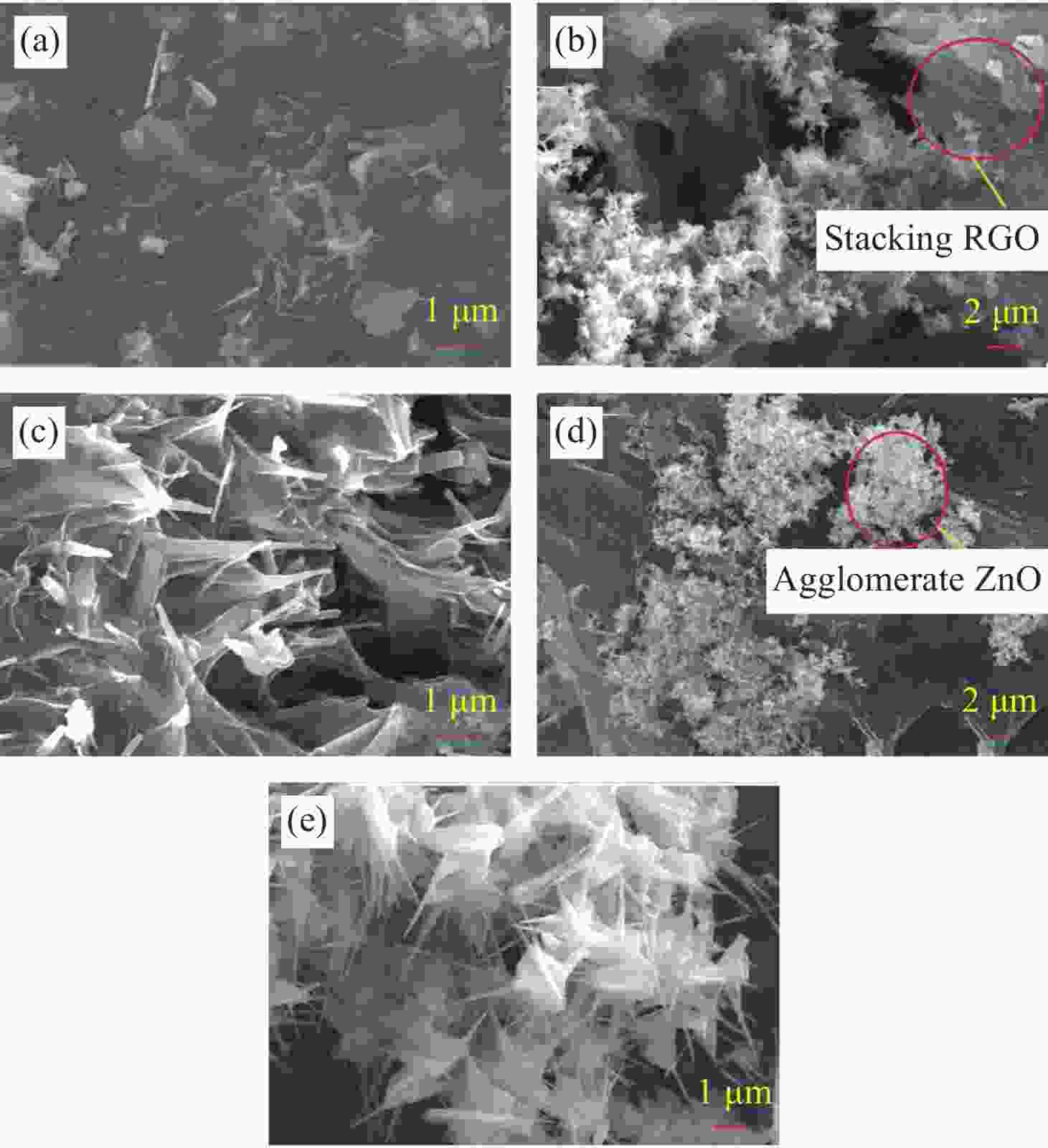
Preparation and wave absorption properties of ZnO@RGO composites
-
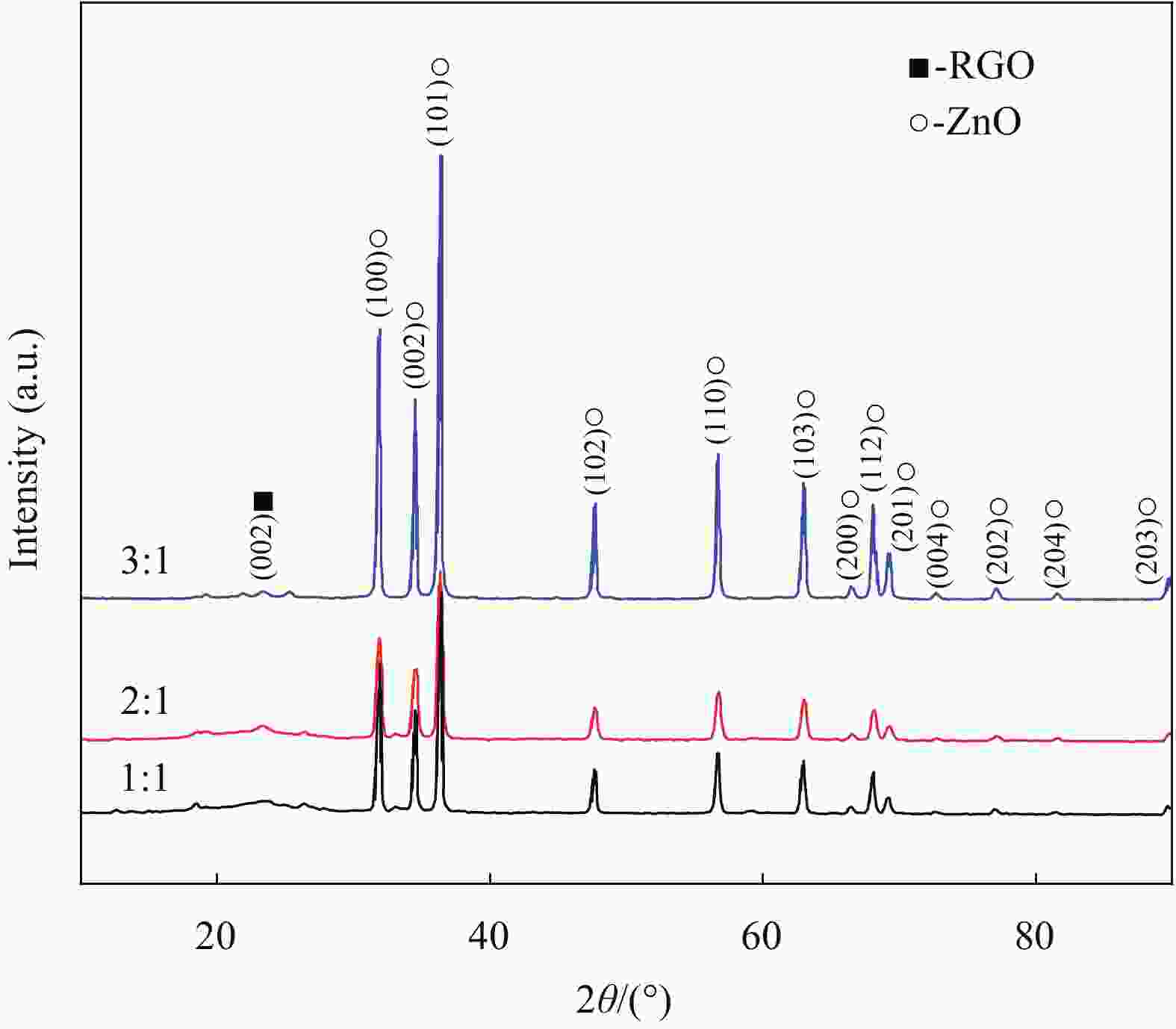
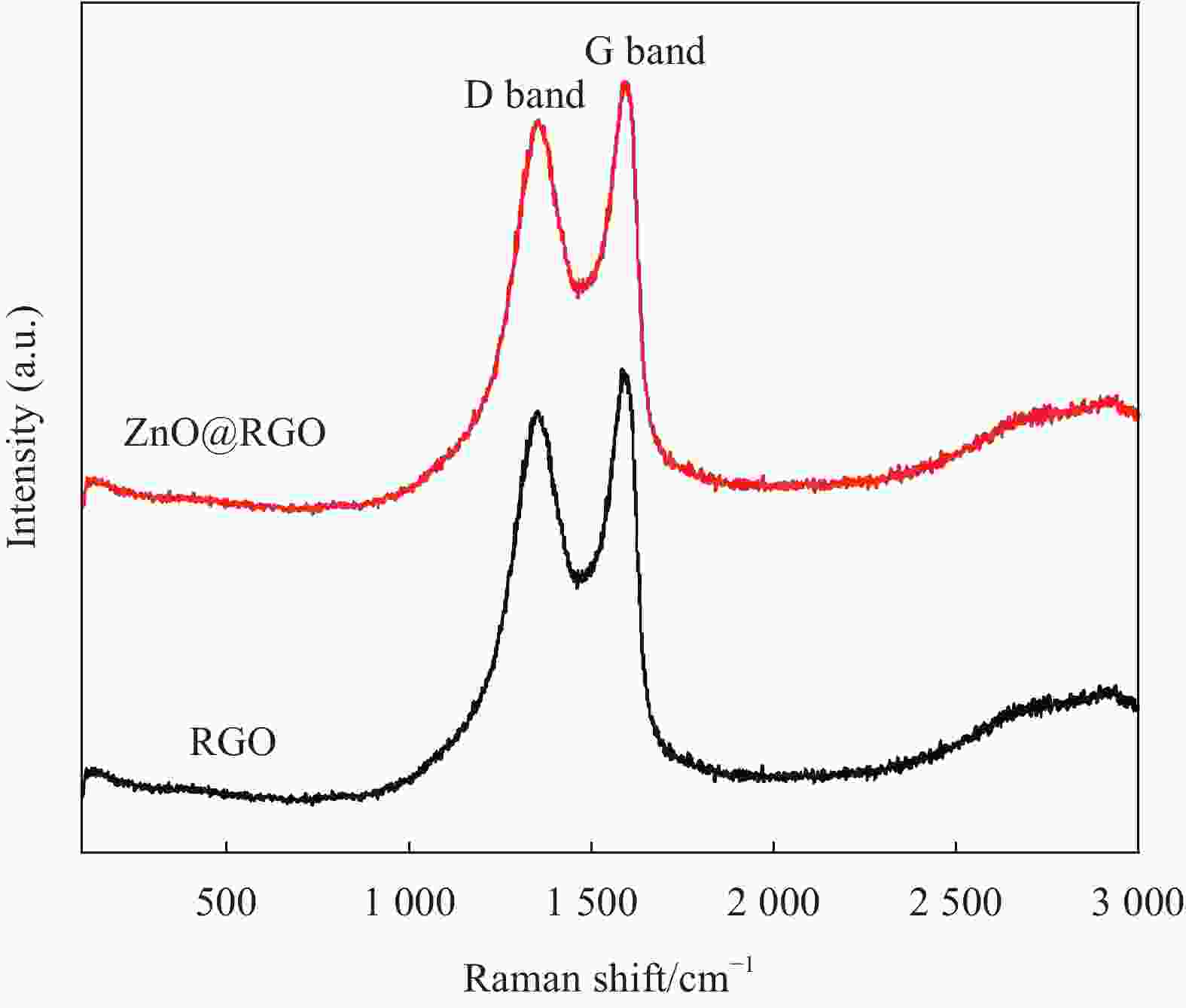
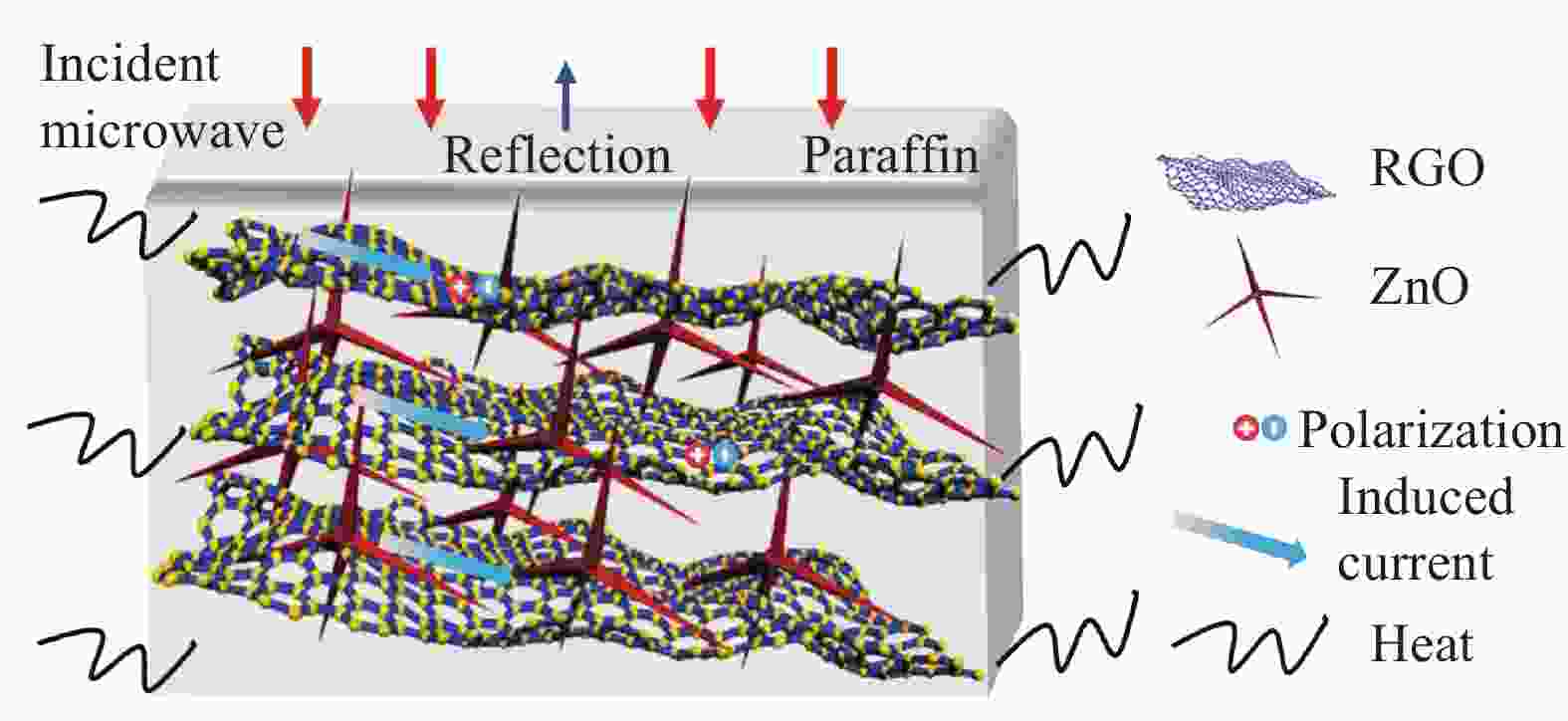
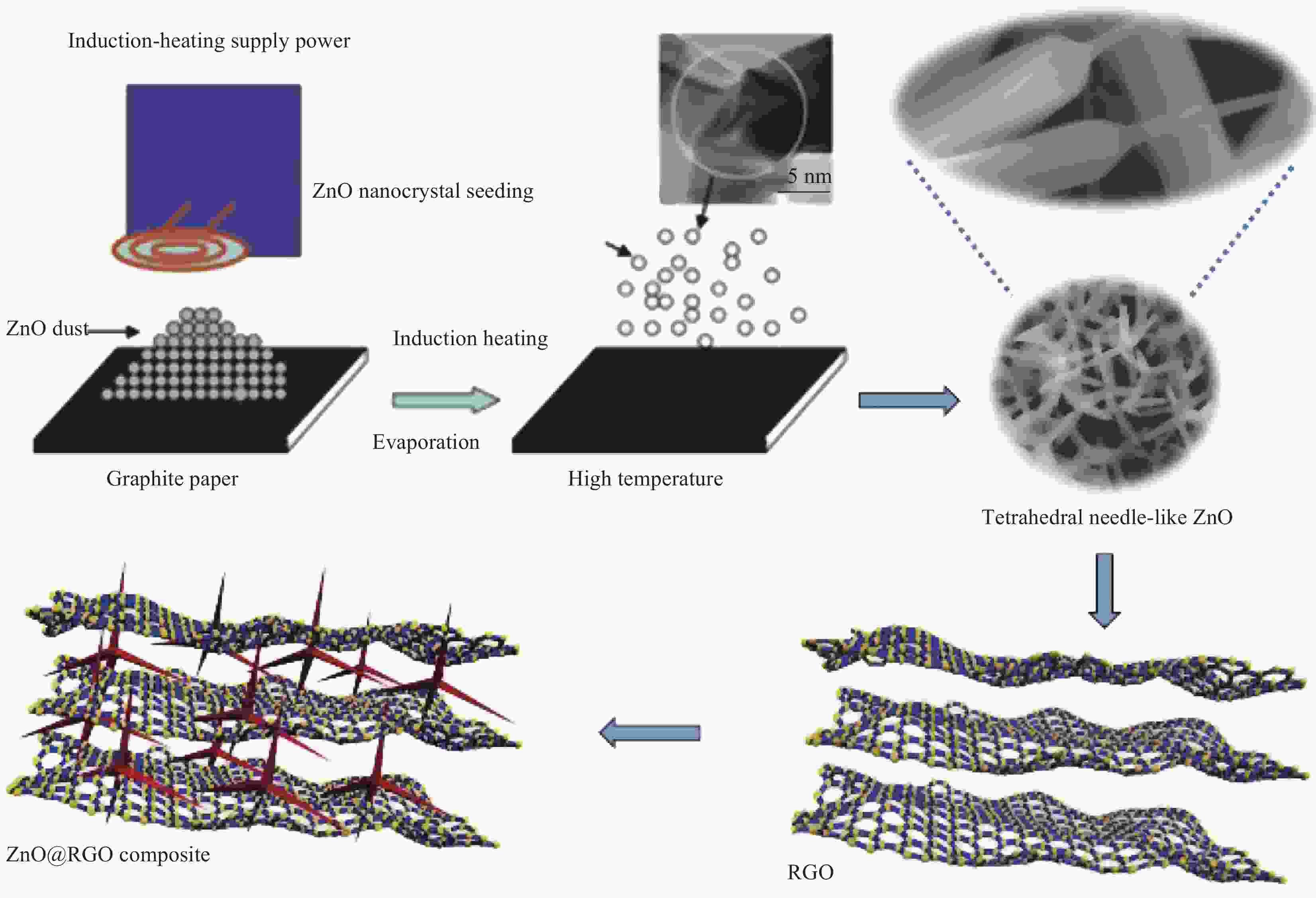
摘要: 随着无线信息技术的飞速发展,电磁干扰问题日益突出,引起了全球的广泛关注。人体长时间暴露于电磁辐射下,会对中枢神经系统、心血管系统和视觉系统等造成不同程度的损伤。解决这一问题的关键在于开发能够吸收电磁波的材料。为了改善还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)的微波吸收性能,采用感应加热的方式成功获得四面体针状氧化锌(ZnO),并通过简单水热法制备了不同比例的ZnO@RGO复合材料。利用SEM、XRD和Raman分别对ZnO@RGO复合材料的形貌、尺寸和结构进行了分析,并且探讨了ZnO含量和石蜡填充量对其电磁参数和吸波性能的影响。ZnO∶GO质量比为3∶1时的ZnO@RGO复合材料拥有最为优异的吸波性能(−44.5 dB; 3 mm)。电磁参数表明ZnO@RGO复合材料的衰减机制可以归结为电导损耗和极化效应。ZnO@RGO复合材料具有较低的反射损耗值和较薄的厚度,在军事隐身领域具有很大的潜力。Abstract: With the rapid development of wireless information technology, electromagnetic interference has become a prominent problem, which has attracted worldwide attention. Exposure to electromagnetic radiation for a long time will damage the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and visual system to varying degrees. The key to solving this problem is to develop materials that can absorb electromagnetic waves. In order to improve the microwave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide (RGO), the tetrahedral needle-like ZnO was successfully obtained by induction heating, and ZnO@RGO composites with different proportions were prepared by simple hydrothermal method. The morphology, size, and phase structure of ZnO@RGO composites were analyzed by SEM, XRD and Raman. And the effects of the mass ratio of ZnO and the paraffin filling amount on the electromagnetic parameters and absorbing properties of ZnO@RGO composites were also discussed. The ZnO@RGO composite with ZnO∶GO mass ratio of 3∶1 has the best wave absorption performance (−44.5 dB; 3 mm). Electromagnetic parame-ters show that the attenuation mechanism of ZnO@RGO composites can be attributed to the conductance loss and polarization effect. ZnO@RGO composites have a low reflection loss value and thin thickness, which has great potential for military stealth.
-
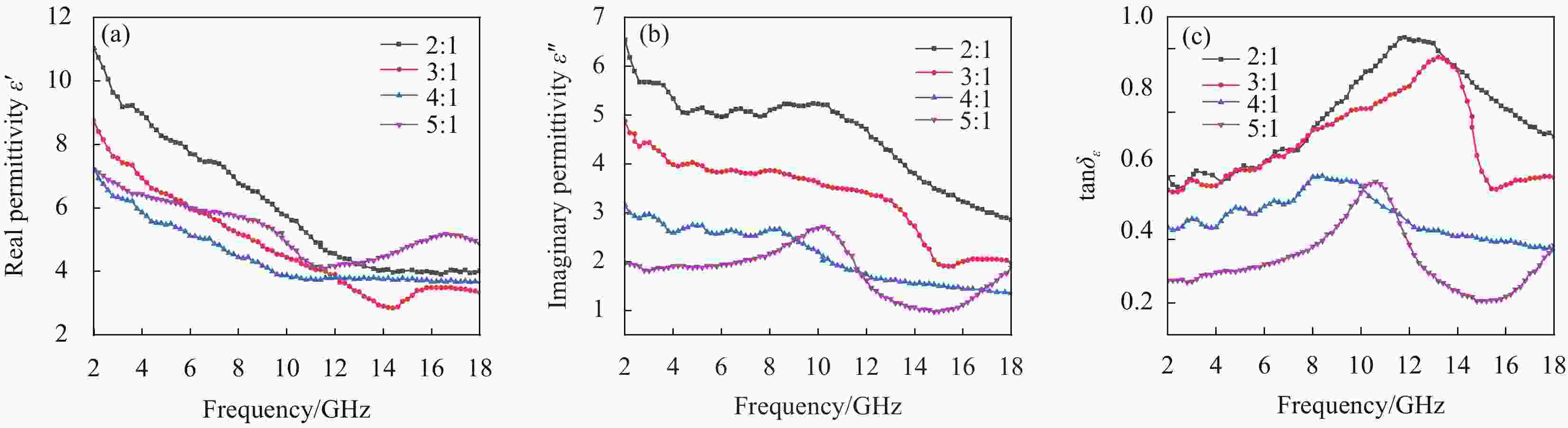
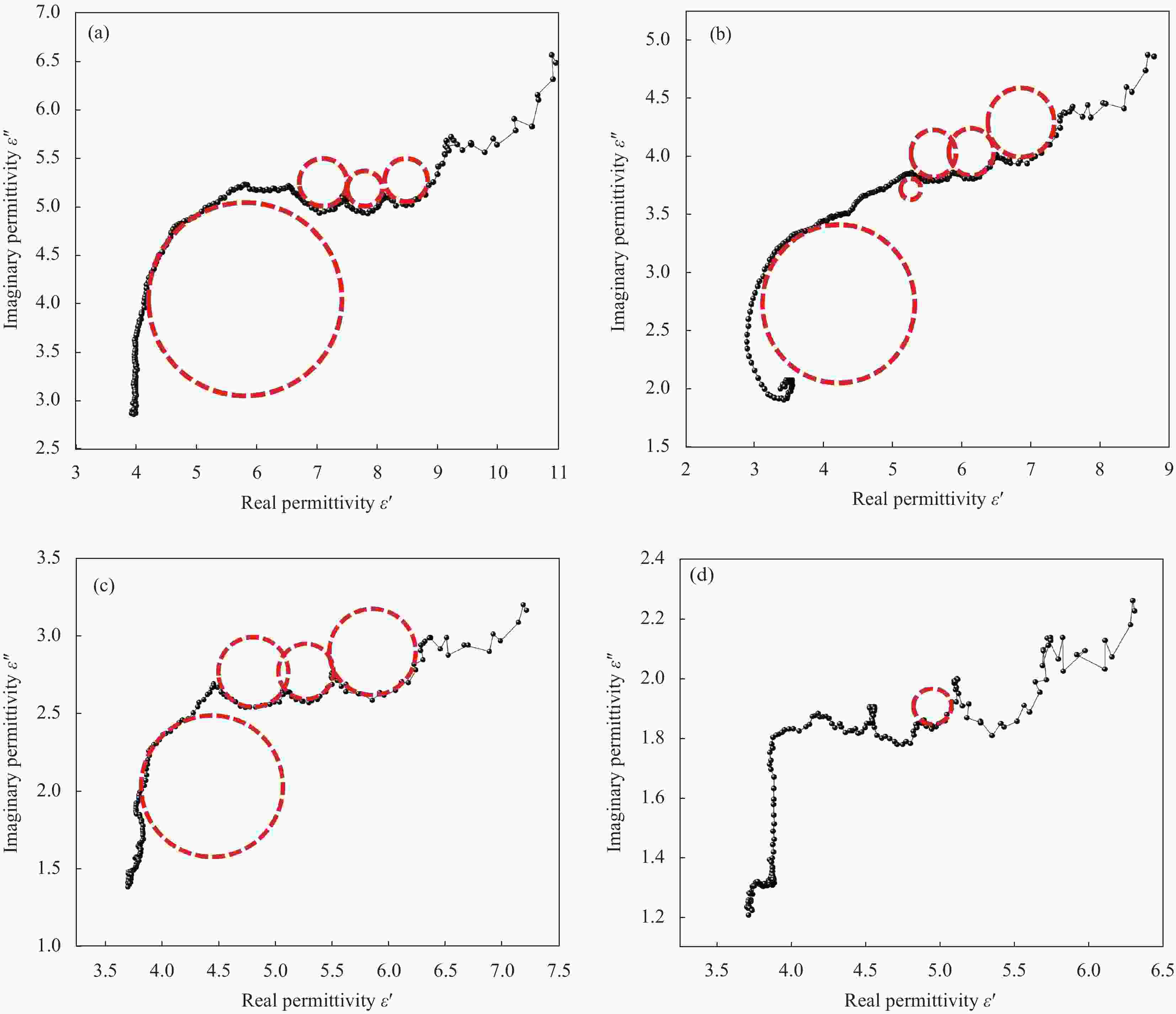
图 7 不同ZnO和RGO质量比的ZnO@RGO复合材料的相对复介电常数:(a) 介电常数实部(
$ \varepsilon ^{'} $ ); (b) 介电常数虚部($ \varepsilon ^{''}$ ); (c) 介电损耗角正切tan$ {\delta }_{\varepsilon} $ Figure 7. Relative dielectric complex constant of ZnO@RGO composites with different mass ratios of ZnO and RGO: (a) Real part of the dielectric constant (
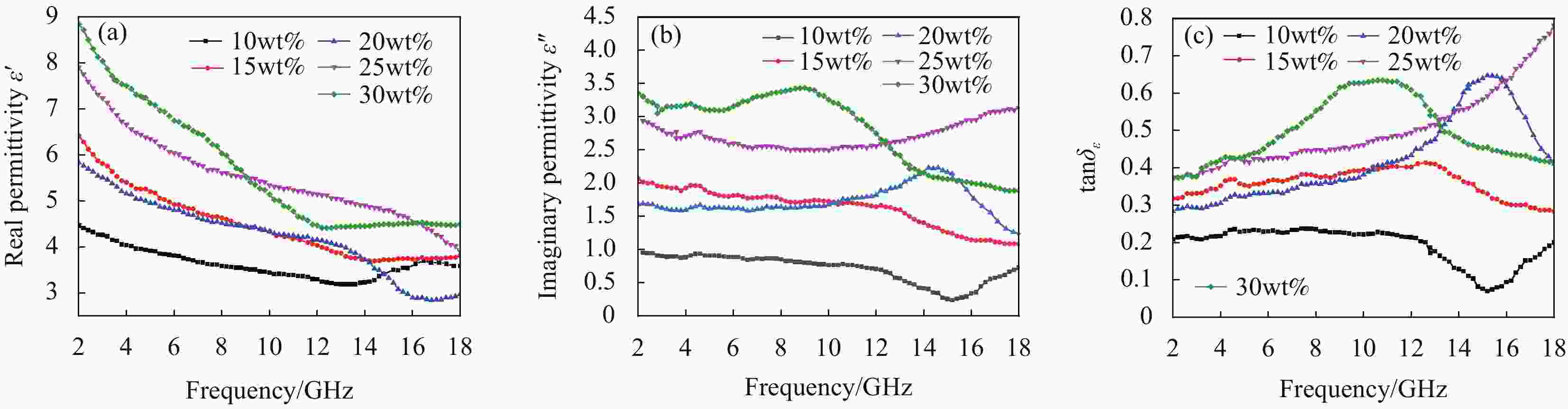
$ \varepsilon ^{'} $ ); (b) Imaginary part of the dielectric constant ($ \varepsilon ^{''}$ ); (c) Tangent to the dielectric loss angle (tan$ {\delta }_{\varepsilon} $ )图 8 不同石蜡填充量的ZnO@RGO复合材料的相对复介电常数:(a) 实部(
$ \varepsilon ^{'} $ ); (b) 虚部($ \varepsilon ^{''}$ ); (c) 介电损耗角正切tan$ {\delta }_{\varepsilon} $ Figure 8. Relative dielectric complex constant of ZnO@RGO composites with different paraffin filling contents: (a) Real part (
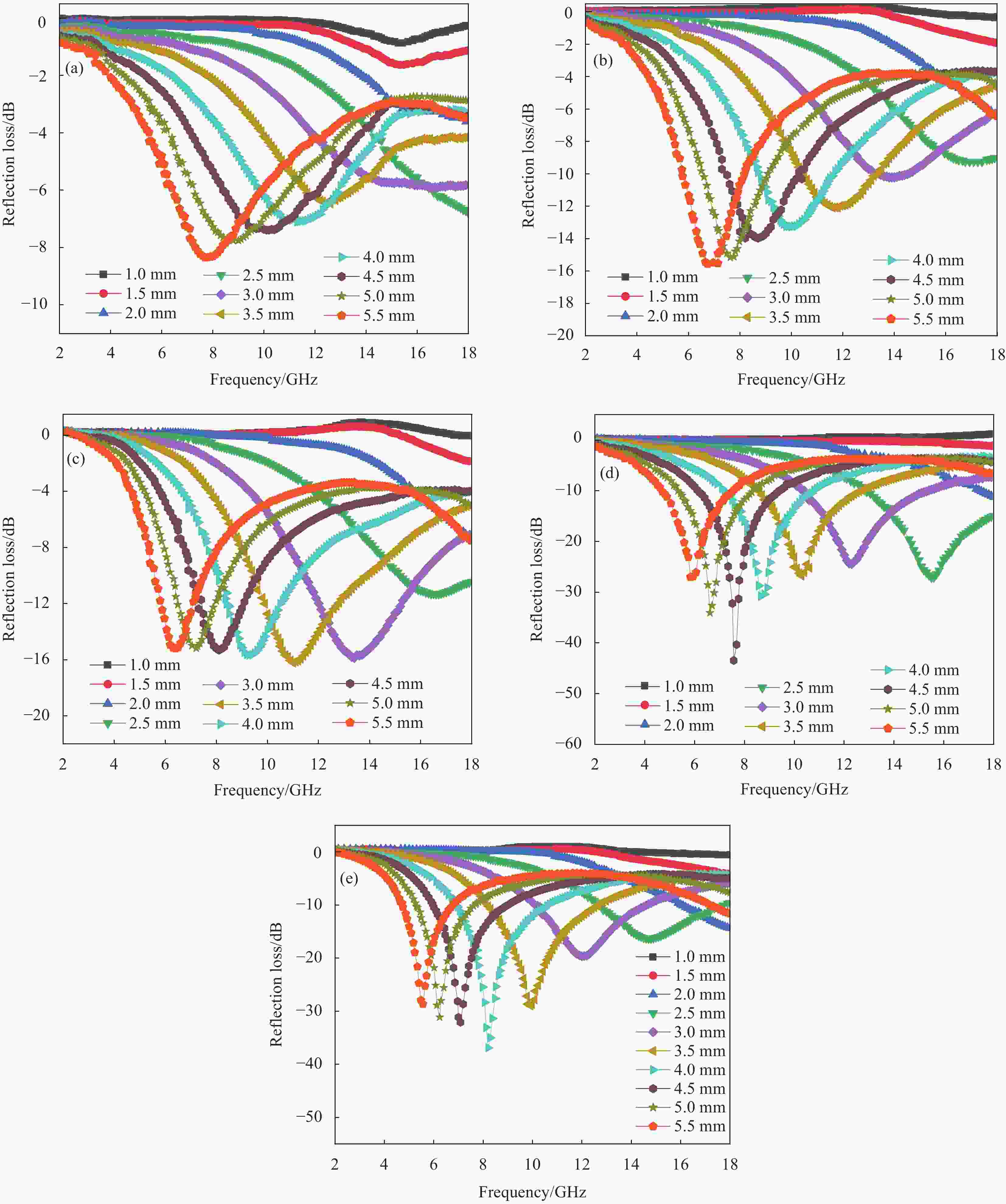
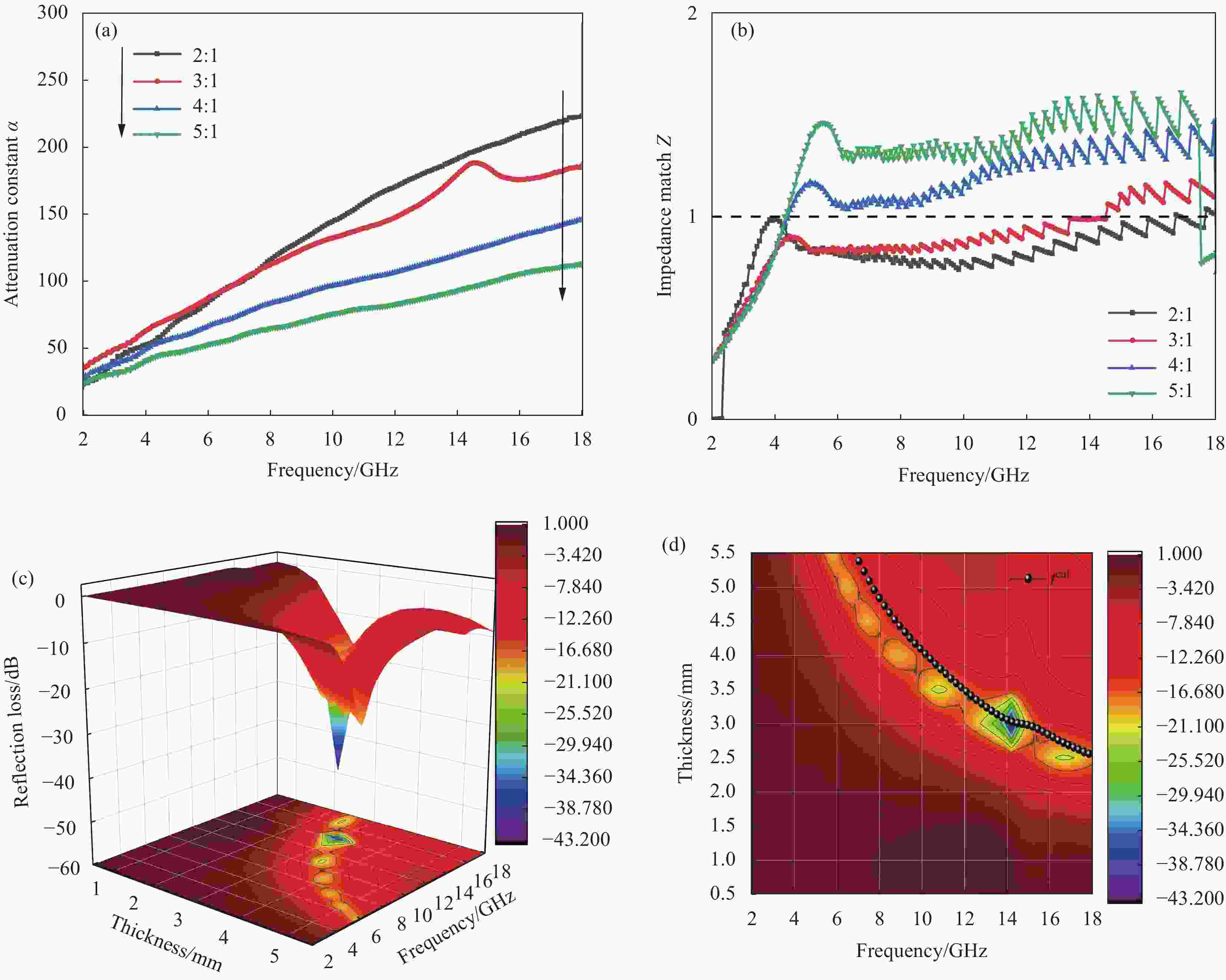
$ \mathit{\varepsilon }^{'} $ ); (b) Imaginary part ($ \varepsilon ^{''}$ ); (c) Tangent to the dielectric loss angle (tan$ {\delta }_{\varepsilon} $ )图 9 不同质量比例ZnO@RGO 复合材料的衰减常数(a)和阻抗匹配 (b); 试样3∶1的3D反射损耗图谱(c)和四分之一波长模型(d)
Figure 9. (a) Attenuation constant of ZnO@RGO composites with different mass ratios; (b) Impedance matching; erent mass ratios; 3D Reflection loss (c) and model of a 1/4 wavelength (d) of the samples with a filling proportion of 3∶1
表 1 近期文献报道的RGO基复合材料的吸波性能
Table 1. Microwave absorbing properties of RGO based composites in recent publications
Absorber Loading/wt% RL/dB Bandwidth/GHz Thickness/mm References Cocoon-like RGO 7 −29.05 5.27 2.00 [30] CeO2−RGO 50 −45.90 4.5 2.00 [31] RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 50 −23.80 2.60 1.50 [32] MoS2/RGO 60 −67.10 5.92 1.95 [33] RGO/Ni 10 −39.03 4.30 2.00 [34] ZnO/RGO 75 −44.50 7.44 3.00 This study Notes: MWCNTs—Multiwalled carbon nanotube; RGO—Reduced graphene oxide. -
[1] WANG Y, GAO X, ZHANG W Z, et al. Synthesis of hierarchical CuS/RGO/PANI/Fe3O4 quaternary composite and enhanced microwave absorption performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,757:372-381. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.05.080 [2] LV H L, ZHANG H Q, JI G B, et al. Interface strategy to achieve tunable high frequency attenuation[J]. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces,2016,8(10):6529-6538. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b12662 [3] WU G L, CHENG Y H, REN Y Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of γ-Fe2O3@C nanorod-carbon sphere compo-site and its application as microwave absorbing material[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015,652(15):346-350. [4] HAN S J, WANG S Y, LI W H, et al. Synthesis of PPy/Ni/RGO and enhancement on its electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Ceramics International,2018,44(9):10352-10361. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2018.03.046 [5] QU B, ZHU C, LI C, ZHANG X, et al. Coupling hollow Fe3O4-Fe nanoparticles with graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbing material[J]. ACS Applied Materials Interfaces,2016,8(6):3730-3735. doi: 10.1021/acsami.5b12789 [6] XIA L, ZHANG X Y, YANG Y N, et al. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties of laminated SiCNW-Cf/lithium-aluminume-silicate (LAS) composites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,748(5):154-162. [7] CHEN Z P, XU C, MA C Q, et al. Lightweight and flexible graphene foam composites for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Advanced Materials,2013,25(9):1296-1300. doi: 10.1002/adma.201204196 [8] QING Y, ZHOU W, LUO F, et al. Microwave electromagnetic properties of carbonyl iron particles and Si/C/N nano-powder filled epoxy-silicone coating[J]. Physica B: Condensed Matter,2010,405(4):1181-1184. doi: 10.1016/j.physb.2009.11.032 [9] DING D H, LUO F, ZHOU W C, et al. Research status and outlook of high temperature radar absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials,2014,29(5):461-169. [10] SHEN W, REN B Y, WU S Z, et al. Facile synthesis of rGO/SmFe5O12/CoFe2O4 ternary nanocomposites: Composition control for superior broadband microwave absorption performance[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,453(30):464-476. [11] ALI K, IQBAL J, JAN T, et al. Synthesis of CuFe2O4-ZnO nanocomposites with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2017,705(25):559-565. [12] LUO J, XU Y, YAO W, et al. Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide-magnetic porous nanospheres-polyaniline com-posites[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2015,117(29):315-321. [13] FU M, JIAO Q, ZHAO Y, et al. Vapor diffusion synthesis of CoFe2O4 hollow sphere/graphene composites as absorbing materials[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(3):735-744. doi: 10.1039/C3TA14050D [14] LIAO L, PENG H L, LIU Z F, et al. Chemistry makes graphene beyond graphene[J]. Journal of American Che-mistry Society,2014,136(35):12194-12200. doi: 10.1021/ja5048297 [15] SU Z B, TAN L, TAO J, et al. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of FeNi nanocrystals decorating reduced graphene oxide[J]. Physical Status Solidi B,2018,255(6):1700553-1700556. doi: 10.1002/pssb.201700553 [16] SU Z B, TAO J, XIANG J Y, et al. Structure evolution and microwave absorption properties of nickel nanoparticles incorporated carbon spheres[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2016,84:445-448. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.08.036 [17] WEN F S, HOU H, XIANG J Y, et al. Fabrication of carbon encapsulated Co3O4 nanoparticles embedded in porous graphitic carbon nanosheets for microwave absorber[J]. Carbon,2015,89:372-377. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.03.057 [18] LU M M, CAO W Q, SHI H L, et al. Multi-wall carbon nano-tubes decorated with ZnO nanocrystals: mild solution-process synthesis and highly efficient microwave absorption properties at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(27):10540-10547. doi: 10.1039/c4ta01715c [19] ZHANG L, ZHANG X H, ZHANG G J, et al. Investigation on the optimization, design and microwave absorption pro-perties of reduced graphene oxide/tetrapod-like ZnO composites[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(14):10197-10203. doi: 10.1039/C4RA12591F [20] LIU J, CAO W Q, JIN H B, et al. Enhanced permittivity and multi-region microwave absorption of nanoneedle-like ZnO in the X-band at elevated temperature[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2015,3(18):4670-4677. doi: 10.1039/C5TC00426H [21] CHEN X Y, GUO H C, WANG T, et al. In-situ fabrication of reduced graphene oxide (rGO)/ZnO heterostructure: surface functional groups induced electrical properties[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2016,196(1):558-564. [22] GE C, LI H J, LI M J, et al. Synthesis of a ZnO nanorod/CVD graphene composite for dihydroxybenzene isomers[J]. Carbon,2015,95:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.08.006 [23] ZHANG B P, LU C X, Li H, et al. Improving microwave adsorption property of ZnO particle by doping graphene[J]. Materials Letters,2014,116(1):16-19. [24] QIN H, LIAO Q L, ZHANG G J, et al. Microwave absorption properties of carbon black and tetrapod-like ZnO whiskers composites[J]. Applied Surface Science,2013,286(1):7-11. [25] HU W B, LIU Y, WITHERS R L, FRANKCOMBE T J, et al. Electron-pinned defect-dipoles for high-performance colossal permittivity materials[J]. Nature Materials,2013,12(9):821-826. doi: 10.1038/nmat3691 [26] QUAN B, LIU W, LIU Y S, et al. Quasi-noble-metal graphene quantum dots deposited stannic oxide with oxygen vacancies: synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic properties[J]. Journal of Colloid Interface Science,2016,481(1):13-19. [27] HAN M K, YIN X W, KONG L, et al. Graphene-wrapped ZnO hollow spheres with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(39):16403-16409. doi: 10.1039/C4TA03033H [28] FENG W, WANG Y M, CHEN J C, et al. Microwave absorbing property optimization of starlike ZnO/reduced graphene oxide doped by ZnO nanocrystal composites[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2017,19(22):14596-14605. doi: 10.1039/C7CP02039B [29] ZHAO G L, XIA L, WU S S, et al. Ultrafast and mass production of ZnO nanotetrapods by induction-heating under air ambient[J]. Materials Letters,2014,118(1):126-129. [30] SHAH A, WANG Y H, HUANG H, et al. Microwave absorption and flexural properties of Fe nanoparticle/carbon fiber/epoxy resin composite plates[J]. Composite Structure,2015,131(1):1132-1141. [31] WANG Z Q, ZHAO P F, HUANG H, et al. Cerium oxide immobilized reduced graphene oxide hybrids with excellent microwave absorbing performance[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2018,20(20):14155-14165. doi: 10.1039/C8CP00160J [32] SHU R W, LI W J, ZHOU X, et al. Facile preparation and microwave absorption properties of RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 hybrid nanocomposites[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,743(30):163-174. [33] QUAN B, LIANG X H, XU G Y, et al. A permittivity regula-ting strategy to achieve high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers with compatibility of impedance matching and energy conservation[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2017,41(3):1259-1266. doi: 10.1039/C6NJ03052A [34] XU W, WANG G S, YIN P G. Designed fabrication of reduced graphene oxides/Ni hybrids for effective electromagnetic absorption and shielding[J]. Carbon,2018,139:759-767. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.07.044 -





 下载:
下载: