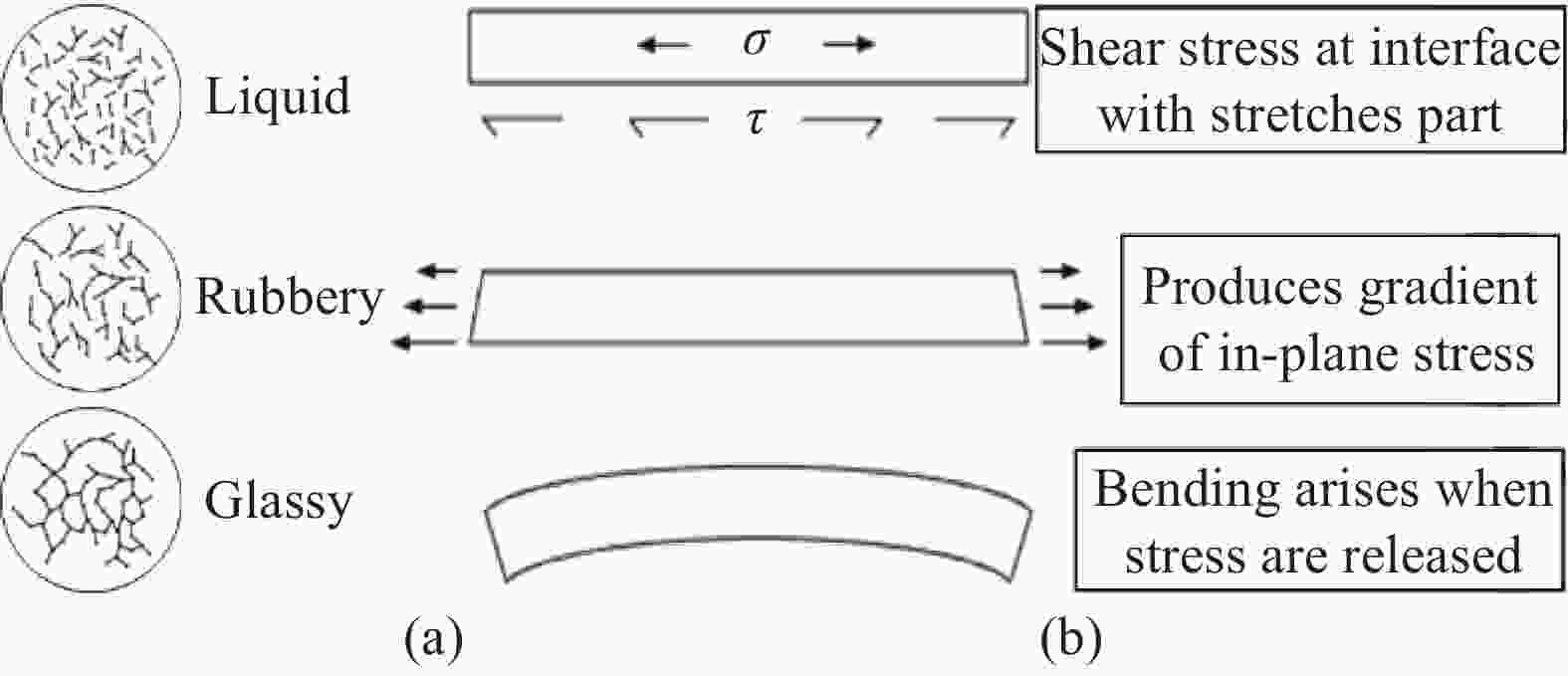
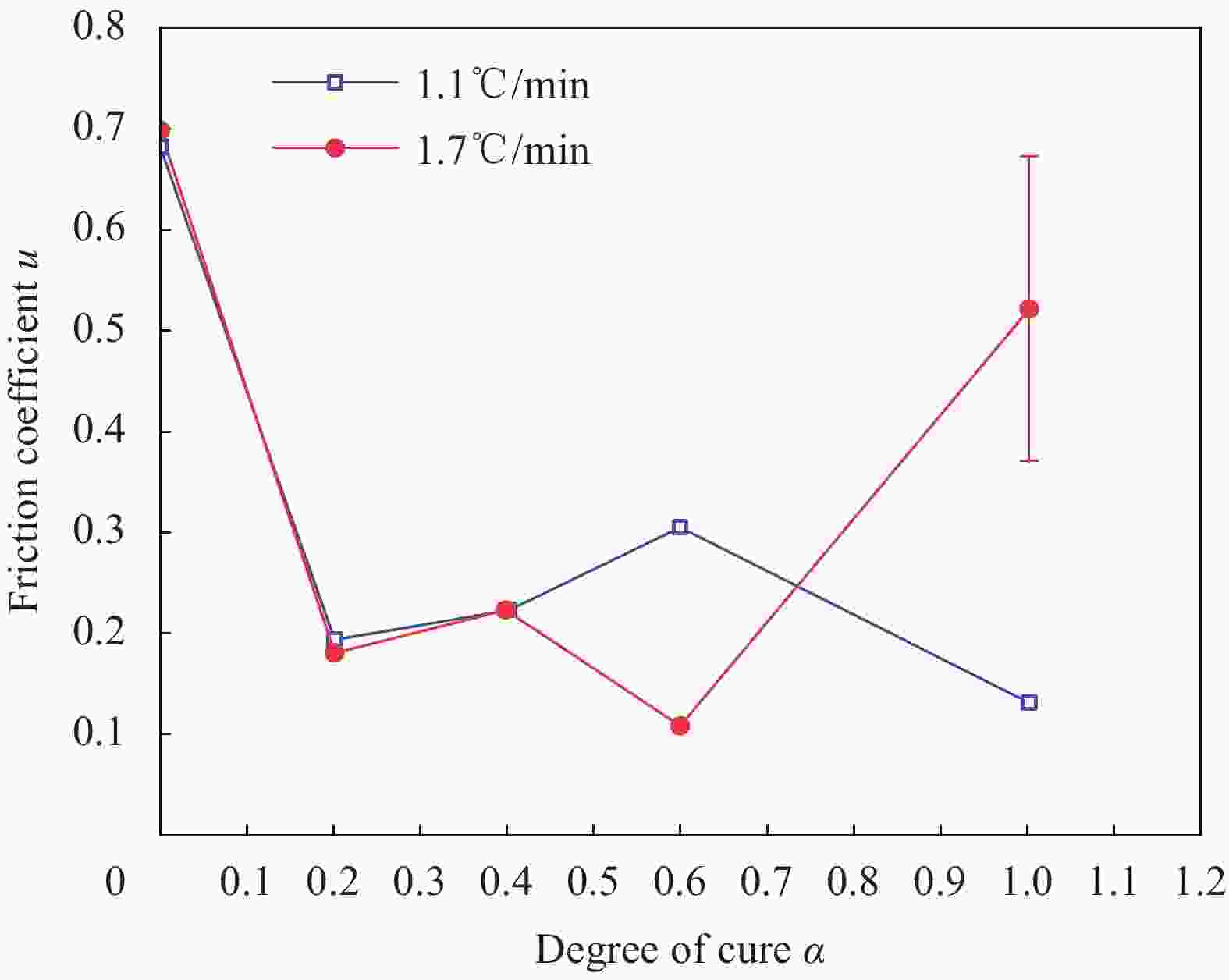
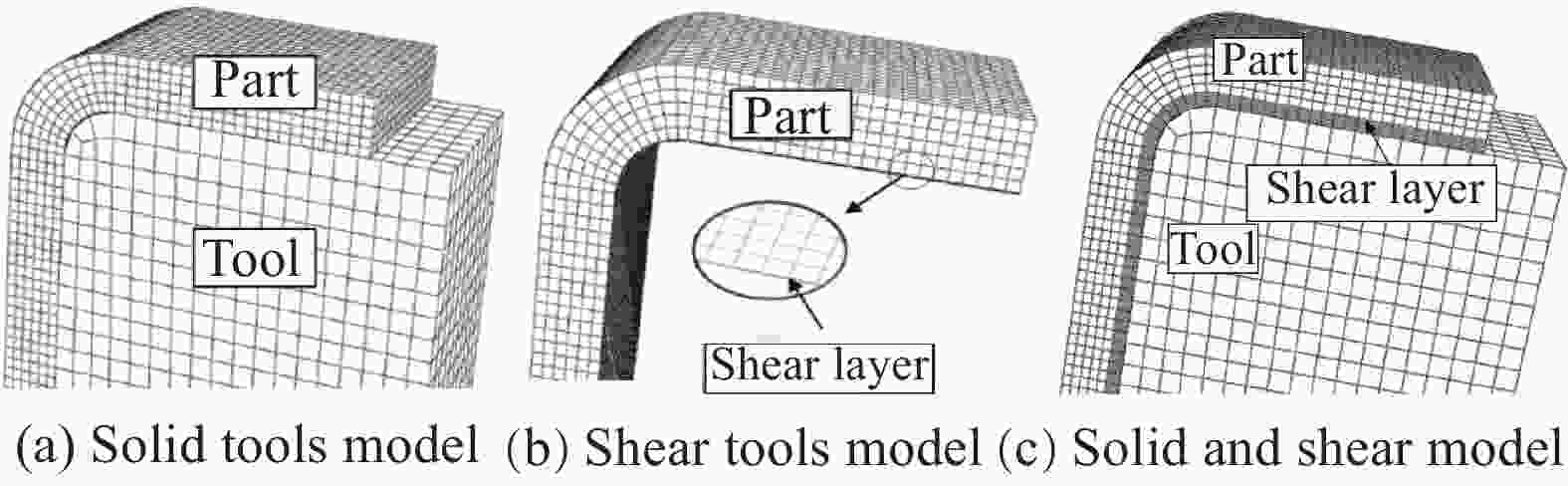
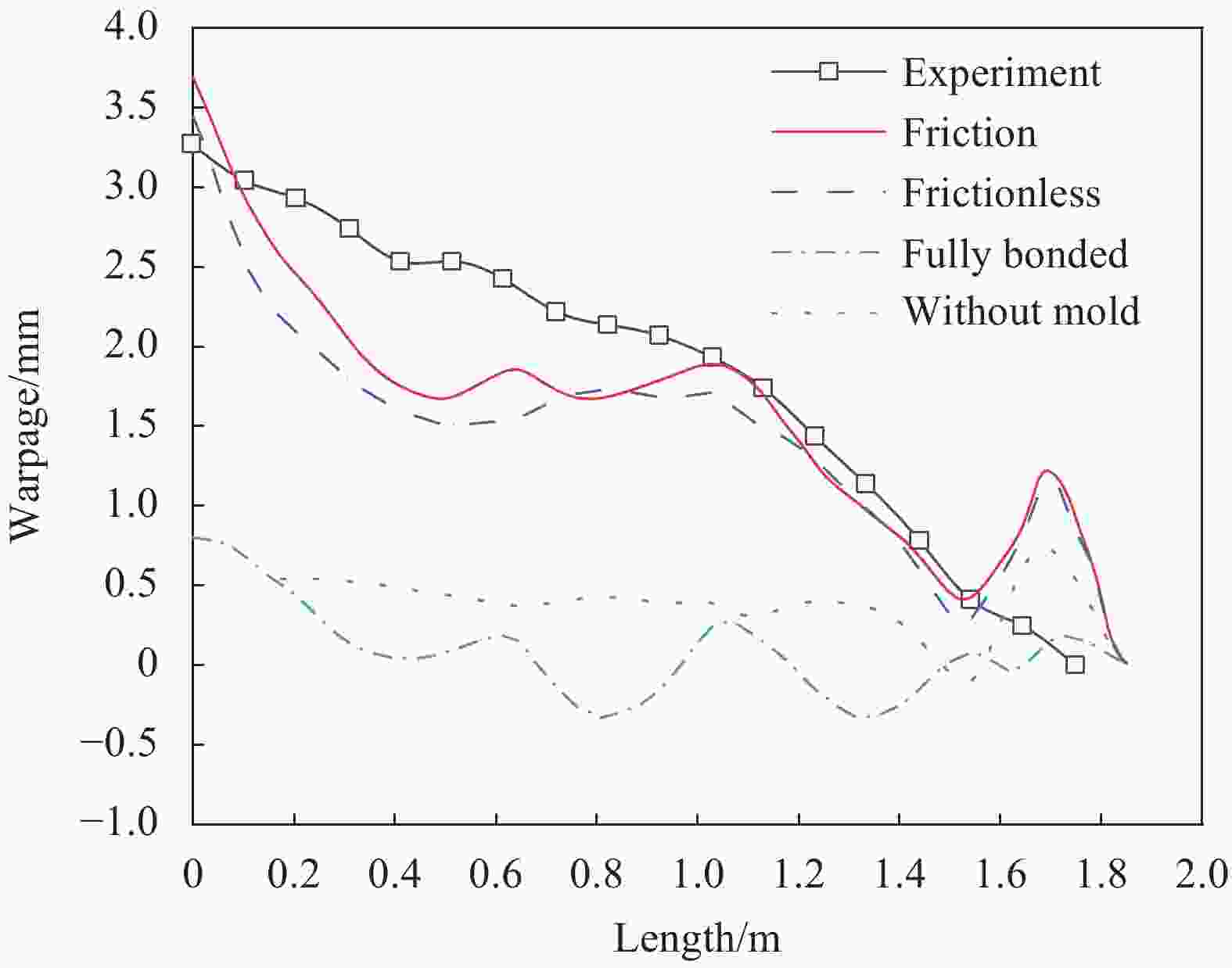
Research and application progress of curing tooling technology for large composite aeronautical components
-
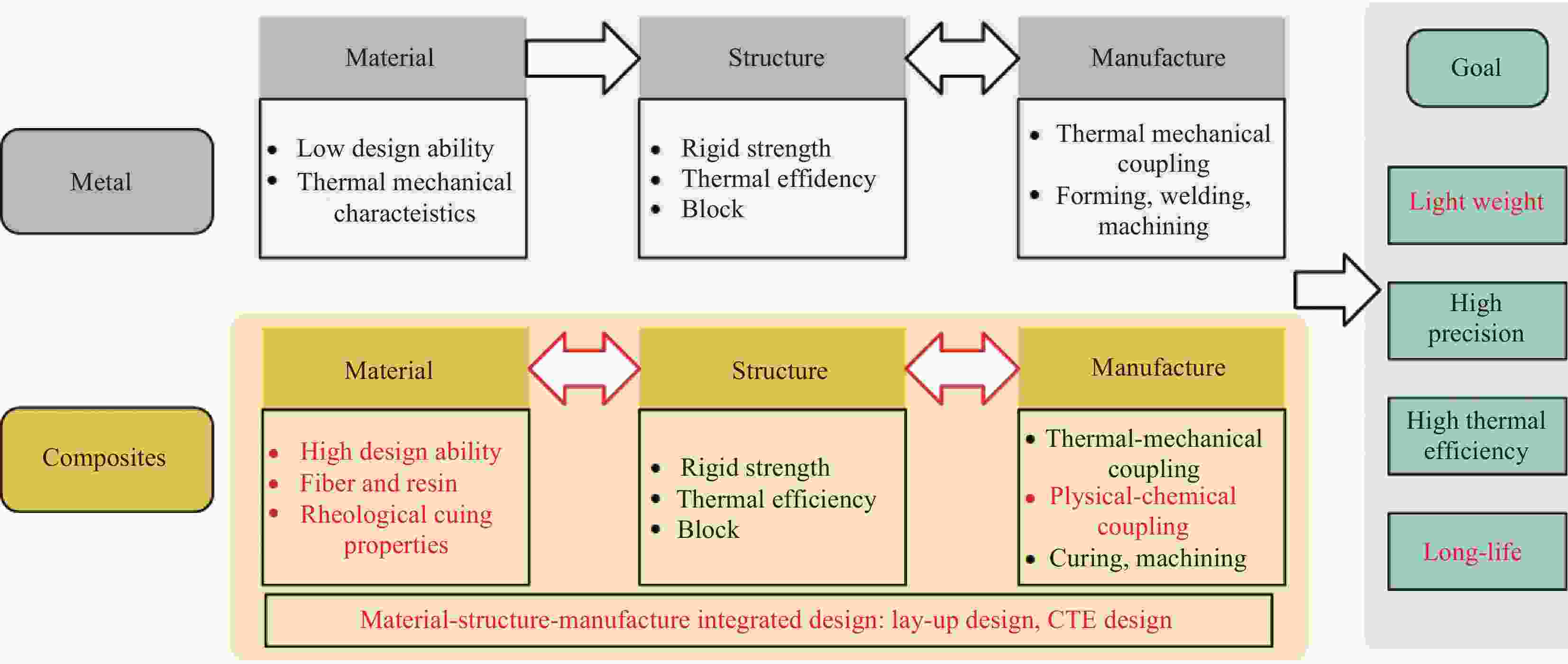
摘要: 固化成型模具是诱导热固性树脂基复合材料构件制造变形的关键因素之一。大型航空用复合材料构件整体化、批量化及高精度高性能发展趋势对固化用模具提出了更高的精度及寿命要求,推动了模具材料、设计及制造工艺方面的新发展,但目前相关研究尚缺乏系统梳理。因此,针对航空用大型复合材料构件对高精度模具的广泛需求,综述了模具对复合材料构件成型精度的影响和作用机制,固化用模具材料及其设计与制造技术现状。重点详述了在制造精度、效率及成本综合考虑下,从模具材料到制造工艺的发展。最后,对当前大型复合材料构件高精度模具在材料、设计及制造技术方面的发展现状进行了总结,并对未来主要研究方向提出了明确建议。Abstract: Curing tooling is one of the key factors to induce the deformation of thermosetting resin matrix compo-site components. The development trend of integrated, mass, high precision and high performance of composite components for large aerospace composite material components has put forward higher requirements on the precision and life of curing tooling, and promoted the new development of tooling materials, design and manufacturing processing. However, there is still a lack of systematic review of relevant research. Therefore, contraposing the widespread demanding of high precision tooling for large aerospace composite material components, this paper summarizes the research status including interfacial functional mechanism between tooling and components, the pro-perties of tooling materials, the structural characteristics and manufacturing processing. The development from tooling material to manufacturing processing is emphasized in detail under the comprehensive consideration of manufacturing precision, efficiency and cost. Finally, the current development status of high precision tooling is summarized in aspect of materials, design and manufacturing technology for large composite components and the main research directions in the future are proposed.
-
表 1 不同模具材料性能对比数据
Table 1. Comparison of performance data of different tooling materials
Materials α/(10−6℃−1) T/℃ ρ/(g·cm−3) E/GPa Tr Gypsum – <80 2.3 0.5-1 – Chemical wood 30 <80 1.4 1.42 RAKU-TOOL® Aluminium 24 <220 2.7 70 AA6082-T6 Steel 12 <220 7.85 210 – Invar 1.1 >25 8.1 150 InvaliteTM Carbon-epoxy 6.5 <160 1.57 60 M81 Hexcel Tool® Carbon-BMI 3.8 <220 1.55 60 M61 Hexcel Tool® Graphite 2.5 >25 1.3-2.0 8-15 – C foam 4.5 >25 0.56 3.5 CFOAMTM Notes:α—Coefficient of thermal expansion of materials; T—Maximum using temperature; ρ—Material density; E—Tensile modulus(for anisotropic material is mean axis modulus); Tr—Typic trademark made of material; BMI—Bismalei-mide. 表 2 阴模和阳模成型特点比较[42]
Table 2. Comparison of molding characteristics between female and male mold
Diagram Applicable parts Advantages Disadvantages Female mold 
External work surface ● Regular shape
● High accuracy● High cost
● Difficult layup
● Low production efficiencyMale mold 
Inner work surface ● Tractable
● Easy layup
● High production efficiency● Poor external surface quality
● Large spring-in angle -
[1] 范玉青, 张丽华. 超大型复合材料机体部件应用技术的新进展−飞机制造技术的新跨越[J]. 航空学报, 2009, 30(3):534-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.03.022FAN Yuqing, ZHANG Lihua. New development of extra large composite aircraft components application technology: Advance of aircraft manufacture technology[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2009,30(3):534-543(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2009.03.022 [2] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1):1-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001DU Shanyi. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(1):1-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2007.01.001 [3] 马立敏, 张嘉振, 岳广全, 等. 复合材料在新一代大型民用飞机中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2015, 32(2):317-322.MA Limin, ZHANG Jiazhen, YUE Guangquan, et al. App-lication of composites in new generation of large civil aircraft[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2015,32(2):317-322(in Chinese). [4] 倪楠楠, 卞凯, 夏璐, 等. 先进复合材料在无人机上的应用[J]. 航空材料学报, 2019, 39(5):45-60.NI Nannan, BIAN Kai, XIA Lu, et al. Application of advanced composite materials for UAV[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials,2019,39(5):45-60(in Chinese). [5] 牛晓坤. 热固性树脂基复合材料固化变形分析[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳航空航天大学, 2018.NIU Xiaokun. Analysis of curing deformation of thermosetting resin matrix composites [D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2018(in Chinese). [6] 何凯, 李成龙, 龚志红, 等. 航空复合材料构件精确制造技术探讨及应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2017, (9):101-105.HE Kai, LI Chenglong, GONG Zhihong, et al. Development and application of precision manufacturing technology of composite in aviation field[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2017, (9):101-105(in Chinese). [7] 王雪明, 谢富原, 李敏, 等. 复合材料构件热压罐成型工艺质量的群子理论分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(4):70-74.WANG Xueming, XIE Fuyuan, LI Min, et al. Sub-cluster theory analysis of process quality for composite components by autoclave process[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2010,27(4):70-74(in Chinese). [8] GRIFFIN O H. Three-dimensional curing stresses in symmetric cross-ply laminates with temperature-dependent properties[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1983,17(5):449-463. doi: 10.1177/002199838301700506 [9] KRAVCHENKO O G, KRAVCHENKO S G, PIPES R B. Cure history dependence of residual deformation in a thermosetting laminate[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,99:186-197. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.04.006 [10] NAWAB Y, SHAHID S, BOYARD N, et al. Chemical shrinkage characterization techniques for thermoset resins and associated composites[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2013,48(16):5387-5409. doi: 10.1007/s10853-013-7333-6 [11] KRAVCHENKO O G, KRAVCHENKO S G, PIPES R B. Chemical and thermal shrinkage in thermosetting prepreg [J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 80: 72-81. [12] 朱凌宇. 热固性树脂基纤维增强复合材料固化变形研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.ZHU Lingyu. Study on curing induced shape distortion for thermosetting resin matrix fibre-reinforced composites [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010(in Chinese). [13] LIAN J Y, XU Z B, RUAN X D. Analysis and control of cured deformation of fiber-reinforced thermosetting compo-sites: A review[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University-Science A,2019,20(5):311-333. doi: 10.1631/jzus.A1800565 [14] LI J, YAO X F, LIU Y H, et al. Curing deformation analysis for the composite T-shaped integrated structures[J]. Applied Composite Materials,2008,15(4/6):207-225. doi: 10.1007/s10443-008-9068-0 [15] 杨晓波, 湛利华, 蒋成标, 等. 模具材料对复合材料制件固化过程应变的影响分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 50(1):24-29.YANG Xiaobo, ZHAN Lihua, JIANG Chengbiao, et al. Influence of mould materials on curing process and deforma-tion of composite part[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2018,50(1):24-29(in Chinese). [16] STEFANIAK D, KAPPEL E, SPRÖWITZ T, et al. Experimental identification of process parameters inducing warpage of autoclave-processed CFRP parts[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(7):1081-1091. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2012.02.013 [17] 丁安心. 热固性树脂基复合材料固化变形数值模拟和理论研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.DING Anxin. Numerical and theoretical study on process-induced distortions in thermoset composites [D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [18] BARAN I, CINAR K, ERSOY N, et al. A review on the mecha-nical modeling of composite manufacturing processes[J]. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering,2017,24(2):365-395. doi: 10.1007/s11831-016-9167-2 [19] BERGLUND L, KENNY J. Processing science for high performance thermoset composites[J]. Sampe Journal,1991,27:27-37. [20] WISNOM M, GIGLIOTTI M, ERSOY N, et al. Mechanisms generating residual stresses and distortion during manufacture of polymer–matrix composite structures[J]. Compo-sites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2006,37(4):522-529. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.05.019 [21] MARTIN C, SEFERIS J, WILHELM M. Frictional resistance of thermoset prepregs and its influence on honeycomb composite processing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,1996,27(10):943-951. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(96)00037-1 [22] ERSOY N, POTTER K, WISNOM M R, et al. An experimental method to study the frictional processes during composites manufacturing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2005,36(11):1536-1544. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.02.010 [23] TWIGG G, POURSARTIP A, FERNLUND G. An experimental method for quantifying tool–part shear interaction during composites processing[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2003,63(13):1985-2002. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(3)00172-6 [24] KAUSHIK V, RAGHAVAN J. Experimental study of tool–part interaction during autoclave processing of thermoset polymer composite structures[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2010,41(9):1210-1218. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.05.003 [25] ZENG X, RAGHAVAN J. Role of tool-part interaction in process-induced warpage of autoclave-manufactured composite structures[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2010,41(9):1174-1183. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.04.017 [26] DE OLIVEIRA R, LAVANCHY S, CHATTON R, et al. Experimental investigation of the effect of the mould thermal expansion on the development of internal stresses during carbon fibre composite processing[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2008,39(7):1083-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.04.011 [27] 岳广全, 张嘉振, 张博明. 模具对复合材料构件固化变形的影响分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(4):206-210.YUE Guangquan, ZHANG Jiazhen, ZHANG Boming. Influence of mold on cure-induced deformation of composite structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(4):206-210(in Chinese). [28] ARAFATH A R A, VAZIRI R, POURSARTIP A. Closed-form solution for process-induced stresses and deformation of a composite part cured on a solid tool: Part I–flat geometries[J]. Composites Part A:Applied Science and Manufacturing,2008,39(7):1106-1117. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2008.04.009 [29] TWIGG G, POURSARTIP A, FERNLUND G. Tool–part interaction in composites processing. Part I: Experimental investigation and analytical model[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2004,35(1):121-133. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00131-3 [30] JOHNSTON A, VAZIRI R, POURSARTIP A. A plane strain model for process-induced deformation of laminated composite structures[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2001,35(16):1435-1469. doi: 10.1106/YXEA-5MH9-76J5-BACK [31] BAPANAPALLI S K, SMITH L V. A linear finite element model to predict processing-induced distortion in FRP laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2005,36(12):1666-1674. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.03.018 [32] 岳广全, 张博明, 戴福洪, 等. 固化过程中模具与复合材料构件相互作用分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(6):167-171.YUE Guangquan, ZHANG Boming, DAI Fuhong, et al. Interaction between mold and composite parts during curing process[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2010,27(6):167-171(in Chinese). [33] KHOUN L, DE OLIVEIRA R, MICHAUD V, et al. Investigation of process-induced strains development by fibre bragg grating sensors in resin transfer moulded compo-sites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2011,42(3):274-282. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2010.11.013 [34] ZHU Q, GEUBELLE P H, LI M, et al. Dimensional accuracy of thermoset composites: Simulation of process induced residual stresses[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2001,35(24):2171-2205. doi: 10.1177/002199801772662000 [35] 刘馨阳, 赵海涛, 袁明清, 等. 模具对复合材料层合板固化成型影响的数值分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(6):1974-1983.LIU Xinyang, ZHAO Haitao, YUAN Mingqing, et al. Numerical analysis of the effect of mold on the curing of composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(6):1974-1983(in Chinese). [36] TWIGG G, POURSARTIP A, FERNLUND G. Tool-part interaction in composites processing. Part II: Numerical modelling[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2004,35(1):135-141. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(03)00132-5 [37] ARAFATH A R A, VAZIRI R, POURSARTIP A. Closed-form solution for process-induced stresses and deformation of a composite part cured on a solid tool: Part II–curved geometries[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2009,40(10):1545-1557. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2009.01.009 [38] 张吉, 廖文和, 李迎光. 模具对柱面复合材料构件固化变形影响的有限元分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(5):191-195.ZHANG Ji, LIAO Wenhe, LI Yingguang. Finite element analysis of the mould influence on process-induced deformation of cylindrical composite part[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(5):191-195(in Chinese). [39] FERNLUND G, RAHMAN N, COURDJI R, et al. Experimental and numerical study of the effect of cure cycle, tool surface, geometry, and lay-up on the dimensional fidelity of autoclave-processed composite parts[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2002,33(3):341-351. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(01)00123-3 [40] JOVEN R, TAVAKOL B, RODRIGUEZ A, et al. Characterization of shear stress at the tool-part interface during autoclave processing of prepreg composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2013,129(4):2017-2028. doi: 10.1002/app.38909 [41] CASTRO F. The importance of surface conditioning in mould preparation[J]. Reinforced Plastics,2009,53(2):26-27. doi: 10.1016/S0034-3617(09)70080-3 [42] RADFORD D W. Balancing mechanisms of distortion to yield distortion-free/shape stable composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2010,29(12):1875-1892. doi: 10.1177/0731684409340707 [43] 刘德博, 湛利华, 丁星星, 等. 模具表面状态对复合材料构件固化变形的影响[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2019, 49(1):63-67.LIU Debo, ZHAN Lihua, DING Xingxing, et al. Influence of tool surface condition on cure-induced deformation of composite structure[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2019,49(1):63-67(in Chinese). [44] SHIELDS A J, HEPBURN D M, KEMP I J, et al. The absorption of mould release agent by epoxy resin[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2000,70(2):253-258. doi: 10.1016/S0141-3910(00)00121-X [45] 叶宏军, 翟全胜, 彭志霞, 等. 复合材料帽形结构水溶芯模共固化成型工艺研究[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2009, 26(4):3-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2009.04.001YE Hongjun, ZHAI Quansheng, PENG Zhixia, et al. Co-curing technology using water dispersible core for the hollow-structure composite parts[J]. Fiber Composites,2009,26(4):3-5(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2009.04.001 [46] EVERHART M C, STAHL J. Reusable shape memory polymer mandrels [C]. Smart Structures and Materials 2005: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2005: 27-34. [47] NA Z, YANG Y Q, MING H, et al. Finite element analysis of pressure on 2024 aluminum alloy created during restricting expansion-deformation heat-treatment[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2012,22(9):2226-2232. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)61453-2 [48] FU J X, LI X D, HWANG W S. Study of the coefficient of thermal expansion for steel Q235 [C]. Advanced Materials Research. Switzerland: Trans Tech Publications Ltd., 2011: 326-330. [49] DONG K, PENG X, ZHANG J, et al. Temperature-dependent thermal expansion behaviors of carbon fiber/epoxy plain woven composites: Experimental and numerical studies[J]. Composite Structures,2017,17(6):329-341. [50] YANG Q, WEI K, YANG X, et al. Microstructures and unique low thermal expansion of invar 36 alloy fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Characterization,2020,166:110-409. [51] SHAH D B, PATEL K, PATEL A I, et al. Experimental investigation on spring-back deformation during autoclave curing of parabolic antenna reflectors[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,115:134-146. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.09.017 [52] 顾轶卓, 李敏, 李艳霞, 等. 飞行器结构用复合材料制造技术与工艺理论进展[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(8):2773-2797.GU Yizhuo, LI Min, LI Yanxia, et al. Progress on manufacturing technology and process theory of aircraft compo-site structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2015,36(8):2773-2797(in Chinese). [53] 曹忠亮, 郭登科, 林国军, 等. 碳纤维复合材料自动铺放关键技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2021, (21):1-20.CAO Zhongliang, GUO Dengke, LIN Guojun, et al. Current situation and development trend of key technologies for automated placement of carbon fiber composites[J]. Materials Reports,2021, (21):1-20(in Chinese). [54] LUCAS R, DANFORD H. Case studies: Low cost, high-strength, large carbon foam tooling[J]. Sampe Journal,2009,45(1):20-28. [55] DU H Y, LIU L W, LENG J S, et al. Shape memory polymer S-shaped mandrel for composite air duct manufacturing[J]. Composite Structures,2015,133:930-938. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2015.08.005 [56] EVERHART M C, NICKERSON D M, HREHA R D. High-temperature reusable shape memory polymer mandrels [C]. Smart Structures and Materials. United States: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, 2006: 61710. [57] LENG J S, LAN X, LIU Y J, et al. Shape-memory polymers and their composites: Stimulus methods and applications[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2011,56(7):1077-1135. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.03.001 [58] ZHANG L, DU H Y, LIU L W, et al. Analysis and design of smart mandrels using shape memory polymers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2014,59:230-237. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.10.085 [59] ZHOU F, ZHANG J W, SONG S T, et al. Effect of temperature on material properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) tendons: Experiments and model assessment[J]. Materials,2019,12(7):1025. doi: 10.3390/ma12071025 [60] 李德尚. 飞机复材零件热压罐成形复材工装设计技术[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.LI Deshang. The composite tool design technologies for aircraft composites parts in autoclave forming [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010(in Chinese). [61] HE C P, XU J J. Finite element analysis of the thermal conductivity and the specific heat of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) composites [C]. 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Electromechanical Automation (AIEA). China: Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers, 2020: 771-774. [62] LACOSTE E, SZYMANSKA K, TEREKHINA S, et al. A multi-scale analysis of local stresses development during the cure of a composite tooling material[J]. International Journal of Material Forming,2013,6(4):467-482. doi: 10.1007/s12289-012-1100-0 [63] BECKWITH S W. Tooling 101 for composites manufacturing[R]. United States: The Composites and Advanced Materials Expo, 2020: 26. [64] HEXCEL. Hextool tooling material user guide[M]. United States: Hexcel Corporation, 2020: 3-33. [65] 刘新, 陈铎, 何辉永, 等. 热塑性颗粒-无机粒子协同增韧碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8):1904-1910.LIU Xin, CHEN Duo, HE Huiyong, et al. Synergistic toughening of thermoplastic particles-inorganic particles to carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(8):1904-1910(in Chinese). [66] NELSON, JAMES M. Development of nanosilica-thermoset matrix resins for prepreg composites[C]. Advanced Materials for Engineering Applications. United States: Technical Proceedings of the 2012 NSTI Nanotechnology Conference and Expo, 2012: 551-555. [67] WIMPENNY D I, GIBBONS G J. Metal spray tooling for composite forming[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 138(1/3): 443-448. [68] JEED A A, ABDULMA, NÄRHI T O, et al. The effect of high fiber fraction on some mechanical properties of unidirectional glass fiber-reinforced composite[J]. Dental Materials Official Publication of the Academy of Dental Materials,2011,27(4):313-321. doi: 10.1016/j.dental.2010.11.007 [69] DONG K, LIU K, ZHANG Q, et al. Experimental and numerical analyses on the thermal conductive behaviors of carbon fiber/epoxy plain woven composites[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2016,102:501-517. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.06.035 [70] GARG M, SHARMA S, MEHTA R. Pristine and amino functionalized carbon nanotubes reinforced glass fiber epoxy composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,76:92-101. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.05.012 [71] 钟云娇, 边文凤. 高模碳纤维细观力学分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(3):668-674. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160418.004ZHONG Yunjiao, BIAN Wenfeng. Micromechanics analysis of high modulus carbon fibers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(3):668-674(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20160418.004 [72] 谭伟, 那景新, 任俊铭, 等. 高温环境下碳纤维增强树脂复合材料的层间力学性能老化行为与失效预测[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(4):859-868. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190619.002TAN Wei, NA Jingxin, REN Junming, et al. Aging behavior and failure prediction of interlaminar mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer at high temperature[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(4):859-868(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190619.002 [73] SOBCINSKI T J. Hybrid lay-up tool: US Patent, 11/831, 767[P]. 2009-02-05. [74] ANTHONY P G, FOX M, SKELTON Z, et al. Hybrid lay-up mold: US Patent, 10427330[P]. 2019-10-01. [75] RICHARDSON M. Tooling to mould and die for[N]. Aerospace Manufacturing: 2018. https://www.aero-mag.com/ascent-aerospace-hyvarc-hybrid-invar-composite-mould. [76] HASAN Z. Tooling for composite aerospace structures manufacturing and applications [M]. United Kingdom: Butterworth Heinemann, 2020. [77] 沈真, 杨胜春. 飞机结构用复合材料的力学性能要求[J]. 材料工程, 2007, (S1):248-252.SHEN Zhen, YANG Shengchun. Property requirements of composite systems applicable to aircraft structures[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2007, (S1):248-252(in Chinese). [78] FAHMY A, RAGAI A. Thermal expansion of graphite/epoxy composites[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,1970,41(13):5112-5115. doi: 10.1063/1.1658620 [79] FAHMY A, RAGAI A. Thermal expansion of laminated fiber composites in the thickness direction[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1974,8(1):90-92. doi: 10.1177/002199837400800109 [80] KELLY A, STEARN R, MCCARTNEY L. Composite materials of controlled thermal expansion[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2006,66(2):154-159. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.04.025 [81] MOREY B. Tooling it up for composites[J]. Society of Manu-facturing Engineers, 2010, 144(4): 57-63. [82] 张吉. 基于有限元模拟的复合材料构件热压罐成型工艺研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2012.ZHANG Ji. Research on composite molding process in autoclave based on FEA [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012(in Chinese). [83] 王乾, 关志东, 王仁宇, 等. 结构参数对复合材料V型构件固化变形影响试验及解析分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(12):2722-2733. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170301.002WANG Qian, GUAN Zhidong, WANG Renyu, et al. Experimental and analytic analysis of the structure parameters on process-induced distortions of V-shaped composite parts[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(12):2722-2733(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170301.002 [84] 祝君军, 文琼华, 罗辑, 等. 模具形式对V型结构复合材料固化变形的影响[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2018, 48(5):44-48.ZHU Junjun, WEN Qionghua, LUO Ji, et al. Effect of mold forming method on curing deformation of V-shaped composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2018,48(5):44-48(in Chinese). [85] ARAFATH A R A. Efficient numerical techniques for predicting process-induced stresses and deformations in composite structures [D]. Canada: University of British Columbia, 2007. [86] HASSAN M H, OTHMAN A R, KAMARUDDIN S. A review on the manufacturing defects of complex-shaped laminate in aircraft composite structures[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2017,91(9):4081-4094. [87] RADFORD D W, RENNICK T S. Separating sources of manufacturing distortion in laminated composites[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2000,19(8):621-641. doi: 10.1177/073168440001900802 [88] XIE G N, LIU J, ZANG W H, et al. Simulation and improvement of temperature distributions of a framed mould during the autoclave composite curing process[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2013,22(1):43-61. doi: 10.1134/S1810232813010062 [89] GNIATCZYK J L, AQUILINA G R, DEAVER D T. Compo-site molding tools and parts and processes of forming molding tools: US Patent, 6309587[P]. 2001-10-30. [90] 王雯, 鲍益东, 樊胜宝, 等. 框架式复材成型模具轻量化设计方法[J]. 航空制造技术, 2018, 61(Z2):82-86.WANG Wen, BAO Yidong, FAN Shengbao, et al. Lightweight design method of frame molding die for compo-site materials[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2018,61(Z2):82-86(in Chinese). [91] 张铖, 梁宪珠, 胡江波, 等. 拓扑优化在框架式模具结构选形中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2012,(9):62-63+68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2012.09.009ZHANG Cheng, LIANG Xianzhu, HU Jiangbo, et al. Appli-cation of topology optimization in structure selection of frame mould[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2012,(9):62-63+68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2012.09.009 [92] 白光辉, 晏冬秀, 张冬梅, 等. 大型复杂框架式模具温度场模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(S1):169-174. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2013.s1.041BAI Guanghui, YAN Dongxiu, ZHANG Dongmei, et al. A study on the temperature field distribute property of large frame type molds[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(S1):169-174(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.2013.s1.041 [93] 赵博伟, 杜发喜, 高原, 等. 基于自动丝束铺放技术的复合材料进气道结构设计及试验验证[J]. 航空工程进展, 2017, 8(3):349-353. doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2017.03.016ZHAO Bowei, DU Faxi, GAO Yuan, et al. Design and experimental verification of composite material inlet structure based on automatic tow laying technology[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2017,8(3):349-353(in Chinese). doi: 10.16615/j.cnki.1674-8190.2017.03.016 [94] 丁玲. 全复合材料无人机机翼结构优化设计[D]. 长春: 中国科学院(长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2014.DING Ling. Structure optimal design for all composite wings of an unmanned aerial vehicle [D]. Changchun: Chinese Academy of Sciences(Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics), 2014(in Chinese). [95] KROGH C, GLUD J A, JAKOBSEN J. Modeling the robotic manipulation of woven carbon fiber prepreg plies onto double curved molds: A path-dependent problem[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2019,53(15):2149-2164. doi: 10.1177/0021998318822722 [96] 王琦, 蒋秋梅, 杨旭锋, 等. 三维机织复合材料残余应力/应变多尺度分析及工艺参数优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(4):1167-1176. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200720.002WANG Qi, JIANG Qiumei, YANG Xufeng, et al. Multiscale analysis and process parameters optimization of residual stress/strain of 3D woven composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(4):1167-1176(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20200720.002 [97] ELKINGTON M, BLOOM D, WARD C, et al. Hand layup: Understanding the manual process[J]. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science,2015,1(3):138-151. [98] RAKHSHBAHAR M, SINAPIUS M. A novel approach: Combination of automated fiber placement (AFP) and additive layer manufacturing (ALM)[J]. Journal of Composites Science,2018,2(3):42. doi: 10.3390/jcs2030042 [99] MALHAN R K, KABIR A M, SHAH B, et al. Determining feasible robot placements in robotic cells for composite prepreg sheet layup[C]. International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference. United States: Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2019. [100] MALHAN R K, KABIR A M, SHEMBEKAR A V, et al. Hybrid cells for multi-layer prepreg composite sheet layup [C]. 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE). Germany: IEEE, 2018: 1466-1472. [101] MALHAN R K, SHEMBEKAR A V, KABIR A M, et al. Automated planning for robotic layup of composite prepreg[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing,2021,67:102020. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2020.102020 [102] MADHUKAR M S, GENIDY M S, RUSSELL J D. A new method to reduce cure-induced stresses in thermoset polymer composites, part I: Test method[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2000,34(22):1882-1904. doi: 10.1106/HUCY-DY2B-2N42-UJBX [103] GOPAL A K, ADALI S, VERIJENKO V E. Optimal temperature profiles for minimum residual stress in the cure process of polymer composites[J]. Composite Structures,2000,48(1):99-106. [104] WHITE S R, HAHN H T. Cure cycle optimization for the reduction of processing-induced residual stresses in composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1993,27(14):1352-1378. doi: 10.1177/002199839302701402 [105] GIGLIOTTI M, WISNOM M R, POTTER K D. Development of curvature during the cure of AS4/8552 [0/90] unsymmetric composite plates[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2003,63(2):187-197. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(02)00195-1 [106] WHITE S R, KIM Y K. Staged curing of composite materials[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,1996,27(3):219-227. doi: 10.1016/1359-835X(95)00023-U [107] SEERS B, TOMLINSON R, FAIRCLOUGH P. Residual stress in fiber reinforced thermosetting composites: A review of measurement techniques[J]. Polymer Compo-sites,2021,42(4):1631-1647. doi: 10.1002/pc.25934 [108] 丁安心, 李书欣, 倪爱清, 等. 热固性树脂基复合材料固化变形和残余应力数值模拟研究综述[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(3):471-485. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170105.001DING Anxin, LI Shuxin, NI Aiqing, et al. A review of numerical simulation of cure-induced distortions and resi-dual stresses in thermoset composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(3):471-485(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20170105.001 [109] 丁安心, 王继辉, 倪爱清, 等. 热固性树脂基复合材料固化变形解析预测研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6):1361-1376. doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180327.001DING Anxin, WANG Jihui, NI Aiqing, et al. A review of analytical prediction of cure-induced distortions in thermoset composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(6):1361-1376(in Chinese). doi: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20180327.001 [110] ALEKSENDRIĆ D, CARLONE P, ĆIROVIĆ V. Optimization of the temperature-time curve for the curing process of thermoset matrix composites[J]. Applied Composite Materials,2016,23(5):1047-1063. doi: 10.1007/s10443-016-9499-y [111] CARLONE P, ALEKSENDRIĆ D, ĆIROVIĆ V, et al. Meta-modeling of the curing process of thermoset matrix compo-sites by means of a FEM–ANN approach[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2014,67:441-448. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2014.08.022 [112] JAHROMI P E, SHOJAEI A, REZA P S M. Prediction and optimization of cure cycle of thick fiber-reinforced compo-site parts using dynamic artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2012,31(18):1201-1215. doi: 10.1177/0731684412451937 -





 下载:
下载: