Research progress of the interleaved thermoset composites by carbon nanomaterials/thermoplastic resin
-
摘要: 碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料(CF/EP)由于其优异的力学性能,被大量应用于工业中,但薄弱的层间性能限制了其优势性能的发挥。层间增韧是有效解决该问题的技术之一。随着材料科学与技术的发展,热塑性树脂、纳米碳材料先后被应用于层间增韧复合材料的研究中。综述了热塑性树脂、纳米碳材料及二者协同层间增韧复合材料的研究进展,分析了热塑/热固双相体系及与纳米碳材料协同增韧复合材料的作用机制,为后续纳米材料/热塑性树脂层间增韧复合材料的研究提供了方向和参考。Abstract: Carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites (CF/EP) have been widely used in industry due to the excellent mechanical properties, but poor interlaminar property limits the performance advantage. Interleaving toughening is one of the valid methods to solve this problem. With the development of material science and technology, the thermoplastic resin and carbon nanomaterials are successively used in the study of the interleaved composites. The research progress of the interleaved composites by thermoplastic resin, carbon nanomaterials and combination of both was reviewed, and the toughening mechanism of thermoplastic/thermoset dualphase system and its synergy with carbon nanomaterials was analyzed, which provided the guideline and reference for the subsequent research on the interleaved composites.
-
表 1 热塑性树脂层间增韧复合材料断裂韧性的部分研究结果
Table 1. Partial research results of the fracture toughness of the interleaved composites by thermoplastic resin
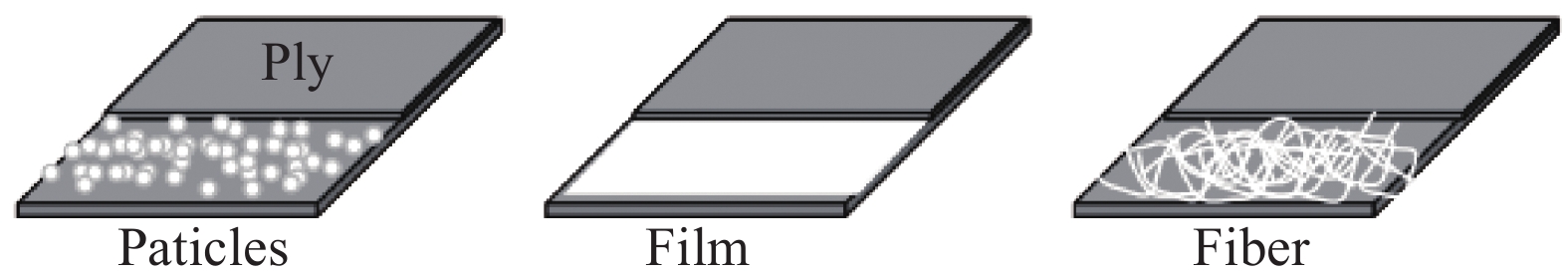
Interleaving method Composite Toughener Toughener content GIC/% GIIC/% Ref Particle CF/EP(T700/TDE85) PEAK 10wt% — 32 [26] CF/EP(T700/TDE85) PA6 10wt% — 41 [26] CF/BMI(U3160/6421) P-PAEK 5 phr 56 42 [38] CF/SPN(T700) PI 15wt% 156 — [39] CF/EP Rubber 6wt% 250 — [40] CF/EP(IM7/8552) PA12 33.3 g/m2 400 — [27] Film CF/EP(T700/6240) PEK-C 10 μm 72 — [29] GF/EP(E-GF/913) PI — 300 130 [31, 41] GF/EP(LT5078-A) TPU — 78 115 [42] CF/EP(T300/YD128) PSF 21wt% 270 — [30] CF/BMI(U3160/6421) P-PAEK 10 g/m2 — 74 [43] GF/EP PET 0.2 mm 40 — [44] Nanofiber CF/EP(T700/AG-80) PSF 5wt% 281 — [35] CFRP(T800/AS4 3501-6) Nylon-66 1wt%-1.4wt% 152 — [45] CF/EP(T300/MTM49-3) PA69 14wt% 28 190 [46] CF/EP(T700/ML5417-A) PA 20 g/m2 145 — [47] CF/EP PA66 12wt% 22 20 [37] CF/EP(GG204P/IMP503Z) Nylon-66 18 g/m2 137 — [48] Notes: CF—Carbon fiber; EP—Epoxy; BMI—Bismaleimide; SPN—Phthalonitrile; PEAK—Poly(aryl ether ketone); PEK-C—Polyetherketone-cardo; PA6—Polyamide 6; PSF—Polysulfone; PI—Polyimide; TPU—Thermoplastic polyurethane; PET—polyethylene terepthalate; P-PEAK—Phosphorus-containing poly(arylene ether ketone); GIC—Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness; GIIC—Mode II interlaminar fracture toughness. 表 2 CNTs层间增韧复合材料断裂韧性的部分研究结果
Table 2. Partial research results of fracture toughness of the interleaved composites by CNTs
Method Composite CNTs content GIC/% GIIC/% Ref. 2.2.1 CFRP(HFW250U-A12-500/Araldite LY1564SPCIN) 9.64 g/m2 — 94 [60] 2.2.1 CFRP(U3160/3266) 50-60 μm −0.8 120 [67] 2.2.1 CFRP(G0926/DERAK-ANE8084) 0.8 g/m2 60 — [68] 2.2.2 CFRP — 17 — [70] 2.2.2 CFRP(T700/L-930HT) 1.32 g/m2 40 140 [71] 2.2.2 CFRP(T300/F-593) 0.1 — 22 [72] 2.2.2 CFRP(T700SC/EP) 0.75 g/m2 21 42 [85] 2.2.2 CFRP(HMC/SE84LV) 0.2 g/m2 13 — [73] 2.2.3 CFRP(TR30S/EP) — — 104 [77] 2.2.3 CFRP(EPJER806) 2 g/m2 171 — [78] 2.2.4 CFRP(CF/EP) — 67 60 [40] 2.2.5 CFRP(T700/E54) 30wt% −17 47 [84] Note: CFRP—Carbon fiber reinforced plastic. 表 3 纳米碳材料/热塑性树脂复合层间增韧复合材料性能力学的部分研究结构
Table 3. Partial research structure of mechanical properties of the interleaved composites by carbon nanomaterial/thermoplastic
Composite Interlayer GIC/% GIIC/% Bending strength/% CAI/% Ref. CFRP(T800/MY0510) PA/MWCNTs/EP 126 — 3 — [88] CF/BMI(T700) CNTs/PEK-C — — — 33 [86] CFRP(HYE/1034E) CNTs/PPS 36 200 — — [94] CFRP(VTP H310) MWCNTs/PVB 200(I+II) — — [90] CF/EP(L160) CNTs/PAN 77 — — — [91] CF/EP CNTs/PSF — 48 — — [92] CF/EP(T300) CNTs/Nylon66 24 — — — [93] GF/EP(E6/DGEBA) CNTs/EMAA — 20 — — [97] CFRP(IM7/EPIKOTEEPIKURE) MWCNTs/PA — 140 — — [98] CF/EP(T800/SCI-550R) GO/PSF 131(I+II) 34 184 [20] CFRP(T700/TDE-85) MWCNTs/PEI 53 33 — 14 [99] CFRP(T700/E-828) MWNTs/PSF — 214 121 — [100] CF/EP MWCNT/P(Stco-GMA) — — 25 — [101] CF/EP(CF3031/ET5284) GO/PA6 81 36 — — [102] CF/EP CNTs/PSF 53 34 27 — [37] CF/BMI(T300) ACNTB/PBI — — 16 42 [87] Notes: MWCNTs—Multi-wall carbon nanotubes; PPS—Polyphenylene sulfide; PVB—Polyvinyl butyral; PAN—Polyacrylonitril; EMAA—Ethylene methacrylic acid; PEI—Poly (ethylene imine); ACNTB—Aligned carbon nanotubes bundle; P(Stco-GMA)—Polystyrene-co-glycidyl methacrylate; PBI—Polybenzimidazole; CAI—Compression after impact. -
[1] 益小苏, 许亚洪, 程群峰, 等. 航空树脂基复合材料的高韧性化研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2008(6):84-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2008.06.017YI X S, XU Y H, CHENG Q F, et al. Research progress on high toughness of aerospace resin matrix composites[J]. Science & Technology Review,2008(6):84-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7857.2008.06.017 [2] MOHAN P. A critical review: The modification, properties, and applications of epoxy eesins[J]. Polymer Plastics Technology and Engineering,2013,52(2):107-125. doi: 10.1080/03602559.2012.727057 [3] 王德中. 环氧树脂的增韧改性[J]. 热固性树脂, 1992(4):55-61.WANG D Z. Toughening modification of epoxy resin[J]. Thermosetting Resin,1992(4):55-61(in Chinese). [4] FRANCIS B, THOMAS S, JOSE J, et al. Hydroxyl terminated poly (ether ether ketone) with pendent met-hyl group toughened epoxy resin: Miscibility, morphology and mechanical properties[J]. Polymer,2005,46:12372-12385. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2005.10.103 [5] POORNIMA V P, DEBORA P, JOSE M K, et al. El-astomer/thermoplastic modified epoxy nanocomposites: The hybrid effect of ‘micro’ and ‘nano’ scale[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R: Reports,2017,116:1-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2017.03.001 [6] DENG S, DJUKIC L, PATON R, et al. Thermoplastic-epoxy interactions and their potential applications in joining composite structures-A review[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2015,68:121-132. [7] JIN J, CUI J, TANG X, et al. Polyetherimid modified bismaleimide resins. II. Effect of polyetherimide content[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2001,81:350-358. doi: 10.1002/app.1445 [8] KINLOCH A J, MOHAMMED R D, TAYLOR A C, et al. The interlaminar toughness of carbon-fibre reinforced plastic composites using ‘hybrid-toughened’ matrices[J]. Journal of Material Science,2006,41:5043-5046. doi: 10.1007/s10853-006-0130-8 [9] 姚佳伟, 刘梦瑶, 牛一凡. PEK-C膜层间增韧碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料的力学性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 36(5):27-35.YAO J W, LIU M Y, NIU Y F. Mechanical properties of PEK-C interlayer toughened carbon fiber/epoxy composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,36(5):27-35(in Chinese). [10] AN X F, JI S Y, TANG B, et al. Toughness improvement of carbon laminates by periodic interleaving thin thermoplastic films[J]. Journal of Materials Science Letters,2002,21(22):1763-1765. doi: 10.1023/A:1020972804838 [11] TARFAOUI M, LAFDI K, MOUMEN A E. Mechanical properties of carbon nanotubes based polymer composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 103: 113-121. [12] RAMAKRISHNAN K, NOEL N, SUBRAMANYAN V. Nitrogen doped carbon nanomaterial as electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in acidic media: To use in electrofenton[J]. Chemistry Select,2020,5(32):10034-10040. doi: 10.1002/slct.202002413 [13] GRUSZKA K M, DURAJSKI A P. Substitution induced and stress controlled magnetism in 2D pyrenebased carbon nanomaterial[J]. Surface Science,2021,709:121836. doi: 10.1016/j.susc.2021.121836 [14] GOJNY F H, WICHMANN M H G, KOPKE U. Carbon nanotube-reinforced epoxy-composites: Enhanced stiffness and fracture toughness at low nanotube content[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2004,64(15):2363-2371. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.04.002 [15] MONTAZERI A, JAVADPOUR J, KHAVANDI A, et al. Mechanical properties of multi-walled carbon nanotube/epoxy composites[J]. Materials and Design,2010,31(9):4202-4208. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.04.018 [16] 刘万弼. 微纳米粒子协同增韧双马树脂及其复合材料的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2017.LIU W B. Research on synergistic toughening of BMI and its composites by micro and nanoparticle[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [17] 方群. 纳米纤维膜在高效空气过滤和碳纤维复合材料层间增韧中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2016.FANG Q. Application research of nanofiber membrane in high efficiency air filtration and interlayer toughening of carbon fiber composite[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [18] GUO Z H, LI Z Q, LIU J S, et al. Exsitu method for toughening glass/epoxy composites by interlaminar films made of polyetherketone cardo and calcium sulfate whisker[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2014,33(21):1966-1975. doi: 10.1177/0731684414550837 [19] 闫丽, 安学峰, 董慧民, 等.“离位”增韧T800H/5228ES复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2015, 43(9): 55-57, 61.YAN L, AN X F, DONG H M, et al. Study on preparation and property of T800H/5228ES composites by Ex-situ toughening method[J]. New Chemical Materials, 2015, 43(9): 55-57, 61(in Chinese). [20] 徐磊. 聚砜增韧改性环氧树脂及其层间增韧液体成型碳纤维复合材料的研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2019.XU L. Study on polysulfone toughened modified epoxy resin and its interlayer toughened liquid formed carbon fiber composite[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2019(in Chinese). [21] 李刚. 聚砜纳米纤维膜增韧环氧树脂及其碳纤维复合材料的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2008.LI G. Study on toughening epoxy resin and its carbon fiber composites with polysulfone nanofiber membrane[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2008(in Chinese). [22] 蒋民强. 聚醚砜层间增韧环氧树脂基复合材料的研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2018.JIANG M Q. Study on epoxy resin matrix composites toughened by polyethersulfone interlayer[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2018(in Chinese). [23] 闫丽, 安学锋. "离位"增韧ES-U3160/5284复合材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2019, 47(4):173-176.YAN L, AN X F. Preparation and properties of “ex situ” toughened ES-U3160/5284 composites[J]. New Chemical Materials,2019,47(4):173-176(in Chinese). [24] SHIVAKUMAR K N, PANDURANGA R, SHARPE M. Interleaved polymer matrix composites-A review[C]//Aiaa/asme/asce/ahs/asc Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. 2013. [25] 董慧民, 益小苏, 安学锋, 等. 纤维增强热固性聚合物基复合材料层间增韧研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(2):273-285.DONG H M, YI X S, AN X F, et al. Research progress in interlayer toughening of fiber-reinforced thermoset polymer matrix composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(2):273-285(in Chinese). [26] 刘新, 陈铎, 何辉永, 等. 热塑性颗粒-无机粒子协同增韧碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8):1904-1910.LIU X, CHEN D, HE H Y, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced epoxy resin composites toughenedby thermoplastic inorganic particles[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(8):1904-1910(in Chinese). [27] WANG W T, YU H N, POTTER K, et al. Effect of the characteristics of nylon microparticles on mode-I interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon-fibre/epoxy composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,138:106073. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2020.106073 [28] GILBERT E N, HAYES B S, SEFERIS J C. Interlayer toughened unidirectional carbon prepreg systems: Effect of preformed particle morphology[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2003,34(3):245-252. doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(02)00141-0 [29] YAO J W, NIU K M, NIU Y F, et al. Toughening efficiency and mechanism of carbon fibre epoxymatrix composites by PEK-C[J]. Composite Structures,2019,229:111431. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111431 [30] YUN N G, YONG G W, KIM S C. Toughening of carbon fiber/epoxy composite by inserting polysulfonefilm to form morhology spectrum[J]. Polymer,2004,45(20):6953-6958. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2004.08.020 [31] YASAEE M, BOND I P, TRASK R S, et al. Mode I interfacial toughening through discontinuous interleaves for damage suppression and control[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2012,43(1):198-207. [32] RAMIREZ V A, HOGG P J, SAMPSON W W. The influence of the nonwoven veil architectures on interlaminar fracture toughness of interleaved composites[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2015,110:103-110. [33] NASH N H, YOUNG T M, STANLEY W F. The influence of a thermoplastic toughening interlayer and hydrothermal conditioning on the Mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon/benzoxazine composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2016,81:111-120. [34] BEYLERGIL B, TANOĞLU M, AKTAŞ E. Effect of polyamide-6, 6 (PA 66) nonwoven veils on the mechanical performance of carbon fiber/epoxy composites[J]. Composite Structures,2018,194:21-35. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.03.097 [35] GANG L, PENG L, CHEN Z, et al. Inhomogeneous toughening of carbon fiber/epoxy composite using electrospun polysulfone nanofibrous membranes by in situ phase separation[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2008,68(3-4):987-994. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.07.010 [36] ZHANG J, YANG T, LIN T, et al. Phase morphology of nanofibre interlayers: Critical factor for toughening carbon/ epoxy composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2012,72(2):256-262. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.11.010 [37] 郑楠. 纳米相层间增韧碳纤维/环氧复合材料研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017.ZHENG N. Study on carbon fiber/epoxy composites toughened by nano phase interlayer[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [38] 张兴迪, 刘刚, 党国栋, 等. 含磷聚芳醚酮颗粒层间增韧碳纤维/双马树脂RTM复合材料[J]. 高分子学报, 2016(9):1254-1262.ZHANG X D, LIU G, DANG G D, et al. Interlaminar toughening carbon fiber/bismaleic resin RTM composites with PEAK-P particles[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2016(9):1254-1262(in Chinese). [39] 赵泽华, 孙劲松, 郭颖, 等. 聚酰亚胺颗粒层间增韧碳纤维/邻苯二甲腈树脂复合材料[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(3):732-740.ZHAO Z H, SUN J S, GUO Y, et al. Carbon fiber/phthalonitrile resin composites toughened by polyimide particles[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(3):732-740(in Chinese). [40] 徐丰. 复合材料层板层间微/纳米颗粒增韧机理研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2016.XU F. Study on toughening mechanism of micro/nano particles in composite laminates[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016(in Chinese). [41] YASAEE M, BOND I P, TRASK R S, et al. Mode II interfacial toughening trough discontinuous interleaves for damage suppression and control[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2011, 43(1): 121-128. [42] 吕广超. TPU无纺布对GF/EP复合材料冲蚀磨损性能和层间韧性的影响[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2018.LV G C. Effect of TPU non woven fabric on erosion wear properties and interlaminar toughness of GF/EP composites[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2018(in Chinese). [43] 张兴迪. 含磷聚芳醚酮"离位"增韧RTM双马树脂基复合材料性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.ZHANG X D. Properties of PEAK-P in situ toughened RTM bismaleic resin matrix composites[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016(in Chinese). [44] LI L, LEE S P, LIEW K M. The Influence of thermoplastic film interleaving on the interlaminar shear strength and Mode I fracture of laminated composites[J]. Journal of Engineering Materials and Technology,1996,118(3):302-309. doi: 10.1115/1.2806810 [45] SHIVAKUMAR K, LINGAIAH S, CHEN H, et al. Polymer nanofabric interleaved composite laminates[J]. Aiaa Journal,2009,47(47):1723-1729. [46] DAELEMANS L, SAM V D H, DE B I, et al. Nanofibre bridging as a toughening mechanism in carbon/epoxy composite laminates interleaved with electrospun polyamide nanofibrous veils[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2015,117:244-256. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.06.021 [47] 康少付, 李进, 瞿立, 等. 共聚酯无纺布定型-增韧碳纤维复合材料的制备及力学性能[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2020(4):53-59.KANG S F, LI J, QU L, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of copolyester non woven fabric setting toughened carbon fiber composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering,2020(4):53-59(in Chinese). [48] BRUGO T M, MINAK G, ZUCCHELLI A, et al. An investigation on the fatigue based delamination of woven carbon-epoxy composite laminates reinforced with polyamide nanofibers[J]. Procedia Engineering,2015,109:65-72. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2015.06.208 [49] 安学锋. 基于复相体系的层状化增韧复合材料研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2004.AN X F. Study on layered toughened composites based on multiphase system[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2004(in Chinese). [50] 程群峰. 双马来酰亚胺树脂基复合材料的离位增韧研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2007.CHENG Q F. In situ toughening of bismaleimide resin matrix composites[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2007(in Chinese). [51] 刘小云, 余英丰, 甘文君, 等. 热塑性树脂改性热固性树脂体系固化反应诱导相分离研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2007, 21(4):34-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2007.04.009LIU X Y, YU Y F, GAN W J, et al. Research progress of curing reaction induced phase separation in thermoplastic resin modified thermosetting resin system[J]. Materials Reports,2007,21(4):34-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2007.04.009 [52] CHENG Q F, FANG Z P, XU Y H, et al. Morphological and spatial Effects on toughness and impact damage resistance of PAEK-toughened BMI and fraphite fiber composite laminates[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics,2009,22(1):87-96. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(08)60073-4 [53] RICO M, LÓPEZ J, MONTERO B, et al. Phase separation and morphology development in a thermoplastic-modified toughened epoxy[J]. European Polymer Journal,2012,48(10):1660-1673. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2012.07.007 [54] 张明. 通用航空环氧树脂的固化和相行为研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空材料研究院, 2006.ZHANG M. Study on curing and phase behavior of general aviation epoxy resin[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Aerial Materials, 2006(in Chinese). [55] INOUE T. Reaction-induced phase decomposition in polymer blends[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,1995,20(1):119-153. doi: 10.1016/0079-6700(94)00032-W [56] 刘青松. 环氧树脂/端羧基丁腈橡胶复合体系固化动力学及性能研究[D]. 长春: 长春工业大学, 2017.LIU Q S. Curing kinetics and properties of epoxy resin/carboxyl terminated NBR composites[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [57] GIRARD R E, SAUTEREAU H, PASCAULT J P. Use of block copolymers to control the morphologies and properties of thermoplastic/thermoset blends[J]. Polymer,1999,40(7):1677-1687. doi: 10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00302-4 [58] HSIEH T H, HUANG Y S, WANG F X, et al. Impact and after-impact properties of nanocarbon aerogels reinforced epoxy/carbon fiber composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2018,206:828-838. [59] 宋丽萍, 张蓬洲. 化学气相沉积法在碳纤维复合材料领域的应用[J]. 化工新型材料, 1994(8):25-26, 32.SONG L P, ZHANG P Z. Application of chemical vapor deposition in the field of carbon fiber composites[J]. New Chemical Materials,1994(8):25-26, 32(in Chinese). [60] 于妍妍, 张远, 高丽敏, 等. 基于碳纳米管薄膜的复合材料层间增韧[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(10):307-314.YU Y Y, ZHANG Y, GAO L M, et al. Interlaminar toughening of composites based on carbon nanotube films[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2019,40(10):307-314(in Chinese). [61] 周海佳, 刘雪芹, 苏庆. 电泳沉积制备功能薄膜材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2008, 22(S2):311-315.ZHOU H J, LIU X Q, SU Q. Research progress of functional thin films prepared by electrophoretic deposition[J]. Materials Reports,2008,22(S2):311-315(in Chinese). [62] 陈师. 电泳沉积法制备CNT/CF及其复合材料界面微观力学行为的拉曼研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016.CHEN S. Raman study on interfacial micromechanical behavior of CNT/CF composites prepared by electrophoretic deposition[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2016(in Chinese). [63] 张哲鹏. 氧化石墨烯基复合膜的制备及油水分离性能研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2020.ZHANG Z P. Preparation of graphene oxide based composite membrane and its oil water separation performance[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2020(in Chinese). [64] SU Y N, ZHANG S C, ZHANG X H, et al. Preparation and properties of carbon nanotubes/carbon fiber/poly (ether ether ketone) multiscale composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,108:89-98. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.02.030 [65] HUNG P Y, LAU K T, QIAO K, et al. Property enhancement of CFRP composites with different graphene oxide employment methods at a cryogenic temperature[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,120:56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.02.012 [66] XU H, TONG X, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Mechanical and electrical properties of laminated composites containing continuous carbon nanotube film interleaves[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2016,127:113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.02.032 [67] 刘刚, 胡晓兰, 张朋, 等. 碳纳米管膜层间改性碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料[J]. 高分子学报, 2013(10):1334-1340.LIU G, HU X L, ZHANG P, et al. Carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites modified by carbon nanotube film[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2013(10):1334-1340(in Chinese). [68] OU Y F, CARLOS G, JUAN J V. Interlaminar toughening in structural carbon fiber/epoxy composites interleaved with carbon nanotube veils[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,124:105477. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105477 [69] LIU B, CAO S H, GAO N Y, et al. Thermosetting CFRP interlaminar toughening with multi-layers graphene and MWCNTs under mode I fracture[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,183:107829. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.107829 [70] ALMUHAMMADI K, ALFANO M, YANG Y, et al. Analysis of interlaminar fracture toughness and damage mechanisms in composite laminates reinforced with sprayed multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Materials & Design,2014,53:921-927. [71] JOSHI S C, DIKSHIT V. Enhancing interlaminar fracture characteristics of woven CFRP prepreg composites through CNT dispersion[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2012,46(6):665-675. doi: 10.1177/0021998311410472 [72] MUJIKA F, VARGAS G, IBARRETXE J, et al. Influence of the modification with MWCNT on the interlaminar fracture properties of long carbon fiber composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2012,43(3):1336-1340. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2011.11.020 [73] ANDRÉS N, BRIAN G F, STEPHEN C H, et al. Enhancing the fracture toughness of hierarchical composites through amino‒functionalised carbon nanotube webs[J]. Composites Part B,2019,165:537-544. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.02.001 [74] LEONARDO S D, NISTA A, CATALANOTTI G, et al. Mode I interlaminar fracture of thin-ply laminates with CNT web at the crack interface[J]. Composite Structures,2019,225:111178. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111178 [75] 张远, 于妍妍, 何静宇, 等. 碳纳米管薄膜增强复合材料I型断裂韧性研究[J]. 碳素科技, 2018, 4(37): 15-20, 32.ZHANG Y, YU Y Y, HE J Y, et al. The mode I fracture toughness of composites enhanced by using carbon nanotube film[J]. Carbon Techniques, 2018, 4(37): 15-20, 32(in Chinese). [76] SHIN Y C, KIM H S, LEE W I. Mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of carbon nanotubes/epoxy film-interleaved carbon fiber composites[J]. Composite Structures,2020,236:111808. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111808 [77] KHAN S U, KIM J K. Improved interlaminar shear properties of multiscale carbon fiber composites with bucky paper interleaves made from carbon nanofibers[J]. Carbon,2012,50(14):5265-5277. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.07.011 [78] NING H M, LI J H, HU N et al. Interlaminar mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced plastic laminates modified with graphene oxide interleaf[J]. Carbon,2015,91:224-233. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.054 [79] DU X S, ZHOU H, SUN W, et al. Graphene/epoxy interleaves for delamination toughening and monitoring of crack damage in carbon fibre/epoxy composite laminates[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2017,140:123-133. [80] JIA J J, DU X S, CHEN C et al. 3D network graphene interlayer for excellent interlaminar toughness and strength in fiber reinforced composites[J]. Carbon,2015(95):978-986. [81] 姚红伟, 钟盛根, 李显华, 等. CNTs强化碳纤维/环氧复合材料界面过渡层及其对界面性能的影响[J]. 材料工程, 2016, 44(12):13-21. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.12.003YAO H W, ZHONG S G, LI X H, et al. Interfacial transition layer of cnts reinforced carbon fiber/epoxy composites and its effect on interfacial properties[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2016,44(12):13-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.12.003 [82] 梁馨, 方洲, 罗丽娟, 等. 碳纳米管改性对碳/环氧复合材料层间性能的影响[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2016, 46(4):56-59, 76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2016.04.014LIANG X, FANG Z, LUO L J, et al. Effect of carbon nanotubes modification on interlaminar properties of carbon/Epoxy Composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2016,46(4):56-59, 76(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2016.04.014 [83] 许民. 纳米碳材料/环氧树脂复合材料的性能研究[D]. 济南: 济南大学, 2013.XU M. Study on properties of nano carbon/epoxy resin composites[D]. Ji'nan: University of Ji'nan, 2013(in Chinese). [84] 代少伟. 氧化石墨烯改性碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2018.DAI S W. Graphene oxide modified carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2018(in Chinese). [85] 邓火英, 王立敏, 冯奕钰, 等. 碳纳米管膜层间增韧对碳纤维复合材料力学性能的影响[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2015, 45(5):31-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2015.05.006DENG Huoying, WANG Limin, FENG Yiyu, et al. Effect of interlaminar toughening of carbon nanotube film on mechanical properties of carbon fiber composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology,2015,45(5):31-35(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2015.05.006 [86] XU X G, ZHOU Z, HEI Y, et al. Improving compression-after-impact performance of carbon–fiber composites by CNTs/thermoplastic hybrid film interlayer[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2014,95:75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2014.01.023 [87] GUAN Q B, YUAN L, WANG Z H, et al. Aminated aligned carbon nanotube bundles/polybenzimidazole hybrid film interleaved thermosetting composites with interface strengthening action[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,152:256-266. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.07.020 [88] LIU D W, GANG L, BO L, et al. Establishment of multi-scale interface in interlayer-toughened CFRP composites by self-assembled PA-MWNTs-EP[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2016,130:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.05.005 [89] 曾庆杨. 微纳米粒子协同层间增韧碳纤维复合材料的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2019.ZENG Q Y. Study on carbon fiber composites toughened by micro nano particles[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [90] KAYNAN O, ATESCAN Y, OZDEN Y E, et al. Mixed Mode delamination in carbon nanotube/nanofiber interlayered composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,154:186-194. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.07.032 [91] ESKIZEYBEK V, YAR A, AVC1 A. CNT-PAN hybrid nanofibrous mat interleaved caron/epoxy laminates with improved Mode I interlaminar fracture toughness[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2018,157:30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.01.021 [92] LI P, LIU D W, ZHU B, et al. Synchronous effects of multiscale reinforced and tougheded CFRP composites by MWNTs-EP/PSF hybrid nanofibers with preferred orientation[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,68:72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2014.09.010 [93] HAMER S, LEIBOVICH H, GREEN A, et al. Mode I and mode II fracture energy of MWCNT reinforced nanofibrilmats interleaved carbon/epoxy laminates[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2014,90:48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.10.013 [94] QUAN D, MISCHO C, BINSFELD L, et al. Fracture behaviour of carbon fiber/epoxy composites interleaved by MWCNT and graphene nanoplatelet-doped thermoplastic veils[J]. Composite Structures,2020,235:111767. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2019.111767 [95] ZHENG N, HUANG Y D, LIU H Y, et al. Improvement of interlaminar fracture toughness in carbon fibre/epoxy composite with carbon nanotubes/polysulfone interleaves[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,140:8-15. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.12.017 [96] GAO Y, LIU L, WU Z J, et al. Toughening and self healing fiber-reinforced polymer composites using carbon nanotube modified poly (ethylene-comethacrylic acid) sandwich membrane[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,124:105510. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105510 [97] 高雅, 刘玲. EMAA/CNT膜对复合材料Ⅱ型层间断裂韧性及自修复率的影响[J]. 复合材料科学与工程, 2020(02):25-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.02.004GAO Y, LIU L. Effect of EMAA/CNT film on mode-II interlaminar fracture toughness and self repairing rate of composites[J]. Composites Science and Engineering,2020(02):25-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0999.2020.02.004 [98] KEVIN L W, SUE H J. Delamination toughness of fiber-reinforced composites containing a carbon nanotube/poly-amide-12 epoxy thin film interlayer[J]. Polymer,2012,53(1):37-42. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2011.11.022 [99] 薛利文. 含碳纳米管的聚醚酰亚胺纳米纤维膜对环氧树脂复合材料力学性能的影响[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2012.XUE L W. Effect of polyetherimide nanofiber film containing carbon nanotubes on mechanical properties of epoxy resin composites[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [100] 朱博. 静电纺丝制备PSF/MWNTs-Epoxy杂化纳米纤维同步增强增韧CFRP实现机制的研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2012.ZHU B. Study on the mechanism of synchronous reinforcement and toughening of PSF/MWNTs epoxy hybrid nanofibers by electrospinning[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [101] BILGE K, OZDEN-YENIGUN E, SIMSEK E, et al. Structural composites hybridized with epoxy compatible polymer/MWCNT nanofibrous interlayers[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2012,72(14):1639-1645. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2012.07.005 [102] ZHAO X R, CHEN W, HAN X, et al. Enhancement of interlaminar fracture toughness in textilereinforced epoxy composites with polyamide 6/graphene oxide interlaminar toughening tackifier[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,191:108094. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108094 [103] ZOU H, WANG K, ZHANG Q, et al. A change of phase morphology in poly(p-phenylene sulfide)/polyamide 66 blends induced by adding multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. Polymer,2006,47(22):7821-7826. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2006.09.008 [104] POTSCHKE P, KRETZSCHMAR B, JANKE A. Use of carbon nanotube filled polycarbonate in blends with montmorillonite filled polypropylene[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67(5):855-860. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2006.02.034 -






 下载:
下载: