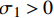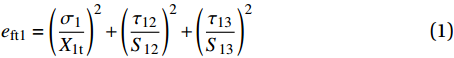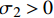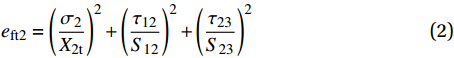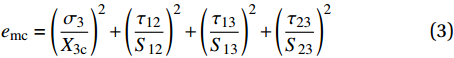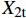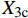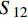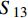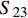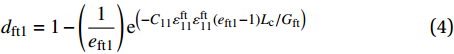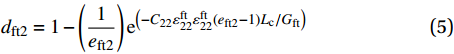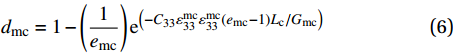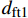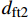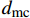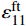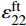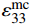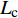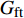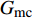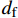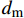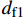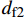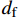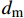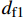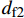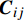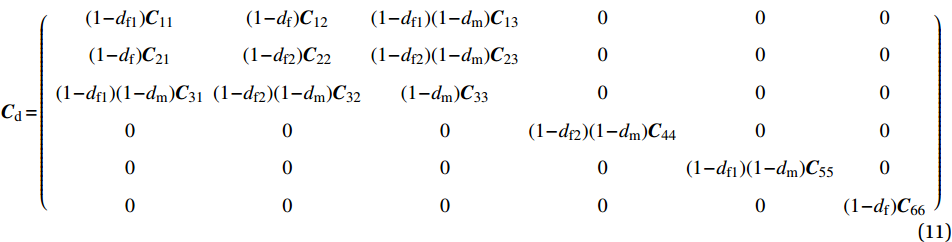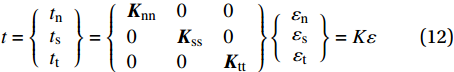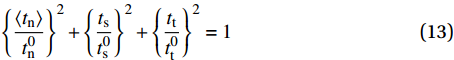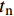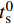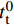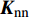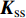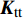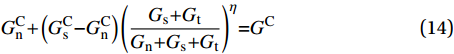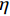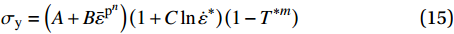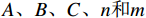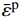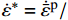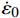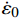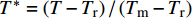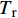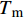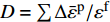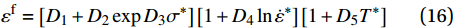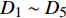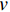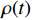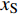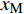Protective performance of PASGT combat helmet under pistol bullet impact
-
摘要: 新型防弹头盔虽然能有效减少手枪弹穿透性损伤,但头盔内表面变形(Back face deformation,BFD)仍有可能对人体头部造成损伤。为准确模拟防弹头盔受到子弹冲击时的瞬态力学响应,基于Abaqus的用户材料子程序VUMAT编写了适用于模拟复合材料防弹头盔力学性能的渐进损伤本构模型,建立了9 mm铅芯手枪弹以343 m/s侵彻PASGT芳纶防弹头盔的有限元模型,从头盔BFD曲线和内表面鼓包形态两方面验证了数值模拟的准确性。防弹头盔失效模式表明,头盔主要发生纤维拉伸、基体压缩和分层失效;子弹侵彻防弹头盔的过程中,头盔上的应力云图在初期呈现较为规则的菱形,然后再慢慢向四周扩散演化为圆形;子弹以三种不同入射角(30°、45°、60°)冲击头盔顶部时均出现了跳弹,反跳后的速度分别为72.9 m/s、165.5 m/s和240.1 m/s。最后采用钝性准则对头盔内表面变形可能造成的颅骨骨折概率进行了估算。Abstract: Although the new combat helmet can effectively reduce the pistol bullet penetrating damage, the back face deformation (BFD) of helmet may cause head injury. In order to accurately simulate the transient mechanical response of combat helmet under bullet impact, a progressive damage constitutive model for simulating the mechanical properties of composite combat helmet was developed based on the user material subroutine VUMAT of Abaqus. The finite element model of 9 mm lead core pistol bullet penetrating PASGT aramid combat helmet with impacting velocity 343 m/s was established. The accuracy of the numerical simulation was verified by the helmet BFD curve and the bulge shape of the inner surface. The failure mode of combat helmet shows that the helmet mainly occurs fiber tension, matrix compression and delamination failure. During the penetrating process, the stress contours on the helmet presents a regular diamond shape at the initial stage, and then slowly diffuses around and evolves into a circle. At three different angles of incidence (30°, 45°, 60°), the velocity of rebound is 72.9 m/s, 165.5 m/s and 240.1 m/s, respectively. Finally, the probability of skull fracture caused by the BFD of the helmet was estimated using the blunt criterion.
-
Keywords:
- combat helmet /
- bullet /
- finite element model /
- penetration /
- back face deformation (BFD)
-
现代战争中,由于新技术不断应用,枪弹和破片杀伤效能不断提高,战场上士兵们的生命受到严重威胁。有资料统计由头部受伤导致的伤亡占总战场死亡人数的50%左右[1],因此防弹头盔的防护性能在战场上对士兵生命安全起着至关重要的作用。子弹在未穿透防弹头盔情况下产生的冲击会经过头盔变形等方式传递到人体头部,造成防护后钝性损伤(Behind armor blunt trauma,BABT)[2],因此目前各国普遍使用的防弹头盔性能测试标准中,头盔内表面变形(Back face deformation, BFD)一直是一项非常重要的测量指标[3]。
近年来,国内外研究者对防弹头盔受到的非贯穿性冲击损伤进行了广泛研究。王昕昇[4]对凯夫拉头盔受到钝性冲击时的能量耗散规律进行了研究,发现入射角度以及入射速度对能量的转变有较为明显的影响。黄艺峰[5]建立了美军地面部队单兵防护系统(Personnel armor system for ground troops,PASGT)头盔致钝性颅脑损伤动物实验模型,对子弹冲击防弹头盔致颅脑损伤的主要致伤机制、损伤机制进行了探讨。蔡志华等[6]、李泽民[7]、王威等[8]对枪弹冲击防弹头盔导致的人体头部非贯穿性损伤进行了数值模拟研究,结果表明头盔的背面变形易引起颅骨骨折与颅内压力增加。Li等[9]对枪弹打击防弹头盔的过程进行了数值模拟,模拟结果的BFD最大值和时间历程与实验数据非常吻合。Jazi等[10]研究了不同防弹头盔衬垫材料对弹道冲击下大脑受到压力大小的影响。Lee等[11]、Tham等[12]进行了弹丸侵彻凯夫拉防弹头盔的数值模拟研究,发现防弹头盔虽然没有被弹丸穿透但是冲击会产生严重的头部损伤。Carlos等[13]分别使用ECE R22.05头部替代模型和人体头部模型对钝击过程中的头部损伤进行了评估,结果表明不同的头部模型计算出的损伤程度也不同。Cai等[14]研究了人类颅骨和脑组织在子弹冲击防弹头盔载荷下的反应,研究结果表明,当子弹撞击防弹头盔时,导致大脑移位和颅内高压的概率更高。Cacoilo等[15]模拟了子弹撞击防弹头盔的过程,并结合头部损伤标准(HIC)准则对头部损伤概率进行了评估。Li等[16]、Palomar等[17]仿真得出了不同子弹撞击速度下的BFD最大值,并结合不同头部损伤准则讨论了影响头部创伤的主要因素(泡沫厚度、头盔厚度等)。准确的头盔内表面变形是研究其对人体头部造成钝性损伤的基础,纤维增强复合材料在高速冲击下的失效模式和过程较为复杂,现有的经典复合材料本构在模拟其冲击失效过程时仍显不足。
本文基于Hashin失效准则和渐进退化损伤演化理论在Abaqus中编写了适用于复合材料防弹头盔的用户材料子程序VUMAT,建立了9 mm 手枪弹冲击PASGT芳纶防弹头盔的数值模型,获得的头盔BFD过程与试验吻合较好。随后研究了子弹侵彻防弹头盔过程中防弹头盔的应力变化过程以及损伤机制,模拟了子弹不同入射角对防弹头盔损伤效应的影响,可为防弹头盔防护性能评估与改进设计提供参考。
1. 数值计算模型
1.1 PASGT防弹头盔以及9 mm 手枪弹建模
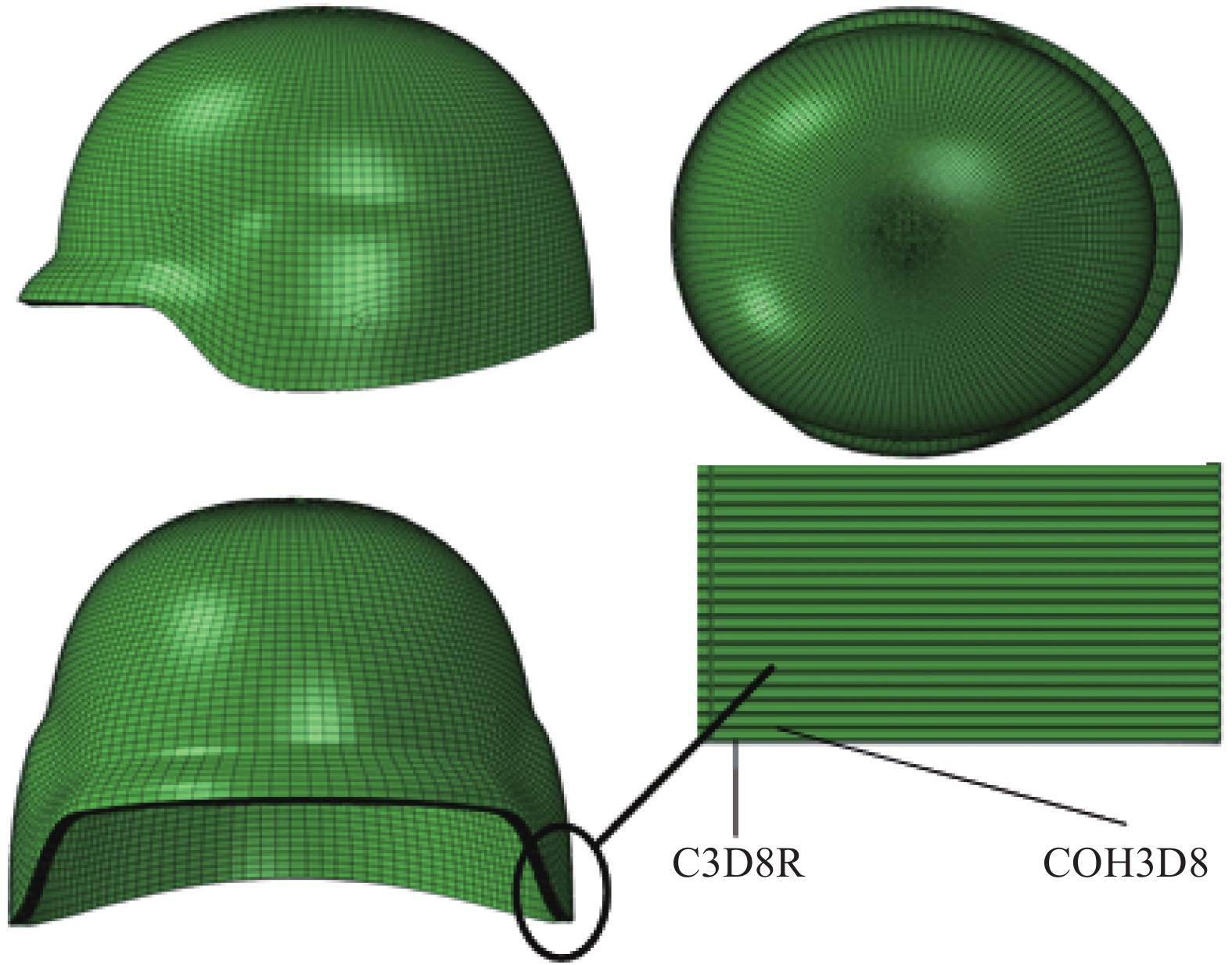
PASGT防弹头盔是由芳纶纤维和热固性树脂组成的纤维增强复合材料头盔(图1)。首先使用3D扫描仪器对PASGT防弹头盔进行扫描,获得其点云数据,得到格式为STL的几何文件。然后使用Geomagic Studio软件进行几何修复,得到能用于划分网格的几何文件,最后导入Hypermesh中进行有限元网格划分。
防弹头盔有限元模型使用8节点六面体线性减缩积分单元(C3D8R),防弹头盔被等效为7层复合编织层,每两层复合编织层之间添加一层零厚度内聚力(Cohesive)单元来模拟层间力学性能,共6层。防弹头盔模型共294705个单元(图2)。手枪弹有限元模型网格类型使用C3D8R,共11264个单元(图3)。
1.2 防弹头盔材料本构与参数
本文使用的PASGT防弹头盔材料模型是基于Abaqus用户材料子程序接口编写的VUMAT,材料失效准则采用Hashin失效准则[18],该准则考虑了编织复合材料经向和纬向两个方向的纤维强度。
纤维失效模式:
经向纤维拉伸失效模式,
σ1>0 eft1=(σ1X1t)2+(τ12S12)2+(τ13S13)2 (1) 纬向纤维拉伸失效模式,
σ2>0 eft2=(σ2X2t)2+(τ12S12)2+(τ23S23)2 (2) 基体失效模式:
基体压缩失效模式,
σ3<0 emc=(σ3X3c)2+(τ12S12)2+(τ13S13)2+(τ23S23)2 (3) 式中:eft1、eft2、emc 分别为经向纤维、纬向纤维和基体的失效指数;σ1、σ2、σ3分别为三个方向上的正应力;
X1t 、X2t 分别为编织层的经向、纬向拉伸强度;X3c 为基体压缩强度;τ12、τ13、τ23为三个方向上的切应力;S12 、S13 、S23 分别为编织层的两个面内剪切强度以及面外剪切强度,具体材料参数如表1所示。ρ/
(g·cm−3)E1/
GPaE2/
GPaE3/
GPav12 v13 v23 G12/
MPaG13/
MPaG23/
MPaXt/
MPaXc/
MPaYt/
MPaYc/
MPaZt/
MPaZc/
MPaS12/
MPaS13/
MPaS23/
MPa1.23 22 22 9 0.25 0.33 0.33 770 2715 2715 800 80 800 80 1200 1200 77 898 898 Notes:ρ—Density; E1, E2, E3—The elastic modulus in X, Y, and Z directions; v12, v13, v23—Poisson's ratios; G12, G23, G13—Shear modulus; Xc, Xt, Yc, Yt, Zc, Zt—Compressive and tensile strength in X, Y, Z directions; S12, S23, S13—Shear strength. 本文采用渐进退化的方法来表征防弹头盔编织层的损伤演化,为了减小有限元计算结果对网格尺寸的依赖性,在损伤演化准则中引入了单元特征长度,损伤变量具体表达式如下[20]:
dft1=1−(1eft1)e(−C11εft11εft11(eft1−1)Lc/Gft) (4) dft2=1−(1eft2)e(−C22εft22εft22(eft2−1)Lc/Gft) (5) dmc=1−(1emc)e(−C33εmc33εmc33(emc−1)Lc/Gmc) (6) 式中:
dft1 、dft2 、dmc 为损伤变量,分别用来表征经向、纬向纤维拉伸和基体压缩三种损伤模式。三个损伤变量的取值范围均为0~1,其中0表示材料尚未发生损伤,1表示材料已经完全失效。另外,添加额外一个状态变量来控制单元的删除,当单元发生纤维拉伸损伤模式,或者三个主方向的应变大于1时,单元被删除,这样能尽可能在保证材料刚度退化准确度的前提下增加计算收敛性[3];εft11 、εft22 、εmc33 分别为材料1方向、2方向上的拉伸断裂应变和3方向上的压缩断裂应变;Lc 为单元特征长度;Gft 、Gmc 分别为纤维拉伸和基体压缩的断裂能密度。引入全局损伤变量df 、dm 、df1 和df2 来进行材料损伤后的刚度折减。由于本文VUMAT中没有考虑纤维方向的压缩损伤和基体方向的拉伸损伤,因此经向、纬向的纤维全局损伤变量即为其拉伸损伤变量,基体全局损伤变量即为其压缩损伤变量,表达式如下:df=1−(1−dft1)(1−dft2) (7) dm=dmc (8) df1=dft1 (9) df2=dft2 (10) 在计算出全局损伤变量
df 、dm 、df1 和df2 之后,代入材料刚度矩阵中即可实现对材料对应损伤模式下的刚度折减,折减后的刚度矩阵如下式所示,其中{{\boldsymbol{C}}_{ij}} (i, j=1,2,3,4,5,6)为材料未发生损伤时的刚度矩阵分量:{{\boldsymbol{C}}_{\rm{d}}} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f1}}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{11}}} & {(1 - {d_{\rm{f}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{12}}} & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f1}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{13}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ {(1 - {d_{\rm{f}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{21}}} & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f2}}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{22}}} & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f2}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{23}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f1}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{31}}} & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f2}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{32}}} & {(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{33}}} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f2}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{44}}} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {(1 - {d_{{\rm{f1}}}})(1 - {d_{\rm{m}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{55}}} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & {(1 - {d_{\rm{f}}}){{\boldsymbol{C}}_{66}}} \end{array}} \right) (11) 1.3 内聚力(Cohesive)单元的本构模型与参数[21]
本文Cohesive单元采用分析过程中较为稳定的双线性本构模型[22](图4)。
其线性段本构关系可以表示为:
t=\left\{\begin{array}{l} t_{\rm{n}} \\ t_{\rm{s}} \\ t_{\rm{t}} \end{array}\right\}=\left\{\begin{array}{lll} {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{nn}} & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{ss}} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & {\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{tt}} \end{array}\right\}\left\{\begin{array}{c} \varepsilon_{\rm{n}} \\ \varepsilon_{\rm{s}} \\ \varepsilon_{\rm{t}} \end{array}\right\}=K \varepsilon (12) Cohesive单元损伤起始准则选择考虑了混合模式载荷的二次正应力准则:
{\left\{ {\frac{{\left\langle {{t_{\rm{n}}}} \right\rangle }}{{t_{\rm{n}}^0}}} \right\}^2} + {\left\{ {\frac{{{t_{\rm{s}}}}}{{t_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{0}}}}} \right\}^2} + {\left\{ {\frac{{{t_{\rm{t}}}}}{{t_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{0}}}}} \right\}^2} = 1 (13) 式中:
{t_{\rm{n}}} 、{t_{\rm{s}}} 、{t_{\rm{t}}} 分别为Cohesive单元三个方向上的应力;t_{\rm{n}}^0 、t_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{0}} 、t_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{0}} 分别为Cohesive单元三个方向上的强度;{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{nn}} 、{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{ss}} 、{\boldsymbol{K}}_{\rm{tt}} 分别为Cohesive单元三个方向上的刚度;εn、εs、εt分别为Cohesive单元三个方向上的名义应变。Cohesive单元损伤起始以后的损伤演化准则采用的是能较好的模拟层合板层间分层的混合模式下的B-K准则[23]:
G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}{\rm{ + }}\left( {G_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{C}}{\rm{ - }}G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}} \right){\left( {\frac{{{G_{\rm{s}}}{\rm{ + }}{G_{\rm{t}}}}}{{{G_{\rm{n}}}{\rm{ + }}{G_{\rm{s}}}{\rm{ + }}{G_{\rm{t}}}}}} \right)^\eta }{\rm{ = }}{G^{\rm{C}}} (14) 式中:
{G^{\rm{C}}} 为B-K准则计算出的混合模式下的等效断裂韧性;\eta 为材料参数。Cohesive单元完整的材料参数如表2所示。
ρ/(g·cm−3) {K_{{\rm{nn}}}}/MPa {K_{{\rm{ss}}}}/MPa {K_{{\rm{tt}}}}/MPa t_{\rm{n}}^0/MPa t_{\rm{s}}^0/MPa t_{\rm{t}}^0/MPa G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) G_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) G_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) 2 4830 4830 4830 34.5 9 9 0.24 0.47 0.47 Notes: ρ—Density; {K_{{\rm{nn}}}}, {K_{{\rm{ss}}}}, {K_{{\rm{tt}}}}—Elastic modulus; t_{\rm{n}}^0, t_{\rm{s}}^0, t_{\rm{t}}^0—Normal and tangential strength; G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}, G_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{C}}, G_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{C}}—Critical energy release rates in mode I, mode II and mode III. 1.4 手枪弹的本构模型与参数
在弹道冲击等有限元分析中金属材料一般使用JOHNSON_COOK材料模型[24]来模拟。该本构适合用来模拟材料在大变形、高应变率和高温环境下的力学响应情况[25]。其本构关系表达式为:
{\sigma _{\rm{y}}} = \left( {A + B{{\bar \varepsilon }^{{{\rm{p}}^{n}}}}} \right)\left( {1 + C\ln {{\dot \varepsilon }^*}} \right)\left( {1 - {T^{*{m}}}} \right) (15) 式中:σy是屈服应力;
A、B、C、n和m 是通过试验测定得出的材料参数;{\bar \varepsilon ^{\rm{p}}} 是有效塑性应变;{\dot \varepsilon ^*} = {\dot {\bar \varepsilon} ^{\rm{p}}}/ {\dot \varepsilon _0} 为无量纲塑性应变率,{\dot \varepsilon _0} 为参考应变率;{T^*} = \left( {T - {T_{\rm{r}}}} \right)/\left( {{T_{\rm{m}}} - {T_{\rm{r}}}} \right) 为无量纲温度,{T_{\rm{r}}} 为室温,{T_{\rm{m}}} 为熔化温度。该模型定义单元的损伤
D = \sum \Delta {\bar \varepsilon ^{\rm{p}}}/{\varepsilon ^{\rm{f}}} ,初始时D = 0 ,当D = 1 时单元失效,\Delta {\bar \varepsilon ^{\rm{p}}} 为一个增量步的塑性应变增量,{\varepsilon ^{\rm{f}}} 为当前应力状态、应变率和温度下的破坏应变。破坏应变{\varepsilon ^{\rm{f}}} 的表达式为:{\varepsilon ^{\rm{f}}} = \left[ {{D_1} + {D_2}\exp {D_3}{\sigma ^*}} \right]\left[ {1 + {D_4}\ln {{\dot \varepsilon }^*}} \right]\left[ {1 + {D_5}{T^*}} \right] (16) 式中:σ*为平均应力;
{D_1}\sim{D_5} 为材料常数。材料参数如表3所示。ρ/(g·cm−3) G/GPa A/MPa B/MPa N C M Tm Tr D1 D2-D5 Lead core 11.34 7 14 18 0.685 0.035 1.68 600 294.0 1.0 0 Copper jacket 8.45 46 90 292 0.01 0.025 1.09 1356 300.15 0.8 0 Notes:G—Shear modulus; A—Initial yield stress; B—Hardening constant; N—Hardening exponent; C—Strain rate constant; M—Thermal softening exponent; Tm—Melting temperature; Tr—Room temperature; D1-D5—Damage constants. 2. 结果验证
2.1 PASGT头盔BFD曲线
课题组之前开展了基于3D-DIC技术的9 mm 手枪弹侵彻PASGT芳纶防弹头盔顶部试验[27]。试验所使用的3D-DIC测试系统主要由两台高速相机(PhantomV2511)、直流光源、相机镜头、同步触发系统、计算工作站和一些辅助工具(固定连接工具、标定、散斑制作工具)等组成(图5)。
试验测量过程:将PASGT防弹头盔的悬挂系统拆除,在头盔内表面根据相机画幅、分辨率等要求制作出符合DIC软件计算要求的散斑。试验用QSZ92式9 mm手枪,发射DAP92 9 mm手枪弹。当试验开始时,子弹发射时产生的强光能够触发红外触发器,进而同步触发两台高速相机进行拍摄。最后通过3D-DIC软件对拍摄的头盔内部散斑变化图片进行分析,得出头盔内表面的变形信息,从而获得弹着点处头盔BFD的瞬态演化过程数据。
试验和数值模拟得到的BFD高度随时间变化过程如图6所示。三组试验中的BFD在到达最大值之前快速增大,并且增大速度在逐渐减小,在0.9 ms附近分别到达最大值27.3 mm、28.1 mm、27.9 mm,然后BFD开始逐渐减小。数值模型中的BFD在0.5 ms之前快速增大,在0.5 ms之后BFD的增加速度逐渐减小,在1 ms附近到达最大值27.6 mm,然后BFD开始逐渐减小。从图6可以看出,数值模拟和试验中的BFD变化过程吻合较好,数值模拟和三组试验BFD最大值的平均值相对误差仅为0.3%。
2.2 PASGT头盔内表面鼓包形态
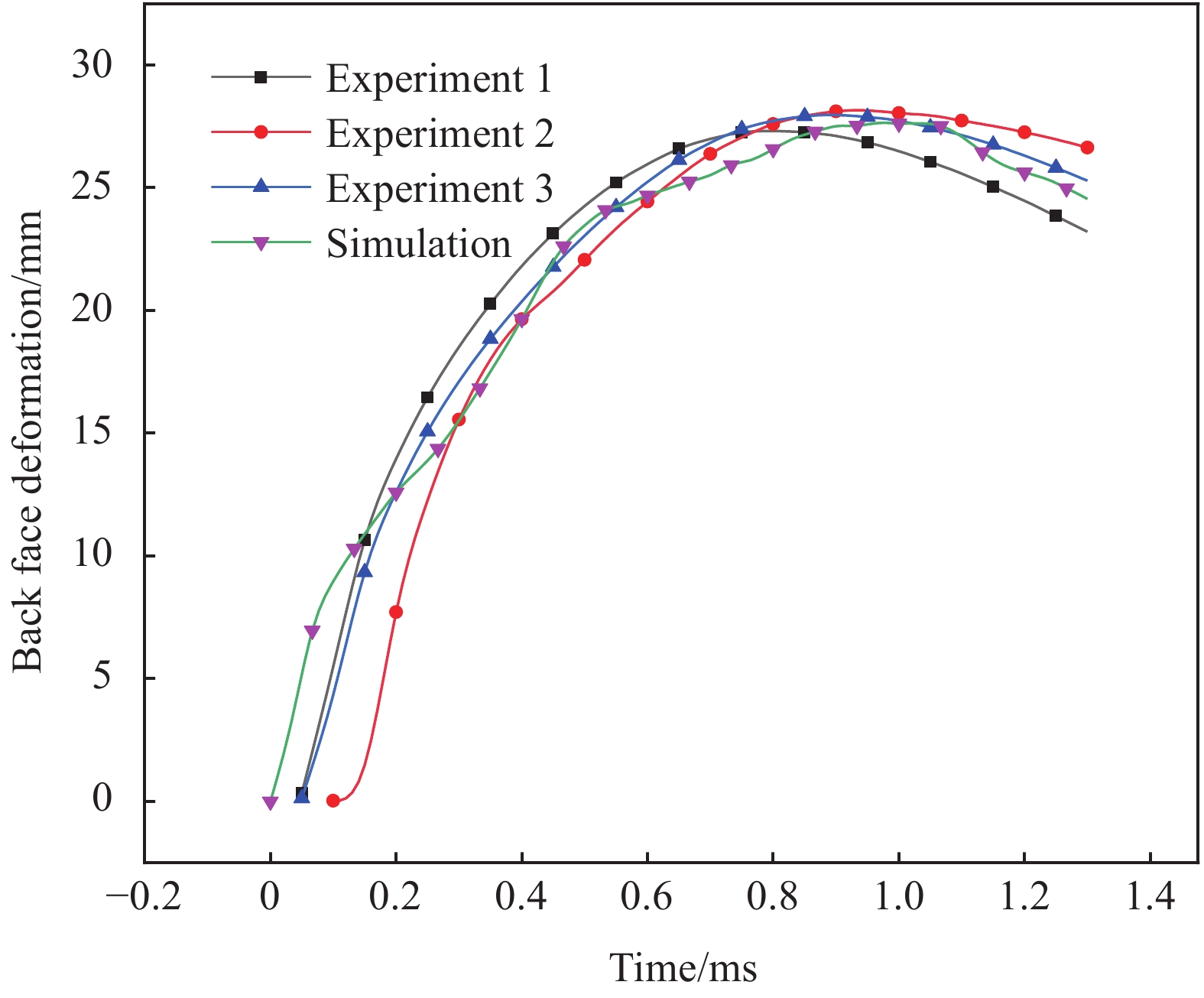
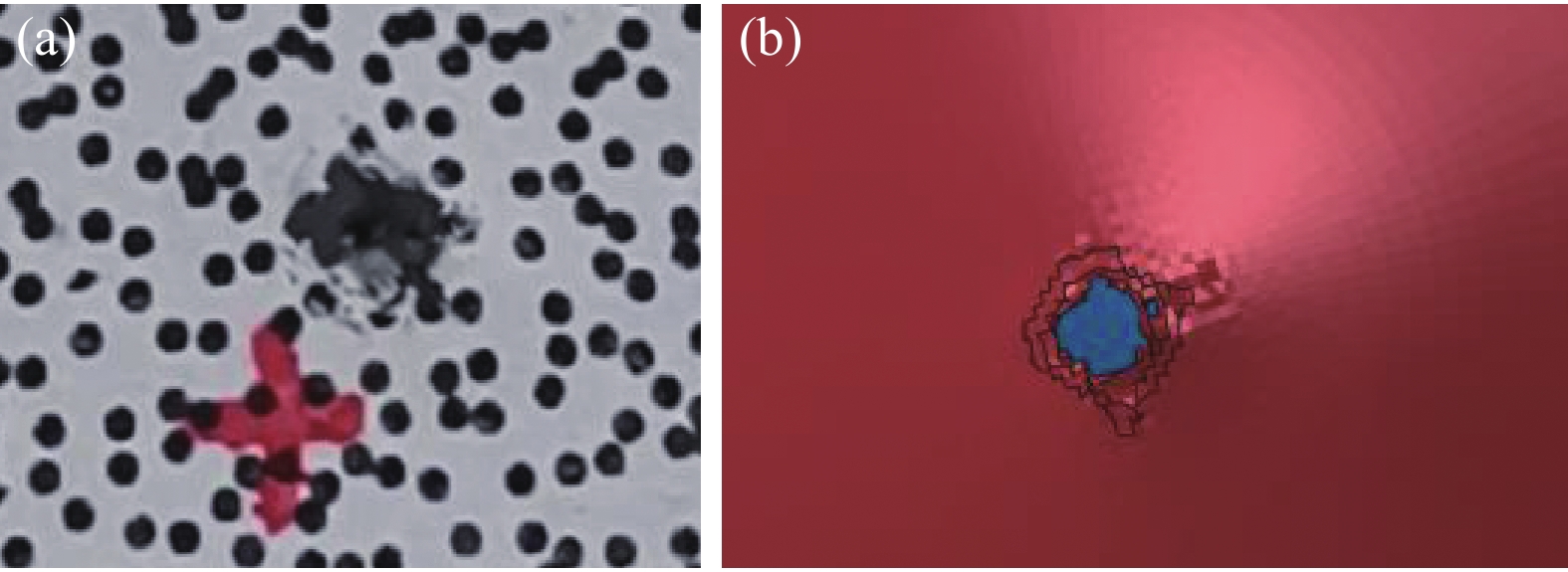
试验和数值模拟中头盔内部鼓包形态变化过程如图7所示。将试验和仿真中的鼓包变形云图范围设置为相同,以变形大于4 mm的区域在图7中竖直方向的最外沿作为鼓包的边缘。当时间为0.15 ms时,头盔内部开始发生明显的变形,试验和数值模拟的鼓包变形区域形状相似,都为较为规则的圆形。0.6 ms时试验和数值模拟的鼓包变形区域都发生了明显的扩大,形状也逐渐向椭圆形演化。0.9 ms时,试验中头盔内部鼓包高度达到最大27.7 mm,变形区域面积也达到最大,变形区域形状仍为椭圆形,竖直方向上的宽度为98.9 mm。此时数值模拟中的变形区域形状为圆角菱形,竖直方向上的宽度为101.9 mm,头盔内部鼓包高度尚未达到最大值。由于试验中很难保证子弹攻角为0°和弹着点精确位于头盔中心,而数值模拟中精确的控制了子弹的攻角与弹着点位置,因此试验和数值模拟中的变形区域形状有一定差异。
数值模拟和试验中鼓包沿直线L的Z方向位移轮廓曲线如图8所示,试验和数值模拟中不同时刻的轮廓曲线中心几乎保持不变,这表明头盔内表面鼓包轮廓在变化过程中最大位移点的位置基本不变。从图中可以看出,除了0.1 ms轮廓曲线的最大值差异较大,其他时刻轮廓位移曲线的最大值结果十分相近。0.1 ms的模拟结果与实验结果差别较大,这主要是由于数值模拟中为了防止单元畸变确保计算能够顺利进行,在子弹刚侵入头盔过程中,将与头盔接触区域单元删除造成的。随着头盔变形增大和子弹侵彻过程逐渐停止,单元基本不发生删除,因而与试验结果会更加吻合。试验与模拟结果在边界都出现了负位移,这是由于头盔内部为曲面,在鼓包变形过程中其边缘挤压未变形区域而形成的。在0.2 ms、0.4 ms和1.1 ms时,数值模拟结果和试验结果的BFD高度相对误差分别为10.5%、4.3%和5.1%。数值模拟较好地再现了侵彻过程中头盔内部鼓包形态随时间的变化过程。
3. 分析与讨论
3.1 PASGT头盔盔壳失效模式
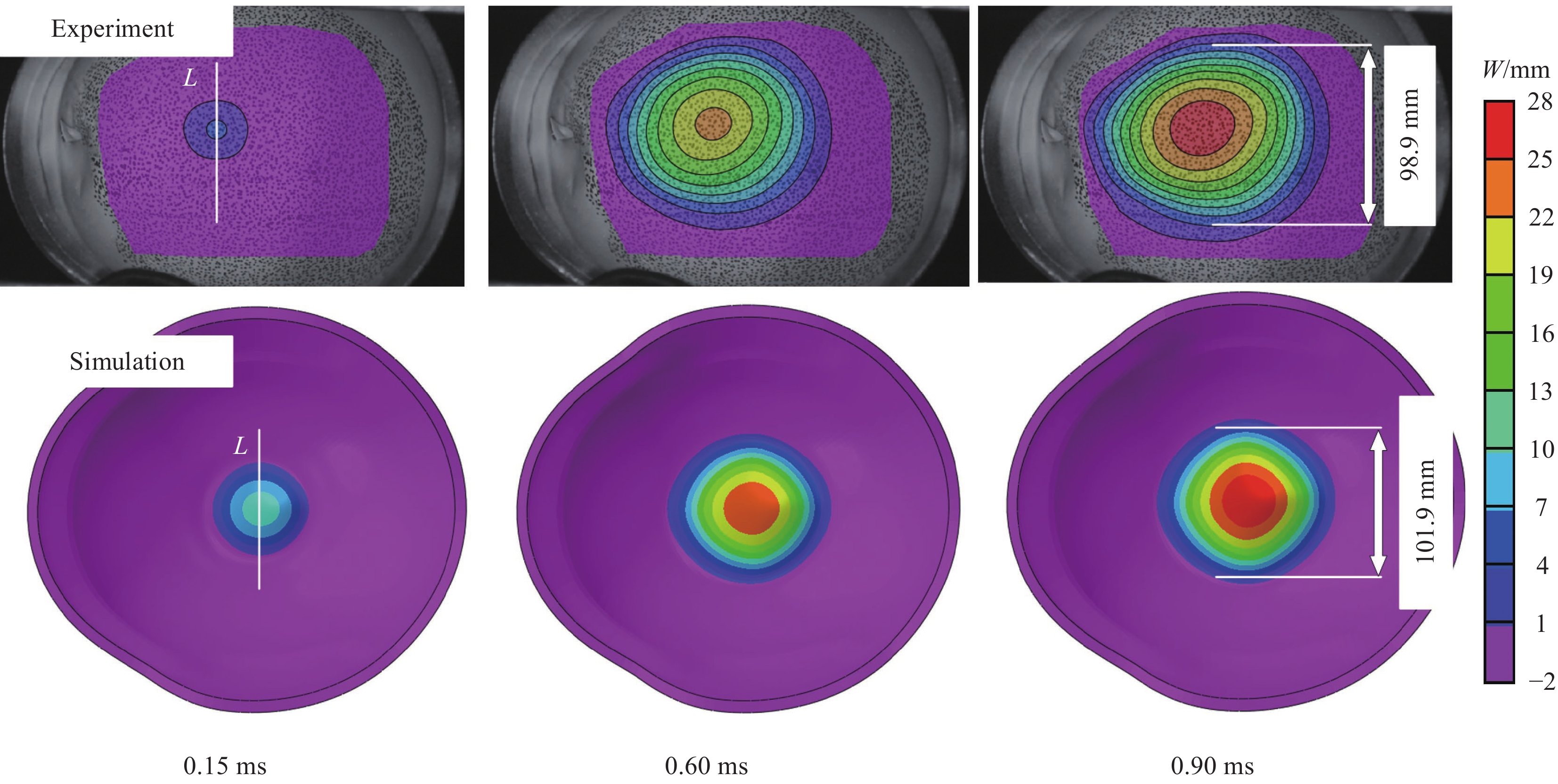
从试验和数值模拟中防弹头盔盔壳外表面破损情况可知(图9),在子弹冲击防弹头盔之后,防弹头盔的外表面无大面积的破坏,破坏区域直径与子弹直径相当。从防弹头盔的外表面破坏情况来看,防弹头盔外层纤维层主要是剪切冲塞破坏,说明在侵彻过程中防弹头盔受到了较大的剪切力作用。
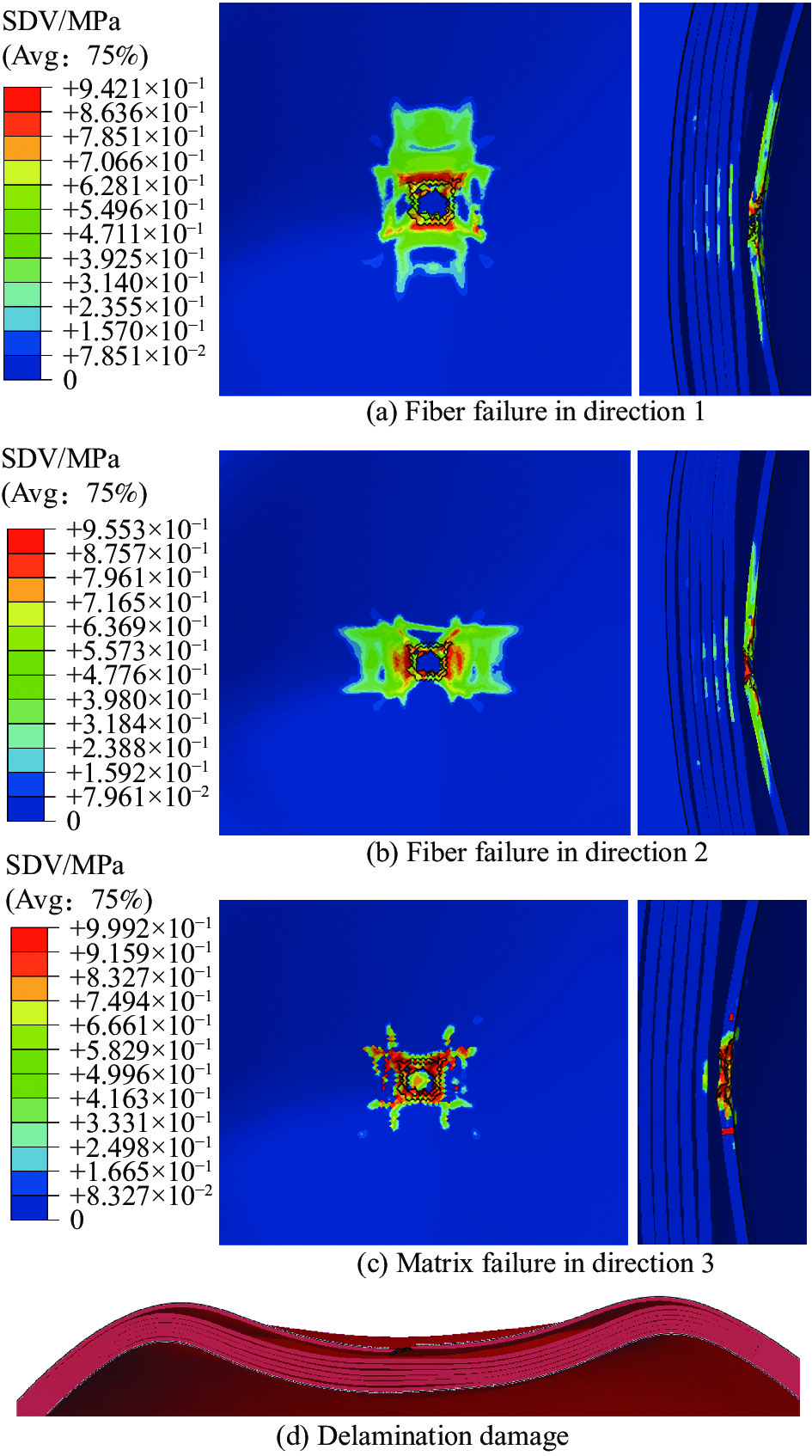
图10为子弹侵彻防弹头盔后盔壳损伤情况,状态变量越大表明相应模式的损伤程度越严重,当纤维拉伸损伤状态变量达到1时,则相应的单元会被删除。可以看出,头盔在被子弹侵彻的区域附近发生了明显的损伤,损伤模式有经纱和纬纱的纤维拉伸损伤以及基体的压缩损伤,还有较大范围的分层损伤,损伤模式与文献[1-2]中的结果相似,这表明数值模拟较好地模拟了子弹侵彻防弹头盔时头盔的损伤情况。经纱的纤维拉伸损伤(1方向)在子弹直接接触的地方损伤严重,有部分单元被删除,损伤状态变量沿着1方向逐渐减小,沿着头盔厚度方向有一定程度的损伤,随着厚度增加,发生损伤的区域逐渐减小,损伤状态变量也越来越小。纬纱的纤维拉伸损伤(2方向)与经纱的纤维拉伸损伤相似,区别在于损伤状态变量沿着纬纱的纤维方向发生变化。基体压缩损伤主要存在与子弹直接接触的区域,这些区域在子弹侵彻的过程中受到了严重的压力,而分层损伤则非常明显,损伤区域也较大,普遍存在与头盔发生较大变形的区域。
3.2 PASGT头盔盔壳等效应力
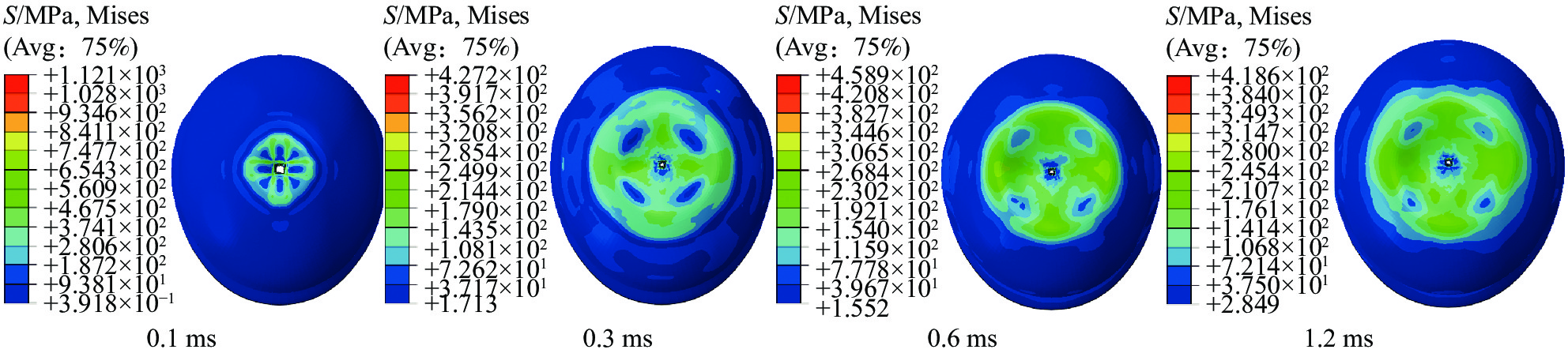
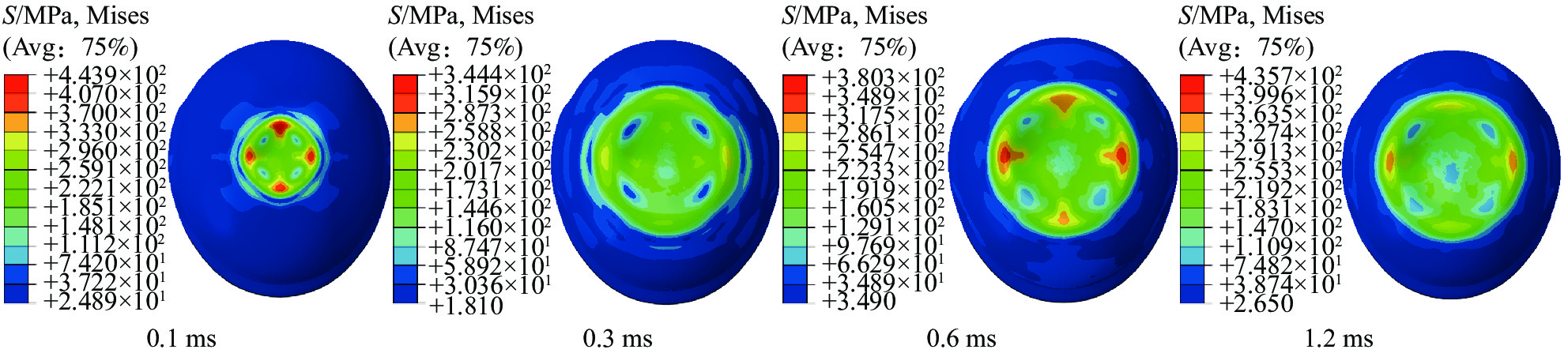
本文选取不同时刻的头盔等效应力进行分析(图11~图13)。头盔表面层在0.1 ms时已经被子弹穿透,此时应力云图呈“十字形”和菱形,最大应力为1121 MPa,之后应力逐渐向四周传播,传播范围较大,应力云图逐渐由菱形演化为圆形,最大应力也明显减小,1.2 ms时最大应力仅为418.6 MPa,但是整个过程中最大应力区域主要集中在与子弹直接接触的区域。头盔中间层在0.1 ms时应力云图呈菱形,最大应力为533.8 MPa,之后应力逐渐向四周传播,应力云图也演化为圆形,1.2 ms时最大应力为378 MPa。与表面层不同,头盔中间层在整个变化过程中最大应力区域主要位于头盔鼓包的边界区域。头盔内表面层与中间层应力云图变化规律较为相似,整个变化过程中最大应力区域也主要位于头盔鼓包的边界区域。在0.1 ms时应力云图呈菱形,最大应力为443.9 MPa,之后应力逐渐向四周传播,应力云图也演化为圆形。1.2 ms时最大应力为435.7 MPa。
总的来说,外表面层在侵彻开始时,由于子弹直接接触,应力较大,最大应力位置位于弹着点附近,而子弹穿透表面层后应力逐渐减小,外表面层变形没有头盔内部变形严重,因此鼓包边界附近的应力较小。中间层和内表面层的变形较大,并且伴随着分层破坏,因此最大应力位置一直位于鼓包变形的边界区域。
3.3 子弹入射角对杀伤效应的影响
在实际战场中,士兵的防弹头盔可能受到不同入射方向子弹的冲击,为了研究子弹不同入射角对防弹头盔毁伤效应的影响,本文使用9 mm铅芯弹以343 m/s的速度分别对头盔顶部进行入射角为30°、45°和60°的斜侵彻数值模拟,仿真结果如图14和图15所示。仿真获取的子弹侵彻过程表明,在上述三种入射角时,子弹均发生了跳弹,反跳后的速度分别为72.9 m/s、165.5 m/s和240.1 m/s。
不同入射角下防弹头盔BFD曲线如图14所示。与垂直侵彻相比,斜侵彻的防弹头盔背面鼓包最大高度以及到达最大高度的时间显著减小,且随着入射角度的增大,鼓包高度在逐渐减小。入射角度为30°时,鼓包高度在0.94 ms达到最大值24.1 mm;入射角度为45°时,鼓包高度在0.82 ms达到最大值20.2 mm;入射角度为60°时,鼓包高度在0.76 ms达到最大值14.9 mm。这是由于斜侵彻时,子弹大多在接触到防弹头盔后一段时间内发生不同程度的跳弹现象,子弹与防弹头盔相互作用时间较短,且子弹的动能没有完全传递到防弹头盔上,导致防弹头盔的鼓包高度明显减小。
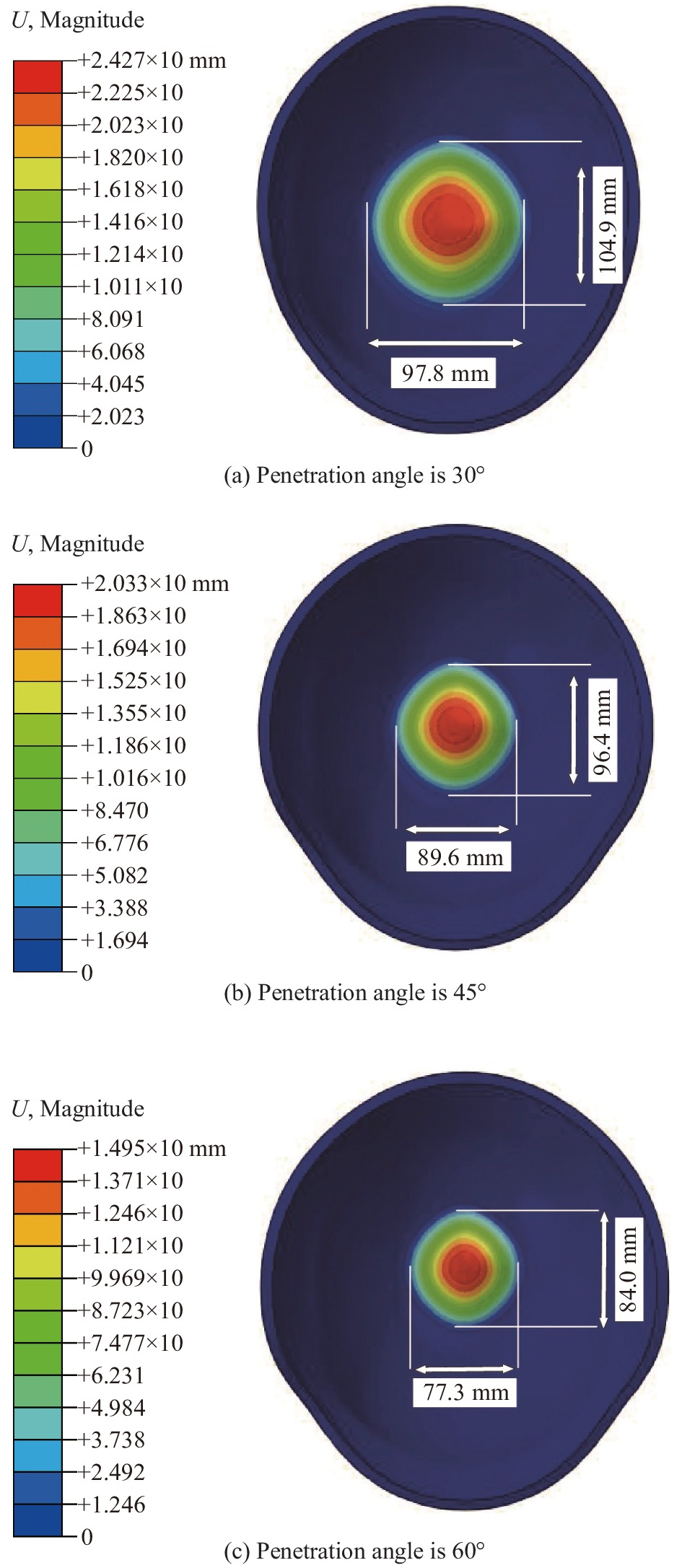
子弹不同入射角下防弹头盔背部最大鼓包轮廓如图15所示。子弹不同入射角度造成防弹头盔鼓包轮廓范围差异较大,当入射角为30°时,鼓包最大轮廓长为104.9 mm,宽为97.8 mm,鼓包轮廓呈现出规则的菱形;当入射角为45°时,鼓包最大轮廓长为96.4 mm,宽为89.6 mm,鼓包轮廓由菱形向椭圆形演化;当入射角为60°时,鼓包最大轮廓长为84.0 mm,宽为77.3 mm,鼓包轮廓演化为椭圆形。表明随着子弹入射角的增大,防弹头盔背部鼓包轮廓范围逐渐减小。
本文采用钝性准则(Blunt criterion,BC)[28]对杀伤效应进行评估:
{V_{{\rm{BC}}}} = {\rm{ln}}\left( {\frac{E}{{{W^{1/3}}TD}}} \right) (17) D = 2\sqrt {A/{\rm{{\text{π}} }}} (18) 式中:E为冲击动能(J),本文为头盔变形区域的能量;W是头部有效质量(kg);T为颅骨厚度(cm);D为撞击物有效直径(cm),本文将颅骨厚度假设为6.8 mm[29]。
E = \left. {\frac{1}{2}\rho (t){S_{\rm{A}}}(t)v{{(t)}^2}} \right|_{{x_{\rm{M}}}}^{{x_{\rm{S}}}} (19) 式中:
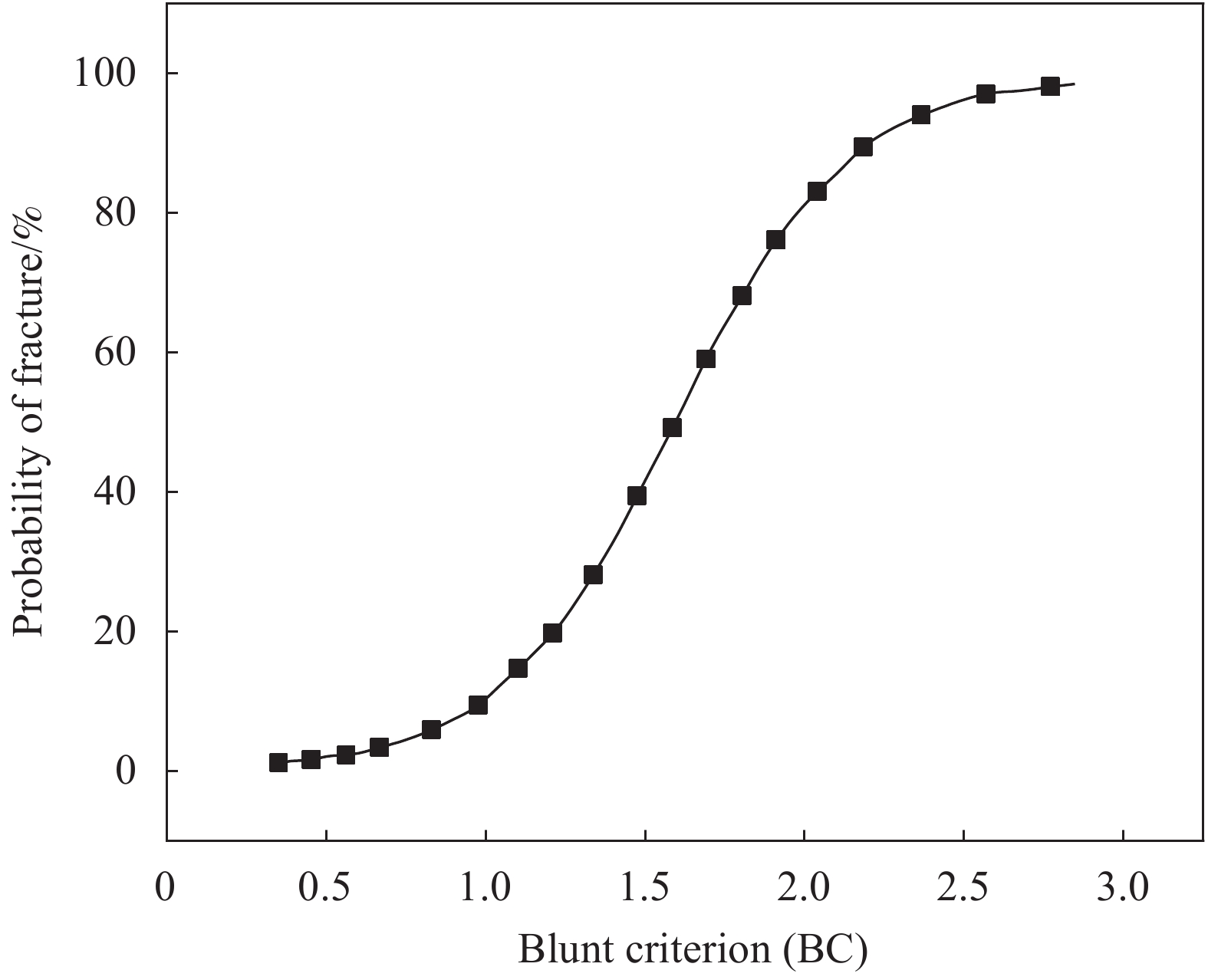
v 为变形区域的平均速度;\rho (t) 为头盔被穿透后剩余未被穿透部分的面密度;{x_{\rm{S}}} 为安全距离;{x_{\rm{M}}} 最大鼓包高度;{S_{\rm{A}}} 为有效面积。E的详细计算过程见参考文献[29],本文中头盔内表面距离颅骨的安全距离假设为12.7 mm[29]。Raymond团队[30]从人体跌落实验中建立了头部损伤与BC之间的关系,如图16所示。
通过BC准则的计算公式以及基于BC准则的颅骨骨折概率函数,对子弹不同入射角度的钝击效应进行评估,如表4所示。结果表明,子弹不同入射角度造成的杀伤效应有显著差异。子弹0°入射造成的颅骨骨折概率为23.4%,而60°入射造成的颅骨骨折概率为0%。
表 4 PASGT防弹头盔钝击评估结果Table 4. Blunt impact assessment results of PASGT helmetAngle of
incidence/(°)VBC Probability of
fracture/%0 1.27 23.4 30 0.93 8.2 45 0.49 2.0 60 –0.93 0 Notes: VBC—Blunt criterion parameter used to predict injury risk. 4. 结 论
(1)基于Abaqus的用户材料子程序VUMAT编写了包含经纱、纬纱拉伸失效和基体压缩失效的渐进损伤材料模型。进行了9 mm手枪弹侵彻PASGT防弹头盔的数值模拟,从头盔内表面变形(Back face deformation,BFD)曲线和鼓包形态变化过程两个方面与弹道试验结果进行对比,验证了该材料模型和数值模拟的准确性。
(2)通过对数值模拟中防弹头盔损伤模式分析以及试验结果观察得出:子弹侵彻防弹头盔的过程中,防弹头盔的损伤模式包括经纱、纬纱的拉伸损伤、基体的压缩损伤和分层损伤。经纱、纬纱和基体的损伤主要集中于弹着点附近,与弹着点距离越远则损伤程度也逐渐减轻。分层损伤区域较大,普遍存在于头盔发生鼓包变形的区域,说明防弹头盔等效编织层的层间力学性能对头盔冲击过程中产生的鼓包影响较为明显。
(3)从防弹头盔不同厚度位置和不同时刻的等效应力分析中发现:在子弹直接接触的防弹头盔外表面层里,最大应力位置集中在弹着点附近,较大的应力集中也导致防弹头盔发生了损伤。在子弹未穿透的中间层和内表面层中,最大应力位置在鼓包的边界区域,并随着鼓包的变化而逐渐向外转移。在整个过程中防弹头盔不同位置应力云图前期都为比较规则的菱形,随着时间的推移应力逐渐向四周传播,应力云图转化为圆形。
(4)从不同入射角度对防弹头盔毁伤效应的研究中发现:随着入射角度的增大,防弹头盔背部鼓包最大高度逐渐减小,鼓包轮廓也逐渐减小,鼓包轮廓形状逐渐由菱形向椭圆形演化。子弹入射角度对防弹头盔造成的毁伤效应影响较大,因此在防弹头盔的设计过程中,可以优化防弹头盔的外表面弧度,尽可能保证子弹在撞击到防弹头盔的瞬间呈斜侵彻状态,有利于减小对头盔佩戴者造成的伤害。
-
ρ/
(g·cm−3)E1/
GPaE2/
GPaE3/
GPa{v_{12}} {v_{13}} {v_{23}} G12/
MPaG13/
MPaG23/
MPaXt/
MPaXc/
MPaYt/
MPaYc/
MPaZt/
MPaZc/
MPaS12/
MPaS13/
MPaS23/
MPa1.23 22 22 9 0.25 0.33 0.33 770 2715 2715 800 80 800 80 1200 1200 77 898 898 Notes:ρ—Density; {E_1}, {E_2}, {E_3}—The elastic modulus in X, Y, and Z directions; {v_{12}}, {v_{13}}, {v_{23}}—Poisson's ratios; {G_{12}}, {G_{23}}, {G_{13}}—Shear modulus; Xc, Xt, Yc, Yt, Zc, Zt—Compressive and tensile strength in X, Y, Z directions; S12, S23, S13—Shear strength. ρ/(g·cm−3) {K_{{\rm{nn}}}}/MPa {K_{{\rm{ss}}}}/MPa {K_{{\rm{tt}}}}/MPa t_{\rm{n}}^0/MPa t_{\rm{s}}^0/MPa t_{\rm{t}}^0/MPa G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) G_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) G_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{C}}/(J·mm−2) 2 4830 4830 4830 34.5 9 9 0.24 0.47 0.47 Notes: ρ—Density; {K_{{\rm{nn}}}}, {K_{{\rm{ss}}}}, {K_{{\rm{tt}}}}—Elastic modulus; t_{\rm{n}}^0, t_{\rm{s}}^0, t_{\rm{t}}^0—Normal and tangential strength; G_{\rm{n}}^{\rm{C}}, G_{\rm{s}}^{\rm{C}}, G_{\rm{t}}^{\rm{C}}—Critical energy release rates in mode I, mode II and mode III. ρ/(g·cm−3) G/GPa A/MPa B/MPa N C M Tm Tr D1 D2-D5 Lead core 11.34 7 14 18 0.685 0.035 1.68 600 294.0 1.0 0 Copper jacket 8.45 46 90 292 0.01 0.025 1.09 1356 300.15 0.8 0 Notes:G—Shear modulus; A—Initial yield stress; B—Hardening constant; N—Hardening exponent; C—Strain rate constant; M—Thermal softening exponent; Tm—Melting temperature; Tr—Room temperature; D1-D5—Damage constants. 表 4 PASGT防弹头盔钝击评估结果
Table 4 Blunt impact assessment results of PASGT helmet
Angle of
incidence/(°)VBC Probability of
fracture/%0 1.27 23.4 30 0.93 8.2 45 0.49 2.0 60 –0.93 0 Notes: VBC—Blunt criterion parameter used to predict injury risk. -
[1] 杨莹雪, 张秀芹, 杨丹, 等. 纤维增强复合材料防弹头盔壳体的研究进展[J]. 北京服装学院学报(自然科学版), 2019, 39(3):93-100. YANG Yingxue, ZHANG Xiuqing, YANG Dan, et al. Research progress of fiber reinforced composite bulletproof helmet shell[J]. Journal of Beijing Institute of Fashion Technology (Natural Sicence Edition),2019,39(3):93-100(in Chinese).
[2] 高晓清, 黄献聪, 周宏, 等. 防弹头盔防非贯穿性损伤性能测试技术研究[J]. 警察技术, 2013(4):66-69. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9875.2013.04.019 GAO Xiaoqing, HUANG Xiancong, ZHOU Hong, et al. Research on test technology of non penetrating damage resistance of bulletproof helmet[J]. Police Technology,2013(4):66-69(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9875.2013.04.019
[3] RODRÍGUEZ-MILLÁN M, ITO T, LOYA J A, et al. Development of numerical model for ballistic resistance evaluation of combat helmet and experimental validation[J]. Materials & Design,2016,110:391-403.
[4] 王昕昇. 头盔钝击过程中能量耗散规律研究[D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2018. WANG Xinsheng. Study on energy dissipation law of helmet blunt impact[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[5] 黄艺峰. 手枪弹击中防弹头盔致颅脑损伤特点及机理的实验研究[D].重庆: 第三军医大学, 2012. HUANG Yifeng. Experimental study on characteristics and mechanism of craniocerebral injury caused by pistol bullet hitting bulletproof helmet[D]. Chongqing: Third Military Medical University, 2012(in Chinese).
[6] 蔡志华, 包正, 王威, 等. 枪弹冲击防弹头盔致头部非贯穿性损伤的数值模拟研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2017, 38(6):1097-1105. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.06.008 CAI Zhihua, BAO Zheng, WANG Wei, et al. Study numerical simulation of non penetrating head damage caused by bullet impact on bullet helmet[J]. Acta Armamentarii,2017,38(6):1097-1105(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2017.06.008
[7] 李泽民. 子弹冲击防弹头盔动力学响应及防护性能仿真研究[D].湘潭: 湖南科技大学, 2016. LI Zeming. Simulation study on dynamic response and protective performance of bullet impact bulletproof helmet[D]. Xiangtan: Hunan University of Science and Technology, 2016 (in Chinese).
[8] 王威, 毛征宇, 李桂兵, 等. 枪弹冲击下新型防弹头盔质量对颈椎损伤影响[J]. 医用生物力学, 2019, 34(4):339-345. WANG Wei, MAO Zhengyu, LI Guibing, et al. Effect of new bullet proof helmet mass on cervical spine injury under bullet impact[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics,2019,34(4):339-345(in Chinese).
[9] LI Y Q, LI X G, GAO X L. Modeling of advanced combat helmet under ballistic impact[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,2015,82(11):111004.
[10] JAZI M S, REZAEI A, KARAMI G, et al. A computational study of influence of helmet padding materials on the human brain under ballistic impacts[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering,2014,17(12):1368-1382.
[11] LEE H P, GONG S W. Finite element analysis for the evaluation of protective functions of helmets against ballistic impact[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering,2010,13(5):537-550.
[12] THAM C Y, TAN V B C, LEE H P. Ballistic impact of a KEVLAR ® helmet: Experiment and simulations[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2007,35(5):304-318.
[13] CARLOS M G, IGNACIO R, JACOBO A M, et al. Evaluation of combat helmet behavior under blunt impact[J]. Applied Sciences,2020,10(23):8470.
[14] CAI Z, HUANG X Y, XIA Y, et al. Study on behind helmet blunt trauma caused by high-speed bullet[J]. Applied Bionics and Biomechanics,2020(7):1-12.
[15] CAÇOILO A, MOURÃO R, TEIXEIRA D F, et al. Modelling ballistic impact on military helmets: The relevance of projectile plasticity[J]. Defence Technology,2020,17(5):1699-1711.
[16] LI X G, GAO X L, KLEIVEN S. Behind helmet blunt trauma induced by ballistic impact: A computational model[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2016,91:56-67.
[17] PALOMAR M, LOZANO-MÍNGUEZ E, RODRÍGUEZ-MILLÁ M, et al. Relevant factors in the design of composite ballistic helmets[J]. Composite Structures,2018,201:49-61.
[18] TAN L B, TSE K M, LEE H P, et al. Performance of an advanced combat helmet with different interior cushioning systems in ballistic impact: Experiments and finite element simulations[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2012,50:99-112.
[19] RUBIO I, RODRÍGUEZ-MILLÁN M, MARCO M, et al. Ballistic performance of aramid composite combat helmet for protection against small projectiles[J]. Composite Structures,2019,226:111153.
[20] 王涛. 基于多尺度方法的平纹机织复合材料低速冲击损伤研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2020. WANG Tao. Research on low velocity impact damage of plane woven composites based on multi-scale method[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2020(in Chinese).
[21] 罗小豪, 温垚珂, 闫文敏, 等. 基于ABAQUS二次开发的球形破片侵彻UHMWPE软质防弹衣数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10): 3373-3386. LUO Xiaohao, WEN Yaoke, YAN Wenmin, et al. Numerical simulation of spherical fragment penetrating UHMWPE soft body armor based on ABAQUS[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(10): 3373-3386(in Chinese).
[22] 程之遥, 张健. 基于内聚力模型的层合板屈曲行为分析[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2020, 36(04): 581-586. CHENG Zhiyao, ZHANG Jian. Buckling behavior analysis of laminated plates based on cohesive force model[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 2020, 36(04): 581-586(in Chinese).
[23] CAMANHO P P, DAVILA C G, DE MOURA M F. Numerical simulation of mixed-mode progressive delamination in composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2003, 37(16): 1415-1438.
[24] JOHNSON G R, COOK W H. Constitutive model and data for metals subjected to large strains, high strain rates and high temperatures[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics,1983,21:541−548.
[25] 舒畅, 程礼, 许煜. Johnson-Cook本构模型参数估计研究[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(5):1073-1083. SHU Chang, CHENG Li, XU Yu. Parameter estimation of Johnson cook constitutive model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2020,30(5):1073-1083(in Chinese).
[26] 孙非, 马力, 朱一辉, 等. 手枪弹对带UHMWPE软防护明胶靶标冲击效应的数值分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(13):20-26. SUN Fei, MA Li, ZHU Yihui, et al. Numerical analysis of impact effect of pistol projectile on gelatin target with UHMWPE soft protection[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2018,37(13):20-26(in Chinese).
[27] 崔广宇. 枪弹对带防弹头盔的人体模拟靶标钝击效应研究[D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2019. CUI Guangyu. Blunt impact effect of bullet on human simulated target with bulletproof helmet[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[28] LARRY M S, DAVID C V, HOWARD R C. Analysis of injury criteria to assess chest and abdominal injury risks in blunt and ballistic impacts[J]. Journal of Trauma,2004,56(3):651-663. DOI: 10.1097/01.TA.0000074108.36517.D4
[29] HISLEY D M, GURGANUS C, DRYSDALE A W. Experimental methodology using digital image correlation to assess ballistic helmet blunt trauma[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,2011,78(5):051022.
[30] RAYMOND D, EE C V, CRAWFORD G, et al. Tolerance of the skull to blunt ballistic temporo-parietal impact[J]. Biomech,2009,42(15):2479-2485. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2009.07.018
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 孔鲁鹏,曾浩,杨波,张哲绎,胡宁,赵丽滨. 防弹头盔选材及结构设计对其防护性能的影响. 河北工业大学学报. 2024(02): 11-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘东旭,温垚珂,董方栋,覃彬,夏海龙,罗小豪. SiC/UHMWPE防弹插板在步枪弹侵彻下的动态响应研究. 振动与冲击. 2023(12): 264-273 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王博,温垚珂,徐诚,刘东旭. 钨合金破片侵彻防弹插板和明胶复合机理研究. 兵器装备工程学报. 2023(11): 38-46+96 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 聂伟晓,温垚珂,董方栋,覃彬,罗小豪,童梁成. 破片侵彻戴防弹头盔头部靶标钝击效应数值模拟. 兵工学报. 2022(09): 2075-2085 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 沈周宇,温垚珂,闫文敏,董方栋,张俊斌,李颖. 手枪弹撞击戴防弹头盔人体头颈部靶标的钝击效应. 兵工学报. 2022(09): 2101-2112 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)
-





 下载:
下载: