Research progress on application of superhydrophobic materials in anti-icing and de-icing technology
-
摘要: 结冰结霜给人们的生活带来诸多不便,大量结冰积冰会影响飞机的飞行安全、推迟火箭发射任务、引起电力网络故障、造成交通运输障碍,甚至引发重大的经济问题和人身安全问题。传统的防/除冰技术耗能大、效率低、易对环境造成污染。超疏水技术利用材料的本征属性,延缓结冰,显著降低冰与基底表面的黏附力,是极具发展前景的防/除冰技术。本文首先对固体表面润湿现象及结冰机制进行了介绍,指出超疏水防/除冰材料面临着低温高湿环境下憎水性丧失,耐久性较差,面向工程的大面积制备方法制约等问题。随后,对低温高湿环境用超疏水防/除冰材料、耐久性、制备方法、多功能复合超疏水防/除冰材料等方面的研究进展进行了综述和分析。最后,对超疏水防/除冰材料在实际工程中的应用进行归纳和总结。在此基础上,展望了超疏水防/除冰材料的研究前景和发展趋势。Abstract: Icing and frosting bring many disadvantages to people's life. Ice accumulation will affect the flight safety of aircraft, delay the rocket launch mission, deform transmission lines and power networks, cause transportation obstacles, and even produce major economic problems and personal safety problems. Conventional anti-icing and de-icing methods are often costly, inefficient, or environmentally harmful. Superhydrophobic technology, which uses the intrinsic properties of materials to delay icing and significantly reduces the ice adhesion between ice and substrate, is a promising anti-icing and deicing technology. In this paper, firstly, the wetting phenomenon of solid surface and ice nucleation mechanism are introduced. It should be indicated that superhydrophobic surfaces face many problems such as the its wettability can be changed with decreasing the temperature and increasing the relative humidity, poor stability and mechanical robustness, and lack of facile and large-scale fabrication methods. Secondly, the research progress of superhydrophobic anti-icing and de-icing materials, stable and mechanically robust superhydrophobic surfaces, fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces and multifunctional anti-icing and de-icing superhydrophobic materials are reviewed and analyzed. Finally, many applications of anti-icing and de-icing superhydrophobic materials in practical engineering are concluded and summarized. On this basis, the development trends and prospects of anti-icing and de-icing superhydrophobic materials are discussed.
-
图 3 刻蚀后的铝基底((a), (b))、苯基三乙氧基硅烷(PTES)修饰 ((c), (d))、十六酸(PA)修饰 ((e), (f)) 及聚二甲基硅氧烷(TTPS)修饰 ((g), (h)) 的改性基底表面形貌和三维表面轮廓[17]
Figure 3. SEM images and three-dimensional surface profiles of theetched sample Al ((a), (b)), and the phenyltriethoxysilane (PTES) ((c), (d)), palmitic acid (PA) ((e), (f)), as well as polydimethylsiloxane (TTPS) ((g), (h)) modified samples[17]
Ra—Surface roughness of the sample
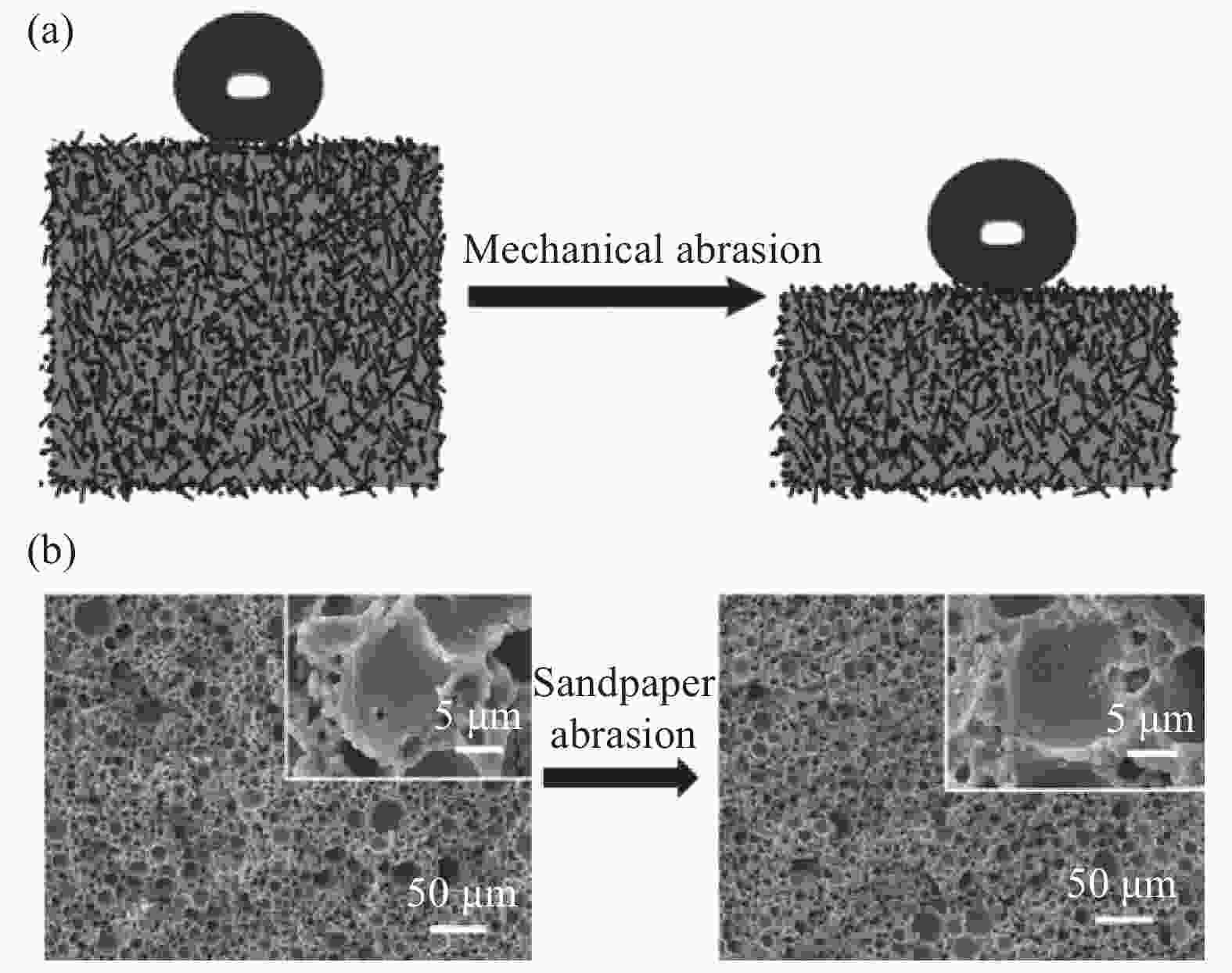
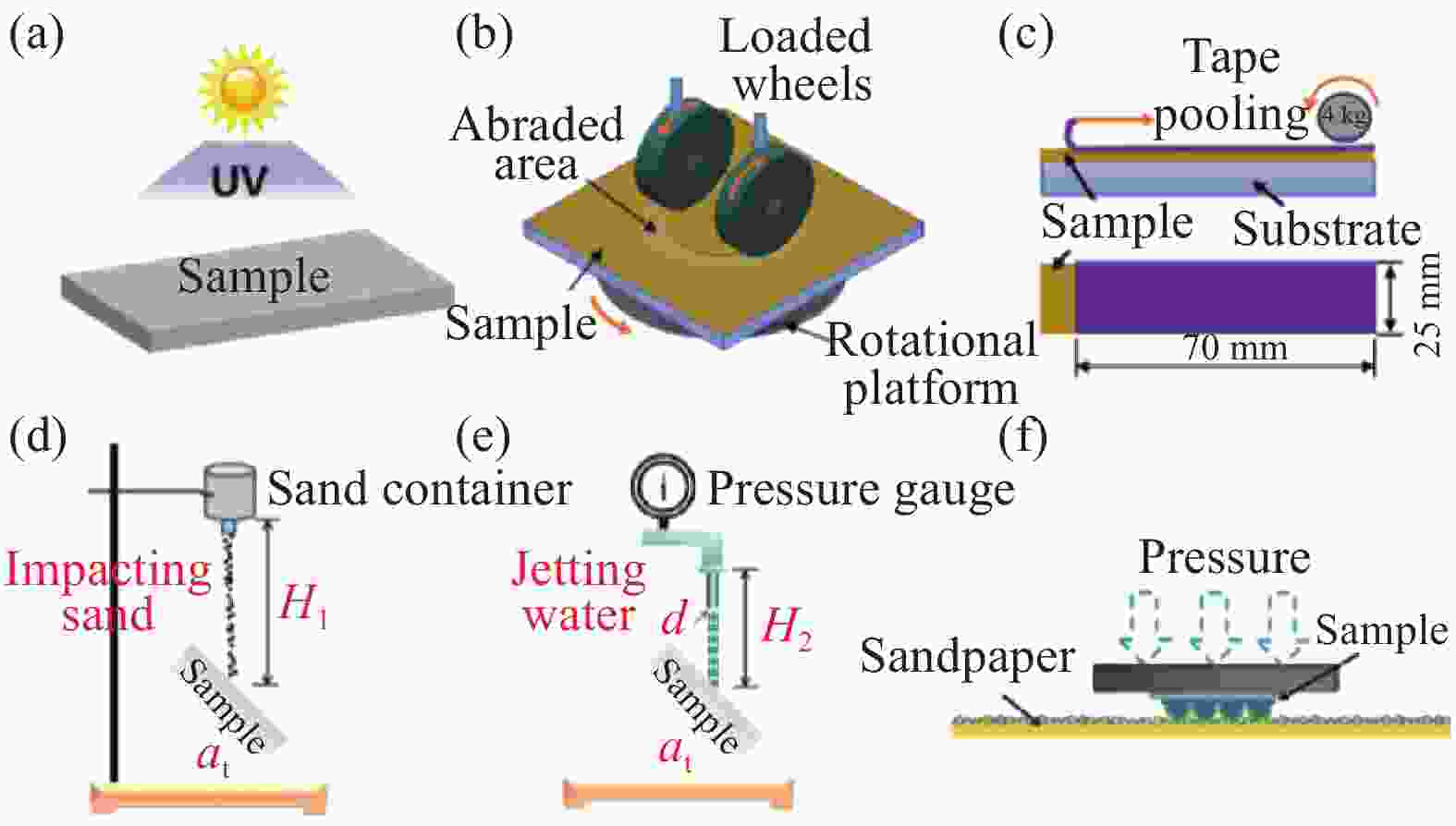
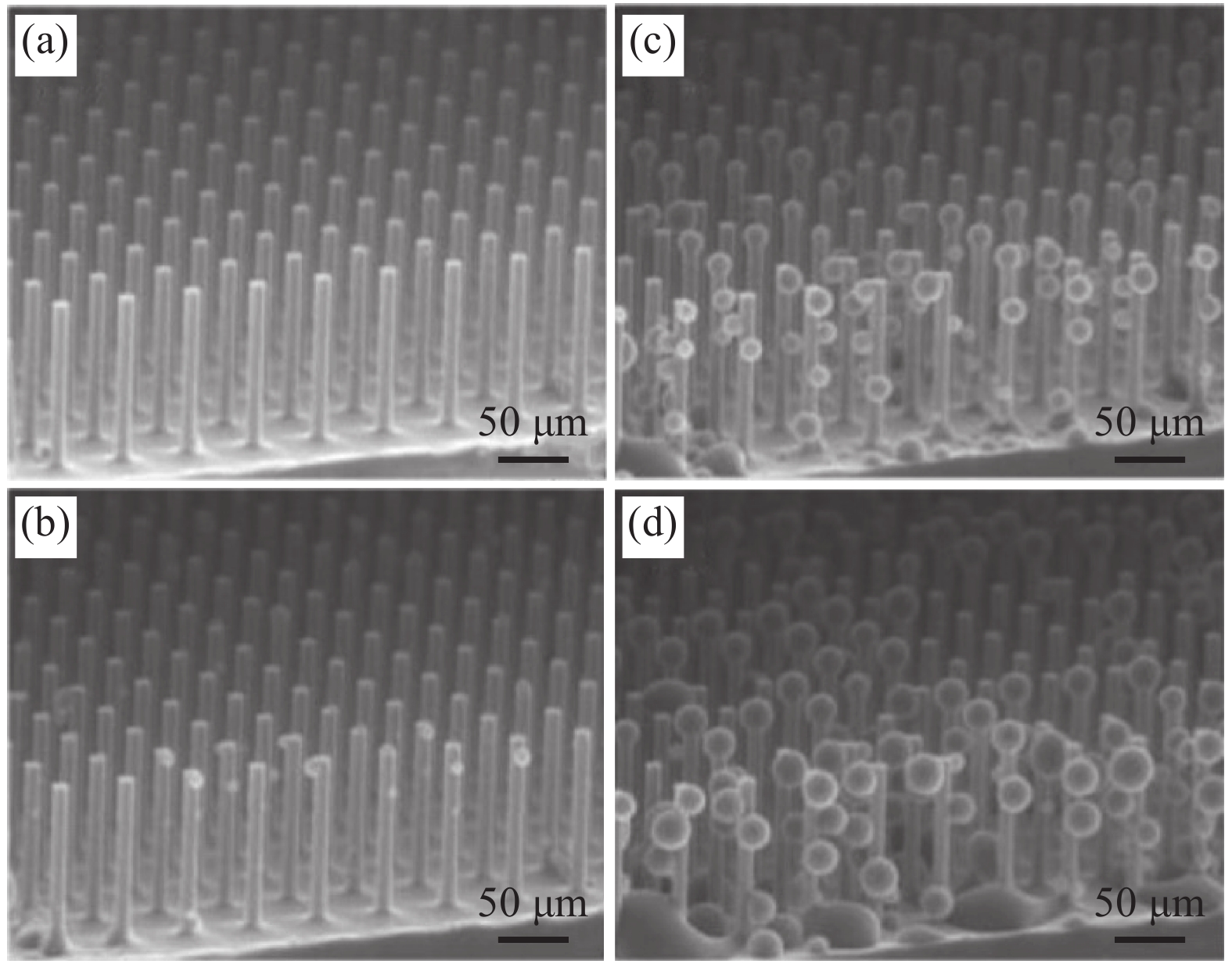
图 7 部分耐久性测试示意图((a) 紫外线辐射;(b)泰伯尔磨损测试;(c)胶带粘结测试;(d)砂砾冲击测试;(e)喷水/滴水测试;(f)砂纸磨损测试[20, 28, 33-34])
Figure 7. Schematic of parts of quantify the durability((a) UV irradiation; (b) Taber abrasion test; (c) Tape adhesion test; (d) Sand impact test; (e) Water jet/dripping test; (f) Sandpaper abrasion test[20, 28, 33-34])
H1—Height of impacting sand; at—Inclination angle of the sample; H2—Height of jetting water; d—Diameter of jetting water
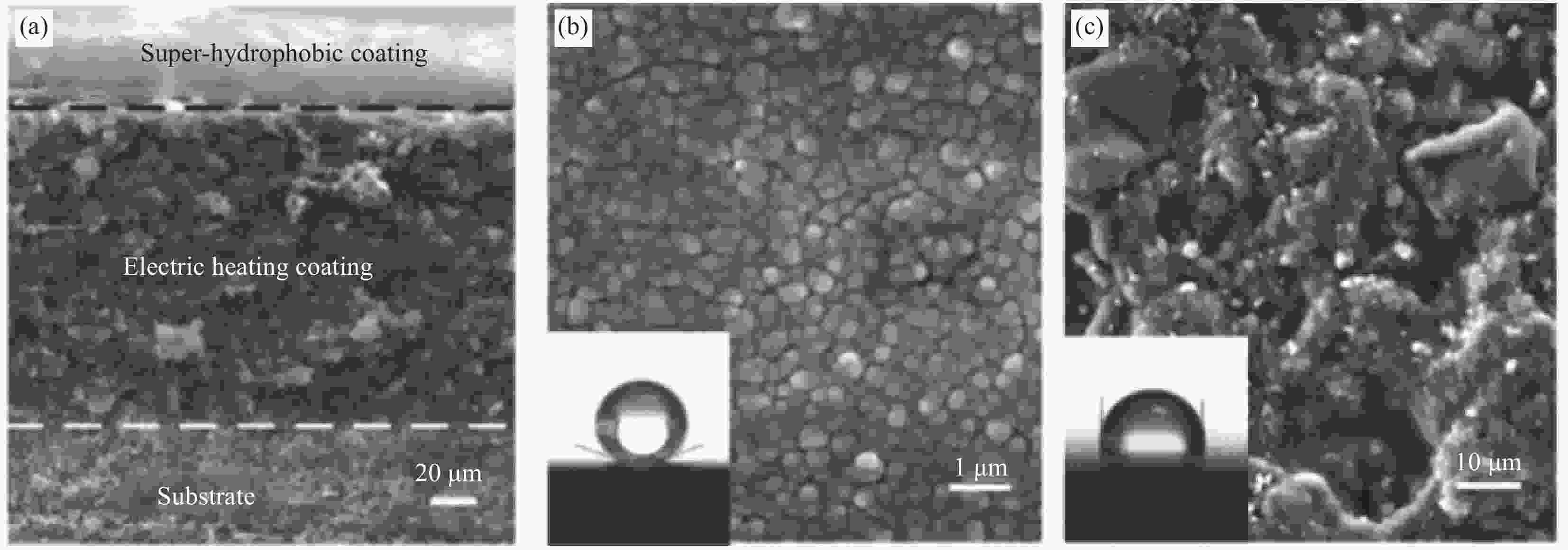
图 14 (a) 超疏水电加热涂层红外热成像;(b1) 除冰实验结果:(b2) 无加热层、(b3) 有加热层[62]
Figure 14. (a) Thermal infrared image of the blade coated with superhydrophobic electrothermal coating; (b1) Digital images after anti-icing test in low icing conditions of the overall rotating blades : (b2) No heating coating, (b3) Blade with superhydrophobic electrothermal coating[62]
表 1 耐久性测试方法总结
Table 1. A summary of common durability characterization techniques
Technique Adopted operation condition Standard Reference UV irradiation Wavelength: Typically 320 nm to 400 nm in the UVA range
(e.g., 365 nm, 340 nm and 325 nm), but 254 nm (UVC) also used
Intensity: Several mW·cm−2 to 100 mW·cm−2
Irradiation time: Several hoursASTM D4329[39] [19,22,24,29-30] Plasma Plasma ype: O2 plasma
Time: Several seconds (e.g, 5 s, 15 s)— [20-21] Tape adhesion test Tapes: Scotch 810 Magic Tape, Scotch 600 tape,VHB 4910 tape
Applied pressure: typical pressure 10 kPa (up to 130 kPa)ASTM D3359[40] [20,23-24,28,31] Taber abrasion test Using a Taber abrasion machine
Applied loads: 150 g, 200 g, 250 g
Speed: Typically 60 r/minASTM D4060[41] [29,34] Sandpaper abrasion test Sandpaper grade: Typically from 80 to 800 grit
Applied pressure: Typically 15 kPa or less (up to 20 kPa)— [20,22,26-28,30-34] Sand impacting Sand particle size: Typically 100 to 300 μm
Height: Typically 25 to 40 cm (up to 110 cm)
Amount: Typically 10 g to 100 g
Sample angle: 45 °— [24,28,37] Water jet/dripping test Droplet size: 22 μL or 100 μL per drop
Height: 30 cm to 50 cm— [24,34,37] Knife scratching test Scratching by hand with a knife — [20,23,25-26] Solution immersion test Aqueous solutions: Pure water, 3.5wt% or 5wt% NaCl
in water, pH 0 to 14, hot or cold— [23-28,32,34] Ice formation/ice removal By mechanical removal, or by melting — [26,36-37] Thermal/Freezing test Environment: air, liquid nitrogen
Temperature: from −196℃ to 350℃— [28,36] -
[1] 王晋, 纪双英, 益小苏, 等. 飞行器防/除冰技术研究进展[J]. 航空制造技术, 2015(S2):30-32.WANG Jin, JI Shuangying, YI Xiaosu, et al. Progress of the aircraft anti-icing/de-icing[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology,2015(S2):30-32(in Chinese). [2] 张薇, 刘长志, 范书群. 基于运载火箭使用环境的超疏水涂层防水防结冰应用研究[J]. 材料科学, 2020, 10(2):84-94. doi: 10.12677/MS.2020.102011ZHANG Wei, LIU Changzhi, FAN Shuqun. Application of super-hydrophobic coating on the waterproof and anti-icing functions based on the environment of space launch vehicles[J]. Material Sciences,2020,10(2):84-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.12677/MS.2020.102011 [3] 刘韬文, 蒙文川, 戴承伟, 等. 风力发电机防冻融冰综述[J]. 湖北电力, 2019, 43(1):10-13.LIU Taowen, MENG Wenchuan, DAI Chengwei, et al. An overview of wind turbine generator anti-freezing and deicing[J]. Hubei Electric Power,2019,43(1):10-13(in Chinese). [4] HUANG X, TEPYLO N, POMMIER-BUDINGER V, et al. A survey of icephobic coatings and their potential use in a hybrid coating/active ice protection system for aerospace applications[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences,2019,105:74-97. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2019.01.002 [5] LV J, SONG Y, JIANG L, et al. Bio-inspired strategies for anti-icing[J]. ACS Nano,2014,8(4):3152-3169. doi: 10.1021/nn406522n [6] YOUNG T. An essay on the cohesion of fluids[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London,1805(95):65-87. [7] WENZEL, ROBERT N. Resistance of soild surfaces to wetting by water[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1936,28(8):988-994. [8] CASSIE A, BAXTER S. Wettability of porous surface[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society,1944,40:546-550. doi: 10.1039/tf9444000546 [9] EBERLE P, TIWARI M K, MAITRA T, et al. Rational nanostructuring of surfaces for extraordinary icephobicity[J]. Nanoscale,2014,6(9):4874-4881. doi: 10.1039/C3NR06644D [10] JUNG S, DORRESTIJN M, RAPS D, et al. Are superhydrophobic surfaces best for icephobicity?[J]. Langmuir,2011,27(6):3059-3066. doi: 10.1021/la104762g [11] HEYDARI G, THORMANN E, JÄRN M, et al. Hydrophobic surfaces: Topography effects on wetting by supercooled water and freezing delay[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2013,117(42):21752-21762. doi: 10.1021/jp404396m [12] VARANASI K K, HSU M, BHATE N, et al. Spatial control in the heterogeneous nucleation of water[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2009,95(9):94101. doi: 10.1063/1.3200951 [13] VARANASI K K, DENG T, SMITH J D, et al. Frost formation and ice adhesion on superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2010,97(23):234102. doi: 10.1063/1.3524513 [14] MILJKOVIC N, ENRIGHT R, WANG E N. Effect of droplet morphology on growth dynamics and heat transfer during condensation on superhydrophobic nanostructured surfaces[J]. ACS Nano,2012,6(2):1776-1785. doi: 10.1021/nn205052a [15] ZHANG Q, HE M, CHEN J, et al. Anti-icing surfaces based on enhanced self-propelled jumping of condensed water microdroplets[J]. Chemical Communications,2013,49(40):4516. doi: 10.1039/c3cc40592c [16] WEN M, WANG L, ZHANG M, et al. Antifogging and icing-delay properties of composite micro- and nanostructured surfaces[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014,6(6):3963-3968. [17] WANG Y, LI M, LV T, et al. Influence of different chemical modifications on the icephobic properties of superhydrophobic surfaces in a condensate environment[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(9):4967-4975. doi: 10.1039/C4TA07077A [18] PAN R, ZHANG H, ZHONG M. Triple-scale superhydrophobic surface with excellent anti-icing and icephobic performance via ultrafast laser hybrid fabrication[J]. ACS Applied Materials& Interfaces,2021,13(1):1743-1753. [19] WANG N, XIONG D, DENG Y, et al. Mechanically robust superhydrophobic steel surface with anti-icing, uv-durability, and corrosion resistance properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(11):6260-6272. [20] LI Y, LI B, ZHAO X, et al. Totally waterborne, nonfluorinated, mechanically robust, and self-healing superhydrophobic coatings for actual anti-icing[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(45):39391-39399. [21] QIN L, CHEN N, ZHU X, et al. A superhydrophobic aerogel with robust self-healability[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6(10):4424-4431. doi: 10.1039/C8TA00323H [22] ZHANG X, GUO Y, CHEN H, et al. A novel damage-tolerant superhydrophobic and superoleophilic material[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(24):9002-9006. doi: 10.1039/C4TA00869C [23] DAVIS A, SURDO S, CAPUTO G, et al. Environmentally benign production of stretchable and robust superhydrophobic silicone monoliths[J]. ACS Applied Materials& Interfaces,2018,10(3):2907-2917. [24] WANG F, PI J, SONG F, et al. A superhydrophobic coating to create multi-functional materials with mechanical/chemical/physicalrobustness[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,381:122539. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122539 [25] ZHANG X, ZHU W, HE G, et al. Flexible and mechanically robust superhydrophobic silicone surfaces with stable Cassie–Baxter state[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(37):14180-14186. doi: 10.1039/C6TA06493K [26] LIU Y, FU K, LIU J, et al. Design and preparation of a multi-fluorination organic superhydrophobic coating with high mechanical robustness and icing delay ability[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,497:143663. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143663 [27] TIAN G, ZHANG M, YAN H, et al. Nonfluorinated, mechanically stable, and durable superhydrophobic 3D foam iron for high efficient oil/water continuous separation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,527:146861. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.146861 [28] WU B, LYU J, PENG C, et al. Inverse infusion processed hierarchical structure towards superhydrophobic coatings with ultrahigh mechanical robustness[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,387:124066. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124066 [29] WONG W S Y, STACHURSKI Z H, NISBET D R, et al. Ultra-durable and transparent self-cleaning surfaces by large-scale self-assembly of hierarchical interpenetrated polymer networks[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(21):13615-13623. [30] ZHI D, LU Y, SATHASIVAM S, et al. Large-scale fabrication of translucent and repairable superhydrophobic spray coatings with remarkable mechanical, chemical durability and UV resistance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(21):10622-10631. doi: 10.1039/C7TA02488F [31] BOBAN M, GOLOVIN K, TOBELMANN B, et al. Smooth, all-solid, low-hysteresis, omniphobic surfaces with enhanced mechanical durability[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(14):11406-11413. [32] CHEN W, ZHANG P, ZANG R, et al. Nacre-inspired mineralized films with high transparency and mechanically robust underwater superoleophobicity[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(11):1907413. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907413 [33] SOJOUDI H, WANG M, BOSCHER N D, et al. Durable and scalable icephobic surfaces: similarities and distinctions from superhydrophobic surfaces[J]. Soft Matter,2016,12:1938-1963. doi: 10.1039/C5SM02295A [34] PENG C, CHEN Z, TIWARI M K. All-organic superhydrophobic coatings with mechanochemical robustness and liquid impalement resistance[J]. Nature Materials,2018,17(4):355-360. doi: 10.1038/s41563-018-0044-2 [35] QING Y, SHI S, LV C, et al. Microskeleton-nanofiller composite with mechanical super-robust superhydrophobicity against abrasion and impact[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(39):1910665. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201910665 [36] JAMIL M I, ZHAN X, CHEN F, et al. Durable and scalable candle soot icephobic coating with nucleation and fracture mechanism[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(34):31532-31542. [37] WU X, ZHAO X, HO J W C, et al. Design and durability study of environmental-friendly room-temperature processable icephobic coatings[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,355:901-909. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.204 [38] KREDER M J, ALVARENGA J, KIM P, et al. Design of anti-icing surfaces: smooth, textured or slippery[J]. Nature Reviews Materials,2016,1(1):15003. [39] ASTM. Standard practice for fluorescent ultraviolet (UV) lamp apparatus exposure of plastics: ASTM D4329[S].West Conhohcken: ASTM, 2013. [40] ASTM. Standard test methods for rating adhesion by tape test: ASTM D3359[S]. West Conhohcken: ASTM, 2017. [41] ASTM. Standard test method for abrasion resistance of organic coatings by the taber abraser: ASTM D4060[S]. West Conhohcken: ASTM, 2014. [42] 赵美蓉, 周惠言, 康文倩, 等. 超疏水表面制备方法的比较[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2):361-379.ZHAO Meirong, ZHOU Huiyan, KANG Wenqian, et al. A comparison of methods for fabricating superhydrophobic surface[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(2):361-379(in Chinese). [43] 张磊, 王斐, 潘蕾. CF/PEEK复合材料表面构筑微纳米结构及其防冰性能的研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(17): 95-101.ZHANG Lei, WANG Fei, PAN Lei. Fabricating micro-nano structure on surface of CF/PEEK composite and study on its anti–icing property[J]. 2019, 62(17): 95-101(in Chinese). [44] 沈一洲, 陶杰, 朱春玲, 等.树脂基复合材料表面制备超疏水微结构防覆冰表面的方法: 中国, CN108044922B[P]. 2019-08-13.SHEN Yizhou, TAO Jie, ZHU Chunling, et al. Preparation of superhydrophobic microstructure anti icing surface on resin matrix composites: China, CN108044922B[P]. 2019-08-13 (in Chinese). [45] SHAO Y, ZHAO J, FAN Y, et al. Shape memory superhydrophobic surface with switchable transition between “Lotus Effect” to “Rose Petal Effect”[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,382:122989. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.122989 [46] WANG Y, XUE J, WANG Q, et al. Verification of icephobic/anti-icing properties of a superhydrophobic surface[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013,5(8):3370-3381. [47] EMELYANENKO A M, BOINOVICH L B, BEZDOMNIKOV A A, et al. Reinforced superhydrophobic coating on silicone rubber for longstanding anti-icing performance in severe conditions[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(28):24210-24219. [48] JIN M, SHEN Y, LUO X, et al. A combination structure of microblock and nanohair fabricated by chemical etching for excellent water repellency and icephobicity[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,455:883-890. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.043 [49] HOU W, SHEN Y, TAO J, et al. Anti-icing performance of the superhydrophobic surface with micro-cubic array structures fabricated by plasma etching[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2020,586:124180. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124180 [50] 尹园. 基于POSS和MOF纳米粒子的防冰表面设计及性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.YIN Yuan. Design and property research of anti-icing surfaces based on nanosized POSS and MOF particles[D]. Changchun: Jinlin University, 2018 (in Chinses). [51] SHEN Y, WU Y, TAO J, et al. Spraying fabrication of durable and transparent coatings for anti-icing application: Dynamic water repellency, icing delay, and ice adhesion[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,11(3):3590-3598. [52] ZHU T, CHENG Y, HUANG J, et al. A transparent superhydrophobic coating with mechanochemical robustness for anti-icing, photocatalysis and self-cleaning[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,399:125746. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125746 [53] WANG T, ZHENG Y, RAJI A O, et al. Passive anti-icing and active deicing films[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(22):14169-14173. [54] CHU Z, JIAO W, HUANG Y, et al. FDTS-modified SiO2/rGO Wrinkled films with a micro-nanoscale hierarchical structure and anti-icing/deicing properties under condensation condition[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces,2019,7(1):1901446. [55] MATSUBAYASHI T, TENJIMBAYASHI M, MANABE K, et al. Integrated anti-icing property of super-repellency and electrothermogenesis exhibited by PEDOT:PSS/cyanoacrylate composite nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(36):24212-24220. [56] WU L, WANG L, GUO Z, et al. Durable and multifunctional superhydrophobic coatings with excellent joule heating and electromagnetic interference shielding performance for flexible sensing electronics[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(37):34338-34347. [57] JIANG G, CHEN L, ZHANG S, et al. Superhydrophobic SiC/CNTs coatings with photothermal deicing and passive anti-icing properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(42):36505-36511. [58] LIU Y, WU Y, LIU Y, et al. Robust photothermal coating strategy for efficient ice removal[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(41):46981-46990. [59] MA L, WANG J, ZHao F, et al. Plasmon-mediated photothermal and superhydrophobic TiN-PTFE film for anti-icing/deicing applications[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,181:107696. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107696 [60] WU B, CUI X, JIANG H, et al. A superhydrophobic coating harvesting mechanical robustness, passive anti-icing and active de-icing performances[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,590:301-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.01.054 [61] 冯放, 沈虎, 赵宏伟, 等. 超疏水MoS2纳米涂层叶片防覆冰特性研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2021, 42(5):1169-1175.FENG Fang, SHEN Hu, ZHAO Hongwei, et al. Research on anti-icing characteristics of superhydrophobic MoS2 nano-coated blade[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics,2021,42(5):1169-1175(in Chinese). [62] ZHAO Z, CHEN H, LIU X, et al. Development of high-efficient synthetic electric heating coating for anti-icing/de-icing[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology,2018,349:340-346. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.06.011 [63] 杨洋, 黄文龙, 李剑, 等. 一种绝缘子超疏水防覆冰涂层覆冰初期的电气试验研究[J]. 高压电器, 2013, 49(1):46-49.YANG Yang, HUANG Wenlong, LI Jian, et al. Electrical tests of super-hydrophobic coating in early stage of icing on insulators[J]. High Voltage Apparatus,2013,49(1):46-49(in Chinese). [64] LI X, YANG B, ZHANG Y, et al. A study on superhydrophobic coating in anti-icing of glass/porcelain insulator[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,2014,69(2):441-447. doi: 10.1007/s10971-013-3243-y [65] DE PAUW D, DOLATABADI A. Effect of superhydrophobic coating on the anti-icing and deicing of an airfoil[J]. Journal of Aircraft,2017,54(2):490-499. doi: 10.2514/1.C033828 [66] 朱宝. 低能耗超疏水电热蒙皮设计及防冰性能研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2018.ZHU Bao. Low Power superhydrophobic electrothermal skin and its anti-icing performance[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2018(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: