Synthesis of bio-nanocomposite and its application in wastewater treatment
-
摘要: 物理、化学和生物等传统污水处理的方法在处理效能、人体健康和环境保护等方面仍有诸多不足之处,而利用生物纳米复合材料可有效解决上述传统污水处理方法存在的问题,是在污水处理中具有巨大应用前景的新型材料。本综述阐述了生物纳米复合材料的合成机制,剖析了生物纳米复合材料进行水处理的吸附、光催化、抗菌机制及其在水中重金属、有机染料、药物、无机盐等污染物去除方面的应用,包括通过取代纳米表面的羟基官能团吸附氟离子,通过静电相互作用和离子相互作用吸附铬离子;吸收特定光谱的能量,催化氧化吸附在表面的污染物,最终使其降解或矿化,复合材料的生物部分能减小带隙,增大吸附面积;该材料可直接与微生物细胞相互作用,中断跨膜电子转移、破坏/穿透细胞包络或氧化细胞成分,或产生活性氧物质等二次产物。分析了该材料目前在控制纳米粒子的形态和粒径,快速提高纳米粒子产量和明确某些尺寸的纳米颗粒的毒性方面存在的问题。提出了未来生物纳米复合材料的发展方向,期望为实现高效可控的绿色生物纳米复合材料生产技术,应专注于细胞和生化过程的确切机制,优化反应参数,改善纳米颗粒的稳定性并探究纳米合成的生物材料范围,形成成熟的生物纳米复合材料合成技术方案。Abstract: Traditional wastewater treatment methods, such as physical, chemical and biological methods, still have many shortcomings in the treatment efficiency, human health and environmental protection, etc. However, the use of bio-nanocomposites can effectively solve the problems existing in the traditional wastewater treatment methods, which is a new material with great application prospects in wastewater treatment. This review described the synthesis mechanism of bio-nanocomposites, analyzed bio-nano composites for adsorption, photocatalytic and antibacterial mechanism of water treatment, and heavy metals in the water, organic dyes, drugs, inorganic salt and other contaminants removal applications, including hydroxyl groups on the surface of the material replaced by fluorine ion adsorption, chromium ions are adsorbed by electrostatic interaction and ion interaction. The biological part of the composite material can reduce the band gap and increase the adsorption area by absorbing the energy of a specific spectrum and catalyzing the oxidation of the pollutants adsorbed on the surface, which will eventually degrade or mineralize them. The material can directly interact with microbial cells to interrupt transmembrane electron transfer, destroy/penetrate cell envelope or oxidize cell components, or produce secondary products such as reactive oxygen species. The problems existing in controlling the morphology and particle size of nanoparticles, rapidly increasing the yield of nanoparticles and clarifying the toxicity of some sizes of nanoparticles were analyzed. In this paper the future development direction of bio-nanocomposites was put forward, achieving efficient control of green bio-nanocomposites production technology was expected. The next step is to focus on the precise mechanism of cellular and biochemical process, optimize the reaction parameters, improve the stability of the nanoparticles, explore the biological materials range of nano composite and form a mature synthesis technology scheme of bio-nanocomposites.
-
Key words:
- bio-nanocomposites /
- synthesis /
- adsorption /
- photocatalytic /
- antibacterial /
- purification /
- wastewater treatment
-
Microorganism used Type of nanoparticles Size/nm Reaction condition Rhodoococcus Au 5-15 Alkaline active agents Tetragonal algae Au 5-35 Enzyme Plectonema boryanum(Cyanobacteria) Ag 1-10
1-100— Shewanella Au 10-20 pH=7 E coli DH5α Au 25-33 — Candida glabrata and Schizosaccharomyces pombe CdS 200 — Verticillium Ag 25±12 Active biomass Microorganism used Type of nanoparticles Size/nm Reaction condition Delftia sp. Bi 20-120 Active biomass Acinetobacter Au 8-12 Purified enzyme Se 100 Lactobacillus kimchi Au 13 Biomass extracts Scenedesmus sp. Ag 15-20 Cell extracts Bacillus sp. Ag 5-15 Extracellular Pseudomonas sp. CdSe 10-20 Living cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa CdS 20-40 Extracelluar matrix Pseudomonas sp. Ag Cell-free supernatant Rhodobacter capsulatus Te — Active cell suspension Geobacter sulfurreducens Au 10-90 Biofilm Gordonia amicalis Au 20 Cell-free supernatant Hulled Oat Ag 5-85 Active biomass Aloe Au 50-350 Biomass extracts Cinnamomum camphor lobe Au, Ag 55-80 Sun dried biomass 表 3 用于水中重金属离子去除的生物纳米复合材料[6, 11]
Table 3. Bio-nanocomposites for the removal of heavy metal ions in water[6, 11]
Bio-nanocomposite Contaminant Bio-material Original CNFs, original CNCs Ag(I) Cellulose Original CNCs from bioethanol, phosphorylated CNFs and CNCs from sludge Cu(II), Fe(III) Cellulose Sodium-substituted succinic anhydride Modified CNCs Pb(II), Cd(II) Cellulose Sulfonated CNFs Au(III) Cellulose Poly(itaconic acid/methacrylic acid) embedded CNC controller/bentonite nanocomposites Co(II) Cellulose Carboxylated CNFs/chitosan magnetic hydrogel beads Pb(II) Cellulose BC/NiHCF membrane Cs(I) Cellulose Nano zero-valent iron beads coated with carboxymethyl chitosan Cr(VI) Chitosan Chitosan/organic rectorite-Fe3O4 composite microspheres Cu(II), Cd(II) Chitosan Nano ZnO/chitosan microspheres Mo Chitosan Chitosan/cerium oxide/iron oxide nanocomposites Cr(VI), Co(II) Chitosan Guar gum and nano-bentonite in the composite hydrogel acrylic network prepared by in-situ incorporation Cr(VI) Guara gum Guar gum nano-zinc oxide bio-composites Cr(VI) Guara gum Polyvinyl alcohol/alginate/zeolite nanohybrids Ni(II), Co(II) Alginate Calcium alginate beads intercepted by glycine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles Cu(II) Calcium alginate Activated carbon/nano zero-valent copper/hydroxyapatite-alginate As(III) Alginate PVA alginate magnetite and titanium dioxide beads Pb(II) Alginate CdS quantum dots immobilized on calcium alginate beads Hg(II) Calcium alginate Iron oxide Cr(VI) Jelly fungi Salicylaldehyde functionalized chitosan nanoparticles Cu(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) Chitosan Nickel oxide/chitosan nanocomposites Zn(II) Chitosan Chitosan/triethanolamine composites Ag(I) Chitosan Thiol functionalized chitin nanofibers As Chitin Chitin networks U Chitin Starch stabilized Fe0 NP Cr(VI) Starch Fe3O4-based starch-poly (acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels Cu(II), Pb(II) Starch γ-Fe2O3@starch As Starch AgNPs-based starch/PEG-polyacrylic acid hydrogel Hg(II) Starch Poly(acrylamide-coa crylic acid) grafted gum incorporated into Fe3O4 NPs hydrogel nanocomposites Pb(II), Cr(VI) and Ni(II) Gum Xanthan gum-g-polyacrylamide/SiO2 Pb(II) Xanthan TiO2/ZnO calcium alginate beads Cu(II) Calcium alginate Nano zero-valent iron immobilized alginate beads Cr(VI) Alginate Polyacrylic acid-sodium alginate nanofibers hydrogel Cu(II) Algin Nano zero-valent iron intercepted by polyvinyl alcohol alginate ester Cu(II), Cr(VI), Zn(II) and As(V) Alginate esters Nano hydroxyapatite/alginate composite beads Ni(II) Alginate Alginate beads immobilized on carbon nanoparticles Co(II),Ni(II) Alginate Calcium alginate beads Removal of Cu(II) from [Cu(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Zn(II)] mixtures Calcium alginate Notes: CNFs—Carbon nanofibers; CNCs—Cellulose nanocrystals; BC/NiHCF—Nickel hexacyanoferrates loaded bacterial cellulose; PVA—Polyvinyl alcohol; NP—Nanoparticle; PEG—Polyethylene glycol. 表 4 用于水中农药、染料、药物及有机污染物去除的生物纳米复合材料[6, 11]
Table 4. Bio-nano composites used for the removal of pesticides, dyes, drugs and organic pollutants in water[6, 11]
Bio-nanocomposite Contaminant Bio-material β-cyclodextrin modified CNCs@Fe3O4@SiO2
superparamagnetic nanorodsProcaine, imipramine Cellulose Polyethylene glycol modified CNCs Paracetamol, sulfamethoxazole, N, N-diethyl-m-amino formamide Cellulose Original CNCs Chlorpyrifos, MB Cellulose Malondialdehyde functionalized CNCs Creatinine Cellulose UiO-66/polydopamine/bacterial cellulose Aspirin, tetracycline hydrochloride Cellulose CNCs grafted with Maleic Anhydride CV Cellulose Amino-functionalized CNCs Acid Red GR Cellulose CNCs/HPAM Nanogels(by casting) MB Cellulose CNFs of MnO2 coating MB Cellulose D-CNCs/PVAm microgels Congo red 4BS, reactive light yellow K-4G, acid red GR Cellulose CMC/GOCOOH beads MB Cellulose CMC/g-C3N4/ZnO MV Cellulose PAETMAC-g-CNC Neutral reactive blue 19(RB19) Cellulose MBCNF/GOPA MG Cellulose CNF/PEI/Ag NPs aerogel membrane 4-NP,MB Cellulose TOCN/CGG hydrogel Thioflavin-T Cellulose D-ZSM/CNF,Cu- and Fe-ZSM/CNF Rhodamine 6B, Reactive blue 4 Cellulose Chitosan-4-nitroacetophenone/CuO-CeO2-Al2O3 and chitosan-4-nitroacetophenone/CuO-CeO2-Fe2O3 Red 60 Chitosan Fe3O4-chitosan microparticles and nanoparticles Bromothymol blue Chitosan Nano-titanium oxide/chitosan/nano-bentonite Levofloxacin and ceftriaxone Chitosan Chitosan-loaded ZnO and Ce-ZnO nanoflowers Bice green Chitosan Pd NPs@Fe3O4/CS-AG Microcapsules 4-NP Chitosan Chitosan membrane Mixture of diclofenac and ketoprofen Chitosan Fe3O4-based starch-poly(acrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels Methylene Purple and Congo Red Starch Oxidized starch NPs Urea Starch Chitosan beads Tartaric yellow, amide black Chitosan Starch and CMC-stabilized nano zero-valent iron Sulfadimidine Starch Nano zero-valent iron modified by starch Acid blue-25 Starch Sodium montmorillonite NPs/P(acrylic-acrylamide)-g starch Saffron Starch Starch modified magnetic Fe0NP Naphthalene Starch Starch coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles Sky blue Starch Mung bean starch/PVA/ZnS nanocomposites Bisphenol A Starch Cellulose/carbon-tube hybrid adsorbent,
with Veron glue polysaccharide as anchoring agentMB Cellulose, carbowelan gum polysaccharide Xanthan gum-stabilized nano-Pd/Fe Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) Xanthan Chitosan-Guar gum hybrid silver nanoparticles bio-nanocomposites Reactive blue 21(RB-21), Reactive red 141, Rhodamine 6G and 4-NP Chitosan, guar gum Wet spinning nano TiO2/chitosan nanocomposite fiber Free fatty acid Chitosan Acrylic acid grafted sodium alginate-based TiO2 hydrogel nanocomposites MV Algin Cellulose nanocrystals alginate hydrogel beads MB Alginate Nano-iron oxide loaded alginate microspheres Bice green Alginate Sodium alginate beads Reactive blue 222 Algin MnFe2O4/calcium alginate nanocomposites, GOx and laccase MB, indigo and acid red 14 Calcium alginate Nano hydroxyapatite/alginate composite beads Rhodamine B(RhB) Alginate Alginate/Fe@Fe3O4 Core/Shell Nanoparticles Norfloxacin Alginate Nanoscale montmorillonite (MMT)/calcium alginate Basic red 46 Calcium alginate Cu Azo dye Coli bacillus Ag Methyl Orange and Congo Red Cryptococcus lactis Au,Ag Methylene Blue and Congo Red Pseudomonas lipolytica PEI-Pt@BC membrane Acid black att Cellulose α-Fe2O3 nanodisk/bacterial cellulose membrane Orange II(OII),MO,RhB,MB,CV Cellulose PMPC/BNC nanocomposites MB,MO Cellulose hPEI modified cellulose-based biological adsorbent Cationic bright yellow M-7G, anionic active yellow X-RG Cellulose CMC-Ni-BC MB,2-NP(nitrophenol) Cellulose BC/PDA/TiO2 RhB,MB,MO Cellulose ZIF-67/BC/CH aerogels Activated red X-3B Cellulose Cellulose acetate-cerium dioxide/zirconia@Cu0 NPs Mixtures of 4-NP-MB, 4-NP-RhB and 4-NP-MB-RhB Cellulose Cellulose/Ag3PO4 Industrial fertilizer wastewater and RhB dye mixture Cellulose Cu@chitosan-silica nanoparticles 1,1-dimethylhydrazine Chitosan Polyvinylidene fluoride/chitosan/dopamine MB and orange G Chitosan Double amino functionalized cellulose nanocrystals/chitosan composites Diclofenac sodium Chitosan Magnetic graphene/chitosan Acid orange 7 Chitosan Fe3O4 NPs coated with carboxymethyl chitosan Direct red 16 Chitosan Chitosan zinc oxide nanospheres MB and saffron Chitosan Cellulose acetate/chitosan/single-walled carbon nanotubes/Fe3O4/TiO2 MB Chitosan Molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) chitosan-TiO2 nanocomposites Rose Bengal Chitosan TiO2(KH-570)-g-(chitosan-glycidyl methacrylate ) Toluene Chitosan Chitosan tripolyphosphate/TiO2 nanocomposites Active orange 16 Chitosan Nanostructure of chitosan-zirconium phosphate Reactive Blue 21, Reactive Red 141, Rhodamine 6G Chitosan crosslinked magnetic EDTA/chitosan/TiO2 Phenol Chitosan Chitosan-AgCl/Ag/TiO2 Toluidine, salicylic acid, 4-aminomethylbenzoic acid Chitosan Titanium dioxide/Achille gum nanogel MB Chitosan Carbon dots-nano zero-valent iron composite based on Achille gum Amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin Tragacanth Guar gum stabilized Pt NPs 4-NP Achille gum, carbon Co-polymer-grafted gum karaya and silica hybrid organic-inorganic hydrogel nanocomposite MB Guara gum Fe3O4 NPs-Adhesive Nanocomposites MB Gum Adhesive and Fe3O4 magnetic NPs nanocomposites RhB Gati gum CoFe2O4@silica-shell@tragacanth gum-grafted-poly (methacrylic acid) Methyl red Gati gum Fe0@guar gum crosslinked soybean lecithin nanogel MV Tragacanth Pd NPs/guar gum Mixture of MO, MB and CR Guara gum Composite copolymer of nano silver chloride and alginate Brilliant cresyl blue Alginate 3D silver/polyethyleneimine/alginate gel beads 4-NP Alginate GOx(glucose oxidase)/MnFe2O4/calcium alginate nanocomposites MB Alginate Bimetallic zero-valent iron silver nanoparticles alginate
beads immobilized in calcium4-chlorophenol Calcium alginate Grafted polyacrylic acid modified polyglycidyl methacrylate CNCs Trypsin Alginate Poly(methacrylic acid-covinylsulfonic acid) grafted magnetic CNCs Hemoglobin, immunoglobulin G Cellulose Palladium nanocatalysts supported on cationic nanocellulose-alginate hydrogel MB Cellulose Calcium alginate activated carbon fiber beads Tetrahydrofuran Cellulose,alginate Magnetite/silica/pectin NPs Fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin and moxifloxacin ) Calcium alginate (PPA3)-Cu and (PPA3/Fe3O4)-Cu nanocomposite hydrogels 2-NP Pectin CNCs/hydrolyzed polyacrylamidenano-hydrogels (by electrospinning) MB Pectin Activated carbon from starch MB Polysaccharide Fe3O4/activated carbon/β-cyclodextrin/sodium alginate MB Starch Ag Malachite green dye Algin Au Aromatic pollutants and azo dyes Aspergillus flavus Pd MB Aspergillus Notes: MB—Methylene blue; CV—Crystal violet;HPAM—Hydrolyzed polyacrylamide; GOCOOH—Carboxylated graphene oxide; CMC—Carboxymethyl cellulose; MV—Methyl violet; PAETMAC—poly acryloyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride; MG—Malachite green; MBCNF/GOPA—Magnetic bacterial cellulose nanofiber/graphene oxide polymer aerogel; PEI—Poly(ethylene imine); TOCN/CGG—TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers/cationic guar gum; D-ZSM—De-aluminated ZSM-5 zeolite; CS—Chitosan; AG—Agar; 4-NP—4-nitrophenol; MO—Methyl orange; BC—Bacterial cellulose; PMPC/BNC—Poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine)/
bacterial nanocellulose; hPEI—Hyperbranched polyethyleneimine; PDA—Polydopamine; ZIF-67/BC/CH—Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67/bacterial cellulose/chitosan; PPA—Crosslinked pectin-(polyvinyl alcohol-co-acrylamide) hydrogel.表 5 用于水中盐等无机污染物去除的生物纳米复合材料[6, 11]
Table 5. Bio-nanocomposite materials used for the removal of inorganic pollutants such as salt in water[6, 11]
Bio-nanocomposite Contaminant Bio-material Aminopropyltriethoxysilane modified, hydroxyl-carbonated apatite modified and epoxy modified CNFs H2S Cellulose Carboxymethyl cellulose/citric acid aerogel Nitrate, nitrite, phosphate Cellulose Zinc ferrite CS, nickel ferrite CS, cobalt ferrite CS Fluoride Chitosan Functionalized chitosan clinoptilolite nanocomposites Nitrate Chitosan Starch-stabilized nano zero-valent iron Nitrate Starch Calcium alginate beads immersed in nanoscale zero-valent iron, magnetite NPs and powdered activated carbon Nitrate Alginate Magnetic hematite and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in PVA alginate beads Iodine Alginate Fe3O4@nano-hydroxyapatite/alginate Fluoride Alginate Te Tellurite Laurella genus Escherichia coli -
[1] 郭书雅, 刘倩, 尹先清. 含聚压裂返排废水的电絮凝处理实验研究[J]. 应用化工, 2020, 49(10):2483-2486, 2492. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.10.018GUO Shuya, LIU Qian, YIN Xianqing. Experimental study on electro-flocculation treatment of fracturing flowback wastewater containing polymer[J]. Applied Chemical Industry,2020,49(10):2483-2486, 2492(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2020.10.018 [2] 郭同玲, 王章领, 邢健. 生化法实现高氯高温稠油污水COD达标排放[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006(02):134-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.02.014GUO Tongling, WANG Zhangling, XING Jian. Biochemical method to achieve COD discharge of high-chlorine and high-temperature heavy oil wastewater[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2006(02):134-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2006.02.014 [3] 张海燕, 王宝辉, 陈颖. 光催化氧化处理含油污水的研究[J]. 化工进展, 2003(1):67-70. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6613.2003.01.017ZHANG Haiyan, WANG Baohui, CHEN Ying. Study on the treatment of oily wastewater by photocatalytic oxidation[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2003(1):67-70(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6613.2003.01.017 [4] 蒋学彬. 膜分离技术在石油工业含油污水处理中的应用研究进展[J]. 油气田环境保护, 2015, 25(05):77-80, 94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3158.2015.05.023JIANG Xuebin. Research progress in the application of membrane separation technology in the treatment of oily wastewater in the petroleum industry[J]. Environmental Protection of Oil & Gas Fields,2015,25(05):77-80, 94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3158.2015.05.023 [5] 张驰, 蔡绪森. 油田污水微生物处理技术研究进展[J]. 石油化工应用, 2014, 33(5):1-3, 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2014.05.001ZHANG Chi, CAI Xusen. Research progress of oilfield wastewater microbial treatment technology[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application,2014,33(5):1-3, 12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2014.05.001 [6] SARAVANAN A, KUMAR P S, KARISHMA S, et al. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications[J]. Chemosphere,2020,264:128580. [7] DAR O A, MALIK M A, TALUKDAR M I A, et al. Bionanocomposites in water treatment[M]//Bionanocomposites. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 505-518. [8] SHUKLA A K, UPADHYAY A K, SINGH L. Algae-mediated biological synthesis of nanoparticles: Applications and prospects[M]//Algae. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 325-338. [9] JACINTO M J, SILVA V C, VALLADÃO D M S, et al. Biosynthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A review[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2020,43(1):1-12. [10] PARVATHY G, SETHULEKSHMI A S, JAYAN J S, et al. Lignin based nano-composites: Synthesis and applications[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2020,145:395-410. [11] NASROLLAHZADEH M, SAJJADI M, IRAVANI S, et al. Starch, cellulose, pectin, gum, alginate, chitin and chitosan derived (nano) materials for sustainable water treatment: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,251:116986. [12] NASROLLAHZADEH M, SAJJADI M, IRAVANI S, et al. Carbon-based sustainable nanomaterials for water treatment: State-of-art and future perspectives[J]. Chemosphere,2020,263:128005. [13] IHSANULLAH I. MXenes (two-dimensional metal carbides) as emerging nanomaterials for water purification: Progress, challenges and prospects[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,388:124340. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124340 [14] 哈什马特. 生物定向合成纳米复合材料和分子印迹聚合物及其在环境中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2019.KHAN H D. Bio-oriented synthesis of nanocomposites and molecularly imprinted polymers and their applications in the environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [15] PRAJAPATI C, JOLLY A, RAVULAPALLI S. Bio inspired synthesis of silver nanoparticles and its applications to spin–orbit interactions of light[J]. Nano Express,2020,1(3):030031. doi: 10.1088/2632-959X/abca4c [16] KLEM M T, WILLITS D, SOLIS D J, et al. Bio-inspired synthesis of protein-encapsulated CoPt nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2005,15(9):1489-1494. doi: 10.1002/adfm.200400453 [17] HUANG J, LIN L, SUN D, et al. Bio-inspired synthesis of metal nanomaterials and applications[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2015,44(17):6330-6374. doi: 10.1039/C5CS00133A [18] SHAABANI A, SHADI M, MOHAMMADIAN R, et al. Multi-component reaction-functionalized chitosan complexed with copper nanoparticles: An efficient catalyst toward A3 coupling and click reactions in water[J]. Applied Organometallic Chemistry,2019,33(9):e5074. [19] VELUSAMY P, KUMAR G V, JEYANTHI V, et al. Bio-inspired green nanoparticles: Synthesis, mechanism, and antibacterial application[J]. Toxicological Research,2016,32(2):95-102. doi: 10.5487/TR.2016.32.2.095 [20] DU L, JIANG H, LIU X, et al. Biosynthesis of gold nanoparticles assisted by Escherichia coli DH5α and its application on direct electrochemistry of hemoglobin[J]. Electrochemistry Communications,2007,9(5):1165-1170. doi: 10.1016/j.elecom.2007.01.007 [21] DAMERON C T, REESE R N, MEHRA R K, et al. Biosynthesis of cadmium sulphide quantum semiconductor crystallites[J]. Nature,1989,338(6216):596-597. doi: 10.1038/338596a0 [22] SENAPATI S, SYED A, MOEEZ S, et al. Intracellular synthesis of gold nanoparticles using alga Tetraselmis kochinensis[J]. Materials Letters,2012,79:116-118. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2012.04.009 [23] AYANO H, MIYAKE M, TERASAWA K, et al. Isolation of a selenite-reducing and cadmium-resistant bacterium Pseudomonas sp. strain RB for microbial synthesis of CdSe nanoparticles[J]. Journal of bioscience and bioengineering,2014,117(5):576-581. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.10.010 [24] BHATIA P, VERMA S, SINHA M. Size-dependent optical response of magneto-plasmonic core-shell nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Nano Research,2018,1(1):1-13. [25] JAYASHREE, JENA, NILOTPALA, et al. Microalga Scenedesmus sp. : A potential low-cost green machine for silver nano-particle synthesis[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2014,24(4):522-533. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1306.06014 [26] CHANDRAN S P, CHAUDHARY M, PASRICHA R, et al. Synthesis of gold nanotriangles and silver nanoparticles using Aloevera plant extract[J]. Biotechnology Progress,2006,22(2):577-583. doi: 10.1021/bp0501423 [27] ANSHUP, VENKATARAMAN J S, SUBRAMANIAM C, et al. Growth of gold nanoparticles in human cells[J]. Langmuir,2005,21(25):11562-11567. doi: 10.1021/la0519249 [28] LARIOS-RODRIGUEZ E, RANGEL-AYON C, CASTILLO S J, et al. Bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles by human epithelial cells, in vivo[J]. Nanotechnology,2011,22(35):355601. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/22/35/355601 [29] 董周焱, MANIK P N R, 肖敏, 等. 微生物合成纳米银的一般方法及产物性质鉴定与生产应用[J]. 微生物学杂志, 2019, 39(3):84-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2019.03.012DONG Zhouyan, MANIK P N R, XIAO Min, et al. General method of microbial synthesis of nano-silver, identification of product properties and production application[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2019,39(3):84-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2019.03.012 [30] SARAVANAN A, KUMAR P S, KARISHMA S, et al. A review on biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles and its environmental applications[J]. Chemosphere,2021,264:128580. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128580 [31] MONDAL P, PURKAIT M. Preparation and characterization of novel green synthesized iron-aluminum nanocomposite and studying its efficiency in fluoride removal[J]. Chemosphere,2019,235:391-402. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.06.189 [32] KONG M, CHEN X G, XING K, et al. Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: A state of the art review[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2010,144(1):51-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012 [33] MIRABEDINI M, KASSAEE M Z, POORSADEGHI S. Novel magnetic chitosan hydrogel film, cross-linked with glyoxal as an efficient adsorbent for removal of toxic Cr(VI) from water[J]. Arabian Journal for Science & Engineering,2017,42(1):115-124. [34] ZHAO Y, GUO L, SHEN W, et al. Function integrated chitosan-based beads with throughout sorption sites and inherent diffusion network for efficient phosphate removal[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,230:115639. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115639 [35] FUJISHIMA A, ZHANG X, TRYK D A. TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena[J]. Surface Science Reports,2008,63(12):515-582. doi: 10.1016/j.surfrep.2008.10.001 [36] LEE S-Y, PARK S-J. TiO2 photocatalyst for water treatment applications[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2013,19(6):1761-1769. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2013.07.012 [37] JAYANTHI KALAIVANI G, SUJA S K. TiO2 (rutile) embedded inulin—A versatile bio-nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,143:51-60. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.054 [38] AHMAD N, SULTANA S, KUMAR G, et al. Polyaniline based hybrid bionanocomposites with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity and antifungal activity[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2019,7(1):102804. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.11.048 [39] CALVETE M J F, PICCIRILLO G, VINAGREIRO C S, et al. Hybrid materials for heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of antibiotics[J]. Coordination Chemistry Reviews,2019,395:63-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2019.05.004 [40] LI Q, MAHENDRA S, LYON D Y, et al. Antimicrobial nanomaterials for water disinfection and microbial control: Potential applications and implications[J]. Water Research,2008,42(18):4591-4602. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.08.015 [41] QI L, XU Z, JIANG X, et al. Preparation and antibacterial activity of chitosan nanoparticles[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2004,339(16):2693-2700. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2004.09.007 [42] RABEA E I, BADAWY E T, STEVENS C V, et al. Chitosan as antimicrobial agent: Applications and mode of action[J]. Biomacromolecules,2003,4(6):1457-1465. doi: 10.1021/bm034130m [43] MANNA S, PRAKASH S, DAS P. Synthesis of graphene oxide nano-materials coated bio-char using carbonaceous industrial waste for phenol separation from water[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2019,581:123818. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123818 [44] PARK S J, LEE S Y, JIN F L. Surface modification of carbon nanotubes for high-performance polymer composites[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 13-59. [45] OLYA M E, PIRKARAMI A. On the positive role of doping Cu and N2 on TiO2 in improving dye degradation efficiency: Providing reaction mechanisms[J]. Korean Jour-nal of Chemical Engineering,2015,32(8):1586-1597. doi: 10.1007/s11814-014-0380-0 [46] ESFAHANI I J, RASHIDI J, IFAEI P, et al. Efficient thermal desalination technologies with renewable energy systems: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering,2016,33(2):351-387. doi: 10.1007/s11814-015-0296-3 [47] LIN P C, HSIEH C T, LIU X, et al. Fabricating efficient flexible organic photovoltaics using an eco-friendly cellulose nanofibers/silver nanowires conductive substrate[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,405:126996. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126996 [48] LIU P, BORRELL P F, BOŽIČ M, et al. Nanocelluloses and their phosphorylated derivatives for selective adsorption of Ag+, Cu2+ and Fe3+ from industrial effluents[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,294:177-185. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.04.001 [49] ZHANG W, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Robust shape-retaining nanocellulose-based aerogels decorated with silver nanoparticles for fast continuous catalytic discoloration of organic dyes[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2020,242:116523. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116523 [50] BATMAZ R, MOHAMMED N, ZAMAN M, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals as promising adsorbents for the removal of cationic dyes[J]. Cellulose,2014,21(3):1655-1665. doi: 10.1007/s10570-014-0168-8 [51] CHEN L, BERRY R M, TAM K C. Synthesis of β-Cyclodextrin-modified cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs)@Fe3O4@SiO2 superparamagnetic nanorods[J]. ACS Sustainable Che-mistry & Engineering,2014,2(4):951-958. [52] HOKKANEN S, REPO E, BHATNAGAR A, et al. Adsorption of hydrogen sulphide from aqueous solutions using modified nano/micro fibrillated cellulose[J]. Environmental Technology,2014,35(18):2334-2346. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2014.903300 [53] DARABITABAR F, YAVARI V, HEDAYATI A, et al. Novel cellulose nanofiber aerogel for aquaculture wastewater treatment[J]. Environmental Technology & Innovation,2020,18:100786. [54] BHATTACHARYA P, SWARNAKAR S, GHOSH S, et al. Disinfection of drinking water via algae mediated green synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles and its toxicity evaluation[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2019,7(1):102867. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2018.102867 [55] ROSTAMI H, KHOSRAVI F, MOHSENI M, et al. Biosynthesis of Ag nanoparticles using isolated bacteria from contaminated sites and its application as an efficient catalyst for hydrazine electrooxidation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,107:343-348. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.179 -





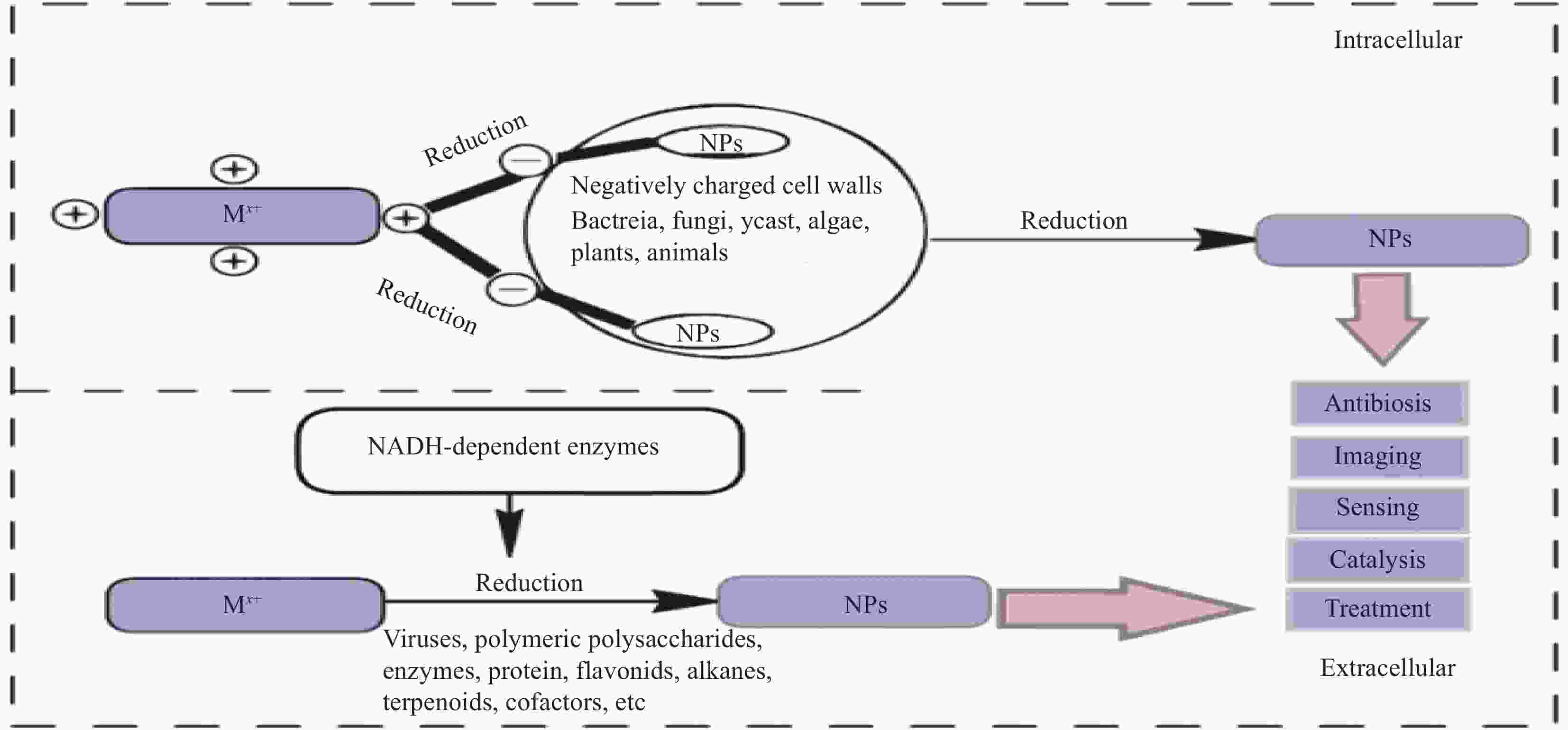
 下载:
下载: