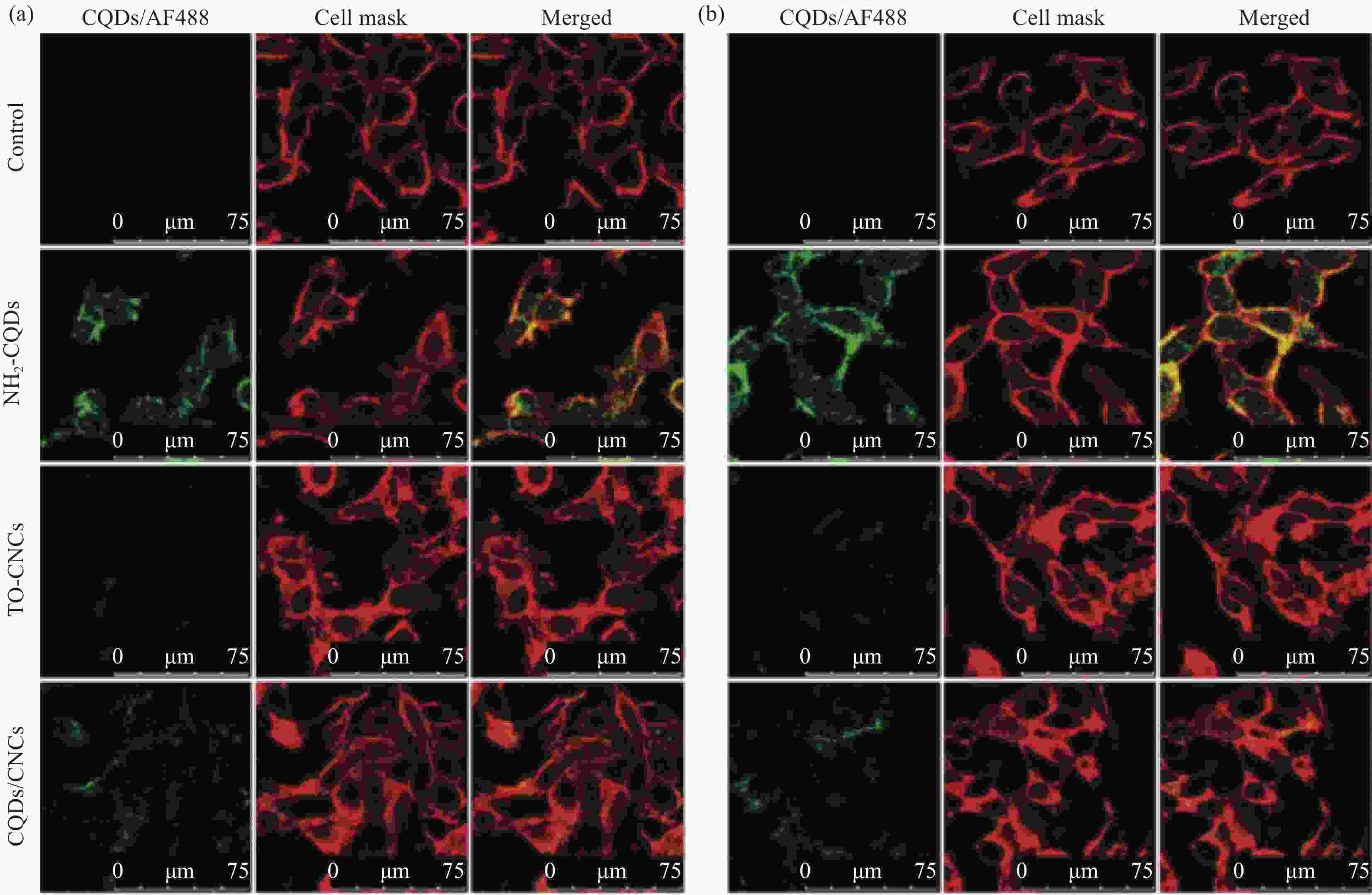
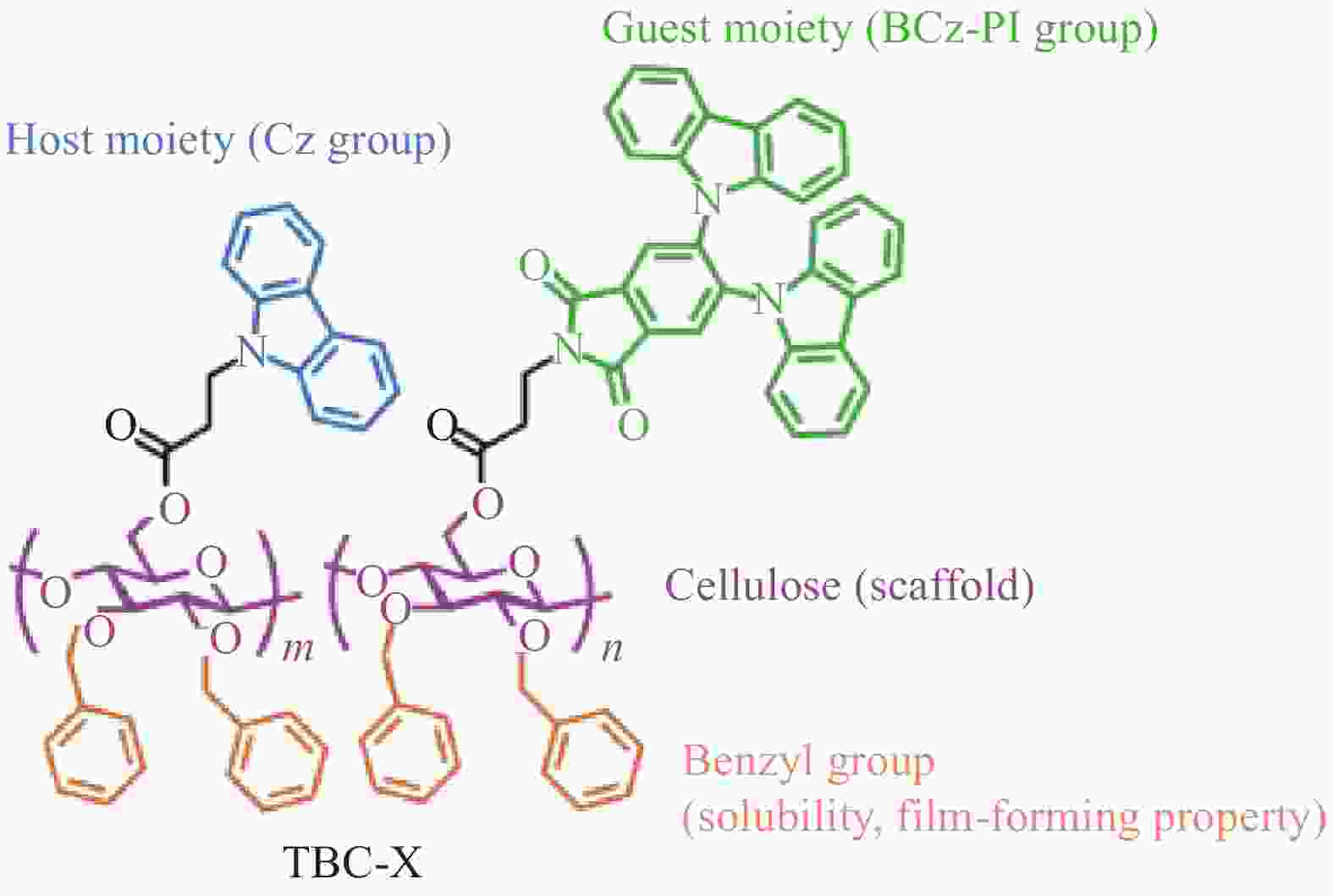
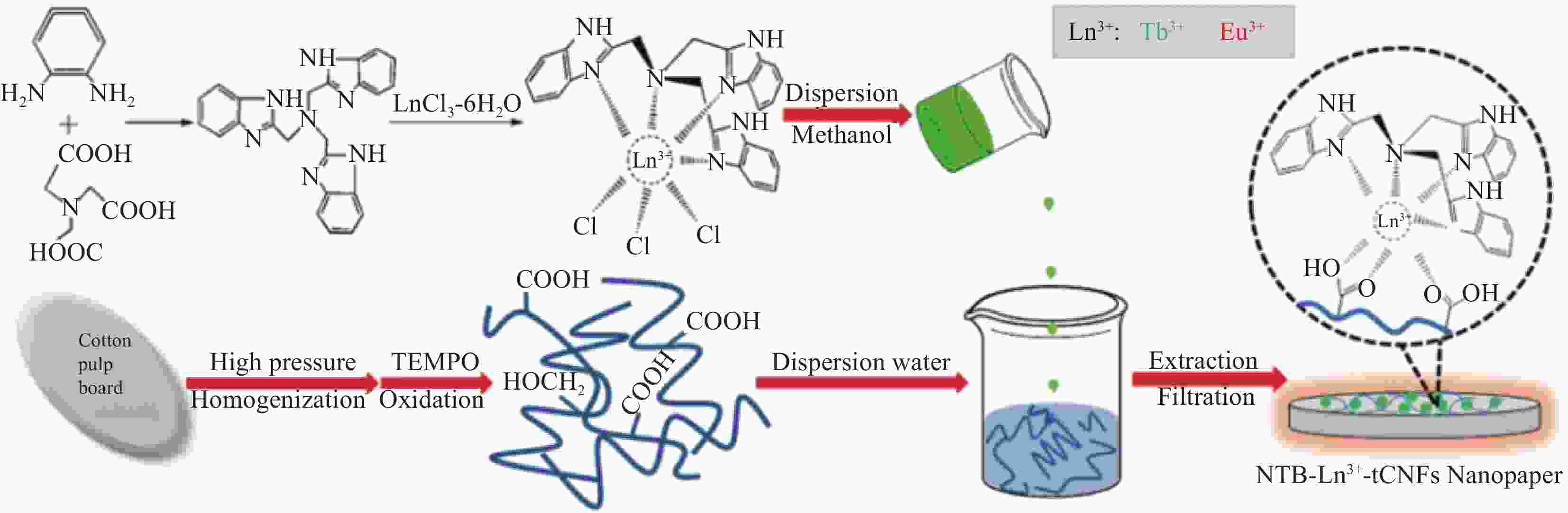
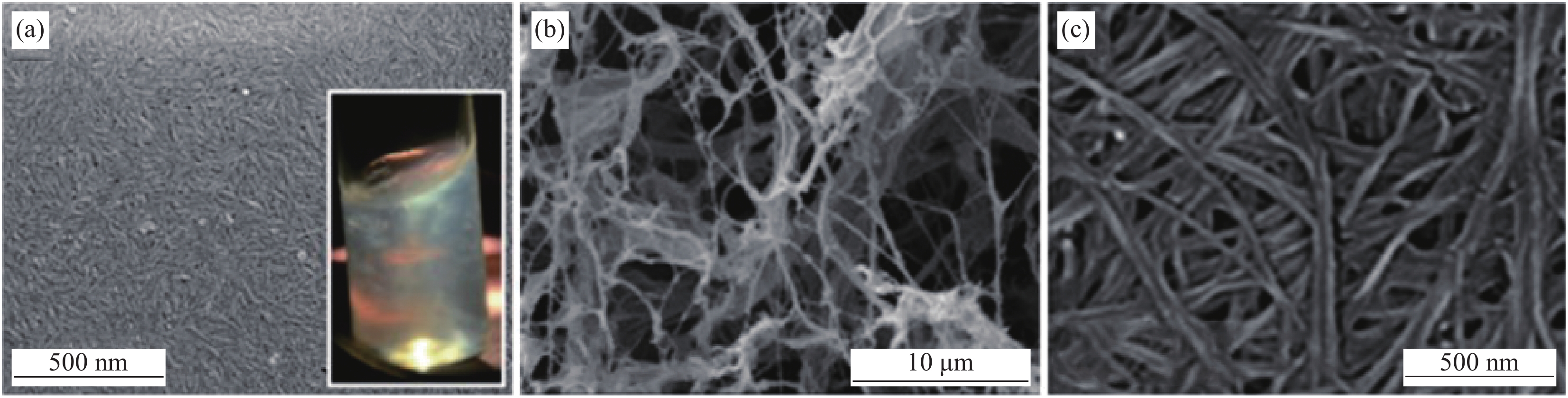
Research progress of nanocellulose-based luminescent materials
-
摘要: 纳米纤维素发光材料不仅具有发光基团特有的光物理或光化学性能,还具备纳米纤维素的可生物降解、生物相容、环境友好等特性,拓展了功能化纤维材料的应用领域。根据制备方法,纳米纤维素发光材料可分为三类:纳米纤维素/碳量子点复合发光材料、纤维素发光碳量子点和纳米纤维素/荧光染料复合发光材料。纳米纤维素发光材料具有独特的光学特性及结构特点,可制成膜、纸、水凝胶、气凝胶等,在离子检测、生物成像、光电应用等领域具有巨大的应用前景。本文介绍了发光材料的发光原理,概述了纳米纤维素发光材料的制备方法及相关应用,对纳米纤维素发光材料面临的挑战及发展趋势进行了总结和展望。Abstract: Nanocellulose-based lumnescent materials are normally obtained by physical and chemical modification of nanocellulose. Due to their unique photophysical or photochemical properties, and the characteristics of biodegradation, biocompatibility and environmental friendliness, nanocellulose-based luminescent materials further extend the universal applications of functionalized cellulose. This article introduces the luminescent principle of luminescent materials, summarizes the preparation methods and related applications of nanocellulose fluorescent materials, and summarizes the challenges and development trend of nanocellulose luminescent materials. According to the different preparation procedures, nanocellulose-based luminescent materials could be divided into three categories: composite luminescent materials of nanocellulose/carbon quantum dots, cellulose luminescent carbon quantum dots and composite luminescent materials of nanocellulose/fluorescent dye. Due to the unique optical and structural characteristics, nanocellulose luminescent materials have been extensively used as membrane, paper, hydrogel, aerogel, etc., and have great prospects in applications on ion detection, biological imaging, and photoelectric applications.
-
Key words:
- cellulose /
- nanocellulose /
- luminescent materials /
- carbon quantum dots /
- fluorescent dyes
-
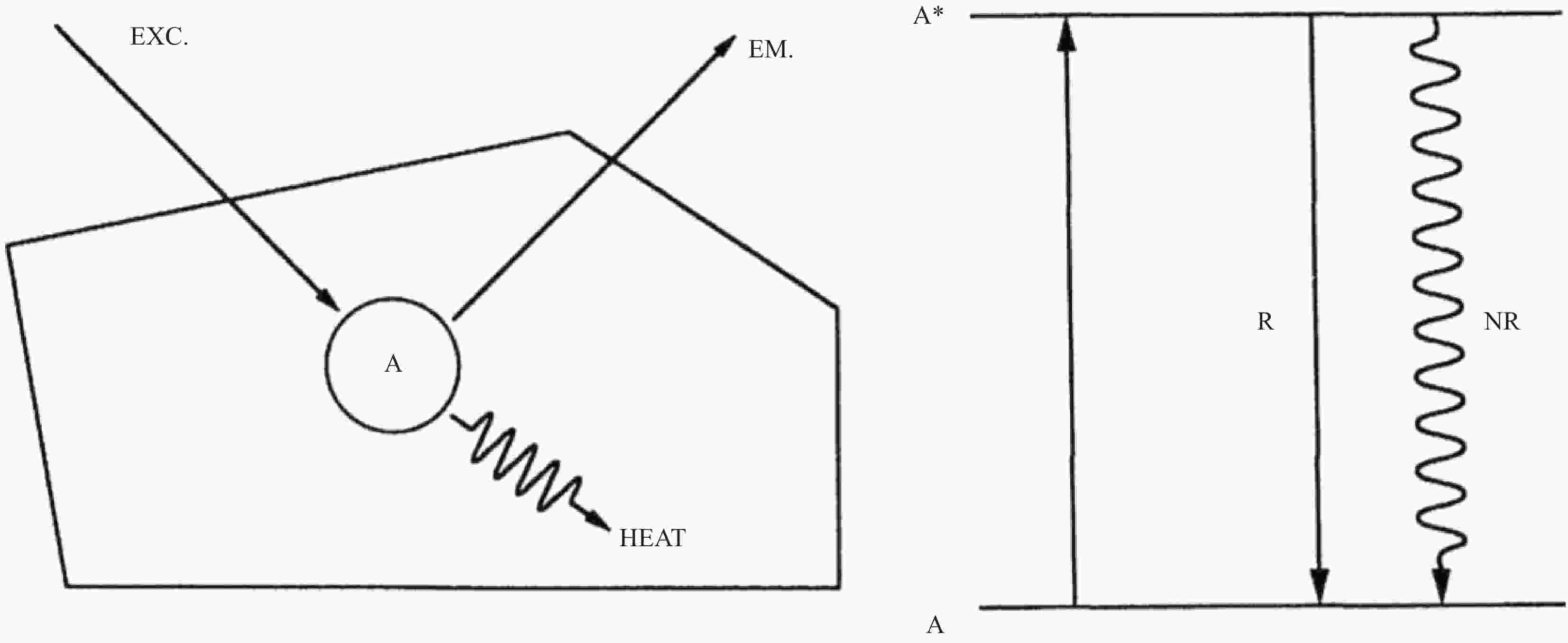
表 1 各种传感器上Fe2+离子的检测极限和响应时间[44]
Table 1. Detection limit and response time of Fe2+ ions on various sensors[44]
Sensors Detection limit/(μmol·L−1) Response time Rhodanmine B 0.2 1 h Terpy-functionalized TiO2 0.0003 30 s Carbon dots 0.02 2 min MoS2/o-phenylenediamine (OPD) /H2O2 0.007 30 s N-aryl-o-acylhydroxylamine 0.5 1 min N-doped carbon dots 10.98 Few seconds Arene-based fluorescent probes 8.54 Few seconds Benzimidazolyl pyridine 0.28 − Phen-methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI)-cellulose acetate (CA) 0.046 (2.6×10−6) fluorescence mode < 2 s Phen-MDI-CA 0.89 (5×10−5) naked-eye mode < 2 s -
[1] 张玲芝. 新型纤维素荧光材料的合成、结构与性能研究[D]. 湖北: 武汉大学, 2013.ZHANG L Z. Synthesis, structure and properties of novel cellulose-based fluorescent materials[D]. Hubei: Wuhan University, 2013 (in Chinese). [2] BEJOY T, MIDHUN C R, ATHIRA K B, et al. Nanocellulose, a versatile green platform: from biosources to materials and their applications[J]. Chemical Reviews,2018,118(24):11575-11625. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00627 [3] LIU K, DU H S, ZHENG T, et al. Recent advances in cellulose and its derivatives for oilfield applications[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,259:117740. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117740 [4] 刘慰, 司传领, 杜海顺, 等. 纳米纤维素基水凝胶的制备及其在生物医学领域的应用进展[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020, 4(5):11-19.LIU W, SI C L, DU H S, et al. Advance in preparation of nanocellulose -based hydrogels and their biomedical applications[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2020,4(5):11-19(in Chinese). [5] MUGDHA D, SURYAWANSHI V B. Analysis of cellulose based nanocomposites & potential applications[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings,2021,45(2):3476-3482. [6] LI Q, WU Y L, FANG R X, et al. Application of nanocellulose as particle stabilizer in food Pickering emulsion: Scope, merits and challenges[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,110:573-583. [7] NISHIL M, LIAN H, MUHAMMAD S I, et al. Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes using functionalized cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,417:129237. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129237 [8] KINGSHUK D, MEHRAN G, FUGEN D, et al. A review of nanocellulose as a new material towards environmental sustainability[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2021,775:145871. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145871 [9] YU S J, SUN J Z, SHI Y F, et al. Nanocellulose from various biomass wastes: its preparation and potential usages towards the high value-added products[J]. Environmental Science and Ecotechnology,2021,5:100077. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2020.100077 [10] N R, MANISHITA R S, JOHN F K. Nanocellulose: a mini-review on types and use in drug delivery systems[J]. Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications,2021,2:100031. doi: 10.1016/j.carpta.2020.100031 [11] 祁康成, 曹贵川. 发光原理与发光材料[M]. 成都: 电子科技大学出版社, 2012: 2-11.QI K C, CAO G C. Luminescent principle and luminescent materials[M]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology Press, 2012: 2-11(in Chinese). [12] BLASSE G, GRABMAIER B C. Luminescent Materials[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag Press, 1994: 1-2. [13] SHAJEEYA A S, SHUBHALAKSHMI S, RAJENDER S, et al. Syntheses of N-doped carbon quantum dots (NCQDs) from bioderived precursors: a timely update[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2021,9(1):3-49. [14] XU X Y, ROBERT R, GU Y L, et al. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nano-tube fragments[J]. Journal of the American Chemical So-ciety,2004,126(40):12736-12737. doi: 10.1021/ja040082h [15] JEFFERY M P, YOUNG S P, JAEHOON L, et al. Spectroscopic and device aspects of nanocrystal quantum dots[J]. Chemical Reviews,2016,116(18):10513-10622. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00169 [16] MARIA K, ZORAN M M, PETR H, et al. Carbon quantum dots modified polyurethane nanocomposite as effective photocatalytic and antibacterial agents[J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering,2018,4(12):3983-3993. [17] LI L, LI W P, MA C, et al. Paper-based electrochemiluminescence immunodevice for carcinoembryonic antigen using nanoporous gold-chitosan hybrids and graphene quantum dots functionalized Au@Pt[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2014,202:314-322. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.087 [18] WU L D, LI M, ZHANG M, et al. Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for tumor marker detection based on nanoporous sliver@carbon dots as labels[J]. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical,2013,186:761-767. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2013.06.092 [19] ZHANG W J, CHEN J, WANG J, et al. Design and synthesis of highly luminescent near-infrared-emitting water-soluble CdTe/CdSe/ZnS core/shell/shell quantum Dots[J]. Inorganic Chemistry,2009,48(20):9723-9731. doi: 10.1021/ic9010949 [20] 韩尊强, 钟伟婷, 王堃. 氮掺杂竹炭基超级电容器电极材料制备与表征[J]. 林业工程学报, 2020, 5(5):76-83.HAN Z Q, ZHONG W T, WANG K. Preparation and examination of nitrogen-doped bamboo porous carbon for supercapacitor materials[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2020,5(5):76-83(in Chinese). [21] KAROLⅡNA J, GUO J Q, ILARI F, et al. Modification of cellulose nanofibrils with luminescent carbon dots[J]. Biomacromolecules,2014,15(3):876-881. doi: 10.1021/bm4017176 [22] GUO J Q, LIU D F, ILARI F, et al. Photoluminescent hybrids of cellulose nanocrystals and carbon quantum dots as cytocompatible probes for in vitro bioimaging[J]. Biomacromolecules,2017,18(7):2045-2055. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00306 [23] GUO X, XU D, YUAN H M, et al. A novel fluorescent nanocellulosic hydrogel based on carbon dots for efficient adsorption and sensitive sensing in heavy metals[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2019,7:27081-27088. doi: 10.1039/C9TA11502A [24] WU B L, ZHU G, ALAIN D, et al. Fluorescent aerogels based on chemical crosslinking between nanocellulose and carbon dots for optical sensor[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(17):16048-16058. [25] 管庆顺, 左克曼, 吴伟兵, 等. 纯水相体系超声雾化法制备荧光磁性纳米纤维素微球[J]. 林业工程学报, 2018, 3(6):68-74.Guan Q S, Zuo K M, Wu W B, et al. Preparation of fluorescent magnetic nanocellulose microspheres by ultrasonic atomization in pure aqueous system[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering,2018,3(6):68-74(in Chinese). [26] ZENG J, YAN L F. Metal-free transparent luminescent cellulose films[J]. Cellulose,2015,22(1):729-736. doi: 10.1007/s10570-014-0485-y [27] YU S J, LI W, YUKI F, et al. Fluorescent spherical sponge cellulose sensors for highly selective and semiquantitative visual analysis: detection of Hg2+ and Cu2+ ions[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(23):19157-19166. [28] 哈丽丹·买买提, 阿卜杜黑热木·阿瓦提, 古妮萨柯孜·伊斯拉木, 等. 纤维素基荧光碳点的制备及应用研究进展[J]. 新疆大学学报 (自然科学版), 2020, 37(1):29-35.MAIMAITI H, AWATI A, YISILAMU G, et al. Progress in preparation and application of cellulose based fluorescent carbon dots[J]. Journal of Xinjiang University (Natural Science Edition),2020,37(1):29-35(in Chinese). [29] 沈培莲. 纤维素基荧光碳点的制备及其应用研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江理工大学, 2017.SHEN P L. 2017. Preparation and application of cellulose based fluorescent carbon dots[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, 2017 (in Chinese). [30] PENG H, TRAVASSEJDIC J. Simple aqueous solution route to luminescent carbogenic dots from carbohydrates[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2009,21(23):5563-5565. doi: 10.1021/cm901593y [31] KRYSMANN M J, KELARAKIS A, GLANNELIS P. Photoluminescent carbogenic nanoparticles directly derived from crude biomass[J]. Green Chemistry,2012,14(11):3141-3145. doi: 10.1039/c2gc35907c [32] WANG C Y, WANG C F, XU P P, et al. Synthesis of cellulose-derived carbon dots using acidic ionic liquid as a catalyst and its application for detection of Hg2+[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2016,51(2):861-867. doi: 10.1007/s10853-015-9410-5 [33] YANG G, WAN X, SU Y, et al. Acidophilic S-doped carbon quantum dots derived from cellulose fibers and their fluorescence sensing performance for metal ions in an extremely strong acid environment[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4:12841-12849. doi: 10.1039/C6TA05943K [34] LENG T Y, ZYGMUNT J J, MAHYAR M, et al. Ensemble and single particle fluorescence characterization of dye-labeled cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Langmuir,2017,33(32):8002-8011. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b01717 [35] KHALED A M, JIMMY A M, KEITH B M, et al. Effect of surface charge on the cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of fluo-rescent labeled cellulose nanocrystals[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2010,2(10):2924-2932. [36] WILLIAM H, HENRI C, TOMMY L H, et al. Fluorescent cellulose microfibrils as substrate for the detection of cellulase activity[J]. Biomacromolecules,2003,4(3):481-487. doi: 10.1021/bm020076i [37] TIFFANY A, ANTHONY P, JOSE M M, et al. Fluorescent labeling and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals with varying charge contents[J]. Biomacromolecules,2013,14(9):3278-3284. doi: 10.1021/bm400879x [38] WANG Q Y, CAI J, CHEN K Q, et al. Construction of fluorescent cellulose biobased plastics and their potential application in anti-counterfeiting banknotes[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2016,301(4):377-382. doi: 10.1002/mame.201500364 [39] TIAN W G, TIAN J T. Synergy of different fluorescent enhancement effects on spiropyran appended onto cellulose[J]. Langmuir,2014,30(11):3223-3227. doi: 10.1021/la404628p [40] ZHANG X G, QIN X Z, CHEN H L. Strong green fluorescent hydrogels with Ba2MgSi2O7: Eu2+ phosphor embedded in cellulose[J]. Luminescence,2017,32:535-538. doi: 10.1002/bio.3209 [41] HUANG J L, LI C J, DEREK G G. Cellulose nanocrystals incorporating fluorescent methylcoumarin groups[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2013,1(9):1160-1164. [42] JAY W G, KAI F M, YONGSOON S, et al. Alexa fluor-labeled fluorescent cellulose nanocrystals for bioimaging solid cellulose in spatially structured microenvironments[J]. Bioconjugate Chemistry,2015,26(3):593-601. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.5b00048 [43] JULIEN R G N, GUILLAUME C, Yu Y, et al. Multicolor fluo-rescent labeling of cellulose nanofibrils by click chemistry[J]. Biomacromolecules,2015,16(4):1293-1300. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00083 [44] HAQ N, TIAN W G, ZHANG J M, et al. Cellulose-based sensor containing phenanthroline for the highly selective and rapid detection of Fe2+ ions with naked eye and fluorescent dual modes[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(2):2114-2121. [45] 任志鹏. 纤维素水凝胶荧光碳点的制备和生物成像研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2020.REN Z P. Preparation and bioimaging of fluorescent carbon dots of cellulose hydrogels[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2020 (in Chinese). [46] MASAYA S, HIROKI O, KATSUAKI S, et al. Thermally activated delayed fluorescence benzyl cellulose derivatives for nondoped organic light-emitting diodes[J]. Macromole-cules,2020,53(8):2864-2873. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.9b02644 [47] ZHANG S F, LIU G, CHANG H, et al. Optical haze nanopaper enhanced ultraviolet harvesting for direct soft-fluorescent emission based on lanthanide complex assembly and oxidized cellulose nanofibrils[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(11):9966-9975. -





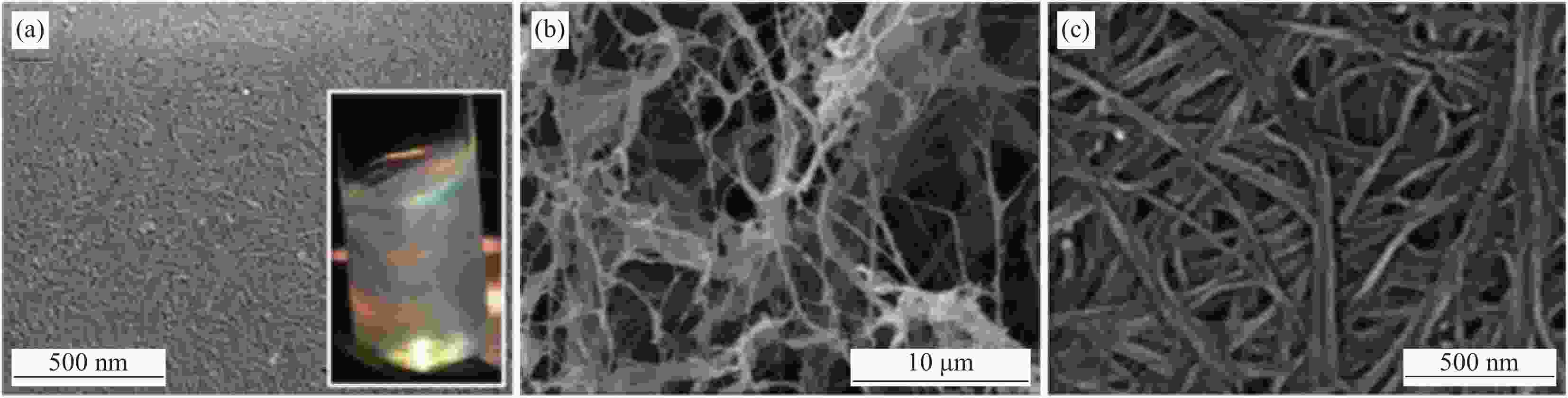
 下载:
下载: