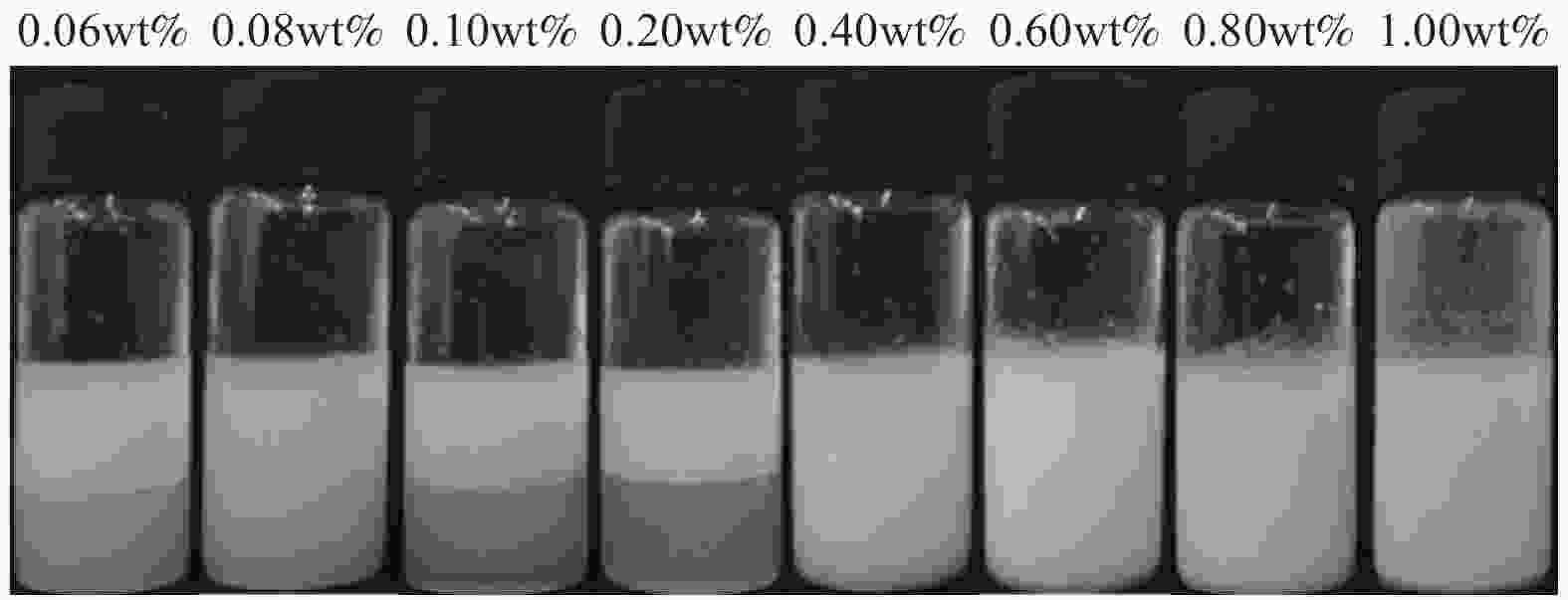
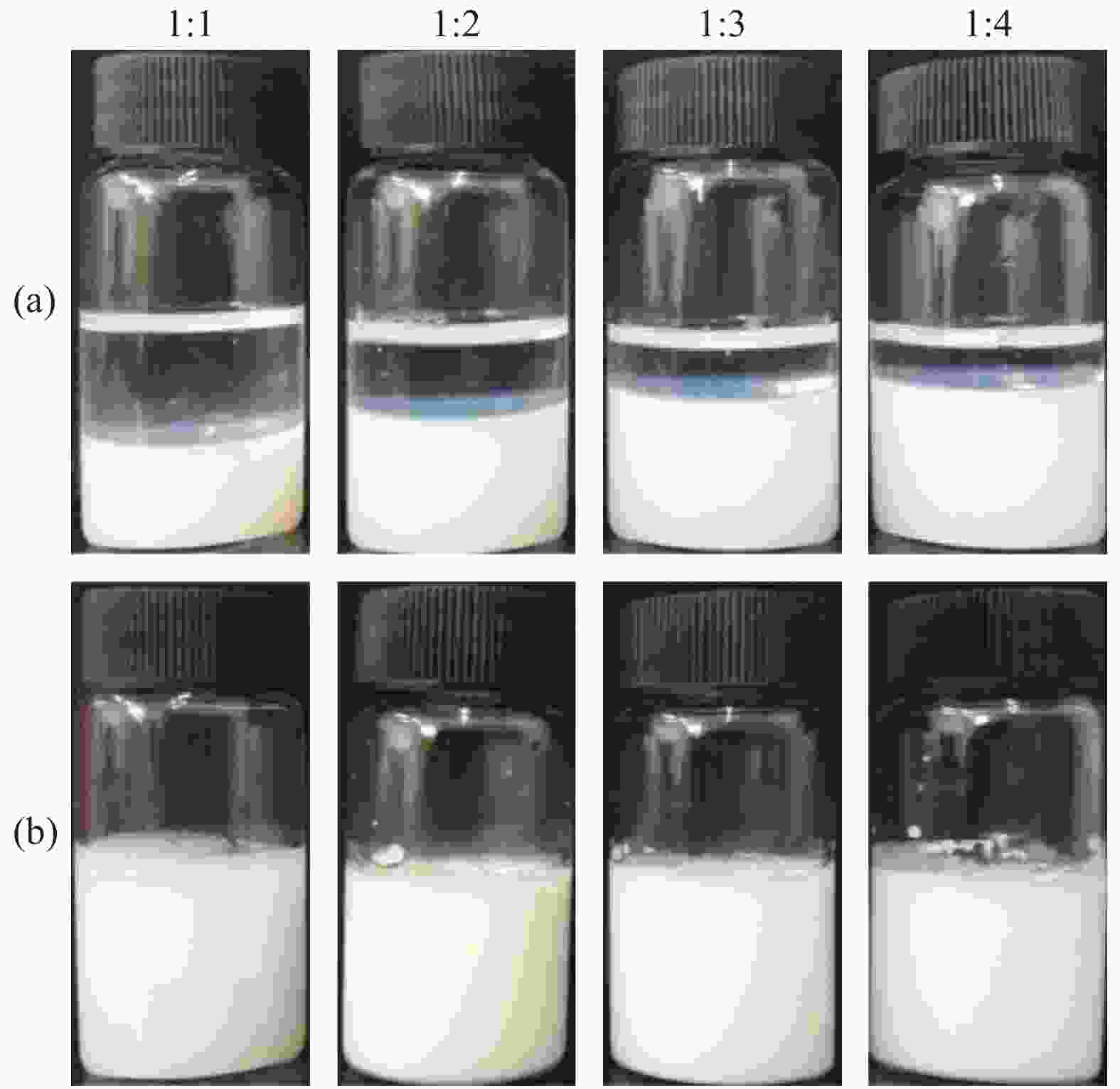
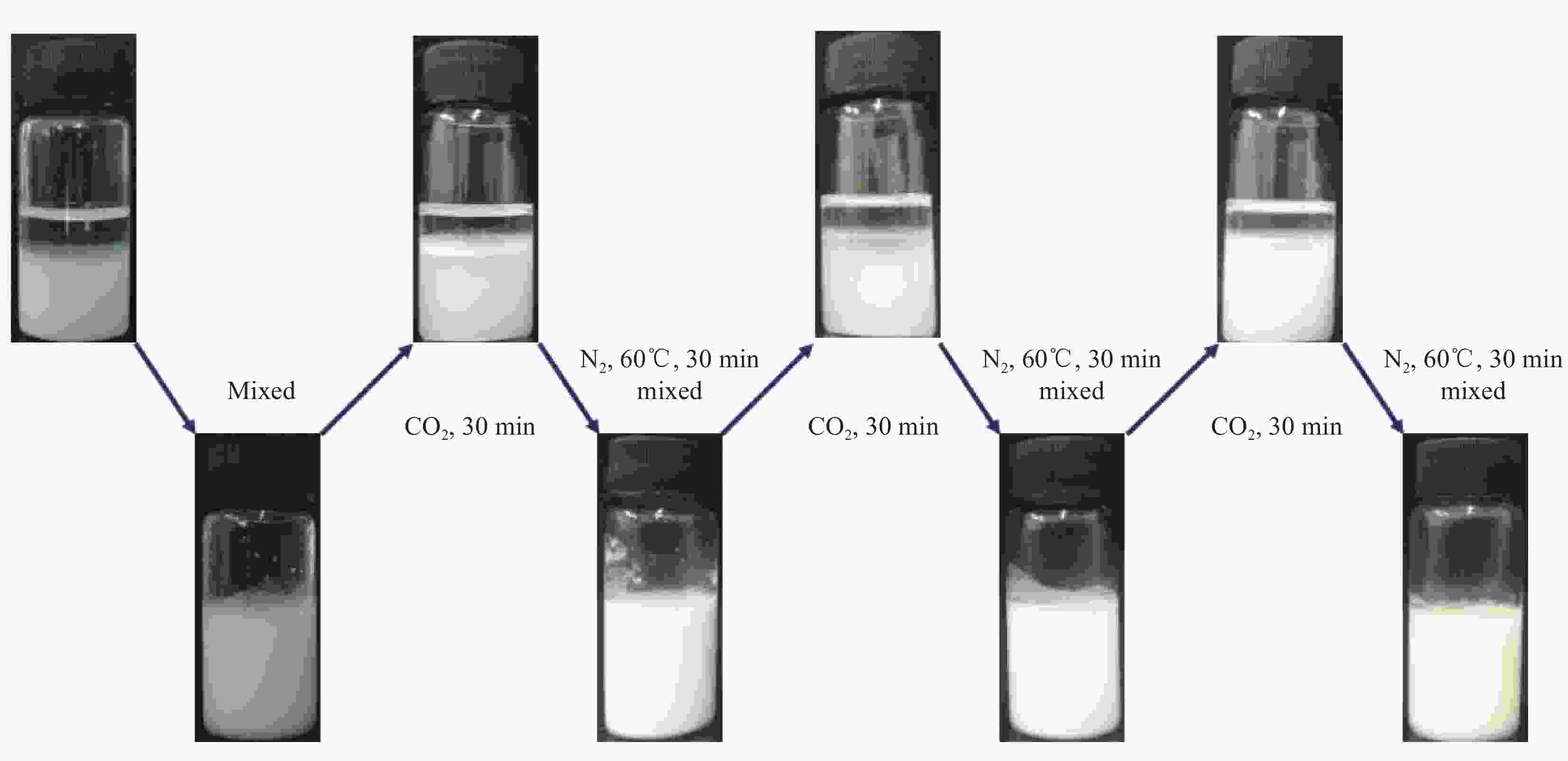
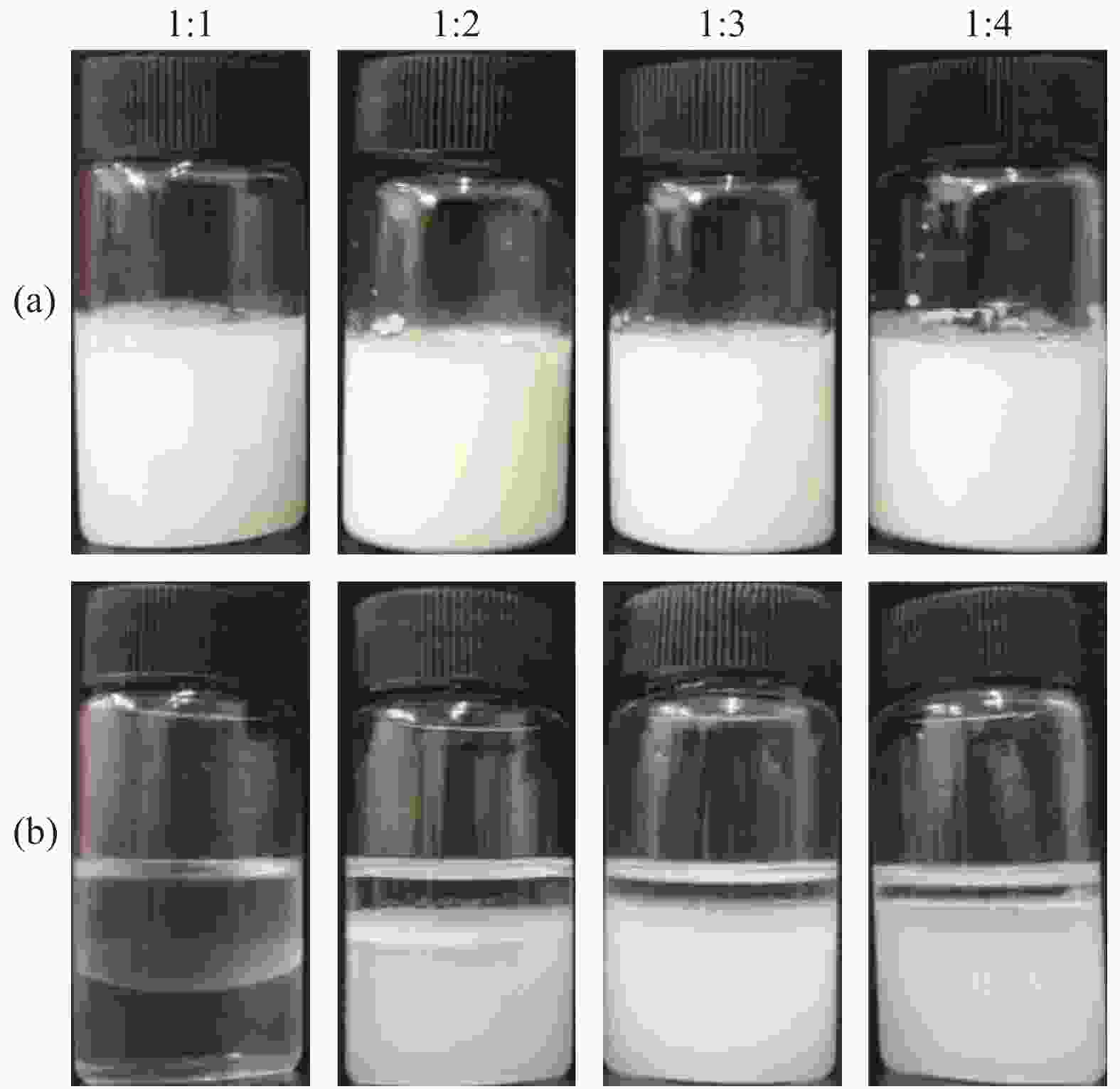
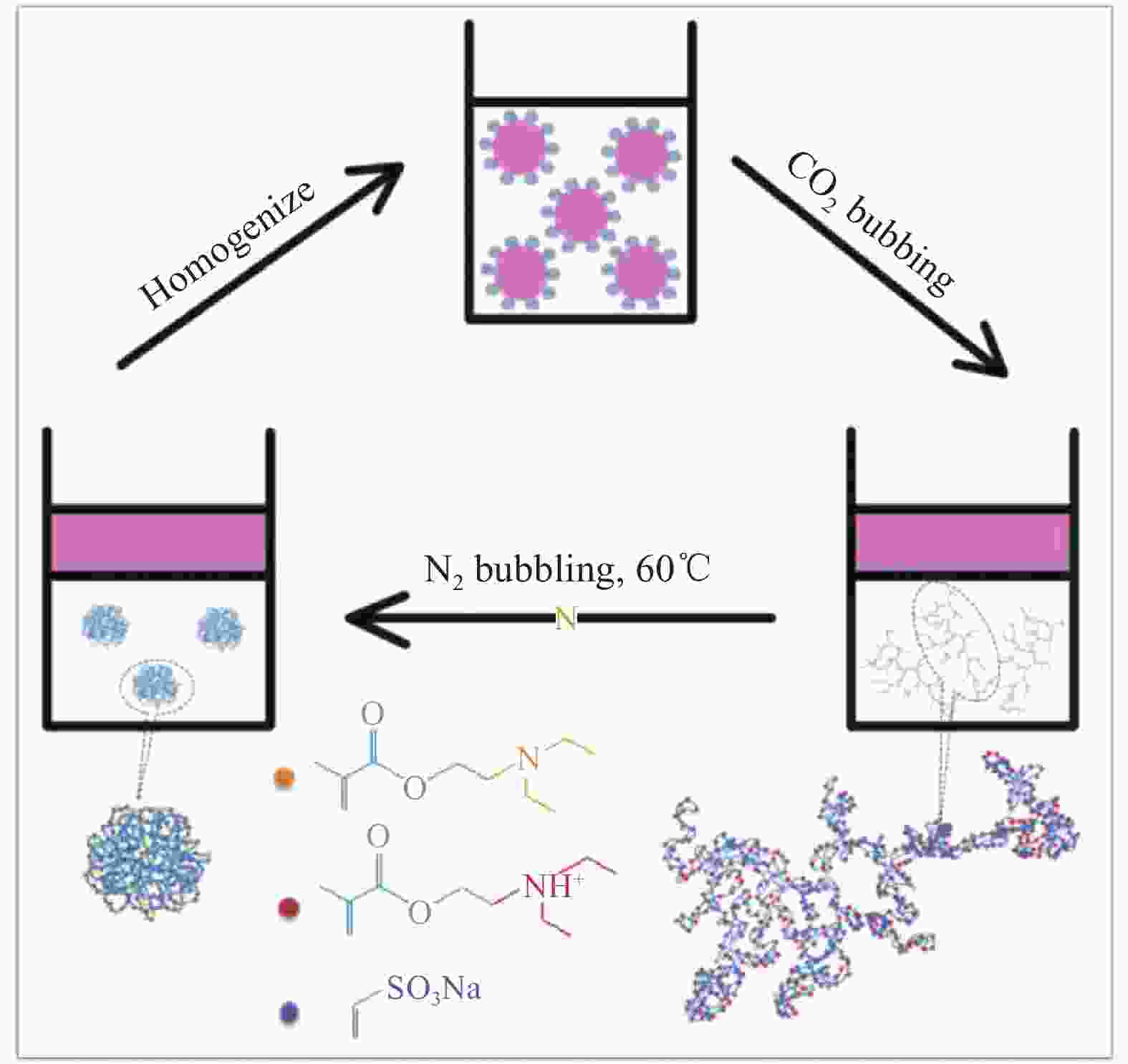
| [1] |
JIE D, WANG Y, JIAN Z, et al. Multiple stimuli-responsive polymeric micelles for controlled release[J]. Soft Matter,2012,9(2):370-373.
|
| [2] |
ZHANG Q. Preparation of N2/CO2 triggered reversibly coagulatable and redispersible latexes by emulsion polymerization of styrene with a reactive switchable surfactant[J]. Langmuir,2012,28(14):5940-5946. doi: 10.1021/la300051w
|
| [3] |
QIAO W, ZHENG Z, SHI Q. Synthesis and properties of a series of CO2 switchable surfactants with imidazoline group[J]. Journal of Surfactants & Detergents,2012,15(5):533-539.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Y M, ZHANG Y D, WANG C, et al. CO2-responsive microemulsion: Reversible switching from an apparent single phase to near-complete phase separation[J]. Green Chemistry,2015,18(2):392-396.
|
| [5] |
JESSOP, P G, SU X, CUNNINGHAM MF. Switchable surfactants at the polystyrene-water interface: Effect of molecular structure[J]. Green Materials,2014,2(2):69-74. doi: 10.1680/gmat.13.00015
|
| [6] |
HAN D, XIA T, BOISSIERE O, et al. General strategy for making CO2-switchable polymers[J]. Acs Macro Letters,2012,1(1):57-61. doi: 10.1021/mz2000175
|
| [7] |
LIU Y. Switchable surfactants[J]. Science,2006,313(5789):958-960. doi: 10.1126/science.1128142
|
| [8] |
ZHANG Y, YIN H, FENG Y. CO2-responsive anionic wormlike micelles based on natural erucic acid[J]. Green Materials,2014,2(2):95-103. doi: 10.1680/gmat.13.00016
|
| [9] |
HAN D, BOISSIERE O, KUMAR S, et al. Two-way CO2-switchable triblock copolymer hydrogels[J]. Macromolecules,2012,45(18):7440-7445. doi: 10.1021/ma3015189
|
| [10] |
BROWN P, BUTTS C P, EASTOE J. Stimuli-responsive surfactants[J]. Soft Matter,2013,9(8):2365-2374. doi: 10.1039/c3sm27716j
|
| [11] |
LIU F, URBAN M W. Recent advances and challenges in designing stimuli-responsive polymers[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2010,35(1-2):3-23. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.10.002
|
| [12] |
MORSE A J, DUPIN D, THOMPSON K L, et al. Novel pickering emulsifiers based on pH-responsive poly(tert-butylaminoethyl methacrylate) latexes[J]. Langmuir the Acs Journal of Surfaces & Colloids,2012,28(32):11733-11740.
|
| [13] |
SCOTT L M. Designing the head group of CO2-triggered switchable surfactants[J]. Rsc Advances,2012,2(11):4925-4931. doi: 10.1039/c2ra01242a
|
| [14] |
BROWN P, WASBROUGH M J, GURKAN B E, et al. CO2-responsive microemulsions based on reactive ionic liquids[J]. Langmuir,2014,30(15):4267-72. doi: 10.1021/la500675g
|
| [15] |
HU J, LIU S. Responsive polymers for detection and sensing applications: Current status and future developments[J]. Macromolecules,2010,43(20):8315-8330. doi: 10.1021/ma1005815
|
| [16] |
DESTRIBATS M, PINAUD F, LAPEYRE V, et al. Pickering emulsions stabilized by soft microgels: Influence of the emulsification process on particle interfacial organization and emulsion properties[J]. Langmuir,2013,29(40):12367-12374. doi: 10.1021/la402921b
|
| [17] |
DESTRIBATS M, EYHARTS M, LAPEYRE V, et al. Impact of pNIPAM microgel size on its ability to stabilize pickering emulsions[J]. Langmuir the Acs Journal of Surfaces & Colloids,2014,30(7):1768-1777.
|
| [18] |
JIANG J, JIANG J, LIU K, et al. Switchable pickering emulsions stabilized by silica nanoparticles hydrophobized in situ with a switchable surfactant[J]. Angewandte Chemie,2013,52(47):12373-12376. doi: 10.1002/anie.201305947
|
| [19] |
MORSE A J, ARMES S P, THONPSON K C, et al. Novel pickering emulsifiers based on pH-responsive poly(2-(diethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) latexes[J]. Langmuir,2013,29(18):5466-5475. doi: 10.1021/la400786a
|
| [20] |
ZHANG Q Y, WANG G Q, YAN W J, et al. Switchable block copolymer surfactants for preparation of reversibly coagulatable and redispersible poly(methyl methacrylate) latexes[J]. Macromolecules,2013,46(4):1261-1267. doi: 10.1021/ma302505r
|
| [21] |
MORSE A J, ARMES S P, MILLS P, et al. Stopped-flow kinetics of pH-responsive polyamine latexes: How fast is the latex-to-microgel transition?[J]. Langmuir the ACS Journal of Surfaces& Colloids,2013,29(49):15209-15216.
|
| [22] |
WANG X, JIANG G H, LI X, et al. Synthesis of multi-responsive polymeric nanocarriers for controlled release of bioactive agents[J]. Polymer Chemistry,2013,4(17):4574-4577. doi: 10.1039/c3py00746d
|
| [23] |
LU H S, GUAN X Q, DAI S S, et al. Application of CO2-triggered switchable surfactants to form emulsion with xinjiang heavy oil[J]. Journal of Dispersion Science and Technology,2014,35(5):655-662. doi: 10.1080/01932691.2013.803254
|
| [24] |
LU H, GUAN X Q, WANG B G, et al. CO2-switchable oil/water emulsion for pipeline transport of heavy oil[J]. Journal of Surfactants and Detergents,2015,18(5):773-782. doi: 10.1007/s11743-015-1712-8
|
| [25] |
RICHTERING W. Responsive emulsions stabilized by stimuli-sensitive microgels: Emulsions with special non-Pickering properties[J]. Langmuir the ACS Journal of Surfaces & Colloids,2014,28(50):17218-17226.
|
| [26] |
WANG J J, WANG H F, LI Y, et al. Formation and CO2/N2 switchable ability of a novel copolymer poly(N, N-diethylaminoethyl methacrylate-co-codium vinyl-sulfonate)[J]. Polymer Science, Series A,2018,60(5):1-6.
|
| [27] |
KUMAR S, TONG X, DORY Y, et al. A CO2-switchable polymer brush for reversible capture and release of proteins[J]. Chemical Communications,2013,49(1):90-92. doi: 10.1039/C2CC36284H
|





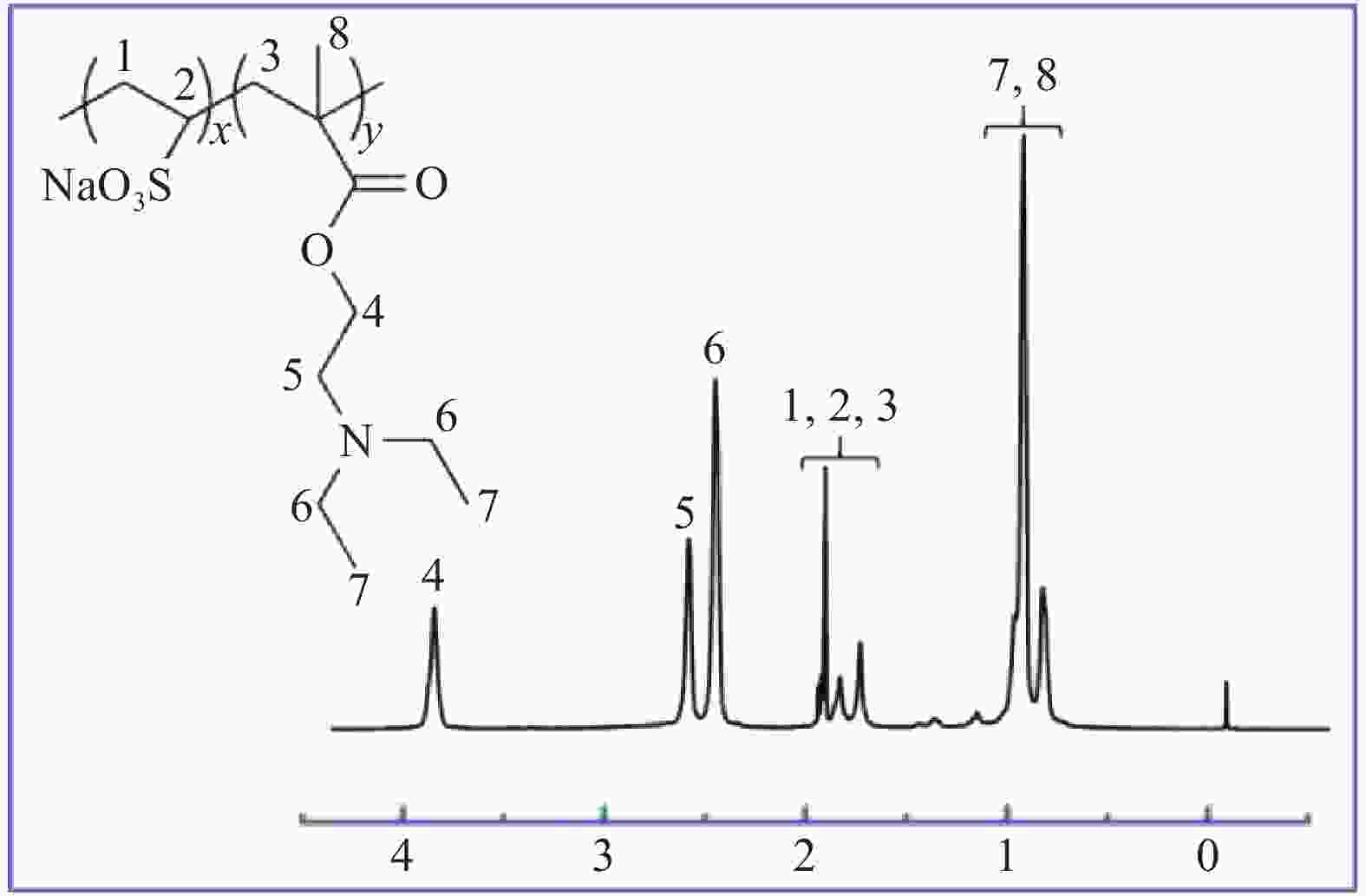
 下载:
下载: