Bending and tensile properties of carbon fiber triaxial woven fabric/epoxy resin composites with holey structure
-
摘要: 以T300碳纤维为增强纤维材料,环氧树脂为树脂基体,采用树脂膜熔渗(Resin film infusion,RFI)工艺制备碳纤维三轴机织物/环氧树脂(Triaxial woven fabric/epoxy resin,TWF/EP)复合材料。通过三点弯曲试验和拉伸试验研究了复合材料试样的面内弯曲性能和面内拉伸性能,采用3D轮廓仪观察拉伸试验后试样的损伤形貌,并分析其损伤机制。研究结果表明:TWF/EP复合材料的弯曲弹性模量表现为准各向同性,复合材料的孔洞率、碳纤维束规格与弯曲弹性模量呈现显著正相关性,与拉伸模量呈现负相关性。在拉伸载荷作用下,TWF/EP复合材料的主要失效模式包括纤维束断裂、纤维束拔出和交错失效,拉伸断裂机制主要为纯剪切破坏、扭转剪切破坏、拉剪耦合破坏。此外,在渐进损伤过程中,应变集中区发生在纱线交织点处。
-
关键词:
- 碳纤维三轴机织复合材料 /
- 准各向同性 /
- 弯曲性能 /
- 拉伸性能 /
- 损伤模式
Abstract: Carbon fiber triaxial woven fabric/epoxy resin (TWF/EP) composite was prepared by resin film infusion (RFI) method, in which T300 carbon fiber was reinforced material, and epoxy resin was matrix.Three-point bending test and tensile test were carried out to study the in-plane bending and in-plane tensile properties. Moreover, 3D profilometer was used to observe the damage morphology of sample after tensile test, and damage mechanism was analyzed. The results show that the bending elastic modulus of TWF/EP composites is quasi-isotropic. The porosity of composite and width of the fiber bundle have significant positive correlation with the bending elastic modulus, and have a negative correlation with the tensile modulus. The primary tensile failure patterns of composites may include tows pull-out, tows fracture and staggered failure. The tensile fracture mechanisms are mainly pure shear failure, torsional shear failure and tenso-shear coupling failure. In addition, the strain concentration region occurs at the interlacing point of the yarn during the progressive damage process. -
复合材料具有比强度和比刚度高、可设计性强、疲劳性能好、重量轻、耐腐蚀等优异性能,被广泛应用于航空航天领域[1]。复合材料薄壁结构承载效率较高,是飞机中常见的结构形式,其中机身侧壁板、梁腹板等结构主要承受剪切载荷的作用。在剪切载荷作用下,机身侧壁板的蒙皮容易局部失稳,已有研究表明,蒙皮失稳后不会立即失效,还能继续承载,表现出较高的承载能力[2-4]。因此,在复合材料薄壁结构设计中应考虑其剪切稳定性,充分发挥后屈曲承载潜力,这对减轻飞机结构重量、提高结构承载效率和确保飞机服役过程中的安全具有重要工程价值。
目前,国内外学者对复合材料薄壁结构的稳定性研究多集中在压缩载荷工况下[5-8],对剪切稳定性的研究相对较少。谭翔飞等[9]基于蒂尔曼和迪奥模型,进行了加强筋间蒙皮剪切屈曲及后屈曲性能理论分析,得出的理论屈曲载荷与试验屈曲载荷的相对误差为7.2%,后屈曲阶段的理论载荷-应变曲线与试验结果的相对误差在10%以内,并确定了后屈曲角随屈曲比的变化规律。汪厚冰等[10]对复合材料帽形加筋壁板的剪切屈曲性能进行了试验、理论分析和数值模拟,并指出选择合适的几何初始缺陷系数利用几何非线性分析方法可模拟蒙皮在剪切载荷作用下的屈曲过程。李真等[11]通过剪切稳定性试验及张力场分析研究了复合材料机身单曲率壁板的剪切失稳及破坏特性。以上研究工作均未考虑冲击损伤,而复合材料结构在使用和维护过程中受到工具坠落、跑道碎石和冰雹等低速冲击的作用容易产生损伤,导致剩余强度急剧下降[12],因此冲击损伤的影响不可忽视。
对含冲击损伤复合材料结构的强度预测,一般采用损伤累积法[13]和软化夹杂法[14-16]。损伤累积法需要进行冲击及压缩等外载作用的全过程分析,计算规模庞大,收敛困难,不便于工程使用。基于实际冲击损伤,采用软化夹杂法对冲击损伤进行等效是一种可行且高效的方法。Fardin等[14]将冲击损伤简化为具有不同材料参数的椭圆夹杂物,Debski等[15]通过减少厚度、降低材料属性将冲击损伤等效,两位学者均高效地计算了复合材料结构冲击后的剩余强度。Li等[16]基于软化夹杂模型建立了一种边缘冲击损伤的简化方法,快速而准确地预测了加筋板的后屈曲行为。然而,以上软化夹杂模型更适用于冲击后压缩剩余强度预测,对于本文冲击后剪切强度预测,还应考虑剪切非线性效应的影响。
本文以无损伤及含冲击损伤的复合材料层合板为研究对象,基于数字图像相关方法(Digital image correlation,DIC)[17]对其在剪切载荷作用下的屈曲后屈曲行为进行了实时测量,分析和总结了冲击损伤对屈曲波形和承载能力的影响。随后,采用软化夹杂法将冲击损伤等效简化,将损伤的几何边界信息写入损伤模型中,建立了考虑剪切非线性效应的复合材料渐进损伤模型,并对试验过程进行数值仿真。最后,讨论了数值仿真结果与试验结果的一致性。
1. 试 验
1.1 试件
试件材料为碳纤维增强环氧树脂基复合材料CCF300/BA3202,单层名义厚度为0.155 mm,材料属性见表1,参考ASTM标准[18-22]测得。试件外廓尺寸为370 mm×250 mm(详见图1),共4件,编号为T1~T4,所有试件铺层顺序为[45/45/0/45/90/0/−45/0]S,名义厚度为2.48 mm。试件四周用玻璃钢加强,加强片与蒙皮之间用J-116 B胶粘接,加强片厚度为2.5 mm。
表 1 CCF300/BA3202碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料性能参数Table 1. Material properties of CCF300/BA3202 carbon fiber reinforced epoxy compositeParameter Value E1/GPa 118 E2/GPa 8.98 G12/GPa 4.21 ν12 0.306 XT/MPa 1835 XC/MPa 1296 YT/MPa 82.5 YC/MPa 240 SL/MPa 166 GIC/(N·mm−1) 0.744 GIIC/(N·mm−1) 1.90 Notes:E1—Longitudinal elastic modulus; E2—Ransverse elastic modulus; G12—Shear modulus; ν12—Poisson's ratio; XT—Longitudinal tensile strength; XC—Longitudinal compressive strength; YT—Transverse tensile strength; YC—Transverse compressive strength; SL—Shear strength; GIC—Mode I fracture toughness ; GIIC—Mode II fracture toughness. 1.2 冲击损伤引入
试验前,在T4试件正中心引入了冲击损伤。冲击采用落锤式冲击设备,冲头质量为1.023 kg,端部为半球形,直径为16 mm,冲击能量为8 J。冲击后立即用凹坑深度仪测量,得到的凹坑深度为0.27 mm。随后,采用EPOCH XT超声波探伤仪进行无损检测,并用白色记号笔对损伤进行标识。A扫结果显示:分层损伤尺寸为18 mm×12 mm,如图2所示。
1.3 试验方法
正式试验前,在试件一侧表面喷涂白漆,待白漆干后喷涂黑漆,形成随机的散斑图案。在试件的另一侧表面粘贴花片,花片的0°、45°、90°方向的应变片与试件铺层方向一致。T1~T3试件应变片粘贴位置及编号见图3,通过1#~4#花片检验加载对称性,通过中心处的5#花片判断初始屈曲。T4试件的5#花片沿着90°方向移动了10 mm。
试验夹具和试件安装如图4所示,采用对角拉伸的方法进行剪切载荷施加。试验在MTS1000 kN试验机上进行,采用道姆公司制造的ARAMIS 3D数字散斑系统测量面外变形,同时采用中国飞机强度研究所自主研发的ST24数据采集系统测量应变。
2. 数值仿真模型
2.1 失效准则
2.1.1 纤维失效准则
复合材料主要失效模式包括纤维拉伸/压缩失效和基体的拉伸/压缩失效等。Hashin准则[23]是最常用的失效准则,但Li等[24]从理论上分析了Hashin纤维拉伸失效判据中包含的剪切应力项可以忽略,并给出了预测纤维拉伸/压缩失效的统一表达式:
fFF=(XC−XT)σ1XTXC+σ21XTXC (1) 式中:
fFF 为纤维失效函数,fFF>1 时表征纤维失效;σ1 为纤维方向应力;XT、XC 分别为单向板纤维方向拉伸、压缩强度。2.1.2 纤维间失效准则
对于纤维间失效,Hashin准则难以反映横向压缩对基体剪切失效的抑制作用。Li等[24]从Mohr失效面理论的基本假设出发,建立了一种纤维间失效准则,可有效预测横向压缩的增强效应。而且,不同于Puck等[25]提出的纤维间失效准则,该准则所有系数均可由基本强度及断裂面角度计算给出,准则形式如下:
fIFF={A1σn+A2σ2n+B2τ2nl+C2τ2ntσn⩾ (2) 式中:
f_{\text {IFF }} 为纤维间失效函数,f_{\mathrm{IFF}}>1 时表征纤维间失效,即基体失效;{\sigma }_{\text{n}}、{\tau }_{\text{nt}}、{\tau }_{\text{nl}} 为潜在断裂面上的应力(如图5所示);A_{1}、A_{2}、B_{2}、 C_{2} 为系数,计算公式如下:\left\{ \begin{gathered} {\sigma _{\text{n}}} = {\sigma _2}{\cos ^2}{\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} + {\sigma _3}{\sin ^2}{\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} + {\tau _{23}}\sin 2{\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} \\ {\tau _{{\text{nt}}}} = \dfrac{{\left( {{\sigma _3} - {\sigma _2}} \right)\sin 2{\theta _{{\text{fp}}}}}}{2} + {\tau _{23}}\cos 2{\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} \\ {\tau _{{\text{nl}}}} = {\tau _{13}}\sin {\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} + {\tau _{12}}\cos {\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. (3) \left\{ \begin{gathered} {A_1} = \dfrac{{{{\sin }^2}{\theta _0} - {{\cos }^2}{\theta _0}}}{{{Y_{\text{C}}}{{\cos }^4}{\theta _0}}} \\ {A_2} = \dfrac{1}{{Y_{\text{T}}^2}}\left[ {1 - {Y_{\text{T}}}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\sin }^2}{\theta _0} - {{\cos }^2}{\theta _0}}}{{{Y_{\text{C}}}{{\cos }^4}{\theta _0}}}} \right)} \right] \\ {B_2} = \dfrac{1}{{S_{\text{L}}^2}} \\ {C_2} = \dfrac{1}{{Y_{\text{C}}^2{{\cos }^4}{\theta _0}}} \\ \end{gathered} \right. (4) 式中:
{\sigma }_{2}、{\sigma }_{3}、{\tau }_{12}、{\tau }_{13}、{\tau }_{23} 为材料主轴坐标系下的应力分量;{Y}_{\text{T}}、{Y}_{\text{C}}、{S}_{\text{L}} 分别为横向拉伸强度、横向压缩强度和面内剪切强度;\theta_{0} 为纯横向压缩失效时的断裂角,本文参考文献[25]取为53°;\theta_{\mathrm{fp}} 为潜在断裂面角度。![]() 图 5 基体潜在断裂面上的应力分量[24]Figure 5. Stress components on potential fracture surface of matrix[24]{\sigma _1} , {\sigma _2} , {\sigma _3} , {\tau _{12}} , {\tau _{13}} , {\tau _{23}} , {\tau _{21}} , {\tau _{31}} , {\tau _{32}} —Stress components in the material's principal axis coordinate system; {\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} —Angle of the potential fracture surface of matrix; {\sigma _{\text{n}}} , {\tau _{{\text{nt}}}} , {\tau _{{\text{nl}}}} —Stress components on potential fracture surface of matrix
图 5 基体潜在断裂面上的应力分量[24]Figure 5. Stress components on potential fracture surface of matrix[24]{\sigma _1} , {\sigma _2} , {\sigma _3} , {\tau _{12}} , {\tau _{13}} , {\tau _{23}} , {\tau _{21}} , {\tau _{31}} , {\tau _{32}} —Stress components in the material's principal axis coordinate system; {\theta _{{\text{fp}}}} —Angle of the potential fracture surface of matrix; {\sigma _{\text{n}}} , {\tau _{{\text{nt}}}} , {\tau _{{\text{nl}}}} —Stress components on potential fracture surface of matrix纤维间失效函数
f_{\mathrm{IFF}} 的最大值及相应的潜在断裂面角度\theta_{\mathrm{fp}} 可通过遍历法[25]、分区黄金搜索法[26]、分区抛物线法[27]求解,综合考虑效率和精度本文采用了分区黄金搜索法。2.2 剪切非线性模型
在面内纵横剪切试验中发现,CCF300/BA3202表现出了明显的剪切非线性行为。因此,本文采用多项式函数描述其剪切非线性响应。同时,注意到剪应力是剪应变的奇函数,剪切应力-应变关系如下:
{\tau _{12}} = \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{{G_1}{\gamma _{12}} + {G_2}\gamma _{12}^2 + {G_3}\gamma _{12}^3 + \cdots }+{G_i}\gamma _{12}^i \\ &\qquad {{\gamma _{12}} < 0} \\ & {{G_1}{\gamma _{12}} - {G_2}\gamma _{12}^2 + {G_3}\gamma _{12}^3 - \cdots }+{G_i}\gamma _{12}^i\\ &\qquad{{\gamma _{12}} \geqslant 0} \end{aligned} \right. (5) 式中:
{\tau }_{12}、{\gamma }_{12} 分别为剪切应力和工程剪应变;G_{i}(i=1,2,3 \cdots) 为系数,由试验数据拟合给出。如图6所示,取前4项时已足够精确,各系数分别为:G1=5.02 GPa、G2=1.48×102 GPa、G3=2.16×103 GPa、G4=1.18×104 GPa。由此,等效剪切刚度
G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} ,计算公式如下:G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} = \left\{ \begin{aligned} & {{G_1} + {G_2}{\gamma _{12}} + {G_3}\gamma _{12}^2 + {G_4}\gamma _{12}^3}&{{\gamma _{12}} < 0} \\ & {{G_1} - {G_2}{\gamma _{12}} + {G_3}\gamma _{12}^2 - {G_4}\gamma _{12}^3}&{{\gamma _{12}} \geqslant 0} \end{aligned} \right. (6) 2.3 基于软化夹杂法的损伤演化模型
材料失效后的损伤演化行为主要由断裂韧性控制,参考Linde等[28]提出的指数型损伤演化模型,并引入单元特征长度以降低模型对网格的依赖性,纤维损伤状态变量dFF及纤维间损伤状态变量dIFF定义如下:
\begin{gathered} {d_{{\text{FF}}}} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 - \dfrac{{\exp (X_{\text{T}}^2{L_{\text{C}}}(1 - {f_{{\text{FF}}}})/({E_1}{G_{{\text{FT}}}}))}}{{{f_{{\text{FF}}}}}}}&{{\sigma _1} \geqslant 0} \\ {1 - \dfrac{{\exp (X_{\text{C}}^2{L_{\text{C}}}(1 - {f_{{\text{FF}}}})/({E_1}{G_{{\text{FC}}}}))}}{{{f_{{\text{FF}}}}}}}&{{\sigma _1} < 0} \end{array}} \right. \\ {d_{{\text{IFF}}}} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {1 - \dfrac{{\exp (Y_{\text{T}}^2{L_{\text{C}}}(1 - {f_{{\text{IFF}}}})/({E_2}{G_{{\text{MT}}}}))}}{{{f_{{\text{IFF}}}}}}}&{{\sigma _{\rm{n}}} \geqslant 0} \\ {1 - \dfrac{{\exp (Y_{\text{C}}^2{L_{\text{C}}}(1 - {f_{{\text{IFF}}}})/({E_2}{G_{{\text{MC}}}}))}}{{{f_{{\text{IFF}}}}}}}&{{\sigma _{\rm{n}}} < 0} \end{array}} \right. \end{gathered} (7) 式中:
L_{\mathrm{C}} 为单元特征长度;G_{\mathrm{FT}} 、G_{\mathrm{FC}} 为纵向拉伸、压缩断裂韧性,目前还没有公认的标准方法进行测试,参考同类材料的性能[29-30],G_{\mathrm{FT}} 、G_{\mathrm{FC}} 分别取为71.4 N·mm−1、35.6 N·mm−1;G_{\text {MT }} 、G_{\mathrm{MC}} 为横向拉伸、压缩断裂韧性,近似取为层间I型、II型断裂韧性。纤维失效后,纵向模量E1、横向模量E2、泊松比ν12、剪切模量G12折减为无损材料值的(1−dFF)倍。纤维间失效后,横向模量E2、泊松比ν12、剪切模量G12折减为无损材料值的(1−dIFF)倍。
对于冲击损伤区,采用软化夹杂法进行等效。文献[16, 29]根据损伤的严重程度,将冲击损伤区划分为两个区域,并分别采用不同的系数对初始性能进行折减。本文研究的试件冲击能量小,冲击点处检测未发现纤维大量断裂的情况,为简化模型,整个损伤区采用同一系数η进行性能折减。
上述基于软化夹杂法的损伤演化模型材料性能退化方案如表2所示。
表 2 材料性能退化方案Table 2. Material performance degradation schemeFail mode No damage zone Impact damage zone None — \begin{gathered} {E_1} \to \eta {E_1} \\ {E_2} \to \eta {E_2} \\ G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \to \eta G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \\ \end{gathered} Fiber failure \begin{gathered} {E_1} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}}){E_1} \\ {E_2} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}}){E_2} \\ G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}})G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \\ {\nu _{12}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}}){\nu _{12}} \\ \end{gathered} \begin{gathered} {E_1} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}})\eta {E_1} \\ {E_2} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}})\eta {E_2} \\ G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}})\eta G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \\ {\nu _{12}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{FF}}}}){\nu _{12}} \\ \end{gathered} Inter-fiber failure \begin{gathered} {E_2} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}}){E_2} \\ G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}})G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \\ {\nu _{12}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}}){\nu _{12}} \\ \end{gathered} \begin{gathered} {E_2} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}})\eta {E_2} \\ G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}})\eta G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} \\ {\nu _{12}} \to (1 - {d_{{\text{IFF}}}}){\nu _{12}} \\ \end{gathered} Notes: G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}} —Equivalent shear modulus; η—Stiffness reduction factor; {d_{{\text{FF}}}} —Fiber damage state variable; {d_{{\text{IFF}}}} —Matrix damage state variable. 2.4 考虑冲击损伤的有限元模型
采用商业有限元软件ABAQUS 6.14对含冲击损伤的层合板进行剪切后屈曲失效分析。
有限元模型中,剪切边框和螺栓进行了如下简化:剪切框架简化为S4 R壳单元(厚度10 mm),并在8个对角点处施加铰接约束;螺栓简化为B31梁单元(直径8 mm),分别与试件及上下剪切框架绑定在一起;剪切边框和螺栓材料均为低碳钢。低碳钢的弹性模量为200 GPa、泊松比为0.3。
试件也均采用S4 R壳单元模拟,其中加强区上下各增加一层玻璃钢(厚度2.5 mm)。玻璃钢纵向模量为53.48 GPa、横向模量为17.7 GPa、剪切模量为5.83 GPa、泊松比为0.278。复合材料单向板本构模型由自定义场子程序USDFLD实现,其中场变量为F1~F4:F1表征纤维损伤、F2表征纤维间损伤、F3表征剪切非线性行为、F4区分是否为冲击损伤区,F4=0时表示非冲击损伤区,F4=1时表示冲击损伤区。F1~F3定义如下:
\begin{gathered} {F_1} = {d_{{\text{FF}}}} \\ {F_2} = {d_{{\text{IFF}}}} \\ {F_3} = 1 - \frac{{G_{12}^{{\text{eq}}}}}{{{G_{12}}}} \end{gathered} (8) 对于含冲击损伤的试件,采用软化夹杂法对冲击损伤进行模拟,并根据单元中心坐标确定单元是否位于冲击损伤区域。试件T4的冲击损伤边界近似于椭圆,且有限元模型原点在试件中心,由此F4可由下式确定:
{F_4} = \left\{ \begin{aligned} & 1&{\frac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} < 1} \\ & 0&{\frac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \frac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} \geqslant 1} \end{aligned} \right. (9) 式中:长半轴a=9 mm;短半轴b=6 mm。
有限元模型网格及边界条件如图7所示:剪切框架网格尺寸为10 mm×10 mm,试件网格尺寸为1 mm×1 mm。边界条件设置如下:在对角坐标系(x'Oy')下,约束y'轴方向的4个主节点的面外平动自由度(Uz'=0),绕x'、y'轴的转动自由度(URx'=URy'=0);x'轴方向的4个主节点仅放开绕z'轴的转动自由度(Ux'=Uy'=Uz'=0,URx'=URy'=0)。加载时+x'轴方向的2个主节点施加沿x'轴方向4 mm位移(Ux'=4 mm)。
通过场变量表征的等效冲击损伤区域如图8所示,本文采用的方法保证了网格的整体质量。
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 试验结果分析
通过粘贴的花片可以测得0°、45°、90°方向的正应变
{\varepsilon }_{0}、{\varepsilon }_{45}、{\varepsilon }_{90} ,由此可以确定测量点的工程剪应变{\gamma _{12}} :{\gamma _{12}} = {\varepsilon _0} + {\varepsilon _{90}} - 2{\varepsilon _{45}} (10) T1试件的载荷-应变曲线如图9所示,其中虚线为拟合的载荷-应变曲线,根据0~40 kN范围内的载荷及应变线性回归得到。加载到64.6 kN以后应变曲线有明显偏转,由此确定试件屈曲载荷约为64.6 kN。其余试件屈曲载荷确定方法与之类似,试验结果统计如表3所示。
表 3 CCF300/BA3202复合材料层板剪切试验结果Table 3. Shear test results of CCF300/BA3202 composite laminatesNumber Buckling load/kN Fracture load/kN Test Average Test Average T1 64.6 64.2 153.5 156.8 T2 65.0 156.2 T3 63.1 160.7 T4 63.0 141.6 不含冲击损伤的试件(T1~T3)屈曲载荷平均值为64.2 kN,破坏载荷平均值为156.8 kN。3个试件的屈曲模态一致,包含3个屈曲半波,沿着垂直于对角拉伸方向分布。破坏模式均为靠近对角拉伸区长边加强片处因应力集中而断裂。无损伤的试件(T1)典型屈曲模态及失效照片如图10所示。
含冲击损伤的试件(T4)屈曲载荷测试值为63.0 kN,破坏载荷测试值为141.6 kN,分别比无损伤试件平均值低1.92%、9.69%。如图11所示,T4试件屈曲模态与无损伤试件一致,破坏模式为损伤沿着冲击点向4个角点扩展直至完全失去承载能力,与无损伤试件不同。对比分析可知:试件中心引入冲击损伤后,损伤尺寸较小,整体刚度变化不明显,因此屈曲载荷变化不大。冲击点附近因后屈曲变形导致应力集中,承载能力明显降低。
3.2 仿真结果与试验对比
试件制造过程中的几何缺陷,特别是翘曲对初始屈曲影响较大,因此数值仿真模型需加以考虑。比较常见的做法是引入一阶屈曲模态作为初始几何缺陷[31],几何缺陷因子ξ定义为缺陷幅值与试件考核区厚度之比。汪厚冰等[10]研究指出几何缺陷因子取值对稳定性影响较大,需进行参数分析确定。
图12为几何缺陷因子和剪切非线性对CCF300/BA3202复合材料层板屈曲载荷、破坏载荷的影响。横坐标表示几何缺陷因子,纵坐标分别表示无损伤试件仿真的屈曲载荷与无损伤试件试验平均屈曲载荷之比、仿真的破坏载荷与无损伤试件试验平均破坏载荷之比。
由图12(a)可以看出,线性剪切响应和非线性剪切响应得到的初始屈曲载荷一致,这是由于初始屈曲时,屈曲应变较小,剪切应力-应变关系接近于线性。随着初始几何缺陷因子增加,分析得到的屈曲载荷随之而减小;初始几何缺陷因子ξ=3%时,与试验结果较接近,相对误差为2.34%。
由图12(b)可以看出,考虑线性剪切响应和非线性剪切响应时的破坏载荷相差较大,采用线性模型误差可达20%以上,而采用非线性模型误差均在5%以内。这是由于临近破坏时,试件剪切应变较高,线性模型已难以反映真实的剪切应力-应变关系。而随着初始几何缺陷因子增加,两种模型分析得到的破坏载荷均无明显变化。
基于以上对无损伤试件的研究结果,对含冲击损伤的试件剪切屈曲后屈曲行为进行分析时,采用非线性剪切响应模型,初始几何缺陷因子取为3%。冲击损伤区刚度折减系数η对承载能力的影响如图13所示,破坏载荷随着η的减小而减小,当η在0.2~0.3之间时与试验结果接近。
η=0.25时,含冲击损伤的试件屈曲载荷、破坏载荷预测值分别为61 kN、139.8 kN,与试验相比,相对误差分别为−3.17%、−1.27%。仿真的屈曲模态、破坏模式见图14、图15,与图11对比看出,数值仿真的屈曲波形、破坏模式均与试验一致,由此表明了本文考虑剪切非线性效应的软化夹杂模型的有效性。
含冲击损伤试件从初始损伤到最终破坏的过程十分短暂,DIC设备未能捕捉到,因此通过数值仿真结果对其失效过程进行分析。T4试件预测的载荷-位移曲线和损伤扩展过程如图16、图17所示:试件加载到61 kN以后开始屈曲,冲击点附近开始往外鼓包,导致应力集中。加载至132 kN后,冲击点附近出现新增损伤。随着继续加载,损伤沿着4个角点缓慢扩展,达到最大载荷139.8 kN后,损伤急剧扩展并迅速掉载,直到完全破坏。这清晰地反映了冲击损伤对损伤起始和扩展的影响。
4. 结 论
以无损伤和含冲击损伤的CCF300/BA3202碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料层合板为研究对象,基于数字图像相关方法(DIC)进行了试验测试,并对试验过程进行了仿真分析,主要结论如下:
(1) 无损伤试件的屈曲载荷、破坏载荷平均值分别为64.2 kN、156.8 kN;引入冲击损伤后,试件屈曲载荷降为63.0 kN,变化不大;承载能力下降至141.6 kN,降幅为9.69%。
(2) 几何缺陷对复合材料层合板的初始剪切屈曲影响显著,本文通过引入一阶屈曲模态模拟获得了与试验一致的初始屈曲载荷(相对误差仅为2.34%);后续可将实际测量的翘曲变形引入模型中以更准确地模拟结构的初始屈曲行为。
(3) 剪切非线性效应对层合板剪切承载能力影响较大,线性模型预测的失效载荷与试验测试值误差超过20%,而考虑了剪切非线性响应的仿真模型预测精度可达5%以内。
(4) 本文采用的考虑剪切非线性效应的软化夹杂法可有效地预测含冲击损伤的复合材料层合板的剪切强度,屈曲载荷、破坏载荷误差分别为−3.17%、−1.27%,得到的屈曲波形、破坏模式均与DIC测量结果一致,可为复合材料结构冲击损伤简化和剪切强度预测提供一种思路。
-
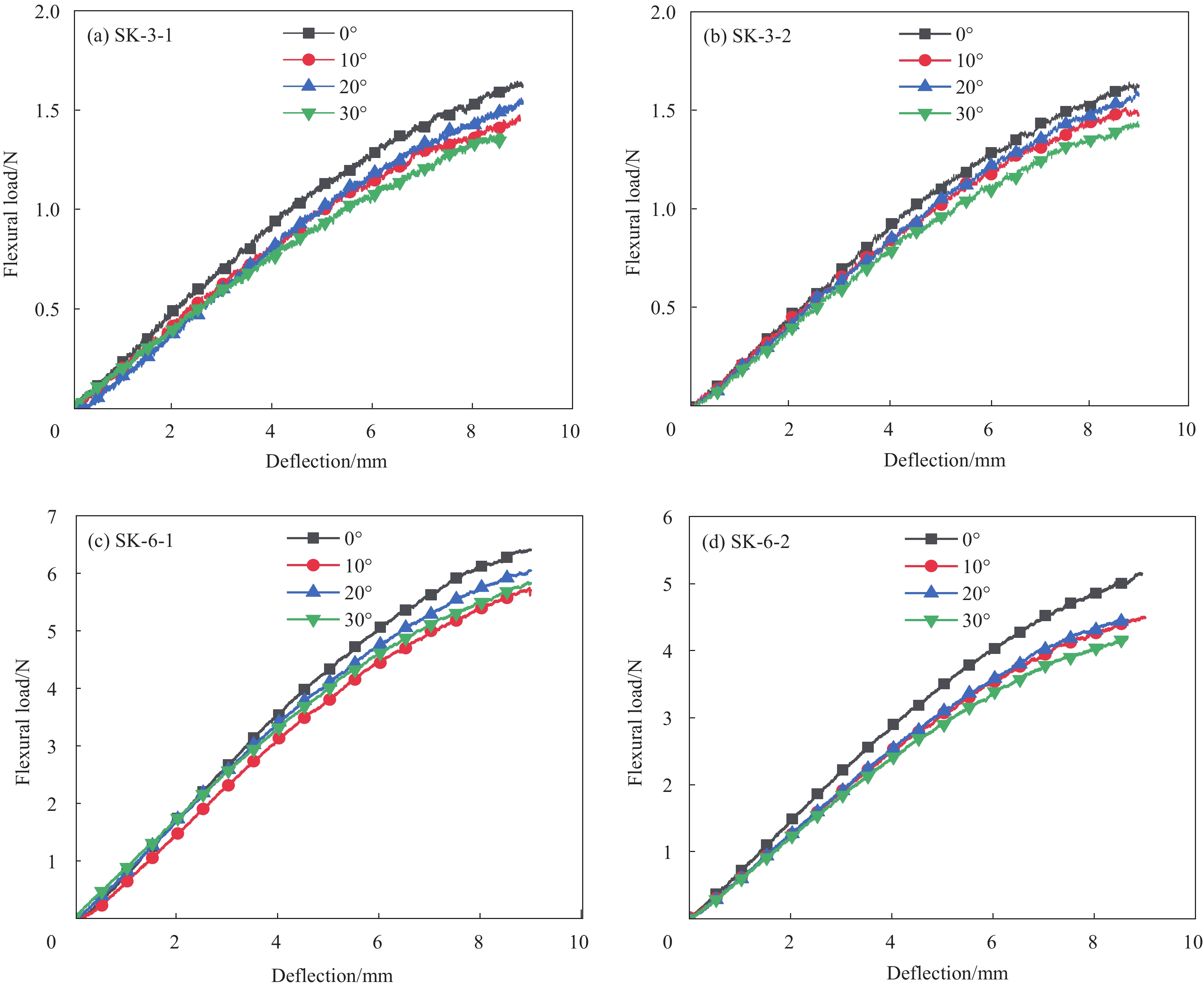
图 1 试验路线示意图:(a)三轴机织物(TWF)织造;(b)基础组织结构示意图;(c)复合成型铺层;(d)三点弯曲试验;(e)面内拉伸试验
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of experimental route: (a) Triaxial woven fabric (TWF) weaving; (b) Schematic diagram of basic triaxial woven fabric; (c) Composite molding layer; (d) Three-point bending test; (e) In-plane tensile test
a—Hexagonal hole side length; b— Triangular hole side length; c—Width of yarn after weaving; L—Yarn center distance; DIC—Digital image correlation method
表 1 三轴机织复合材料结构参数
Table 1 Structural parameters of triaxial woven fabric composites
No. Carbon fiber Yarn center distance/mm Porosity/% Thickness/mm Area density /(g·m−2) SK-3-1 T300-3K 4.5 34 0.389 250.0 SK-3-2 5.5 41 0.345 212.2 SK-6-1 T300-6K 5.5 34 0.458 383.3 SK-6-2 6.0 37 0.403 330.3 -
[1] RAO Y, ZHNAG C, LI W. Structural analysis for triaxial woven fabric composites of carbon fiber[J]. Composite Structures,2019,219:42-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.03.013
[2] TYLER T. Developments in triaxial woven fabrics[M]. UK: Woodhead Publishing, 2011: 141-163.
[3] 孙洁, 施楣梧, 钱坤. 平面三向织物的结构与性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2014, 35(6):154-162. SUN Jie, SHI Meiwu, QIAN Kun. Structure and properties of planar three-dimensional fabrics[J]. Journal of Textile Rsearch,2014,35(6):154-162(in Chinese).
[4] DATASHVILI L, BAIER H. Active and morphing aerospace structures—A synthesis between advanced materials, structures and mechanisms[J]. International Journal of Aeronautical and Space Sciences,2011,12(3):225-240. DOI: 10.5139/IJASS.2011.12.3.225
[5] SANTIAGO P J, BAIER H. Advances in deployable structures and surfaces for large apertures in space[J]. CEAS Space Journal,2013,5(3-4):89-115. DOI: 10.1007/s12567-013-0048-3
[6] ERICSSON A, RUMPLER R, SJOBERG D, et al. A combined electromagnetic and acoustic analysis of a triaxial carbon fiber weave for reflector antenna applications[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology,2016,58:401-417. DOI: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.08.033
[7] RUDO D N. Triaxial weave for reinforcing dental resins: US Patent, 121063B1[P]. 2009-01-21.
[8] MESSIRY M E, ELTAHAN E. Stab resistance of triaxial woven fabrics for soft body armor[J]. Journal of Industrial Textiles,2016,45(5):1062-1082. DOI: 10.1177/1528083714551441
[9] MATSUMOTO N, WAKABAYASHI M, SANEKAT H. Golf club shaft: US Patent, 20090305811A1[P]. 2009-6-3.
[10] 白江波, 熊峻江, 高军鹏, 等. 间隙率对三轴向机织复合材料弹性性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2014(3):14-20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2014.03.003 BAI Jiangbo, XIONG Junjiang, GAO Junpeng, et al. Effect of gap ratio on elastic properties of triaxial woven composites[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2014(3):14-20(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2014.03.003
[11] AOKI T, KOSUGI Y, WATANABE A. Fatigue characteristic and damage accumulation mechanism of triaxially-woven fabric composite[C]//Colorado, USA: 52nd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, 2011: 1-13.
[12] KUEH A B H. Buckling of sandwich columns reinforced by triaxial weave fabric composite skin-sheets[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2013,66:45-54. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2012.10.007
[13] 周红涛. 平面三向织物增强橡胶复合材料力学性能及损伤行为研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2020. ZHOU Hongtao. Study on mechanical properties and damage behavior of planar three-dimensional fabric reinforced rubber composites [D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2020(in Chinese).
[14] 沙迪, 禹旭敏, 赵将, 等. 碳纤维三向织物/环氧树脂复合材料的制备与力学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4):838-845. DOI: 10.7503/cjcu20190513 SHA Di, YU Xumin, ZHAO Jiang, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of carbon fiber triaxial woven fabric/epoxy resin composites[J]. Chemical Journal of Chinese Universities,2020,41(4):838-845(in Chinese). DOI: 10.7503/cjcu20190513
[15] 易淼. 三向织物织造及其复合材料拉伸机理研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2019. YI Miao. Study on the tensile mechanism of three-dimensional fabric weaving and its composites [D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2019(in Chinese).
[16] KUEH A, PELLEGRINO S. Triaxial weave fabric composites, D-STRUCT/TR223[R]. Cambridgeshire, UK: European Space Agency Contractor Report, 2007.
[17] AOKI T, KOSUGIY, WATANABE A, et al. Durability of tri-axially woven fabric composites for space applications[C]//Jeiu, Island: 18th International Conference on Composite Materials, 2011: 1-6.
[18] AOKI T, YOSHIDA K. Mechanical and thermal behaviors of triaxially-woven carbon/epoxy fabric composite[C]//Rhode, Island: 47th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, 2006: 1-9.
[19] ZHAO Q, HOA S V, OUELLETTE P. Progressive failure of triaxial woven fabric (TWF) composites with open holes[J]. Composite Structures,2004,65(3-4):419-431. DOI: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2003.12.004
[20] DATASHVILI L. Multifunctional and dimensionally stable flexible fiber composites for space applications[J]. Acta Astronautica,2010,66(7-8):1081-1086. DOI: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.09.026
[21] American Society for Testing Materials. Standard test methods for flexural properties of unreinforced and reinforced plastics and electrical insulating materials: ASTM-D790—2017 [S]. United States: American Society for Testing Materials International, 2017.
[22] American Society for Testing Materials. Standard test method for tensile properties of polymer matrix composite materials: ASTM-D3039/D3090M—2007[S]. United States: American Society for Testing Materials International, 2007.
[23] ZHOU X T , MA X F , FAN Y S , et al. Tensile and bending behavior of thin-walled triaxial weave fabric composites[J]. Journal of Engineered Fibers and Fabrics,2019,14:1-10.
[24] 沈观林, 胡更开, 刘彬. 复合材料力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2013: 178-185. SHEN Guanlin, HU Gengkai, LIU Bin. Mechanics of composite materials [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2013: 178-185(in Chinese).
[25] HESLEHURST B R. 复合材料及结构的缺陷与损伤[M]. 张晓军, 张玮, 张有宏, 译. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 56-63. HESLEHURST B R. Defects and damage of composite materials and structures [M]. Translated by ZHANG Xiaojun, ZHANG Wei, ZHANG Youhong. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 56-63(in Chinese)
-




 下载:
下载: