zheng. Research on electrodeposition technology of biopolymer and their nanocomposites[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [37] REZAYAT M, BLUNDELL R K, CAMP J E, et al. Green one-step synthesis of catalytically active palladium nanoparticles supported on cellulose nanocrystals[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2014,2(5):1241-1250. [38] AN X, LONG Y, NI Y. Cellulose nanocrystal/hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide/silver nanoparticle compo-site as a catalyst for reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,156:253-258. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.099 [39] CIRTIU C M, ALEXANDRE F, DUNLOP-Brière. Cellulose nanocrystallites as an efficient support for nanoparticles of palladium: Application for catalytic hydrogenation and Heck coupling under mild conditions[J]. Green Chemistry,2011,13(2):288-291. doi: 10.1039/C0GC00326C [40] 远冰冰. 乙基纤维素基复合膜材料微观结构与丙烯/丙烷分离性能研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015.YUAN Bingbing. Study on micro-structure and propylene/propane separation properties of ethyl cellulose composite membrane materials[D]. Qingdao: College of Chemical Engineering China University of Petroleum (East China), 2015(in Chinese). [41] CHEN Q, ZHENG K, FAN Q, et al. Solvability and thermal response of cellulose with different crystal configurations[J]. Frontiers of Engineering Management,2019,6(1):62-69. doi: 10.1007/s42524-019-0001-z [42] 高俊. 羟基磷灰石及其复合材料负载型纳米金属催化剂制备、结构和性能的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2017.GAO Jun. The preparation of acid/based-modified metal nanocatalysts and the study of their structure and catalytic performance[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [43] AMINU M, AHMAD M B, ZOBIR H M, et al. Synthesis of nanocrystalline cellulose stabilized copper nanoparticles[J]. Journal of Nanomaterials,2016,2016(8):1-7. [44] LI Z, JIA Z, NI T, et al. Green and facile synthesis of fibrous Ag/cotton composites and their catalytic properties for 4-nitrophenol reduction[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,426(31):160-168. [45] BOUAZIZI N, EL A A, CAMPAGNE C, et al. Polyfunctional cotton fabrics with catalytic activity and antibacterial capacity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,351(1):328-339. [46] KESHIPOUR S, SHOJAEI S, SHAABANI A. Palladium nano-particles supported on ethylenediamine-functionalized cellulose as a novel and efficient catalyst for the Heck and Sonogashira couplings in water[J]. Cellulose,2013,20(2):973-980. doi: 10.1007/s10570-012-9852-8 [47] DUAN C, LIU C, MENG X, et al. Fabrication of carboxymethylated cellulose fibers supporting Ag NPs@MOF-199s nanocatalysts for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry,2019,5(33):1-10. [48] 欧阳金波, 那兵, 周利民, 等. 基于MOF结构的超级电容器电极材料研究进展[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(3):267-270.OUYANG Jinbo, NA Bing, ZHOU Limin, et al. MOF-based electrode materials for supercapacitor[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science),2018,41(3):267-270(in Chinese). [49] 许兰兰, 王松, 刘玉霞, 等. 微波法合成金属-有机骨架材料研究应用进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(4):1-5.XU Lanlan, WANG Song, LIU Yuxia, et al. Advance on research and application of MOF prepared by MW method[J]. New Chemical Material,2019,47(4):1-5(in Chinese). [50] 陈袁曦. 材料表面微生物改性及细菌纤维素复合材料的制备与性能研究[D]. 上海: 华东理工大学, 2014.CHEN Yuanxi. Preparation and properties of bacterial cellulose composites and biological surface modification[D]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology, 2014(in Chinese). [51] 郭倩. 改性细菌纤维素基复合导电材料的制备及其应用研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2019.GUO Qian. Preparation and application of modified bacterial cellulose matrix composite conductive materials[D]. Xi’an: Shanxi University of Science & Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [52] 仲华维. 细菌纤维素的发酵生产及应用研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2013.ZHONG Huaxiong. Study on fermentation production and application of bacterial cellulose[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Techology, 2013(in Chinese). [53] 杨华. 细菌纤维素的改性及应用[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2016.YANG Hua. Modification and application of bacterial cellulose[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science & Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [54] CHEN M, KANG H, GONG Y, et al. Bacterial cellulose supported gold nanoparticles with excellent catalytic properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(39):21717-21726. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b07150 [55] 胡伟立. 细菌纤维素表面修饰及功能化[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2013.HU Weili. Surface modification and functionalization of bacterial cellulose[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2013(in Chinese). [56] 杜倩雯. 细菌纤维素基复合水凝胶的制备及其性能研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2014.DU Qianwen. Profunction and characterization of bacterial cellulose nanocompsite hydrogel[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2014(in Chinese). [57] 陈燕, 陈仕艳, 姚晶晶, 等. 细菌纤维素负载金纳米粒子复合膜的制备及催化性能[J]. 合成纤维, 2016, 45(12):12-17.CHEN Yan, CHEN Shiyan, YAO Jingjing, et al. The study of preparation and catalytic performance of bacterial cellulose-supported gold nanoparticles[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China,2016,45(12):12-17(in Chinese). [58] YANG Y, CHEN Z, WU X, et al. Nanoporous cellulose membrane doped with silver for continuous catalytic decolorization of organic dyes[J]. Cellulose,2018,25(4):2547-2558. doi: 10.1007/s10570-018-1710-x [59] HUANG L, CHEN X, NGUYEN T X, et al. Nano-cellulose 3D-networks as controlled-release drug carriers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2013,1(23):2976-2984. doi: 10.1039/c3tb20149j [60] 舒顺新. 基于纤维素的一维纳米复合材料的制备与表征[D]. 杭州: 浙江理工大学, 2013.SHU Shunxin. Preparation and characterization of one dimensional nanocomposites based on cellulose[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2013(in Chinese). [61] 符庆金, 王燕云, 梁帅博, 等. 纳米纤维素在功能纳米材料中的应用进展[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2020, 3(1):175-182.FU Qingjin, WANG Yanyun, LIANG Shuaibo, et al. Progress in the application of nanocellulose in functional nano-materials[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering,2020,3(1):175-182(in Chinese). [62] AKIHIRO A, HIROTAKA K, AKIRA I, et al. Synthesis and catalytic features of hybrid metal nanoparticles supported on cellulose nanofibers[J]. Catalysts,2011,1(1):83-96. doi: 10.3390/catal1010083 [63] WOHLHAUSER S, KUHNT T, MEESORN W, et al. One-component nanocomposites based on polymer-grafted cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Macromolecules,2020,53(3):821-834. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b01612 [64] WU X, LU C, ZHOU Z, et al. Green synthesis and formation mechanism of cellulose nanocrystal-supported gold nanoparticles with enhanced catalytic performance[J]. Environmental Science Nano,2014,1(1):71-79. doi: 10.1039/c3en00066d [65] MUSA A, AHMAD M B, HUSSEIN M Z, et al. Preparation, characterization and catalytic activity of biomaterial-supported copper nanoparticles[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates,2017,43(2):801-815. doi: 10.1007/s11164-016-2665-x [66] HOKKANEN S, REPO E, SILLANP M. Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by succinic anhydride modified mercerized nanocellulose[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,223:40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.054 [67] LIU P, BORRELL P F, BOZIC M, et al. Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,294(30):177-185. [68] ANIRUDHAN T S, REJEENA S R. Adsorption and hydrolytic activity of trypsin on a carboxylate-functionalized cation exchanger prepared from nanocellulose[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science,2012,381(1):125-136. [69] HUANG J L, GRAY D G, LI C J. A(3)-Coupling catalyzed by robust Au nanoparticles covalently bonded to HS-functionalized cellulose nanocrystalline films[J]. Blstn Journal of Organic Chemistry,2013,9(1):1388-1396. [70] LAM E, HRAPOVIC S, MAJID E, et al. Catalysis using gold nanoparticles decorated on nanocrystalline cellulose[J]. Nanoscale,2012,4(3):997-1002. doi: 10.1039/c2nr11558a [71] WANG Y, ZHANG X, HE X, et al. In situ synthesis of MnO2 coated cellulose nanofibers hybrid for effective removal of methylene blue[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,1(110):302-308. [72] MAYAKRISHNAN G, BANG H, YUAN G, et al. Noble metal/functionalized cellulose nanofiber composites for catalytic applications[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,1(132):554-564. [73] KOGA H, TOKUNAGA E, HIDAKA M, et al. Topochemical synthesis and catalysis of metal nanoparticles exposed on crystalline cellulose nanofibers[J]. Chemical Communications,2010,46(45):8567-8569. doi: 10.1039/c0cc02754e [74] NIU T, Xu J, XIAO W, et al. Cellulose-based catalytic membranes fabricated by deposition of gold nanoparticles on natural cellulose nanofibres[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4(10):4901-4904. doi: 10.1039/c3ra44622k [75] LI Y, XU L, XU B, et al. Cellulose sponge supported palladium nanoparticles as recyclable cross-coupling catalysts[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(20):17155-17162. [76] 丁海燕, 侯瑞婷, 李运, 等. 纤维素及其衍生物在皮革中的应用[J]. 中国皮革, 2019, 2019(12):29-35.DING Haiyan, HOU Ruiting, LI Yun, et al. Applications of cellulose and its derivatives in leather[J]. China Leather,2019,2019(12):29-35(in Chinese). [77] SARA P. Strength and barrier enhancements of cellophane and cellulose derivative films: A review[J]. Bioresources,2013,8(2):3098-3121. [78] 谢丽源, 甘炳成. 羧甲基纤维素钠在食品工业中的应用研究[J]. 农产品加工(学刊), 2007(1):51-54.XIE Liyuan, GAN Bingcheng. Application of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose in food industry[J]. Products Processing,2007(1):51-54(in Chinese). [79] SOLOMON M M, GERENGI H, UMOREN S A. Carboxymethyl cellulose/silver nanoparticles composite: Synthesis, characterization and application as a benign corrosion inhibitor for St37 steel in 15% H2SO4 medium[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6376-6389. [80] HEBEISH A A, EL-RAFIE M H, ABDEL-MOHDY F A, et al. Carboxymethyl cellulose for green synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,82(3):933-941. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.020 [81] LIIMATAINEN H, SIRUIOE J, SUNDMAN O, et al. Use of nanoparticular and soluble anionic celluloses in coagulation-flocculation treatment of kaolin suspension[J]. Water Research,2012,46(7):2159-2166. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.035 [82] 曲莉. 纤维素衍生物稳定金属纳米粒子催化α-蒎烯加氢反应的研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2018.QU Li. Study on cellulose derivative stabilized metal nanoparticles as a catalyst for hydrogenation of α-pinene[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [83] XIA Y, GAO Z N, LIAO X M, et al. One-step green synthesis of silver nanobelts assisted by sodium carboxymethylcellulose for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol[J]. CrystEngComm,2007,9(1):12-14. doi: 10.1039/B616744F [84] MOHAMED A H, BRAHIM B, FIRDOUSSI E L, et al. Colloidal nickel(0)-carboxymethyl cellulose particles: A biopolymer-inorganic catalyst for hydrogenation of nitro-aromatics and carbonyl compounds[J]. Catalysis Communications,2013,1(32):92-100. [85] ZHANG H, YANG Y, DAI W, et al. An aqueous-phase catalytic process for the selective hydrogenation of acetylene with monodisperse water soluble palladium nanoparticles as catalyst[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology,2012,2(7):1319-1323. [86] UETANI K, YANO H. Nanofibrillation of wood pulp using a high-speed blender[J]. Biomacromolecules,2011,12(2):348-353. doi: 10.1021/bm101103p -





 下载:
下载: