Current status of carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites recycling and re-manufacturing
-
摘要: 优异性能的碳纤维增强聚合物基复合材料(CFRPs)在各领域的快速应用发展给复合材料废弃物的回收带来了挑战,尤其是碳纤维增强热固性复合材料。为有效回收碳纤维增强复合材料,促进复合材料产业的可持续发展,本文从多个角度对废弃CFRPs回收再利用研究现状进行综述,包括各回收工艺技术特点、应用领域及可降解树脂实现回收CFRPs的新策略。最后对CFRPs回收再利用技术的未来发展趋势进行了展望。Abstract: The rapid application and development of high-performance carbon fiber reinforced polymer composites (CFRPs) brought challenges for the recovery of composite waste. Recycling of carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composites has been particularly demanding. This paper reviewed the research status of CFRPs waste recycling from multiple perspectives in order to effectively promote their sustainability. Characteristics of various recycling technologies, application fields and new strategies for recycling CFRPs with biodegradable resin were reviewed. Finally, the future development trend of CFRPS recycling technology was prospected.
-
Key words:
- carbon fiber /
- carbon composites /
- reinforced polymer /
- composites waste /
- recycling techniques
-
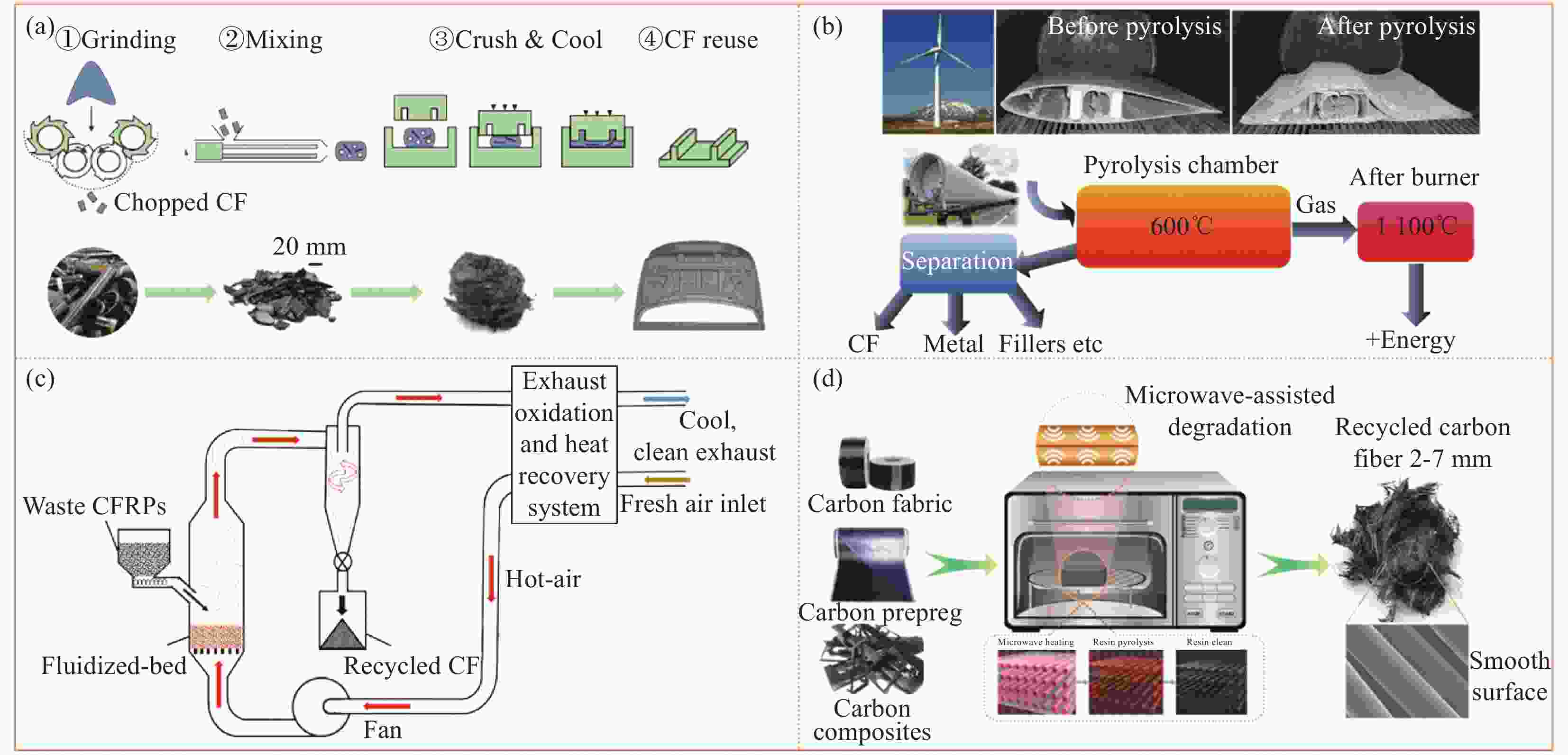
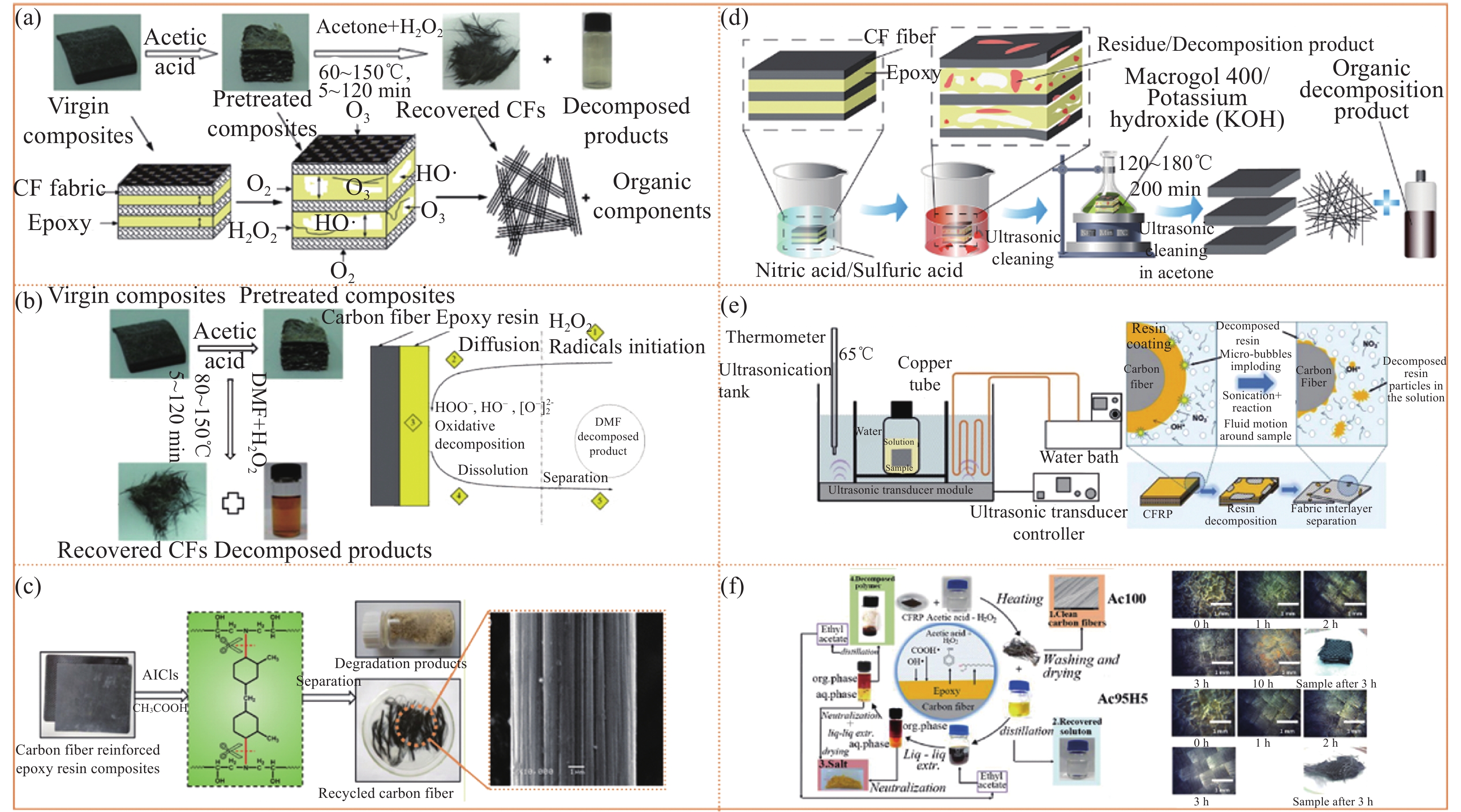
图 2 (a) 过氧化氢与丙酮混合溶液降解碳纤维增强复合材料(CFRPs)[34];(b) N,N-二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)与过氧化氢混合溶液降解 CFRPs[35];(c) CFRPs中C—N键选择性断裂降解[39];(d) 硝酸、聚乙二醇和KOH实现温和条件下CFRPs降解[36];(e) 超声化学法降解CFRPs[40];(f) 过氧乙酸降解CFRPs[41]
Figure 2. (a) Degradation of carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRPs) by a mixture solution of hydrogen peroxide and acetone[34]; (b) Degradation of mixed solution with N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF) and hydrogen peroxide[35]; (c) Degradation by selective breakage of C—N bond in CFRPs[39]; (d) Degradation of CFRPs under mild conditions achieved by nitric acid, polyethylene glycol and KOH[36]; (e) Degradation of CFRPs by ultrasonic chemical method[40]; (f) Degradation of CFRPs by peroxyacetic acid[41]
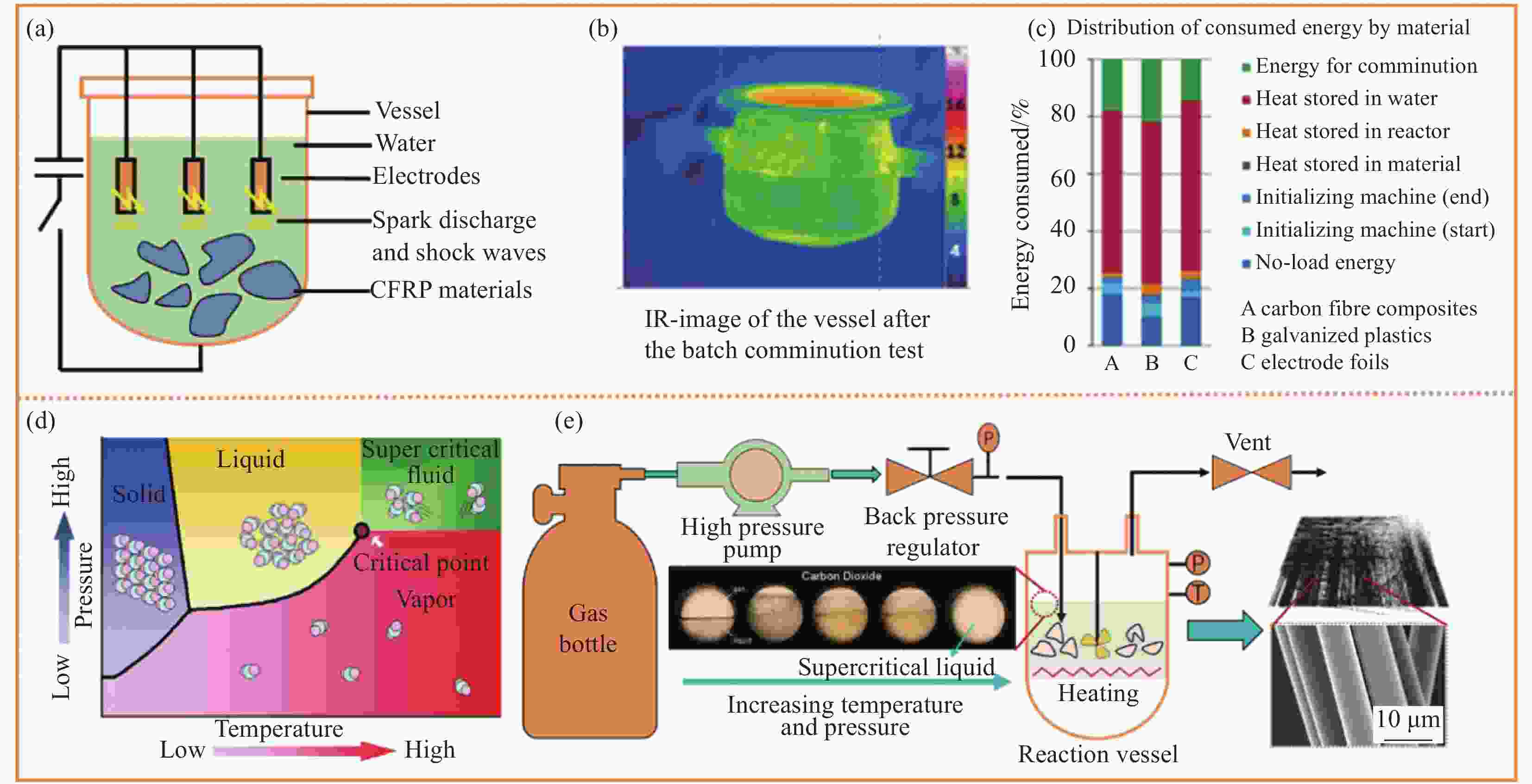
图 3 (a) 电化学法降解废弃CFRPs技术示意图;(b) 后处理工艺红外成像;(c) 不同材料能量消耗分布超/亚临界流体法工艺条件示意图;(d) 超临界流体概述图;(e) 超临界流体回收CFRPs示意图
Figure 3. (a) Diagram of degradation of waste CFRPs by electrochemical technology; (b) Infrared imaging by post-treatment process; (c) Diagram of the process conditions of super/subcritical fluid method with different material energy consumption distribution; (d) Overview of supercritical fluids; (e) Diagram of recovery of CFRPs by supercritical fluid
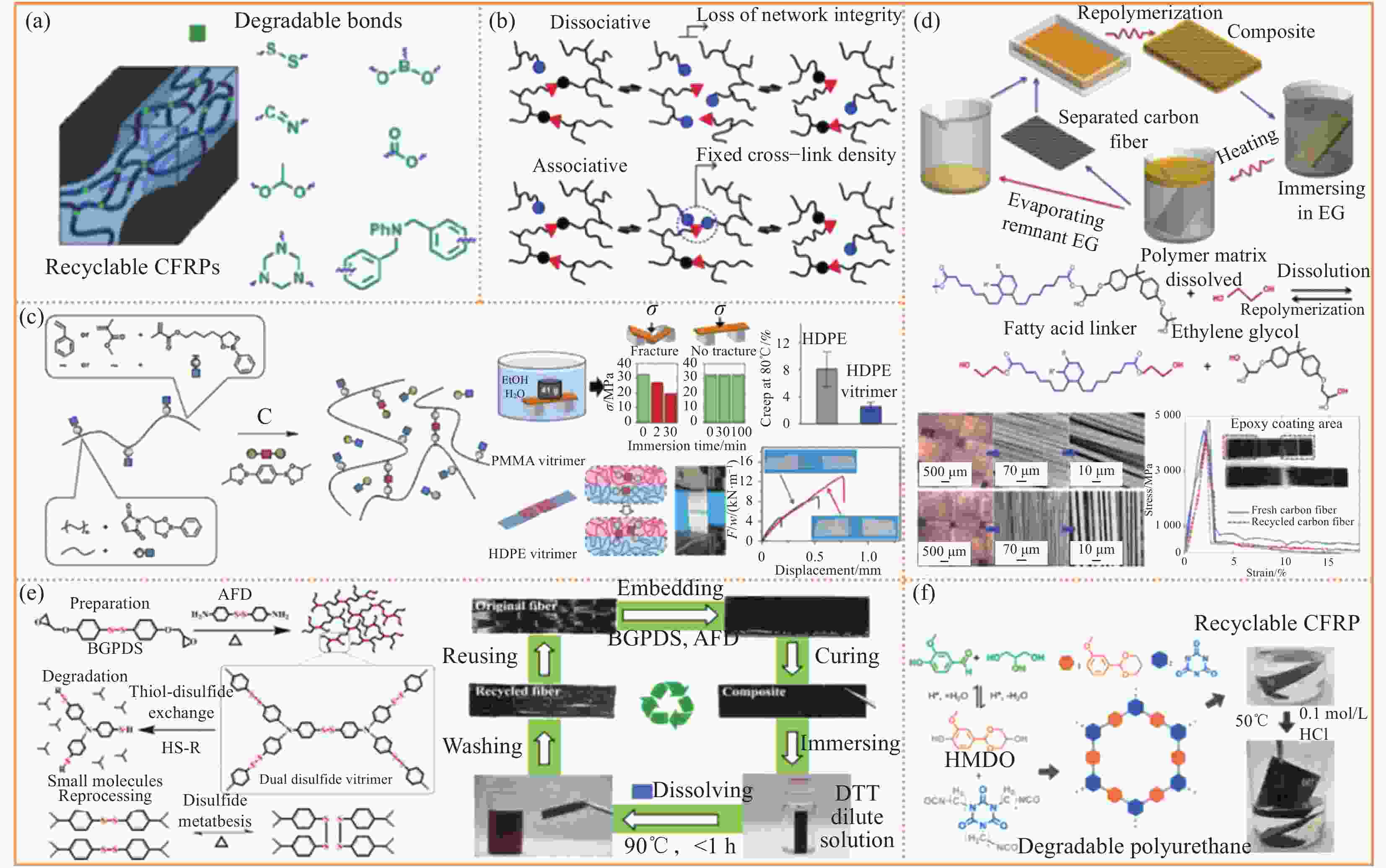
图 4 (a) 基于可降解CFRP设计[55];(b) 解离型共价适应网络(CANs)和结合型CANs[60];(c) Vitrimer合成及优异的耐溶剂性、抗蠕变性和可焊接性[62];(d) 基于脂肪酸的可回收CFRP[63];(e) 基于芳族二硫交联键的可回收CFRP[64];(f) 生物基可回收CFRP[65]
Figure 4. (a) Design based on degradable CFRPs[55]; (b) Dissociated covalent adaptation networks (CANs) and bound CANs [60]; (c) Vitrimer synthesis and excellent solvent resistance, creep resistance and weldability[62]; (d) Recoverable CFRPs based on fatty acid[63]; (e) Recoverable CFRPs based on aromatic disulfide cross-linking bond[64]; (f) Bio-based recoverable CFRPs[65]
PMMA—Polymethyl methacrylate; HDPE—high-density polyethylene; EG—Ethylene glycol; BGPDS—Bis(4-glycidyloxyphenyl)disulfide; AFD—4-aminophenyl disulfide;DTT—Dithiothreitol; HDMO—2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-dioxan-5-ol; σ—Stress
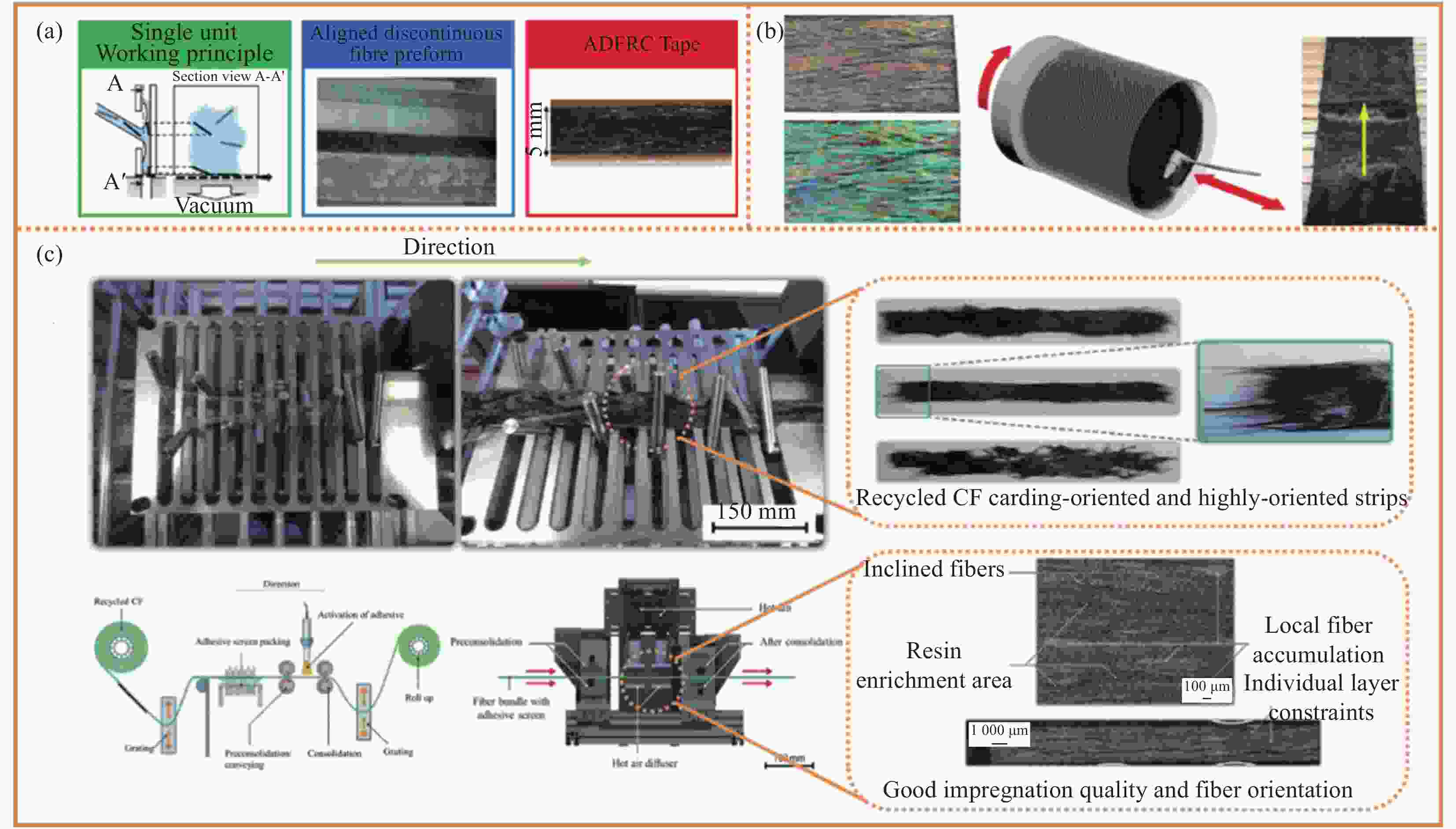
图 5 (a) 高性能不连续纤维法(HiPerDiF)纤维取向法[71];(b) 机械与工程学院开发的工艺(I2M)取向法制备碳纤维带[72];(c) ELG碳纤维公司、德国纺织纤维研究所(DITF)、德国凯撒斯劳滕的复合材料研究所(IVW)和本田欧洲研发公司合作开发的长纤维取向回收再利用工艺
Figure 5. (a) High performance discontinuous fiber method (HiPerDiF) fiber orientation method[72]; (b) Preparation of carbon fiber tape by institut de mécanique et d’ingénierie (I2M) orientation method[72]; (c) ELG carbon fibers company, German Institute for Textile Fibers (DITF), Institute for Composite Materials (IVW), Kaiserslautern, Germany and long fiber orientation recovery and recycling process developed in collaboration with Honda Europe R&D
ADFRC—Aligned discontinuous fibre composite
表 1 现有主要机械法回收技术公司及产品应用
Table 1. Major existing companies in mechanical recovery technology and product applications
Company Country Products Characteristics Eco-Wolf, Inc. American Short fiber(<3 cm) Fiber damaged greatly; short fiber obtained; Generally suitable for recycling low-cost raw materials: glass fiber Reprocover Belgium Hatches, Street facilities, Double track train tracks, etc Hambleside Danelow England Packing, Injection molding, etc Filon Products Ltd. England Trash cans, Concrete, etc MCR-group Plactic Omnium France Asphalt, concrete, composite materials, etc 表 2 热处理回收法优缺点及现有主要热处理法回收技术公司
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of heat treatment recovery method and existing major companies on technology of heat treatment recovery method
Method Company Scale/(kg·year−1) Products Characteristic Pyrolysis Carbon Conversions
(USA)2 000 000 Nonwoven mat Commercial production, harmful gases, properties decrease (10%-20%) ELG Carbon Fibre (UK) 2 000 000 Short fiber, nonwoven, milled fibre Nantong Fuyuan New Material Technology Co. Ltd 1 500 000 Nonwoven, non-bearing components CFK Valley Stade Recycling GmbH & Co. KG (Germany) 1 000 000 Chopped and grinded fiber Fluidized bed pyrolysis University of Nottingham (UK) 1 000 000 – Cleaner fiber surface, short fiber, properties decreased greatly Milled Carbon Ltd. Lab Milled fibre Sicomp Lab – Microwave pyrolysis Taiwan Yonghong Advanced Materials Co. Ltd (80-100) ×103 Car seat, tailplane, automobile and leisure products Recovery rate >90%, cleaner fiber surface, strength retention rate >90%, non-toxic, low cost Firebird Advanced Materisls Inc. Lab – University of Nottingham (UK) Lab – 表 3 化学回收法特点及用途
Table 3. Characteristics and applications of chemical recovery method
Method Advantage Disadvantage Products Company Solvolysis Strength basically maintained; Process simple Degradation mechanism is complex, Operation is difficult, Environmental pollution, Laboratory stage Lightweight components, SMC products, etc Adesso, Adherent Technologies, Siemens, Hitachi Chemical Electrochemical recycling Recycling larger size CFRPs, Simple procedure, Green and friendly High voltage, High energy consumption, Fiber property decreases greatly Construction, carbon fiber mats, etc – Supercritical/
Sub-critical solventLittle fiber damage, Controllable fiber size Incomplete degradation, High cost, Harsh conditions, Laboratory stage Additive and filler University of Nottingham, CMBC Laboratory, Panasonic Electric Works Co. Note: SMC—Sheet molding compound. -
[1] TANG S F, HU C L. Design, preparation and properties of carbon fiber reinforced ultra-high temperature ceramic composites for aerospace applications: A review[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2017,33:117-130. [2] MACHADO J, GAMARRA P, MARQUES E, et al. Numerical study of the behaviour of composite mixed adhesive joints under impact strength for the automotive industry[J]. Composite Structures,2018,185:373-380. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.11.045 [3] ONWUDILI J A, MISKOLCZI N, NAGY T, et al. Recovery of glass fibre and carbon fibres from reinforced thermosets by batch pyrolysis and investigation of fibre re-using as reinforcement in LDPE matrix[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,91:154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.01.055 [4] PICKERING S, TURNER T, MENG F. Developments in the fluidised bed process for fibre recovery from thermoset composites[C]//2nd Annual Composites and Advanced Materials Expo, CAMX 2015: 2384-2394. [5] DT新材料. 从碳纤维复合材料回收政策看行业现状[EB/OL]. (2017-11-16) [2021-05-28]. https://www.sohu.com/a/204670276_777213.DT new materials. Review: The current situation of the industry from the recycling policy of carbon fiber composite materials[EB/OL]. (2017-11-16) [2021-05-28]. https://www.sohu.com/a/204670276_777213(in Chinese). [6] LEON M, KIM B, HELGA N P, et al. Materials for wind turbine blades: An overview[J]. Materials (Basel),2017,10(11):1285. doi: 10.3390/ma10111285 [7] 郭强, 徐恒元, 何凯, 等. 树脂基复合材料废弃物回收再利用现状及发展趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2019(S02):634-638.GUO Qiang, XU Hengyuan, HE Kai, et al. Status and development trend of resin matrix composite waste recycling[J]. Materials Reports,2019(S02):634-638(in Chinese). [8] SWATI V, BHUVANESHWARI B, KUMAR G R. Recycling, reclamation and re-manufacturing of carbon fibres[J]. Current Opinion in Green & Sustainable Chemistry,2018,13:86-90. [9] MENG F, ELSO O, ZHAO Y, et al. Comparing life cycle energy and global warming potential of carbon fibre compo-site recycling technologies and waste management options[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6:9854-9865. [10] MELENDI-ESPINA S, MORRIS C, TURNER T, et al. Recycling of carbon fibre composites[C]. In: Proceedings of Carbon 2016. Penn State University, State College, United States, Conference, Conference 2016. [11] PALMER J, GHITA O R, SAVAGE L. Successful closed-loop recycling of thermoset composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2009; 40: 490–498. [12] CHEN J L, WANG J H, NI A Q. Recycling and reuse of composite materials for wind turbine blades: An overview[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2019,38(12):567-577. doi: 10.1177/0731684419833470 [13] 徐佳, 孙超明. 树脂基复合材料废弃物的回收利用技术[J]. 玻璃钢/复合材料, 2009(4):100-103.XU Jia, SUN Chaoming. Recycling technology of resin matrix composites waste[J]. Fiber Reinforced Plastics Composites,2009(4):100-103(in Chinese). [14] OLIVEUX G, LUKE O D, GARY L A. Current status of recycling of fibre reinforced polymers: Review of technologies, reuse and resulting properties[J]. Progress in Materials Science,2015,72:61-99. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.01.004 [15] MICHAEL O, JANET M T, EYLEM A, et al. Thermoset composite recycling-Driving forces, development, and evolution of new opportunities[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2018,52(8):1033-1043. doi: 10.1177/0021998317720000 [16] NAIA G, ALEX L U, JON S I, et al. Thermo-catalytic treatment of vapors in the recycling process of carbon fiber-poly (Benzoxazine) composite waste by pyrolysis[J]. Catalysts,2018,8(11):523. doi: 10.3390/catal8110523 [17] LORIS G, CHIARA L, LAURA M, et al. Pyrolysis of fiberglass/polyester composites: Recovery and characterization of obtained products[J]. FME Transactions,2016,44(4):405-414. doi: 10.5937/fmet1604405G [18] PICKERING S. Recycling technologies for thermoset composite materials-current status[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2006,37(8):1206-1215. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.05.030 [19] YANG J, LIU J, LIU W, et al. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced epoxy resin composites under various oxygen concentrations in nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere[J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis,2015,112:253-261. doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2015.01.017 [20] KIM K W, LEE H M, AN J H, et al. Recycling and characterization of carbon fibers from carbon fiber reinforced epoxy matrix composites by a novel super-heated-steam method[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2017,203(Pt3):872-879. [21] SHUAIB N A, MATIVENGA P. Energy intensity and quality of recyclate in composite recycling[C]//ASME 2015 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2015, V002T05A005. [22] 马全胜, 王宝铭. 碳纤维复合材料回收及利用现状[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2016, 033(4):28-30, 27.MA Quansheng, WANG Baoming. Recycling and reuse of carbon fibre composites[J]. Fiber Composites,2016,033(4):28-30, 27(in Chinese). [23] 罗益锋. 碳纤维复合材料废弃物的回收与再利用技术发展[J]. 纺织导报, 2013(12):36-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3025.2013.12.010LUO Yifeng. Technology development of recovery & reuse of carbon fiber composite[J]. Fiber Technology,2013(12):36-39(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3025.2013.12.010 [24] LINE S. Commercialisation of the carbon fibre recycling process[C]//Carbon Fibre Recycling and Reuse Conference, 2009. [25] SONIA M E, CHRIS M A. TURNER T A, et al. Recycling of carbon fibre composites[C]//Carbon, 2016. [26] ZHU J H, CHEN P Y, SU M N, et al. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced plastics by electrically driven heterogeneous catalytic degradation of epoxy resin[J]. Green Chemistry,2019,21(7):1635-1647. doi: 10.1039/C8GC03672A [27] 张灵静, 陈桦, 蒋建军, 等. 碳纤维增强热固性复合材料回收再利用技术研究进展[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2019(7):134-140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2019.07.025ZHANG Lingjing, CHEN Hua, JIANG Jianjun, et al. Advances in recycling technology for carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composites[J]. Engineering Plastics Applications,2019(7):134-140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2019.07.025 [28] LESTER E , KINGMAN S , WONG K H , et al. Microwave heating as a means for carbon fibre recovery from polymer composites: A technical feasibility study[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 2004, 39(10): 1549-1556. [29] 阮芳涛, 施建, 徐珍珍, 等. 碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料的回收及其再利用研究进展[J]. 纺织学报, 2019, 40(6):152-157.RUAN Fangtao, SHI Jian, XU Zhenzhen, et al. Advances in the recycling of carbon fiber reinforced resin matrix composites[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2019,40(6):152-157(in Chinese). [30] 邓建英. 微波热解碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料回收碳纤维的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019.DENG Jianying. Study on microwave pyrolysis of carbon fiber/epoxy composites to recover carbon fibers[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [31] 薛敏敏. 台湾永虹公开全球首套高效碳纤维复合材料再生系统[J]. 合成纤维, 2018, 47(12):52.XUE Minmin. Taiwan Yonghong has unveiled the world's first highly efficient carbon fiber composite regeneration system[J]. Synthetic Fiber in China,2018,47(12):52(in Chinese). [32] LIU Y Y, MENG L, HUANG Y D, et al. Recycling of carbon/epoxy composites[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2010,94(5):1912-1916. [33] ZHANG J, CHEVALI V S, WANG H, et al. Current status of carbon fibre and carbon fibre composites recycling[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,193:108053. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108053 [34] LI J, XU P L, WANG Y Z, et al. A promising strategy for chemical recycling of carbon fiber /thermoset composites: Self-accelerating decomposition in a mild oxidative system[J]. Green Chemistry,2012,14:3260-3263. doi: 10.1039/c2gc36294e [35] XU P, LI J, DING J. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre/epoxy composites in a mixed solution of peroxide hydrogen and N, N-dimethylformamide[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2013,82:54-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2013.04.002 [36] JIANG J, DENG G, CHEN X, et al. On the successful chemical recycling of carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites under the mild condition[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,151:243-251. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.08.007 [37] LIIU T, GUO X L, LIU W C. Selective cleavage of ester linkages of anhydride-cured epoxy using a benign method and reuse of the decomposed polymer in new epoxy preparation[J]. Green Chemistry,2017,19(18):4364-4372. doi: 10.1039/C7GC01737E [38] DENG T, LIU Y, HOU X L, et al. Cleavage of C–N bonds in carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites[J]. Green Chemistry,2015,17(4):2141-2145. doi: 10.1039/C4GC02512A [39] WANG Y Q, CUI X J, HOU X L, et al. Chemical recycling of unsaturated polyester resin and its composites via selective cleavage of ester bond[J]. Green Chemistry,2015,17(9):4527-4532. doi: 10.1039/C5GC01048A [40] DAS M, VARUGHESE S. A novel sonochemical approach for enhanced recovery of carbon fiber from CFRP waste using mild acid-peroxide mixture[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2016,4(4):2080-2087. [41] MOHAN D, RINU C, SUSY V. An efficient method of recycling of CFRP waste using peracetic acid[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(2):1564-1571. [42] 碳纤复材. Ai-Carbon 公司开发出碳纤维常温回收新方法[EB/OL]. (2021-03-06) [2021-05-28]. http://www.360doc.com/content/21/0306/10/72738858_965428299.shtml.CARBON composite. A new method to recycle carbon fiber at room temperature was developed by Ai-Carbon[EB/OL]. (2021-03-06) [2021-05-28]. http://www.360doc.com/content/21/0306/10/72738858_965428299.shtml(in Chinese). [43] SUN H, GUO G, MEMON S A, et al. Recycling of carbon fibers from carbon fiber reinforced polymer using electrochemical method[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2015,78:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.07.015 [44] 陈丕钰. 碳纤维增强复合材料的电化学回收方法研究[D]. 深圳: 深圳大学, 2017.CHEN Piyu. Study of electrochemical recovery methods for carbon fiber reinforced composites[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen University, 2017(in Chinese). [45] ZHU J H, CHEN P Y, SU M N, et al. Recycling of carbon fibre reinforced plastics by electrically driven heterogeneous catalytic degradation of epoxy resin[J]. Green Chemistry,2019,21(22):1635-1647. [46] MATSUDA S, OSHIMA K, MASAKI H, et al. Effect of annealing on the separation of resin from CFRP cross-ply laminate via electrical treatment[J]. Composite Structures,2019,234(8):111665. [47] LIU Y, LIU J, JIANG Z, et al. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced epoxy resin composites in subcritical water: Synergistic effect of phenol and KOH on the decompo-sition efficiency[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2012,97(3):214-220. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.12.028 [48] LIU J, WANG K, MA L, et al. Insight into the role of potassium hydroxide for accelerating the degradation of anhydride-cured epoxy resin in subcritical methanol[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2016,107:605-611. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2015.07.022 [49] KIM YN, KIM Y O, KIM S Y, et al. Application of supercritical water for green recycling of epoxy-based carbon fiber reinforced plastic[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2019,173:66-72. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.01.026 [50] 赵志培. 超临界水/醇混合流体回收CF/EP复合材料的工艺研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2017.ZHAO Zhipei. Process study of supercritical water/alcohol mixture for fluid recovery of CF/EP composites[D]. Hefei :Hefei University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [51] RAUL P H, DODDS C, HYDE J, et al. Chemical recycling of carbon fibre reinforced composites in nearcritical and supercritical water[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2008,39(3):454-461. [52] JIANG G. Recycling carbon fiber/epoxy resin composites using supercritical propanol[C]//Proceeding of International Conference on Composite Materials, 2007. [53] OKAJIMA I , HIRAMATSU M , SAKO T . Recycling of carbon fiber reinforced plastics using subcritical water[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 222: 243-246. [54] IBARRA R M, SASAKI M, GOTO M, et al. Carbon fiber recovery using water and benzyl alcohol in subcritical and supercritical conditions for chemical recycling of thermoset composite materials[J]. Journal of Material Cycles and Waste Management,2015,17:369-379. doi: 10.1007/s10163-014-0252-z [55] WANG B, MA S, YAN S, et al. Readily recyclable carbon fiber reinforced composites based on degradable thermosets: A review[J]. Green Chemistry,2019,21(21):5781-5796. doi: 10.1039/C9GC01760G [56] MORELL M, ERBER M, RAMIS X, et al. New epoxy thermosets modified with hyperbranched poly(ester-amide) of different molecular weight[J]. European Polymer Journal,2010,46(7):1498-1509. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2010.04.015 [57] MORELL M, XAVIER F F, RAMIS X, et al. Synthesis of a new hyperbranched polyaminoester and its use as a reactive modifier in anionic curing of DGEBA thermosets[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics,2010,211(17):1879-1889. doi: 10.1002/macp.201000152 [58] NAVARRO C A, GIFFIN C R, ZHANG B, et al. A structural chemistry look at composites recycling[J]. Materials Horizons,2020,7(10):2479-2486. doi: 10.1039/D0MH01085E [59] 周立生, 刘剑侠, 吴淑新, 等. 类玻璃高分子材料的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(S01):585-591.ZHOU Lisheng, LIU Jianxia, WU Shuxin, et al. Advances in the study of glass-like polymeric materials[J]. Materials Reports,2020,34(S01):585-591(in Chinese). [60] 刘湍, 费铭恩, 赵保明, 等. 生物基类玻璃高分子材料的研究进展[J]. 高分子学报, 2020, 8:817-832. doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2020.20047LIU Tuan, FEI Ming’en, ZHAO Baoming, et al. Advances in the research of bio-based glassy polymers[J]. Acta Polymerica Sinica,2020,8:817-832(in Chinese). doi: 10.11777/j.issn1000-3304.2020.20047 [61] DAMIEN M, MATHIEU C, TOURNIHAC F, et al. Silica-like malleable materials from permanent organic networks[J]. Science,2011,334(6058):965-968. doi: 10.1126/science.1212648 [62] MAX R, TRYSTAN D, ROB W, et al. High-performance vitrimers from commodity thermoplastics through dioxaborolane metathesis[J]. Science,2017,356(6333):62-65. doi: 10.1126/science.aah5281 [63] KAI Y, QIAN S, DUNN M L, et al. Carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composite with near 100% recyclability[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2016,26(33):6098-6106. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201602056 [64] SI H W, LIN Z, WU Y P, et al. Rapidly reprocessable, degradable epoxy vitrimer and recyclable carbon fiber reinforced thermoset composites relied on high contents of exchangeable aromatic disulfide crosslinks[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2020,199(2):108278. [65] WANG B, MA S, XU X, et al. High-performance, bio-based, degradable polyurethane thermoset and its application in readily recyclable carbon fiber composites[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2020,8(30):11162-11170. [66] 刘旭. 一种连续纤维增强热塑性复合材料废料回收利用方法: 中国, CN103786352A[P]. 2014-05-14.LIU Xu. A method for recycling waste of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites: China, CN103786352A[P]. 2014-05-14(in Chinese). [67] OTHEGUY M E, GIBSON A G, FINDON E, et al. Recycling of end-of-life thermoplastic composite boats[J]. Plastics, Rubber and Composites,2009,38(9-10):406-411. doi: 10.1179/146580109X12540995045642 [68] FLEMMING T, KRESS G, FLEMMING M. Fatigue fracture behavior of a new aligned short-carbon-fiber reinforced thermoplastic prepreg[J]. Advance Composite Material,1996,5(2):151-159. doi: 10.1163/156855196X00068 [69] LIU X, TAKAHASHI J, WAN Y, et al. Determination of transverse flexural and shear moduli of chopped carbon fiber tape-reinforced thermoplastic by vibration[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2018,52:21-31. [70] 佚名. 英国计划从回收的碳纤维中开发纱与织物[J]. 高科技纤维与应用, 2011, 4:54.UNKOWN. UK project to develop yarn and fabric from recycled carbon fiber[J]. High Technology Fiber & Application,2011,4:54(in Chinese). [71] MARCO L L, YU H H, MESIAM J, et al. Aligned discontinuous intermingled reclaimed/virgin carbon fibre compo-sites for high performance and pseudo-ductile behaviour in interlaminated carbon-glass hybrids[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,143:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.02.028 [72] OLIVEUX G, BAILLEUL J L, GILLET A, et al. Recovery and reuse of discontinuous carbon fibres by solvolysis: Realignment and properties of remanufactured materials[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,139:99-108. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2016.11.001 -





 下载:
下载: